Green Servitization in the Single-Use Medical Device Industry: How Device OEMs Create Supply Chain Circularity through Reprocessing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sustainability in the Medical Device Industry
1.2. Medical Devices and Single-Use Medical Devices
1.3. Servitization and Green Servitization
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Green Service Portfolios
3.2. PSS Business Models
3.3. Strategic Intent
3.4. Collaborative Relationships
3.5. Capabilities
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Managerial Implications
4.2. Utilitarian Implications
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Opportunities for Further Research
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cimprich, A.; Santillan-Saldivar, J.; Thiel, C.L.; Sonnemann, G.; Young, S.B. Potential for industrial ecology to support healthcare sustainability: Scoping review of a fragmented literature and conceptual framework for future research. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Huang, K.X.; Lagasse, R.; Senay, E.; Dubrow, R.; Sherman, J.D. Health Care Pollution And Public Health Damage In The United States: An Update. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Environmentally Sustainable Health Systems: A Strategic Document. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/341239/ESHS_Revised_WHO_web.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- MacNeill, A.J.; Hopf, H.; Khanuja, A.; Alizamir, S.; Bilec, M.; Eckelman, M.J.; Hernandez, L.; McGain, F.; Simonsen, K.; Thiel, C.; et al. Transforming the Medical Device Industry: Road Map to a Circular Economy. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Care without Harm. Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Available online: https://noharm-global.org/sites/default/files/documents-files/5961/HealthCaresClimateFootprint_092319.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Luo, O.D.; Carson, J.J.K.; Sanderson, V.; Vincent, R. Training future healthcare sustainability leaders: Lessons learned from a Canadian-wide medical student community of practice. J. Clim. Chang. Health 2021, 4, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye, G.; Pronovost, P.J.; Makary, M.A. Commentary: A Call to Go Green in Health Care by Reprocessing Medical Equipment. Acad. Med. 2010, 85, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moultrie, J.; Sutcliffe, L.; Maier, A. Exploratory study of the state of environmentally conscious design in the medical device industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Countries Commit to Develop Climate-Smart Health Care at COP26 UN Climate Conference. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/09-11-2021-countries-commit-to-develop-climate-smart-health-care-at-cop26-un-climate-conference (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Kuhl, C.; Bourlakis, M.; Aktas, E.; Skipworth, H. How Does Servitisation Affect Supply Chain Circularity?—A Systematic Literature Review. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 33, 703–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzzo, D.; Carvalho, M.M.; Balkenende, R.; Mascarenhas, J. Circular business models in the medical device industry: Paths towards sustainable healthcare. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, F.F.; Cusumano, M.A.; Kahl, S.J. Services and the Business Models of Product Firms: An Empirical Analysis of the Software Industry. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choo, A.; Narayanan, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Sarkar, S. Introducing goods innovation, service innovation, or both? Investigating the tension in managing innovation revenue streams for manufacturing and service firms. J. Oper. Manag. 2021, 67, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaga, W.; Reinartz, W.J. Hybrid Offerings: How Manufacturing Firms Combine Goods and Services Successfully. J. Mark. 2011, 75, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocca, S.; Ganz, W. Requirements for developing green services. Serv. Ind. J. 2015, 35, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antioco, M.; Moenaert, R.K.; Lindgreen, A.; Wetzels, M.G.M. Organizational antecedents to and consequences of service business orientations in manufacturing companies. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2008, 36, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spring, M.; Araujo, L. Product biographies in servitization and the circular economy. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 60, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedettini, O.; Swink, M.; Neely, A. Examining the influence of service additions on manufacturing firms’ bankruptcy likelihood. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 60, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opazo-Basaez, M.; Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Bustinza, O.E. Uncovering Productivity Gains of Digital and Green Servitization: Implications from the Automotive Industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marić, J.; Opazo-Basádez, M. Green servitization for flexible and sustainable supply chain operations: A review of reverse logistics services in manufacturing. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2019, 20, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiola, M.; Schiavone, F.; Grandinetti, R.; Chen, J.S. Digital servitization and sustainability through networking: Some evidences from IoT-based business models. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 132, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.V.; Bellos, I. The Potential of Servicizing as a Green Business Model. Manag. Sci. 2017, 63, 1545–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsdemir, A.; Deshpande, V.; Parlakturk, A.K. Is Servicization a Win-Win Strategy? Profitability and Environmental Implications of Servicization. MSom-Manuf. Serv. Oper. 2019, 21, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, H.; Haldimann, M.; Saul, C.J. Competing in business-to-business sectors through pay-per-use services. J. Serv. Manag. 2017, 28, 914–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genzlinger, F.; Zejnilovic, L.; Bustinza, O.F. Servitization in the automotive industry: How car manufacturers become mobility service providers. Strat. Chang. 2020, 29, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boerdonk, P.J.M.; Krikke, H.R.; Lambrechts, W. New business models in circular economy: A multiple case study into touch points creating customer values in health care. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 125375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health System. Delivering a ‘net zero’ National Health Service. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/greenernhs/wp-content/uploads/sites/51/2020/10/delivering-a-net-zero-national-health-service.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Kane, G.M.; Bakker, C.A.; Balkenende, A.R. Towards design strategies for circular medical products. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereno, A.; Eriksson, D. A multi-stakeholder perspective on sustainable healthcare: From 2030 onwards. Futures 2020, 122, 102605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, J.D.; Thiel, C.; MacNeill, A.; Eckelman, M.J.; Dubrow, R.; Hopf, H.; Lagasse, R.; Bialowitz, J.; Costello, A.; Forbes, M.; et al. The Green Print: Advancement of Environmental Sustainability in Healthcare. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Sherman, J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, A.C.; Veiga, A.; Mauricio, A.C.; Lopes, M.A.; Santos, J.D.; Neto, B. Assessment of the environmental impacts of medical devices: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 9641–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, A.; Maga, D.; Thonemann, N. Combining Life Cycle Assessment and Circularity Assessment to Analyze Environmental Impacts of the Medical Remanufacturing of Electrophysiology Catheters. Sustainability 2021, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.A. The circular economy’s closed loop and product service systems for sustainable development: A review and appraisal. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, M.; Lichtnegger, S.; Gibson, S.; Saunders, R. Evaluating the Waste Prevention Potential of a Multi- versus Single-Use Surgical Stapler. Risk. Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 3911–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocken, N.M.P.; De Pauw, I.; Bakker, C.; Van der Grinten, B. Product design and business model strategies for a circular economy. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2016, 33, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieder, M.; Rashid, A. Towards circular economy implementation: A comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, L.L.; Pigosso, D.C.A.; Niero, M.; Bech, N.M.; McAloone, T.C. Product/Service-Systems for a Circular Economy: The Route to Decoupling Economic Growth from Resource Consumption? J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Sadagopan, M.; Rosado, L. Circular economy—From review of theories and practices to development of implementation tools. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, S.; Landis, A. Assessing the environmental, human health, and economic impacts of reprocessed medical devices in a Phoenix hospital’s supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, C.; Vaccari, M.; Tudor, T. Recovering value from used medical instruments: A case study of laryngoscopes in England and Italy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukelich, D. Reprocessing and Remanufacturing of Single-Use Medical Devices. Available online: https://basicmedicalkey.com/reprocessing-and-remanufacturing-of-single-use-medical-devices/ (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. Global Regulatory Framework for Medical Devices including In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241512350 (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Thording, L. Medical Device Reprocessing Could Be Used to Drive Sustainable, Financially Viable Healthcare. Available online: https://www.mddionline.com/general-hospital/circular-healthcare-economy-suppliers-lawmakerstimes (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Association of Medical Device Reprocessors. Global Regulatory Standards for Single-Use Device Reprocessing/Remanufacturing. Available online: http://amdr.org/amdr-document-signup-form/ (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Reprocessing Medical Devices in Health Care Settings: Validation Methods and Labeling. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/80265/download (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Single-Use Medical Devices: Implications and Consequences of Reuse. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/956268/Single_use_medical_devices.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Grosskopf, V.; Jakel, C. Legal framework conditions for the reprocessing of medical devices. GMS Krankenhhyg. Interdiszip. 2008, 3, Doc24. [Google Scholar]
- Fähling, J.; Köbler, F.; Leimeister, J.M.; Krcmar, H. From products to product-service systems: IT-driven transformation of a medical equipment manufacturer. J. Inf. Technol. Teach. Cases 2014, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaulding, E. The role of chemical disinfection in the prevention of nosocomial infections. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nosocomial Infections, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 August 1970; American Hospital Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1971; pp. 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, V.G.; Baines, T.; Baldwin, J.; Ridgway, K.; Petridis, P.; Bigdeli, A.Z.; Uren, V.; Andrews, D. Using gamification to transform the adoption of servitization. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 63, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongur, S.; Engwall, M. The business model dilemma of technology shifts. Technovation 2014, 34, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabetino, R.; Kohtamaki, M.; Lehtonen, H.; Kostama, H. Developing the concept of life-cycle service offering. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 49, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, M.; Yannou, B.; Leroy, Y.; Cluzel, F. Heavy vehicles on the road towards the circular economy: Analysis and comparison with the automotive industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, C.J.; Whalen, K.A. Circular Economy Business Models: A Critical Examination. J. Econ. Issues 2020, 54, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen Mac Arthur Foundation. Caterpillar: Design and Business Model Considerations for Heavy Machinery Remanufacturing. Available online: https://ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/circular-examples/design-and-business-model-considerations-for-heavy-machinery-remanufacturing (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Johnson, M.R.; McCarthy, I.P. Product recovery decisions within the context of Extended Producer Responsibility. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2014, 34, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, A.; Menz, W. The Theory-Generating Expert Interview: Epistemological Interest, Forms of Knowledge, Interaction. In Interviewing Experts; Bogner, A., Litting, B., Menz, W., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 43–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storbacka, K. A solution business model: Capabilities and management practices for integrated solutions. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2011, 40, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohtamaki, M.; Partanen, J.; Moller, K. Making a profit with R&D services—The critical role of relational capital. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2013, 42, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.; Schroeder, A.; Kapoor, K.K.; Bigdeli, A.Z.; Baines, T. Behind the scenes of digital servitization: Actualising IoT-enabled affordances. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 89, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddats, C.; Naik, P.; Bigdeli, A.Z. Creating value in servitization through digital service innovations. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 104, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch, C.; Marx, E.; Benz, L.; Hartmann, E.; Matzner, M. Capabilities of digital servitization: Evidence from the socio-technical systems theory. Technol. Soc. 2022, 176, 121361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, J.; Laudel, G. On Interviewing “Good” and “Bad” Experts. In Interviewing Experts; Bogner, A., Litting, B., Menz, W., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raddats, C.O.; Burton, J. Creating multi-vendor solutions: The resources and capabilities required. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2014, 29, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremyr, I.; Witell, L.; Lofberg, N.; Edvardsson, B.; Fundin, A. Understanding new service development and service innovation through innovation modes. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2014, 29, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salonen, A.; Jaakkola, E. Firm boundary decisions in solution business: Examining internal vs. external resource integration. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 51, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.; Story, V.M.; Raddats, C.; Zolkiewski, J. Overcoming the challenges that hinder new service development by manufacturers with diverse services strategies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 192, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, J.; McCluskey, S.; Turley, E.; King, N. The Utility of Template Analysis in Qualitative Psychology Research. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2015, 12, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliva, R.; Kallenberg, R. Managing the transition from products to services. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 2003, 14, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedettini, O.; Neely, A. Investigating a revised service transition concept. Serv. Bus. 2018, 12, 701–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, V. Product services: From a service supporting the product to a service supporting the client. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2001, 16, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reim, W.; Parida, V.; Ortqvist, D. Product-Service Systems (PSS) business models and tactics—A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A. Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguste, B.G.; Harmon, E.P.; Pandit, V. The right service strategies for product companies. McKinsey Q. 2006, 1, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalkowski, C.; Kindstrom, D.; Witell, L. Internalisation or externalisation? Examining organisational arrangements for industrial services. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2011, 21, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigel, S.; Hadwich, K. Success factors of service networks in the context of servitization—Development and verification of an impact model. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2018, 74, 254–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedettini, O.; Neely, A. Service providers and firm performance: Investigating the non-linear effect of dependence. J. Serv. Manag. 2019, 30, 716–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.; Ronnberg-Sjodin, D.; Wincent, J.; Kohtamaki, M. Mastering the Transition to Product-Service Provision Insights into Business Models, Learning Activities, and Capabilities. Res. Technol. Manag. 2014, 57, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.; Parida, V.; Isaksson, O. Understanding product-service system innovation capabilities development for manufacturing companies. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2015, 26, 763–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddats, C.; Zolkiewski, J.; Story, V.M.; Burton, J.; Baines, T.; Bigdeli, A.Z. Interactively developed capabilities: Evidence from dyadic servitization relationships. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raddats, C.; Easingwood, C. Services growth options for B2B product-centric businesses. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2010, 39, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, S.M.; Smith, H.J.; Linder, J.C. The power of business models. Bus. Horiz. 2005, 48, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Business Models, Business Strategy and Innovation. Long Range Plan. 2010, 43, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Evans, S. Product-service system business model archetypes and sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mont, O. Product-Service Systems; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]


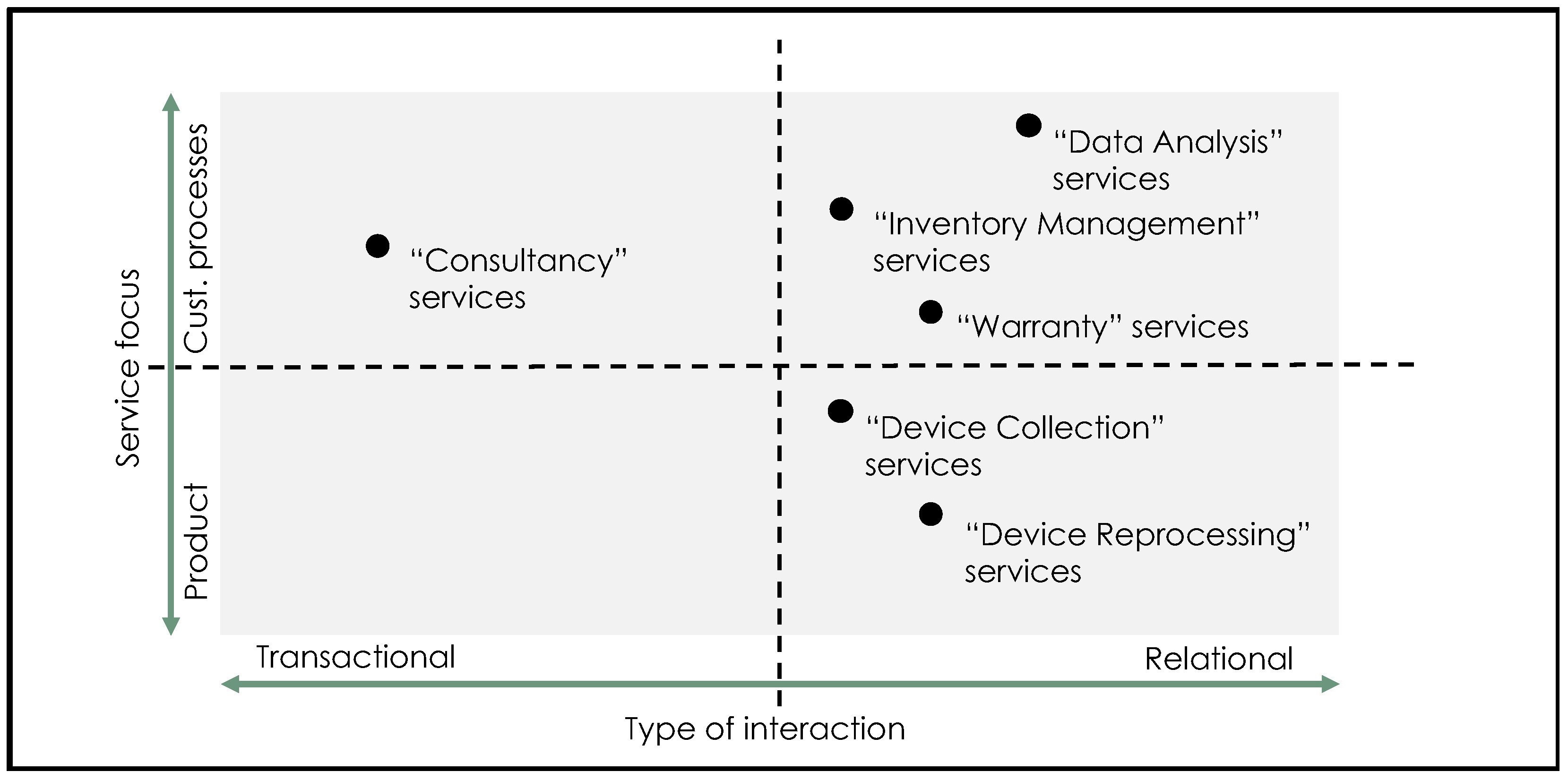
| Theme | References | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Green service portfolios | Oliva and Kallenberg [72] Rabetino et al. [54] Benedettini and Neely [73] Mathieu [74] | “Sometimes the manufacturing contract does not allow for the customers to buy back products, but they still want the green, environmental piece. So, at that point, … [company X] does work for the customers and it does still collect … [Company X] does not charge for any of those collections. That is part of its service model and value proposition to customers.” |
| “… [company X] sends out to its customers on a monthly basis data that shows how many devices did you collect, which kinds of devices were collected, how many devices that came from your plant were rejected because of kicks or other damage, how much money did you save, how many pounds did you divert from the landfills, and … what savings you did not realize because you either mishandled the devices or did not buy back to the quantity that you could.” | ||
| PSS business models | Reim et al. [75] Tukker [76] | “… that is our program where we do new products and reprocessed products at one fixed cost”. |
| “The delivery of a total service model is typically advantageous to the buyer but just as frequently organizations are pushing back on it... So, because of this mechanism, there is a limit to how much we can go in and take over an entire activity area such as the acquisition of devices for procedures.” | ||
| Strategic intent | Aguste et al. [77] | “There is such a growing cost of healthcare, as you know… There is also significant waste and at that time reprocessing was one of the fastest growing markets in single-use devices here domestically… So, for … [company X] to acquire … [company Y] was more of a growth acquisition in a market disruptive type of play.” |
| “I think that… [company X] acquired … [company Y] to curtail or control, even minimize, the impact of reprocessing.” | ||
| Collaborative relationships | Kowalkowski et al. [78] Weigel et al. [79] Benedettini and Neely [80] | “… [company X] has agreements with some OEMs to reprocess their devices. These OEMs share with … [company X] complete information about their products.” |
| “… [company X] partners with logistic providers for device collection and delivery. It also defines OEMs for which it reprocesses devices as business partners.” | ||
| Capabilities | Ulaga and Reinartz [14] Parida et al. [81] Wallin et al. [82] Raddats et al. [83] | “When we analyze new products, we may have to make material analyses, have to identify the specification based on the standards and on original products and that takes of course quite a long time and quite a high effort to do to identify and to define the specifications of the products.” |
| “We have extremely sophisticated data capabilities and in the end that is probably one of our core competences when it comes to producing the best results.” |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benedettini, O. Green Servitization in the Single-Use Medical Device Industry: How Device OEMs Create Supply Chain Circularity through Reprocessing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912670
Benedettini O. Green Servitization in the Single-Use Medical Device Industry: How Device OEMs Create Supply Chain Circularity through Reprocessing. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912670
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenedettini, Ornella. 2022. "Green Servitization in the Single-Use Medical Device Industry: How Device OEMs Create Supply Chain Circularity through Reprocessing" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912670
APA StyleBenedettini, O. (2022). Green Servitization in the Single-Use Medical Device Industry: How Device OEMs Create Supply Chain Circularity through Reprocessing. Sustainability, 14(19), 12670. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912670






