Abstract
Education is the cornerstone of improving people’s lives and achieving global sustainability. Intelligent systems assist sustainable education with various benefits, including recommending a personalized learning environment to learners. The classroom learning environment facilitates human tutors to interact with every learner and obtain the opportunity to understand the learner’s psychology and then provide learning material (access learner previous knowledge and well-align the learning material as per learner requirement) to them accordingly. Implementing this cognitive intelligence in Intelligent Tutoring System is quite tricky. This research focused on mimicking human tutor cognitive intelligence in the computer-aided system of offering an exclusive curriculum or quality education for sustainable learners. The prime focus of this research article was to evaluate the proposed SeisTutor using Kirkpatrick four-phase evaluation model. The experimental results depict the enhanced learning gained through intelligence incorporated SeisTutor against the intelligence absence, as demonstrated.
1. Introduction
Quality education is a core element of sustainable development, intended to ensure equitable and inclusive quality education and encourage opportunities for lifelong learning for all. Research claims that education is critical to livelihood and the world’s long-term viability [1,2]. New digital technologies are transforming education in both informal and formal learning environments. This overarching goal is linked to several general issues influencing education in the digital era. Some of the significant developments and their impact on education can be stated as follows: (a) educational objectives; (b) learning environments and ecosystems; (c) learning and teaching processes; and (d) educational policy and governance.
According to the Sustainable Development Goal, equality (male and female) to access excellent technical learning and training practices is anticipated by 2030 [3]. Education is the cornerstone of improving people’s lives and achieving global sustainability [1,2]. Furthermore, equitable and inclusive education equips people to devise innovative solutions for their day-to-day lives. Incorporating digital inclusion and good quality educational practice enables the learners to deliver motivation, knowledge, and opportunities; offer skill training to employ SDG explication; and resolve the SDG challenges [4,5].
Human, cultural, ethical, and ecological principles are described as sustainable education development. It offers good teaching practices to societies that aid the growth of communities, institutions, organizations, and the competitive environment. Thus, it enhances the economic and social life [6,7]. Intelligent systems assist sustainable education with a wide variety of benefits, including recommending a personalized learning environment to learners [8].
The value of utilizing automated systems over long-duration teaching practices is becoming more apparent. Incorporating Artificial intelligence and expert systems in education helps gauge real-world scenarios. E-learning, technology, applications, e-teaching principles, and sustainable development are the most vital parts of a sustainable e-learning environment. The principles of intelligent learning or e-learning comprise the framework, models, and theories, whereas the principle of intelligent tutoring or e-teaching comprises a program, curriculum, and pedagogy. Good teaching practices and evaluation models, collaborative, and custom-tailored or personalized learning approaches work together to determine and recommend a custom-tailored pedagogy or tutoring strategy [9].
Personalization emphasizes self-development and the academic realm. The learners’ self-growth depends on the skill and knowledge gained through online courses and internet communities. A custom-tailored or personalized learning environment encompasses learning tools, services, and application or system that recommends learning per learners’ needs based on learner capabilities, a low-cost tutoring environment, and a personalized learner profile [10].
In order to effectively meet this learner-centric requirement, an intelligent tutoring system can offer personalized learning experiences to learners. The intelligent tutoring system (ITS) is an artificial intelligence technique that offers the learner exclusive learning material, aligned and gathered as per the learner’s grasping ability and preferred media of learning.
SeisTutor was developed for learning “Seismic Data Interpretation” as a subject domain of this research. This research aims to provide pastoral care to learners by cost-effectively offering one-to-one, customized learning material. SeisTutor offers a personalized learning environment. It brings personalization in identifying tutoring strategy (based on pretest (learning style test and domain knowledge test)), exclusive curriculum design, and observation of learner psychological state of mind during learning sessions. The feature of personalization is built on many aspects, such as accuracy of predicting tutoring strategy (based on pretest), curriculum design, and psychological parameters. The only technique to determine the performance of the personalization facility of SeisTutor is to appraise the system in actual circumstances (learners who are learning the course material). Appraise acts as a critical element for quality assurance because it enables the learner to provide valuable feedback on the learning experience and on learning content, which further helps to understand the learner’s perspective and makes the learning better.
The assessment of SeisTutor was accompanied in the 2018–2019 scholastic year. The objective of the evaluation was to examine how effectively SeisTutor personalized itself to fulfill the learner’s needs and whether SeisTutor helps enhance the learning gain for learning the “Seismic Data Interpretation” domain. In order to accomplish this, the following program was outlined:
- Perform a schematic literature review on how to evaluate the efficacy of learning;
- Generate an assessment for determining the efficacy of learning;
- Perform analysis to identify how efficiently learners learn with SeisTutor.
This article is organized into five sections. It begins with a schematic literature review on the evaluation of learning with ITS (Section 2). Further, Section 3 introduces the architecture of SeisTutor in detail, which includes the general description and mathematical justification of its functionalities. Section 4 illustrates the experimental analysis performed to evaluate the effectiveness of SeisTutor systematically. Section 5 elaborates on the comparative analysis with current work, and in Section 6, we finally conclude the implication of this work.
2. Background and Preliminaries
In this section, comprehensive coverage of the development of a sustainable, intelligent tutoring system (ITS) from traditional computer-aided instruction (CAI) to artificial intelligence techniques embedded tutoring systems and the evaluation prototype are discussed.
The academic realm provides a framework for considering long-term sustainable education [11]. Incorporating AI and expert systems in education plays a vital role in offering learning (in the form of blended, online, virtualization, visualization, etc.) at work, home, coffee shops, museums, city streets, and parks. Another trend is shifting our perceptions of context and spaces of learning. Finally, it considers the potential of digitally mediated learning to be accessible anytime and anywhere [12]. Here the teaching environment expanded temporally and spatially. Ubiquitous learning abandons the discrepancy between formal and informal learning. A planned curriculum and competent facilitators play a role in keeping individuals actively engaged; however, the learning is more inclined to need, purpose, and context [13]. These necessitate a paradigm shift from “curriculum-based” to “problem-based” learning, requiring a rethinking of learning motivations, processes, and content. One of the most remarkable features of providing learners with online learning possibilities is that they have significantly more autonomy and choice in pursuing paths of study that are fascinating and meaningful to them. Learning evolves from a recipient, passive model to a more self-directed, collaborative, and active model [14,15]. Teachers can collaborate with domain experts and technology to develop a learning environment that appropriately recognizes learner challenges and recommend an adaptive instructional strategy that can help understand the concept effectively. The goal of a “flipped” learning environment is not to replace teachers; instead, it is to automate the learning processes; enable the teachers to focus their talents, energies, experience, and creativity on tutoring.
Computer-aided instruction (CAI) systems store the learning material, which the learner further uses in different ways (representation) [16]. These systems have several limitations. These systems mainly focused on quantitative education (teacher-centric) rather than qualitative nature (learner-centric) education. The CAI systems adopt a highly primitive tutoring strategy, which leads to less interaction between the CAI tutor and the learner. Further advancement led to the origin of the field of Intelligent Computer-Aided Instruction (ICAI) or Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS) [17].
In 1950, The first ITS was technologized as CAI [18]. McDonald, Woolf developed intelligence embedded computer-aided instruction, which delivers learning material by establishing effective interaction with the learner. Thus, these systems emulate the cognitive intelligence of humans only to a small extent, i.e., provide necessary guidance based on the learner’s action.
ITS, developed by [19], creates questions on vocabulary and arithmetic but cannot adapt and model learner needs. In advancement to this, several adaptive systems were developed by the researchers [20,21,22]. Advancement in the learning systems led to significant modifications in the architecture of ITS. Further improvements in Pedagogy Model led to adapting the learning material to learner competency. Thus, incorporating AI techniques shifted to fine-tune pedagogical recommendation and learner feedback.
Physics is a well-documented subject domain. An intelligent tutoring system developed by the Andes comprises physics as the knowledge domain [23,24]. The Andes incorporates an intelligent feature of determining performance parameters, predicting learners’ subsequent actions, and identifying and recommending a suitable strategy. For decision-making, they utilize a Bayesian network.
In order to adjudge previous learner knowledge, pretest plays an important role. ITS developed by [25] offers a personalized learning environment by offering learning material to the learner based on previous knowledge about the course. The pathfinder technique was used to determine the previous knowledge of the learner. ITS developed by [26] proposed a solution for determining the learners’ curriculum by utilizing a profile framework.
Further advancement in this field uses a data mining technique to mine the meaningful learning path for the learner. This system tracks learner activity during learning and recommends the most suitable learning path. ITS developed by [27] incorporated two methodologies: determining the learning path and recommending the learning path. Initially, the system utilizes the apriori algorithm to generate an initial course coverage plan; they used course-concept analysis to determine the association among the course-concept and then adjudged the preferable course coverage plan.
Another [28] proposal uses a fuzzy rule base technique to determine the association between the list of materials and learner requirements based on web navigation. In the recent development in technologies, some concepts of ontologies, genetic-based algorithms, and artificial neural networks are used to recommend a suitable course coverage plan [29,30].
ITS developed by [31] utilizes the nature-inspired algorithm to adjudge the custom-tailored learning path. They used two critical parameters for fitness function; one is difficulty level and other associations between the course concepts. Another research work on e-learning systems makes use of the nature-inspired algorithm for determining optimal course coverage plans based on the incorrect response on the pretest [32,33].
In [34], the author used ACO techniques to recommend an adaptive learning path by considering the learner’s learning style. The authors of [35] utilized self-organizing techniques to recommend optimal course coverage plans to the learner. Similar practices can be applied through a probabilistic technique. In which nodes indicate the pedagogy items and edges indicate the hypertext links (preferred probabilities), and learners act as ants who have to traverse all the nodes [36,37,38] (Skinner. et al.; Brusilovsky. et al., 1996; Karampiperis. et al., 2004; Dhabi. et al., 2006; Bert van den Berg. et al., 2005).
Evaluating and validating an ITS is a challenging task due to the lack of standard agreement and procedure. The primarily used prototype for evaluating the training program of ITS is the prototype established by Donald Kirkpatrick [39,40]. Many researchers revised this prototype, but its basic architecture is still the same [41,42].
Kirkpatrick’s prototype comprises four stages of evaluation, shown in Figure 1 and briefly discussed in Figure 2.
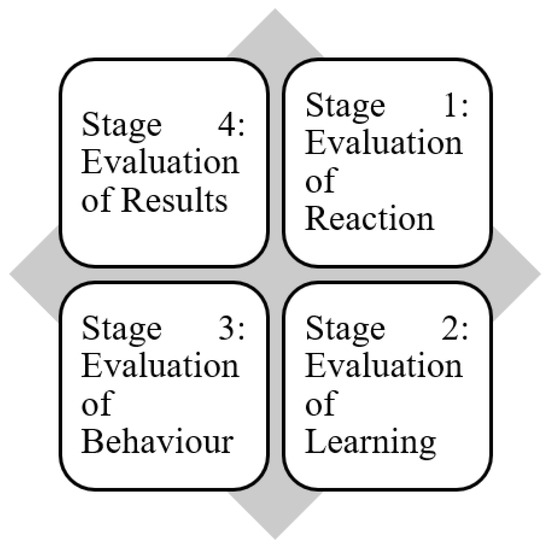
Figure 1.
Kirkpatrick’s four stages of evaluation.

Figure 2.
Brief illustration of Kirkpatrick’s four phases or stages of assessment. Evaluation of Reaction [43,44,45], Evaluation of Learning [42,46,47], Evaluation of Results [45].
Computing results is the best way to quantify the effectiveness of any learning program, but it is challenging to conduct. The authors of Ref. [48] provided a statement regarding the evaluation that not all learning programs focus on impacting the learning performance of a learner; instead, they can perform for a purpose. Other researcher uses the Kirkpatrick model as a base model. The author of Ref. [49] introduced the fifth level of the Kirkpatrick model named Return of Investment (ROI), which is used to measure the effectiveness of learning or investment.
Kirkpatrick’s model is considered a base model for judging the efficacy of a training program by Ref. [48]. Their suggestion is to set the initial objective (from the learning program) and then monitor the fulfillment of objectives after the learning program. The authors of Ref. [50] disapprove of Kirkpatrick’s model, giving the following reason:
- Offline Test (Written Test) lacks validity and reliability in quantifying knowledge, skill, and attitude (KSA);
- The 100% response rate is idealistic;
- Control groups are not feasible in the learning program context.
Furthermore, educational organizations recommend considering the merits and demerits of various evaluation prototypes and methodologies to build an organizational-specific evaluation prototype that fulfills their requirements [51]. Furthermore, it was proposed that the evaluation prototype prioritizes both education practices and findings [52]. Valid, reliable, inexpensive, and acceptable is the feature of an ideal evaluation prototype. Moreover, the evaluation prototype may encompass quantitative, objective, subjective, and qualitative methods. Thus, evaluation results are advantageous for determining the learning attainments of the learning program [53,54,55,56].
The conclusion drawn from the literature recommends that the learning program include three levels of Kirkpatrick’s prototype. Kirkpatrick Level 3 and level 4 are very challenging to observe in an educational learning program [57] because level 1 and level 2 can be quantified during an ongoing learning session. However, levels 3 and level 4 require post-assessment analysis. Level 4 needs the rigorous observation of the inference of the learning program. For evaluation, there is no articulated framework. As per [57], continuous feedback and instruction help the learner achieve the best learning skills [58,59,60,61,62].
3. Proposed Prototype
This section illustrates the SeisTutor architecture and briefly discusses functionality incorporated in SeisTutor. SeisTutor is an ITS explicitly designed for the “Seismic Data Interpretation” subject domain. SeisTutor recommends learning contents as per learner performance in pretest (prior knowledge assessment test). In addition, SeisTutor keeps track of the learner’s behavior (psychological state) during the entire learning session and conducts a test to determine the degree of understanding of the topic. SeisTutor is adaptive, i.e., content and link-level [63]. Adaptive content level indicates that the learners with different performances in the pretest (prior knowledge test) obtain different learning material. Before indulging learners in the learning session, SeisTutor enables learners to go through a pretest. There are two kinds of assessments performed in pretest: a learning style test and a prior knowledge test. The current focus of this research is on the prior knowledge test. SeisTutor observes the learner’s performance during the tests and aligns the learning material accordingly.
For link elimination, ideally, the curriculum covers all the links of sub-topics to learn—however, the links eliminated are not in the determined curriculum for the learner. SeisTutor continually observes and stores the learner’s action, performance, and behavior. This information is further utilized for making intelligent strategic plans for recommendation and evaluation work.
3.1. SEISTUTOR Architecture
SeisTutor follows all the guidelines for implementing an intelligent tutoring system. The critical functional model of an ITS is the domain model, learner model, pedagogy model, and learner interface. SeisTutor architecture comprises a learner interface, pedagogy model, learner model, and domain model [64,65,66]. The following subsection briefly illustrates the various components involved in SeisTutor.
3.1.1. Domain Model
This model is described as a cluster of concepts. Here concept terminologies indicate the single topic. Other terminologies are used in the different research papers, such as knowledge element, object, learning outcome, and attribute. In the current context, concepts possess a prerequisite relationship to each other. Each concept is further segregated into learning units. SeisTutor utilizes unit variant technologies to attain content-level adaptation. Content level adaptation indicates that the system has alternative units and recommends the learning units based on learner grasping and learning style [67,68,69].
3.1.2. Pedagogy Model
This model consists of various rules and logic that build a knowledge infrastructure essential for adapting the learning materials as per the learner’s:
Curriculum Planner
The planner generates a curriculum as a sequence of learning units covered during the learning session [64];
Learning Assessment
Learning assessment is the process of determining the learner’s learning process. The accuracy of this adjudging model acts as a critical factor that affects the adaptation practice;
Understanding Assessment
The understanding assessment identifies the learner’s degree of understanding of the concept. SeisTutor makes any decision by referring to all the models, such as determining the curriculum for the learner and offering the learning content as per the learner’s grasping level and learning style.
3.1.3. Learner Model
SeisTutor captures three characteristics of a learner. This model captures the learner’s activity during the learning session and stores and updates the learner’s information for making the decision. This information is fruitful for the system to adapt based on learner characteristics (grasping level and learning style).
Learner Demographic Information
Learner demographic information includes learner’s basic details, such as name, learner username, and email id. This information is used to create the learner profile and collected when the first-time learner signup with SeisTutor.
Psychological State
It recognizes the learner’s emotions during the tutoring session. Recognizing the psychological state of mind is essential because it helps determine how far the learner liked the learning contents during the learning session. SeisTutor determines six emotions, i.e., smile, sad, neutral, surprise, fear, and anger.
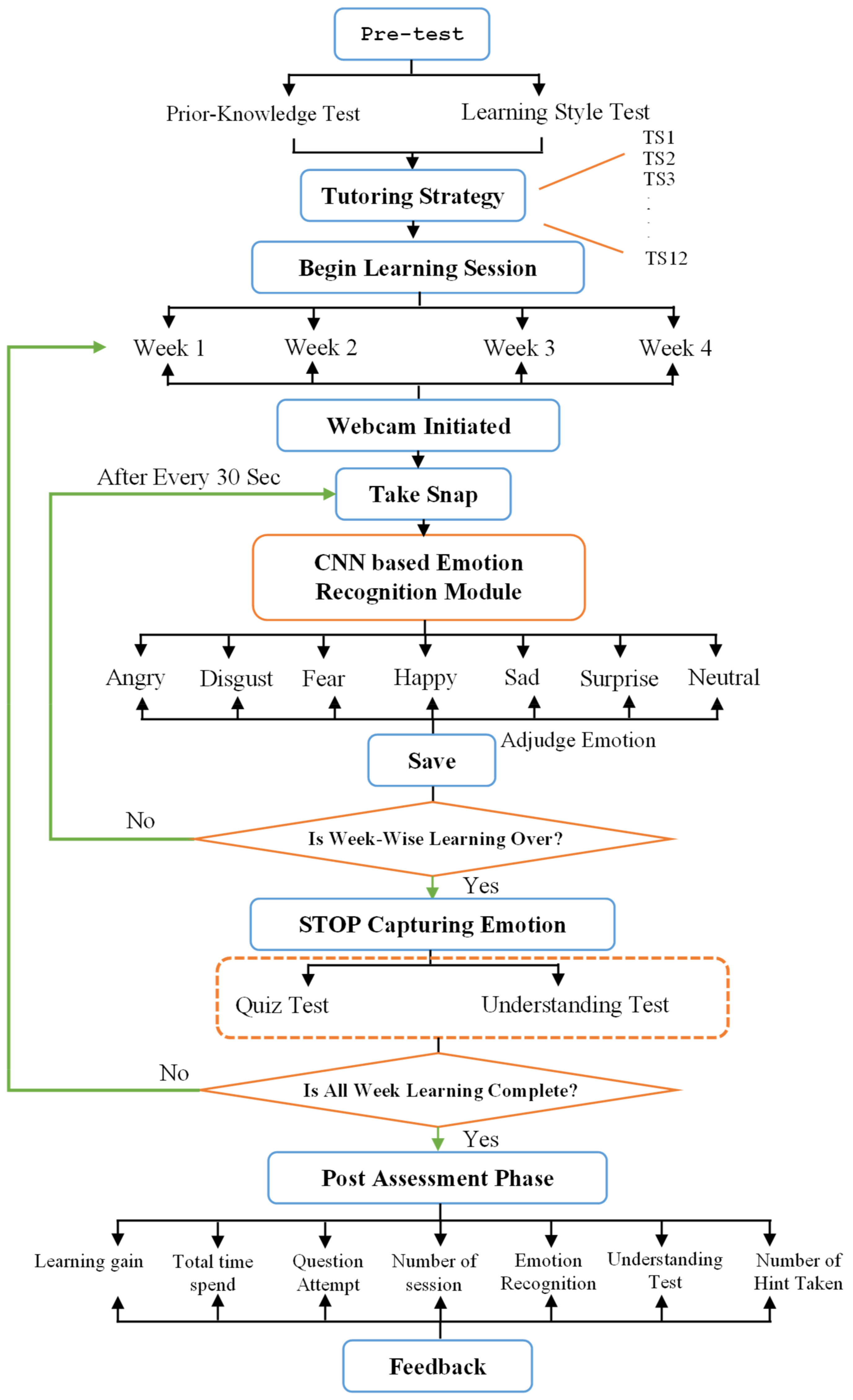
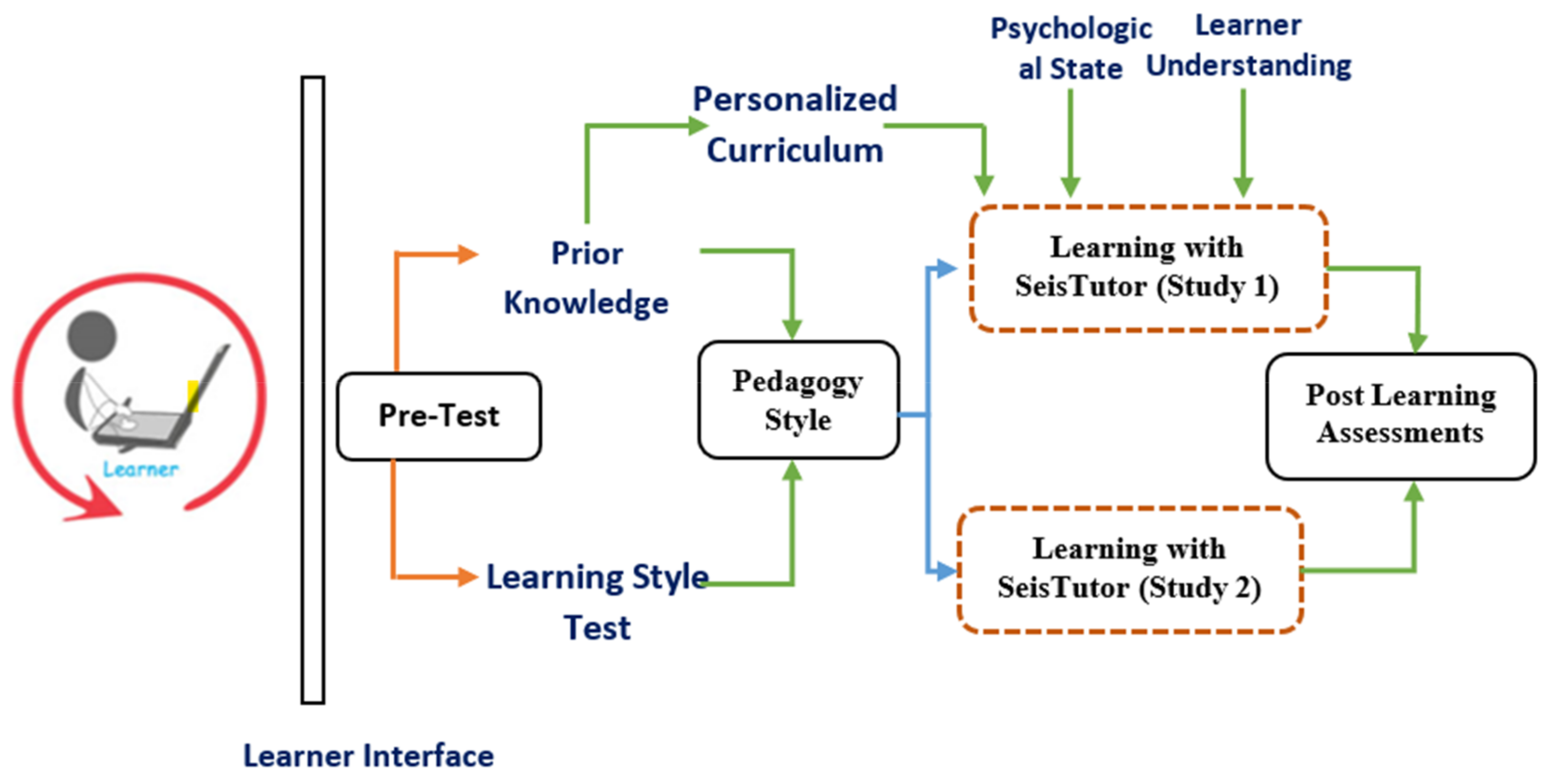
This psychological state recognition module becomes triggered as soon as the learner starts the learning session, as shown in Figure 3. Initially, participants belong to both the studies and undergo the initial assessment phase (Pretest); after the pretest, their learner profile and learning style are determined. The I2A2 learning style prototype is utilized to ascertain the learning style [67]. Here I2A2 is the name of the learning style, i.e., imagistic (learning through observing), intuitive (learning through interpreting written words), acoustic (learning through listening), active (learning through action). Based on tutoring strategy (study 2 (learner study without customized learning) and study 1 (learner study with customized learning)) and course coverage plan, the suitable mode of learning (study 1 (learner study with customized learning)) is chosen by the learner and pedagogy model and offers customized content through learner interface. Thus, SeisTutor examines the participant’s attainment in the pretest and predicts the individualized tutoring strategy (study 2 (learner study without customized learning) and study 1 (learner study with customized learning)) and custom-tailored curriculum for the applicants (study 1 (learner study with customized learning)).
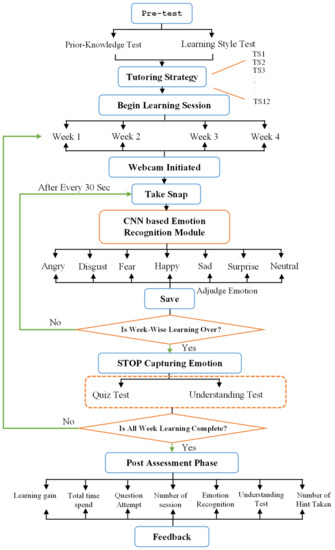
Figure 3.
Flow Diagram of CNN-based Emotion Recognition module.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the CNN-based emotion recognition module is instantiated as soon as the learner begins the learning session. This emotion recognition module takes the snap of the learner via webcam, which acts as an input to the CNN-based emotion recognition module. This module determines the learner’s psychological (emotion) state, which is gauged for future analysis (phase 1: Evaluation of Reaction). The gathering psychological (emotion) state is repeated until the learner completes all the learning contents (topics) associated with all the weeks.
Learner Performance
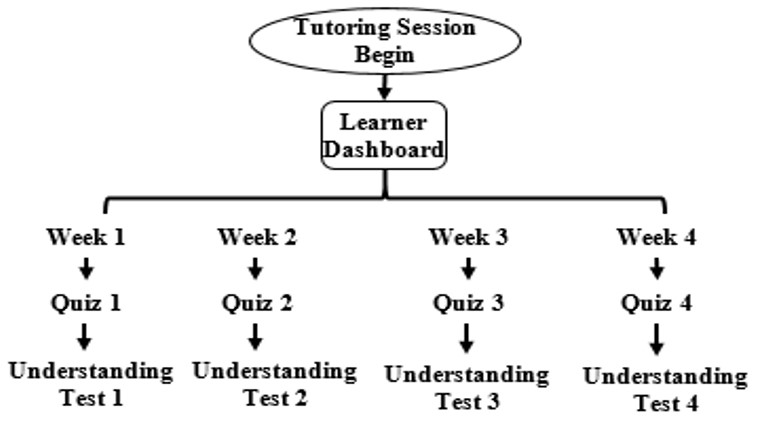
It evaluates the learner’s performance by quantifying their learning by organizing quizzes and tests. Learner performance was quantified based on one parameter, i.e., the number of correct responses. As soon as learners finish the learning content of each week, they have to complete a quiz and understanding test. One quiz is associated with every week (shown in Figure 4). Each quiz contains five questions, and each question contains only one hint. Hints appear to the learner based on the learner’s request to seek help to solve the question. SeisTutor asks the learner to summarize the learned concepts in understanding the test. Based on the user entered information, dictionary-based sentimental analysis is performed. The result gives a score out of 100, which tells the learner’s overall understanding of the concepts.
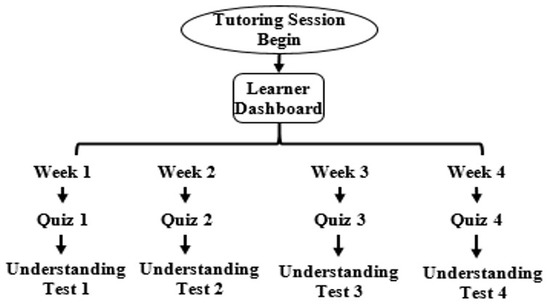
Figure 4.
Quiz and Understanding Test Representation.
In order to determine the overall learning gain, SeisTutor has pretest and post-test assessment scores. The average learning gain is computed (using Equation (1)).
Learning History
It keeps track of the learner’s activity, such as login time, total time spent, etc., and its interaction details during the entire tutoring session. SeisTutor utilizes this information to make necessary action, which further helps to make the whole learning process effective.
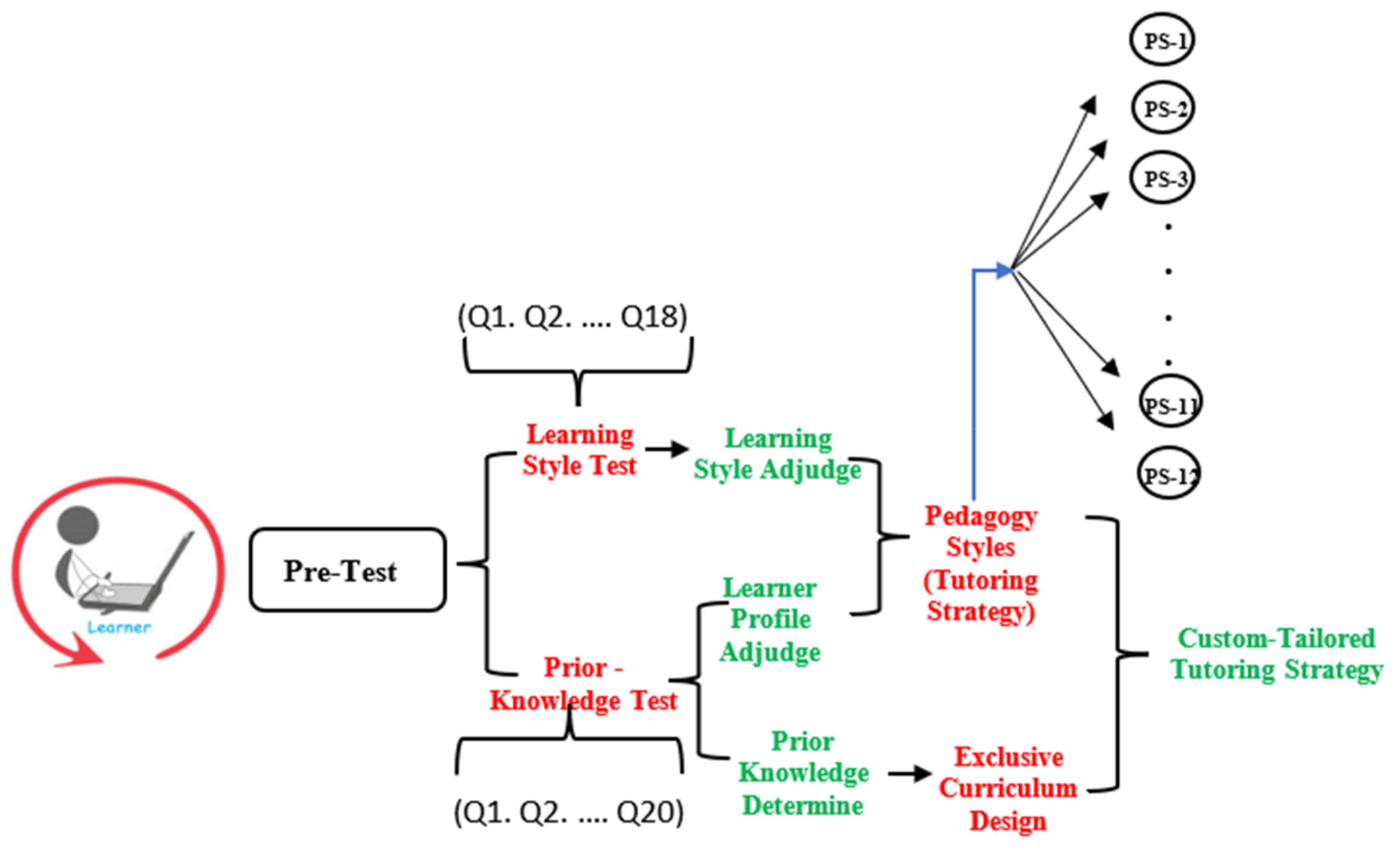
In order to start tutoring with SeisTutor, learners need to register themselves first (see Figure 5). After registration, SeisTutor creates a learner account and instructs the learner to complete a pretest. Pretests are comprised of two tests:
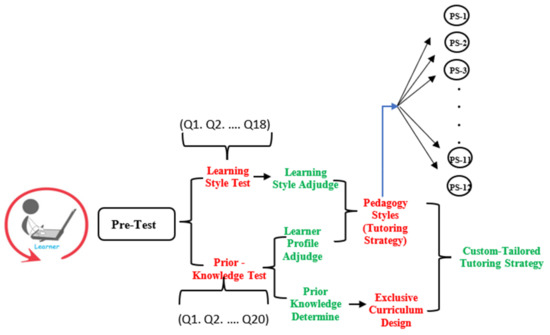
Figure 5.
Flow diagram of learner characteristics model.
- Prior Knowledge Test;
- Learning Style Test.
Prior Knowledge Test
The prior or Previous Knowledge test is the preliminary test used to identify the domain’s elementary knowledge to know the learner’s initial learning level. This test is responsible for analyzing the learner’s knowledge about the domain. The domain model examined the test result and categorized the learner into three learning profiles, i.e., “beginner, intermediate and expert” (see Figure 5). A further outcome of this result is also responsible for determining the curriculum, which is exclusively designed for the learner. This test comprises twenty questions, and all the questions are verified by the domain expert of seismic data interpretation.
Learning Style Test
This test is responsible for determining preferred media for learning. The research has noticed that learner performance is gradually increased if learning material is provided as per preferred learning media (see Figure 5). Thus, this test analyses the learn-er-preferred media. The learner model examines the test result and categorizes the learner into four learning styles, i.e., “Imagistic, Acoustic, Intuitive, and Active”.
Based on these two tests, the pedagogy model determines the tutoring strategy (the result of learning profile and learning style). A tutoring session then begins with the determined tutoring strategy. As soon as learning begins, psychological features are triggered, capturing learner emotions and saving the results in the database for future reference. After completion of every week, the learner is tested. Based on the test result, learner performance and degree of understanding are computed.
3.1.4. Learner Interface Model
This model helps to establish communication between the learning system and the learner via multiple visualization tools (audio, video, textual, navigation, etc.).
4. Evaluation of SeisTutor
After tutoring, post-tutoring assessments of learners are performed by SeisTutor. This section depicts the analysis used to determine the impact of both the studies, i.e., study 1 (learner study with customized learning) and study 2 (learner study without customized learning) learning methods with SeisTutor. Study 1 (learner study with customized learning) exercises learning practices with features such as personalized curriculum design, recognition of the psychological state of the learner during the learning process, and learner’s degree of understanding of taught concepts. When it is not practiced, it is characterized as study 2 (learner study without customized learning). An experimental comparison of both the study groups was tabulated (see Figure 6 and Table 1). These variances help to identify the discrepancy in the learning experiences.
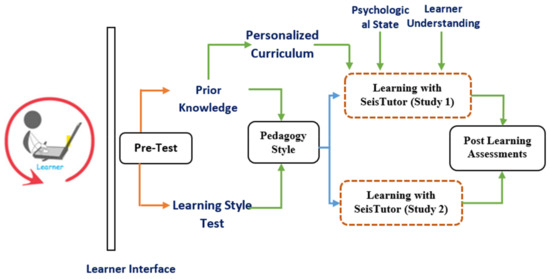
Figure 6.
Flow of accomplishing the evaluation process.

Table 1.
Feature of study 1 (learner study with customized learning) and study 2 (learner study without customized learning) evaluation groups.
4.1. Experimental Design and Methodology
The SeisTutor evaluation is the fundamental piece of the development of this framework. In order to quantify the adequacy and effectiveness of SeisTutor, assessment tests were conducted. The SeisTutor was tested on a selected population of students, teachers, and both (teachers and students) from an anonymous university. A total of 60 learners was volunteered in the evaluation process. Based on their compliance in the participation, a compliance agreement form was issued that demonstrates essential details related to the assessment process. It is requisite for each applicant to give their approval for participation in the assessment process. Applicants were haphazardly assigned one of the groups. Thirty-two applicants were in study 1 (learner study with customized learning), and the remaining were in study 2 (learner study without customized learning).
Out of 60 learners, 30% are learners pursuing graduation, 17% are graduates, 35% are post-graduates, and the remaining minimum qualifications are doctorate (Ph.D.).
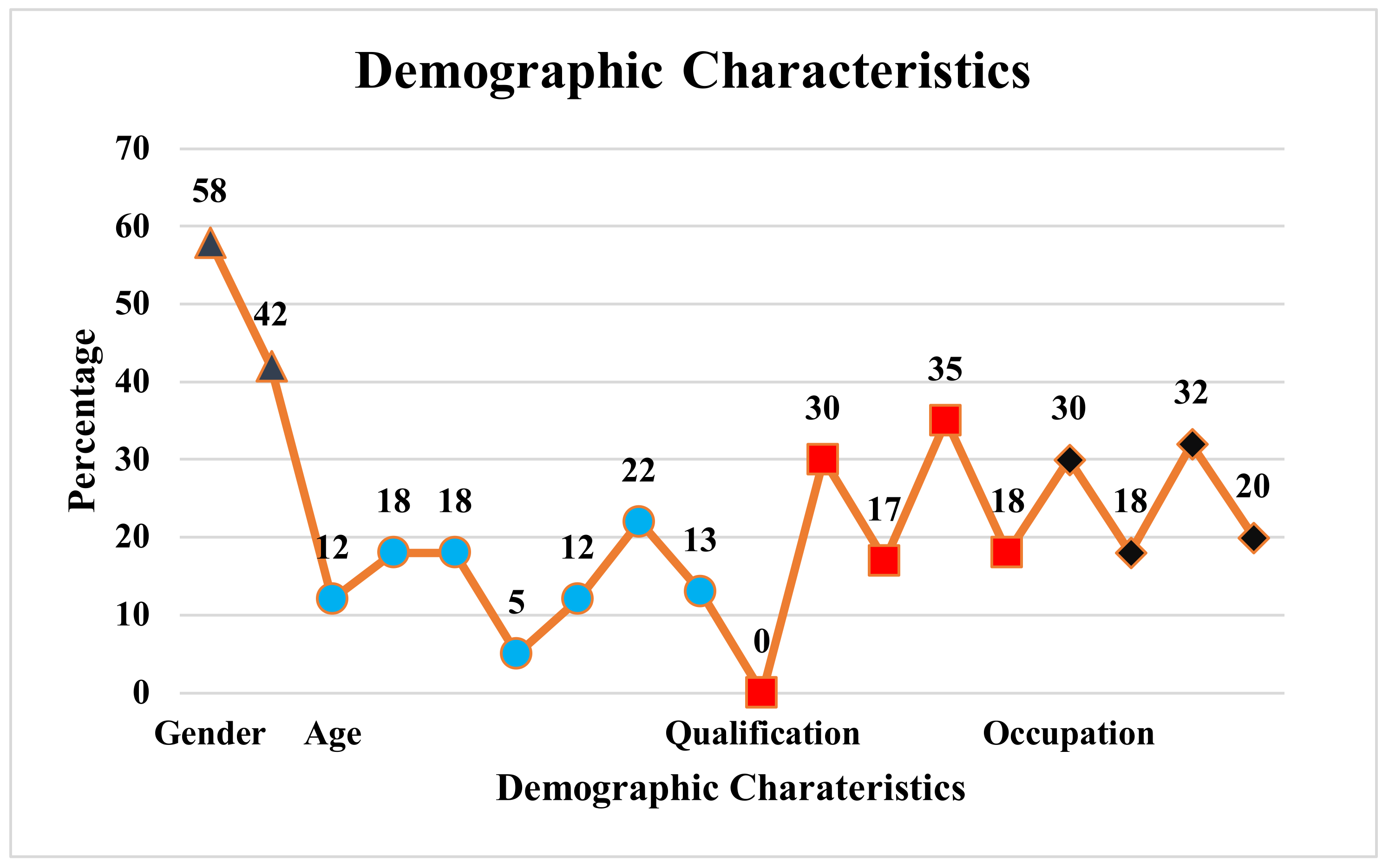
Twelve percent of learners were in the 18–20 age group, 18% of learners were in the 20–22 and 22–24 age group, 5% of learners were in the 24–28 age group, 12% of learners were in the 28–32 age group, 22% of learners were in the 32–34, and the remaining were in thh above 34 age group (shown in Figure 7. SeisTutor is explicitly created for the “Seismic-Data-Interpretation” domain. As a result, it is intended to be used by participants or learners belonging to the petroleum engineering and exploration domain. Thus, to quantify the effectiveness of SeisTutor, undergraduate learners (B.Tech/B.E. Petroleum engineering), teachers (Petroleum Engineering dept), and others (government exploration industry) are taken into consideration (refer to Figure 7).
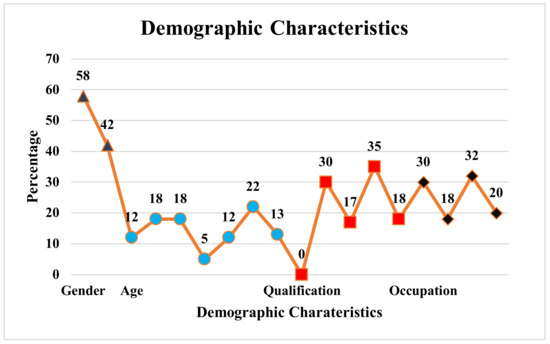
Figure 7.
Learner Demographic Characteristics.
The learner underwent a pretest as soon as they were registered with SeisTutor. Their learning style and grasping level (learning level) were adjudged as 28 learners, as mentioned above, were in study 1 (learner study with customized learning). Based on their responses in the pretest, the custom-tailored curriculum was determined, which is realigned and reorganized from the domain (content) capsule. SeisTutor examines every learner involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning), identifies their psychological state (emotions) during the learning session, and quantifies the degree of understanding of the concepts. The remaining learners in study 2 (learner study with customized learning) follow the standard curriculum for learning, i.e., contents in the same sequence (irrespective of their prior knowledge about the domain). Thus, all the learners follow the same learning path. The point to underline is that their pretest performance is not used for exclusive learning path recommendations. The learning session begins weekly for both the study groups and subsequent post-assessment tests.
4.2. Data Preparation
Before analysis, obtained data underwent a data screening phase. In this phase, the elimination of missing values and data normalization was performed. For deducing conclusion about the effectiveness of learning through SeisTutor, learner’s performances, i.e., prior knowledge test (pretest), understanding test, psychological state results, and quiz test (post-test) during learning, were taken into consideration. SPSS version 25 was used for accomplished analysis.
4.3. Min Max Normalization
The learner classification parameters (prior knowledge test (0–5), post-assessment test (0–5), learning gain (0–5), learner emotion (0–100)) of each learner were used and normalized using the methods called Min–Max. It converts a value of , and converges in the range of [A,B]. The formula for score standardization is specified below, where A is the lowest range; B is the highest range. In our case [A,B] is [0, 10];
5. Result and Discussions
The evaluation of SeisTutor was performed using the Kirkpatrick evaluation model. As discussed in Section 2, the Kirkpatrick evaluation prototype comprises of four-phase shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
5.1. Kirkpatrick Phase 1: Evaluation of Reaction
Evaluation of reaction as its name indicates the reaction (emotion) of the learner during learning or how far the learner likes the learning content and teaching process, i.e., pedagogy. SeisTutor incorporates an emotion recognition module and an open-end questionnaire (Learner Feedback).
The Min–Max normalization utilizes to maintain the uniformity, which converges the original values in the scope of [0, 10].
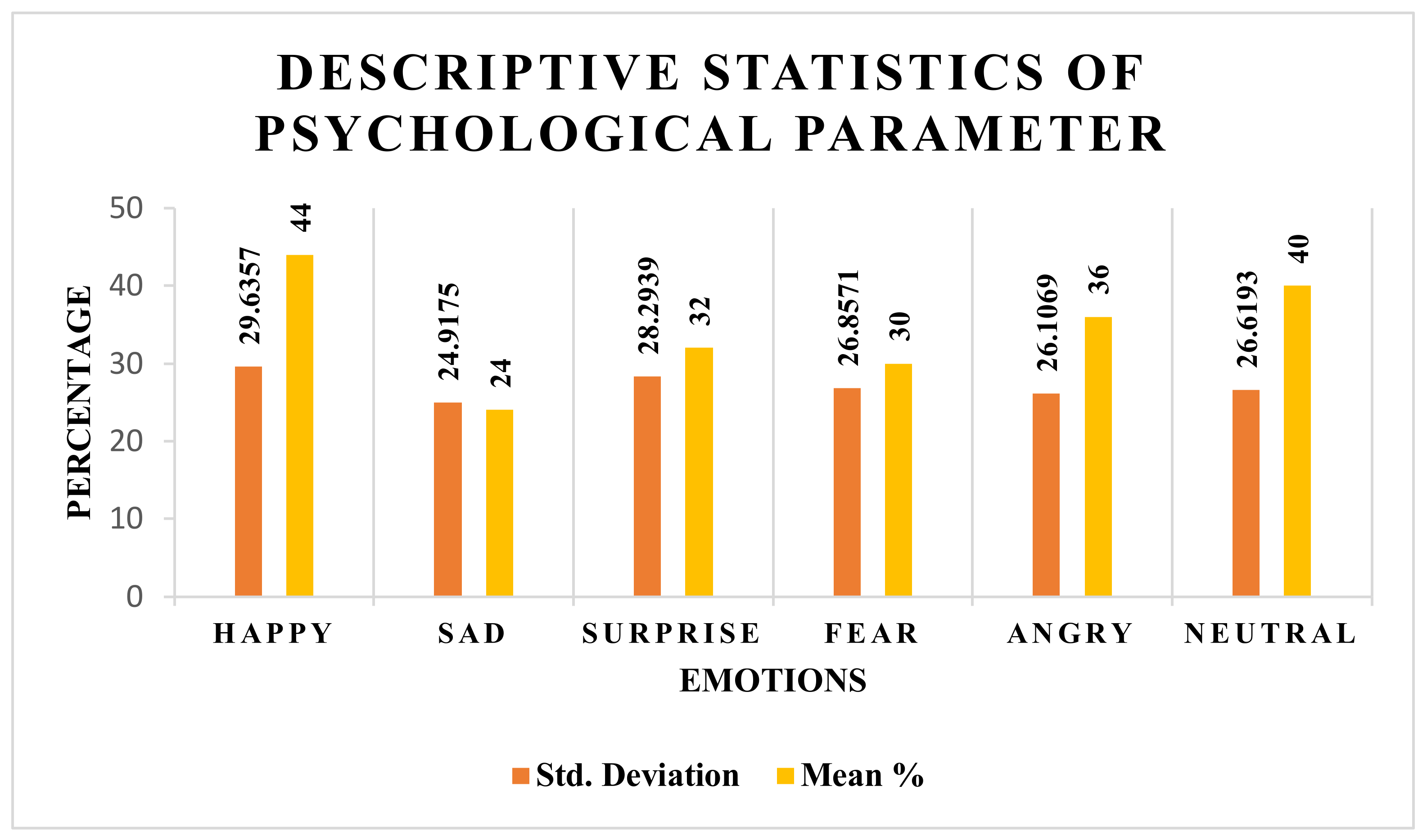
As mentioned above in Table 1, the psychological state of the learner was determined only for the applicants involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning). Thus, their descriptive states are shown in Figure 8. From the stats shown in Figure 9, the average mean score percentage among 28 applicants is 44% for the emotion happy, 40% for the emotion neutral, 36% for the emotion angry, 32% for the emotion surprise, 30% for the emotion fear, and 24% for the emotion sad. Thus, one can deduce with confidence that, on average, learners are happy with the learning content and teaching process, i.e., pedagogy.
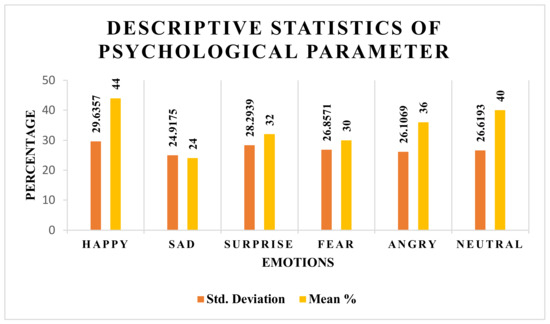
Figure 8.
Descriptive statistics of psychological parameter of learner for study 1 (learner study with customized learning).
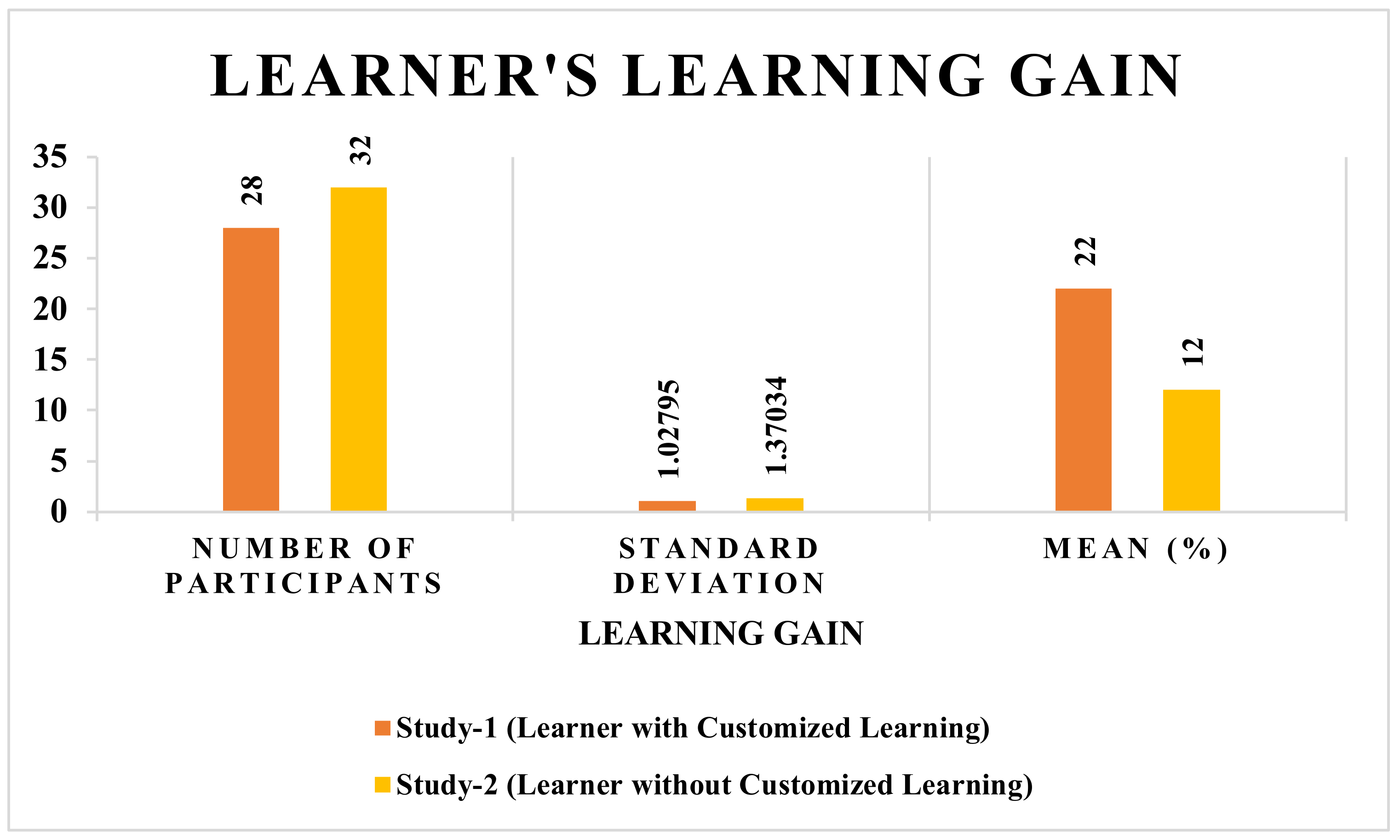
Figure 9.
Learning gain of study 1 (learner study with customized learning) and study 2 (learner study without customized learning).
5.2. Kirkpatrick Phase 2: Evaluation of Learning
Evaluation of learning, as its name indicates, is how effectively learners grasp the learning content. SeisTutor conducts a small quiz and degree of the understanding test to adjudge the learner’s overall learning.
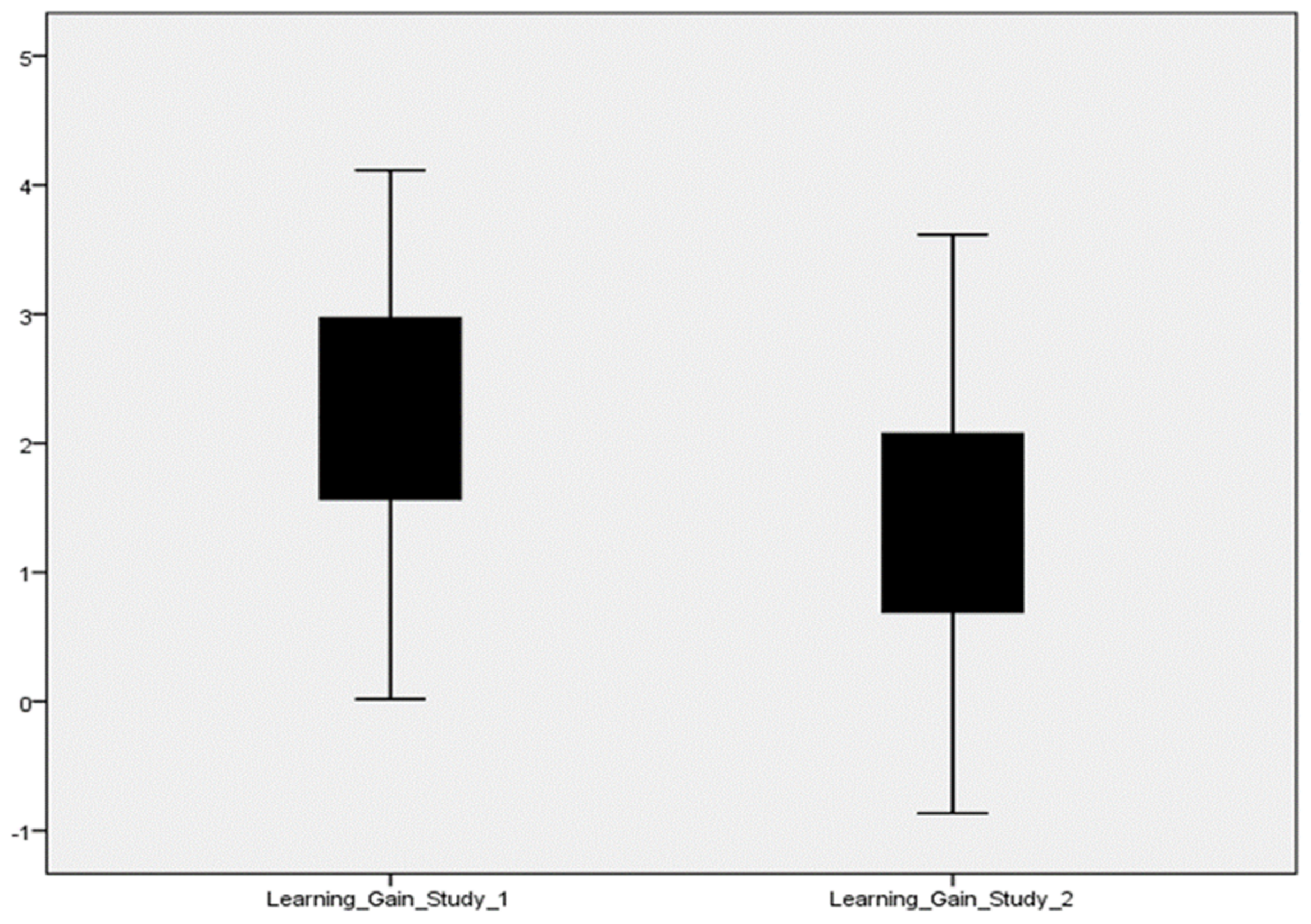
The average learning gain of applicants involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) is 22%, and in study 2 (learner study without customized learning), it is 12%. Thus, it is concluded that if learning material is offered as per the learner’s inclination with an exclusively designed curriculum based on the learner’s previous knowledge, then the proposed SeisTutor succeeds in enhancing the learner’s curiosity and interest, which indirectly enhance the overall learning gain (refer Figure 9 and Figure 10).
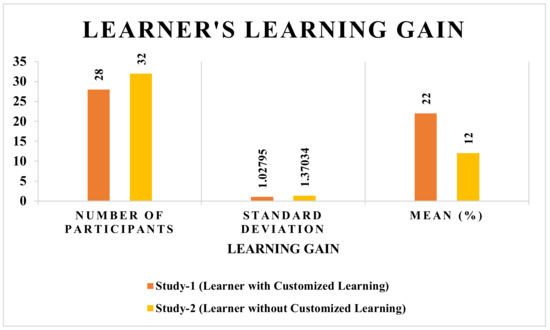
Figure 10.
Learner’s Learning Gain.
These tests were performed on learning gain and degree of understanding of study 1 (learner study with customized learning) through SeisTutor. Figure 10 illustrates the progressive learning gain of 22% discovered among learners, those applicants who participated in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) SeisTutor. Furthermore, this information (statistical) was used in the analysis, i.e., Bivariate Pearson Correlation.
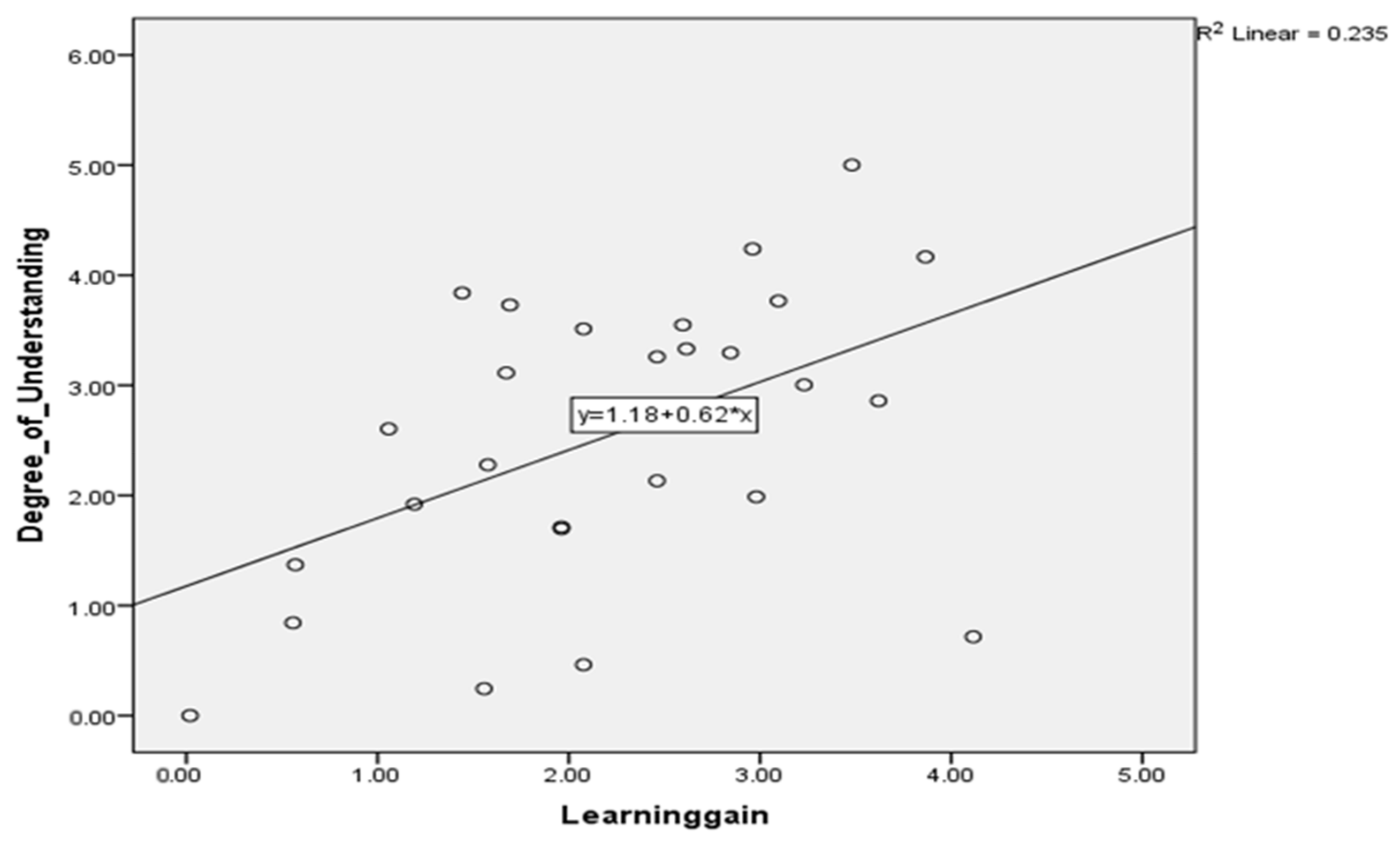
Understanding tests were designed and conducted only for study 1 (learner study with customized learning) because it strongly proves the effectiveness of learning gain achieved by intelligent features incorporated SeisTutor. Here, the correlation of learning gain with itself is one because a variable or parameter is perfectly interrelated. The Pearson correlation of learning gain with a degree of understanding is 0.484, and the significance is two-tailed, i.e., the p-value is less than 0.01 (refer to Table 2 and Table 3). Thus, one can confidently say that Learning gain and degree of understanding are statistically significant linear relationships. (see Figure 11).

Table 2.
Average mean score of learning gain and degree of understanding.

Table 3.
Correlation matrix between learning gain and degree of understanding.
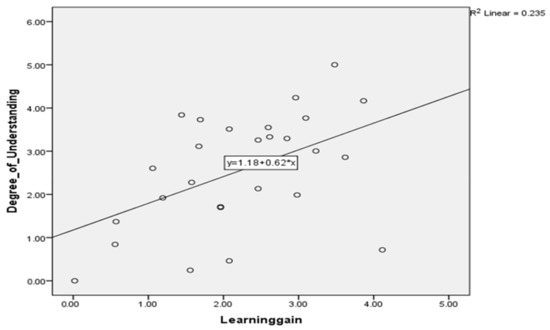
Figure 11.
Linear relationship with learning gain and degree of understanding.
5.3. Kirkpatrick Phase 3: Evaluation of Behaviour
Evaluation of behavior is quite tuff to quantify. In order to measure this, SeisTutor collects feedback from the applicants. As the learner completes all the learning concepts every week, SeisTutor requests the learner’s feedback. In this section, a conclusion from the learner feedback is drawn.
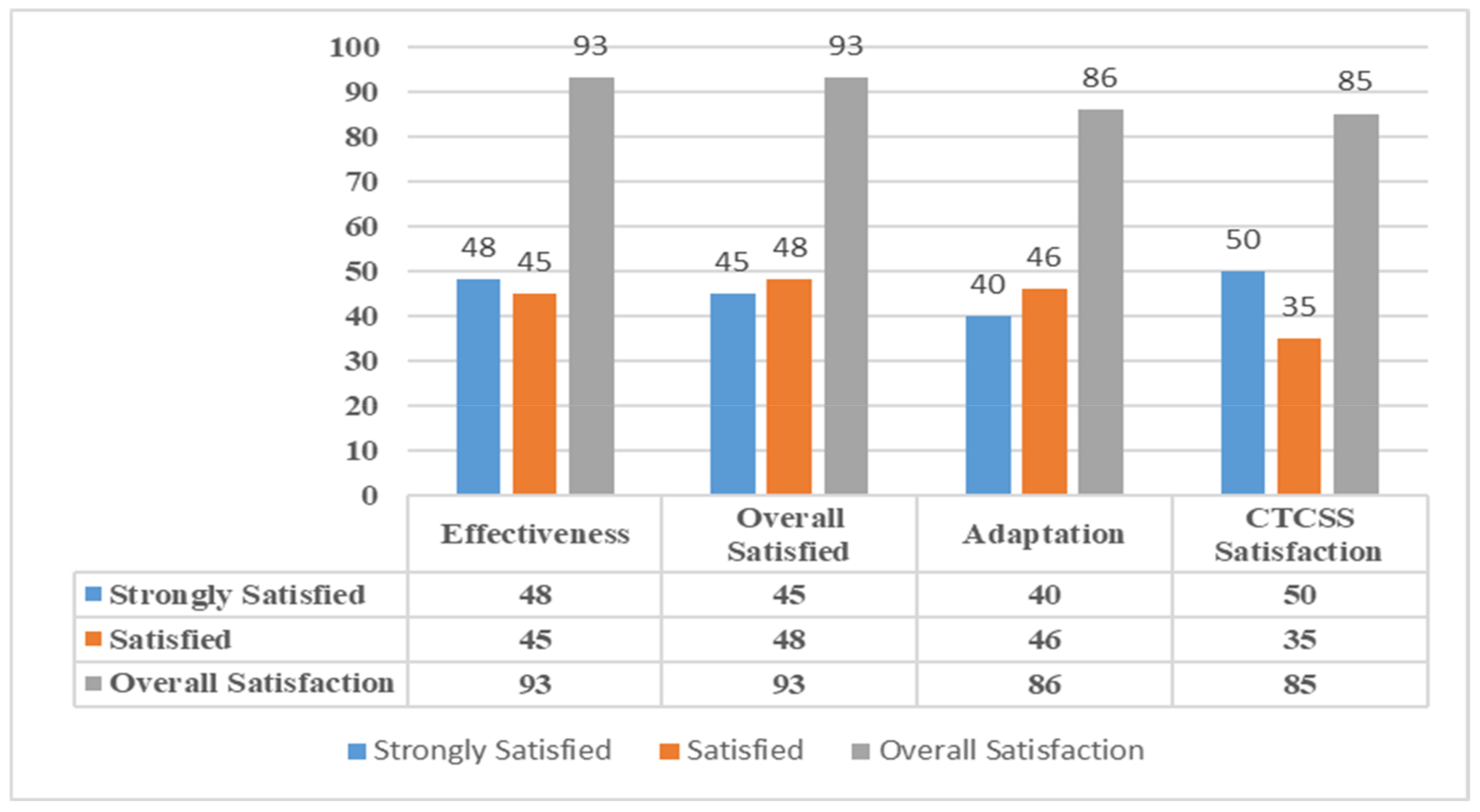
Learners who were the impeccable part of this evaluation of SeisTutor had a good perception of the system, and their feedbacks were very encouraging. It was shown in their reactions whether they would like to recommend the SeisTutor to others who need to take this study. Around 93% of the learners showed that they would recommend it to others, out of which 48% showed strong agreement, and the remaining 45% agreed on a recommendation as well (see Table 4 and Figure 12). The overall satisfaction with SeisTutor was around 93%, out of which 45% were strongly satisfied, and 48% were satisfied as well. It was also observed that learners’ studies became productive with the SeisTutor.

Table 4.
Learner feedback on effectiveness of SeisTutor.
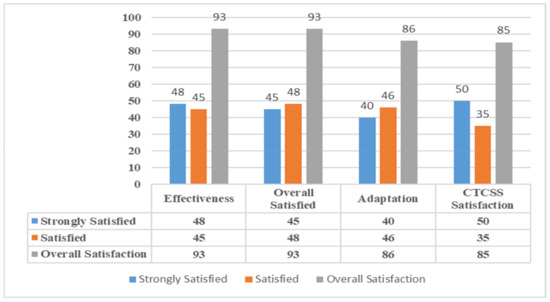
Figure 12.
Evaluation of learner behavior based on learner feedback.
Few questions were asked on the impact of the intelligent features provided by SeisTutor and were collected and summarized in Table 4 As some intelligent features are not provided for study 2 (learner study without customized learning) applicants, 28 effective feedback was taken into consideration from study 1 (learner study with customized learning) participants.
Most of the participants were happy with the tutoring strategy provided by the system, with 86% satisfaction, which includes 46% who were satisfied and 40% who were strongly satisfied. Eighty-five percent of participants felt that learning from their own learning experience made them perform better, with 40% who were strongly satisfied and 45% were satisfied. The participants were happy with the recommended exclusive curriculum by the system with 85% satisfaction, which includes 35% who were satisfied and 50% who were strongly satisfied. Most of the participants were happy with the recommended custom-tailored curriculum provided by the system, with 85% satisfaction, which includes 39% who were satisfied and 46% strongly satisfied. Ninety-two percent of participants agreed that the understanding test each week corresponds to the lesson taught, 39% strongly agreed, and 53% also agreed. Lastly, 82% of students agreed with the psychological parameter accurately determined with SeisTutor, with 39% who strongly agreed to this and 43% who were satisfied (see Table 5 and Figure 12).

Table 5.
Learner Feedback on Adaptivity of SeisTutor.
The overall impact of the support provided by SeisTutor on the learning process was assessed through the learner’s feedback questionnaire answered by 60 participants (see Table 6 and Figure 12). The analyzed results showed that 87% of the students were happy with SeisTutor supports, with 47% satisfied and 40% strongly satisfied. In addition, 78% of the students were happy with the system navigation support to find the needed information, with 43% satisfied and 35% strongly satisfied. Lastly, out of 80% of the students, 42% had a strong agreement, and 38% agreed that the SeisTutor pre-learning procedure was beneficial for learning.

Table 6.
Learner feedback on SeisTutor ongoing learning support.
The usefulness of the lesson components such as lesson explanations, revisions, presented quizzes, and the question hints in the learning process were evaluated in Table 7. The questionnaire feedback results show that 85% of students were happy with the content explained by SeisTutor, with 47% satisfied and 38% strongly satisfied. Moreover, 78% of students showed interest and agreed that the tutoring resources were adequate, with 35% strongly satisfied and 43% satisfied. It is clear that the quizzes and hints were realistic and focused on the learning contents provided by SeisTutor.

Table 7.
Learner Feedbacks on learning material, quizzes and overall SeisTutor support.
The impact of the interactive graphical user interface, content organization, and design features of SeisTutor in the learning process was evaluated through the learner questionnaire responses described in Table 8. The questionnaire results revealed that 77% of the learners were 40% strongly satisfied and 37% satisfied with the interactive GUI and content organization of SeisTutor. Eighty percent of the learners were 44% strongly satisfied and 36% satisfied with SeisTutor to compel and support to complete the quizzes and lessons. Finally, students were happy with the account setup process with the system, which maintains the learners learning progress, grades, and basic account information.

Table 8.
Learner Feedback on learning material presentation and on overall SeisTutor’s look and feel.
The learner’s overall evaluation of the SeisTutor showed that 82% of learners agreed that tutoring should begin based on the learner profile considering their learning style and previous knowledge. Most of the students were unaware of their learning style, and about 80% of students never knew about it. Most of the students liked the artificial intelligence features such as automatic selection of the tutoring strategies, dynamically assessing the learner attainment, and flipping the tutoring plan or strategy.
The learner’s feedback questionnaire responses were retrieved and analyzed in an accessible fashion. Some learners put their suggestions to improve the productivity of SeisTutor. Most of the suggestions were general and related to the improvement of the system, and few were pessimistic regarding improvement of the quality of learning contents, improving the quality of the video lessons, and hints provided by the system. At last, through the overall evaluation of SeisTutor, 87% of learners agreed that they improved their learning performance and outcomes.
5.4. Kirkpatrick Phase 4: Evaluation of Results
Evaluation of results illustrates the overall impact of learning on the learner. In order to quantify the effectiveness of learning, paired wise sample T-test was performed on existing information, i.e., pretest and post-test results of participants involved in both the studies (study 1 (learner study with customized learning) and study 2 (learner study without customized learning)). Here two cases are taken into consideration.
Case_1:
A Paired_Sampled_T-Test performed on study 1 (learner study with customized learning) consists of intelligent features depicted in Table 1;
Hypothesis_Case_1.0:
Let the participants involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) have similar pretest and post-test mean scores;
Hypothesis_Case_1.1:
Let the participants involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) not have similar pretest and post-test mean scores;
Case_2:
A Paired-Sampled-T-Test performed on study 2 (learner study without customized learning), which consist of feature depicted in Table 1;
Hypothesis_Case_2.0:
Let the participants involved in study 2 (learner study without customized learning) have similar pretest and post-test mean scores;
Hypothesis_Case_2.1:
Let the participants involved in study 2 (learner study without customized learning) not have similar pretest and post-test mean scores.
The calculated T value (,) for study 1 (learner study with customized learning) is 11.410, (see Table 9 and Table 10. On average post-test scores were 2.21786 points higher than pretest scores. Here the calculated is greater that , thus hypothesis 1.0 is rejected. From Table 9 and Table 10 one can deduce with confidence that there is a significant difference between pretest and post-test scores. The calculated T value (,) for study 2 (learner study without customized learning) is 5.312, (see Table 11 and Table 12). On average, post-test scores were 1.24719 points higher than pretest scores. Here the calculated , is greater than , thus hypothesis 2.0 is rejected. From Table 11 and Table 12, one can deduce with confidence that there is a significant difference between pretest and post-test scores.

Table 9.
Statistical results of paired sample T-test of study 1 (learner study with customized learning).

Table 10.
Paired sample T-test results of study 1 (learner study with customized learning).

Table 11.
Statistical results of paired sample T-test of study 2 (learner study without customized learning).

Table 12.
Paired sample T-test results of study 2 (learner study without customized learning).
Both the studies reject the null hypothesis, which means both the studies provide effective training. However, this research aims to identify which study has a high impact on enhancing learning gain. In conclusion, the aim of both the studies was compared. Study 1 (learner study with customized learning) is higher than Study 2 (learner study without customized learning). Thus, study 1 (learner study with customized learning) has a significant difference in the post tutoring and pretest scores and provides more effective training than study 2 (learner study without customized learning).
From the research, it was observed that quality education plays a vital role in providing sustainable development of society and its need. Quality education includes a personalized learning environment and teaching process.
Learners of all ages are empowered with the knowledge and skills to confront the linked global challenges that we face, including climate change, environmental degradation, and the loss of biodiversity. Education for sustainable development empowers learners of all ages.
An intelligent tutoring system named SeisTutor was developed to accomplish the objective of personalized learning, which observes the learner’s preferences, grasping level, and knowledge level and recommends a personalized curriculum (learning environment) and personalized teaching process. This analysis concludes that the intelligent incorporated SeisTutor used in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) outperforms the SeisTutor used in study 2 (learner study without customized learning) in providing custom-tailored intended curriculum, identifying learner sentiments while learning, and computing the learner’s overall degree of knowledge that meets the learner’s sustainable needs. Thus, SeisTutor used in study 1 can provide effective quality education for sustainability.
Practicing sustainability empowers humans to construct knowledge, explore values, and develop an appreciation of the environment and its relationship to their worlds. This lays the foundations for sustainable education.
6. Conclusions
This article demonstrates the proposed sustainable personalized intelligent tutoring system prototype, named as SeisTutor. From the research, it was noted that a learner receives repetitive learning content, which indirectly disorients the learner. Thus, to address this issue, a bug model was utilized, which analyzes the bugs and recommends the custom-tailored curriculum to the learner. This technique helps to bring empathy to ITS. SeisTutor is not a passive tutor; it also analyses the learner’s behavior, i.e., the psychological state of the learner during learning, which helps to understand the learner’s experience with SeisTutor (about learning content). The experimental results revealed that SeisTutor utilized by participants in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) provided a customized learning sequence or path of learning material that endorses effective learning. Experimental analysis reveals the effective learning gain (when the learner receives the custom-tailored sequenced learning material) of 44.34% compared to SeisTutor used in study 2 (learner study without customized learning) (not sequenced learning material). In order to evaluate the overall effectiveness of SeisTutor, the Kirkpatrick four-phase evaluation model was utilized. The analysis reveals that the participants involved in study 1 (learner study with customized learning) attain, while study 2 (learner study without customized learning) attains study 1 (learner study with customized learning) provides effective learning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. and V.K.G.; methodology, N.S.; software, A.K.M.; validation, A.K.M. and R.K.M.; formal analysis, N.S.; investigation, V.K.G.; resources, N.N.; data curation, R.K.M. and N.N.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, N.S. and V.K.G.; visualization, A.K.M.; supervision, R.K.M. and V.K.G.; project administration, R.K.M. and N.N.; funding acquisition, N.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ghosn-Chelala, M. Exploring sustainable learning and practice of digital citizenship: Education and place-based challenges. Educ. Citizsh. Soc. Justice 2018, 14, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybach, I. Institutional aspects of educational quality management in higher educational establishments. Econ. Dev. 2019, 18, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeren, E. Understanding Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 4 on “quality education” from micro, meso and macro perspectives. Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guijarro, F.; Poyatos, J. Designing a Sustainable Development Goal Index through a Goal Programming Model: The Case of EU-28 Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanemann, U. Examining the application of the lifelong learning principle to the literacy target in the fourth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 4). Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T. Research on educational leadership and management. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 2018, 46, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K. The human side of management. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2019, 33, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siemens, G. Connectivism: A Learning Theory for the Digital Age. 2004. Available online: www.elearnspace.org/Articles/connectivs.htm (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Beetham, H.; Sharpe, R. Rethinking Pedagogy for Digital Age: Designing and Delivering E-Learning; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Samah, N.A.; Yahaya, N.; Ali, M.B. Individual differences in online personalized learning Environment. Educ. Res. Rev. 2011, 6, 516–521. [Google Scholar]
- De Castell, S.; Droumeva, M.; Jenson, J. Building as interface: Sustainable educational ecologies. Medien. Z. Für Theor. Und Prax. Der Medien. 2014, 24, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burbules, N.C. Meanings of “ubiquitous learning”. In Ubiquitous Learning; Cope, B., Kalantzis, M., Eds.; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sharples, M.; De Roock, R.; Ferguson, R.; Gaved, M.; Herodotou, C.; Koh, E.; Kukulska-Hulme, A.; Looi, C.; McAndrew, P.; Rienties, B.; et al. Innovating Pedagogy 2016: Open University Innovation Report 5; Keynes, M., Ed.; Institute of Educational Technology, Open University: Edinburgh, Scotland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burbules, N.C. El aprendizaje ubicuo: Nuevos contextos, nuevos procesos. Rev. Entramados Educ. Y Soc. 2014, 1, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Burbules, N.C. Ubiquitous learning and the future of teaching. In Teacher Education in a Transnational World; Bruno-Jofre, R., Johnston, S., Eds.; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2014; pp. 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, R.W.; Yazdani, M. (Eds.) Artificial Intelligence and Education: Learning Environments and Tutoring Systems; Intellect: Bristol, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Nwana, H.S. Intelligent tutoring systems: An overview. Artif. Intell. Rev. 1990, 4, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.F. Teaching Machines. Science 1961, 205, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Uhr, L. Teaching machine programs that generate problems as a function of interaction with students. In Proceedings of the 1969 24th National Conference, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 August 1969; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sleeman, D.; Brown, J.S. Introduction: Intelligent Tutoring Systems; Intelligent Tutoring Systems, Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, P.; Hartley, J.R. Some learning models for arithmetic tasks and their use in computer based learning. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 1971, 41, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppes, P. On using computers to individualize instruction. In The Computer in American Education; Association for Educational Data Systems: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gertner, A.S.; VanLehn, K. Andes: A coached problem solving environment for physics. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference, Berlin, Germany, 8–11 June 2022; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Conati, C.; Gertner, A.; Vanlehn, K.; Druzdzel, M.J. Online student modeling for coached problem solving using Bayesian networks. In User Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H. Enhancement of student learning performance using personalized diagnosis and remedial learning system. Comput. Educ. 2011, 56, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoran, X.; Di, Z.; Fu, L.W.; Tak-Lam, W.; Yanghui, R.; Simon, H.W. Discover Learning Path for Group Users: A ProÞle-based Approach. Neurocomputing 2017, 254, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, T.-C.; Wang, T.-I. A mining based approach on discovering courses pattern for constructing suitable learning path. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4156–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, R. Dynamic Composition of Curriculum for Personalized E-Learning; Knowledge Science & Engineering Institute, Beijing Normal University: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Karampiperis, P.; Sampson, D. Adaptive Instructional Planning using Ontologies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT’04), Joensuu, Finland, 30 August–1 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dron, J. Achieving Self-Organisation in Network-Based Learning Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brighton, Brighton, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.M. Intelligent web-based learning system with personalized learning path guidance. Comput. Educ. 2008, 51, 787–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbonifo, O.C.; Obolo, O.A. Genetic Algorithm-Based Curriculum Sequencing Model for Personalised E-Learning System. Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng. 2018, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seridi, H.; Sari, T.; Sellami, M. Adaptive Instructional Planning in Intelligent Learning Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT’06), Kerkrade, The Netherlands, 5–7 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, C.-M.; Chen, C.-M.; Chang, M.-H.; Chen, S.-C. Intelligent Web-based tutoring System with Personalized Learning Path Guidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT’07), Niigata, Japan, 18–20 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bonabeau, E.; Dorigo, M.; Theraulaz, G. Swarm Intelligence: From Natural to Artificial Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Brusilovsky, P.; Schwarz, E.; Weber, G. ELMART: An intelligent Tutoring System on World Wide Web. In Third International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems ITS-96; Frasson, C., Gauthier, G., Lesgold, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; pp. 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Dahbi, A.; Elkamoun, N.; Berraissoul, A. Adaptation and Optimisation of Pedagogical Paths by Ant’s Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information and Communication Technology (ICTTA’06), Damascus, Syria, 24–28 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg, B.; Van Es, R.; Tattersall, C.; Janssen, J.; Manderveld, J.; Brouns, F.; Kurves, H.; Koper, R. Swarm-based Sequencing recommendations in E-Learning. In Proceedings of the 2005 5th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA’05), Warsaw, Poland, 8–10 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, D.L. Techniques for evaluating training programs. Train. Dev. J. 1979, 33, 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, D. Evaluating Training Programs; Berrett-Koehler: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, R. A critical analysis of evaluation practice: The Kirkpatrick model and the principle of beneficence. Eval. Program Plan. 2004, 27, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, G.J.; Kleiner, B.H. How to measure management training and development effectiveness. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 1990, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, D.L.; Kirkpatrick, J.D. The Transfer of Learning to Behavior: Using the Four Levels to Improve Performance; Berrett Koehler Publication: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, D.L.; Kirkpatrick, J.D. Evaluating Training Programs: The Four Levels, 3rd ed.; Berrett Koehler Publication: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, D.L.; Kirkpatrick, J.D. Implementing the Four Levels; Berrett Koehler Publication: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, M.S.; Holton, E.F.; Swanson, R.A. The Adult Learner, 5th ed.; Gulf Publishing Company: Houston, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, U.D.; Schneckenberg, D. Changing Cultures in Higher Education: Moving Ahead to Future Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy, G.M.; Buller, P.F. Five uneasy pieces in the training evaluation puzzle. Train. Dev. J. 1990, 44, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.J. A rational approach to evaluating training programs including calculating ROI. J. Lend. Credit. Risk Manag. 1997, 79, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, T.C.; Hedberg, J.G. Interactive Learning Systems Evaluation; Educational Technology: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, J.L.; Sanders, J.R.; Worthen, B.R. Program Evaluation: Alternative Approaches and Practical Guidelines, 3rd ed.; Allyn and Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Musal, B.; Taskiran, C.; Gursel, Y.; Ozan, S.; Timbil, S.; Velipasaoglu, S. An example of program evaluation project in undergraduate medical education. Educ. Health 2008, 21, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, J. ABC of learning and teaching in medicine: Evaluation. Br. Med. J. 2003, 326, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, A.; Peersman, G.; Oliver, S.; Mauthner, M.; Oakley, A. A systematic review of the effectiveness of health promotion interventions in the workplace. Occup. Med. 1999, 49, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinert, Y.; Mann, K.; Centeno, A.; Dolmans, D.; Spencer, J.; Gelula, M.; Prideaux, D. A systematic review of faculty development initiatives designed to improve teaching effectiveness in medical education: BEME Guide No. 8. Med. Teach. 2006, 28, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, A.A.; Al-Bareeq, J.M.; Al-Halili, A. Evaluation of research writing workshop. Bahrain Med. Bull. 2003, 25, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Praslova, L. Adaptation of Kirkpatrick’s four level model of training criteria to assessment of learning outcomes and program evaluation in Higher Education. Educ. Assess. Eval. Account. 2010, 22, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitchener, J.; Young, S.; Cameron, D. The effect of different types of corrective feedback on ESL student writing. J. Second Lang. Writ. 2005, 14, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, N.; Tapper, J. Discipline specific academic writing: What content teachers comment on. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2000, 19, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polio, C.; Fleck, C.; Leder, N. “If I Only Had More Time:” ESL Learners’ Changes in Linguistic Accuracy on Essay. J. Second. Lang. Writ. 1998, 7, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, N.; Klobucar, A. Automated essay evaluation and the teaching of writing. In Handbook of Automated Essay Evaluation: Current Applications and New Directions; Shermis, M.D., Burstein, J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 16–35. [Google Scholar]
- Aryadoust, V.; Mehran, P.; Alizadeh, P. Validating a computer-assisted language learning attitude instrument used in Iranian EFL context: An evidence-based approach. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. J. 2016, 29, 561–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, J.; Kayser-Kirkpatrick, W. The Kirkpatrick Four Levels: A Fresh Look after 55 Years; Kirkpatrick Partners: Ocean City, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Ahuja, N.J.; Kumar, A. A Novel Architecture for Learner-Centric Curriculum Sequencing in Adaptive Intelligent Tutoring System. J. Cases Inf. Technol. (JCIT) 2018, 20, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Ahuja, N.J. Bug Model Based Intelligent Recommender System with Exclusive Curriculum Sequencing for Learner-Centric Tutoring. Int. J. Web-Based Learn. Teach. Technol. (IJWLTT) 2019, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Ahuja, N.J. Implementation and Evaluation of Intelligence Incorporated Tutoring System. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. (IJITEE) 2019, 8, 4548–4558. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Ahuja, N.J. Assessment of Learning Style of Learner using I 2A 2 Learning Style Model. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. (IJITEE) 2019, 8, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Ahuja, N.J. Empirical Analysis of Explicating the Tacit Knowledge Background, Challenges and Experimental findings. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. (IJITEE) 2019, 8, 4559–4568. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, A.; Ahuja, N.J. Implementation and Evaluation of Personalized Intelligent Tutoring System. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. (IJITEE) 2019, 8, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).