Abstract
In this paper, an integrated methodology is developed to determine optimum areas for Photovoltaic (PV) installations that minimize the relevant visual disturbance and satisfy spatial constraints associated with land use, as well as environmental and techno-economic siting factors. The visual disturbance due to PV installations is quantified by introducing and calculating the “Social Disturbance” (SDIS) indicator, whereas optimum locations are determined for predefined values of two siting preferences (maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance and minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations). Thematic maps of appropriate selected exclusion criteria are produced, followed by a cumulative weighted viewshed analysis, where the SDIS indicator is calculated. Optimum solutions are then determined by developing and employing a Genetic Algorithms (GAs) optimization process. The methodology is applied for the municipality of La Palma Del Condado in Spain for 100 different combinations of the two siting preferences. The optimization results are also employed to create a flexible and easy-to-use web-GIS application, facilitating policy-makers to choose the set of solutions that better fulfils their preferences. The GAs algorithm offers the ability to determine distinguishable, but compact, regions of optimum locations in the region, whereas the results indicate the strong dependence of the optimum areas upon the two siting preferences.
1. Introduction
The solar Photovoltaic (PV) market presents one of the most dynamic renewable energies markets, and its growth is expected to rise [1]. Due to their environmental and economic benefits, PV plants provide energy for numerous applications, in addition to the electrical grid supply, such as solar irrigation [2], seawater desalination [3], groundwater pumping [4], as well as the combined production of agricultural crops and power [5]. The technology of PVs is continuously being developed to improve solar cells efficiency (e.g., [6,7]). Regarding the deployment of PVs in residential areas, many researchers have developed and applied various relevant tools and methods, including, for example, tools that provide access to PV datasets [8] and advanced integrated approaches for rooftop solar energy assessments (e.g., [9,10,11]). Furthermore, there is a number of studies focusing on PV plants’ allocation in rural areas (e.g., [12,13]).
When considering the site selection criteria for installing PV plants, it is necessary to take into consideration the associated potential risks (however small they might be) [14,15], while at the same time setting the regulations that will not prevent the PV plants’ further expansion. Authorities often regulate the PV plants’ deployment based on environmental and social criteria [16]. As an inaccurate sitting of PV plants might lead to public oppositions, it is necessary, when proposing regulations, to take into account all those parameters that will make citizens feel safe and, thus, will increase public acceptance [17,18,19]. Specifically, in Spain, where the methodology of this paper is applied, there is an ongoing discussion about proposing and adopting the best regulations [20,21], as the Spanish solar energy market, despite its early development, had been stable through the previous decade [22,23]. One of the most important aspects for legal regulations is simplicity, as regions with lower administrative complexity are likely to have better PV ratios [24].
A way to increase the public acceptance of PVs is to decrease the associated social disturbance by avoiding the placement of PVs in areas of high visibility. This, in turn, requires the implementation of a viewshed analysis within the site selection process. The latter analysis enables the identification of geographical areas or landscape components/objects (viewsheds), which can be seen from one observer based on the observer’s spatial location and the terrain elevation. In its simplest form, the so-called “binary” viewshed analysis, it produces a raster map with Boolean values [0, 1], where the visibility of a pixel from the observer is denoted by “1” and non-visibility by “0” [25,26]. Up to now, numerous variants of the aforementioned traditional viewshed analysis have been developed and applied. These include, for example, the cumulative viewshed analysis (e.g., [27]), where the visibility of an object is quantified based on multiple, different viewpoint locations (observers), as well as the fuzzy viewshed analysis (e.g., [25,28,29,30]), which determines the likelihood of an object to be seen, while accounting for the distance-decay effect in visibility. The latter effect can be also considered by performing a “weighted” viewshed analysis, where weighting factors are assigned to different visibility distances based on various distance-decay functions (e.g., [31,32]).
Even though viewshed analysis models have been criticized in terms of their accuracy (e.g., [33,34]), they remain a very popular tool in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for territorial planning and landscape analysis. Accordingly, there are numerous studies of viewshed analysis for various landscape components (e.g., [26,31,35,36]), whereas, up to now, only a few focus on PV site selection [32,37]. Specifically, in [37], ranking of feasible areas for new PV installations according to their visibility was realized by conducting a fuzzy viewshed analysis, which enables the calculation of the maximum number of hours in a mean day in which the PV plant may be viewed by each potential observer. The proposed methodology was applied for two different Spanish municipalities. Zorzano-Alba et al. [32] developed a GIS-based methodology to identify areas for new PV plants in regions with special landscape or cultural protection that will have low or high visibility for a set of moving observers, with an application to the La Rioja region in Northern Spain. Visibility was quantified by calculating the “Global Accumulated Perception Time” variable, which was defined as the cumulative total hours in a year in which the proposed PV installation can be seen by observers moving along roads/paths in the area under investigation. Logarithmic functions were used to account for the distance-decay effect.
The utilization of a viewshed analysis within the PV plants’ site selection facilitates the objective identification and/or ranking of suitable, in terms of visibility, areas. Moving one step further, a viewshed analysis could be combined with an adequate optimization method, such as Genetic Algorithms (GAs), to determine, in a mathematically integrated manner, areas for PV installations that minimize visibility and satisfy potential spatial constraints imposed by various siting factors. GAs correspond to a characteristic evolutionary algorithm that mimics the process of natural evolution according to the “survival of the fittest” rule by deploying relevant computational operators [38,39,40]. Up to now, GAs have been widely used by various researchers to solve other forms of PVs allocation/site selection problems, including, for example: the optimum allocation of PVs in terms of minimizing power losses [41], the determination of optimum PV plants’ locations according to the seasonal and diurnal cycles related to the system load and solar generation profiles [42], the optimum placement of hybrid PV–wind systems in terms of minimizing costs [43], as well as the determination of sustainable geographical clusters (territories) to satisfy energy demands by solar and wind energy exploitation [44].
In the present paper, an integrated methodology is developed to identify optimum areas for PV installations on municipality scale that minimize the relevant visual disturbance, while satisfying, at the same time, spatial constraints associated with land use, and environmental and techno-economic siting factors. The visual disturbance of the public due to PV installations is quantified by introducing and calculating an indicator called herein the “Social Disturbance” (SDIS) indicator. The largest the SDIS indicator for an area is, the higher the visibility of this area will be, advocating higher visual disturbance of the public (i.e., social disturbance) due to PV installations in this area. The proposed methodology is applied for the municipality of La Palma Del Condado located in in the province of Huelva, Andalucia, Spain. Initially, thematic maps of exclusion siting criteria with their incompatibility zones and a Digital Surface Model (DSM) of the region are developed using GIS. A cumulative weighted viewshed analysis follows to calculate the SDIS indicator. Successively, the optimization problem is solved by developing a GAs-driven optimization process, where optimum locations are determined for predefined values of the following two siting preferences: (a) the maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance; and (b) the minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations. By modifying the values of the aforementioned preferences, different sets of optimum solutions are obtained. These solutions are, finally, employed as a basis to create a flexible and easy-to-use web-GIS application, facilitating policy-makers to choose the set of solutions that better fulfils their preferences/strategies. The mitigation of social oppositions resulting from visual disturbances of PV installations presents an important factor that can contribute to the sustainable site selection of these renewable energy systems. The present paper tackles this problem and fills existing research gaps by: (a) explicitly formulating the PV site selection problem as an optimization problem, where areas that minimize the PVs’ visual disturbance and satisfy spatial constraints are being sought; and (b) proposing an integrated methodology to solve the aforementioned optimization problem, where GIS databases, viewshed analysis, and GAs are efficiently combined.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, the study area is presented. Section 3 includes a detailed description of the components of the developed methodology. The results of the present paper are presented and discussed in Section 4, and, finally, in Section 5, the concluding remarks and key findings of this investigation are cited.
2. Study Area
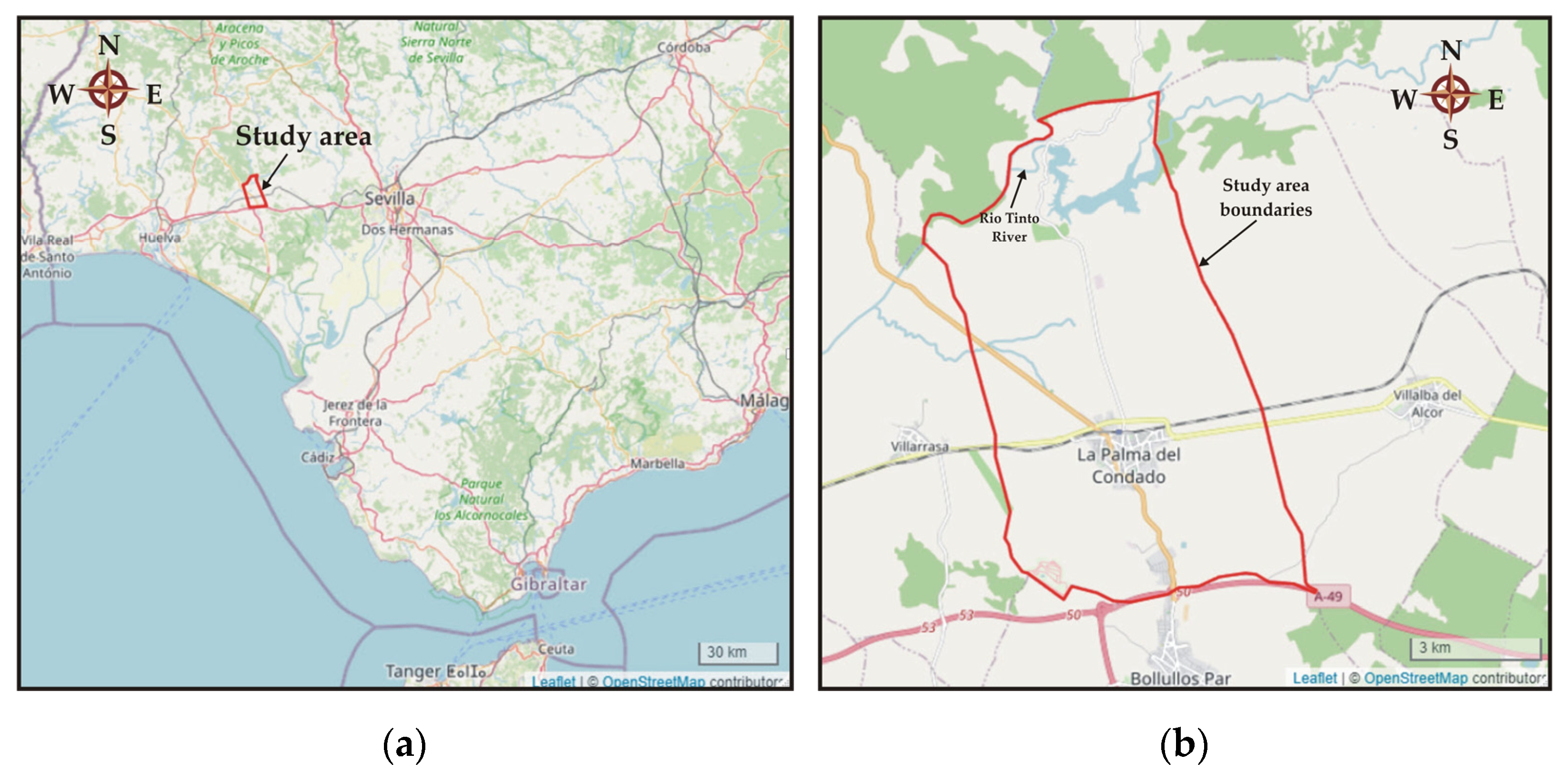
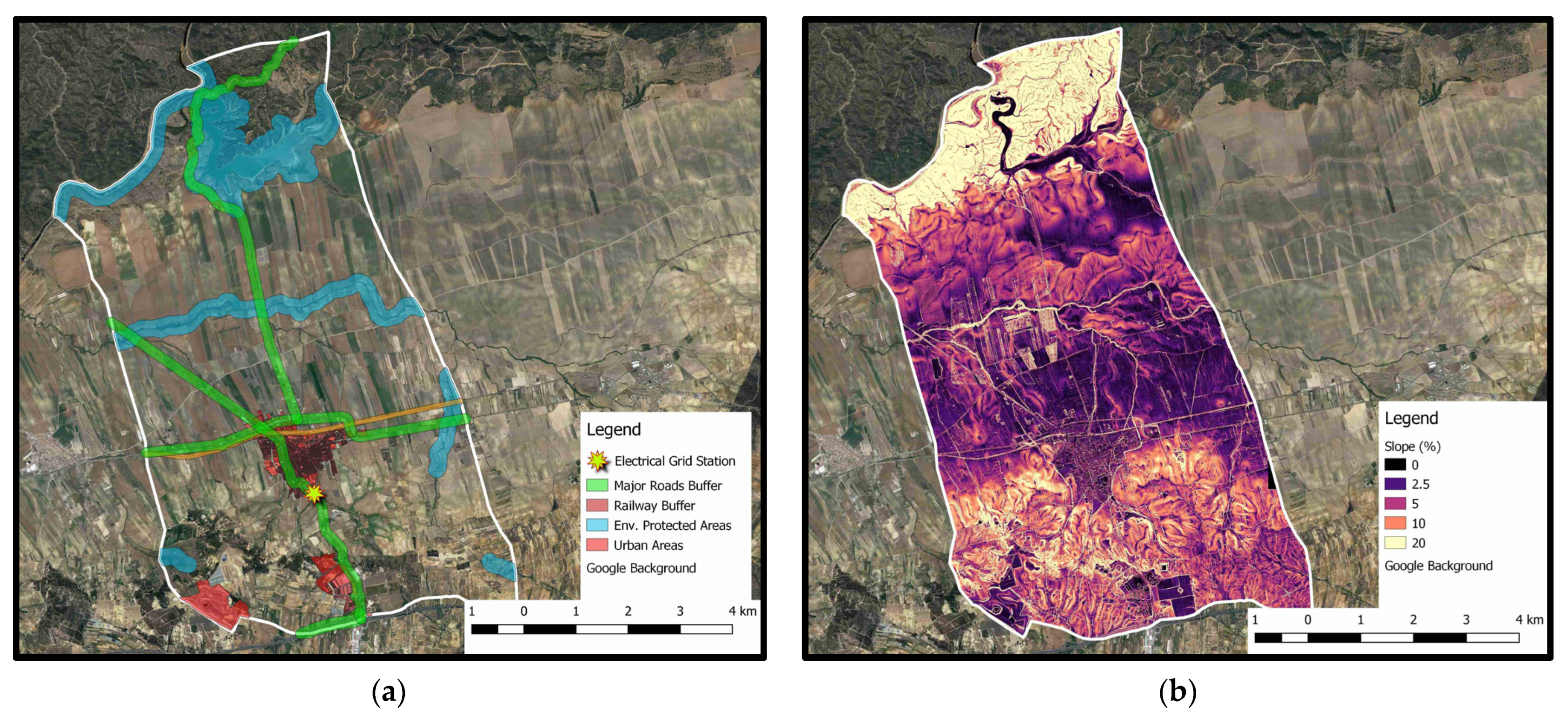
The region under investigation corresponds to the municipality of La Palma Del Condado located in Andalucia, Spain, in the province of Huelva (Figure 1a). The municipality has (2021) a population of approximately 10,700 people [45] and covers an area of 60.5 km2. The study area (Figure 1b) consists of agricultural lands, including vineyards that are critical for the local economy, residences, and urban areas, main roads, and railways. Furthermore, it is surrounded by Natura 2000 areas. Specifically, the Rio Tinto River (Figure 1b), as well as the wider Natura 2000 zone in the northern part of the area, are famous attractions to tourists and scientists because of the special characteristics of their aquatic environment.
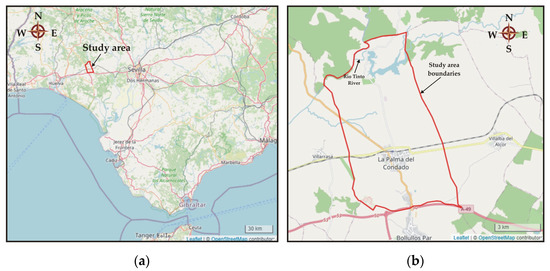
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the study area in the wider area of Andalusia, Spain; (b) boundaries of the study area.
High temperatures and solar radiation values make the study area favorable in terms of PV productivity [46]. It should be mentioned, however, that, currently, a specific spatial planning framework for deploying PVs in the region does not exist and the municipality adopts general siting criteria applicable to any type of structure (e.g., buildings) for new PV installations. Along these lines, the municipality targets to develop a relevant framework that will make it possible for investors to install PVs, while, at the same time, respecting the physical and the socio-economic environment.
3. Methodology
The developed methodology in this paper aims at identifying optimum areas for PV installations on municipality scale that minimize the relevant visual disturbance, quantified by the SDIS indicator, and satisfy spatial constraints related to land use, environmental, as well as to techno-economic siting factors. By minimizing the SDIS indicator, mitigation of potential social oppositions and negative impacts on land activities (e.g., tourism, residency construction) can be achieved.
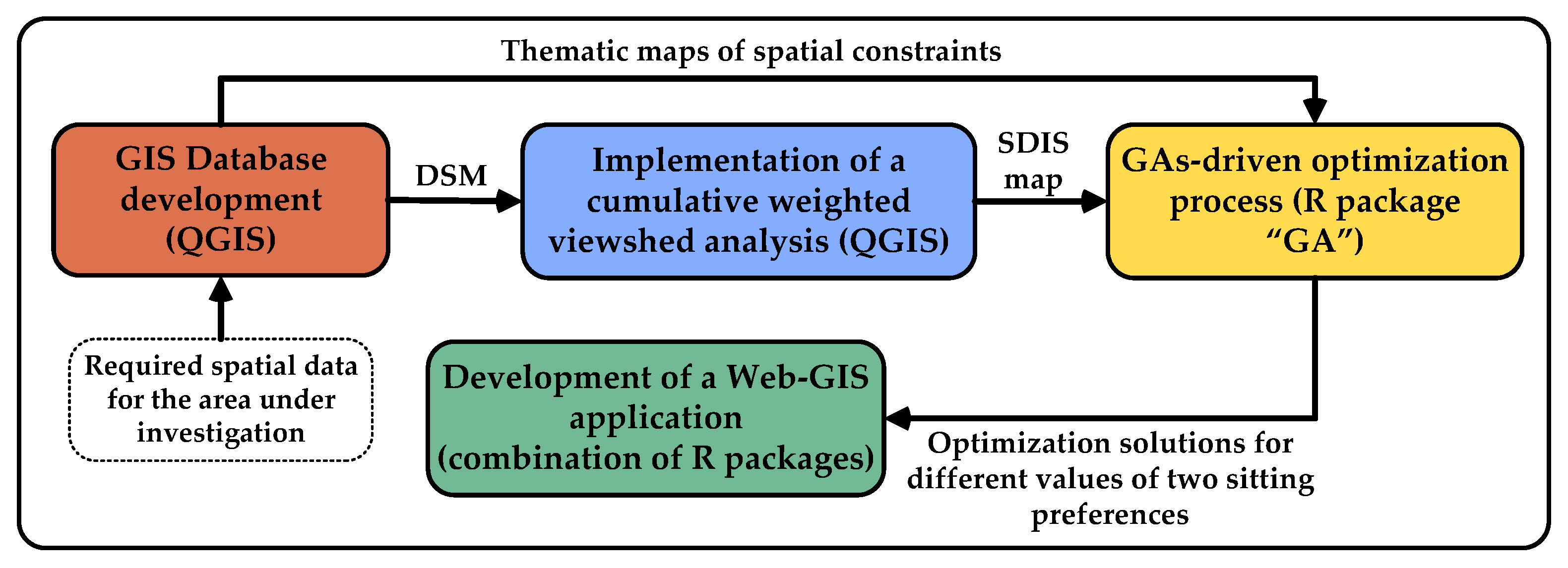
The whole methodology is shown schematically in Figure 2. Initially, a GIS database is created, including thematic maps of exclusion criteria with their incompatibility zones (spatial constraints), and a DSM of the region. The latter model is successively deployed in order to perform a cumulative weighted viewshed analysis, where viewshed maps are created and the SDIS indicator is calculated and mapped. The spatial constraints and the SDIS maps are, then, used to perform a GAs-driven optimization process, where optimum locations are determined for predefined values of two siting preferences corresponding to: (a) the maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance; and (b) the minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations. By modifying the values of the aforementioned siting preferences, different sets of optimum solutions are obtained, which are, finally, used as a basis to create a web-GIS application. The latter tool enables the visualization of PV plants’ optimum locations in the study area for different bounds of the PV locations—grid station in-between distance and of the PV locations’ total coverage area, facilitating policy-makers to choose a set of solutions that fulfils better their preferences on the above factors. In the following sections, the components of the present methodology are described in detail.
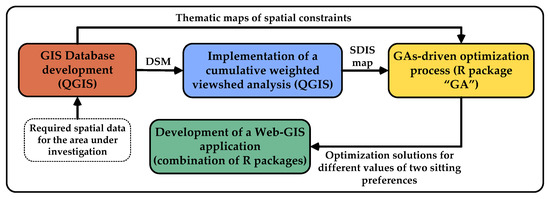
Figure 2.
Schematic view of the methodology developed and applied in the present paper.
3.1. Development of the GIS Database
In order to solve the examined siting optimization problem, the development of an adequate GIS database is initially required. This database includes: (a) thematic maps of exclusion criteria (with their incompatibility zones) that impose spatial limitations for the PV installations in the study area based on utilization restrictions, and environmental and techno-economic considerations; and (b) a DSM that is deployed in the preceding viewshed analysis. In the present analysis, five (5) exclusion criteria have been taken into account (Table 1).

Table 1.
Exclusion criteria and their incompatibility zones considered in the present analysis.
EC1 contributes to mitigate the potential environmental risk associated with PV installations. By applying this criterion, all Natura 2000 zones of recognized natural and ecological value (e.g., [15]) are not considered suitable for the deployment of PVs. The same holds true for the areas within a distance of 150 m from the aforementioned zones. This distance has been selected based on relevant limits available in the literature (e.g., 500 m in [49,50], 100 m in [51]), taking into account the size of the examined study area.
EC2 and EC3 are considered for safety and technical reasons. EC2 excludes the existing major roads and all areas within a distance of 100 m from them, which has been defined according to the relevant limits found in the literature (e.g., [49,52]). In a similar manner, EC3 excludes the existing railway network and a 50 m buffer safety zone from it. The latter limit has been selected according to [53].
Regarding EC4, all non-agricultural areas (e.g., urban areas, residences etc.) are excluded from the optimization process. The same holds true for vineyards, since, according to the municipality authorities, they are considered extremely important for the local economy.
As for EC5, the deployment of PVs in areas with large terrain slopes leads to high investment costs. Accordingly, an upper bound of the terrain slope is taken into account for technical–economic reasons. A wide range of the aforementioned bound can be found in the literature: 2% in [46], 15% in [15], and 25% in [51,54]. In the present paper, the value of 5% has been selected.
All spatial data related to the exclusion criteria were collected from various sources (Table 1), and they were appropriately processed to develop the GIS database and the relevant thematic maps using QGIS. In the case of EC5, the gradient field consideration requires an adequate Digital Terrain Model (DTM). For this purpose, Lidar data have been used and processed using R package, “lidR” [55]. The developed DTM model was inserted in QGIS, and the thematic map of EC5 (raster format) was created using the “slope” function. The high accuracy of the produced map (the Lidar data accuracy was 1.5 points/m2) can result in standalone points with very large slope terrain values (representing, for example, a tree). To reduce the effect of these outliers, the average slope of the polygons examined was calculated. If this average value was smaller than 5%, the polygon was considered as a potential area for PV installations in terms of EC5. It is noted that Lidar data were also used to create the DSM model required in the viewshed analysis, including both the ground elevation and the objects’ elevations (buildings, trees etc.).
Finally, it should be mentioned that the exclusion criteria of Table 1 have been selected by taking into account the special features of the examined region, although numerous other criteria can be found in the relevant literature. For example, historical heritages or archeological sites have not been considered, since they do not exist in the study area. The altitude has also been omitted, since the maximum altitude of the examined region (<200 m) is far away from the upper bound of 1500–2000 m found in the literature [15]. In a similar manner, solar radiation (e.g., [46]) and temperature (e.g., [56]) have not been considered as exclusion criteria, since the limited area of the municipality examined leads to negligible variations of the two aforementioned quantities.
3.2. Vieswhed Analysis
In the present investigation, a cumulative weighted viewshed analysis is performed by aggregating the visibility from multiple observers, while taking into account the effect of the distance between the observers and the locations of the PV installations. The overall aim of this analysis, which is realized using the “QGIS visibility analysis” plugin [57], is the quantification and the mapping of the SDIS indicator in the study area.
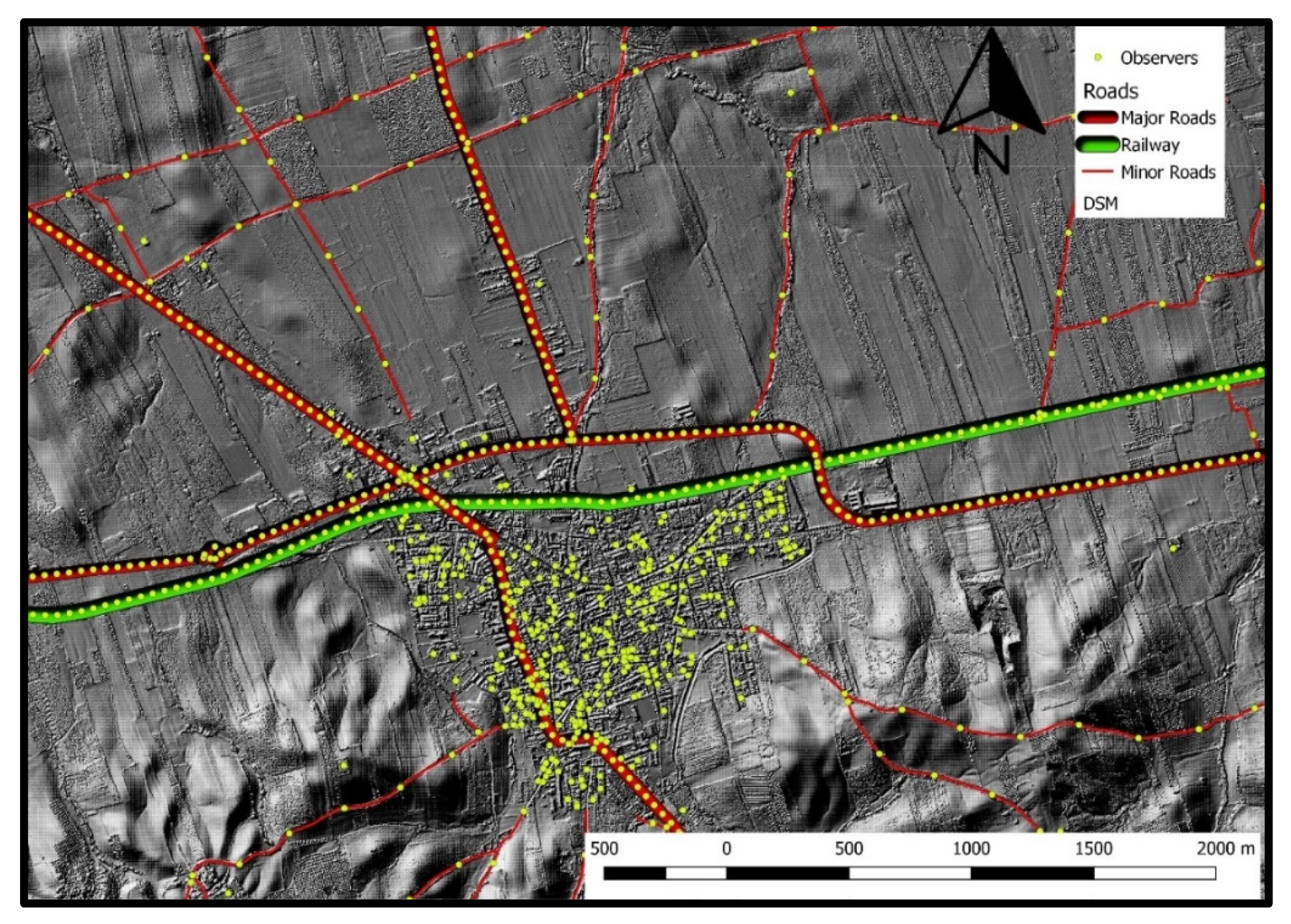
Starting with the observers, two categories of observers have been taken into account corresponding to residents and drivers. Thus, the spatial placement of the observers has been performed according to the residences’ (buildings) location and the roads’ traffic, respectively. The residences have been represented as spatial polygons (based on the relevant data obtained from the municipality), and 10% of them were randomly chosen by applying a uniform distribution function to the polygons’ IDs. Successively, each of the selected polygons has been replaced by a point in QGIS representing one observer. Regarding the roads, these spatial entities have been divided into major and minor ones based on their traffic characteristics. In the case of the major roads, 10% of the daily traffic was chosen for reasons of conciseness. This percentage was then divided over the total length of each road, leading to 1 observer per 50 m. Due to the absence of data for the minor roads, a proportion of 1/5 was chosen between the major and the minor roads, resulting in 1 observer per 250 m in the latter roads’ category. The railroad in the area was treated similarly to the major roads (i.e., 1 observer per 50 m). Furthermore, some extra observers not belonging to the aforementioned categories were placed in the Natura 2000 region, since this zone and especially the Rio Tinto River attract many visitors due their great environmental importance. The location of the observers in a region around the La Palma Del Condado city is shown in Figure 3.
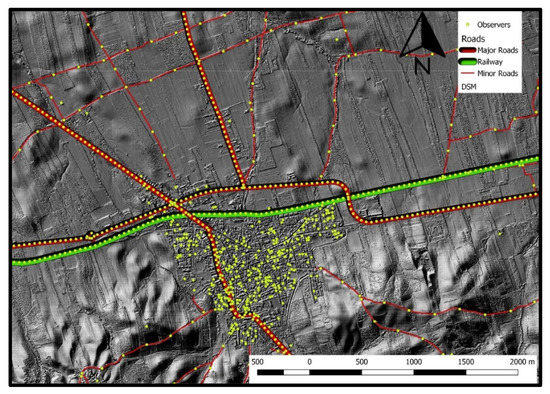
Figure 3.
Locations of the observers on the major and minor roads and on the railway in a region around the La Palma Del Condado city along with the developed DSM.
Regarding the distance between the observers and the locations of the PV installations, the closer the distance is, the higher the disturbance perceived by the observers will be. The concept presented is similar to “utility functions” that are often used in economics [58]. Let us consider M different classes of viewshed maps, with an jth, , class corresponding to a predefined maximum visibility distance, rj. By weighting and aggregating the aforementioned viewshed maps, the disturbance, , of an ith, , observer, relevant to a point/pixel, pix, can be quantified according to Equation (1):
In the above equation, cj, , corresponds to the weight of the jth viewshed class defined below, whereas , , , is equal to 1 if the examined point/pixel for the jth viewshed class can be seen by the ith observer, or equal to 0 if the opposite holds true.
By summing up the values of for all the N observers, the SDIS indicator for each point/pixel, , is obtained (see Equation (2) below). for all points/pixels in the study area forms the SDIS map.
The question that arises is how the cj, j = 1,…,M, values are determined. To answer this question, it is necessary to take into consideration two factors. The first one is that the disturbance of an observer decreases in a non-linear way with respect to the distance. The non-linear relationship between an object and an observer has been already indicated in the literature [31,59,60]. The second factor is that the disturbances of all the observers will be aggregated; therefore, the principle of additivity needs to be fulfilled, in a way that the final SDIS map will offer trustworthy results. To fulfil these two requirements, Equation (3) is introduced to calculate cj, j = 1,…, M:
where rM is the maximum distance that an observer can see in the case of the M class viewshed (largest maximum distance among all classes), whereas the value of “+1” is used in order to consider the M class as the reference class. For applying Equation (3), the parameter y needs to be defined, having in mind that the smaller the y value is, the more emphasis will be given on objects cited close to an observer. In the present paper, y has been taken as equal to e and, thus, cj, j = 1,…, M, is finally calculated suing Equation (4) as follows:
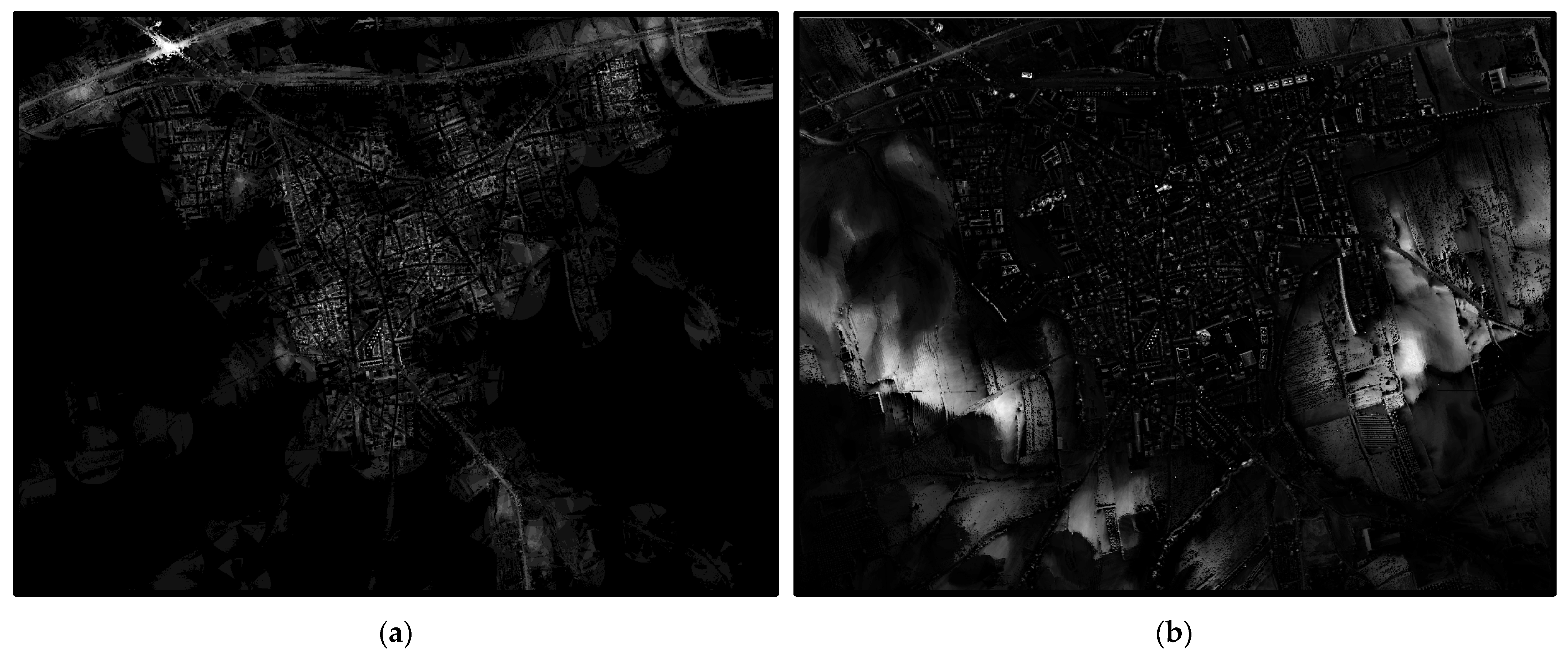
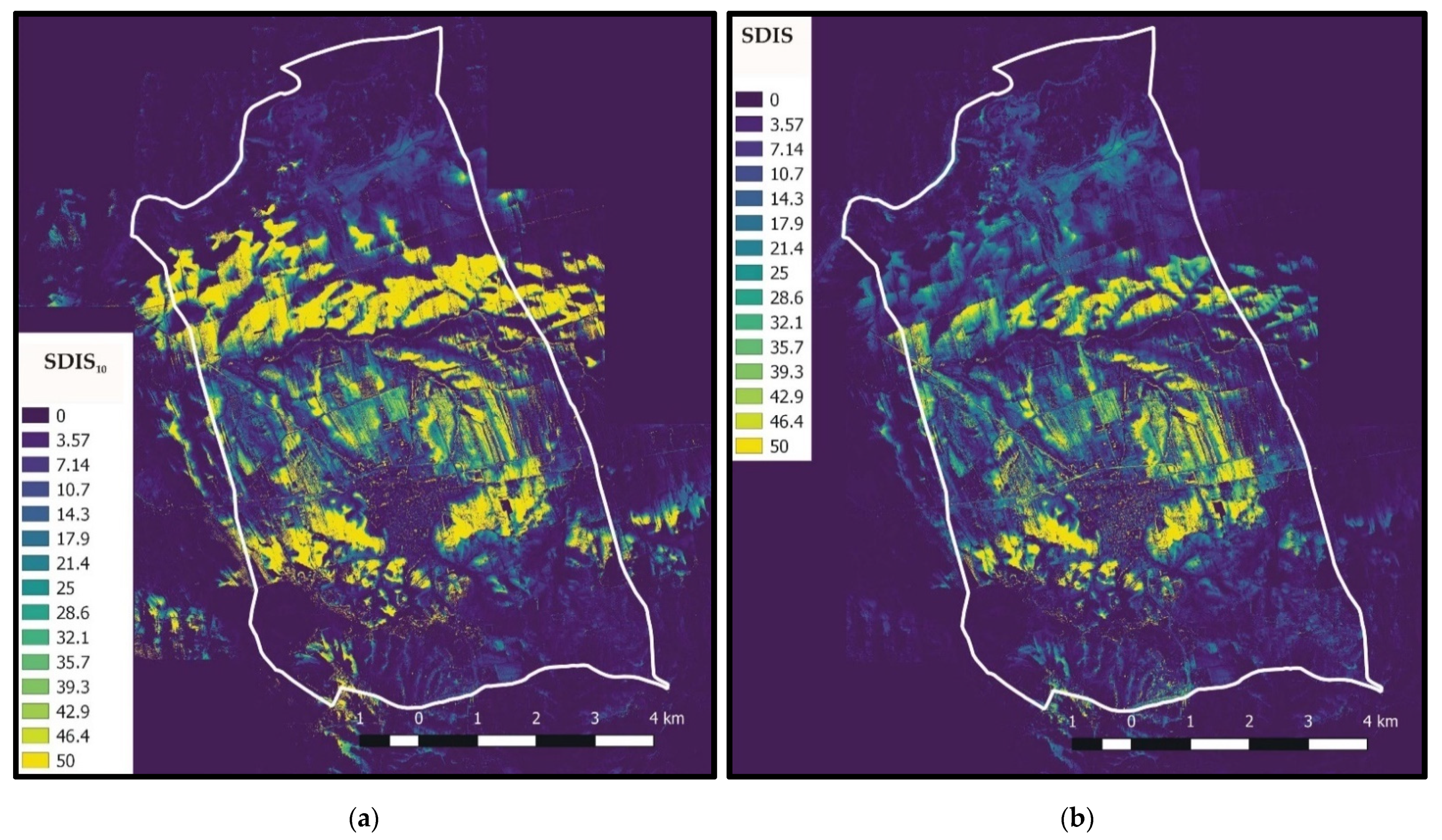
In total, 10 classes of viewshed maps have been considered with rj and cj, j = 1,…, 10, values shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the increase of rj leads to a nonlinear decrease of cj. The maximum distance of the 10th class, r10, is of high importance, since an area located at distance from an observer larger than r10 does not disturb the observer. The intermediate classes support a better discretization of the distances, and, furthermore, they introduce some extra importance to the smaller distances. The reader should have in mind that as the weighted viewshed maps are aggregated (Equation (1)), for a PV placed between 0 m and 100 m from an observer, the will be equal to 28.859 and not equal to 4.912. Figure 4 includes two cumulative viewshed maps for r1 = 100 m and r6 = 1000 m, assuming c1 = c6 =1 in a region around the La Palma Del Condado city. Cumulative weighted viewshed maps, along with the final DSIS map, are cited and discussed in the Results section.

Table 2.
rj and cj values of the 10 viewshed classes considered in the present analysis.

Figure 4.
Cumulative (not weighted) viewshed maps in a region around the La Palma Del Condado city for two different maximum visibility distances: (a) 100 m; (b) 1000 m (white areas correspond to the most visible areas).
3.3. Optimization Process
The present GAs-driven optimization process aims at identifying optimum areas for PV installations on municipality scale that minimize the SDIS indicator and satisfy spatial constraints introduced with the exclusion criteria of Table 1. Optimum locations are determined for predefined values of two siting preferences: (a) the maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance; and (b) the minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations.
In order to form the examined optimization problem, SP is defined as a spatial entity corresponding to a spatially projected vector (polygon or spatial polygon data frame). The overall region, OR, examined (municipality) is divided into K spatial entities; namely, , where is the cardinality of the OR superset. Each SPk, , has a set of spatial and non-spatial attributes, , defined as:
In Equation (5), includes the land use information of SPk related to EC4 (Table 1), is the average slope terrain gradient (%) of SPk related to EC5 (Table 1), corresponds to the SDIS of SPk, is the coverage area (m2) of , whereas is the distance (m) between the electrical grid station and the most distant point of SPk. Furthermore, represents the set (category) where an SPk belongs, and can take the labelled values of “A”, “B” or “C” according to Table 3. Set A includes the optimum solutions; namely, all SPs that minimize the DSIS indicator, satisfy none of the exclusion criteria, and are consistent with the two siting preferences. Set C includes that satisfy any of the EC1, EC2, or EC3 exclusion criteria, while, at the same time, correspond to pure non-agricultural areas (EC4). Finally, in set B, SPs that do not belong to either A or B sets are included. Specifically, set B contains SPs that satisfy only EC5 and/or EC4 (i.e., they correspond to vineyards). Accordingly, in this set, areas that are not eligible for PV installations only due to economic reasons are classified. Furthermore, it contains SPs that although do not satisfy any of the exclusion criteria, they do not correspond to solutions that lead to minimum DSIS values and/or are consistent with the two siting preferences.

Table 3.
Classification of SPs into sets.
Based on all the above, the GAs optimization process developed herein seeks to determine the SPs that belong to set A by matching and classifying each SPk, , to one of the A, B, or C sets. This problem has many similarities with graph theory and matching problems [61], as the SPs will be matched to a set according to their attributes. The aforementioned matching and classification are implemented in two successive stages. In the first stage, SPs that satisfy EC1–EC4 are determined by deploying the relevant data and the thematic maps of the GIS database, and by performing the required spatial intersections using a relevant R package. If, for example, an SPk intersects with the 150 m buffer of an environmentally protected area (EC1), then ATk,set = “C”. Similarly, for EC4, if ATk,use ≠ “agricultural”, then ATk,set = “C”. The intersections are performed in each GAs iteration following an approach that will be presented later in this section. The aforementioned SPs are classified to the C set and are subtracted from the OR superset. Each ∉ is taken into account in the second stage, where the GAs algorithm determines the elements (SPs) of the A set according to Table 3. Thus, the objective function of the present optimization problem is defined as follows:
where .
Equation (6) implies that the GAs algorithm seeks for optimum SPs in terms of minimizing the sum of their SDIS indicators. Furthermore, the solution is subjected to the following constraints:
In Equation (9), DGmax denotes the maximum allowable distance from the grid station for installing PVs, whereas in Equation (10), Areamin corresponds to the minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations. By setting different values for DGmin and Areamin based on relevant preferences, different optimum solutions can be obtained. Having solved the optimization problem described by Equations (6)–(10) and, thus, having determined the SPs that belong to the A set, the remaining SPs are classified to set B.
In order to label the ATk,use attribute (Equation (7)), the land use data included in the GIS database are used. Similarly, by deploying the slope terrain raster map of the GIS database, the attribute (Equation (8)) is quantified and is taken as equal to the average value of the raster pixels that fall inside an SP. As for the attribute (Equation (6)), the final SDIS raster produced from the viewshed analysis is “clipped” using the spatial features of an SP as a “mask”. The masked (Equation (2)) values are then summed up to quantify .
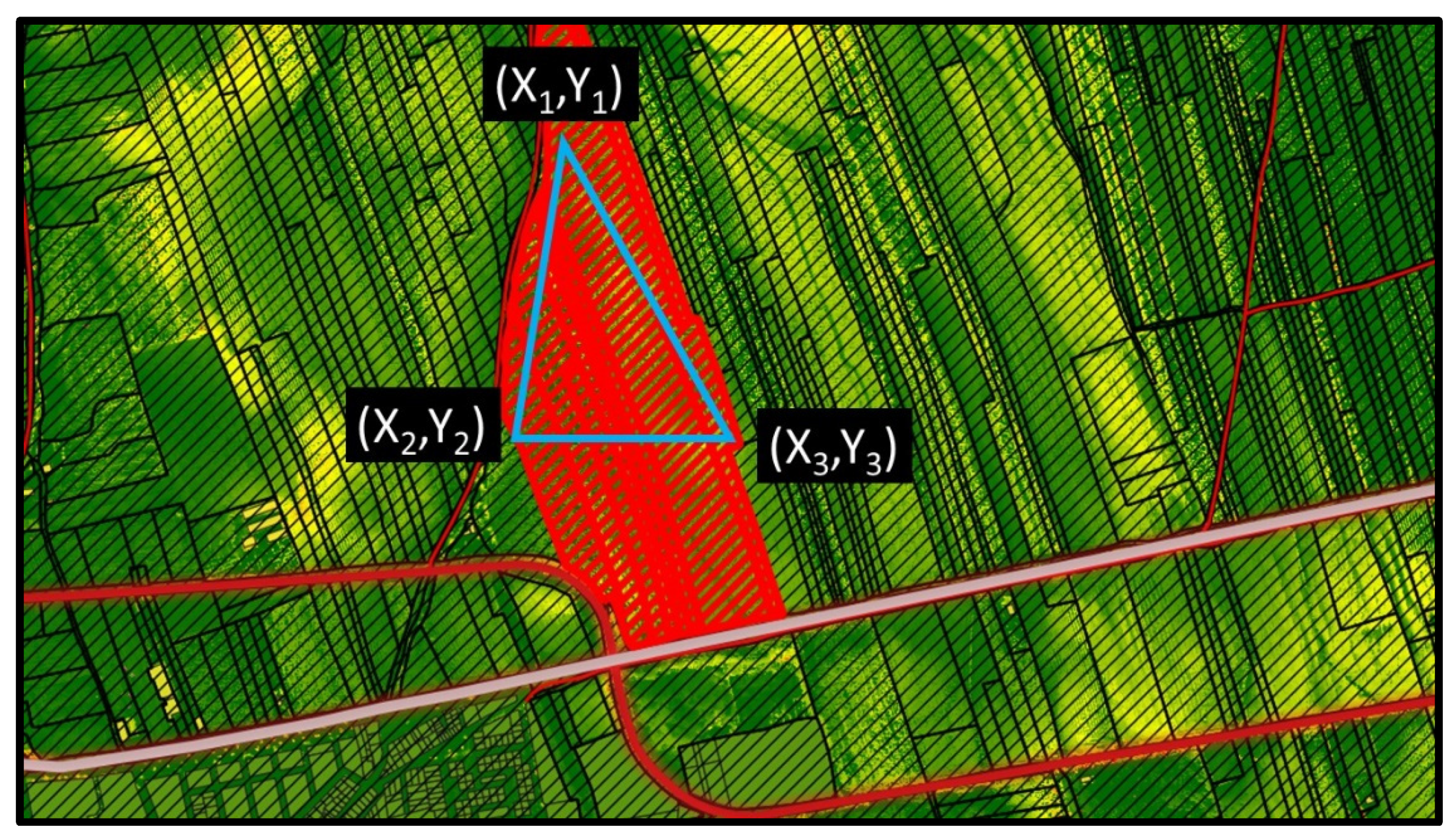
In order to solve the present optimization problem, GAs are deployed, which are numerically realized using the R package, “GA” [62]. GAs are based on the iterative generation of populations of chromosomes, representing possible optimum solutions based on the “survival of the fittest” rule [38,39,40]. Accordingly, the generation of populations of possible SPs with ATk,set = “A” could have been considered. This approach, however, would result to extensively sparse optimum solutions within the examined region, which, in turn, would be difficult to be realized in terms of regional planning. For this reason, another approach is deployed in the present paper, facilitating the formation of compact regions with . Specifically, a chromosome is represented by two distinctive triangles, which intersect with and include a number of SPs (Figure 5). At each iteration, the GAs algorithm initially finds the SPs of the triangles that belong to the C set and excludes them from further analysis. For the remaining SPs of the two triangles, Equations (6)–(10) are then applied, and the SPs satisfying those equations (i.e., SPs∈A) correspond to a potential optimum solution.
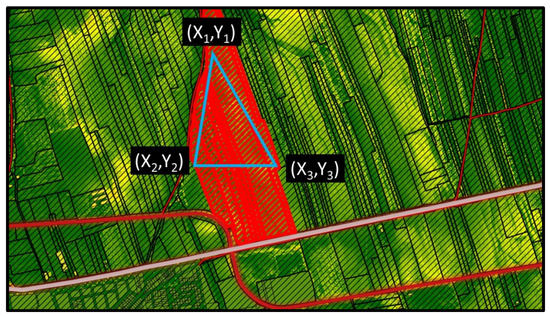
Figure 5.
One of the two triangles of a chromosome, intersecting with and including a number of SPs (red blocks). Xi, Yi, i = 1,2,3, are the spatial coordinates of the triangle’s vertices in the deployed X − Y grid. Red lines correspond to minor roads, the pink line represents the railway, and the background is the SDIS raster.
A X − Y grid of 10 m is deployed in the area that has the dimensions, 11.227 km × 14.593 km. Considering that 210 = 1024 and 211 = 2048, any of the X, Y coordinates require 11 bits to be represented in a binary form. Accordingly, 22 bits are required to create a point, 66 to create one triangle, and 132 to create two triangles. The latter 132 bits correspond to a chromosome (i.e., a possible solution to the optimization problem containing SPs that belong to the A set). Three-hundred generations of a population of 125 chromosomes each have been used. The mutation and the crossover probability have been set to 35% and 85%, respectively, determining which of the chromosomes will survive to the next generation. Elitism has been also deployed, letting the best five chromosomes survive always to the next generation. Penalties with successively decreasing values are assigned in the algorithm in a sequential manner as follows: (i) for points or triangle areas that fall outside of the examined region, as well as for triangles that intersect with each other (penalties with the largest values); (ii) for limitations resulting from the exclusion criteria of Table 1 related to set C (penalties with intermediate values); and, finally, (iii) for limitations resulting from the constraints described by Equations (7)–(10) (penalties with the smaller values). In this way, the algorithm efficiently promotes the chromosomes that fulfill as many requirements as possible.
In the present paper, optimum solutions have been found for 100 different combinations of DGmax and Areamin values. More specifically, 10 different DGmax values have been taken into account, varying from 2.5 km to 7.0 km, with a step of 0.5 km. Regarding Areamin, 10 different values of this quantity have been also considered, from 0.5 km2 (≈0.8% of the overall region) to 5.0 km2 (8% of the overall region), with a step of 0.5 km2. To perform all the required computations, the computer cluster, Aristotelis of Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, has been used, deploying 125 CPUs simultaneously, one for every chromosome of each generation. The corresponding results are, finally, used as a basis to create a relevant web-GIS application, which is presented in the next section. This application is realized by using the R packages, “shiny” [63], “leaflet” [64], “tmap” [65], and “plotly” [66].
4. Results and Discussion
In this section, the results of the present analysis are presented and discussed. Starting with the thematic maps of the exclusion criteria, Figure 6a shows the incompatibility zones of EC1–EC4 (Table 1), whereas in Figure 6b, the slope terrain thematic map (EC5, Table 1) is cited. Areas that fall within the incompatibility zones of Figure 6a cover 26.9 km2 and belong to set C. Most of these areas correspond to environmentally protected areas, followed by minor roads and non-agricultural areas.
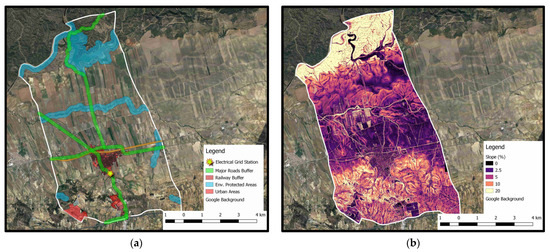
Figure 6.
(a) Incompatibility zones of EC1–EC4; (b) slope terrain thematic map (EC5).
With regard to the viewshed analysis, Figure 7a shows a cumulative weighted viewshed map indicatively for a maximum observation distance of 5000 m (10th viewshed class of Table 2, with r10 = 5000 m and c10 = 1), whereas in Figure 7b, the finally produced SDIS map, where all viewshed classes of Table 2 are taken into account, is presented. In Figure 7a, the symbol SDIS10 has been used in the legend to denote results that have been obtained for all N observers (Equation (1)), but for , in Equation (2). The results of Figure 7a indicate large SDIS10 values in the high elevation areas, since those areas correspond to the most visible ones from a large distance. However, it can be seen that the SDIS map (Figure 7b) offers better results in terms of disturbance, since it accounts for the largest effect of the nearest objects on the visibility in an efficient manner. Accordingly, large SDIS values are bounded in areas located close to the roads and the residencies.
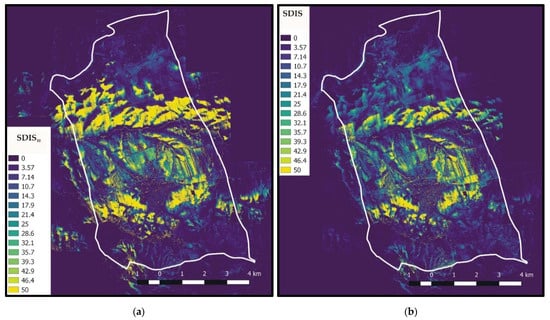
Figure 7.
(a) Cumulative weighted viewshed with maximum visibility of 5000 m; (b) SDIS map.
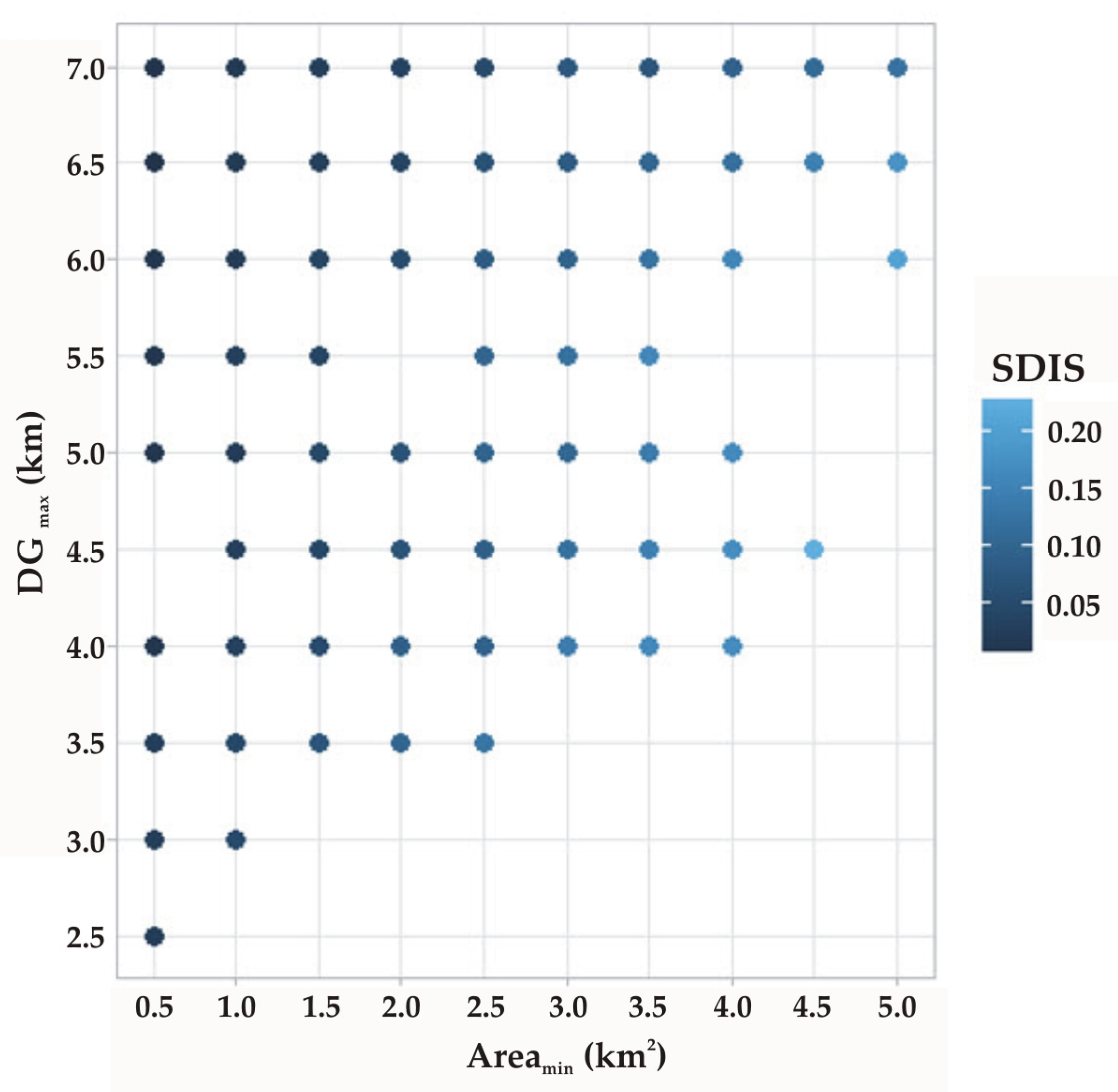
As for the optimization results, the minimum values of the objective function described by Equation (6) (i.e., sum of the SDIS values over all optimum areas) obtained for the 100 different DGmax and Areamin combinations are summarized in Table 4. In this table, values ≥ 2.5 correspond to penalty values and denote DGmax and Areamin combinations without any possible solutions (i.e., A = {}). The results of Table 4 indicate that for a given DGmax value, the increase of the minimum allowable total coverage area for PV installations (Areamin) generally leads to larger SDIS values. This is attributed to the fact that by increasing Areamin, larger areas suitable for installing PVs can be allocated, leading to a larger social disturbance. The opposite holds true for DGmax, since for a given Areamin, the increase of DGmax reduces the space suitable for PV installations, and, thus, it leads, in general, to smaller SDIS values. The effect of the DGmax and Areamin siting preferences on the optimization results is also shown schematically in Figure 8, where the minimum SDIS values of Table 4 for the 67 non-empty solution sets are plotted. It is also interesting to note that empty solution sets are mainly obtained for numerous Areamin values, when DGmax ≤ 3.5 km. For example, for DGmax = 2.5 km, only one optimum solution has been obtained in the case of the smallest examined Areamin (equal to 0.5 km2). This, in turn, illustrates that for small DGmax values, extensive areas for PV installations cannot be found in the region.

Table 4.
Minimum values of the objective function for the examined DGmax and Areamin combinations. Results with values < 2.5 should be multiplied by 109.
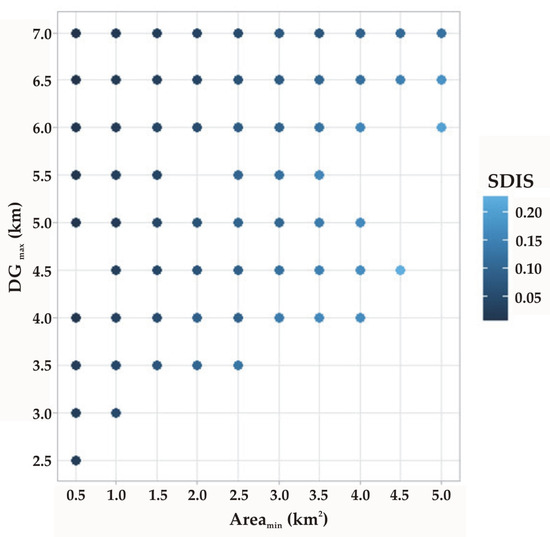
Figure 8.
Minimum values of the objective function for the examined DGmax and Areamin combinations that lead to non-empty solution sets (values of the SDSIS indicator have to be multiplied by 109).
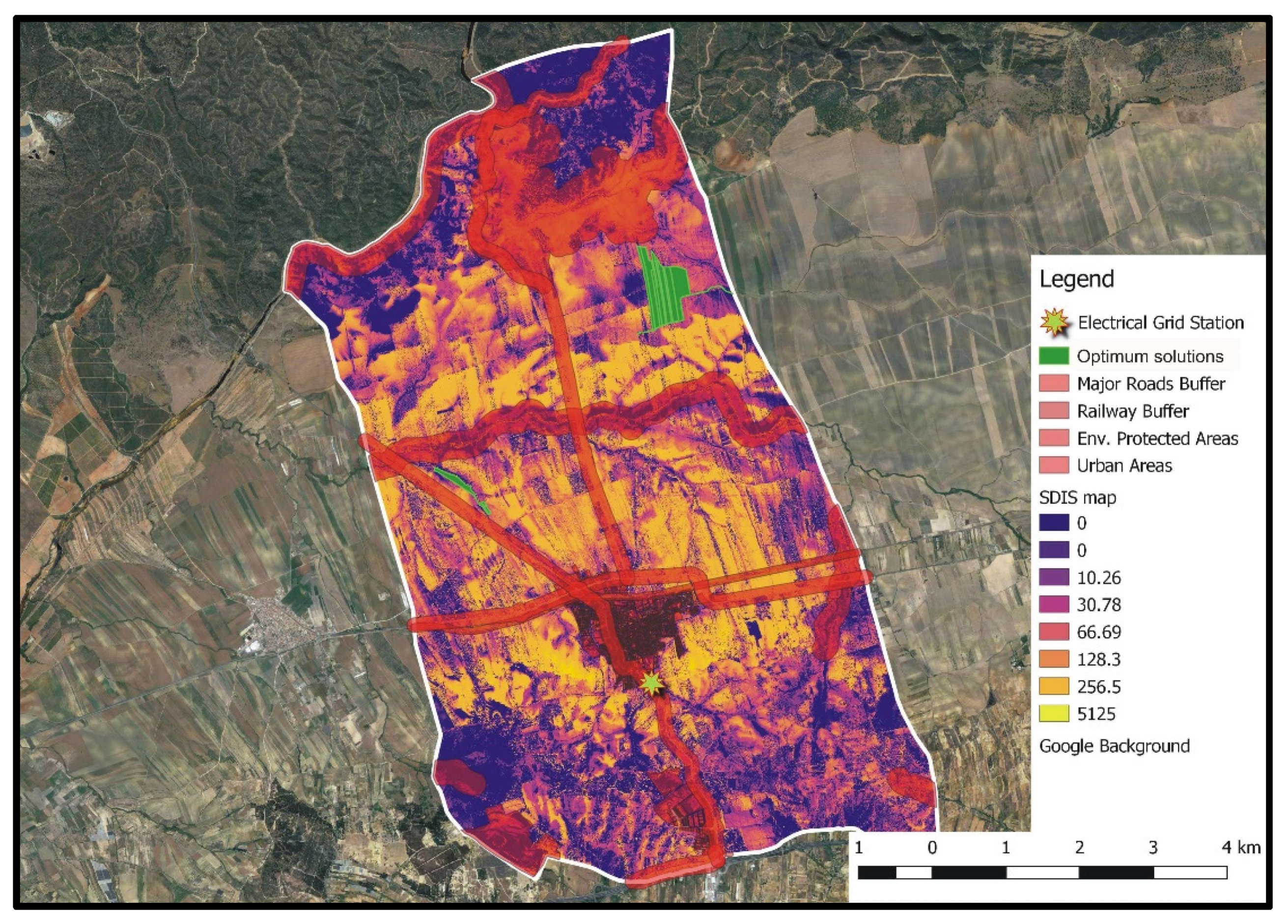
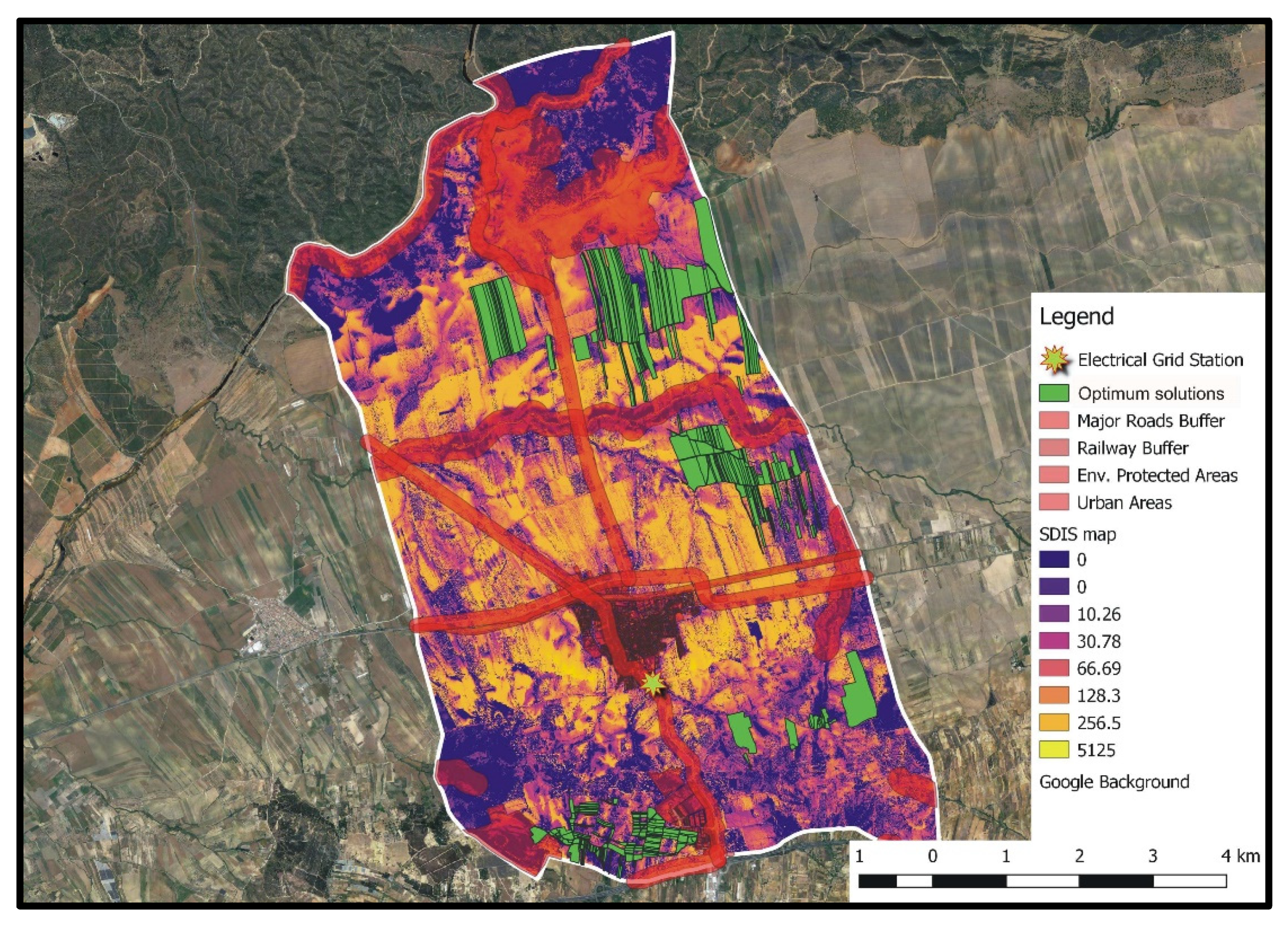
Figure 9 shows the entities of the A set (i.e., optimum solutions) for DGmax = 7.0 km and Areamin = 0.5 km2 (smallest examined low bound of PV locations’ total coverage area), whereas in Figure 10, the A set entities corresponding to the aforementioned DGmax, but to Areamin = 5.0 km2 (largest examined low bound of PV locations’ total coverage area), are presented.
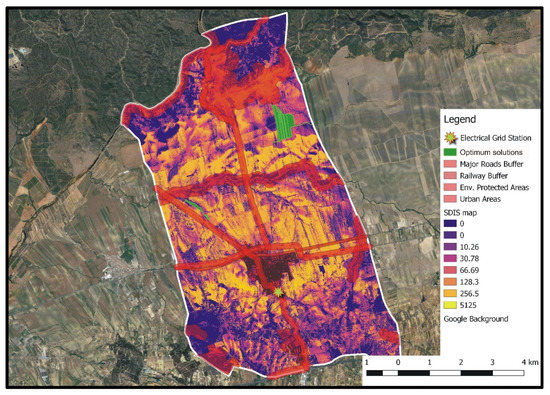
Figure 9.
Set A optimum solutions for DGmax = 7.0 km and Areamin = 0.5 km2 (values of the SDIS map have to be multiplied by 109).
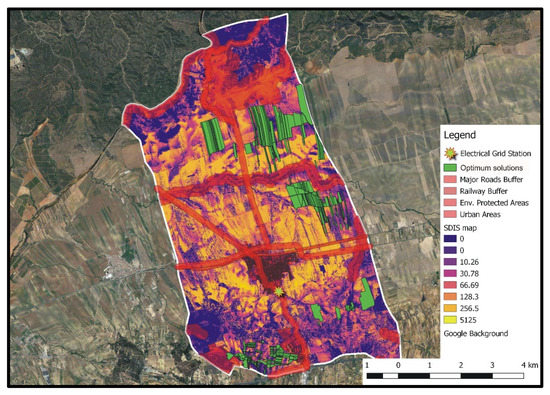
Figure 10.
Set A optimum solutions for DGmax = 7.0 km and Areamin = 5.0 km2 (values of the SDIS map have to be multiplied by 109).
It can be easily concluded that for both siting preferences combinations, the optimum areas for PV installations correspond to agricultural parcels that have low visibility, while not intersecting with the incompatibility zones of any of the exclusion criteria considered herein. Furthermore, distinctive compact regions of closely located agricultural parcels are formed. In the case of Areamin = 0.5 km2 (Figure 9), optimum locations are bounded in the north-eastern region of the study area. Some of these locations also correspond to optimum solutions when Areamin = 5.0 km2 (Figure 10). However, for this Areamin value, a larger number of optimum areas are obtained, which are also distributed in the form of compact regions within the whole examined study area. Although only two triangles are deployed in the GAs algorithm to identify optimum spatial entities (see Section 3.3), the results of Figure 10 clearly indicate that distinguishable compact regions of optimum locations for PV installations can be realized. This is attributed to the ability of the algorithm to create large-size triangles, which, at the end of the iterative optimization process, will include only spatial entities belonging to set A.
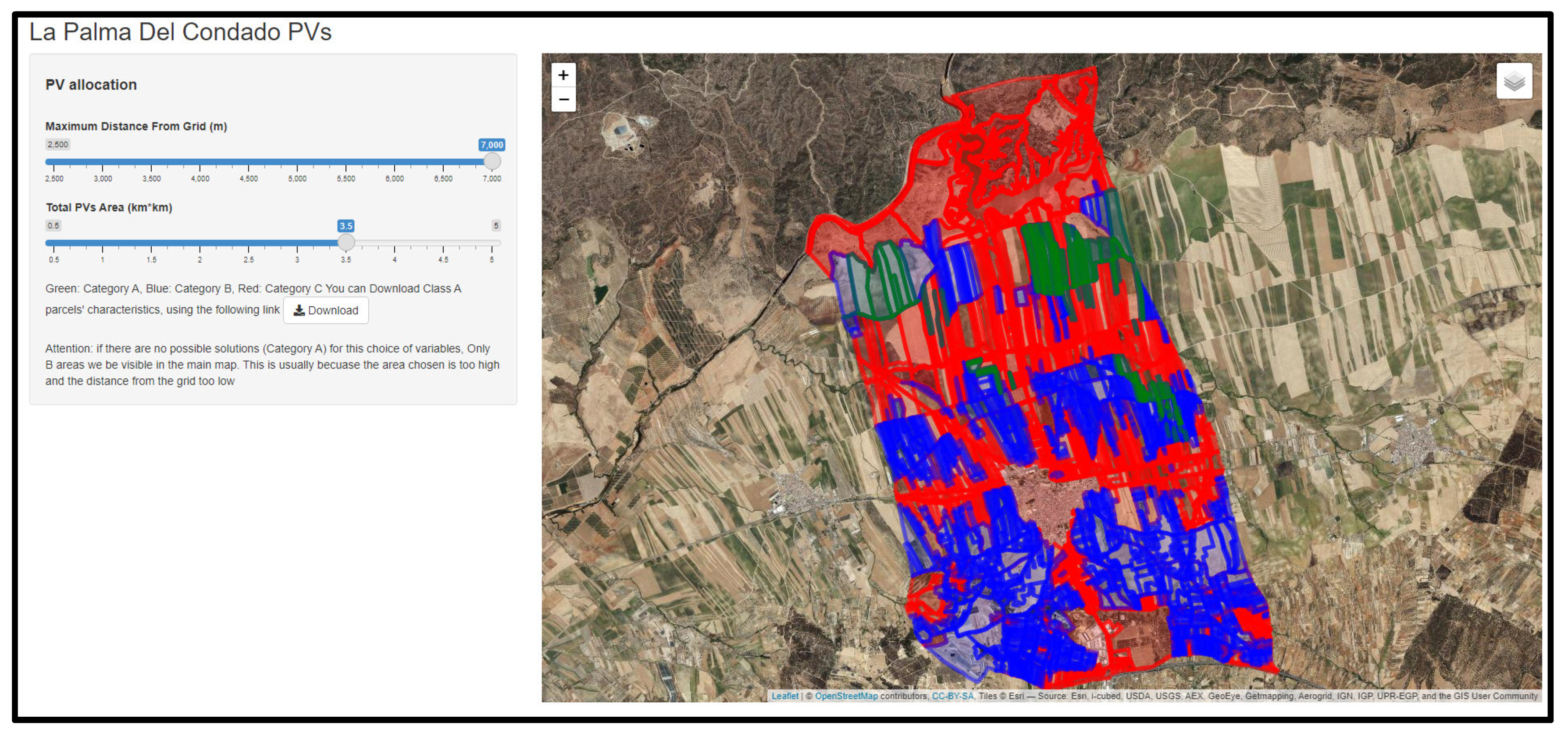
Finally, Figure 11 shows a snapshot of the web-GIS application developed by taking into account the results of the GAs-driven optimization process for all the examined DGmax and Areamin combinations. The user can: (a) set, via bars, his/her preferences regarding the values of DGmax and Areamin; (b) visualize all the results (optimum areas, as well as spatial entities belonging to B and C sets); and (c) download a matrix that contains all spatial information (e.g., official IDs) related to the areas of set A.
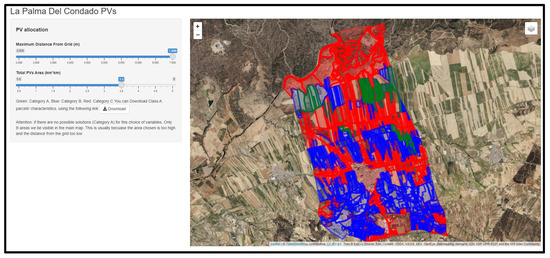
Figure 11.
A view of the web-GIS application for selecting optimum locations for PV installation in La Palma del Condado municipality.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, an integrated methodology has been developed to identify optimum areas for PV installations on municipality scale that minimize the relevant visual disturbance and satisfy spatial constraints related to land use, environmental, and techno-economic siting factors. The visual disturbance of the public due to PV installations is quantified by introducing and calculating the SDIS indicator, whereas optimum locations are determined for the predefined values of two siting preferences (maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance; and minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations). In addition to the development of standard thematic maps of exclusion criteria, a cumulative weighted viewshed analysis is realized to quantify the SDIS indicator, and then optimum solutions are determined by developing a GAs-driven optimization process. The proposed methodology is applied for the municipality of La Palma Del Condado located in the province of Huelva, Andalucia, Spain, for 100 different combinations of DGmax (maximum allowable PV locations—grid station distance) and Areamin (minimum allowable total coverage area of PV installations). The main conclusions of the present investigation can be summarized as follows:
- The map of the proposed SDIS indicator can be easily created by both researchers and practitioners with low computational cost, and it accounts for the larger effect of the nearest objects on the visibility in an efficient manner. Accordingly, it can offer more realistic results than traditional viewsheds for assessing the visual effect of PV installations to the public.
- For a given DGmax value, the increase of Areamin facilitates the allocation of larger optimally suitable areas for installing PVs; thus, the aforementioned increase leads generally to larger SDIS values. The opposite holds true for DGmax, since, from a physical point of view, the increase of DGmax for a given Areamin value reduces the space suitable for PV installations.For the examined study area, the GAs-driven optimization process has led to empty optimum solution sets for numerous Areamin values, especially when DGmax ≤ 3.5 km, demonstrating that for small DGmax values, extensive areas for PV installations cannot be found in the region.
- The developed GAs-driven optimization process offers the ability to determine distinguishable, but compact, regions of optimum locations for PV installations within the examined region, facilitating relevant regional planning decisions. The consideration of the SDIS indicator in the objective function can contribute to the mitigation of potential social oppositions and negative impacts on land activities, since optimum areas correspond to those that will have the minimum visual impact to the community.
- The developed web-GIS application presents a flexible and easy-to-use tool that enables the visualization of PV plants’ optimum locations in the study area for different bounds of the PV locations—grid station in-between distance and of the PV locations’ total coverage area. Accordingly, it facilitates policy-makers to choose the set of solutions that better fulfils their preferences/strategies related to the above factors. The flexibility of the tool can also contribute to the reduction of bureaucracy, as well as to the further boost of the local solar energy market in an environmentally friendly and socially accepted manner.
The proposed methodology is general and can be easily applied to other regions in or outside Spain in order to identify optimum areas for PV installations by appropriately modifying, if necessary, the set of the exclusion criteria according to the spatial conditions, legislation limitations, and/or any special features of the examined region. Furthermore, the calculation of the SDIS indicator by considering additional factors that can affect visibility (e.g., temporal variations), as well as the deployment of another evolutionary optimization method to solve the examined optimization problem and the comparison of results, including computational cost aspects, with the ones of the present study, could represent items for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.N., M.G. and E.L.; methodology, N.N., E.L. and M.G.; software, N.N.; formal analysis, N.N.; investigation, N.N. and M.G.; data curation, N.N.; writing—original draft preparation, N.N.; writing—review and editing, E.L. and M.G.; visualization, N.N. and E.L.; supervision, E.L. and M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the EUROPEAN UNION’s HORIZON 2020 RESEARCH and INNOVATION PROGRAMME under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement, no. 778039 (Project: “Planning and Engagement Arenas for Renewable Energy Landscapes” (PEARLS)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The first and the third author would like to thank the local authorities of La Palma Del Condado for supporting the realization of this work by providing relevant data. The optimization results of the present investigation have been obtained using the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUTh) High Performance Computing Infrastructure and Resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
PV, Photovoltaic; SDIS, Social Disturbance; GAs, Genetic Algorithms; GIS, Geographic Information Systems; DSM, Digital Surface Model; DTM, Digital Terrain Model; EC, Exclusion Criterion.
References
- Hussin, F.; Issabayeva, G.; Aroua, M.K. Solar photovoltaic applications: Opportunities and challenges. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 34, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefore, N.; Closas, A.; Schmitter, P. Solar for all: A framework to deliver inclusive and environmentally sustainable solar irrigation for smallholder agriculture. Energy Policy 2021, 154, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Torres, A.M.; García-Rodríguez, L.; del Moral, M.J. Preliminary assessment of innovative seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) desalination powered by a hybrid solar photovoltaic (PV)—Tidal range energy system. Desalination 2020, 477, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilarydoss, S. Suitability, sizing, economics, environmental impacts and limitations of solar photovoltaic water pumping system for groundwater irrigation—A brief review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, C.; Scognamiglio, A. Agrivoltaic systems design and assessment: A critical review, and a descriptive model towards a sustainable landscape vision (three-dimensional agrivoltaic patterns). Sustainability 2021, 13, 6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Qin, J.; Du, S.; Lu, X.; Tong, J.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Utilizing non-conjugated small-molecular tetrasodium iminodisuccinateas electron transport layer enabled improving efficiency of organic solar cells. Opt. Mater. 2022, 129, 112520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Ren, Y.; Shen, H.; Tong, J.; Du, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, J. A new alcohol-soluble polymer PFN-ID as cathode interlayer to optimize performance of conventional polymer solar cells by increasing electron mobility. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2200199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. SolarData: An R package for easy access of publicly available solar datasets. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, A3–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, C.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Y.A. novel 3D-geographic information system and deep learning integrated approach for high-accuracy building rooftop solar energy potential characterization of high-density cities. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 117985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Shan, M.; Rong, X.; Yang, X. Estimating the spatial distribution of solar photovoltaic power generation potential on different types of rural rooftops using a deep learning network applied to satellite images. Appl. Energy 2022, 315, 119025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Nelson, J.R.; Tong, D.; Grubesic, T.H. A spatial optimization approach to increase the accuracy of rooftop solar energy assessments. Appl. Energy 2022, 316, 119128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, P.; Murali, J.; Sakthivadivel, D.; Vigneswaran, V.S. Opportunities and challenges in setting up solar photo voltaic based micro grids for electrification in rural areas of India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3320–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.C.; Machado, L.A.; Vitoriano, C.T.; Fernández Ramírez, L.M. Land Requirement Scenarios of PV Plants in Brazil. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ’18), Salamanca, Spain, 21–23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mendas, A.; Delali, A. Integration of MultiCriteria Decision Analysis in GIS to develop land suitability for agriculture: Application to durum wheat cultivation in the region of Mleta in Algeria. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 83, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaita-Pradas, I.; Marques-Perez, I.; Gallego, A.; Segura, B. Analyzing territory for the sustainable development of solar photovoltaic power using GIS databases. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, O.; Birging, A.; Widén, J.; Lingfors, D. PV park site selection for utility-scale solar guides combining GIS and power flow analysis: A case study on a Swedish municipality. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, J.; Schweizer-Ries, P.; Wemheuer, C. Public acceptance of renewable energies: Results from case studies in Germany. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 4136–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.; Ames, D.P.; Solan, D.; Lee, R.; Carlisle, J. Using GIS analytics and social preference data to evaluate utility-scale solar power site suitability. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, S. ‘Photovoltaic landscapes’: Design and assessment. A critical review for a new transdisciplinary design vision. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Mediavilla, M.; Alonso-Tristán, C.; Rodríguez-Amigo, M.C.; García-Calderón, T. Implementation of PV plants in Spain: A case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronas, S.; de la Hoz, J.; Alonso, À.; Martín, H. 23 years of development of the solar power generation sector in Spain: A comprehensive review of the period 1998–2020 from a regulatory perspective. Energies 2022, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón-Estevan, D.; Peñalvo-López, E.; Alfonso Solar, D. The Spanish turn against renewable energy development. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarloza, A.; Heras-Saizarbitoria, I.; Allur, E.; Larrea, A. Regulatory cuts and economic and financial performance of Spanish solar power companies: An empirical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Hoz, J.; Martín, H.; Martins, B.; Matas, J.; Miret, J. Evaluating the impact of the administrative procedure and the landscape policy on grid connected PV systems (GCPVS) on-floor in Spain in the period 2004–2008: To which extent a limiting factor? Energy Policy 2013, 63, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.F. First experiments in viewshed uncertainty: Simulating fuzzy viewsheds. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1992, 58, 345. [Google Scholar]
- Nutsford, D.; Reitsma, F.; Pearson, A.L.; Kingham, S. Personalising the viewshed: Visibility analysis from the human perspective. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, D. Cumulative viewshed analysis: A GIS-based method for investigating intervisibility, and its archaeological application. In Archaeology and Geographic Information Systems: A European Perspective; Lock, G., Stancic, Z., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1995; pp. 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Loots, L.; Nackaerts, K.; Waelkens, M. Fuzzy Viewshed Analysis of the Hellenistic City Defence System at Sagalassos, Turkey. In Proceedings of the 25th Anniversary Conference of Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology (CAA 1997), Birmingham, UK, 10–17 April 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hognogi, G.G.; Pop, A.M.; Mălăescu, S.; Nistor, M.M. Increasing territorial planning activities through viewshed analysis. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, N.C.; Vukomanovic, J.; Costanza, J.; Singh, K.K. From viewsheds to viewscapes: Trends in landscape visibility and visual quality research. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 224, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.M.; Huck, J.J.; Lindley, S. Modelling and mapping eye-level greenness visibility exposure using multi-source data at high spatial resolutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzano-Alba, E.; Fernandez-Jimenez, L.A.; Garcia-Garrido, E.; Lara-Santillan, P.M.; Falces, A.; Zorzano-Santamaria, P.J.; Capellan-Villacian, C.; Mendoza-Villena, M. Visibility assessment of new photovoltaic power plants in areas with special landscape value. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.F. Algorithm and implementation uncertainty in viewshed analysis. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1993, 7, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouček, T.; Lagner, O.; Šímová, P. How does data accuracy influence the reliability of digital viewshed models? A case study with wind turbines. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 64, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garré, S.; Meeus, S.; Gulinck, H. The dual role of roads in the visual landscape: A case-study in the area around Mechelen (Belgium). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B.M.; Coops, N.C.; Stenhouse, G.B.; Burton, A.C.; Nelson, T.A. Building a perceptual zone of influence for wildlife: Delineating the effects of roads on grizzly bear movement. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Jimenez, L.A.; Mendoza-Villena, M.; Zorzano-Santamaria, P.; Garcia-Garrido, E.; Lara-Santillan, P.; Zorzano-Alba, E.; Falces, A. Site selection for new PV power plants based on their observability. Renew. Energy 2015, 78, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Katsifarakis, K.L.; Kontos, Y.N. Genetic algorithms: A mature mio-inspired optimization technique for difficult problems. In Nature-Inspired Methods for Metaheuristics Optimization: Algorithms and Applications in Science and Engineering, Modeling and Optimization in Science and Technologies; Bennis, F., Bhattacharjya, R.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 16, pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadi, M.H.; Al-Hinai, A.S.; Al-Abri, N.N.; Al-Busafi, Y.H.; Al-Sadairi, R.S. Optimal allocation of solar PV systems in rural areas using genetic algorithms: A case study. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2013, 6, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, V.; Strauss, J.M.; Vermeulen, H.J. Optimisation of Solar PV Plant Locations for Grid Support using Genetic Algorithm and Pattern Search. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon 2016), Melaka City, Malaysia, 28–30 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Masoum, M.A.; Badejani, S.M.M.; Kalantar, M. Optimal Placement of Hybrid PV-wind Systems using Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT), Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 19–21 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yanık, S.; Sürer, Ö.; Öztayşi, B. Designing sustainable energy regions using genetic algorithms and location-allocation approach. Energy 2016, 97, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Statistics and Cartography of Andalucia. Available online: https://www.juntadeandalucia.es/institutodeestadisticaycartografia/sima/ficha.htm?mun=21054 (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Carrión, J.A.; Espín Estrella, A.; Aznar Dols, F.; Ridao, A.R. The electricity production capacity of photovoltaic power plants and the selection of solar energy sites in Andalusia (Spain). Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Natura2000. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/natura-13/natura-2000-spatial-data (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Spanish National Georaphic Institute. Available online: http://centrodedescargas.cnig.es/CentroDescargas/locale?request_locale=es (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Spyridonidou, S.; Sismani, G.; Loukogeorgaki, E.; Vagiona, D.G.; Ulanovsky, H.; Madar, D. Sustainable spatial energy planning of large-scale wind and PV farms in Israel: A collaborative and participatory planning approach. Energies 2021, 14, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, M. GIS-based solar farms site selection using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in Karapinar region, Konya/Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, I.; Gašparović, M. Determining optimal solar power plant locations based on remote sensing and GIS methods: A case study from Croatia. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arán Carrión, J.; Espín Estrella, A.; Aznar Dols, F.; Zamorano Toro, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Ramos Ridao, A. Environmental decision-support systems for evaluating the carrying capacity of land areas: Optimal site selection for grid-connected photovoltaic power plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2358–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercan, E.; Saracoglu, B.O.; Bilgilioğlu, S.S.; Eymen, A.; Tapkın, S. Geographic information system-based investment system for photovoltaic power plants location analysis in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, M.; Hakdaoui, M.; Maanan, M. The evaluation of solar farm locations applying Geographic Information System and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making methods: Case study in southern Morocco. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, J.R.; Auty, D.; Coops, N.C.; Tompalski, P.; Goodbody, T.R.H.; Meador, A.S.; Bourdon, J.F.; de Boissieu, F.; Achim, A. lidR: An R package for analysis of Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šúri, M.; Huld, T.A.; Dunlop, E.D. PV-GIS: A web-based solar radiation database for the calculation of PV potential in Europe. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2005, 24, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuckovic, Z. Advanced viewshed analysis: A Quantum GIS plug-in for the analysis of visual landscapes. J. Open Source Softw. 2016, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishburn, P.C. Utility Theory for Decision Making; Research Analysis Corporation: McLean Virginia, VA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kumsap, C.; Borne, F.; Moss, D. The technique of distance decayed visibility for forest landscape visualization. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 723–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Gao, B. Assessing visual green effects of individual urban trees using airborne Lidar data. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunke, H. Graph Matching: Theoretical Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications. In Proceedings of the Vision Interface Conference (VI’2000), Montréal, QC, Canada, 14–17 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Scrucca, L. On some extensions to GA package: Hybrid optimisation, parallelisation and islands evolution. R J. 2017, 9, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiny: Web Application Framework for R. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=shiny (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- LeafletR: Open-Source JavaScript Library for Mobile-Friendly Interactive Maps, R Package Version 0.4-0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Archive/leafletR/ (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Tennekes, M. tmap: Thematic Maps in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 84, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotly: R Package for Creating Interactive Web-Based Graphs via the Open Source JavaScript Graphing Library. Available online: https://plot.ly (accessed on 4 September 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).