Coupling Hydrological and Hydrodynamic Models for Assessing the Impact of Water Pollution on Lake Evaporation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
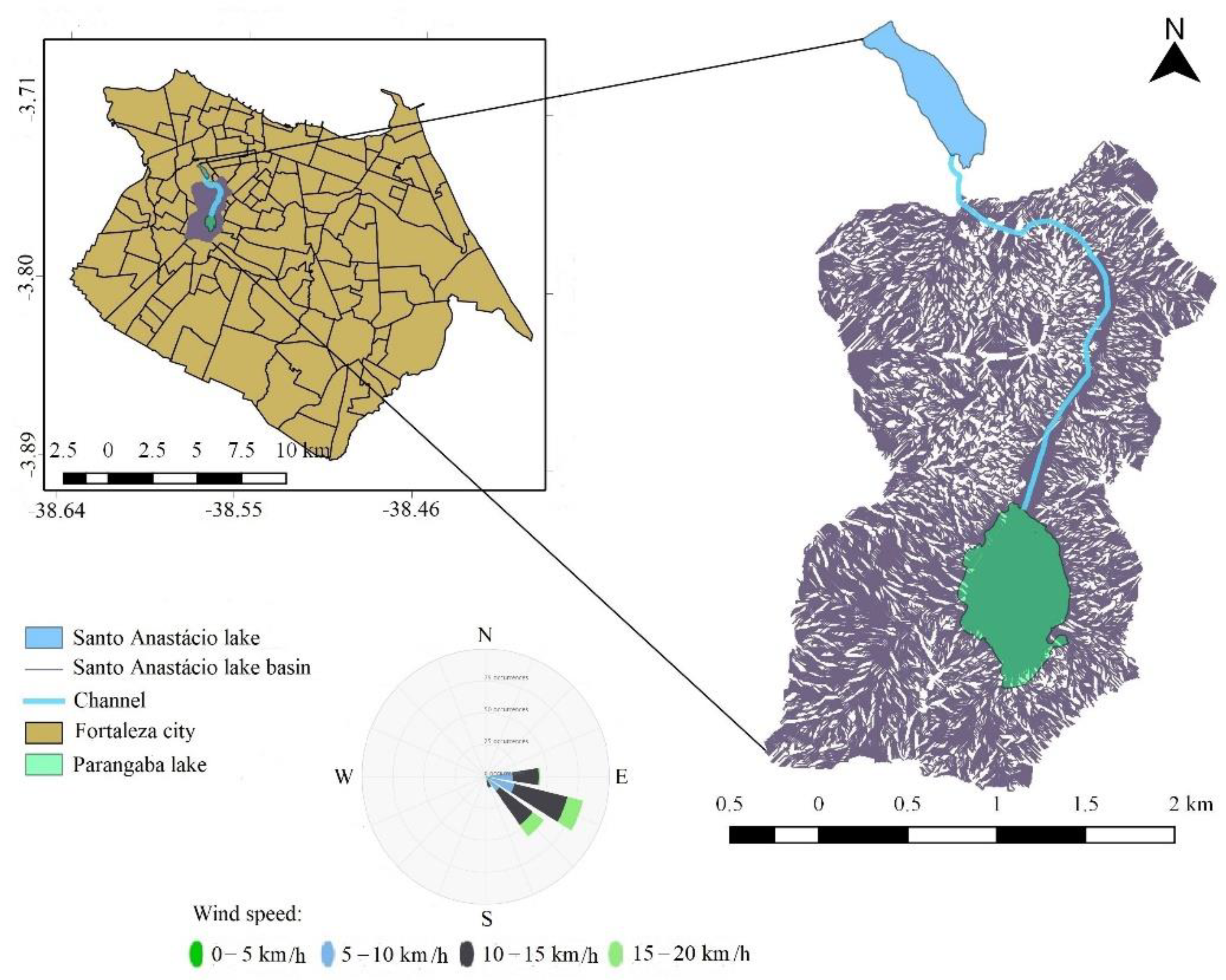
2.1. Study Area
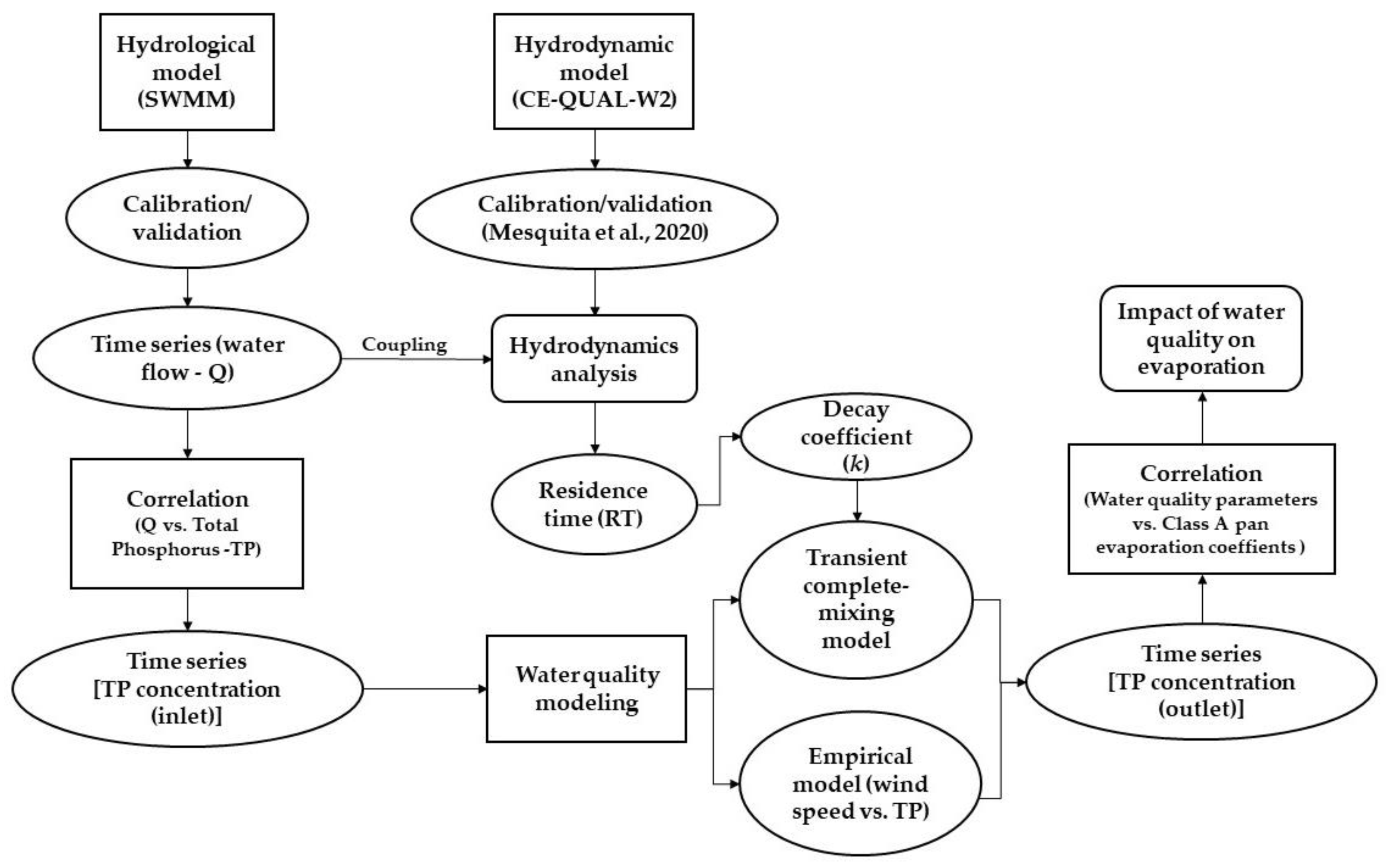
2.2. Field Data and Study Framework
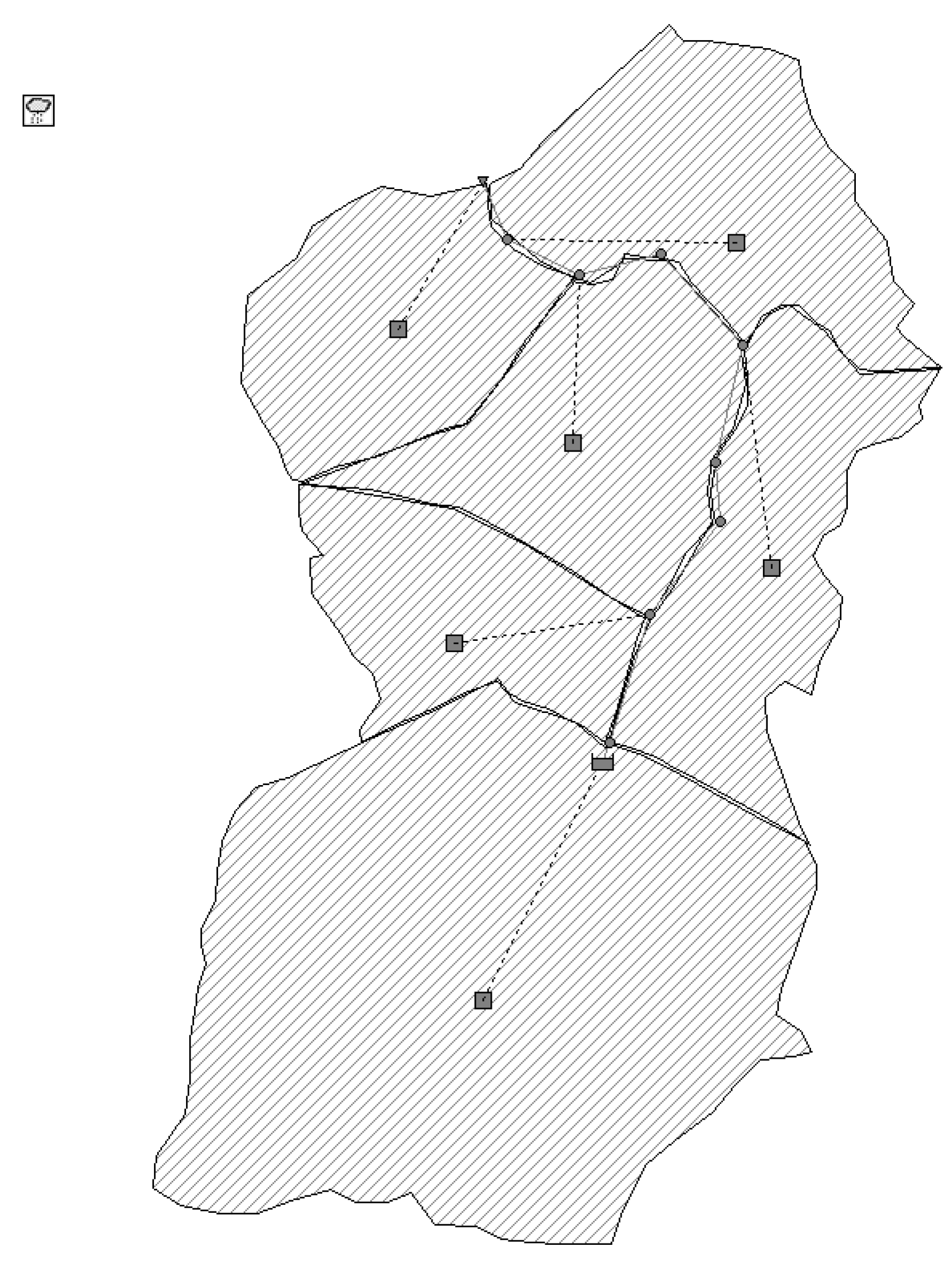
2.3. Hydrological and Hydraulic Modeling
2.4. Hydrodynamic Modeling of the Lake
2.5. Integrated Basin and Lake Analysis
2.6. Water Quality Modeling and Evaporation
2.7. Scenarios
3. Results
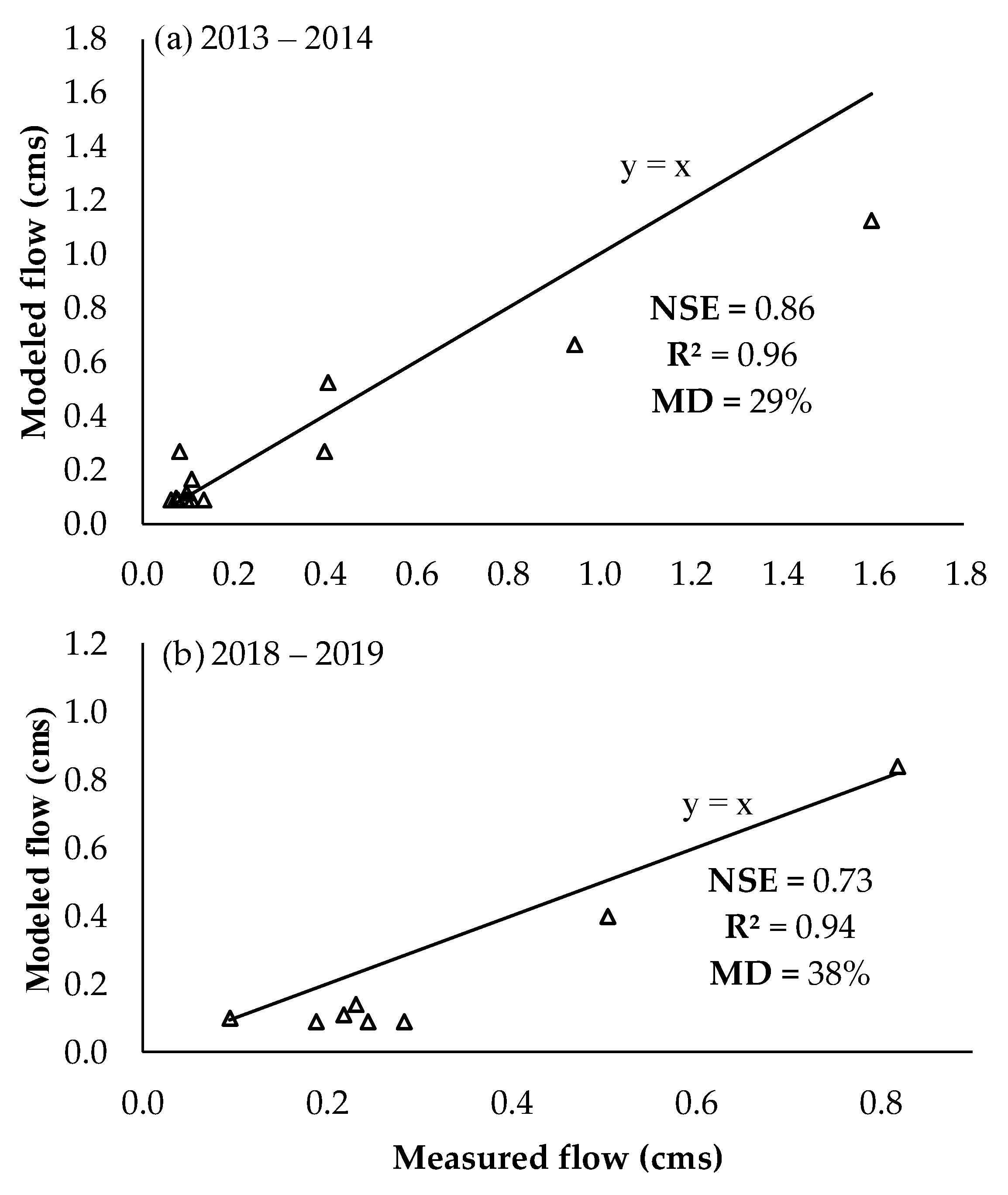
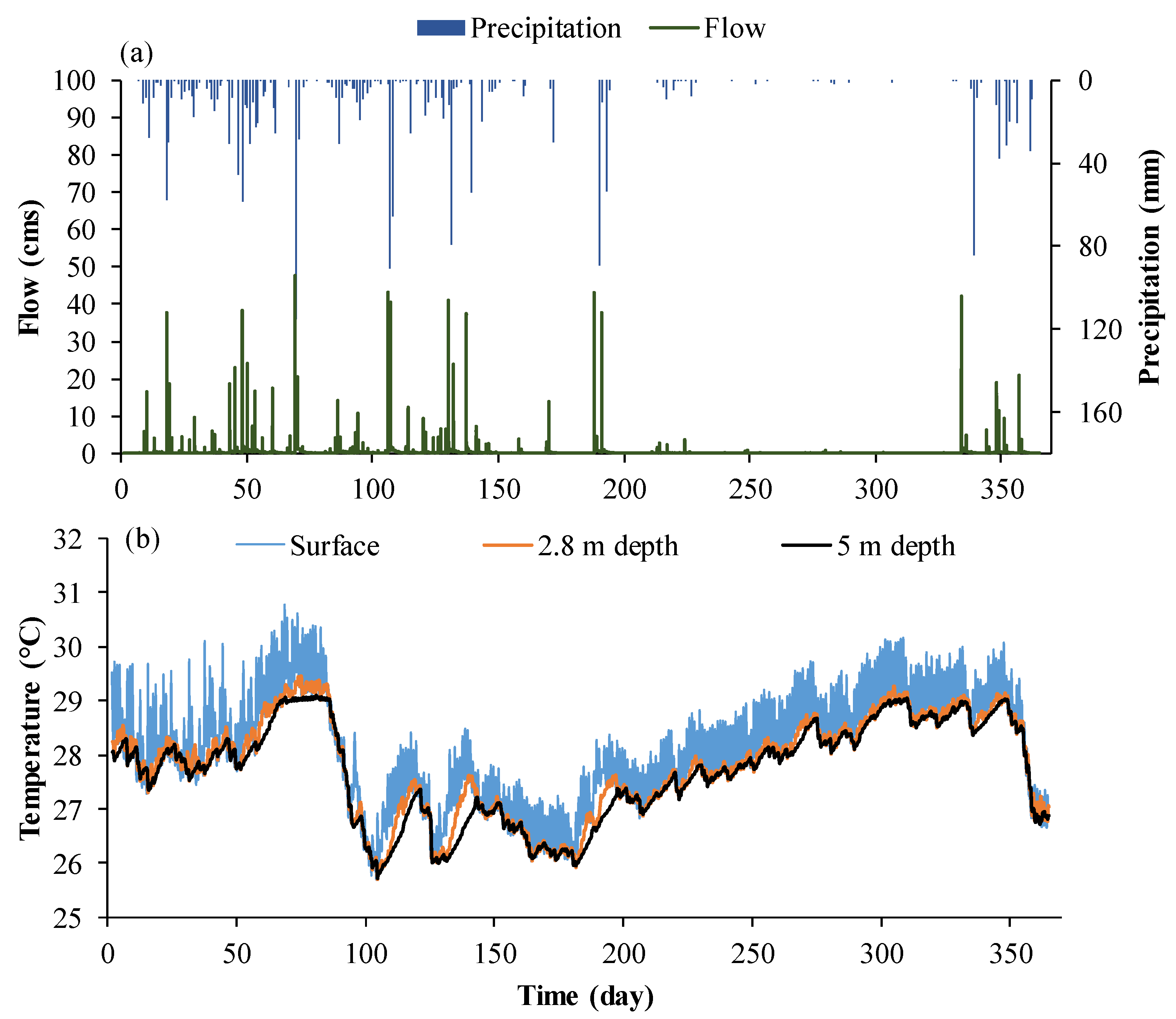
3.1. Hydrological Model and Analysis of Hydrological Variability
3.2. Inflow and Outflow
3.3. Hydrodynamic Modeling
3.3.1. Impact of Hydrological Variability on Hydrodynamics
3.3.2. Hydraulic Residence Time
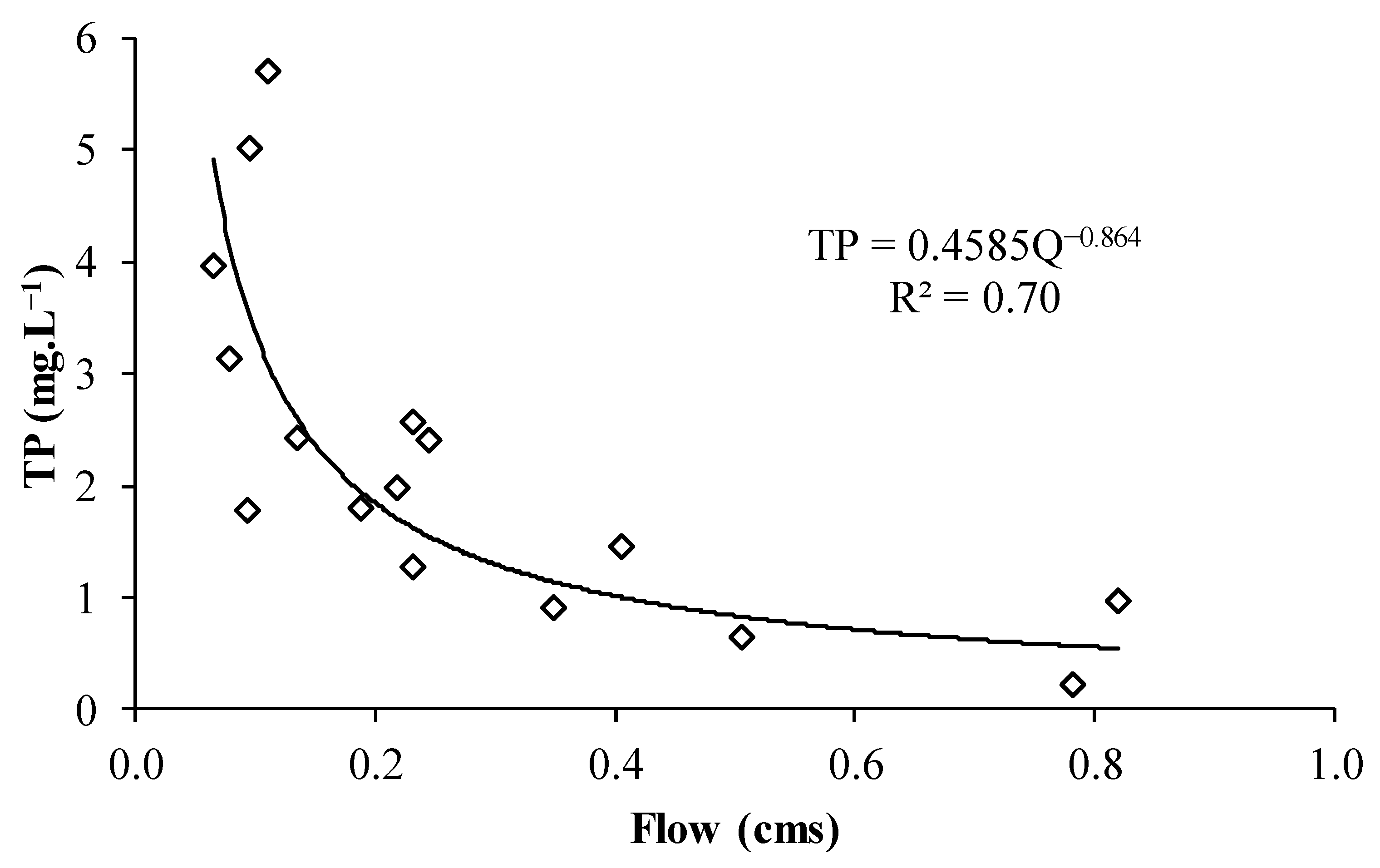
3.4. Impact of Inlet Flow on Water Quality
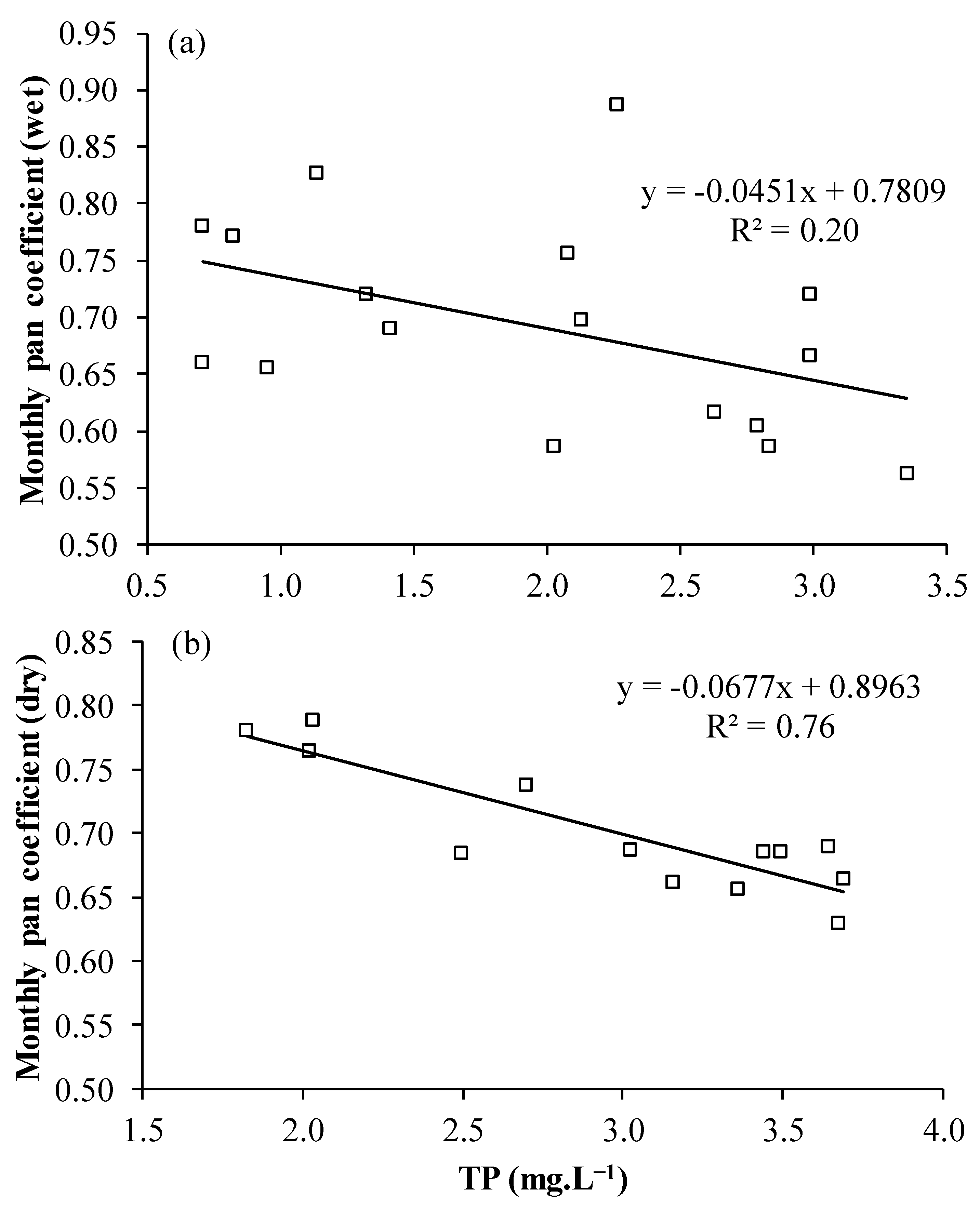
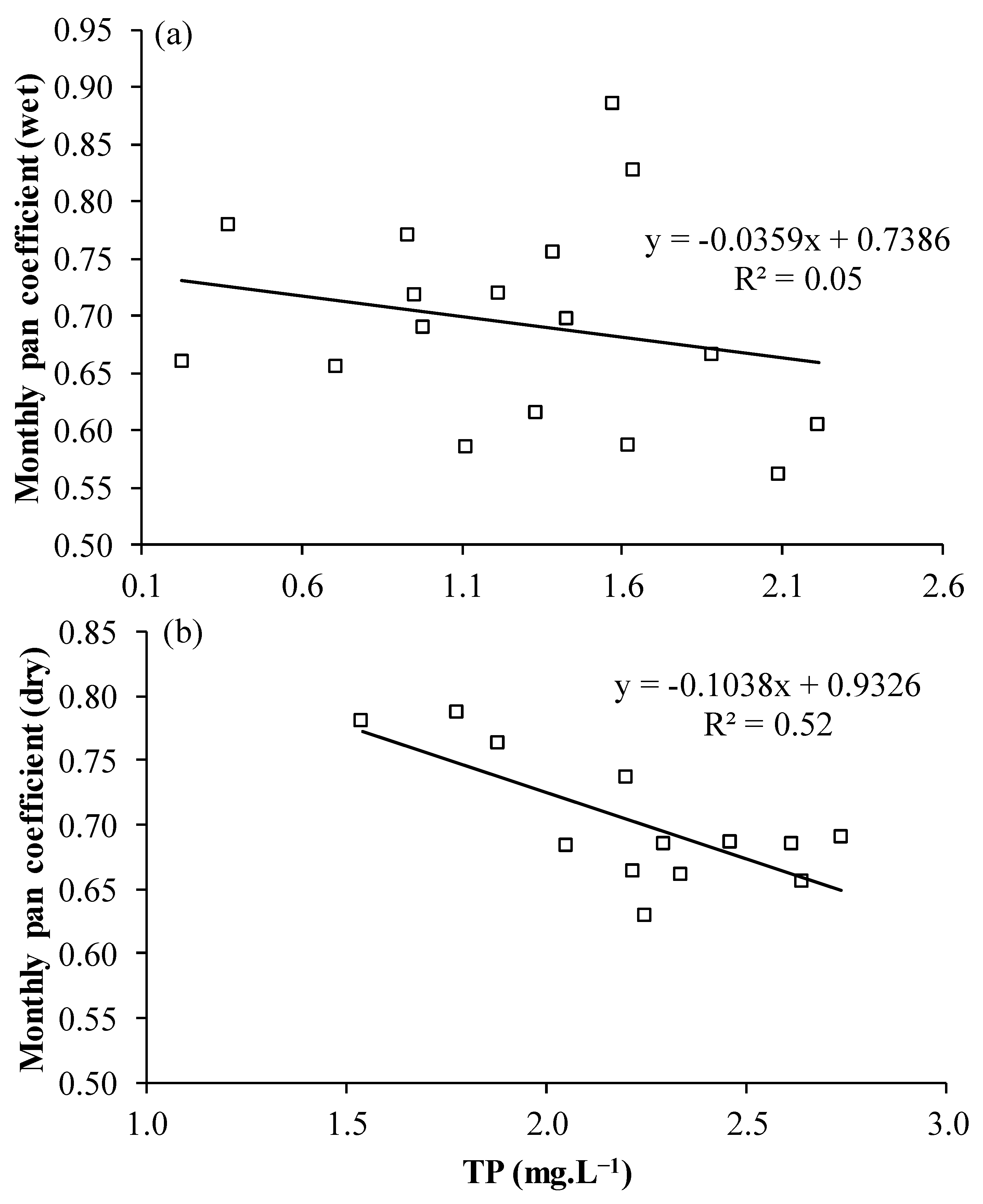
3.5. Impact of Water Quality on Evaporation Rates
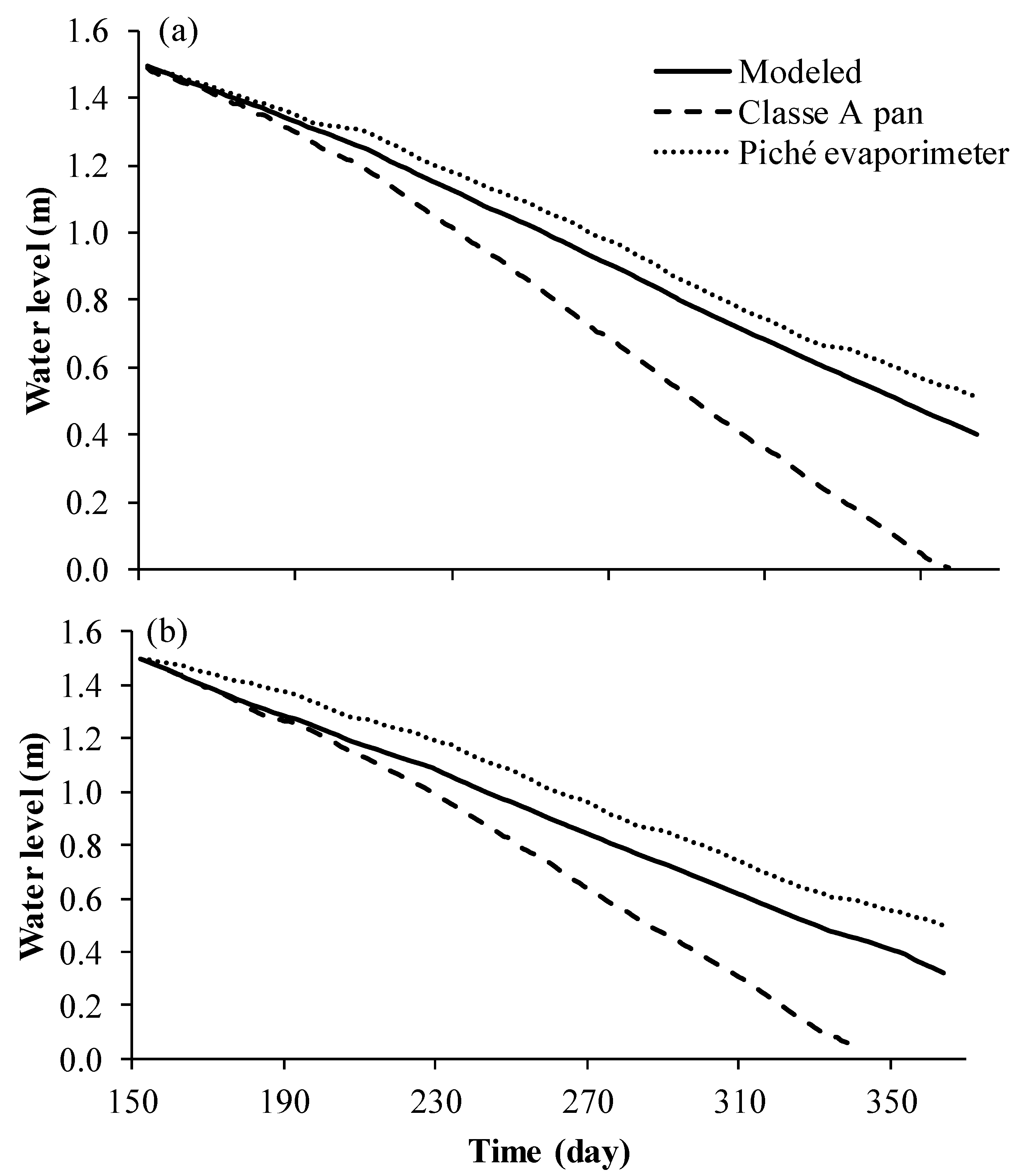
3.6. Scenario Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidl, M.; Hadrich, B.; Palmier, L.; Petrucci, G.; Nascimento, N. Impact of Urbanisation (Trends) on Runoff Behaviour of Pampulha Watersheds (Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14259–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, J.B.F.; Pereira, S.P.; Neto, I.E.L. Urban Drainage Modeling and Evaluation of Bacteriological Loads in the Vertente Marítima of Fortaleza, Ceará. Eng. Sanit. E Ambient. 2020, 25, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, G.M.; Lima Neto, I.E. Removal of Organic Matter in Stormwater Ponds: A Plug-Flow Model Generalisation from Waste Stabilisation Ponds to Shallow Rivers. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, G.M.; Lima Neto, I.E.; Becker, H. Phosphorus Dynamics in a Highly Polluted Urban Drainage Channelshallow Reservoir System in the Brazilian Semiarid. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2019, 91, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, R.F.; Rocha, S.M.G.; Lima Neto, I.E. Impact of Flow Conditions on Coliform Dynamics in an Urban Lake in the Brazilian Semiarid. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yuanxi, L.; Yu, L.; Mingxiang, X.; Liping, Z.; Qiuliang, D. Impacts of Rainfall Intensity and Urbanization on Water Environment of Urban Lakes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, R.L.G.; Caliman, A.; Cabral, C.R.; de Carvalho Araújo, F.; Guérin, J.; Dantas, F.d.C.C.; Quesado, L.B.; Venticinque, E.M.; Guariento, R.D.; Amado, A.M.; et al. Precipitation, Landscape Properties and Land Use Interactively Affect Water Quality of Tropical Freshwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, J.S.; Rose, K.C. Physical Responses of Small Temperate Lakes to Variation in Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentrations. Limnol Oceanogr 2013, 58, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watras, C.J.; Morrison, K.A.; Rubsam, J.L. Effect of DOC on Evaporation from Small Wisconsin Lakes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Mesquita, J.B.; Lima Neto, I.E.; Raabe, A.; de Araújo, J.C. The Influence of Hydroclimatic Conditions and Water Quality on Evaporation Rates of a Tropical Lake. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Chahar, B.R.; Dhanya, C.T. GIS-Based SWMM Model for Simulating the Catchment Response to Flood Events. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjeily, Y.A.; Abbas, O.; Sadek, M.; Shahrour, I.; Chehade, F.H. Flood Forecasting within Urban Drainage Systems Using NARX Neural Network. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Fernandez, A.; Zhu, D.Z.; Zhang, W.; Loewen, M.R.; van Duin, B.; Chen, L.; Mahmood, K.; Zhao, S.; Jia, H. Land Cover Based Simulation of Urban Stormwater Runoff and Pollutant Loading. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Carmo, M.; Gastaldini, C.; Maria, E.; Dias De Paiva, C.; Dias De Paiva, J.B.; Ferreira Paz, M.; Cláudia, M.; Kraemmer, N. Aplicação de Modelo Matemático a Dados de Ciclos de Estratificação Térmica e de Qualidade Da Água Do Reservatório Do Vacacaí-Mirim. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos Porto Alegre 2004, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, S.M.G.; Mesquita, J.B.F.; Lima Neto, I.E. Modelagem hidrodinâmica e avaliação do decaimento do fósforo em um lago urbano hipereutrófico. Revista AIDIS de Ingeniería y Ciencias Ambientales Investigación Desarrollo y Práctica 2020, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, R.; Brito, D.; Mateus, M.; Kenov, I.; Fornaro, A.; Neves, R.; Alves, C.N. Impact Evaluation of a Pisciculture in the Tucuruí Reservoir (Pará, Brazil) Using a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Moreira M., G.A.; Hinegk, L.; Salvadore, A.; Zolezzi, G.; Hölker, F.; Domecq, S.R.A.M.; Bocci, M.; Carrer, S.; de Nat, L.; Escribá, J.; et al. Eutrophication, Research and Management History of the Shallow Ypacaraí Lake (Paraguay). Sustainability 2018, 10, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sabóia, M.A.M.; de Souza Filho, F.d.A.; de Araújo Júnior, L.M.; Silveira, C.D.S. Avaliação Do Impacto Das Mudanças Climáticas No Sistema de Drenagem Urbana Em Localidades Situadas Em Baixas Latitudes: Um Estudo de Caso Em Fortaleza-CE. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hidr. 2017, 22, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Filho, F.A.; Martins, E.S.P.R.; Porto, M. O Processo de Mistura em Reservatórios do Semi-Árido e sua Implicação na Qualidade da Água. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hidr. 2006, 11, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.M.V.; Silva, T.F.D.G.; Vinçon-Leite, B.; Eleutério, J.C.; de Lima, L.C.; Nascimento, N.D.O. Modelling Drought Impacts on the Hydrodynamics of a Tropical Water Supply Reservoir. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, F.; Roozbahani, A.; Massah Bavani, A.R. Developing a Framework for Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Thermal Stratification of Dam Reservoirs. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2295–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Sharma, S.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Debolskiy, A.; Golub, M.; Mercado-Bettín, D.; Perroud, M.; Stepanenko, V.; Tan, Z.; Grant, L.; et al. Phenological Shifts in Lake Stratification under Climate Change. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokulil, M.T.; de Eyto, E.; Maberly, S.C.; May, L.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Woolway, R.I. Increasing Maximum Lake Surface Temperature under Climate Change. Clim. Chang. 2021, 165, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toné, A.; Lima Neto, I. Modelagem Simplificada Do Fósforo Total Em Lagos e Reservatórios Brasileiros. Revista DAE 2019, 221, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debele, B.; Srinivasan, R.; Parlange, J.Y. Coupling Upland Watershed and Downstream Waterbody Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Models (SWAT and CE-QUAL-W2) for Better Water Resources Management in Complex River Basins. Environ. Model. Assess. 2008, 13, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, D.; Ramos, T.B.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Morais, M.; Neves, R. Integrated Modelling for Water Quality Management in a Eutrophic Reservoir in South-Eastern Portugal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Storm Water Management Model User’s Manual Version 5.1 Office of Research and Development Water Supply and Water Resources Division; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Wells, S.A. CE-QUAL-W2: A Two-Dimensional, Later-Ally Averaged, Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, Version 4.2.2 User Manual: Part 1 Introduction, Model Download Package, How to Run the Model; Portland State University: Portland, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ceará. Perfil Básico Municipal; Instituto de Pesquisa e Estratégia Econômica do Ceará: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- INMET (Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia). Normais Climatológicas do Brasil 1961–1990; Organizadores: Ramos, Andrea Malheiros; Santos, Luiz André Rodrigues dos; Fortes, Lauro Tadeu Guimarães; INMET: Brasília, Brazil, 2009.
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environmental Federation, Ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, M.R.B. O Crescimento Urbano e o Risco à Poluição das Águas Subterrâneas Freáticas no Entorno da Lagoa da Parangaba, Fortaleza–Ceará. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2013; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Zouabi-Aloui, B.; Gueddari, M. Two-Dimensional Modelling of Hydrodynamics and Water Quality of a Stratified Dam Reservoir in the Southern Side of the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3037–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Brett, M.T.; Brattebo, S.K.; Welch, E.B. How Well Does the Mechanistic Water Quality Model CE-QUAL-W2 Represent Biogeochemical Responses to Climatic and Hydrologic Forcing? Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6609–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A. Scientific Fundamentals of the Eutrophication of Lakes and Flowing Waters, with Particular Reference to Nitrogen and Phosphorus as Factors in Eutrophication; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 1968.
- Delmiro Rocha, M.D.J.; Lima Neto, I.E. Phosphorus Mass Balance and Input Load Estimation from the Wet and Dry Periods in Tropical Semiarid Reservoirs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10027–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C. Surface Water-Quality Modeling; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Warsta, L.; Niemi, T.J.; Taka, M.; Krebs, G.; Haahti, K.; Koivusalo, H.; Kokkonen, T. Development and Application of an Automated Subcatchment Generator for SWMM Using Open Data. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, C.H.A.; Lima Neto, I.E. Effect of Artificial Circulation on the Removal Kinetics of Cyanobacteria in a Hypereutrophic Shallow Lake. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 06017010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperling, M. Introdução à Qualidade Das Águas e Ao Tratamento de Esgotos, 3rd ed.; Departamento de Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental-Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, I.S.; Costa, C.A.G.; Lima Neto, I.E.; Hopkinson, C. Trends of Evaporation in Brazilian Tropical Reservoirs Using Remote Sensing. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos De Araújo, J. Assoreamento Em Reservatórios Do Semi-Árido: Modelagem e Validação. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2003, 8, 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, L.D.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, H.G.; Ao, H.Y. The Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen Balance in Sediment-Water Microcosms and Implications to Dredging Projects. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ding, Q.; Jin, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yao, S.; Xue, B. Recording and Response of Persistent Toxic Substances (PTSs) in Urban Lake Sediments to Anthropogenic Activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Meraj, G.; Pandit, A.K. Assessing the Influence of Stream Flow and Precipitation Regimes on Water Quality of the Major Inflow Stream of Wular Lake in Kashmir Himalaya. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daityari, S.; Khan, M.Y.A. Temporal and Spatial Variations in the Engineering Properties of the Sediments in Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, B.B.; Carvalho, T.R.A.; Brosinsky, A.; Foerster, S.; Medeiros, P.H.A. From waste to resource: Cost-benefit analysis of reservoir sediment reuse for soil fertilization in a semiarid catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Khan, M.Y.A. ANN Modeling of the Complex Discharge-Sediment Concentration Relationship in Bhagirathi River Basin of the Himalaya. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, G.; Mizukawa, A.; Antonelli, J.; de Almeida Brehm Goulart, F.; Filippe, T.C.; Rodrigues de Azevedo, J.C. Determination of Parabens, Triclosan, and Lipid Regulators in a Subtropical Urban River: Effects of Urban Occupation. Water Air. Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

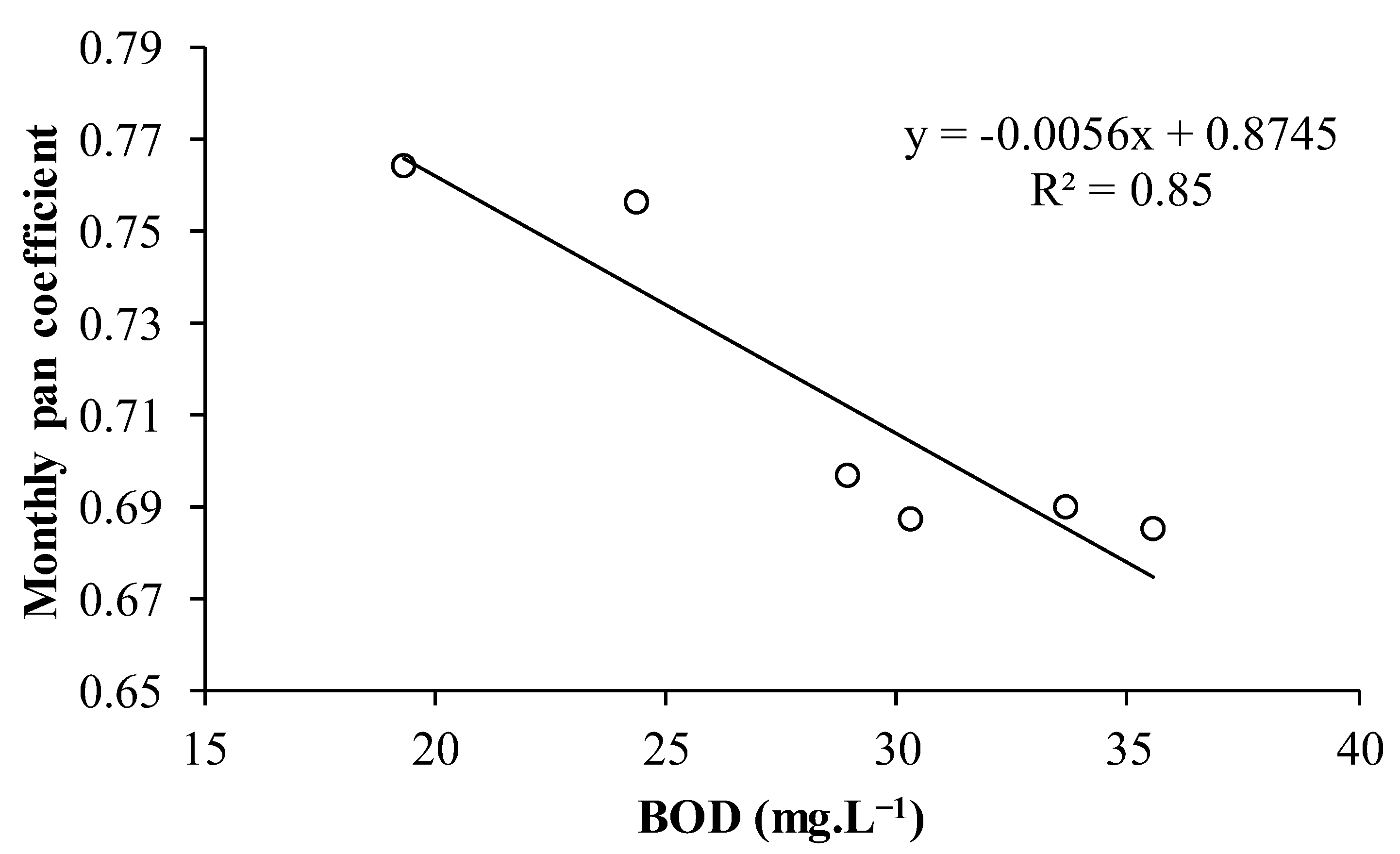
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesquita, J.B.d.F.; Lima Neto, I.E. Coupling Hydrological and Hydrodynamic Models for Assessing the Impact of Water Pollution on Lake Evaporation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013465
Mesquita JBdF, Lima Neto IE. Coupling Hydrological and Hydrodynamic Models for Assessing the Impact of Water Pollution on Lake Evaporation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013465
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesquita, Janine Brandão de Farias, and Iran Eduardo Lima Neto. 2022. "Coupling Hydrological and Hydrodynamic Models for Assessing the Impact of Water Pollution on Lake Evaporation" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013465
APA StyleMesquita, J. B. d. F., & Lima Neto, I. E. (2022). Coupling Hydrological and Hydrodynamic Models for Assessing the Impact of Water Pollution on Lake Evaporation. Sustainability, 14(20), 13465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013465





