A GIS-Based Analysis of the Carbon-Oxygen Balance of Urban Forests in the Southern Mountainous Area of Jinan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
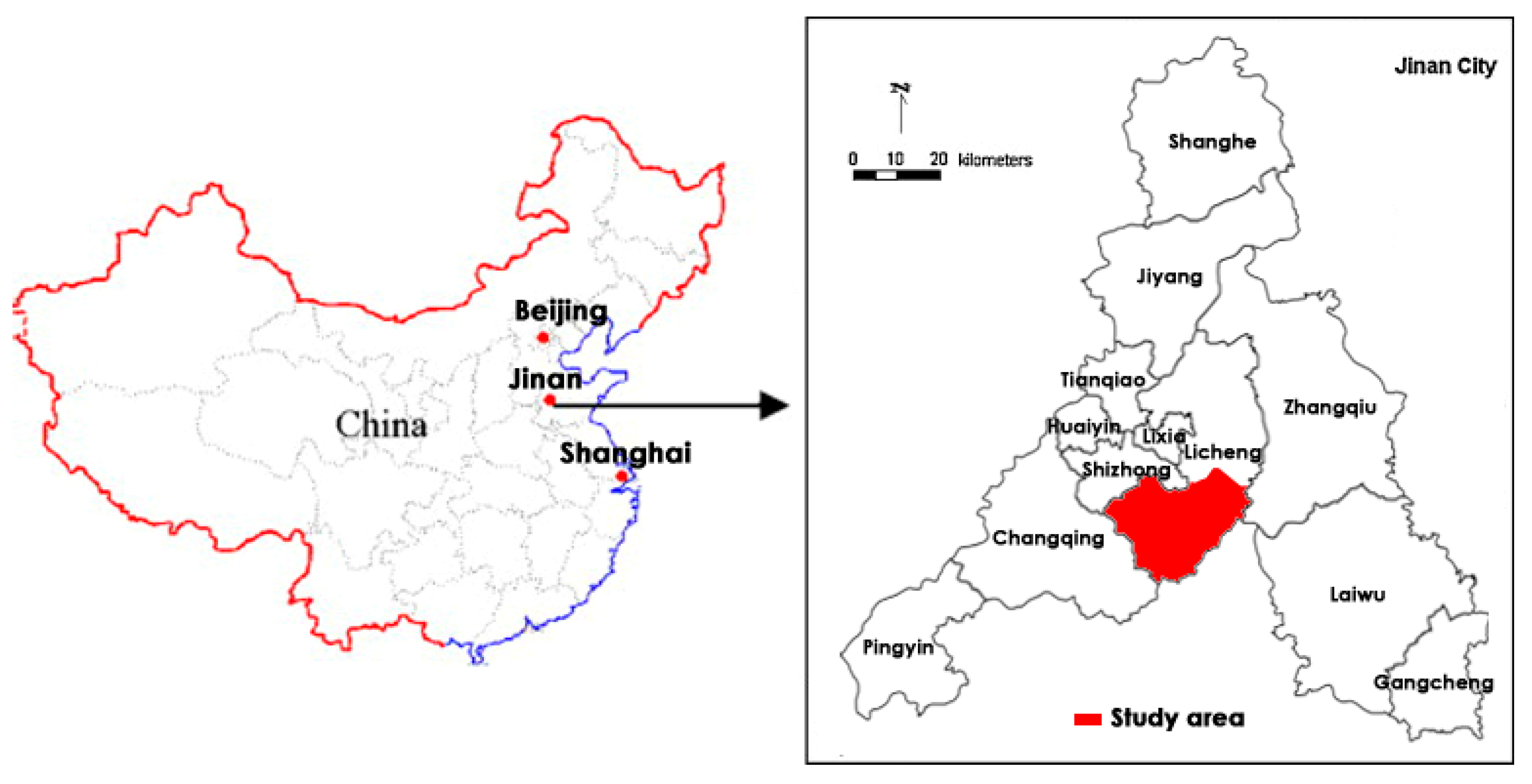
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Image Pre-Processing and Remote Sensing Interpretation
2.4. Carbon-Oxygen Balance Method of Urban Forests
2.4.1. Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release Method
- (1)
- Carbon sequestration model
- (2)
- Oxygen release model
2.4.2. Carbon Release and Oxygen Consumption Model
- (1)
- Carbon release model
- (2)
- Oxygen consumption model
2.4.3. Carbon Release and Oxygen Consumption Model
3. Results
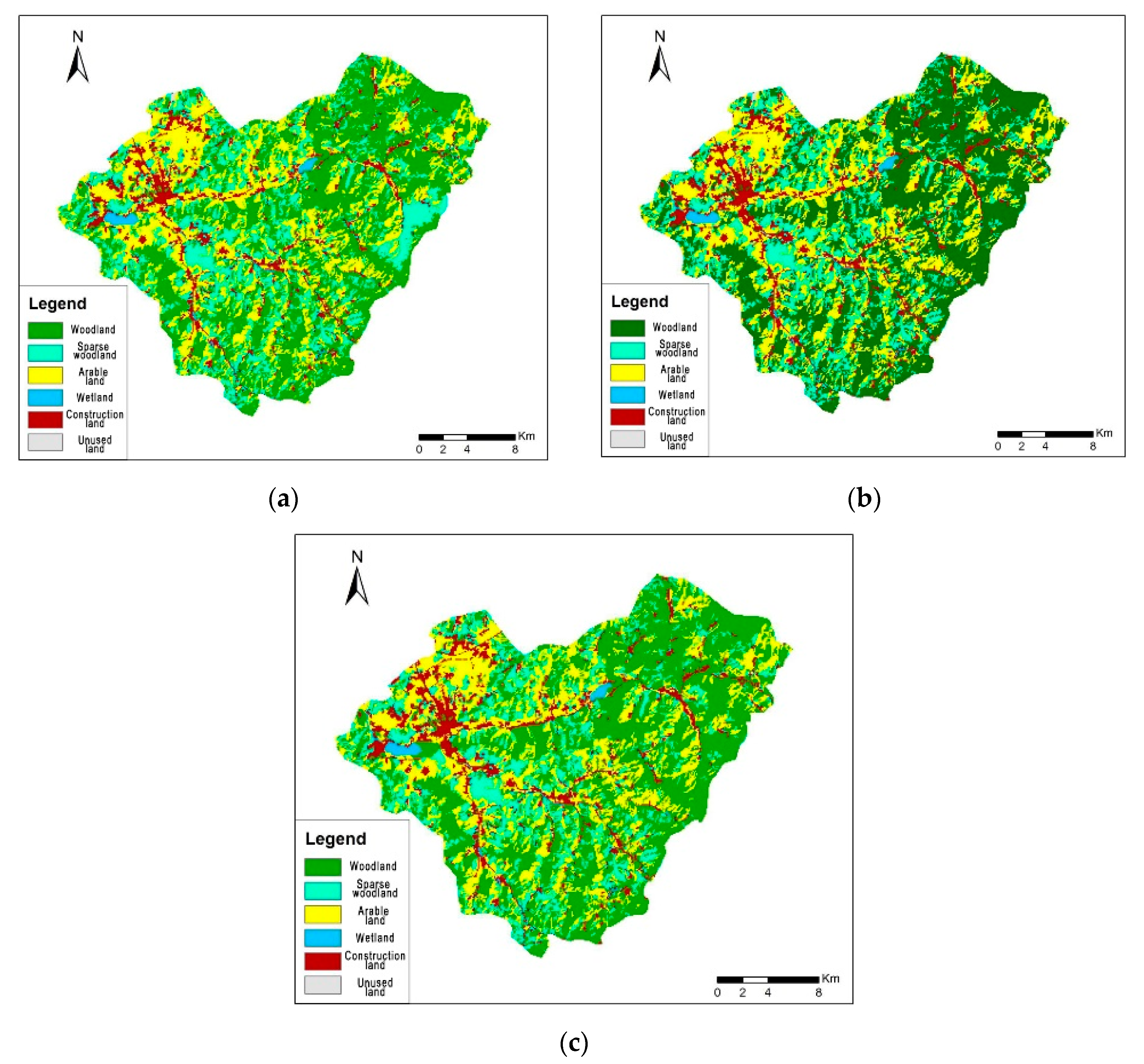
3.1. Urban Forest Land-Use Change
3.2. Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release of Urban Forests
3.3. Carbon Release and Oxygen Consumption
3.4. Carbon-Oxygen Balance Capacity of Urban Forests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Gu, P.; Feng, H.; Yin, Y.; Chen, W.; Cheng, B. Changes in precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River Basin during 1960–2019 and the association with global warming, ENSO, and local effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Reichstein, M.; Bahn, M.; Thonicke, K.; Frank, D.; Mahecha, M.D.; Smith, P.; Van der Velde, M.; Vicca, S.; Babst, F. Effects of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle: Concepts, processes and potential future impacts. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2861–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoro, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. CO2 emission sources, greenhouse gases, and the global warming effect. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sundara Rajoo, K.; Karam, D.S.; Abdu, A.; Rosli, Z.; James Gerusu, G. Urban Forest Research in Malaysia: A Systematic Review. Forests 2021, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, A.; Ahirwal, J.; Sahoo, U.K. Evaluation of ecosystem carbon storage in major forest types of Eastern Himalaya: Implications for carbon sink management. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, M.D.; Usman, M.; Khan, S.; Shehzad, F.; Galadima, A.; Ehsan, M.F.; Ghanem, A.S.; Humayun, M. CO2 towards fuels: A review of catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to hydrocarbons. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, C.M.; Wang, C.; Wetterlund, E. Exploring the role of forest biomass in abating fossil CO2 emissions in the iron and steel industry–The case of Sweden. Appl. Energy 2021, 288, 116558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiara, T.; García-Labiano, F.; Abad, A.; Gayán, P.; de Diego, L.; Izquierdo, M.; Adánez, J. Negative CO2 emissions through the use of biofuels in chemical looping technology: A review. Appl. Energy 2018, 232, 657–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y. Seasonal Photosynthesis and Carbon Assimilation of Dynamics in a Zelkova serrata (Thunb.) Makino Plantation. Forests 2021, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Carbon cycling and storage in mangrove forests. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Mughal, N.; Zhao, J.; Shabbir, M.S.; Niedbała, G.; Jain, V.; Anwar, A. Does globalization matter for environmental degradation? Nexus among energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy Policy 2021, 153, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchard, E.T.; Feldpausch, T.R.; Brienen, R.J.; Lopez-Gonzalez, G.; Monteagudo, A.; Baker, T.R.; Lewis, S.L.; Lloyd, J.; Quesada, C.A.; Gloor, M. Markedly divergent estimates of Amazon forest carbon density from ground plots and satellites. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Ducey, M.J.; Heath, L.S. Assessing net carbon sequestration on urban and community forests of northern New England, USA. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, K.F.; Haight, R.G.; Jung, S.; Locke, D.H.; O′Neil-Dunne, J. The marginal cost of carbon abatement from planting street trees in New York City. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.N. Analysis of carbon sequestration and oxygen release capabilities of 25 afforestation plants in Tianjin. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 641, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.; Roldan, C.; Ghosh, S.; Yung, S.-H. Greening rail infrastructure for carbon benefits. Procedia Eng. 2017, 180, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Cui, G.; Zheng, H.; Guan, C.; Chen, F. Integrative analysis of carbon structure and carbon sink function for major crop production in China’s typical agriculture regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P. Carbon sequestration potential of forest vegetation in China from 2003 to 2050: Predicting forest vegetation growth based on climate and the environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chuai, X. Carbon sinks/sources’ spatiotemporal evolution in China and its response to built-up land expansion. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dinda, S.; Chatterjee, N.D.; Dutta, S.; Bera, D. Spatial-explicit carbon emission-sequestration balance estimation and evaluation of emission susceptible zones in an Eastern Himalayan city using Pressure-Sensitivity-Resilience framework: An approach towards achieving low carbon cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Cui, S.; Hua, L.; Lin, T. A new carbon and oxygen balance model based on ecological service of urban vegetation. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Kong, Z.-h.; Escobedo, F.J.; Gao, J. Impacts of urban forests on offsetting carbon emissions from industrial energy use in Hangzhou, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, D.H.; Yang, P.P.; Li, K.K.; Qin, B.L.; Kong, Y.F. Research on Ecological Compensation of Urban Green Space: A Case Study on Jinan City. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 295, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shi, T.; Ma, F. Green space ecological planning based on carbon-oxygen balance in Shenyang, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 283, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T.; Podest, E.; Schroeder, R.; Pinto, N.; McDonald, K.; Glagolev, M.; Filippov, I.; Maksyutov, S.; Heimann, M.; Chen, X. Modeling the large-scale effects of surface moisture heterogeneity on wetland carbon fluxes in the West Siberian Lowland. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 6559–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J. The impact of terrestrial ecosystems on carbon assimilation and oxygen production in the Guanzhong-Tianshui economic region of China. Biol. Environ. Proc. R. Ir. Acad. 2015, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahtahmassebi, A.R.; Li, C.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Gan, M.; Wang, K.; Malik, A.; Blackburn, G.A. Remote sensing of urban green spaces: A review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 57, 126946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trlica, A.; Hutyra, L.R.; Morreale, L.L.; Smith, I.A.; Reinmann, A.B. Current and future biomass carbon uptake in Boston’s urban forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Statistics Press. Jinan Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jinan City Planning Bureau. “Multiple in One Planning” for the Southern Mountain Area of Jinan City (2017–2035); Jinan City Planning Bureau: Jinan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook; LSDS-1574; Department of the Interior US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yin, K.; Lin, T. Analysis of the carbon and oxygen balance of a complex urban ecosystem: A case study in the coastal city of Xiamen. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 1808–1816. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, M.; Song, W.; Yang, J. Impacts of the terrestrial ecosystem changes on the carbon fixation and oxygen release services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 8482–8493. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Lu, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, C. Evaluation of carbon and oxygen balances in urban ecosystems using land use/land cover and statistical data. Sustainability 2015, 7, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, X.; Bai, B. An accounting of CO2 emission in chinese cities and spatial pattern analysis. Urban Environ. Stud. 2020, 1, 67–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, Y.; Chen, Y. Scenario model study of land use structure optimization in Wuhan under carbon-oxygen balance constraints. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 2030–2037. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zeng, C.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M. An assessment of forest biomass carbon storage and ecological compensation based on surface area: A case study of Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zheng, H.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; Shen, G.; Zhai, C. Changes in spatio-temporal patterns of urban forest and its above-ground carbon storage: Implication for urban CO2 emissions mitigation under China’s rapid urban expansion and greening. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X. Carbon storage and sequestration by urban forests in Shenyang, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fridley, D.; Lu, H.; Price, L.; Zhou, N. Has coal use peaked in China: Near-term trends in China’s coal consumption. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperon-Rodriguez, M.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Lenoir, J.; Baumgartner, J.B.; Beaumont, L.J.; Nipperess, D.A.; Power, S.A.; Richard, B.; Rymer, P.D.; Gallagher, R.V. Climate change increases global risk to urban forests. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lin, J.; Shi, X.-D.; Jiang, K.-J.; Zhao, G.-L. Coordinated reduction of CO2 emissions and environmental impacts with integrated city-level LEAP and LCA method: A case study of Jinan, China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Research Direction | Author (s) | Study Area | Date | Method | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon sequestration amount of different forest plant species and land-use types | Zheng et al. [13] | New England, USA | 2013 | Net forest carbon sequestration methodology | Urban forests’ carbon sequestration amount |
| Kovacs et al. [14] | New York, USA | 2013 | National tree benefit calculator model | Three types of trees’ carbon sequestration amount | |
| Wang et al. [15] | Tianjin, China | 2014 | Portable photosynthesis test system | CSOR capacity of 25 afforestation trees | |
| Blair et al. [16] | Sydney, Australian | 2017 | I-Tree Eco tool | Carbon sink amount of street trees | |
| She et al. [17] | China | 2017 | Carbon footprint method | Crops’ carbon sink capacity | |
| Qiu et al. [18] | China | 2020 | National forest inventory | Carbon sink of economic, shrubbery and bamboo forests | |
| Ye and Chuai [19] | China | 2022 | net ecosystem productivity models | Carbon sink effects of built-up land expansion | |
| Ghosh et al. [20] | Gangtok, Sikkim | 2022 | Integrated valuation of ecosystem services and trade-offs method | Carbon sequestration capacity of urban land-use land-cover | |
| Carbon-oxygen balance analyzes of urban forests | Yin et al. [21] | Xiamen, China | 2010 | Urban carbon-oxygen balance model | Urban CROC measuring |
| Zhao et al. [22] | Hangzhou, China | 2010 | Volume-derived biomass equations | Carbon balance between urban forests and industrial energy | |
| Lu et al. [23] | Jinan, China | 2006 | Green equivalent method | Green space’s carbon-oxygen balance pattern | |
| Tang et al. [24] | Shenyang, China | 2019 | Carbon-oxygen balance method | Urban carbon-oxygen balance assessment |
| Types of Urban Forest Land Use | Carbon Sequestration or Oxygen Release | Parameter Value (t/(yr·km2)) |
|---|---|---|
| Woodland | Carbon sequestration () | 903 |
| Sparse woodland | 493 | |
| Arable land | 686 | |
| Wetland | 450 | |
| Woodland | Oxygen release () | 665 |
| Sparse woodland | 363 | |
| Arable land | 505 | |
| Wetland | 331 |
| Project | Convert Standard Coal Coefficient (t/t) | Converted Carbon Release Coefficient (t/t) () | Converted Oxygen Consumption Coefficient (t/t) () |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 0.7143 | 2.492 | 2.13 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 1.988 | 3.428 |
| Diesel | 1.4571 | 2.167 | 3.428 |
| Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 2.219 | 3.428 |
| Liquefied petroleum gas | 1.7143 | 1.828 | 3.636 |
| Land-Use Types | 2000 | 2010 | 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Area (km2) | Proportion | Land Area (km2) | Proportion | Land Area (km2) | Proportion | |
| Woodland | 252.12 | 44.12% | 266.41 | 46.62% | 272.04 | 47.61% |
| Sparse woodland | 124.96 | 21.87% | 111.2 | 19.46% | 106.35 | 18.61% |
| Arable land | 175.55 | 30.72% | 169.98 | 29.75% | 167.79 | 29.37% |
| Wetland | 4.87 | 0.85% | 4.97 | 0.87% | 4.91 | 0.86% |
| Total | 557.5 | 97.57% | 552.55 | 96.7% | 551.09 | 96.45% |
| Land-Use Types | CSOR * in 2000 | CSOR in 2010 | CSOR in 2019 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Sequestration (104t) | Oxygen Release (104t) | Carbon Sequestration (104t) | Oxygen Release (104t) | Carbon Sequestration (104t) | Oxygen Release (104t) | |
| Woodland | 22.77 | 16.77 | 24.06 | 17.72 | 24.57 | 18.09 |
| Sparse woodland | 6.16 | 4.54 | 5.48 | 4.04 | 5.24 | 3.86 |
| Arable land | 12.04 | 8.87 | 11.66 | 8.58 | 11.51 | 8.47 |
| Wetland | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| Total | 41.19 | 30.34 | 41.42 | 30.50 | 41.54 | 30.58 |
| Project | Year | Jinan’s Consumption (104t) | Consumption (104t) | Converted Consumption (104t) | CROC * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Release (104t) | Percentage | Oxygen Consumption (104t) | Percentage | |||||
| Coal | 2000 | 361.11 | 20.15 | 14.39 | 35.87 | 72.06% | 30.66 | 57.39% |
| 2010 | 1091.22 | 60.89 | 43.49 | 108.38 | 73.42% | 92.63 | 59.19% | |
| 2019 | 1237.10 | 69.03 | 49.31 | 122.87 | 72.32% | 105.02 | 58.21% | |
| Gasoline | 2000 | 16.31 | 0.91 | 1.32 | 2.63 | 5.28% | 4.53 | 8.48% |
| 2010 | 48.39 | 2.70 | 3.93 | 7.81 | 5.29% | 13.47 | 8.61% | |
| 2019 | 41.58 | 2.32 | 3.38 | 6.72 | 3.95% | 11.58 | 6.42% | |
| Diesel | 2000 | 38.53 | 2.15 | 3.13 | 6.79 | 13.64% | 10.74 | 20.10% |
| 2010 | 86.38 | 4.82 | 7.02 | 15.21 | 10.31% | 24.07 | 15.38% | |
| 2019 | 75.99 | 4.24 | 6.18 | 13.38 | 7.88% | 21.17 | 11.73% | |
| Fuel oil | 2000 | 18.46 | 1.03 | 1.47 | 3.26 | 6.54% | 5.03 | 9.42% |
| 2010 | 75.27 | 4.20 | 6.00 | 13.31 | 9.01% | 20.56 | 13.14% | |
| 2019 | 138.89 | 7.75 | 11.08 | 24.58 | 14.47% | 37.96 | 21.04% | |
| Liquefied petroleum gas | 2000 | 7.17 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 1.24 | 2.49% | 2.47 | 4.62% |
| 2010 | 16.67 | 0.93 | 1.59 | 2.90 | 1.97% | 5.78 | 3.69% | |
| 2019 | 13.44 | 0.75 | 1.29 | 2.35 | 1.38% | 4.67 | 2.59% | |
| Total | 2000 | 441.40 | 24.63 | 20.99 | 49.78 | 100.00% | 53.42 | 100.00% |
| 2010 | 1317.56 | 73.52 | 62.03 | 147.61 | 100.00% | 156.51 | 100.00% | |
| 2019 | 1506.99 | 84.09 | 71.22 | 169.89 | 100.00% | 180.41 | 100.00% | |
| Year | Carbon Balance Coefficient | Oxygen Balance Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 1.21 | 1.76 |
| 2010 | 3.56 | 5.13 |
| 2019 | 4.09 | 5.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Mu, H.; Gao, Y.; Lu, M.; Liu, C. A GIS-Based Analysis of the Carbon-Oxygen Balance of Urban Forests in the Southern Mountainous Area of Jinan, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16135. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316135
Li D, Mu H, Gao Y, Lu M, Liu C. A GIS-Based Analysis of the Carbon-Oxygen Balance of Urban Forests in the Southern Mountainous Area of Jinan, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(23):16135. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316135
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Donghe, Huigang Mu, Yelin Gao, Min Lu, and Chunlu Liu. 2022. "A GIS-Based Analysis of the Carbon-Oxygen Balance of Urban Forests in the Southern Mountainous Area of Jinan, China" Sustainability 14, no. 23: 16135. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316135
APA StyleLi, D., Mu, H., Gao, Y., Lu, M., & Liu, C. (2022). A GIS-Based Analysis of the Carbon-Oxygen Balance of Urban Forests in the Southern Mountainous Area of Jinan, China. Sustainability, 14(23), 16135. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142316135







