The Economy–Environment Nexus: Sustainable Development Goals Interlinkages in Austria
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Which synergies and trade-offs exist both within and between all 17 SDGs in Austria?
- Focusing on interactions of economic and environmental SDGs, which concrete causal relationships exist between socio-economic activity and environmental conditions in Austria?
2. Background
2.1. Trade-Offs between Socio-Economic Development and Environmental Preservation
2.2. SDG Interlinkages Depend on the Specific Context and the Method Used
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. Expert Judgement
4. Results
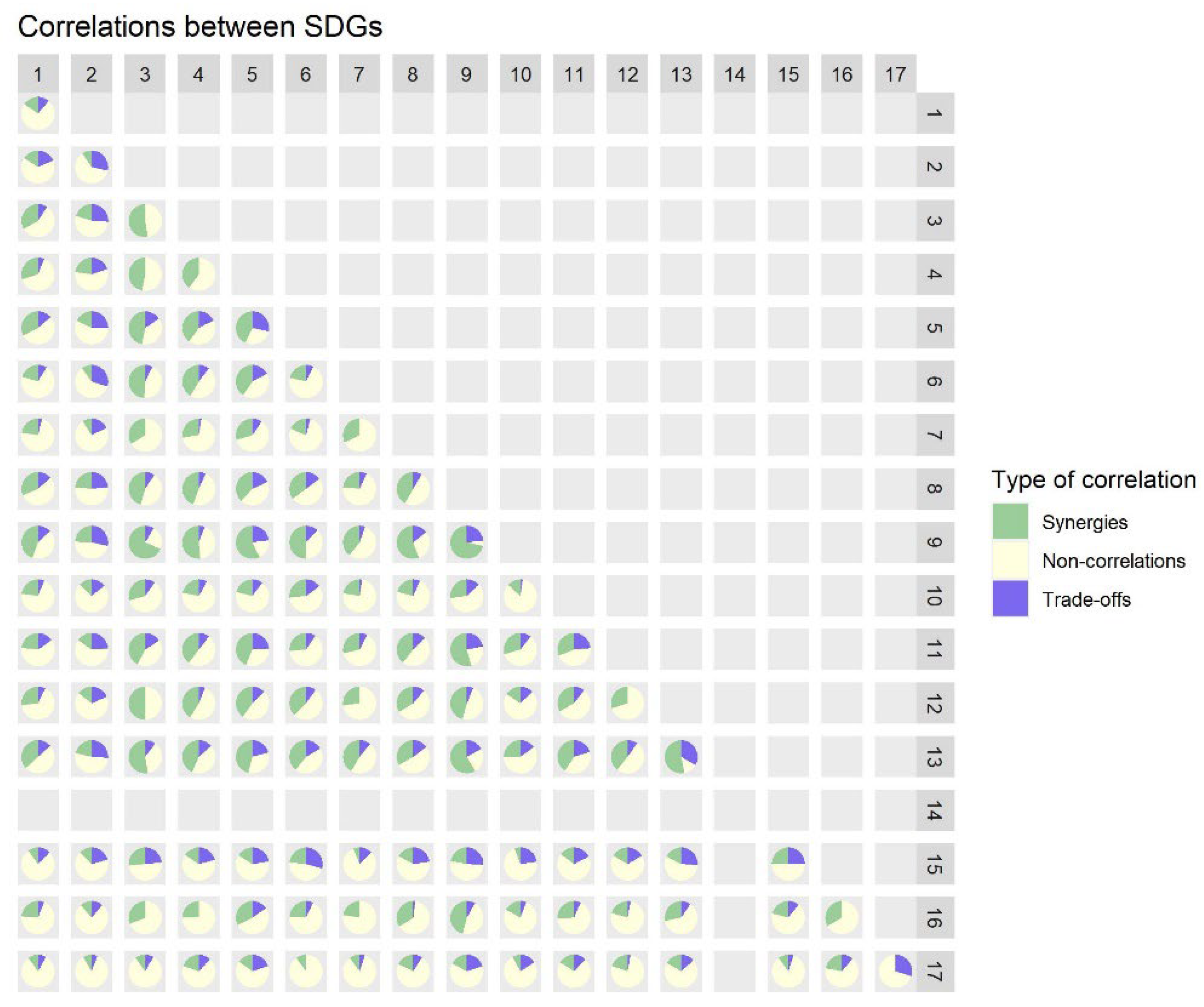
4.1. Correlation Analysis
4.1.1. Interlinkages within the SDGs in Austria
4.1.2. Interlinkages between the SDGs in Austria
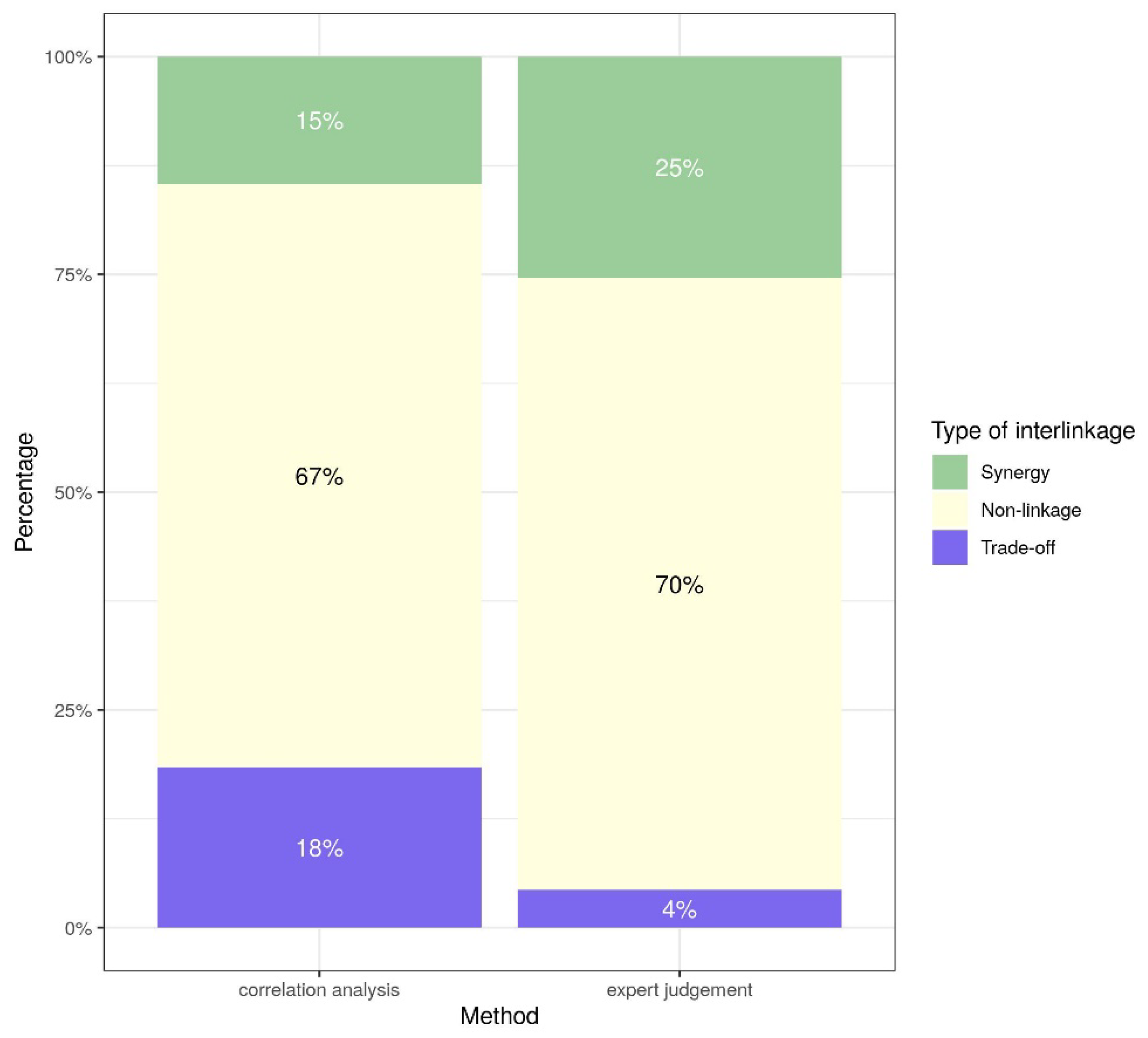
4.2. Comparison of Methods for Economy–Environment Nexus Interlinkages
4.3. Economy–Environment Nexus Interlinkages Identified by Both Methods
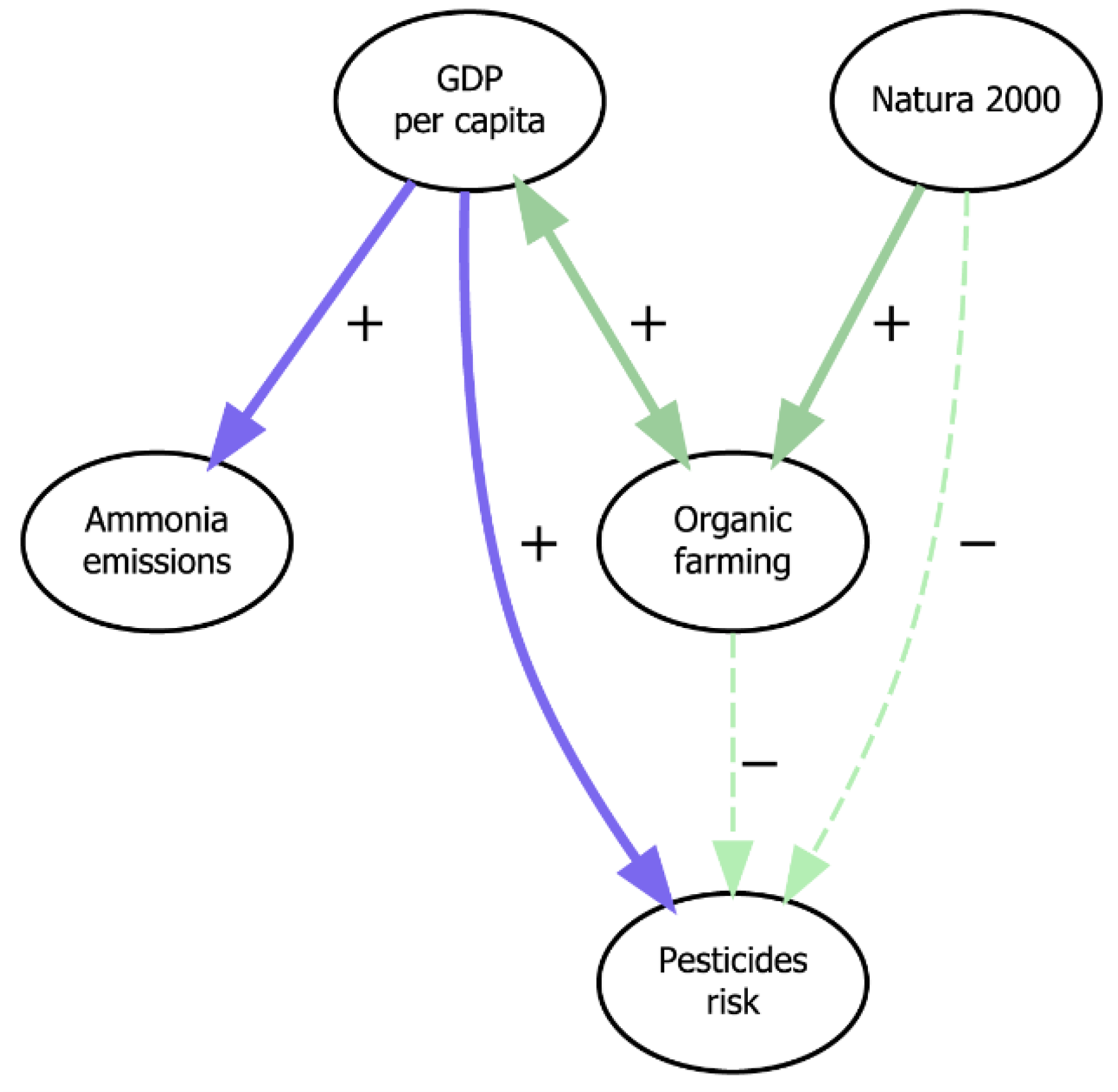
4.3.1. Agriculture Interlinkages
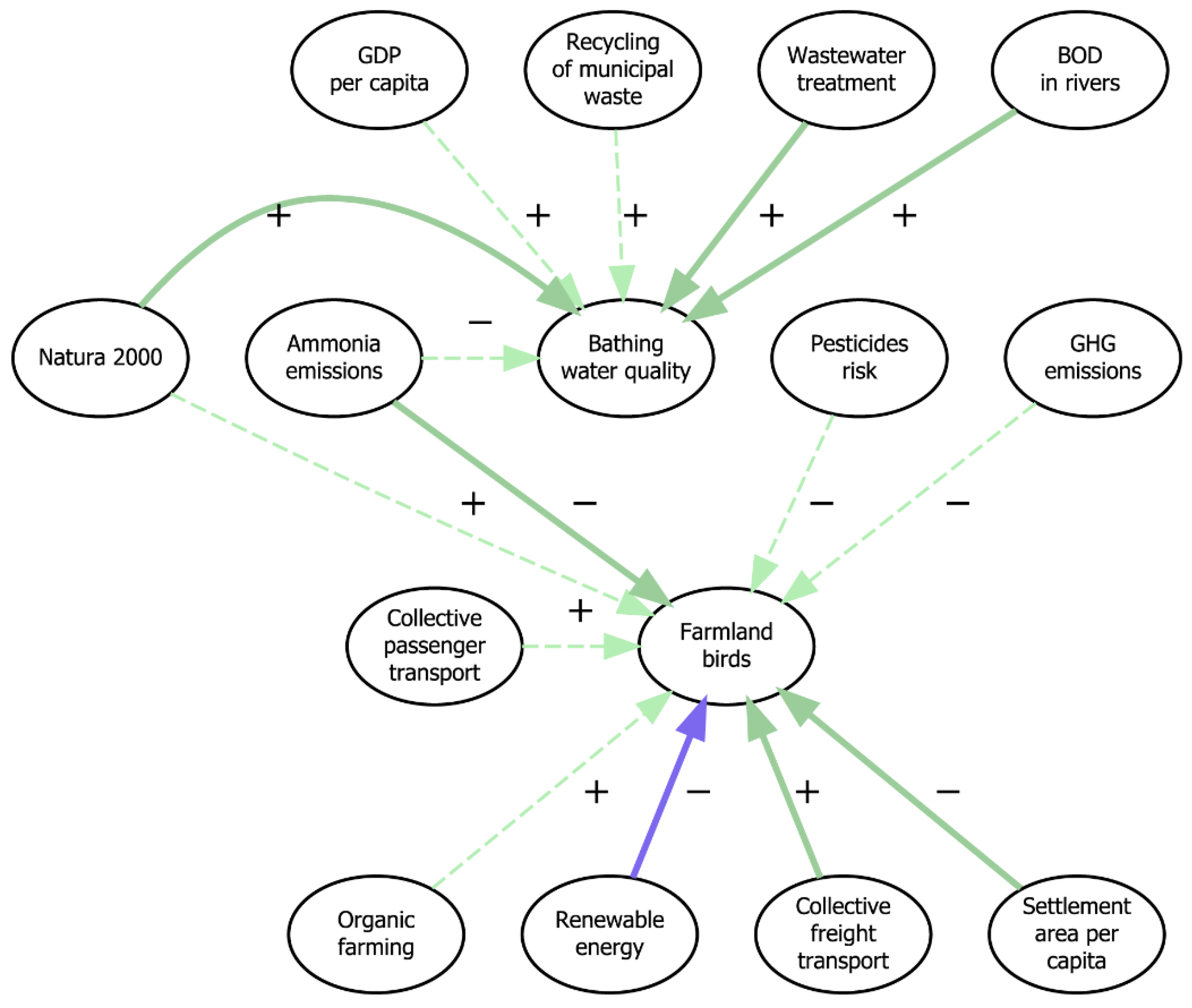
4.3.2. Water Interlinkages
4.3.3. Climate and Energy Interlinkages
4.3.4. Ecosystems Interlinkages
4.3.5. Resource Use Interlinkages
4.3.6. Economy–Environment Nexus Interlinkages in Austria
5. Discussion
5.1. Interlinkages of All 17 SDGs in Austria
5.2. The Economy–Environment Nexus
5.3. Methodological Considerations
5.4. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, W.; Mooney, H.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.; Chopra, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.; Hassan, R.; et al. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Synthesis Report; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IPBES Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019.
- O’Neill, D.W.; Fanning, A.L.; Lamb, W.F.; Steinberger, J.K. A good life for all within planetary boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hametner, M. Economics without ecology: How the SDGs fail to align socioeconomic development with environmental sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 199, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F.; Gingrich, S.; Eisenmenger, N.; Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Growth in global materials use, GDP and population during the 20th century. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Raworth, K. A Safe and just Space for Humanity: Can We Live within the Doughnut? Oxfam: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S., III; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 1–33. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol14/iss2/art32/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Eisenmenger, N.; Pichler, M.; Krenmayr, N.; Noll, D.; Plank, B.; Schalmann, E.; Wandl, M.-T.; Gingrich, S. The Sustainable Development Goals prioritize economic growth over sustainable resource use: A critical reflection on the SDGs from a socio-ecological perspective. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Robra, B.; Heikkurinen, P. Degrowth and the sustainable development goals. Decent Work. Econ. Growth 2019, 3, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Requejo-Castro, D.; Giné-Garriga, R.; Pérez-Foguet, A. Data-driven Bayesian network modelling to explore the relationships between SDG 6 and the 2030 Agenda. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostetckaia, M.; Hametner, M. How Sustainable Development Goals interlinkages influence European Union countries’ progress towards the 2030 Agenda. Sustain. Dev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, C.; Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Are we successful in turning trade-offs into synergies? Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J.P. A Systematic Study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, C.W.; Nicholls, R.J.; Lázár, A.N.; Chapman, A.; Schaafsma, M.; Salehin, M. Potential trade-offs between the sustainable development goals in coastal Bangladesh. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.; Behrens, P.; de Koning, A.; Heijungs, R.; Sprecher, B.; Tukker, A. Trade-offs between social and environmental Sustainable Development Goals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 90, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICSU, A. Guide to SDG Interactions: From Science to Implementation; Griggs, D.J., Nilsson, M., Stevance, A., McCollum, D., Eds.; International Council for Science: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, M.; Griggs, D.; Visbeck, M. Policy: Map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. News 2016, 534, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H.; Nilsson, M.; Skånberg, K. Towards systemic and contextual priority setting for implementing the 2030 Agenda. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronzon, T.; Sanjuan, A. Friends or foes? A compatibility assessment of bioeconomy-related Sustainable Development Goals for European policy coherence. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 254, 119832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.G.; Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Swartz, W.; Cheung, W.; Guy, J.A.; Kenny, T.-A.; McOwen, C.J.; Asch, R.; Geffert, J.L.; Wabnitz, C.C. A rapid assessment of co-benefits and trade-offs among Sustainable Development Goals. Mar. Policy 2018, 93, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Chisholm, E.; Griggs, D.; Howden-Chapman, P.; McCollum, D.; Messerli, P.; Neumann, B.; Stevance, A.-S.; Visbeck, M.; Stafford-Smith, M. Mapping interactions between the sustainable development goals: Lessons learned and ways forward. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H.; Skånberg, K.; Dzebo, A.; Viaud, V. SDGs and the environment in the EU: A systems view to improve coherence. In Report Commissioned by the European Environment Agency; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, A.; Janetschek, H.; Malerba, D. Translating Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interdependencies into Policy Advice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/generalassembly/docs/globalcompact/A_RES_70_1_E.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Cling, J.-P.; Eghbal-Teherani, S.; Orzoni, M.; Plateau, C. The interlinkages between the SDG indicators and the differentiation between EU countries: It is (mainly) the economy! Stat. J. IAOS 2020, 36, 455–470. [Google Scholar]
- Tosun, J.; Leininger, J. Governing the interlinkages between the sustainable development goals: Approaches to attain policy integration. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 1700036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennich, T.; Weitz, N.; Carlsen, H. Deciphering the scientific literature on SDG interactions: A review and reading guide. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallis, G. In defence of degrowth. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickel, J. The contradiction of the sustainable development goals: Growth versus ecology on a finite planet. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickel, J.; Kallis, G. Is green growth possible? New Political Econ. 2020, 25, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hametner, M.; Kostetckaia, M. Frontrunners and laggards: How fast are the EU member states progressing towards the sustainable development goals? Ecol. Econ. 2020, 177, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T. Prosperity without Growth: The Transition to a Sustainable Economy. 2009. Available online: https://www.sd-commission.org.uk/data/files/publications/prosperity_without_growth_report.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.L.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W. The limits to growth. New York 1972, 102, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Springmann, M.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Rayner, M.; Scarborough, P. Analysis and valuation of the health and climate change cobenefits of dietary change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, D. Towards integration at last? The sustainable development goals as a network of targets. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Burgess, J.C. The Sustainable Development Goals and the systems approach to sustainability. Econ. E-J. 2017, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, S.; Adshead, D.; Fay, M.; Hallegatte, S.; Harvey, M.; Meller, H.; O’Regan, N.; Rozenberg, J.; Watkins, G.; Hall, J.W. Infrastructure for sustainable development. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, D.L.; Echeverri, L.G.; Busch, S.; Pachauri, S.; Parkinson, S.; Rogelj, J.; Krey, V.; Minx, J.C.; Nilsson, M.; Stevance, A.-S. Connecting the sustainable development goals by their energy inter-linkages. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 033006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, A.; Borchardt, S.; Neher, F.; Buscaglia, D. Interlinkages and Policy Coherence for the Sustainable Development Goals Implementation: An Operational Method to Identify Trade-offs and Co-Benefits in a Systemic Way; Joint Research Centre (JRC): Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, H.L.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Hilaire, J.; Minx, J.C.; Harmsen, M.J.; Krey, V.; Popp, A.; Riahi, K.; Luderer, G. Analysing interactions among sustainable development goals with integrated assessment models. Glob. Transit. 2019, 1, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytimäki, J.; Lonkila, K.-M.; Furman, E.; Korhonen-Kurki, K.; Lähteenoja, S. Untangling the interactions of sustainability targets: Synergies and trade-offs in the Northern European context. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 3458–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Truffert, M.; Metz, F.; Fischer, M.; Rueff, H.; Messerli, P. Interactions among Sustainable Development Goals: Knowledge for identifying multipliers and virtuous cycles. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1236–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel Ramos, C.; Laurenti, R. Synergies and Trade-offs among Sustainable Development Goals: The Case of Spain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.; Kroll, C.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Woelm, F. Sustainable Development Report 2021; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guijarro, F.; Poyatos, J.A. Designing a sustainable development goal index through a goal programming model: The Case of EU-28 Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, A.; Schiltz, F. Measuring sustainable development goals performance: How to monitor policy action in the 2030 Agenda implementation? Ecol. Econ. 2019, 164, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P.; Kropp, J.P. Variations in sustainable development goal interactions: Population, regional, and income disaggregation. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Comparison of Values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients on the Same Sets of Data. Quaest. Geogr. 2011, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Forero, L.; Castañeda, G.; Guerrero, O.A. Estimating networks of sustainable development goals. Inf. Manag. 2020, 59, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrique, T.; Barth, J.; Briens, F.; Kerschner, C.; Kraus-Polk, A.; Kuokkanen, A.; Spangenberg, J. Decoupling Debunked. Evidence and Arguments against Green Growth as a Sole Strategy for Sustainability. A Study Edited by the European Environment Bureau EEB 2019. Available online: https://eeb.org/library/decoupling-debunked (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Nilsson, M.; Weitz, N. Governing trade-offs and building coherence in policy-making for the 2030 agenda. Politics Gov. 2019, 7, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| SDG | Indicator | Used in Expert Judgement | Used in Correlation Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDG 2 | Ammonia emissions from agriculture | ✓ | ✓ |
| Area under organic farming | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Harmonised risk indicator for pesticides (HRI1) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SDGs 2 and 6 | Nitrate in groundwater | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDGs 2 and 15 | Farmland bird index | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDG 6 | Water exploitation index plus (WEI+) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Bathing sites with excellent water quality (inland) | |||
| SDGs 6 and 11 | Population connected to at least secondary wastewater treatment | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDGs 6 and 15 | Biochemical oxygen demand in rivers | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDGs 6 and 15 | Phosphate in rivers | ✓ | Excluded due to insufficient time series |
| SDG 7 | Primary energy consumption | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDGs 7 and 13 | Share of renewable energy consumption in gross final energy consumption | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDG 8 | Real GDP per capita | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDG 9 | Share of rail and inland waterways in inland freight transport | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDGs 9 and 11 | Share of buses and trains in inland passenger transport | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDG 11 | Recycling rate of municipal waste | ✓ | ✓ |
| Settlement area per capita | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SDG 12 | Circular material use rate | ✓ | ✓ |
| Domestic material consumption (DMC) | ✓ | ✓ | |
| SDG 13 | Greenhouse gas emissions | ✓ | ✓ |
| SDG 15 | Share of forest area | ✓ | ✓ |
| Soil sealing index | ✓ | Excluded due to insufficient time series | |
| Surface of terrestrial sites designated under Natura 2000 | ✓ | ✓ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urban, P.; Hametner, M. The Economy–Environment Nexus: Sustainable Development Goals Interlinkages in Austria. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912281
Urban P, Hametner M. The Economy–Environment Nexus: Sustainable Development Goals Interlinkages in Austria. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912281
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrban, Patricia, and Markus Hametner. 2022. "The Economy–Environment Nexus: Sustainable Development Goals Interlinkages in Austria" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912281
APA StyleUrban, P., & Hametner, M. (2022). The Economy–Environment Nexus: Sustainable Development Goals Interlinkages in Austria. Sustainability, 14(19), 12281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912281






