Lead Extraction Methods in Roadside Soils and Its Relationship with Soil Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Soil Analyses
2.3. Lead Extraction Methods
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Parameters
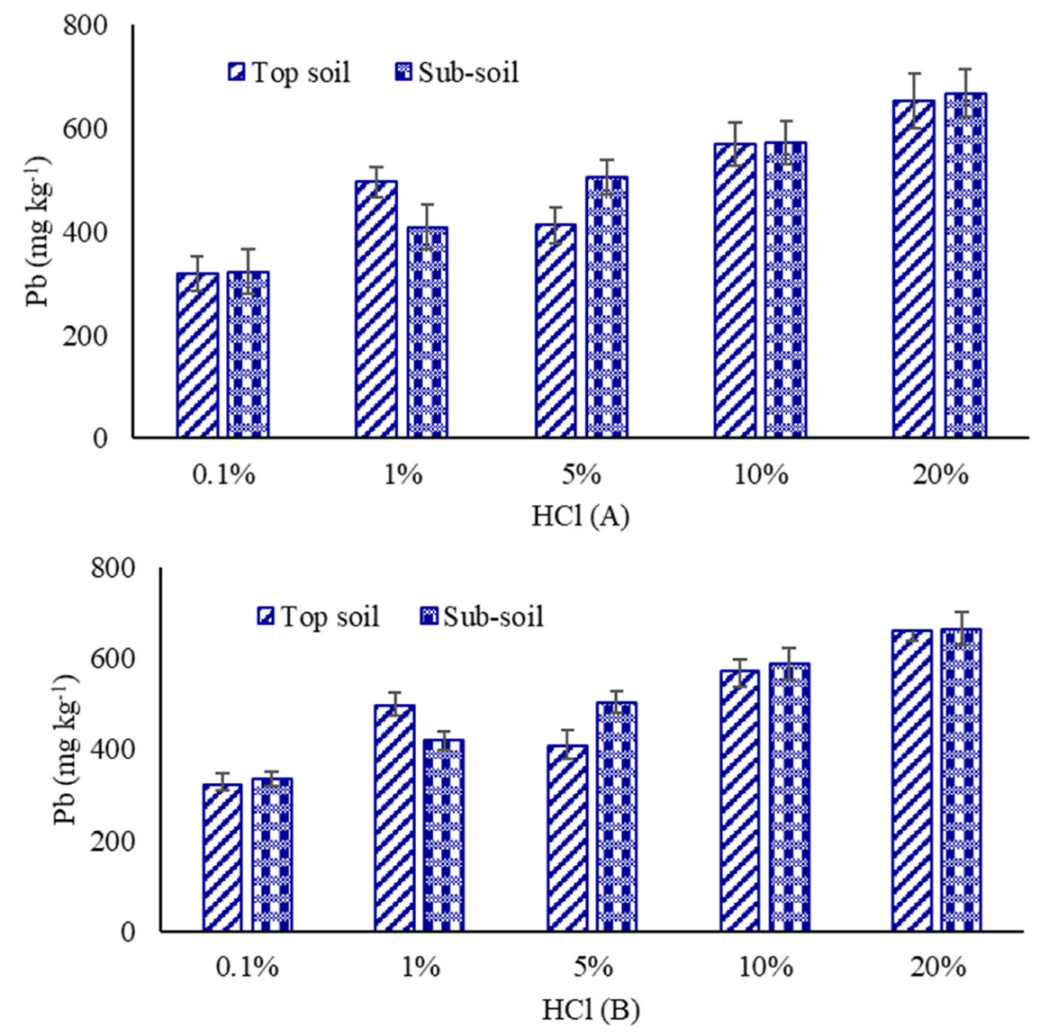
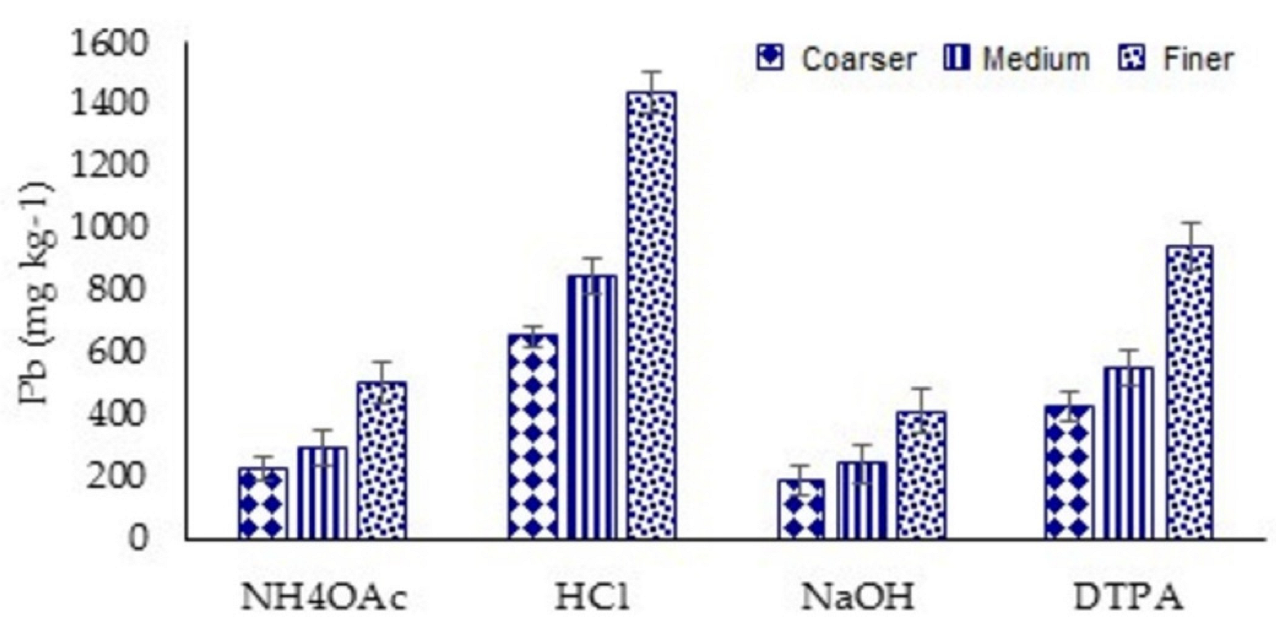
3.2. Extraction of Lead from Soil Using Different Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naveed, N.H.; Batool, A.I.; Rehman, F.U.; Hameed, U. Leaves of roadside plants as bioindicator of traffic related lead pollution during different seasons in Sargodha, Pakistan. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 770–774. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Ding, M.Y.; Chen, D.P. Adsorption properties of mesoporous silicas for organic pollutants in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués, M.J.; Salvador, A.; Morales-Rubio, A.E.; Guardia, M.D. Chromium speciation in liquid matrices: A survey of the literature. Fresenius, J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 367, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.; Kwong, A. Ethanol as a lead replacement: Phasing out leaded gasoline in Africa. Energy Policy 2001, 29, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, W.H.; Alex, W.H. Environmental lead exposure induces changes in the heme biosynthetic pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1997, 12, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztas, T.; Sibel, A. Distribution patterns of lead accumulation in roadside soils: A case study from Erzurum, Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 18, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P. Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földi, C.; Sauermann, S.; Dohrmann, R.; Mansfeldt, T. Traffic-related distribution of antimony in roadside soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzyl, J. Lead and cadmium contamination of soil and vegetables in the upper silesia region of Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 96, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, K.F.; Hale, W.H.G.; Headley, A.D.; Athar, M. Heavy metal contamination of roadside soils of Northern England. Soil Water Res. 2006, 1, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Franck, U.; Herbarth, O.; Langer, O.; Stark, H.J.; Treide, A. Lead levels in deciduous teeth in relation to tooth type and tissue as well as to maternal behavior and selected individual environmental parameters of children. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekong, E.B.; Jaar, B.G.; Weaver, V.M. Lead-related nephrotoxicity: A review of the epidemiologic evidence. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maria, A.; Kevin, A.; Jolly, W.; Pingitore, N.E. Blood lead in the 21st Century: The sub-microgram challenge. J. Blood Med. 2010, 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A.; Ayodele, E.T.; Oyediran, G.O.; Oluyemi, E.A. Levels and speciation of heavy metals in soils of industrial southern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 85, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, Y.K.; Bates, T.E. Chemical pools of cadmium, nickel and zinc in polluted soil and some preliminary indications of their availability to plants. J. Soil Sci. 1981, 33, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuman, L. Fractionation method for soil microelements. Soil Sci. 1985, 140, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.M.; Lopez-Valdivia, L.M.; Novillo, J.; Obrador, A.; Rico, M.I. Comparison of EDTA and sequential extraction tests for phytoavailability prediction of manganese and zinc in agricultural alkaline soils. Geoderma 2006, 132, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.; Irshad, M.; Sher, S.; Hayat, F.; Ashraf, A.; Masood, S.; Waseem, M. Relationship of Selected Soil Properties with the Micronutrients in Salt-Affected Soils. Land 2022, 11, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.G.M.; Tokunaga, S.; Maekawa, T. Extraction of arsenic in a synthetic arsenic contaminated soil using phosphate. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasay, S.A.; Parker, W.; van Geel, P.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Tokunaga, S. Arsenic pollution of a loam soil: Retention form and decontamination. J. Soil Contam. 2000, 9, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, S.; Hakuta, T. Acid washing and stabilization of an artificial arsenic-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Pandey, V.; Misra, J.; Yunus, M.; Ahmad, K.J. Atmospheric lead pollution from vehicular emissions–Measurements in plants, soil and milk samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1997, 45, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). Arsenic Treatment Technologies for Soil, Waste, and Water; EPA-542-R-02-004; National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP): Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2002; pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, B.P.; Miller, W.P. Effectiveness of phosphate and hydroxide for desorption of arsenic and selenium species from iron oxides. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legiec, I.A.; Griffin, L.P.; Walling, P.D., Jr.; Breske, T.C.; Angelo, M.S.; Isaacson, R.S.; Lanza, M.B. DuPont soil washing technology program and treatment of arsenic contaminated soil. Environ. Prog. 1997, 16, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, P.H.T. The use of extractants in studies on trace metals in soils, sewage sludges and sludge-treated soils. Adv. Soil Sci. 1989, 9, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaileh, K.M.; Hussein, R.M.; Abu-Elhaj, S. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in roadside surface soil and vegetation from the West Bank. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 47, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis (Part 2); American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Part 2; Chemical and Microbiological Properties, ASA, SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.O. Nitric-perchloric acid wet digestion in an open vessel. In Handbook of Reference Methods for Plant Analysis; Kalra, Y., Ed.; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute SAS System: Release 8.02; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 1999.
- Codex General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Foods, Joint FAO/WHO Joint Food Standards Programme; Codex Alimentarious Commission: Rome, Italy, 1996.
- Szwalec, A.; Mundaa, P.; Kdzior, R.; Pawlik, J. Monitoring and assessment of cadmium, lead, zinc and copper concentrations in arable roadside soils in terms of different traffic conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EEC. Proposal for a Council Directive on the Protection of the Environment, and Particularly of when Sewage Sludge is Used in Agriculture; EEC 5559/86; Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- VROM. Environmental quality objectives in Netherlands. In A Review of Environmental Quality Objectives and Their Policy frameWork in Netherlands. Risk Assessment and Environmental Quality Division, Directorate for Chemicals, External Safety and Radiation Projection; Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnaiah, H.; Somashekar, R.K. Heavy metal contamination in roadside soil and their mobility in relations to pH and organic carbon. Soil Sediment Contam. 2002, 11, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirdere, S.; Yaman, M. Determination of lead, cadmium and copper in roadside soil and plants in Elazig, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, A.J.; Johnson, A.H.; Siccama, T.G.; Mader, D.L. Trace metal profiles in the forest floor of New England. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martınez, C.E.; Motto, H.L. Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasrina, R.C.; Rowshon, A.; Mustafizur, A.M.R.; Rafiqul, I.; Ali, M.P. Heavy metals contamination in vegetables and its growing soil. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Miragaya, J. Levels, chemical fractionation, and solubility of lead in roadside soils of Caracas, Venezuela. Soil Sci. 1984, 138, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, S.; Funakawa, S.; Nishigaki, M.; Kilasara, M.; Kosaki, T. Dynamics of fractionated P and P budget in soil under different land management in two Tanzanian croplands with contrasting soil textures. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 162, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B.; Mart´ınez, C.E. Copper phytotoxicity in a contaminated soil: Remediation tests with adsorptive materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4386–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H. Cadmium soil sorption at low concentrations: I. Effect of time, cadmium load, pH, and calcium. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1984, 21, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Curtin, D. Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 215–272. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; Hong, S.Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.S. Soil pH increase under paddy in South Korea between 2000 and 2012. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 221, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.E. Principles and Practice of Soil Science: The Soil as a Natural Resource; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, T.J. Lead accumulation in roadside soil and grass. Nature 1970, 225, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, M.; Zhang, M.; Suzuki, M.; Tsukimura, K.; Ohta, M. Characterization of Pb-bearing minerals in polluted soils from closed mine sites. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, A.S.; Hawker, D. Distribution of vehicular lead in roadside soils of major roads of Brisbane, Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 118, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Ehteshami, M.; Sadrnejad, S.A. Lead Contamination and Pollution Indexes in Roadside Soil in Tehran, Iran. Iran. J. Health Sci. 2015, 3, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- William, H.S. Lead Contamination of the Roadside Ecosystem. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1976, 26, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culbard, E.B.; Thornton, I.; Watt, J.; Weatley, M.; Moorcraft, S.; Thompson, M. Metal contamination in British suburban dusts and soils. J. Environ. Qual. 1988, 17, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Rehman, S. Lead and cadmium contamination of different roadside soils and plants in Peshawar city, Pakistan. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.A.; van Raij, B.; Abreu, M.F.; Santos, W.R.; Andrade, J.C. Efficiency of multinutrient extractants for the determination of available copper in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1996, 27, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Vázquez, E.; Caridad-Cancela, R.; Taboada-Castro, M.M.; Paz-Donzález, A.; Abreu, C.A. Trace elements extracted by DTPA and Mehlich-3 from agricultural soils with and without compost additions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.A.; Abreu, M.F.; Andrade, J.C.; Raij, B. van. Restrictions in the use of correlation coefficients in comparing methods for the determination of the micronutrients in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.A.; van Raij, B.; Gabe, U.; Abreu, M.F.; Paz-González, A. Efficiency of multinutrient extractants for the determining of available zinc in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sites | pH | EC | OM | Ca * | Mg * | K * | Clay | Silt | Sand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µS cm−1 | % | mg kg−1 | % | ||||||
| Abbottabad areas | |||||||||
| S1 | 7.56 ± 0.03 | 137.0 ± 2.3 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 25.2 ± 1.2 | 119.4 ± 2.4 | 122.1 ± 4.5 | 34.0 ± 1.2 | 15.0 ± 0.3 | 51.0 ± 1.2 |
| S2 | 7.78 ± 0.02 | 166.1 ± 2.4 | 4.1 ± 0.1 | 30.7 ± 1.4 | 80.5 ± 3.3 | 101.7 ± 2.7 | 18.0 ± 2.0 | 15.5 ± 0.4 | 66.5 ± 2.0 |
| S3 | 7.59 ± 0.04 | 154.6 ± 1.8 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 15.8 ± 0.9 | 80.5 ± 2.1 | 112.4 ± 3.7 | 17.0 ± 0.9 | 22.4 ± 0.5 | 60.6 ± 1.3 |
| S4 | 6.89 ± 0.03 | 104.7 ± 2.0 | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 45.5 ± 2.2 | 67.8 ± 2.1 | 145.6 ± 3.4 | 39.0 ± 1.2 | 24.0 ± 0.4 | 17.0 ± 1.0 |
| S5 | 7.88 ± 0.02 | 119.1 ± 2.4 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 18.7 ± 1.0 | 90.5 ± 3.1 | 181.9 ± 4.0 | 48.0 ± 2.0 | 35.0 ± 0.4 | 17.0 ± 0.7 |
| S6 | 8.13 ± 0.02 | 224.4 ± 3.4 | 1.2 ± 0.02 | 47.1 ± 2.4 | 41.1 ± 2.0 | 91.4 ± 3.8 | 19.0 ± 1.1 | 28.0 ± 1.0 | 53.0 ± 2.8 |
| Haripur areas | |||||||||
| S1 | 7.97 ± 0.03 | 98.9 ± 2.6 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 46.1 ± 2.1 | 79.3 ± 1.7 | 83.4 ± 3.2 | 22.0 ± 0.7 | 34.0 ± 1.2 | 44.0 ± 2.0 |
| S2 | 7.68 ± 0.02 | 187.4 ± 2.0 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 88.1 ± 2.0 | 61.0 ± 1.8 | 67.3 ± 2.8 | 37.5 ± 0.8 | 30.0 ± 2.0 | 32.5 ± 1.2 |
| S3 | 7.87 ± 0.02 | 166.1 ± 3.4 | 4.2 ± 0.1 | 71.1 ± 2.3 | 68.4 ± 2.1 | 74.9 ± 3.1 | 24.0 ± 1.0 | 30.5 ± 1.7 | 45.0 ± 2.0 |
| S4 | 7.67 ± 0.02 | 171.0 ± 3.2 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 72.9 ± 2.0 | 72.6 ± 1.6 | 92.7 ± 2.6 | 42.5 ± 2.1 | 20.0 ± 0.4 | 37.5 ± 1.1 |
| S5 | 8.14 ± 0.02 | 101.6 ± 3.1 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 94.0 ± 2.1 | 47.0 ± 1.0 | 73.8 ± 2.6 | 17.5 ± 2.1 | 25.0 ± 0.7 | 57.5 ± 1.0 |
| S6 | 7.63 ± 0.04 | 111.4 ± 3.2 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 78.5 ± 1.2 | 88.9 ± 3.1 | 53.6 ± 1.7 | 17.5 ± 0.6 | 30.0 ± 0.9 | 52.5 ± 2.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, S.; Irshad, M.; Tariq, M.A.U.R.; Mohiuddin, M.; Ashraf, M.; Bibi, S.; Shaukat, N.; Shah, A.A.; Ng, A.W.M. Lead Extraction Methods in Roadside Soils and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013207
Nawaz S, Irshad M, Tariq MAUR, Mohiuddin M, Ashraf M, Bibi S, Shaukat N, Shah AA, Ng AWM. Lead Extraction Methods in Roadside Soils and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013207
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Shazia, Muhammad Irshad, Muhammad Atiq Ur Rehman Tariq, Muhammad Mohiuddin, Muhammad Ashraf, Sumera Bibi, Nadeem Shaukat, Ashfaq Ahmad Shah, and Anne Wai Man Ng. 2022. "Lead Extraction Methods in Roadside Soils and Its Relationship with Soil Properties" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013207
APA StyleNawaz, S., Irshad, M., Tariq, M. A. U. R., Mohiuddin, M., Ashraf, M., Bibi, S., Shaukat, N., Shah, A. A., & Ng, A. W. M. (2022). Lead Extraction Methods in Roadside Soils and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. Sustainability, 14(20), 13207. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013207









