Assessment of Different Envelope Configurations via Optimization Analysis and Thermal Performance Indicators: A Case Study in a Tropical Climate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Critical Parameters in Humid Tropical Regions
1.2. The Envelope
- Control of heat flow by selecting materials with high thermal mass.
- Facades with reflective surfaces or with radioactive filters (windows).
- Orientation considering the annual position of the Earth with respect to the Sun.
- Insulating structures that restrict heat penetration.
- Moisture control through waterproof foundations and drains to limit moisture.
- Control of air flow through openings (doors, windows, high ceilings) to renew the interior air in search of good quality for the occupants.
1.3. Humid Tropical Regions in America
2. Materials and Methods
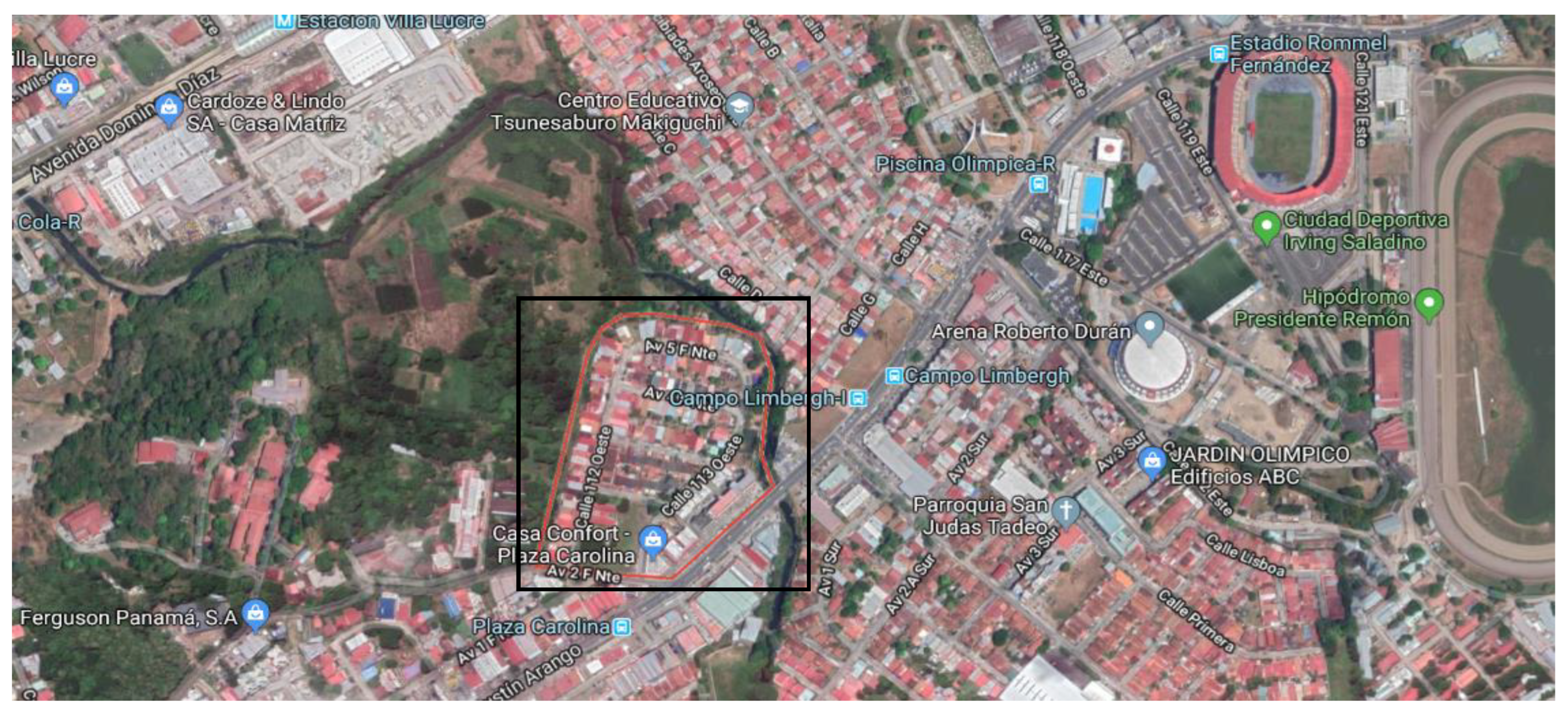
2.1. Geographic Location and Meteorological Data
2.2. Building Description and Occupancy Profiles
2.3. Model Validation
2.4. Numerical Study and Optimization Analysis
2.5. Envelope Performance Indicators
2.6. Thermal Comfort Indicators
3. Results Analaysis
3.1. Behavioral and Sensitivity Analysis
3.2. Optimization Analysis
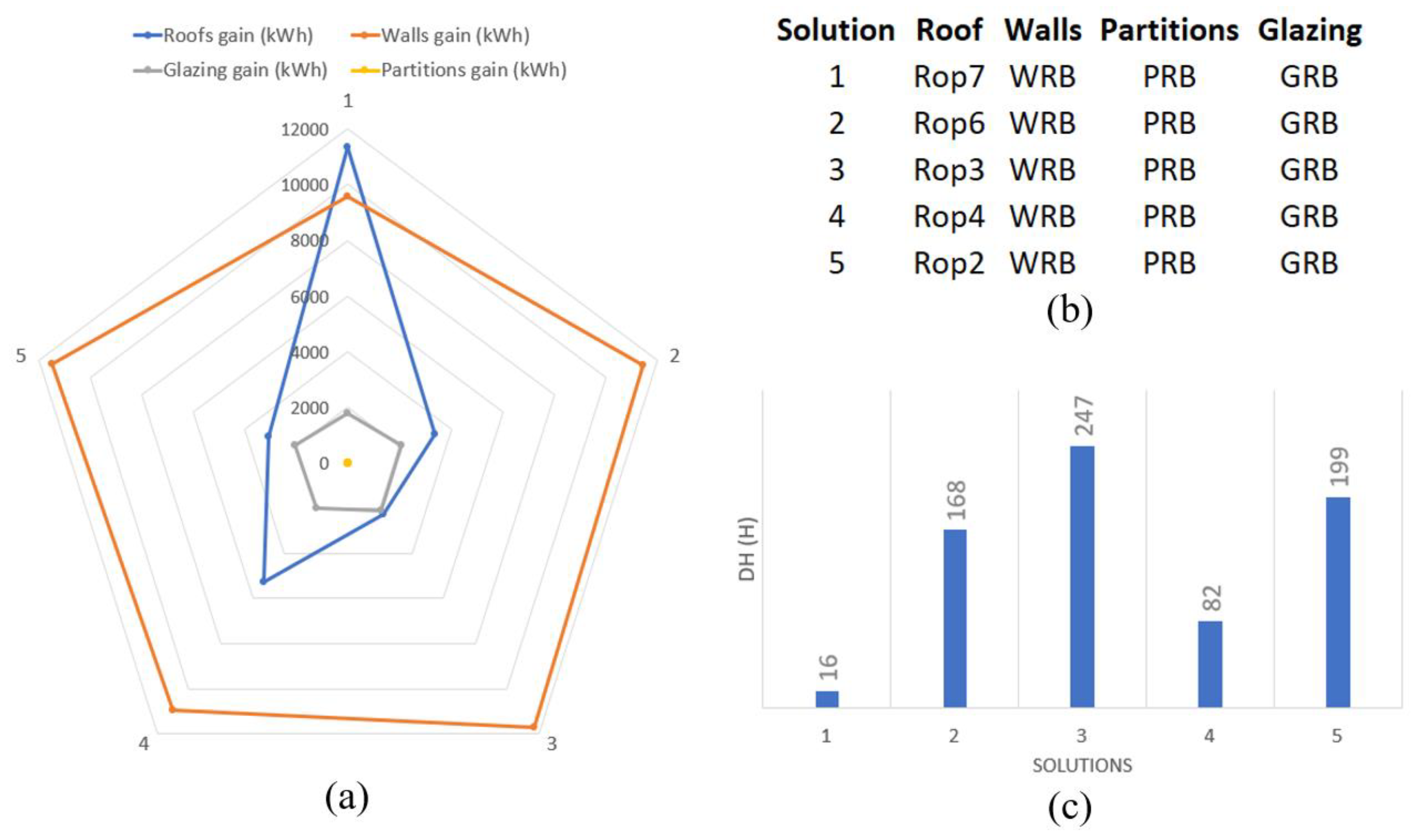
- Choosing an envelope configuration with a roof layout with low TMD and low ID values, along with wall and partition layouts with high TMD and low ID, seems to be the adequate option (solution 1 in Figure 7).
- The reference building glazing type appears to be adequate for every solution, but this might be due to no significant changes presented for the glazing heat gains.
- Optimization analysis could have been performed to minimize the wall or roof heat gains, together with minimizing the DH; however, it would have led to achieving the same best solution. It should be noted that the results presented here correspond to a specific case study, and thus it might only apply to such a case (Figure 2).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centro Nacional de Despacho. Sistema de Información en Tiempo Real (SITR): Generación; Centro Nacional de Despacho: Panama City, Panama, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agencia Internacional de Energías Renovables (IRENA). Evaluación del Estado de Preparación de las Energías Renovables: Panamá; Technical Report; Agencia Internacional de Energías Renovables: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaria Nacional de Energía. El Mercado Eléctrico de la República de Panamá; Secretaría Nacional de Energía: Panama City, Panama, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). 2019 Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction; UN Environment and IEA, 2019; Available online: https://www.worldgbc.org/sites/default/files/2019%20Global%20Status%20Report%20for%20Buildings%20and%20Construction.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- Pathirana, S.; Rodrigo, A.; Halwatura, R. Effect of building shape, orientation, window to wall ratios and zones on energy efficiency and thermal comfort of naturally ventilated houses in tropical climate. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2019, 10, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W. A Review of Sensitivity Analysis Methods in Building Energy Analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 20, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedzadeh, S.; Pour Rahimian, F.; Rastogi, P.; Glesk, I. Tuning machine learning models for prediction of building energy loads. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrahimi, S.; Farid, M.; Chin, L. The effect of building envelope on the thermal comfort and energy saving for high-rise buildings in hot–humid climate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandos, H. Principios y Estrategias del Diseño bioclimático en la Arquitectura y el Urbanismo, Eficiencia Energética; Consejo Superior de los Colegios de Arquitectos de España: Madrid, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Baño, A. La Arquitectura Bioclimática: Términos Nuevos, Conceptos Antiguos. Introducción al diseño de Espacios Desde La óptica Medioambiental; Departamento de Arquitectura de la Universidad de Alcalá: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Johra, H.; Heiselberg, P.; Dréau, J.L.; Le, J. Influence of envelope, structural thermal mass and indoor content on the building heating energy flexibility. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zheng, W.; Jin, H. Analysis of the indoor thermal environment and passive energy-saving optimization design of rural dwellings in Zhalantun, inner mongolia, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avendaño-Vera, C.; Martinez-Soto, A.; Marincioni, V. Determination of optimal thermal inertia of building materials for housing in different Chilean climate zones. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, P.; Aggarwal, S.K. Thermal performance of a building envelope—An evaluative approach. IJRAR-Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2017, 4, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, P.; Pancholi, M.; Sood, D.; Rakshit, D. Dynamic optimization of multi-retrofit building envelope for enhanced energy performance with a case study in hot Indian climate. Energy 2020, 197, 117263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.M.; Alessandro, M.D.; D’Alessandro, M. Indoor thermal comfort review: The tropics as the next frontier. Urban Clim. 2019, 29, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicens, G.D.I.; Castro, S.S.; Vicente, R.; De Ignacio Vivens, G.; Soutullo Castro, S.; López-Zaldivar, O.; Lozano-Diez, R.V.; Verdú Vázquez, A. Sobre inercia térmica y aislamiento de viviendas en clima cálido-húmedo. On thermal inertia and insulation of buildings in warm-humid climate. ADE 2018, 4, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvero, F.; Rodrigues, F.; Montelpare, S. A parametric study and performance evaluation of energy retrofit solutions for buildings located in the hot-humid climate of Paraguay—Sensitivity analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araúz, J.; Mora, D.; Chen Austin, M. Impact of the Envelope Layout in the Thermal Behavior of Buildings in Panama: A Numerical Study. In Proceedings of the 7th International Engineering, Sciences and Technology Conference (IESTEC), Panama City, Panama, 9–11 October 2019; IEEE: Panama City, Panama, 2019; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaceta Oficial, Resolución de la JTIA N°035, 26 de junio 2019; Ministerio de Obras Públicas/Junta Técnica de Ingeniería y Arquitectura: Panama City, Panama, 2019; p. 61.
- Mora, D.; Araúz, J.; Chen Austin, M. Towards Nearly Zero Energy Buildings in Panama through Low-Consumption Techniques: A Numerical Study towards Nearly Zero Energy Buildings in Panama through Low-Consumption Techniques: A Numerical Study. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference, Panama City, Panama, 17 December 2019; p. 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, A.; Batista, M.; Sanchez, J.; James, A. Aislante térmico a base de materiales orgánicos Development of a thermal-insulation based on organic materials. Rev. Iniciacion Cient. 2018, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labastid, D.; Bolobosky, M.; Mogollón, L.; James, A. Implementación de un Intercambiador de Calor en Techos de Zinc. KEG 2018, 3, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segundo, D.; Araúz, A.; Mora, A.; Perén, J.I. Primer paso en la eficiencia energética, confort ambiental y sostenibilidad de edificios en Panamá: Percepción ambiental de usuarios de la Casa Matriz del Banco Nacional de Panamá. Rev. Iniciacion Cient. 2017, 3, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal, R.; Robles, J.; Solís, J.; Vargas, J.; Marín, N. Sistema de análisis energético y de temperatura de las ventanas de un aula de clase con y sin aislamiento térmico Energetic and temperature analysis system of classroom windows with and without thermal insulation. Rev. Iniciacion Cient. 2018, 4, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, S.; Mikkelsen, N.; Woodward, J. Long-term rates of mass wasting in Mesters Vig, northeast Greenland: Notes on a re-survey. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2002, 13, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.R.; Bandera, C.F. Validation of calibrated energy models: Common errors. Energies 2017, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DesignBuilder Software Ltd.—Optimisation. Available online: https://designbuilder.co.uk/optimisation (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- Gaceta Oficial; Secretaría Nacional de Energía. Resolución N° 3142 del 17 de Noviembre de 2016, que Adopta la guía de Construcción Sostenible Para el Ahorro de energía en Edificaciones y Medidas Para el uso Racional y Eficiente de la Energía, para la Construcción de Nuevas Edificaciones en la República; Secretaría Nacional de Energía: Panama City, Panama, 2016; Volume 3142, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Raut, A.; Khatoon, S.; Goud, P. A comparative study on effects of various insulating layers of roof system on energy usage of building envelope. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 354, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra Florensa, R.; Coch Roura, H. Arquitectura y Energía Natural, 1st ed.; Number 40 in Politext; Edicions UPC: Barcelona, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, C.; Koenigsberger, O.H.; Evans, M. Climate and House Design; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Jannat, N.; Hussien, A.; Abdullah, B.; Cotgrave, A. A comparative simulation study of the thermal performances of the building envelope wall materials in the tropics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Occupancy and Energy Consumption | Profiles |
|---|---|
| Overall occupation (3 people) | Mon to Fri: 19h00 a 05h00 Sat to Sun: 0h00 a 23h59 |
| Luminaires in common areas: hallway, garage, laundry, and kitchen (15 W) | Sun to Sat: 19h00 a 07h00 |
| Room luminaire (15 W) | Sun to Sat: 19h00 a 22h00 |
| Dining room fans (50 W) | Mon to Fri: 05h00 a 06h30 Sat to Sun: 17h00 a 22h00 |
| Room fans (50 W) | Sun to Sat: 22h00 a 05h00 |
| PC: desktop (40 W) | Sun to Sat: 19h00 a 01h00 |
| Refrigerator (70 W) | Sun to Sat: 00h00 a 23h59 |
| Air conditioner (1 TON) | Sun to Sat: 22h00 a 05h00 |
| Layout | e (m) | k (W/m-K) | (kg/m) | c (J/Kg-K) | ce (×10) | U (W/mK) | TMD | ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRB | Zinc | 0.0005 | 113 | 7000 | 390 | 1.36 | 7.143 | - | 3.16 × 10 |
| Rop1 | Stone chipping | 0.025 | 0.96 | 1800 | 1000 | 45 | 3.439 | 0.32 | 0.3355 |
| Asphalt | 0.019 | 0.7 | 2100 | 1000 | 39.9 | ||||
| screed | 0.04 | 0.41 | 1200 | 840 | 40.3 | ||||
| Rop2 | Asphalt | 0.019 | 0.7 | 2100 | 1000 | 39.9 | 0.252 | 0.8 | 0.904 |
| Fireboard | 0.013 | 0.06 | 300 | 1000 | 3.9 | ||||
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.122 | 0.034 | 35 | 1400 | 5.98 | ||||
| Rop3 | Clay Tile | 0.025 | 1 | 2000 | 800 | 40 | 0.211 | 0.82 | 0.9595 |
| MW Stone | 0.1819 | 0.04 | 30 | 840 | 4.58 | ||||
| Roofing Felt | 0.005 | 0.19 | 960 | 837 | 4.02 | ||||
| Rop4 | Asphalt | 0.019 | 0.7 | 2100 | 1000 | 39.9 | 0.486 | 0.24 | 0.6861 |
| Fireboard | 0.013 | 0.06 | 300 | 1000 | 3.9 | ||||
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.048 | 0.034 | 35 | 1400 | 2.35 | ||||
| Cast Concrete | 0.1 | 0.38 | 1200 | 1000 | 120 | ||||
| Rop5 | Zinc | 0.0005 | 113 | 7000 | 390 | 1.36 | 0.496 | 0.46 | 0.93 |
| EPS Standard | 0.075 | 0.04 | 15 | 1400 | 1.57 | ||||
| Rop6 | Asphalt | 0.019 | 0.7 | 2100 | 1000 | 39.9 | 0.258 | 0.87 | 0.334 |
| Fireboard | 0.013 | 0.06 | 300 | 1000 | 3.9 | ||||
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.044 | 0.034 | 35 | 1400 | 2.16 | ||||
| Rop7 | Asphalt | 0.019 | 0.7 | 2100 | 1000 | 39.9 | 1.546 | 0.244 | 0.335 |
| Fireboard | 0.013 | 0.06 | 300 | 1000 | 3.9 | ||||
| Cast Concrete | 0.1 | 0.38 | 1200 | 1000 | 120 | ||||
| Layout | e (m) | k (W/m-K) | (kg/m) | c (J/Kg-K) | ce (×10) | U (W/mK) | TMD | ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRB | Cement/plaster/ mortar-cement blocks | 0.01 | 0.33 | 2040 | 520 | 10.6 | 3.017 | 0.92 | 0.091 |
| Concrete block (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 1.63 | 1000 | 2300 | 230 | ||||
| Cement/plaster/ mortar-cement blocks | 0.01 | 0.33 | 2040 | 520 | 10.6 | ||||
| Pop1 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.825 | 0.6 | 0.5156 |
| Air gap | 0.025 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 30.03 | ||||
| Phenolic foam | 0.025 | 0.04 | 1400 | 30 | 1.05 | ||||
| Concrete block (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 1.63 | 1000 | 2300 | 230 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Pop2 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.465 | 0.62 | 0.5813 |
| Urea formaldehyde Foam | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1400 | 10 | 0.7 | ||||
| Thermalite high strength | 0.1 | 0.19 | 1050 | 760 | 79.8 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Pop3 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 1.562 | 0.472 | 1.74 |
| Air gap | 0.05 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 60.06 | ||||
| Brickwork inner | 0.105 | 0.62 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | ||||
| Plaster (dense) | 0.013 | 0.5 | 1000 | 1300 | 16.9 | ||||
| Pop4 | Concrete block (lightweight) | 0.1 | 0.19 | 1000 | 600 | 60 | 1.272 | - | 0.6695 |
| Pop5 | Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | 1.054 | 0.103 | 0.0856 |
| Concrete block (lightweight) | 0.1 | 0.19 | 1000 | 600 | 60 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Pop6 | Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | 2.067 | 0.936 | 0.168 |
| Concrete block (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 1.63 | 1000 | 2300 | 230 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Pop7 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.596 | 0.603 | 0.3725 |
| Air gap 10 mm | 0.025 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 30.03 | ||||
| Phenolic foam | 0.025 | 0.04 | 1400 | 30 | 1.05 | ||||
| Concrete block (lightweight) | 0.1 | 0.19 | 1000 | 600 | 60 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Pop8 | Gypsum plasterboard | 0.015 | 0.25 | 1000 | 900 | 13.5 | 1.887 | 0.5 | 0.1132 |
| Air gap 10 mm | 0.05 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 60.06 | ||||
| Gypsum plasterboard | 0.015 | 0.25 | 1000 | 900 | 13.5 | ||||
| Pop9 | Plywood (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 0.15 | 1420 | 700 | 99.4 | 1.195 | - | 0.7967 |
| Layout | e (m) | k (W/m-K) | (kg/m) | c (J/Kg-K) | ce (×10) | U (W/m-K) | TMD | ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WRB | Cement/plaster/ mortar-cement blocks | 0.01 | 0.33 | 2040 | 520 | 10.6 | 3.859 | 0.916 | 0.1169 |
| Concrete block (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 1.63 | 1000 | 2300 | 230 | ||||
| Cement/plaster/ mortar-cement blocks | 0.01 | 0.33 | 2040 | 520 | 10.6 | ||||
| Wop1 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.251 | 0.464 | 0.8674 |
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.1175 | 0.034 | 1400 | 35 | 5.76 | ||||
| Concrete block (medium) | 0.1 | 0.51 | 1000 | 1400 | 140 | ||||
| Gypsum plastering | 0.013 | 0.4 | 1000 | 1000 | 13 | ||||
| Wop2 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.156 | 0.467 | 0.9176 |
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.2 | 0.034 | 1400 | 35 | 9.8 | ||||
| Concrete block (medium) | 0.105 | 0.51 | 1000 | 1400 | 147 | ||||
| Gypsum plastering | 0.015 | 0.4 | 1000 | 1000 | 15 | ||||
| Wop3 | Lightweight metallic cladding | 0.006 | 0.29 | 1000 | 1250 | 7.5 | 0.375 | 0.305 | 0.9154 |
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.083 | 0.034 | 1400 | 35 | 4.1 | ||||
| Gypsum plastering | 0.013 | 0.4 | 1000 | 1000 | 13 | ||||
| Wop4 | Brickwork outer | 0.1 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 136 | 0.351 | 0.478 | 0.8197 |
| XPS Extruded Polystyrene CO blowing | 0.0794 | 0.034 | 1400 | 35 | 3.89 | ||||
| Concrete block (medium) | 0.1 | 0.51 | 1000 | 1400 | 140 | ||||
| Gypsum plastering | 0.013 | 0.4 | 1000 | 1000 | 13 | ||||
| Wop5 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 2.071 | 0.489 | 0.067 |
| Brickwork inner | 0.1 | 0.62 | 800 | 1700 | 136 | ||||
| Gypsum plastering | 0.013 | 0.4 | 1000 | 1000 | 13 | ||||
| Wop6 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.825 | 0.603 | 0.5156 |
| Air gap | 0.025 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 30.03 | ||||
| Phenolic foam | 0.025 | 0.04 | 1400 | 30 | 1.05 | ||||
| Concrete block (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 1.63 | 1000 | 2300 | 230 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Wop7 | Brickwork outer | 0.105 | 0.84 | 800 | 1700 | 142.8 | 0.596 | 0.87 | 0.3725 |
| Air gap 10 mm | 0.025 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 30.03 | ||||
| Phenolic foam | 0.025 | 0.04 | 1400 | 30 | 1.05 | ||||
| Concrete block (lightweight) | 0.1 | 0.19 | 1000 | 600 | 60 | ||||
| Plaster (lightweight) | 0.013 | 0.16 | 1000 | 600 | 7.8 | ||||
| Wop8 | Concrete block (lightweight) | 0.2 | 0.19 | 1000 | 600 | 120 | 0.708 | 0.026 | 0.3933 |
| Air gap 10 mm | 0.025 | 0.045 | 1.2 | 1001 | 30.03 | ||||
| Steel | 0.001 | 50 | 450 | 7800 | 3.51 | ||||
| Gypsum plasterboard | 0.01 | 0.25 | 1000 | 900 | 9 | ||||
| Wop9 | Plywood (heavyweight) | 0.1 | 0.15 | 1420 | 700 | 99.4 | 1.195 | - | 0.7967 |
| Months | Energy Consumption from Simulation (kWh) | Energy Consumption from Bills (kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Jan | 252.67 | 266.00 |
| Feb | 228.93 | 225.00 |
| Mar | 254.51 | 216.00 |
| Apr | 244.76 | 216.00 |
| May | 252.67 | 232.00 |
| Jun | 246.60 | 232.00 |
| Jul | 252.67 | 232.00 |
| Aug | 253.59 | 289.00 |
| Sep | 245.68 | 231.00 |
| Oct | 252.67 | 228.00 |
| Nov | 245.68 | 231.00 |
| Dec | 253.59 | 260.00 |
| Energy Consumption Due to Air Conditioner (kWh) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
| RB | 76.0 | 61.9 | 65.5 | 78.2 | 90.0 | 92.3 | 88.7 | 92.7 | 90.4 | 92.4 | 86.7 | 90.0 |
| RB+Pareto1 | 74.0 | 53.4 | 58.9 | 62.9 | 76.9 | 87.3 | 85.8 | 78.1 | 90.0 | 91.0 | 83.1 | 85.7 |
| Difference (%) | 2.6 | 13.7 | 10.1 | 19.6 | 14.6 | 5.4 | 3.3 | 15.7 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 4.2 | 4.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araúz, J.; Mora, D.; Chen Austin, M. Assessment of Different Envelope Configurations via Optimization Analysis and Thermal Performance Indicators: A Case Study in a Tropical Climate. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042013
Araúz J, Mora D, Chen Austin M. Assessment of Different Envelope Configurations via Optimization Analysis and Thermal Performance Indicators: A Case Study in a Tropical Climate. Sustainability. 2022; 14(4):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042013
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraúz, Jesús, Dafni Mora, and Miguel Chen Austin. 2022. "Assessment of Different Envelope Configurations via Optimization Analysis and Thermal Performance Indicators: A Case Study in a Tropical Climate" Sustainability 14, no. 4: 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042013
APA StyleAraúz, J., Mora, D., & Chen Austin, M. (2022). Assessment of Different Envelope Configurations via Optimization Analysis and Thermal Performance Indicators: A Case Study in a Tropical Climate. Sustainability, 14(4), 2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14042013








