Facile Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 Derived from Iron-Rich Sludge as Magnetic Catalyst for the Degradation of Organic Contaminants by Peroxymonosulfate Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Catalysts
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Experimental Procedures
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raw Iron-Rich Sludge and Fe3O4@SiO2
3.2. Evaluation of CIP Removal by Raw Iron-Rich Sludge
3.2.1. Adsorption Capacity of Iron-Rich Sludge
3.2.2. Persulfate Activation by Iron-Rich Sludge
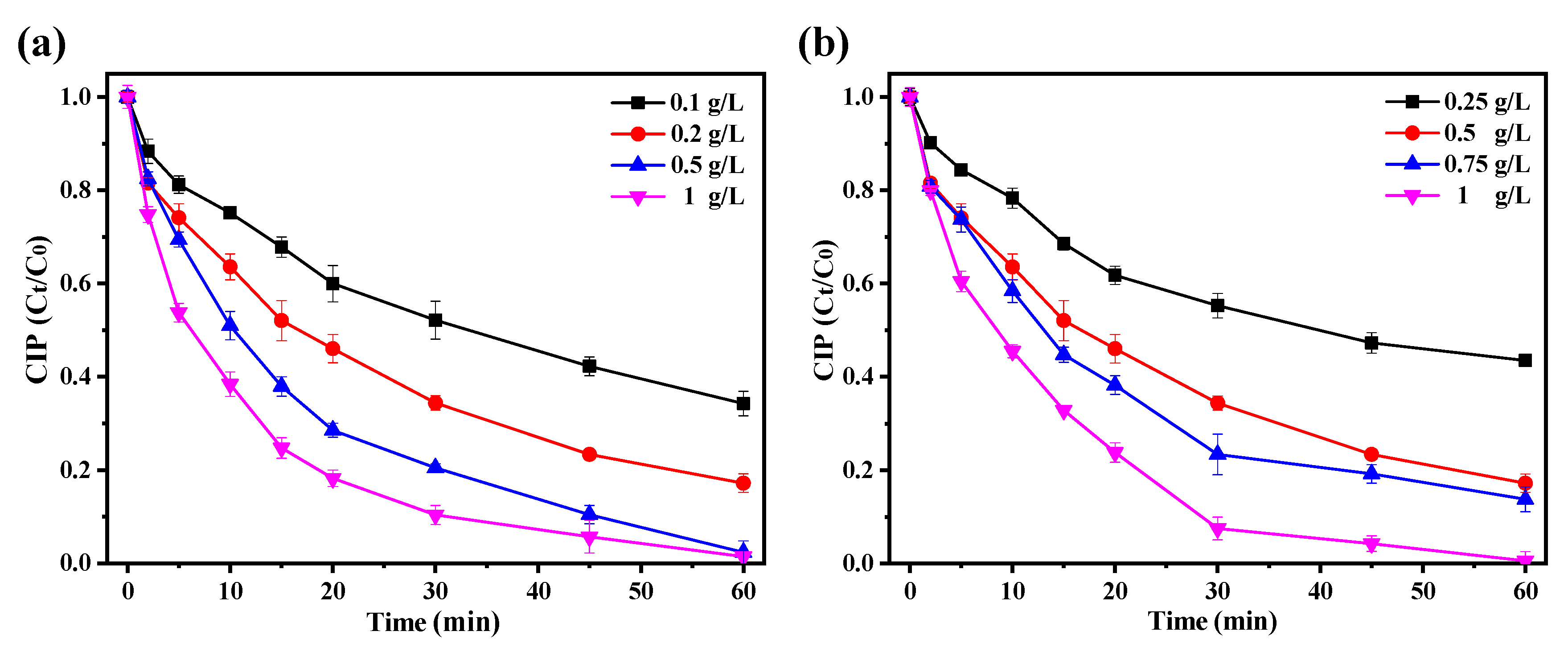
3.3. Catalytic Performance of Fe3O4@SiO2
3.4. Effects of Initial pH and Temperature
3.5. ROS in Fe3O4@SiO2-PMS System
3.6. Possible Activation Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; He, J.; Xin, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Enhanced bioproduction of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge by potassium ferrate pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, A.; Wang, H. Study on the feasibility and stability of drinking water treatment sludge (DWTS)@zeolite to remove phosphorus from constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, F. Synthesis of hydrotalcite-like compounds with drinking water treatment residuals for phosphorus recovery from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 301, 126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gong, M.; Wang, M.; Feng, A.; Wang, L.; Ma, P.; Yuan, S. Influence of AlCl3 and oxidant catalysts on hydrogen production from the supercritical water gasification of dewatered sewage sludge and model compounds. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 31262–31274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhuge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pham, P.N.; Zhang, C.; Duan, W.; Ma, X. Reuse of drinking water treatment sludge in mortar as substitutions of both fly ash and sand based on two treatment methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.W.; Hwang, M.J.; Park, D.S.; Ahn, K.H. Comprehensive reuse of drinking water treatment residuals in coagulation and adsorption processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Silvetti, M.; Garau, G.; Demurtas, D.; Deiana, S. Copper(II) and lead(II) removal from aqueous solution by water treatment residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Cai, M.; Zhang, J. Preparation of a new low-cost substrate prepared from drinking water treatment sludge (DWTS)/bentonite/zeolite/fly ash for rapid phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.; Smith, A.D.; Judd, S.J.; Jarvis, P. Acidified and ultrafiltered recovered coagulants from water treatment works sludge for removal of phosphorus from wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 88, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuster, A.C.; Huser, B.J.; Thongdamrongtham, S.; Padungthon, S.; Junggoth, R.; Kuster, A.T. Drinking water treatment residual as a ballast to sink Microcystis cyanobacteria and inactivate phosphorus in tropical lake water. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, G.; Ma, J. Peroxymonosulfate activation by hydroxylamine-drinking water treatment residuals for the degradation of atrazine. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Shen, C.H.; Guo, J.; Guo, H.; Yin, Y.F.; Xu, X.J.; Fei, Z.H.; Liu, Z.T.; Wen, X.J. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co3O4/Bi2WO6 p-n heterojunction composites for the degradation of ciprofloxacin under visible light irradiation. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 588, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. FeCo bimetallic metal organic framework nanosheets as peroxymonosulfate activator for selective oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 1385–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ye, C.; Cai, A.; Huai, L.; Zhou, S.; Dong, F.; Li, X.; Ma, X. S-doping α-Fe2O3 induced efficient electron-hole separation for enhanced persulfate activation toward carbamazepine oxidation: Experimental and DFT study. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, X.; Guo, X.; Jia, C.; Li, B.; Zhao, E.; Wu, J. Efficient degradation of imidacloprid in soil by thermally activated persulfate process: Performance, kinetics, and mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gong, H.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Meng, L.; Gan, L. Mechanistic study on the combination of ultrasound and peroxymonosulfate for the decomposition of endocrine disrupting compounds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Rodríguez, E.; Moreno-Andrés, J.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Effect of the water matrix and reactor configuration on Enterococcus sp. inactivation by UV-A activated PMS or H2O2. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhu, H.; Deng, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Deng, L. New insight into peroxymonosulfate activation by CoAl-LDH derived CoOOH: Oxygen vacancies rather than Co species redox pairs induced process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ok, Y.S.; An, T. Persistent free radicals in carbon-based materials on transformation of refractory organic contaminants (ROCs) in water: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 137, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Lin, J.; Lu, J.; Song, W.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z. Selective degradation of parachlorophenol using Fe/Fe3O4@CPPy nanocomposites via the dual nonradical/radical peroxymonosulfate activation mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Roles of the mineral constituents in sludge derived biochar in persulfate activation for phenol degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Ren, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Kong, M.; Zheng, S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Monodispersed CuFe2O4 nanoparticles anchored on natural kaolinite as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for bisphenol A degradation. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 253, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Stuckman, M.; Howard, B.H.; Bank, T.L.; Roth, E.A.; Macala, M.K.; Lopano, C.; Soong, Y.; Granite, E.J. Application of sequential extraction and hydrothermal treatment for characterization and enrichment of rare earth elements from coal fly ash. Fuel 2018, 232, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Lin, K.; Gan, J. Enhanced ozonation of ciprofloxacin in the presence of bromide: Kinetics, products, pathways, and toxicity. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, A.; Banerjee, A.M.; Pai, M.R.; Meena, S.S.; Pai, R.V.; Tewari, R.; Yusuf, S.M.; Tripathi, A.K.; Bharadwaj, S.R. Nanostructured Fe2O3 dispersed on SiO2 as catalyst for high temperature sulfuric acid decomposition—Structural and morphological modifications on catalytic use and relevance of Fe2O3-SiO2 interactions. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 217, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Gao, J.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D. Activation of persulfate by quinones: Free radical reactions and implication for the degradation of PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4605–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Crittenden, J.C.; Zhou, S.; Gao, N.; Li, J. Mesoporous manganese Cobaltite nanocages as effective and reusable heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activators for Carbamazepine degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, G.; He, M.; Ouyang, W. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by magnetic catalysts derived from drinking water treatment residuals for the degradation of atrazine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Ye, C.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Luo, H.; Li, X. Magnetic Co/Fe nanocomposites derived from ferric sludge as an efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Bo, S.; Qin, Y.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S. Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, C.; Mao, Q.; Wang, C.; Yan, J. Nonradicals induced degradation of organic pollutants by peroxydisulfate (PDS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Recent advances and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Comparison of sulfate and hydroxyl radical based advanced oxidation of phenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 224, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Niu, H.Y.; Niu, C.G.; Guo, H.; Liang, S.; Yang, Y.Y. Metal-organic framework-derived CuCo/carbon as an efficient magnetic heterogeneous catalyst for persulfate activation and ciprofloxacin degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, M.; Ye, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M. Metal-based catalysts for persulfate and peroxymonosulfate activation in heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Removal of high concentration p-nitrophenol in aqueous solution by zero valent iron with ultrasonic irradiation (US-ZVI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadaei, S.; Noorisepehr, M.; Pourzamani, H.; Salari, M.; Moradnia, M.; Darvishmotevalli, M.; Mengelizadeh, N. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for degradation of Reactive Black 5: Batch and column study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, F.; Liu, X.; Lian, C.; Wang, S. Magnetic core-shell CuFe2O4@C3N4 hybrids for visible light photocatalysis of Orange II. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.-L.; Wu, K.; Xu, D.-A.; Chao, C.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.-D. A modified Arrhenius equation to predict the reaction rate constant of Anyuan pulverized-coal pyrolysis at different heating rates. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 148, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, R.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Z. Chemical kinetic analysis of the activation energy of diffusion coefficient of sulfate ion in concrete. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 753, 137596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Bian, R.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S. Natural diatomite mediated spherically monodispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for efficient catalytic oxidation of bisphenol A through activating peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Ding, W.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Y. The overlooked role of Co(OH)2 in Co3O4 activated PMS system: Suppression of Co2+ leaching and enhanced degradation performance of antibiotics with rGO. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Ni, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Q.; Xue, B.; Chang, C.-C.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y. MOF Derived Co-Fe nitrogen doped graphite carbon@crosslinked magnetic chitosan Micro-nanoreactor for environmental applications: Synergy enhancement effect of adsorption-PMS activation. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 319, 121926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qin, Y.; Yao, C.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S. Preparation of cobalt/hydrochar using the intrinsic features of rice hulls for dynamic carbamazepine degradation via efficient PMS activation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Lin, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Cui, F. Effect of cations on the enhanced adsorption of cationic dye in Fe3O4-loaded biochar and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Chen, R.; Liu, H. Novel urchin-like Co5Mn-LDH hierarchical nanoarrays: Formation mechanism and its performance in PMS activation and norfloxacin degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Catalysts | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron-rich sludge | 21.486 | 0.059 | 133.655 |
| Fe3O4@SiO2 | 50.352 | 0.103 | 57.563 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, X. Facile Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 Derived from Iron-Rich Sludge as Magnetic Catalyst for the Degradation of Organic Contaminants by Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16419. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416419
Wang Z, Zhu S, Deng J, Li H, Wang L, Luo H, Tang Z, Li X. Facile Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 Derived from Iron-Rich Sludge as Magnetic Catalyst for the Degradation of Organic Contaminants by Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(24):16419. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416419
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiwei, Shijun Zhu, Jing Deng, Haojie Li, Liang Wang, Haojin Luo, Zehe Tang, and Xueyan Li. 2022. "Facile Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 Derived from Iron-Rich Sludge as Magnetic Catalyst for the Degradation of Organic Contaminants by Peroxymonosulfate Activation" Sustainability 14, no. 24: 16419. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416419
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhu, S., Deng, J., Li, H., Wang, L., Luo, H., Tang, Z., & Li, X. (2022). Facile Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2 Derived from Iron-Rich Sludge as Magnetic Catalyst for the Degradation of Organic Contaminants by Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Sustainability, 14(24), 16419. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416419






