Abstract
Traditional electrokinetic (EK) technology can remove contaminants from soil, but the efficiency is generally low. This study reports on the combination of enhanced EK and a waste ferric hydroxide (Fe(OH)3) permeable reactive barrier (PRB) for the remediation of soil in sulfide mine areas. Hydroxyethylene diphosphonic acid (HEDP) and FeCl3 were used as a compound chelating agent. The experimental results showed that EK combined with PRB technology (95.32% Cd removal) was more effective than single EK in removing cadmium (Cd) from the contaminated soil, because of the compound chelating agent and PRB filled with sustainable Fe(OH)3 adsorbent. Additionally, the application of PRB in combination with HEDP was able to increase the sulfate removal rate to 96.19%. The accumulated energy consumption of these two systems was 182.4 and 356 kWh/m3, respectively, after EK remediation using PRB.
1. Introduction
Mine tailings’ contamination is a widespread problem for the exploitation and utilization of metal sulfide mineral resources. The natural weathering and oxidation of mine tailings in sulfide mine areas can generate and release a large amount of acid mine drainage (AMD) containing toxic and harmful heavy metals and sulfate ions [1]. AMD enters the soil, which not only damages the soil environment and reduces the yield of crops, but also introduces a large number of toxic and harmful heavy metal ions. These heavy metal ions can exist stably in the environment for a long time, and it is difficult for organisms to degrade all of them, so they pose a threat to human health through the food chain [2]. Contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas has become one of the major environmental problems, and its remediation is an urgent requirement for sustainable development.
Advanced technologies have been used to remediate contaminated soils. To date, there are two main approaches to remediating contaminated soils. One is to migrate heavy metals out of the soil so that they are completely removed, such as through soil washing, thermal treatment and biological remediation. The other is to immobilize them in the soil and reduce their toxicity and mobility, such as through solidification, vitrification and chemical stabilization [3,4,5]. Electrokinetic (EK) technique has been recognized as an emerging cost-effective technique for the remediation in composite contaminated soil, which is favored by researchers at home and abroad. Compared with other techniques, the EK technique is suitable to operate in low-permeability clay and in situ remediation, being characterized by its stability, efficiency and economy [6]. The principle of the EK technique is to remediate contaminated soil by applying a direct current across electrodes placed on both sides of the contaminated soil, which induces the dissolved contaminants to move to the anode or cathode chamber under the action of electro-migration (EM), electrophoresis, electro-osmosis (EO), and free diffusion [7,8]. EM refers to the directional movement of charged ions in the soil towards electrodes under the action of the electric field, and is usually faster than EO and electrophoresis. In the EK process, EM is the main way in which charged contaminants in the soil migrate from the soil [9].
In the process of EK remediation, H+ and OH− generated by water electrolysis will enter the soil under the action of the electric field, causing changes in soil pH. The soil pH can affect the process of heavy metal adsorption and desorption, with a significant impact on EK remediation [10]. Therefore, the choice of chelating agent is crucial, and the mechanism by which chelating agents interact with contaminated soil varies. Acidic chelating agents could use acidity to dissolve contaminants in the soil, while salt chelating agents could rely on strong electrolytes to increase the electric current and the migration of ions [11,12]. In addition, a single chelating agent can no longer meet the remediation requirements, and compound chelating agents are gradually being studied. Yuan et al. [13] reported that a compound chelating agent (citric acid + calcium chloride), combined the advantages of two different compositions, with the advantage of a high removal efficiency for multi-heavy metals. It was found that the use of HCl as a chelating agent has a better effect on heavy-metals-contaminated soil, and could accelerate the removal of heavy metals due to the chloride ions’ ability to form ionic complexes with heavy metals. However, HCl, as a strong acid, may cause secondary contamination to the soil [14,15]. Small-molecule organic acids, such as hydroxyethylene diphosphonic acid (HEDP), with low toxicity and easy biodegradability, are used as chelating agents to enhance the removal efficiency of metal extraction from soil. Salt chelating agents such as sodium and calcium salts are commonly used for EK remediation, but there are relatively few studies on the use of iron salts as electrolytes. It has been shown that ferric chloride is chemically milder and converts large amounts of mobile fractions of cadmium (Cd) while causing less damage to the soil structure [14]. The results of soil-leaching studies also showed that acid and ferric chloride, as a compound leaching agent, could also improve the leaching efficiency of heavy metals [16,17]. Although HEDP and ferric chloride have been shown to promote electro-osmotic flow and the desorption of contaminants in soil, their potential application as a compound chelating agent in EK remediation has not been extensively studied.
EK technique can also be combined with the permeable reactive barrier (PRB) to improve the remediation efficiency. When the contaminants migrate to PRB built by the reactive materials, the contaminants could be blocked by adsorption, precipitation or even chemical degradation of the reactive materials to achieve soil remediation [18]. Thus, the potential application of iron-based reactive materials to fill PRB has received more attention in recent years due to their wide sources, environmental friendliness and low cost. The commonly used zero-valent iron has achieved more significant efficiency in heavy-metals-contaminated soil remediation, but the cost is high and it is susceptible to acid corrosion during the EK process [19]. While the sludge of ferric hydroxide (Fe(OH)3) is generally discarded as industry waste, the results of the study showed that Fe(OH)3 can be used as an adsorbent to effectively remove heavy metals and sulfate [20,21]. It has been reported that the low-cost granular Fe(OH)3, a by-product from coal mine drainage sludge, successfully removed aqueous arsenate [22]. However, few studies reported in the literature have used the Fe(OH)3 to remediate contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas. The metals and sulfate in soil are less mobile to remove than those in water. This makes it difficult to use PRB with Fe(OH)3 to remediate contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas.
Therefore, the EK/waste Fe(OH)3 PRB system could be an effective remediation system that is capable of transporting more contaminants in soils compared to traditional EK/PRB systems. In this paper, cadmium- and sulfate-contaminated soil, configured in the laboratory, was taken as the research object, and the EK technology combined with PRB was used to carry out the simulated soil remediation in sulfide mine areas, aiming to increase the efficiency. In addition, the effect of two chelating agents (HEDP and FeCl3)on the contaminants’ migration and remediation efficiency was investigated using EK. The newly prepared Fe(OH)3 was used as a reactive material to adsorb and precipitate Cd and sulfate. We expected to find environmentally benign and sustainable chelating agents and PRB, which can simultaneously remove heavy metal and sulfate efficiently.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Soil, and Characterization
Commercial kaolin was purchased from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (China). The initial physicochemical characteristics of the kaolin were summarized in Table 1. Approximately 0.2 kg of dry kaolin was used for each experiment. Soil samples were contaminated with nitrate of Cd and anhydrous sodium sulphate, mechanically stirring for 30 min to achieve 43.20 mg/kg of Cd and 1500 mg/kg of sulfate contamination for each experiment, with an initial moisture content of 40% in all EK experiments. Soil samples were divided into five equally sliced sections (S1–S5, from the anode to cathode). In addition, three samples were collected from different parts of each sliced section for analysis before the initiation of each EK experiment to ensure a uniform distribution of contaminants and moisture content. The Fe(OH)3 was newly prepared using the precipitation method with 1.2 g of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O for use as a reactive material for filling the PRB.

Table 1.
The initial physicochemical characteristics of the kaolin.
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.2.1. pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
Soil samples were dried and homogenized before and after EK experiments. A total of 8.0 g of sieved soil of each sliced section was added in 50 mL centrifugation tube containing 20.0 mL of ultrapure water, shaken for 30 min and left for 1 h. The soil pH and EC of the supernatant were measured separately using a pH meter (PHS-3C, Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and an EC meter (DDSJ-308A, Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., China) [23].
2.2.2. Determination of Cd Concentration
The Cd extraction procedure was as follows: 3.0 g of air-dried and sieved soil of each sliced section was added to a 50 mL centrifugation tube containing 27.0 mL of 1 M HCl, shaken at 200 rpm for 6 h, and then centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatant was filtered through 0.45 μm filters and analyzed using an atomic absorption spectrometer, ZEEnit700P [13].
2.2.3. Determination of Sulfate Concentration
The sulfate extraction procedure was as follows: 5.0 g of air-dried and sieved soil of each sliced section was added to a 50 mL centrifugation tube containing 25.0 mL of ultrapure water, shaken at 200 rpm for 30 min, and then centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min. A total of 10 mL of the supernatant and 5 mL of conditioning reagent (25 mL of glycerol, 15 mL of conc. HCl acid and 50 mL of 95% isopropyl alcohol were added to the same beaker; a total of 37.5 g of NaCl was dissolved in ultrapure water; all the contents were mixed and added to a 250 mL standard measuring flask using ultrapure water) were added to 0.1 g of barium chloride dihydrate crystals and added to a 100 mL standard measuring flask using ultrapure water, with stirring for 60 s. Sulfate concentration was estimated by the turbidimetry method with the help of UV-Visible spectrophotometer in the wavelength range of 420 nm [24].
2.2.4. Removal Efficiency and Accumulated Energy Consumption
The contaminants’ removal efficiency (η) was determined as follows:
where C0 and C represent the initial and final contaminants concentration (mg/L), respectively.
The following equation was used to calculate the accumulated energy consumption (AEC):
where Vs is the volume of soil sample, U is the voltage difference between the two graphite electrodes, I is the measured electric current, and t is the EK remediation time. AEC accumulated as kWh/m3.
2.2.5. EK Experimental Setup
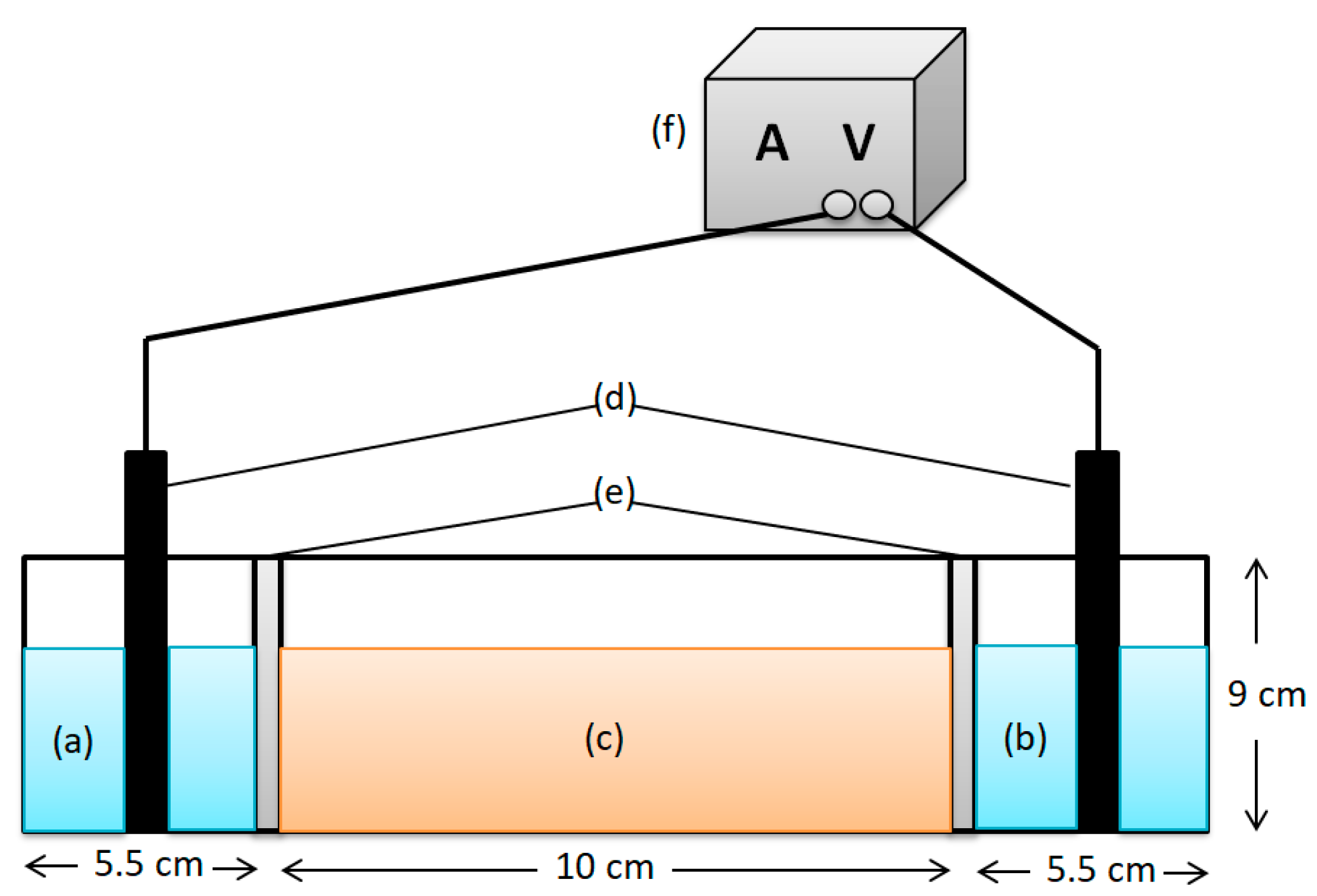
In the present study, the EK experimental setup was constructed of acrylic plates, which were divided into three compartments: a soil chamber (10 cm × 4 cm × 9 cm) and two electrode chambers (5.5 cm × 4 cm × 9 cm) (Figure 1). In this study, six EK experiments were conducted to investigate the effect of the chelating agent and PRB on EK to remove Cd and sulfate from the soil. Table 2 lists the systems used for the transport, in which the anode and cathode chambers were filled with appropriate electrolyte. The electrolyte levels in both chambers were kept equal. Graphite electrodes (10 cm × 3 cm × 1 cm) were used for the anode and cathode. A specific constant voltage gradient of 1 V/cm was generated using the DC power supply (KPS-3005D, Dongguan Bufan Electronics Instrument Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) for 2 days. The real-time current was monitored using an ammeter in a series circuit.
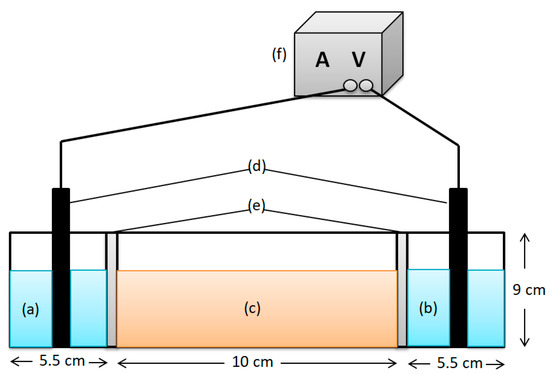
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the EK experimental setup: (a) anode chamber, (b) cathode chamber, (c) soil chamber, (d) graphite electrodes, (e) PRB, (f) DC power.

Table 2.
System of the EK experiment.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil pH and EC after EK Remediation
Figure 2A illustrates the pH and EC in different sections (from anode to cathode) of the soil after EK remediation. The H+ generated by the anode electrolysis decreased the pH of soil near the anode, while the OH− generated by the cathode electrolysis increased the pH of soil near the cathode, so the soil pH showed a gradual increase from the anode to the cathode (S1 to S5) [25]. The initial pH of the simulated contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas was 5.78. In the case of EK-H2O, the area about 6cm from the anode was acidic and the rest of the area was alkaline, predominantly due to the water electrolysis as well as reduction reactions at the anode and cathode [3]. The pH of the soil sample at S5 was 10.74, which was too large to cause the soil environment to be too alkaline, and the study showed that the rate and direction of electro-osmotic flow were affected by the over-acidic and over-alkaline environment [3]. A similar pattern was observed in the case of EK-H2O-PRB. It can be seen from the figure that, after EK remediation, the soil pH of the experimental group with the chelating agent was acidic overall, between 2.45 and 3.55. The main reason for this is that the electric current of the experimental group with the added chelating agent was greater than that of EK-H2O. Therefore, more H+ was electrolyzed, while H+ moved faster than OH− in the soil [8]. Moreover, HEDP is an organic acid and, when added to the soil as an electrolyte, it had a certain effect on soil pH. Thus, the addition of an appropriate chelating agent can alleviate the reactions of water electrolysis and resistive polarization, which can facilitate the desorption and migration of contaminants from the soil. A small increase in soil pH was observed in the PRB addition experimental group compared to that of the PRB-free experimental group, mainly due to the fact that Fe(OH)3 in solution could react spontaneously with dissolved oxygen or H2O, consuming H+ or producing OH− [21]. In general, the result indicated that the existence of PRB did not modify the soil pH.
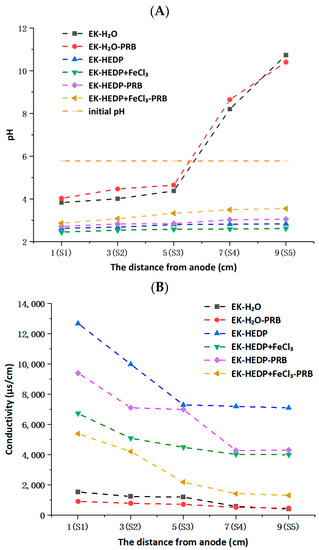
Figure 2.
(A) Soil pH and (B) EC after EK remediation.
The initial EC of the simulated contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas was 96.09 μS/cm. As shown in Figure 2B, inversely to the trend of soil pH, all EK experiments showed an overall decreasing trend in EC from anode to cathode, indicating that the number of mobile ions near the anode was more than that near the cathode, which may be due to the development of an acid front increasing ions’ mobility. The EC of the cathode region was lower due to the precipitation of hydroxide and carbonate under alkaline conditions [26]. Thus, compared with the PRB-free experimental group, a lower EC was expected in the experimental group with added PRB, mainly due to the higher soil pH. In the case of EK-HEDP, HEDP activated Cd and sulfate in the soil and caused desorption, adding a large amount of H+, as well as hydroxyl groups, to the remediation system. HEDP is a degradable chelating agent, which gradually degrades with time, meaning that the activation capacity decreases, and the soil EC decreases [25]. This fact was supported by the EC measurements.
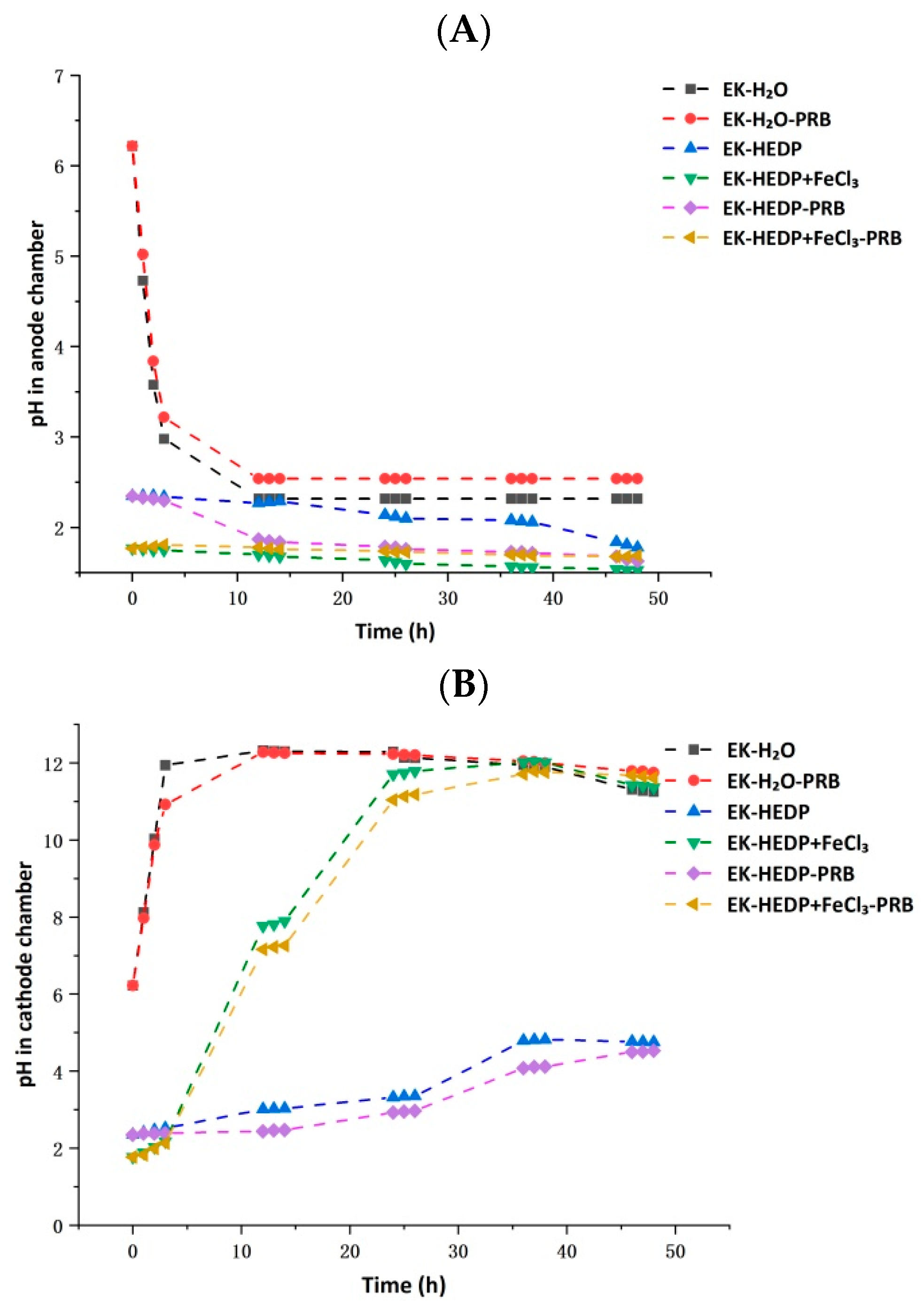
3.2. pH in the Anode and Cathode Chambers during EK Process
The trend of changes in the pH of the anode and cathode chambers is depicted in Figure 3. In the case of EK-H2O and EK-H2O-PRB, after 12 h EK remediation, the pH of the cathode chamber increased from 6.22 to about 12.30, and that of the anode chamber decreased to about 2.40, showing strong acidity and strong alkalinity in the anode and cathode chambers, respectively. In the case of EK-HEDP+FeCl3 and EK-HEDP+FeCl3-PRB, after 24 h EK remediation, the pH of the cathode electrolyte rapidly increased from 1.77 to about 11.00 and then stabilized, while the pH of the anode electrolyte did not much change. Compared to other experiments, in the case of EK-HEDP and EK-HEDP-PRB, the trend of changes in electrolyte pH was smaller. HEDP in the electrolyte behaved as a buffer, which rapidly neutralized the OH− produced in the cathode through the electrolysis reaction [18]. The significant variations in the cathode chamber pH in other experiments were due to the low buffering capacity of the solutions. Variations in pH in these experiments were dependent on the generation of H+ and OH− during the water electrolysis process. H+ and OH− rapidly accumulated in the electrolysis chambers and reached high levels, which entered the soil chamber under the action of the electric field and consumed some of the H+ and OH−. The effect of the subsequently generated H+ and OH− on the pH of the electrolysis chambers started to decrease, so the strong acidity and strong alkalinity remained basically stable after 24 h EK remediation [7].
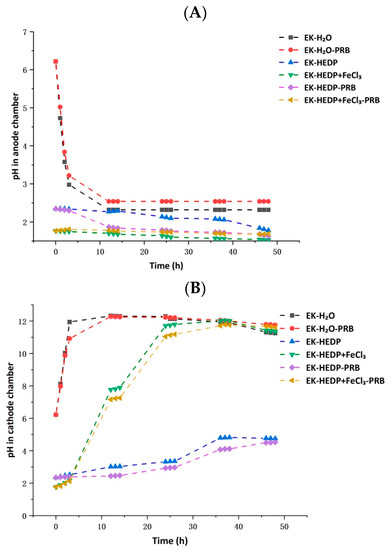
Figure 3.
Changes in pH in the (A) anode chamber, and (B) cathode chamber over time during EK remediation.
3.3. Distribution of Cd in Contaminated Soil after EK Remediation
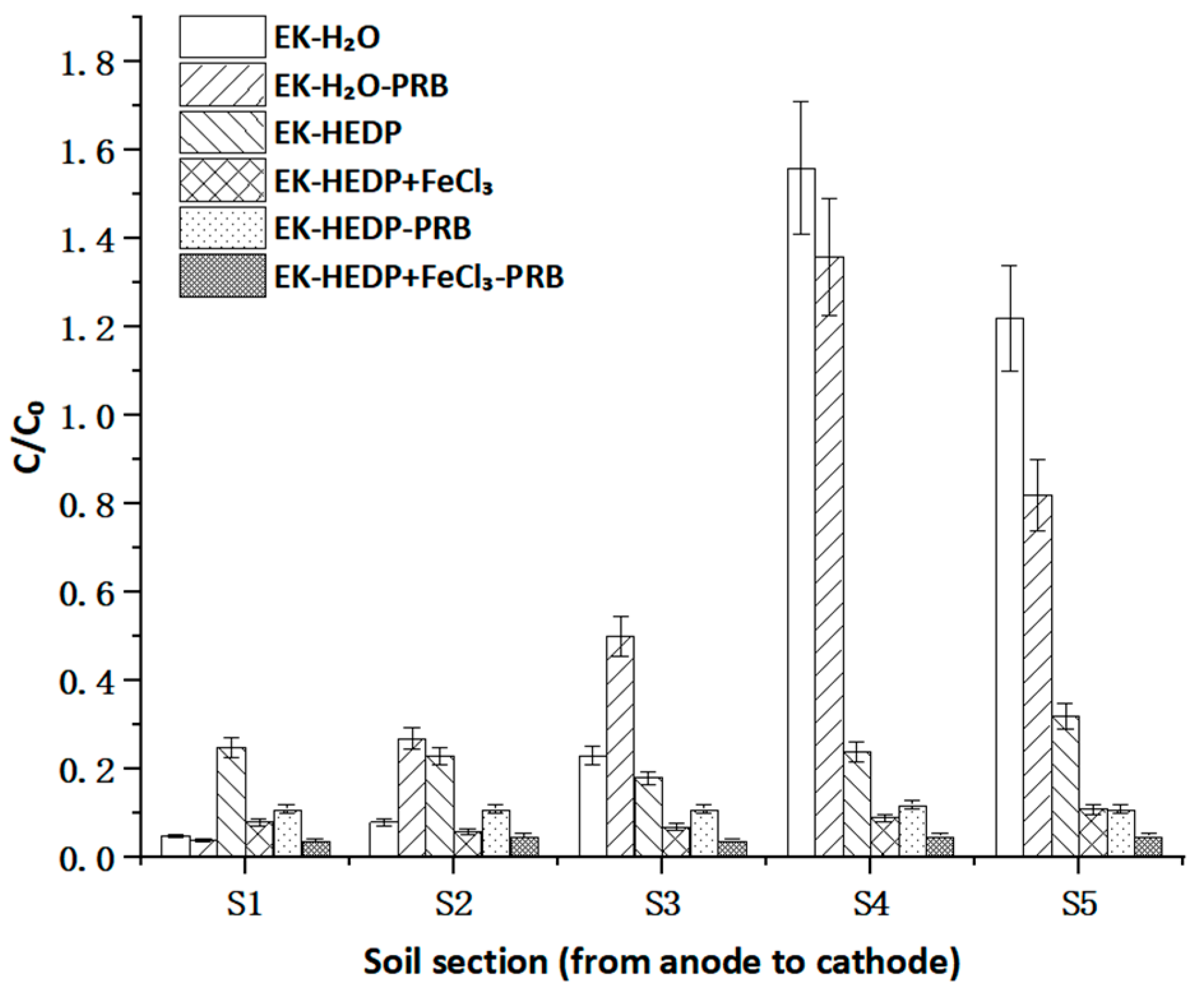
The results of Cd distribution in the five contaminated soil sections after EK remediation are depicted in Figure 4. The removal efficiencies of Cd under EK-H2O, EK-H2O-PRB, EK-HEDP, EK-HEDP+FeCl3, EK-HEDP-PRB, EK-HEDP+FeCl3-PRB were 37.25%, 40.15%, 75.56%, 91.76%, 88.55% and 95.32%, respectively. In the case of EK-H2O and EK-H2O-PRB, the Cd distribution showed an increasing trend, from anode to cathode, and the highest Cd accumulation was found in S4. As the OH− generated by the cathode entered the soil and led to the highest pH in S5, it generated precipitation with Cd and formed focusing phenomena, hindering the migration of subsequent ions [27,28]. The results indicate that the traditional EK technique could only remove some Cd in anode regions, to a considerable extent, with lots of Cd contaminants accumulating in the central and cathode regions, similar to previous research. It is suggested that a single EK technique limited the removal efficiency of Cd and the application of a chelating agent was necessary [29]. The migration of Cd during the EK process was mainly carried out in two ways: the mobilization of positively charged Cd under the electric field and the electro-osmotic flow containing Cd. The direction of this was from the anode to the cathode [30]. Cd could also be removed as soluble Cd and other Cd complexes by EO [29]. HEDP, as an electron-donating cathodic chelating agent, may easily bond with the empty orbitals on Cd surface to form anionic cadmium complexes. They migrated in the opposite direction of Cd migration, resulting in the lowest concentration in the middle. As an environmentally friendly chelating agent, HEDP’s multi-group ligands can form stable and soluble complexes with reactive heavy metal ions over a wide pH range [25]. Therefore, a very low Cd concentration was expected in S3 with the addition of chelating agents. This suggested that HEDP was able to promote the resolution of Cd from soil particles and the formation of soluble complexes, thus enhancing the Cd removal efficiency. It is worth noting that a similar pattern was observed in the case of EK-HEDP+FeCl3, but its removal efficiency for Cd was higher that of the case of EK-HEDP in all soil sections. This suggests that the removal efficiency of the compound chelating agent used as an electrolyte was better than that of single HEDP. A possible reason for this might be that Cl− could form Cd-Cl with Cd2+, which is a stable and soluble complex that could prevent Cd from being adsorbed by soil colloids again [25]. The removal efficiency of Cd in the experimental group with the application of PRB was higher than that in the experimental group without PRB, mainly due to the adsorption and interception of Cd by PRB, which slowed down the polarization phenomenon [20]. Moreover, a combination of EO, EM, and PRB led to a more uniform Cd removal from the soil and, to some extent, resolved the problem of Cd accumulating in S4 and cathode regions by single EK [29]. In general, the EK technique could remove part of Cd, but the removal efficiency of Cd was much less than that of the applications of chelating agents and PRB with EK.
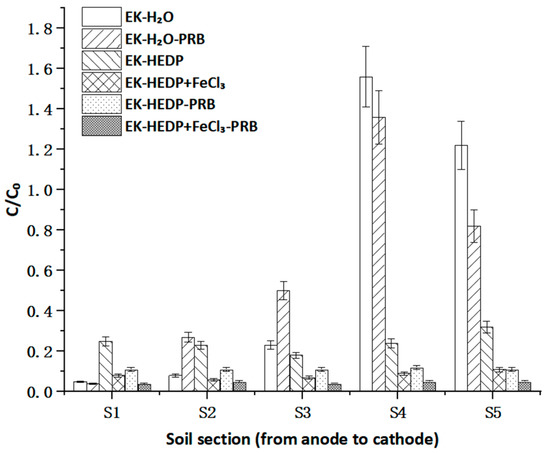
Figure 4.
The distribution of Cd in contaminated soil sections after EK remediation; C0 is the initial concentration of Cd and C is the residual concentration of Cd.
3.4. Distribution of Sulfate in Contaminated Soil after EK Remediation
The results of sulfate distribution in five contaminated soil sections after EK remediation are depicted in Figure 5. The removal efficiencies of sulfate under EK-H2O, EK-H2O-PRB, EK-HEDP, EK-HEDP+FeCl3, EK-HEDP-PRB, EK-HEDP+FeCl3-PRB were 55.87%, 61.22%, 90.80%, 85.20%, 96.19% and 87.31%, respectively. In all the EK experiments, the residual concentration of sulfate gradually increased from cathode to anode and significantly concentrated in S1, indicating that the direction of sulfate migration was from cathode to anode. In the case of EK-H2O with no enhancement during the EK process, the highest sulfate accumulation was observed near the anode section (S1), and the highest amount of sulfate removal (around 94.30%) was found near the cathode section (S5). In contrast, HEDP treatments resulted in obvious changes in the contaminated soil in all the kaolin sections. In the 0.2 M HEDP treatment, the residual rates of sulfate were less than 20% from S1 to S5. Similarly, in the case of EK-HEDP+FeCl3, the residual rates of sulfate also showed a slightly increasing trend from cathode to anode but the sulfate residual rates were higher than that of EK-HEDP. This suggests that the removal efficiency of HEDP and FeCl3 used as an electrolyte was less effective than that of single HEDP, which may be due to the greater role that HEDP plays in removing sulfate in such a system. The colloidal Fe(OH)3 had strong adsorption, and sulfate could agglomerate with the high-valent iron ions on the surface of Fe(OH)3 to form an inner complex, especially in such an acidic environment [20]. Thus, the removal efficiency of sulfate in the experimental group with the application of PRB was higher than that in the experimental group without PRB.

Figure 5.
The distribution of sulfate in contaminated soil sections after EK remediation; C0 is the initial concentration of sulfate and C is the residual concentration of sulfate.
3.5. Electric Current across the Soil Chamber and Accumulated Energy Consumption
The variations in electric current across the soil chamber and accumulated energy consumption during EK process in all experiments are depicted in Figure 6. All experiments exhibited approximately the same trend. The electric current in the system showed a sharp increase, rising from the initial value to the highest value in the initial period of time and then gradually decreasing. In general, the initial and final electric current was obviously low in all EK experiments. The main cause of the ascending electric current in the early days may be due to the gradual dissolution of certain available contaminants and the chelating agent’s migration into the contaminated soil under the electric field during the EK process [26]. The infiltration of the electrolyte solution into the soil pores due to EO and EM led to the mobilization of complex forms of Cd and sulfate, resulting in an increase in electric current [18]. It is worth noting that the chelating agent facilitated the solubility of inorganic contaminants, leading to the growth of the electric current during the EK process. The highest electric current was found in the EK-HEDP system, indicating that the complexation of HEDP with contaminants most significantly contributed to the electric current. The decrease in electric current over time could be attributed to the reduction in the concentration of mobile charged ions in the soil and indicate the migration of toxic and hazardous metals and soil remediation, which is compatible with the results of similar studies [31]. In addition, some mineral ions near the cathode chamber experienced chemical precipitation under alkaline conditions, where the soil resistance increased and the electric current gradually decreased. Moreover, the appearance of concentration polarization and resistance polarization phenomena in the later stages of EK remediation was considered to be another reason for electric current decreasing, causing an increase in resistance [32].

Figure 6.
(A) Changes in the electric current, and (B) accumulated energy consumption over time during EK remediation.
The AEC showed a steady rise over two days in all EK experiments (Figure 6B). The calculated AEC values were as follows: WEK-HEDP = 414.47 kWh/m3 > WEK-HEDP-PRB = 356 kWh/m3 > WEK-HEDP+FeCl3 = 227.27 kWh/m3 > WEK-HEDP+FeCl3-PRB = 182.4 kWh/m3 > WEK-H2O = 15.97 kWh/m3 > WEK-H2O-PRB = 13.37 kWh/m3. The main cause of the ascending AEC in the early stage may be the mobile ions in the soil, which contributed more to the electric current. In the late stage of EK remediation, the AEC slowly increased after the deposition of Cd ions because of the focusing phenomena [9]. A lower AEC was found in the systems in which PRB was installed on either side of the soil sample, indicating that Fe(OH)3-filled PRB reacted with contaminants and formed precipitated forms of complex species, which may be responsible for the noticeable decrease in AEC [33]. Additionally, the use of H2O as an electrolyte in EK, coupled with PRB, led to a decrease in AEC. The compound chelating agent treatment showed a similar AEC variation over time to the HEDP treatment, which has a lower AEC than HEDP treatment. When EK was coupled with chelating agents, HEDP was responsible for the higher AEC, which may be due to its greater role in increasing the EK efficiency in such a system.
4. Conclusions
The experimental results showed that the traditional EK technique could only remove some Cd in anode regions and some sulfate in cathode regions, which limited its removal efficiency and practical applications. The EK/waste Fe(OH)3 PRB system had the highest Cd removal rate (around 95.32%) with the application of compound chelating agent (HEDP and FeCl3). The EK/waste Fe(OH)3 PRB system had the highest sulfate removal rate (around 96.19%) with the application of a single chelating agent, HEDP. Moreover, the combination of a chelating agent and waste Fe(OH)3-permeable reactive barrier using EK led to a more uniform contaminant removal from the soil. Overall, the use of a compound chelating agent mobilized more ions with strong bonds, and waste Fe(OH)3, as a resource reuse material, is more cost-effective for Cd and sulfate adsorption compared to other materials. Therefore, it seems that the application of a compound chelating agent along with PRB containing effective materials during EK remediation can positively influence contaminants’ removal from contaminated soil in sulfide mine areas.
Author Contributions
Y.F.: responsible for the design, experiment, and draft of the manuscript. L.T.: assisted testing; C.L. and Q.L.: supervision. D.L.: organized, supervised, and guided the whole work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Plan Project (2020YFC1808500) and Guangxi University Technology Development Project (GXU-BFY-2020-028).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Vázquez, S.; Arroyo-Torralvo, F.; Vilches, L.F.; Zhang, Z. Remediation of acid mine drainage. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.M.; Van, H.T.; Vinh, N.D.; Hoa Duong, T.M.; Hanh Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ha Tran, T.N.; Hoang, T.K.; Tran, T.P.; Nguyen, L.H.; et al. Enhancement of exchangeable Cd and Pb immobilization in contaminated soil using Mg/Al LDH-zeolite as an effective adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17007–17019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res. 2018, 147, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.A.M.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Mian, M.M.; Ali, M.U.; Ahmed, R.; Cheema, A.I.; Naushad, M. Contrasting effects of biochar and hydrothermally treated coal gangue on leachability, bioavailability, speciation and accumulation of heavy metals by rapeseed in copper mine tailings. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 191, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.A.M.; Irshad, S.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.U.; Dan, C.; Abbas, Q.; Liu, G.; Yang, X. Interactive assessment of lignite and bamboo-biochar for geochemical speciation, modulation and uptake of Cu and other heavy metals in the copper mine tailing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vocciante, M.; Dovì, V.; Ferro, S. Sustainability in ElectroKinetic Remediation Processes: A Critical Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kwon, M.J.; Choi, J.; Baek, K.; O Loughlin, E.J. The transport behavior of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn during electrokinetic remediation of a contaminated soil using electrolyte conditioning. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameselle, C. Enhancement Of Electro-Osmotic Flow During The Electrokinetic Treatment Of A Contaminated Soil. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Cui, C. Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils by electrokinetic technology: Mechanisms and applicability. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Olson, J.R.; Bian, L.; Rogerson, P.A. Analysis of heavy metal sources in soil using kriging interpolation on principal components. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4999–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Niinae, M.; Koga, T.; Akita, T.; Ohta, M.; Choso, T. EDDS-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated clay soils under neutral pH conditions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 440, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ammami, M.; Benamar, A.; Mezazigh, S.; Wang, H. Effect of EDTA, EDDS, NTA and citric acid on electrokinetic remediation of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn contaminated dredged marine sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10577–10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Guo, N.; Yu, H. Development of novel assisting agents for the electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated kaolin. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Kim, D.H.; Yoo, J.C.; Baek, K. Electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from dredged marine sediment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tian, G. Using electrode electrolytes to enhance electrokinetic removal of heavy metals from electroplating sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, P.; Zhao, J.; Dong, C. Remediation of cadmium- and lead-contaminated agricultural soil by composite washing with chlorides and citric acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5563–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, C.; Hu, P. Remediation of Cadmium and Lead Contaminated Farmland Soil by Washing with Combined Organic Acids and FeCl3. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Lv, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Removal of cadmium in contaminated kaolin by new-style electrokinetic remediation using array electrodes coupled with permeable reactive barrier. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Huang, C.; Wan, J. Remediation of contaminated soils by enhanced nanoscale zero valent iron. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Letterman, R.D. Modeling cadmium and sulfate adsorption by Fe(OH)/SiO2 mixed oxides. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Reich, T.; Kersten, M.; Jing, C. Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Acid Complexation Affects Antimony(III) Adsorption by Granular Ferric Hydroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5221–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Kang, C.; Mohan, D.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.S.; Jeon, B. Waste sludge derived adsorbents for arsenate removal from water. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.M.; Deng, C.F.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Cang, L.; Deng, C.F. Effects of catholyte conditioning on electrokinetic extraction of copper from mine tailings. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, S.; Selvaraj, S.; Selvaraj, H.; Santhanam, M.; Pazos, M. Electrokinetic remediation: Challenging and optimization of electrolyte for sulfate removal in textile effluent-contaminated farming soil. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81052–81058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, S.; Xu, W.; Shen, K.; Long, Z. Leaching Behaviour and Enhanced Phytoextraction of Additives for Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Pennisetum sp. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2020, 104, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cang, L.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, D.; Duan, T.; Wang, R. EDTA-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of aged electroplating contaminated soil assisted by combining dual cation-exchange membranes and circulation methods. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. Exchange electrode-electrokinetic remediation of Cr-contaminated soil using solar energy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameselle, C.; Gouveia, S. Electrokinetic remediation for the removal of organic contaminants in soils. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 79, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, S.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, T. An electrokinetic/activated alumina permeable reactive barrier-system for the treatment of fluorine-contaminated soil. Clean Technol. Environ. 2016, 18, 2691–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, B.; Guo, P.; Wang, S.; Guo, S. Enhanced electrokinetic remediation and simulation of cadmium-contaminated soil by superimposed electric field. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Butt, M.K. Pb2+ ions mobility perturbation by iron particles during electrokinetic remediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, A.K.; Yang, C.; Malkhandi, S.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Narayanan, S.R. Enhancing the Performance of the Rechargeable Iron Electrode in Alkaline Batteries with Bismuth Oxide and Iron Sulfide Additives. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A2078–A2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A.; Khodadadi Darban, A. Application of enhanced electrokinetic approach to remediate Cr-contaminated soil: Effect of chelating agents and permeable reactive barrier. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).