Survey Study of the Cultural Integration of International Students in East China under Ecosystem Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Obstacles in Cross-Cultural Communication
1.2. Inadequate Adaptation to Overseas Students’ Daily Lives
1.3. The Need to Optimize and Improve the Education Model and Quality of International Students
1.4. The Management of International Students Still Needs to Be Improved
2. Hypotheses and Measures
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Review of the Theory of Cultural Integration
2.1.2. Review of Ecosystem Theory
2.2. Indices Adopted
2.2.1. Life Adaption
2.2.2. Interpersonal Communication
2.2.3. Study Adaptation
2.2.4. Training System
2.2.5. Cultural Integration
3. Research Design
3.1. Sampling and Questionnaire Distribution
3.1.1. Scale Selection
3.1.2. Sampling Design
3.1.3. Quality Monitoring
3.2. Participants’ Demographic Characteristics
3.3. Questionnaire Analysis
3.3.1. Reliability Test
3.3.2. Validity Test
3.3.3. Principal Component Analysis
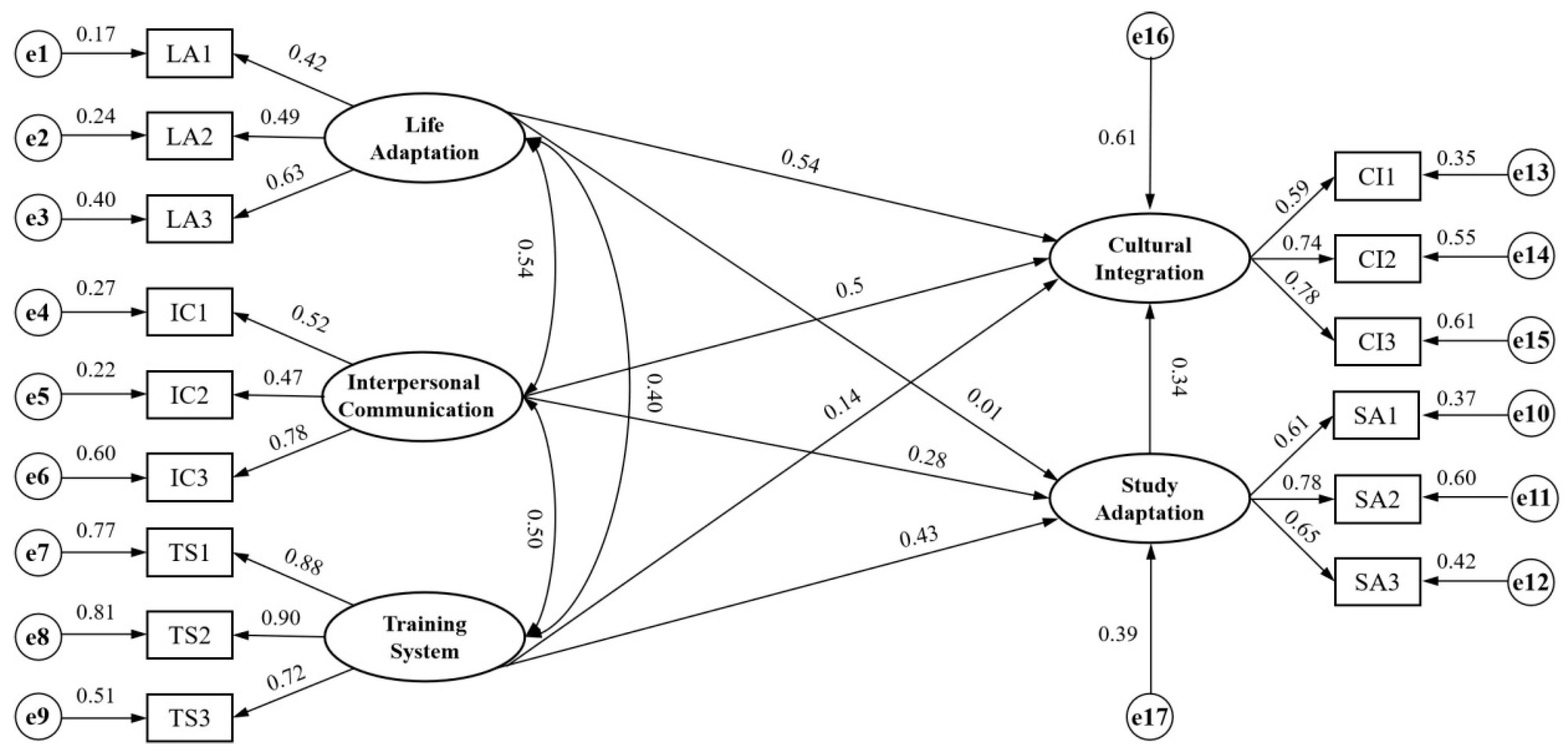
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Structural Equation Model (SEM)
4.2. Model Fitting and Path Analysis
4.2.1. Hypothesis Model
4.2.2. Model Modification
4.2.3. Model Checking
4.2.4. Model Results
- Analysis of Standardized Path Results
- 2.
- Analysis of the Mediating Effect of Study Adaptation
- 3.
- Difference Analysis of Social and Demographic Factors
- (1)
- Gender and Age. The independent-sample t-test was used to analyze the influence of gender and age. The analysis results are shown in Table 8. The significance level of international students’ gender on cultural integration is 0.915. The significance level of the age of international students in China on cultural integration is 0.722. As this greatly exceeds 0.05, the null hypothesis of the independent-sample t-test is accepted. That is, there is no significant difference between international students’ gender and age on cultural integration.
- (2)
- Education level
5. Conclusions
5.1. The Cultural Integration of International Students Is Jointly Affected by Multiple Real-Life Factors
5.2. Life Adaptation and Interpersonal Communication Are the Basic Factors for International Students’ Cultural Integration
5.3. The Major Impacts of the Training System on the Cultural Integration of International Students through Study Adaptation
6. Suggestions
6.1. Pay Attention to Informal Organization Guidance and Enhance the Individual Adaptability of International Students
6.2. Improve the Education and Training System to Improve the Study Adaptation Level of International Students
6.3. Strengthen International Exchanges and Cooperation to Help International Students Better Adapt to Culture
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Dai, K. Foreign-born Chinese students learning in China: (re)shaping intercultural identity in higher education institution. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2021, 80, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C. Strategic management and development trend of sino-foreign cooperative university in the new era of open education development. Budapest. Int. Res. Crit. Linguist. Educ. BirLE J. 2020, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapka, M.; Buchtele, R. The usual discourse of sustainable development and its impact on students of economics: A case from Czech higher education context. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2022, 23, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddese, E.T.; Gessel, D.; Han, X. Chinese language learning anxiety: The case of international students in northeast normal university. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 14, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, S.; Peacock, N. Overcoming Linguistic and Cultural Barriers to Integration: An Investigation of Two Models; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009; Volume 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ashdown, B.K.; Smith, W. Chinese international students’ value acculturation while studying in the united states. Int. J. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2014, 4, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Quanjiang, G.; Michael, L.I.; Chun, L.; Chuang, W. Developing literacy or focusing on interaction: New Zealand students’ strategic efforts related to Chinese language learning during study abroad in China. System 2021, 98, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.F.; Yen, J.R. The most familiar stranger: The acculturation of mainland Chinese students studying in Taiwan. Contemp. Issues Educ. Res. CIER 2018, 11, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solano, A.C.; Perugini, M. Acculturation in International Students in Argentina: Factors That Predict Adaptation; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rathakrishnan, B.; Singh, S.; Kamaluddin, M.R.; Ghazali, M.F.; Yahaya, A.; Mohamed, N.H. Homesickness and Sociocultural Adaptation Towards Perceived Stress among International Students of a Public University in Sabah: An Exploration Study for Social Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pownall, I. Student identity and group teaching as factors shaping intention to attend a class. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2012, 10, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikula, P.T.; Sibley, J. Supporting international students’ academic acculturation and sense of academic self-efficacy. Transit. J. Transient Migr. 2020, 4, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveh, G.; Shelef, A. Analyzing attitudes of students toward the use of technology for learning: Simplicity is the key to successful implementation in higher education. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2021, 35, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beregovaya, O.A.; Lopatina, S.S.; Oturgasheva, N.V. Tutor support as a tool of social-cultural adaptation of international students in Russian universities. Vysš. obraz Ross. 2020, 29, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biney, P.A.; Cheng, M.Y. International students’ decision to study in China: A study of some selected international students from universities in China. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2021, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.; Liujinya, Y.; Yue, S. “We’re away from everything”: Understanding the struggles faced by internationalized schools in non-urban contexts in China. SAGE Open 2022, 12, 214–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbollie, C.; Gong, S.S. Emerging destination mobility. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2020, 34, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. An Analysis of Ralph’s Fate in Typical American from the Perspective of Cultural Adaptation. Campus Engl. 2016, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, A.M.; Catling, C.; Hogan, R.; Homer, C. Addressing culture shock in first year midwifery students: Maximising the initial clinical experience. Women Birth 2014, 27, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimares, L.; Massuda, J., Jr.; Demarch, R.B.; Ogata, A.; Oliveira, F. Cross-cultural adaptation of dimensions of corporate safety scorecard to the Brazilian Portuguese language. Rev. Bras. Med. Trab. 2018, 16, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, A. Scholars discuss the opportunities and challenges of trilateral cooperation among China, Japan and the ROK. Chin. J. Soc. Sc. 2020, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Toward an experimental ecology of human development. Am. Psychol. 1977, 32, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. A Report on Longitudinal Evaluations of Preschool Programs, Vol. II: Is Early Intervention Effective? (Washington, DC: Office of Development, Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, 1974, ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED093501); Bronfenbrenner, Ecological Systems Theory. Ann. Child Dev. 1989, 6, 185–246. [Google Scholar]
- Yarrow, L.J.; Zaslow, M. Review of the ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Am. J. Orthopsychiatr. 1981, 51, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, G.H., Jr. The life course paradigm: Social change and individual development. In Examining Lives in Context: Perspectives on the Ecology of Human Development; Moen, P., Elder, G.H., Jr., Lüscher, K., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 101–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, N.C. Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory. College Student Development: Applying Theory to Practice on the Diverse Campus. 2017. Available online: https://www.simplypsychology.org/Bronfenbrenner.html (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Ungar, M.; Ghazinour, M.; Richter, J. Annual research review: What is resilience within the social ecology of human development? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatr. 2013, 54, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez-Agosto, N.M.; Soto-Crespo, J.G.; Vizcarrondo-Oppenheimer, M.; Vega-Molina, S.; García Coll, C. Bronfenbrenner’s bioecological theory revision: Moving culture from the macro into the micro. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 12, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Tian, F. Talent ecological environment, growth expectation and overseas talent return intention. Hum. Resour. Dev. China 2022, 9, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Study on International students’ school integration group work under the background of cultural differences. Beijing Univ. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2020, 8, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, M. Stress-related growth associated with acculturation and mental health among international students. J. Humanist. Psychol. 2021, 2, 0022167820979654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, K.; Temizkan, V. The effects of educational service quality and socio-cultural adaptation difficulties on international students’ higher education satisfaction. SAGE Open 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.D.; Sahin, H.; Nazli, A. International medical students’ adaptation to university life in Turkey. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2020, 11, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.A. The buddy programme: Integration and social support for international students. J. Comp. Int. Higher Educ. 2019, 11, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, Á.; Papp, Z.Z.; Luu, L.A.N. Social contact configurations of international students at school and outside of school: Implications for acculturation orientations and psychological adjustment. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2020, 77, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atteraya, M.S. Acculturation stressors and academic adjustment among Nepalese students in South Korean higher education institutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, I.W.; Yusoff, M.S.; Marinsah, S.A.; Mokhtar, S.; Ramlie, H.A.; Shah, M.K.M. Acculturation strategy and different cultural results among the international students of the public university of Malaysia. J. Tour. Hosp. Environ. Manag. 2020, 5, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Shoaib, M.; Ghaffari, A.S. The relationship between acculturative stress, depression, anxiety and religious coping among international students in China. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2020, 12, 15253–15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, A.V.; Liventsova, E.Y.; Fakhretdinova, A.P.; Kostyukova, T.A. International student migrants from Asian countries: Features of their ethnic identity and acculturation strategies. Prospects Sci. Educ. 2020, 48, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, J. Master student teaching and training in an international context. Lect. Notes Mech. Eng. 2020, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, P.B.; Esteves, N.R. Teaching sustainability-oriented capabilities using active learning approach. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2021, 22, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataliia, M.; Inna, V. Interactive methods of teaching the humanities in higher education institutions. IJMH 2020, 4, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fute, A.Z. The danger of acculturation process phase to international students’ academic achievement: A case study of Zhejiang Normal University. Asian J. Educ. Soc. Stud. 2020, 12, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, J. Reflections on the management of international students in colleges of universities under the background of “double first-class”. Sci. Educ. Lit. Early Issue 2020, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yuen, M.; Horta, H. Factors influencing the life satisfaction of international students in mainland China. Int. J. Adv. Couns. 2020, 42, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.; Lu, G.; Yin, H.; Li, L. Student engagement for sustainability of Chinese international education: The case of international undergraduate students in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamitewoko, E. International students labour and school attendance: Evidence from China. Theor. Econ. Lett. 2021, 11, 962–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, A.; Ward, C.; Fetvadjiev, V.H. Cross-cultural transition and psychological adaptation of international students: The mediating role of host national connectedness. Front. Educ. 2020, 5, 539950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, Y.; Xia, Z. The effect of perceived discrimination on cross-cultural adaptation of international students: Moderating roles of autonomous orientation and integration strategy. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tsokalidou, R. Thoughts on the use of “le” in teaching Chinese to speakers of other languages: Problems and suggestions. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2021, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, K.; Horr, B.; Netenjakob, I.T.; Varhegyi, V.; Manarte, J.; Migda, A.M. Silent protest: Cross-cultural adaptation processes of international students and faculty. Int. J. Divers. Educ. 2021, 21, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.; van Dam, R.M. Food, culture, and identity in multicultural societies: Insights from Singapore. Appetite 2020, 149, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Wang, F.Y. Ternary Taiji models of the traditional Chinese self: Centered on Confucian, Taoist, and Buddhist cultures. J. Humanist. Psychol. 2021, 1, 00221678211016957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glas, S. Exclusionary Contexts Frustrate Cultural Integration: Migrant Acculturation Into Support for Gender Equality in the Labor Market in Western Europe. Int. Migr. Rev. 2022, 56, 01979183211059171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaliyski, P.; Welzel, C.; Hien, J. A community of shared values? Dimensions and dynamics of cultural integration in the European Union. J. Eur. Integr. 2022, 44, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.N.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W.H.; Xia, X.; Li, X.T. Risk of adverse perinatal outcomes and antenatal depression based on the Zung self-rating depression scale. Reprod. Dev. Med. 2021, 5, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.Y.; Xu, Z. Social and cultural adaptation of Koreans in China and its adaptive strategies: Based on an investigation of the Korean community in Yuanwang Road, Guangzhou. Qinghai Ethn. Stud. 2022, 2, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Urban acculturation and subjective well-being of migrant children: A moderated mediation model. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2021, 3, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, J.P.C.; Mohammed, P.J.; Saleh, S.T. Students’ motivations to study abroad: The case of international students at the university of Debrecen. Cent. Eur. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 2, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J. Service Quality in higher education institutions: Qualitative evidence from the students’ perspectives using Maslow hierarchy of needs. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2020, 12, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. How Chinese multinational corporations solve cross-cultural conflicts in internationalization—A case study of SAIC’s merging of SsangYong motor. Adv. Soc. Sci. Res. J. 2021, 8, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.N.E. Raising undergraduate students’ level of academic readiness through teaching intercultural communication. Adv. Journal. Commun. 2022, 10, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Latent Variable | Observed Variable | Explanation of Indicators | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Life Adaptation (LA) | LA1 | Living environment | Safe, comfortable, and stable |
| LA2 | Pace of life | Local socioeconomic development and living standards | |
| LA3 | Living habits | Food, shopping, transportation, communication | |
| Interpersonal Communication (IC) | IC1 | Making friend party | Campus integration and social exchange |
| IC2 | Language communication | Language attitude motivation; pragmatic choice | |
| IC3 | Values | Religious belief, value transfer | |
| Training System (TS) | TS1 | Teaching content | Rationality, scientificity, perfection |
| TS2 | Management mode | Housemaster, logistics, scholarship | |
| TS3 | Quality of education | Academic achievements, foreign language ability, curriculum system | |
| Study Adaptation (SA) | SA1 | Classroom learning | Teaching content, teacher–student interaction |
| SA2 | After-class discussion | Initiative, diversity, professionalism | |
| SA3 | Relationship between teachers and students | Teaching, administration | |
| Cultural Integration (CI) | CI1 | Social environment | Cultural exchange atmosphere |
| CI2 | Special holidays | Know, love, participate | |
| CI3 | Traditional culture | Food, thought, history | |
| Variable | Variable Definitions | Frequency | Percentage | Variable | Variable Definitions | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 806 | 53% | Age | 25 years and under | 745 | 49% |
| Female | 714 | 47% | 26–55 years | 775 | 51% | ||
| Major | Literature and History | 593 | 39% | Education Level | Undergraduate | 532 | 35% |
| Science and Technology | 426 | 28% | Postgraduate and above | 988 | 65% | ||
| Agricultural Medicine | 501 | 33% |
| International Students’ Cultural Integration Factor (Dimension) | Element | Factor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Training System | TS1 | 0.872 | 0.113 | 0.161 | 0.174 | 0.089 |
| TS2 | 0.866 | 0.141 | 0.212 | 0.15 | 0.039 | |
| TS3 | 0.792 | 0.185 | 0.157 | 0.012 | 0.142 | |
| Cultural Integration | CI1 | 0.087 | 0.8 | 0.053 | 0.141 | 0.035 |
| CI2 | 0.185 | 0.776 | 0.237 | 0.022 | 0.158 | |
| CI3 | 0.274 | 0.628 | 0.166 | 0.129 | 0.395 | |
| Study Adaption | SA1 | 0.135 | −0.042 | 0.822 | 0.048 | 0.149 |
| SA2 | 0.257 | 0.261 | 0.704 | 0.062 | 0.094 | |
| SA3 | 0.154 | 0.255 | 0.697 | 0.198 | −0.132 | |
| Interpersonal Communication | IC1 | 0.121 | −0.056 | 0.181 | 0.722 | 0.063 |
| IC2 | −0.018 | 0.281 | −0.097 | 0.706 | 0.095 | |
| IC3 | 0.26 | 0.086 | 0.281 | 0.659 | 0.103 | |
| Life Adaption | LA1 | 0.042 | 0.052 | 0.109 | −0.099 | 0.803 |
| LA2 | 0.029 | 0.083 | −0.081 | 0.394 | 0.588 | |
| LA3 | 0.178 | 0.236 | 0.052 | 0.192 | 0.572 | |
| Eigenvalues | 3.879 | 2.223 | 2.208 | 1.996 | 1.684 | |
| Percentage of variance | 18.529 | 16.949 | 15.405 | 13.931 | 12.453 | |
| Cumulative percentage | 18.529 | 35.478 | 50.883 | 64.814 | 77.267 | |
| Statistical Test Volume | Adapted Standard or Critical Value | Measurement Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | p < 0.05 (significant) | 120.127 (p = 0.002 < 0.05) | qualified |
| Chi-square degree of freedom ratio | <3.00 | 1.502 | qualified |
| RMSEA (root mean square error of approximation) | <0.08 | 0.05 | qualified |
| GFI (goodness-of-fit index) | >0.90 | 0.931 | qualified |
| AGFI (adjusted goodness-of-fit index) | >0.90 | 0.897 | unqualified |
| CFI (comparative fit index) | >0.90 | 0.956 | qualified |
| PNFI (parsimonious normed fit index) | >0.50 | 0.673 | qualified |
| PGFI (parsimonious goodness-of-fit index) | >0.50 | 0.621 | qualified |
| NFI (norm fit index) | >0.90 | 0.883 | unqualified |
| TLI (Tucker–Lewis index) | >0.90 | 0.943 | qualified |
| Statistical Test Volume | Adapted Standard or Critical Value | Measurement Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| X2 | p < 0.05 (significant) | 99.995 (p = 0.047 < 0.05) | qualified |
| Chi-square degree of freedom ratio | <3.00 | 1.282 | qualified |
| RMSEA (root mean square error of approximation) | <0.08 | 0.037 | qualified |
| GFI (goodness-of-fit index) | >0.90 | 0.940 | qualified |
| AGFI (adjusted goodness-of-fit index) | >0.90 | 0.908 | qualified |
| CFI (comparative fit index) | >0.90 | 0.976 | qualified |
| PNFI (parsimonious normed fit index) | >0.50 | 0.670 | qualified |
| PGFI (parsimonious goodness-of-fit index) | >0.50 | 0.611 | qualified |
| NFI (norm fit index) | >0.90 | 0.903 | qualified |
| TLI (Tucker–Lewis index) | >0.90 | 0.968 | qualified |
| Path | Estimate | SE | CR | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Integration | ← | Life Adaption | 0.492 | 0.175 | 3.001 | 0.003 |
| Cultural Integration | ← | Interpersonal Communication | −0.078 | 0.118 | −0.575 | 0.565 |
| Cultural Integration | ← | Training System | 0.183 | 0.097 | 1.732 | 0.083 |
| Cultural Integration | ← | Study Adaption | 0.356 | 0.121 | 2.847 | 0.004 |
| Study Adaption | ← | Life Adaption | 0.009 | 0.143 | 0.073 | 0.942 |
| Study Adaption | ← | Interpersonal Communication | 0.281 | 0.123 | 2.058 | 0.040 |
| Study Adaption | ← | Training System | 0.434 | 0.102 | 3.998 | *** |
| Path | Estimate | SE | 95% Confidence Interval | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| M1 | 0.004 | 0.245 | −0.273 | 0.136 | 0.870 |
| M2 | 0.058 | 0.344 | −0.021 | 0.703 | 0.083 |
| M3 | 0.141 | 0.128 | 0.029 | 0.457 | 0.012 |
| Variable | Cultural Integration | T | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 4.0749 ± 0.64984 | 0.378 | 0.915 |
| Female | 4.0394 ± 0.64857 | |||
| Age | 18–25 years | 4.0000 ± 0.68638 | −1.392 | 0.722 |
| 26–55 years | 4.1262 ± 0.60700 | |||
| Education Level | Cultural Integration | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | |
| Undergraduate | 4.0509 | 0.64437 |
| Postgraduate and above | 4.0677 | 0.65232 |
| F | 0.031 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Li, G.; Wan, M.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Survey Study of the Cultural Integration of International Students in East China under Ecosystem Theory. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14485. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114485
Zhu J, Li G, Wan M, Li S, Sun L, Li J, Wang X. Survey Study of the Cultural Integration of International Students in East China under Ecosystem Theory. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):14485. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114485
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junqi, Guangxia Li, Ming Wan, Shanshan Li, Liyan Sun, Jie Li, and Xue Wang. 2022. "Survey Study of the Cultural Integration of International Students in East China under Ecosystem Theory" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 14485. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114485
APA StyleZhu, J., Li, G., Wan, M., Li, S., Sun, L., Li, J., & Wang, X. (2022). Survey Study of the Cultural Integration of International Students in East China under Ecosystem Theory. Sustainability, 14(21), 14485. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114485






