Abstract
The analysis of historical village landscape characteristics and the influential driving factors of their evolutions can provide an essential decision-making basis for rural sustainable development strategies and landscape planning. How to obtain historical village landscape data at a time when objectively recorded data, such as remote sensing images, were unavailable is a key problem that restricts the analysis of village landscape evolution characteristics. As local villagers are important knowledge sources regarding historical village landscapes, a participatory data collection and analysis approach was used for village historical landscape data in this paper using a virtual globe-based three-dimensional participatory geographic information system (3D PGIS). Taking Duimengshan village, Guizhou, China, as a case study, the 3D landscape of the Duimengshan village and corresponding major historical events in four historical periods, 1958, 1980, 1995, and 2015, were collected in an on-site, interactive way by researchers with the participation of local villagers, and its land-use structure, ecosystem service values, and landscape pattern were analyzed. The results show that the historical landscapes in the four periods were strongly related to important local historical events. The 3D PGIS greatly mobilized the enthusiasm of villagers to participate with its intuitive 3D display form and simple and easy-to-use operation mode. It can be concluded that the historical landscape memory of local villagers and the oral inheritance information handed down from generation to generation can be utilized to make up for the lack of remote sensing and other objective data in the collection and acquisition of historical village landscape data. The obtained historical village landscape characteristics and their evolution laws can be used in future participatory rural planning and landscape design.
1. Introduction
Village landscapes, which integrate small-scale croplands, settlements, and other types of land, are an important part of a territorial space, covering more than 2 million square kilometers across China [1,2,3,4]. Since the end of the 1970s, with the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization, the development of rural areas in China has generally lagged far behind that of the cities, leading to a series of problems, such as village hollowing and fragmentation, and disordered development of the village landscape [1,5,6,7]. In some developed areas, the rural space has been reconstructed by excessively imitating the urban model, resulting in the loss of historical unique features in the village landscape. In this context, a series of development strategies, such as “New Rural Construction”, “Beautiful Countryside”, and “Rural Revitalization”, were put forward by the Chinese government, aiming to reconstruct the rural space and narrow the gap between urban and rural development.
The rural landscape is the result of longstanding natural events, human–nature interactions, and changes in natural circulation [8]. Therefore, the evolution of the historical rural landscape provides a medium for understanding the human–nature interactions in villages [9,10,11]. As a unique overlay result of the accumulated and discernible landscape elements in the countryside, the current village landscape objectively records the evolution of the village in time and space and the internal development mechanism, which can assist in understanding how the past village landscape formed as well as what changed and why [12,13]. To pursue a sustainable development path for a rural area, it is necessary to not only understand its current situation, but also to be familiar with its historical changes and understand the development mechanism. The results of the analysis of historical landscape changes consist of quantitative, statistical information on land-use changes [14], which could provide an essential basis for tackling current environmental questions in spatial planning [15,16]. The rules that describe the relationships between the driving forces of landscape changes and their evolution can be generated from the analysis of a time series of landscape changes and driving forces, and can be used to predict future scenarios within the assumed political and economic frameworks [17,18].
Rural landscape management is essential to ensure sustainability and the healthy functioning of rural ecosystems. Understanding the values that people assign to the land at smaller scales can be used to evaluate how humans interact with the land at broader scales [19,20]. The social values which determine where, how, and to what extent human activities can occur on the landscape play an indispensable role in changing the structure and function of landscapes [21,22,23]. Various methods have been used to incorporate social-value information into land analysis, assessment, and management at varying scales [24,25,26,27,28]. However, methods that allow for a wider range of stakeholders to participate are needed to better understand small-scale interactions between SVs and landscapes.
Communication and participation are essential to accessing sustainable rural landscape development [29]. Therefore, public participation has become increasingly important in the knowledge acquisition and landscape planning of historical rural landscapes [30,31]. The rural landscape is the result of the local people’s long-term production and daily life. As the direct creators, users, and maintainers of the local landscapes, the local villagers have not only witnessed the past and current local landscape and have rich local landscape knowledge, they can also construct the landscape using this knowledge [32]. Villagers are local “landscape ecologists”, who best know the historical changes and problems of the local landscape and, therefore, are the best-qualified to explain the natural and human reasons for these factors [32]. They have special wisdom regarding the human–land relationship and play an irreplaceable role in maintaining and improving the local landscape [13,33]. Therefore, to study the generation, evolution, and driving forces of a specific rural landscape, methods that are easily understandable and acceptable to non-professionals are highly required to dig deep into the local landscape knowledge in local villagers’ memories [34].
Various tools, such as participatory GIS, semi-directed meetings, photo-elicitation, and cognitive mapping, integrated with expert approaches, have been applied to effectively promote communication with locals [10]. In recent years, participatory GIS has become one of the important application branches of GIS, combining the spatial data visualization and spatial analysis abilities of traditional GIS with tools specifically designed to assist in public participation, which can greatly improve public participation in planning [25,35,36]. Since 3D visualization is more conducive to the creation of an intuitive communication platform between planners and various stakeholders than 2D, the application of 3D visualization technology to participatory geographic information systems has become a recent trend. This paper proposes a participatory village historical landscape data acquisition and analysis method based on a three-dimensional participatory geographic information system (3D PGIS), aiming to fully mine the historical landscape knowledge of local villagers and provide support for further research on rural landscape reconstruction and sustainable development planning.
2. Related Work
Remote sensing (RS) images are commonly used to extract historical landscapes [10,18,37,38,39,40,41,42]. However, it is impossible to obtain earlier period remote sensing data since remote sensing technology has only been widely developed in recent decades. Moreover, remote sensing images, especially high-resolution remote sensing images, are usually less available in rural areas than in urban areas. Therefore, historical village landscape data collection cannot be carried out without the participation of local residents. PGIS together with other methods such as high-resolution RS imaging and Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) has been widely used to obtain local landscape knowledge in historical landscape studies [31,43]. With the development of information technologies, PGISs have been used in the participatory landscape collection process in multiple forms such as desktop applications [44], mobile applications [45], and Web applications [46,47,48,49].
Visualization is the basis of the cognition, description, and communication of landscape changes. Therefore, landscape visualization plays a crucial role in public participation in historical landscape data collection. With the development of technology, the means of landscape visualization have evolved from paper-based sketches and maps to digital maps (e.g., CAD maps), GIS maps, and 3D visualizations. However, the 2D map, which is commonly used in current PGISs [31,43], has a high degree of abstraction, making it hard to explain the idea of planners to various stakeholders [50]. In participatory rural landscape data collection, 2D mapping is not sufficient to support the participation of local residents, as they usually lack professional mapping knowledge. Visualization has been one of the core issues in PGIS [35]. Landscape planners or evaluators could more smoothly and conveniently communicate with local residents if they could share real-time and intuitive visualization information with local residents using PGIS [28,51,52,53].
Three-dimensional visualization has been applied in support of public participation in a number of academic works (see, for example, [10,46,51,54,55]). However, traditional 3D visualization solutions that create 3D landscape scenes using 3D modeling software, such as 3D Studio Max, AutoCAD, and SketchUp, are time- and labor-intensive and, therefore, are generally used to present planning scenarios for specific projects. Therefore, 3D visualization-based PGIS (3D PGIS) is expected to solve this problem by providing an interactive 3D environment to enhance communication among planners and participators. In recent years, studies have shown that virtual globe-based 3D visualization technology is quite suitable for the creation of a 3D environment for public participation. As a result, virtual globe technology has been applied to the development of PGIS to publicize planning information [56] and support collaborations between decision makers and public participants at different stages through synchronous online meetings or on-site [50].
Three-dimensional PGIS has broad application prospects in participatory historical village landscape collection. Local villagers prefer face-to-face interactions to the online model because they are usually unfamiliar with computer technology. To solve this challenge in rural historical landscape data collection in China, a virtual globe-based 3D PGIS is used in this paper. The historical landscape characteristics are then evaluated using the integrated landscape analysis tools.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Area
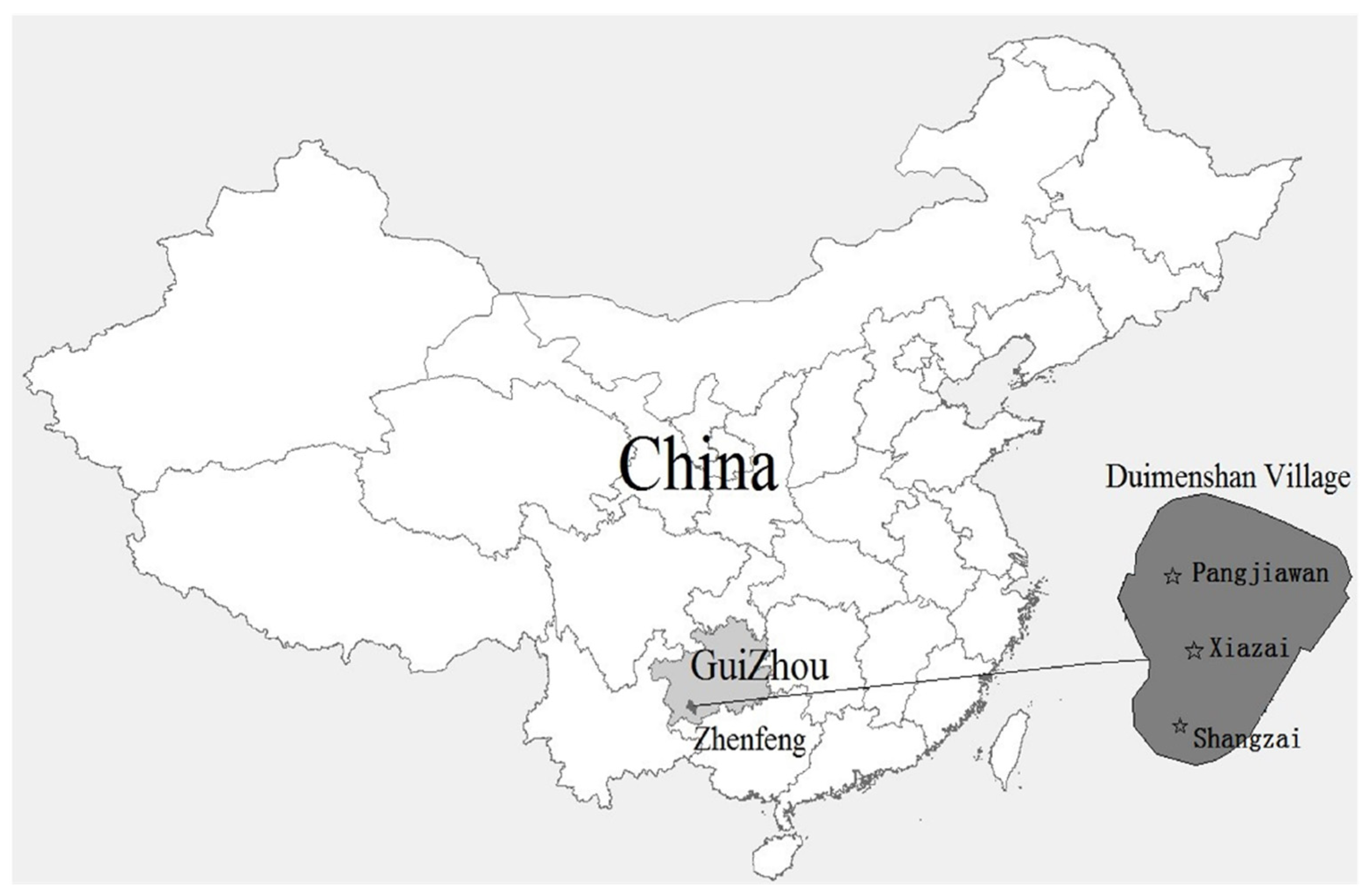
Duimenshan Village, about 20 km from Zhenfeng County and 100 km from Xinyi City, located in Zhenfeng County, Southwest Guizhou Province, China, covering an area of some 33.67 hectares, is a state-level integrated demonstration pilot for rural revitalization. There are 2984 people from 650 households of Han, Buyi, Miao and other ethnic minorities. The “Twelve tunes of Buyi bronze drum”, which is one of the ancient percussion instruments of the Buyi nationality and was approved by the State Council and listed in the first batch of the national intangible cultural heritage list, is preserved here. Duimenshan Village consists of three villager groups, which are, from north to south, Shangzai, Xiazai, and Pangjiawan (Figure 1). The topography is generally low in the north and high in the south and is a typical low-hilly landscape. The altitude of most of the area ranges from about 1294 m to 1370 m. The village enjoys a subtropical humid monsoon climate. The annual average temperature is 16.6 °C. There are 220 frost-free days per year. The annual precipitation is between 1000 and 1400 mm. The local villagers mainly depend on flue-cured tobacco planting and processing for their livelihood. Other plants, such as rice, corn, and coix seed, are occasionally planted. The landscape of Duimenshan Village has changed dramatically since 1958 and has been influenced by the long local history and culture, which is of unique research value.
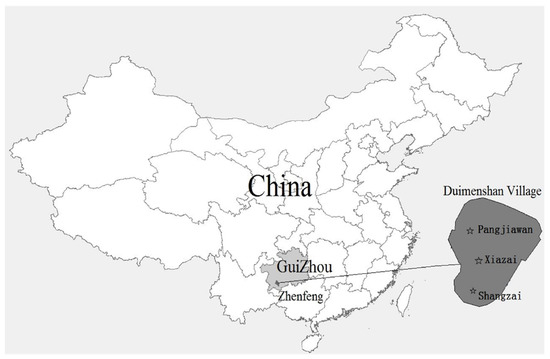
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
3.2. Main Research Methods
A virtual globe-based 3D PGIS named “XYPGIS” was used to support public participation in village landscape data collection and analysis in this study. “XYPGIS”, developed by Yu, L.J. et al. in 2020, is a virtual globe-based 3D PGIS. It provides a rich set of landscape interactive generation tools, allowing for participators, such as researchers, planners, and local residents, to interactively create 3D models of historical landscape elements, such as roads, environmental entities, borderlines, and buildings. The simplified drawing method enables users to create a 3D virtual landscape using mouse-clicking and dragging operations. Three-dimensional visualization allows for local residents who may have not any professional knowledge to intuitively describe their memorized local historical landscape. Therefore, it can provide a communication platform for landscape data collection. Moreover, XYPGIS also provides a rich set of analysis tools that can be used for the evaluation of recovered historical rural landscapes, such as land use structure analysis, land use balance sheet analysis, ecological service value analysis, and space syntax analysis.
The historical landscape evolution characteristics of Duimenshan village are analyzed, looking at land use structure, ecological service value, and landscape pattern indexes, using the XYPGIS analysis tools. The land use structure is calculated according to the “Classification of land use status (GB/T21010-2007)”. Ecological service values are calculated using the Terrestrial Ecosystem Unit Area Ecological Service Value in China (yuan/hm2)” (Table 1) [57,58]. Estimates of the ecosystem services value were calculated as follows:

Table 1.
Terrestrial ecosystem unit area ecological service value in China (yuan/hm2) (Reprinted with permission from Ref. [57]. Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.C, 2003).
In the formula, is the ecosystem service value of type , is the distribution area of the k-th land use type in the study area, and is the ecosystem service value per unit area of the k-th land use type.
Six landscape pattern indexes were used in this study, including the Shannon diversity index (SHDI), patch richness (PR), patch density index (PD), connectivity index (CONTAG), contiguity index (CONTIG), and landscape shape index (LSI) [59]
The SHDI value can be determined as follows
where is the proportion of the grid boxes occupied by patch type i, and I is the number of patch types. This proportion can be estimated as , where is the total number of grid boxes belonging to the i-th type.
The PR value can be calculated as follows
where m is the number of patch types (classes) present in the landscape excluding the landscape border if present.
The PD value can be determined as follows:
where, is the number of all landscape patches, and is the total area of the landscape patches.
The CONTAG value can be determined as follows
where is the adjacency table for all classes divided by the sum of that table and is the number of classes in the landscape.
The LSI value can be determined as follows
where, is the total length of all patch boundaries in the landscape, and is the total area of the landscape patches.
The CONTIG value can be determined as follows
where, is the contiguity value for the pixel in patch ; is the sum of the values in a 3-by-3 cell template; is the area of the patch in terms of the number of cells.
3.3. Research Time Period and Data Acquisition
The landscape survey and analysis were implemented using the XYPGIS and participatory rural appraisal (PRA) technologies including semi-structured interviews, seasonal calendars, timelines, and group discussions. Current and former village cadres were selected as participants, as they were familiar with the village development in recent periods and some of them had basic landscape planning knowledge or computer knowledge. The aged villagers who were aware of major village incidents and seasonal calendars in the reviewable period were also invited to participate in the landscape data collection. Current and former village cadres and elders who were aware of major village incidents and seasonal calendars in the reviewable period were invited to participate in the landscape data collection. The years 1958, 1980, 1995, and 2015 were determined to be the four time periods of interest for landscape restoration and evaluation according to the details presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Recognition basis of the historical landscape data collection.
The 2015 landscape data of Duimenshan village were obtained based on the 2015 remote sensing image and translated to a 3D landscape scene using the interactive landscape design tools of the XYPGIS. The 1958, 1980, and 1995 landscapes of Duimenshan were obtained by adding, deleting, and modifying the 2015 3D landscape elements based on the memories of the invited local villagers after several on-site discussion meetings. The 2015 landscape data were validated by the 2015 remote sensing image. However, it was impossible to validate the collected data from other periods as traditional landscape maps or remote sensing images were not available. Therefore, the collected historical landscape data of other periods were mutually verified by the historical memory of the on-site participants until all the participants reached a consensus.
4. Results
4.1. Historical Landscape Characteristics of Duimenshan village
4.1.1. The 2015 Landscape of Duimenshan Village
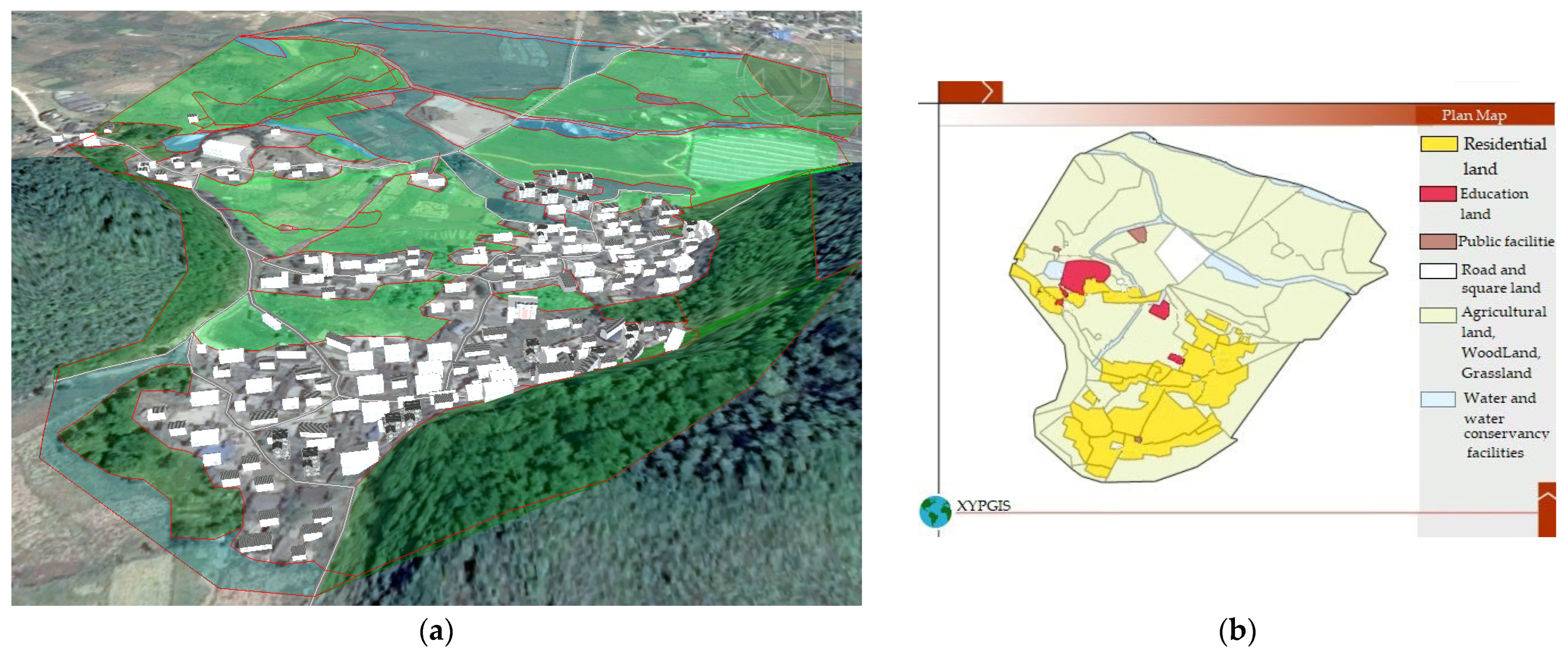
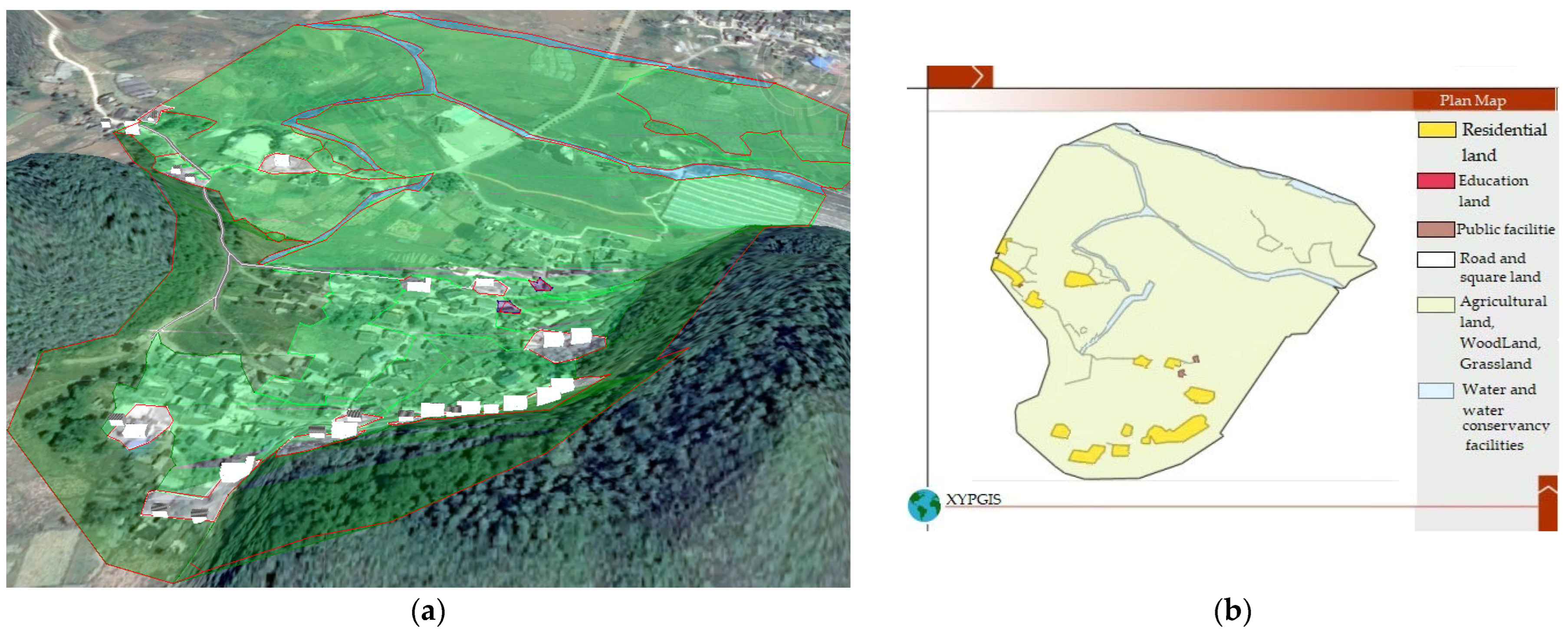
As shown in Figure 2, the 2015 landscape of Duimenshan Village presented a freestyle pattern. Three major country roads, which linked the three villager groups (Shangzai, Xiazai, and Pangjiawan), connected the village with the outside from the north, west, and south, respectively. Local houses were mainly one- or two-floor single-family detached buildings. There were also a few three- or four-floor single-family detached buildings scattered in some areas. Houses in Shangzai and Xiazai were built backing hills and facing north and were located in the middle area between two hills on the southeastern and northwestern sides of the village. Houses in Pangjiawan were located along a northwest road that connects the village to the outside from the northwest. There were a primary school in the northwestern, a kindergarten and a villager committee in the middle, a clinic next to the villager committee, two small shops in the northwestern, and an outdoor activity square in the northwestern. Two east–west streamlets were located in the northern region of the village. There was also a north–south streamlet in the western region of the village, with little water. Moreover, there were three ponds in the northern region of the village. Agricultural land was mainly distributed in the northern region of the village. There was some agricultural land in the middle of the village and at the foot of the south mountain. Approximately half of the agricultural land was dry land, which was the main land use type in the northwestern and middle regions of the village and at the foot of the south mountain. The other half comprised paddy fields, which were mainly located in the eastern region of the village. Forest land was mainly located on the hillside of the two hills and in the southern area between the two hills.
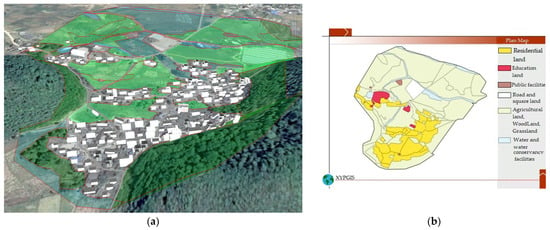
Figure 2.
2015 landscape and planar graph: (a) 3D map; (b) Planar graph.
4.1.2. The 1995 Landscape of Duimenshan Village
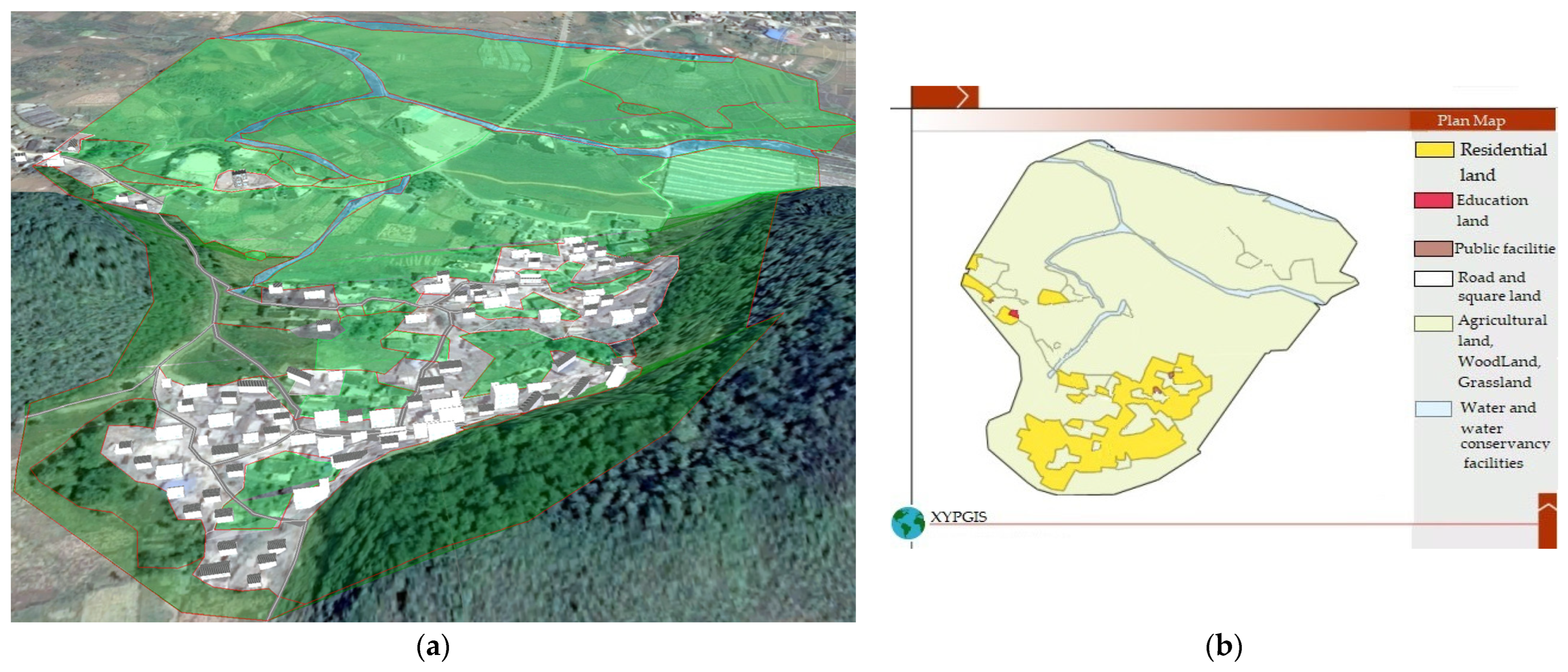
As shown in Figure 3, the general landscape pattern of the 1995 landscape of Duimenshan village was similar to that of 2015. Three major village roads cross the village and connect with the outside from the north, west, and south. Houses were 1-floor and 2-floor single-family buildings and were mainly built backing the hills and facing the north. The houses of Shangzai and Xiazai were mainly located at the foot of the hill in the southeastern region of the village and the area between the two hills. The houses of Pangjiawan were located along the northwest road from the northwest entrance to the foot of the northwest hill. A small shop was located in the northwestern region of the village. There were two streamlets in the northern region of the village and a streamlet with a small amount of water in the western region of the village. There was much more agricultural land in 1995 than in 2015, distributed throughout the northern and middle regions of the village and at the foot of the south hill. In total, 90% of the 1995 agricultural land comprised paddy fields that were distributed throughout the northern and middle regions of the village. Dry land was mainly located in a small region at the foot of the south hill. The woodland, which was mainly distributed on the slopes of the two southern mountains and the region between them, was larger than that in 2015, due, in part, to woodlands in the southwestern region of the village in 1995 changing to agricultural land in 2015.
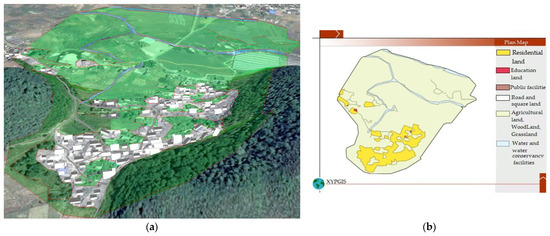
Figure 3.
1995 landscape and planar graph: (a) 3D map; (b) Planar graph.
4.1.3. The 1980 Landscape of Duimenshan Village
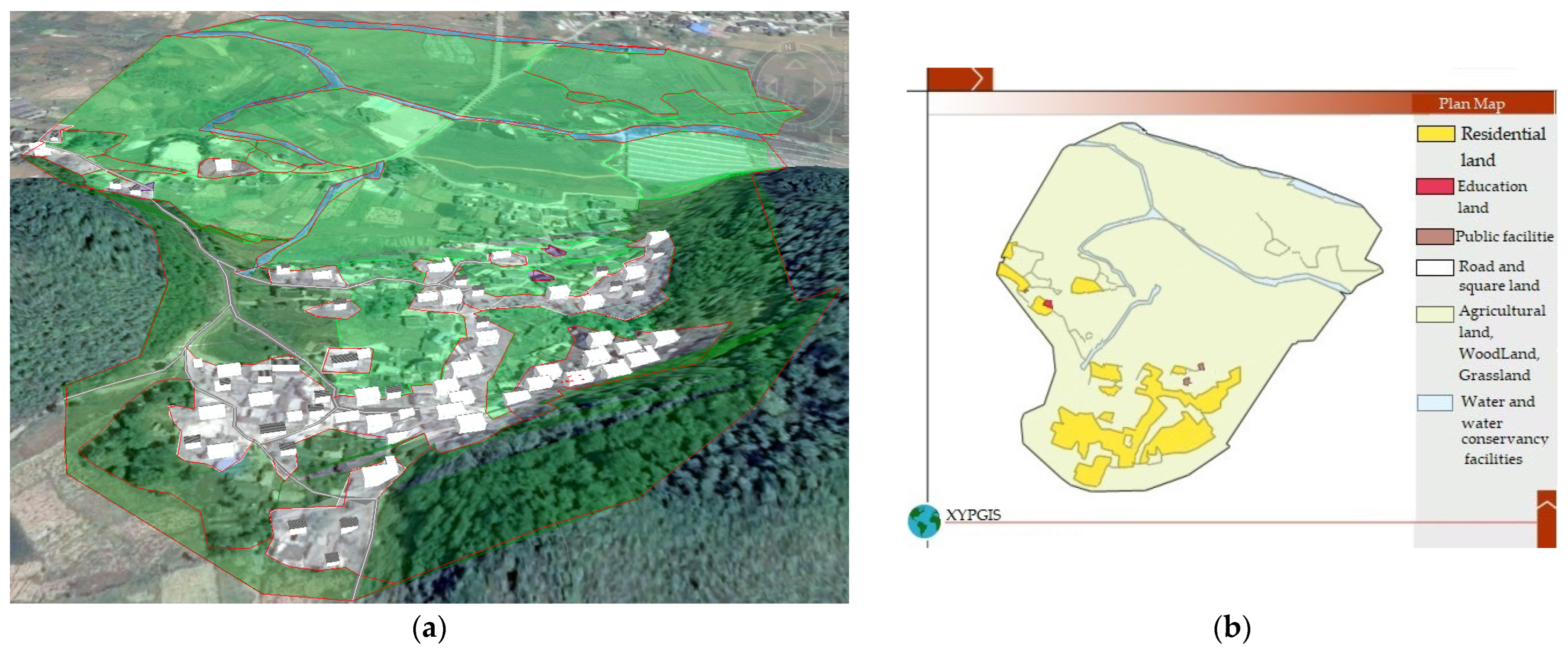
As shown in Figure 4, the road network of 1980 consisted of three major dirt roads which connected the village with the outside from the north, west, and south and a number of small dirt roads which linked houses to major roads. The number of houses in 1980 was much lower than that in 1995. They were mainly one-floor buildings facing north, which were distributed at the foot of the hills in the southeast of the village. There was a small shop in the northwestern, two east–west streamlets in the north, and a small north–south streamlet in the western. The agricultural land in 1980 was slightly larger than that in 1995 and was distributed throughout the northern region of the village, the central region, and the area at the foot of the south mountains. Nearly 95% of agricultural lands were paddy fields that were mainly distributed in the middle and northern regions of the village. Dry land was only distributed in a small area at the foot of the south hills. In addition to the increase in the paddy field area, the distribution of dry land in paddy fields in 1980 was similar to that in 1995. The forest land was mainly distributed throughout the slopes of the two mountains in the southern region and the area between the two mountains in the south. The forest land area in 1980 showed little difference to that in 1995.
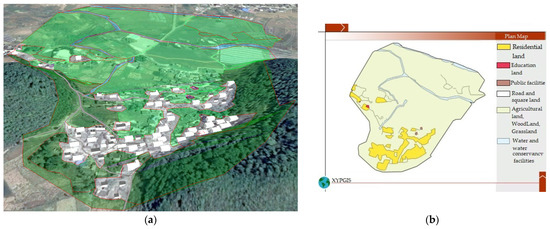
Figure 4.
1980 landscape and planar graph: (a) 3D map; (b) Planar graph.
4.1.4. The 1958 Landscape of Duimenshan Village
As shown in Figure 5, the road network of Duimenshan village was relatively simple and presented a ring layout in 1958. It consisted of three village roads that connected the village with the outside from the north, west, and south. The roads in 1958 were very few and narrow. The houses were mainly one-floor and north-facing buildings and mainly located at the foot of the mountain in the southeast corner of the village. There were some small thatched cottages in the region between the two mountains. A few houses in Pangjiawan were scattered at the foot of the mountain in the western region of the village.
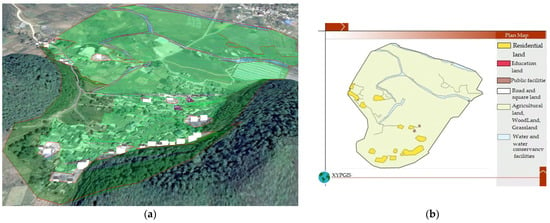
Figure 5.
1958 landscape and planar graph: (a) 3D map; (b) Planar graph.
There were two east–west streamlets in the northern region of the village and a small north–south streamlet in the western region of the village. The village was dominated by agricultural land, which was larger than that in 1980. In total, 95% of the agricultural lands were paddy fields in 1958. Dry land was mainly distributed in the area at the foot of the south hill. The forest land was mainly distributed on the slopes of the two mountains in the southern region and the area between the two mountains in the southern region. Some forest land at the foot of two mountains in the southern region in 1958 changed to residential land in 1980. The forest in the southern region between two mountains was cut down during the Great Leap Forward time.
4.2. Analysis of Landscape Evolution Characteristics
- Evolution characteristics of land use structure
As shown in Table 3, woodlands decreased from 1958 to 2015. Residential land and transportation land increased overall from 1958 to 2015. Public management and service land significantly increased from 1995 to 2015. Due to the introduction of flue-cured tobacco cultivation in 1995, the proportion of paddy fields compared to cultivated land decreased from 97.76% to 43.79%. Accordingly, the corresponding proportion of dry land increased from 0.211% to 55.59%. Other types of land use changed little.

Table 3.
Land use areas in four historical periods (ha).
- Evolution characteristics of ecological service value
As shown in Table 4, the ecological service value of Duimenshan Village decreased from 1958 to 2015. In particular, from 1995 to 2015, the ecological service value decreased by 50.54%, whereas the ecological service value decreased by 9.71% between 1958 and 1995. The ecological service value for climate change, recreational culture, waste disposal, and water conservation declined by 57.83%, 56.01%, 52.56%, and 52.39% from 1995 to 2015, respectively. However, the ecological service value for raw materials hardly changed. As a result of the increase in agricultural land, the ecological service value of food production also increased by 76.42%.

Table 4.
Ecological service value in four historical periods (yuan).
- Evolution characteristics of landscape pattern
As shown in Table 5, the patch richness of the landscape of Duimenshan Village increased from 1958 to 2015, indicating that the village land types showed a diversification trend. From 1995 to 2015, the village landscape changed rapidly. The fragrant diversity index, modified Simpson diversity index, patch density, and landscape shape index surged in this period, suggesting that land-use types tended to be balanced and discretely increased. Moreover, although various types of construction land were dominant patch types and trended to be aggregately distributed, landscape connectivity significantly decreased from 1958 to 1980. The main reason for this is that the woodlands, which formed a corridor, were originally cut down, causing the spatial structure connectivity to weaken. The landscape shape indexes significantly increased from 1958 to 1980 and from 1995 to 2015, indicating that patch edges were complicated. From the land-use change perspective, the complexity of the patch edges increased due to the agricultural land and forestry land being occupied by other land types.

Table 5.
Landscape pattern indexes in the four historical periods.
- Analysis of the Dependence of changes
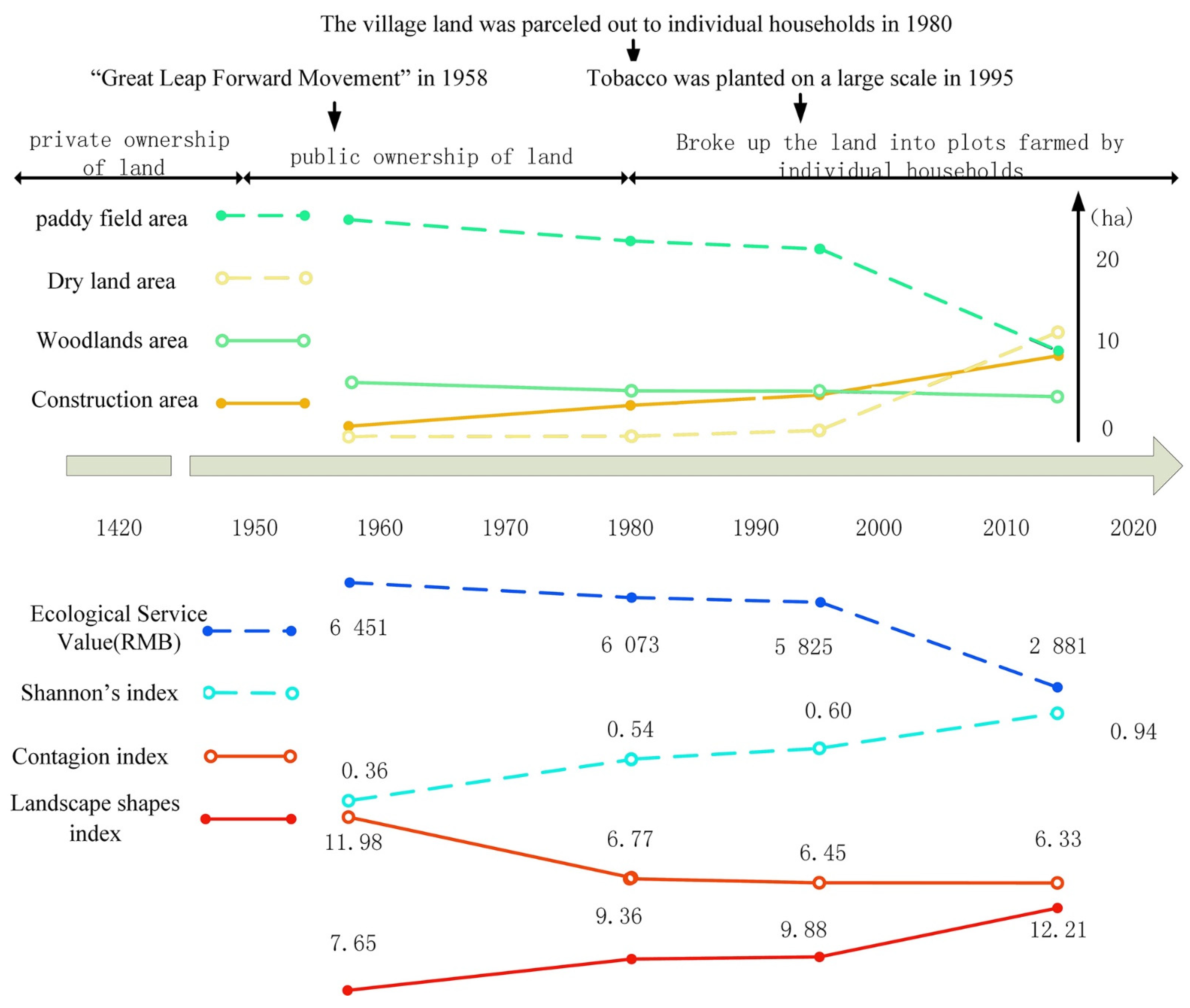
As shown in Figure 6, the landscape changes in Duimenshan Village mainly occurred in the periods from 1958 to 1980 and from 1995 to 2015. Although village land was distributed to individual families in the 1980s, there were no structural changes in people’s production and lifestyle, therefore, this resulted in relatively gentle landscape changes from 1980 to 1995. Paddy fields declined yearly from 1985 and began to show a sharp descending trend from 1995. The forest basically presented a linear downward trend. Construction land showed a linear upward trend. However, the dryland area rapidly increased from 1995, mainly due to the conversion of a large number of paddy fields to dry land because of the large-scale planting of tobacco.
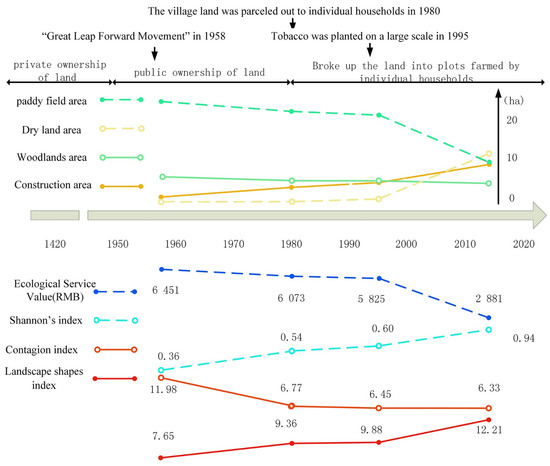
Figure 6.
Analysis of the dependence of changes between land use and ecological service value, landscape pattern of Duimenshan village’s historical landscapes.
The changes in land-use patterns led to a decline in the ecological service function. Figure 6 shows that the changing trend of ecological service value is basically similar to that of the paddy field. From 1958 to 1980, there were no significant changes in the ecological service value due to the few changes in the overall land use structure. However, since the large-scale planting of tobacco in 1995, the proportion of paddy fields in Duimenshan village has rapidly declined, and was almost the same as that of dry lands in 2015, which led to the overall ecological service value significantly decreasing.
The landscape pattern indexes generally reflect the land-use changes. Figure 6 shows that the change in each indicator was strongly related to changes in landscape land use, which can be divided into two periods: the slow change period (from 1958 to 1980) and the severe change period (from 1995 to 2015). The change in diversity index, namely, the SHDI, showed an increasing trend in terms of landscape diversity, but increased more rapidly from 1995 to 2015. This is consistent with the changes in residential land because the expansion of residential land leads to an increase in landscape fragmentation. In addition, various public management and service facilities have rapidly developed and were evenly distributed, which has significantly increased the diversity of the landscape. The CONTAG showed a downward trend, and the connectivity between regional landscape patches decreased, which indicated that the landscape of Duimenshan village was more dispersed and patchily distributed during 1958–2015. The landscape shape index (LSI) showed a fluctuating decrease, indicating a decrease in landscape edge heterogeneity in the region. From 1958 to 1980, the spatial connectivity of the landscape significantly decreased, because the forest was originally used as a landscape corridor, but was cut down due to the “Great Leap Forward Movement”.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The landscape consistently provides long-term, landscape-specific ecosystem services, which are essential for maintaining and improving human well-being in a regional context [60]. The analysis of the evolution characteristics of the historical village landscape is the basic work of creating village landscape planning and sustainable development strategies. In the last 100 years, the rural landscape of China has significantly changed due to local human activities [11]. This study shows that the ecological service function of the landscape of Duimenshan village has declined each year. The landscape of Duimenshan village presents characteristics of decreasing landscape diversity, increasing landscape fragmentation, weakening connectivity between regional landscape patches, and decreasing landscape edge heterogeneity. Historical events and policies are important driving factors of rural landscape evolution. The analysis of the historical landscape evolution characteristics and historical social and economic events in Duimenshan Village shows that the evolution of historical landscape characteristics is consistent with historical events. In 1958, a large number of trees were cut down during the “Great Leap Forward Movement”, resulting in a significant decline in the spatial connectivity of the landscape. Since the large-scale planting of tobacco in 1995, although the income of local villagers has increased, a large number of paddy fields have been converted to dry fields, resulting in a significant decline in the ecological service functions of the landscape. Therefore, how to improve the village landscape pattern and enhance the ecological service functions of the landscape while ensuring socio-economic development is a major challenge for future village sustainable development planning.
Village historical landscape data of different periods form the premise of analyzing historical village landscape changes [10,11,13]. Traditional objective data, for instance, remote sensing images, have been widely used in the collection of village historical landscape data in recent studies [37,40]. However, it is extremely difficult to obtain remote sensing data or historical landscape maps from a relatively distant time in the past, especially in rural areas. In view of this, based on the fact that the historical landscape memory of the local villagers is an indispensable source of historical village landscape data, this paper uses the participatory method, taking Duimenshan village as an example, to consider the historical landscape of the village and the historical events that affect the changes in landscape pattern from the historical memory of the villagers.
How to increase local villagers’ participation in the process of collecting historical landscape data is one of the major challenges in village landscape analysis and planning [31,35,47]. In traditional participatory rural planning, planners usually need to spend a lot of time expressing villagers’ opinions on the map after multiple rounds of interactions. As traditional PGIS usually adopts the display form of a 2D map, which is not sufficient to provide an intuitive communication platform, XYPGIS, a 3D PGIS based on virtual-globe technology, was used in this paper to assist local villagers in participating in the collection and analysis of the historical landscape data of local villages [50,51,52,61].
Taking Duimenshan village in Guizhou Province, China, as an example, the landscape data of Duimenshan village in different historical periods were collected and visualized in three dimensions with the participation of local villagers. The results show that 3D landscape visualization technology has greatly mobilized the enthusiasm of local villagers. Researchers can quickly generate 3D landscape scenes from local villagers’ memories on-site with the support of 3D landscape interactive generation tools of the XYPGIS. Researchers and villagers can communicate intuitively and comment on 3D landscape scenes in different historical periods in real-time to maximize the effectiveness and authenticity of this communication.
Traditional village planning needs the help of professional analysis models and software to analyze the historical landscape of the village. As a rural design and communication platform, XYPGIS enables planners to obtain the characteristics of the village’s historical landscape in real-time based on the integrated professional landscape characteristic analysis tools, which solves the contradiction between the single function of the traditional landscape analysis tools and the complexity of GIS. Therefore, the method of collecting and analyzing historical villages’ landscape data based on XYPGIS can improve the efficiency of professional landscape planners and provide a way for non-professionals to directly participate in the village landscape design and decision-making process.
The limitation of the participatory historical landscape data acquisition method used in this study is that the historical landscape’s traceability depends on the memory of the local villagers. First, the acquisition of historical landscape data is limited by the memory of local villagers, so the landscape of historical periods cannot be acquired. Due to the limitation of local villagers’ memory bias, more villagers must participate to verify each other’s memories to improve the accuracy and reliability of the more distant historical landscape data. Moreover, the reliability of the historical knowledge passed down from generation to generation beyond the historical period experienced by villagers is usually very low. This means that this study period reaches back to 1954, which is as far back as local villagers could remember.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Y. and X.Z.; methodology, L.Y. and X.Z.; software, L.Y.; validation, F.H.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.Z. and F.H.; visualization, L.Y.; project administration, X.Z.; funding acquisition, L.Y.; Writing—review & editing, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Digital Simulation and Evaluation Model for Reconstruction of Town and Village Settlements Space” of the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2018YFD1100305.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Key Research and Development Program of China for financial support. Special thanks are given to the local villagers of Duimenshan Village, Guizhou Province, China for their participation. Finally, the authors acknowledge the contribution of anonymous reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, J.; Wu, B. Revitalizing traditional villages through rural tourism: A case study of Yuanjia Village, Shaanxi Province, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 63, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, M.; Nasar, J.L.; Chun, B. Neighborhood satisfaction, physical and perceived naturalness and openness. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, B.-S.; Ellis, C.D.; Leiva, P.I.; Rogers, G.O. Landscape Components, Land Use, and Neighborhood Satisfaction. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2010, 37, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Neerchal, N.; Peng, K.; Xiao, H.S.; Wang, H.Q.; Yan, Z.A.; Li, S.C.; Wu, J.X.; Jiao, J.G.; Hua, O.Y.; et al. Estimating Long-Term Changes in China’s Village Landscapes. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B. Traditional Village Landscape Integration Based on Social Network Analysis: A Case Study of the Yuan River Basin in South-Western China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, T. The spatio-temporal patterns of urban–rural development transformation in China since 1990. Habitat Int. 2016, 53, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Rao, X.; Duan, P. The Rural Gentrification and Its Impacts in Traditional Villages—A Case Study of Xixinan Village, in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markuszewska, I. Sentimentality versus Transformation of the Historical Traditional Rural Landscape (A Case Study: The Landscape of Dutch Law Settlement in Poland). Quaest. Geogr. 2019, 38, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullotta, S.; Barbera, G. Mapping traditional cultural landscapes in the Mediterranean area using a combined multidisciplinary approach: Method and application to Mount Etna (Sicily; Italy). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, A.; Statuto, D.; Picuno, P. Rural landscape planning through spatial modelling and image processing of historical maps. Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, W. Alterations of Historic Rural Landscape Based on the Multifunctional Approach: The Case of Coastal Fishing Villages in the Yangtze River Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezant, J.; Grant, K. The post-medieval rural landscape: Towards a landscape archaeology? Post-Mediev. Archaeol. 2016, 50, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.; Harvey, D. Landscape Archaeology, Heritage and the Community in Devon: An Oral History Approach. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2005, 11, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelorosso, R.; Leone, A.; Lorenzo, B. Land cover and land use change in the Italian central Apennines. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, M.; Andreoli, M.; Gorelli, S.; Jussila, H. A DSS model for the governance of sustainable rural landscape: A first application to the cultural landscape of Orcia Valley (Tuscany, Italy). Land Use Policy 2016, 56, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Walz, U.; Neubert, M.; Rosenberg, M. Changes to Central European landscapes—Analysing historical maps to approach current environmental issues, examples from Saxony, Central Germany. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change in Tropical Regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, J.I.; Kasanko, M.; McCormick, N.; Lavalle, C. Modelling dynamic spatial processes: Simulation of urban future scenarios through cellular automata. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, K.; Hutchinson, S.; Moore, T.; Hutchinson, J.M.S. Analysis of publication trends in ecosystem services research. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 25, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastandeh, A.; Carnes, M.; Jarchow, M. Spatial analysis of landscape social values in multifunctional landscapes of the Upper Missouri River Basin. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.M.; Gobster, P.H. Interpreting landscape change: Measured biophysical change and surrounding social context. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieninger, T.; Bieling, C.; Fagerholm, N.; Byg, A.; Hartel, T.; Hurley, P.; Lopez-Santiago, C.A.; Nagabhatla, N.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Raymond, C.M.; et al. The role of cultural ecosystem services in landscape management and planning. Curr. Opin. Env. Sust. 2015, 14, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, E.; Verheyen, K.; Valdes, A.; Solino, M.; Jacobsen, J.B.; De Smedt, P.; Ehrmann, S.; Gartner, S.; Gorriz, E.; Decocq, G. Promoting biodiversity values of small forest patches in agricultural landscapes: Ecological drivers and social demand. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.G.; Reed, P. Social Landscape Metrics: Measures for Understanding Place Values from Public Participation Geographic Information Systems (PPGIS). Landsc. Res. 2012, 37, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, R. Public Participation Geographic Information Systems: A Literature Review and Framework. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2006, 96, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Semmens, D.J.; Clement, J.M. An application of Social Values for Ecosystem Services (SolVES) to three national forests in Colorado and Wyoming. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenweg, K.; Williams, K.; Cerveny, L.; Styers, D. Is recreation a landscape value?: Exploring underlying values in landscape values mapping. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 185, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Reed, P.; Raymond, C.M. Mapping place values: 10 lessons from two decades of public participation GIS empirical research. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 116, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volker, K. Local commitment for sustainable rural landscape development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1997, 63, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, L.P.; Hambly Odame, H. Broadband for a sustainable digital future of rural communities: A reflexive interactive assessment. J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 54, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Cinderby, S.; Forrester, J. Enhancing participation: Experiences of participatory geographic information systems in Shanxi province, China. Appl. Geogr. 2008, 28, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. Landscape pattern, perception and visualisation in the visual management of forests. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.; Velázquez, A.; Verdinelli, G.B.; Priego-Santander, Á.G.; McCall, M.K.; Boada, M. Rural People’s Knowledge and Perception of Landscape: A Case Study From the Mexican Pacific Coast. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2012, 25, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Sandoval, C.; Flanders, D.N.; Kozak, R.A. Participatory landscape planning and sustainable community development: Methodological observations from a case study in rural Mexico. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 94, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Kyttä, M. Key issues and research priorities for public participation GIS (PPGIS): A synthesis based on empirical research. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Fagerholm, N. Empirical PPGIS/PGIS mapping of ecosystem services: A review and evaluation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Tong, D.; Li, X. Planning control over rural land transformation in Hong Kong: A remote sensing analysis of spatio-temporal land use change patterns. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, C.; Pu, T.; Zhang, L. Regional landscape transformation and sustainability of the rural homegarden agroforestry system in the Chengdu Plain, China. Reg. Sustain. 2022, 3, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessel, B. Elements, characteristics and character—Information functions of landscapes in terms of indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, D.O.; Opiyo, S.B. Detection of historical landscape changes in Lake Victoria Basin, Kenya, using remote sensing multi-spectral indices. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2022, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovsky, J.; Gaitani, N.; Gustavsen, A. A systematic review of urban climate research in cold and polar climate regions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberly, B.; Robin, M.; Patrick, M. Participatory GIS for strengthening transboundary marine governance in SIDS. Nat. Resour. Forum 2013, 37, 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- Cinderby, S. How Communities Can Use Geographical Information Systems. In Towards Understanding Community; Clay, C., Madden, M., Potts, L., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.; Brabyn, L. An analysis of the relationships between multiple values and physical landscapes at a regional scale using public participation GIS and landscape character classification. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 107, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, M.A.; Minghini, M.; Zamboni, G. Public participation in GIS via mobile applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafrance, F.; Daniel, S.; Dragicevic, S. Multidimensional Web GIS Approach for Citizen Participation on Urban Evolution. ISPRS Int. J. Geo. -Inf. 2019, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Rhodes, J.; Dade, M. An evaluation of participatory mapping methods to assess urban park benefits. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.K.; Masullo, M.; Maffei, L.; Meng, F.Y.; Vorlander, M. A demonstrator tool of web-based virtual reality for participatory evaluation of urban sound environment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 170, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, A.D.; Gorsevski, P.V. A web-based participatory GIS (PGIS) for offshore wind farm suitability within Lake Erie, Ohio. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2015, 41, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Zhang, X.T.; He, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, D.C. Participatory Rural Spatial Planning Based on a Virtual Globe-Based 3D PGIS. ISPRS Int. J. Geo.-Inf. 2020, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, A.; Appleton, K.; Warren-Kretzschmar, B.; Von Haaren, C. Using 3D visualization methods in landscape planning: An evaluation of options and practical issues. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissen, U.; Schroth, O.; Lange, E.; Schmid, W.A. Approaches to integrating indicators into 3D landscape visualisations and their benefits for participative planning situations. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 89, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onitsuka, K.; Ninomiya, K.; Hoshino, S. Potential of 3D Visualization for Collaborative Rural Landscape Planning with Remote Participants. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, T.L.J.; Gaborit, N. Using Virtual Environment Technology to Improve Public Participation in Urban Planning Process. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2007, 133, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.R.; Omtzigt, N.; Koomen, E.; de Blois, F.S. 3D visualisations in simulations of future land use: Exploring the possibilities of new, standard visualisation tools. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2008, 1, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, H.; He, Z.; Gong, J. A virtual globe-based 3D visualization and interactive framework for public participation in urban planning processes. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2010, 34, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y. The influences of land use changes on the value of ecosystem services in Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramstad, W.E.; Tveit, M.S.; Fjellstad, W.J.; Fry, G.L.A. Relationships between visual landscape preferences and map-based indicators of landscape structure. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, P. Landscape visualizations: Applications and requirements of 3D visualization software for environmental planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2006, 30, 815–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).