Endplate Design and Topology Optimization of Fuel Cell Stack Clamped with Bolts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Endplate Design, Materials and Methodology
3. Results and Discussions
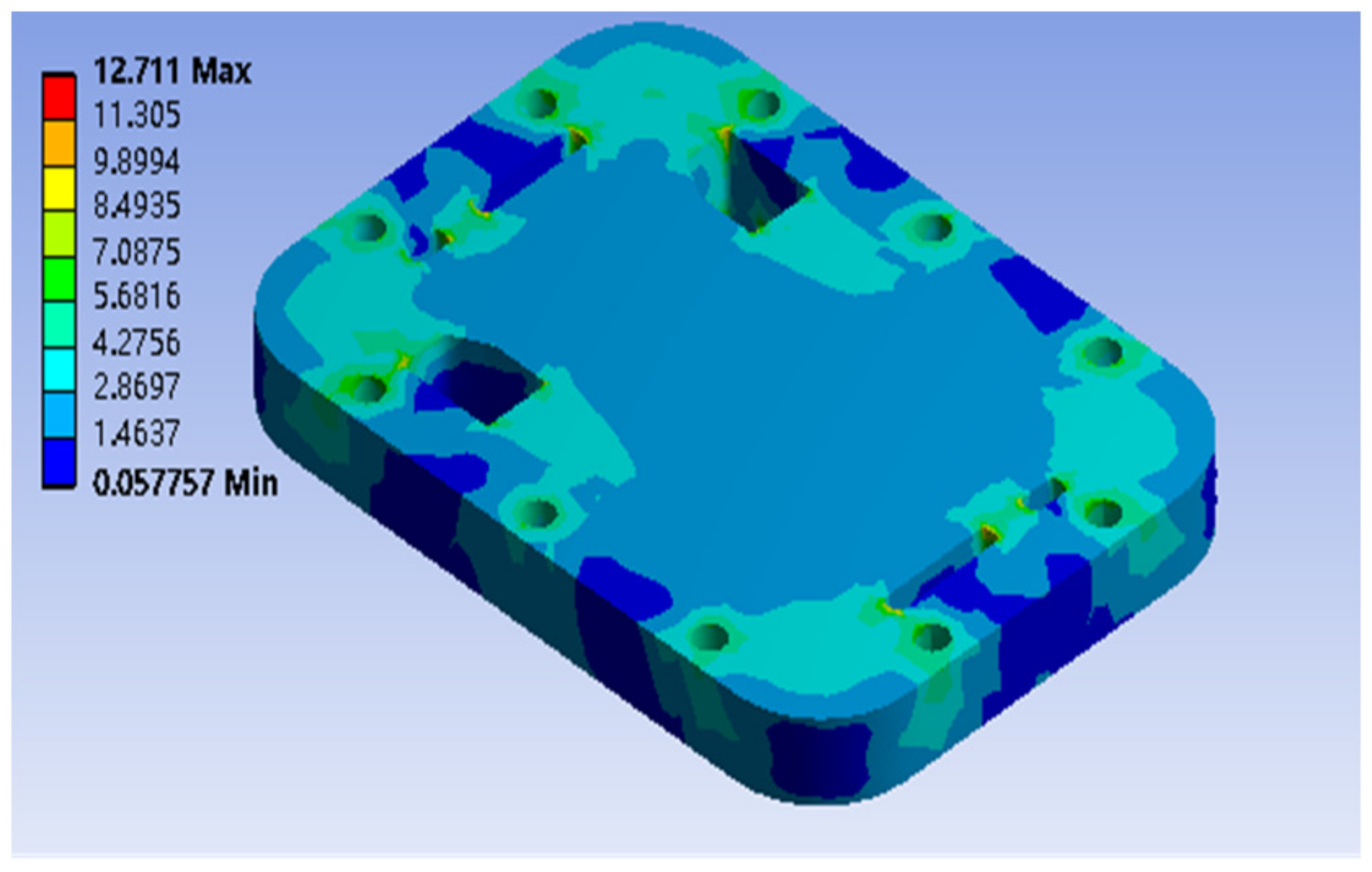
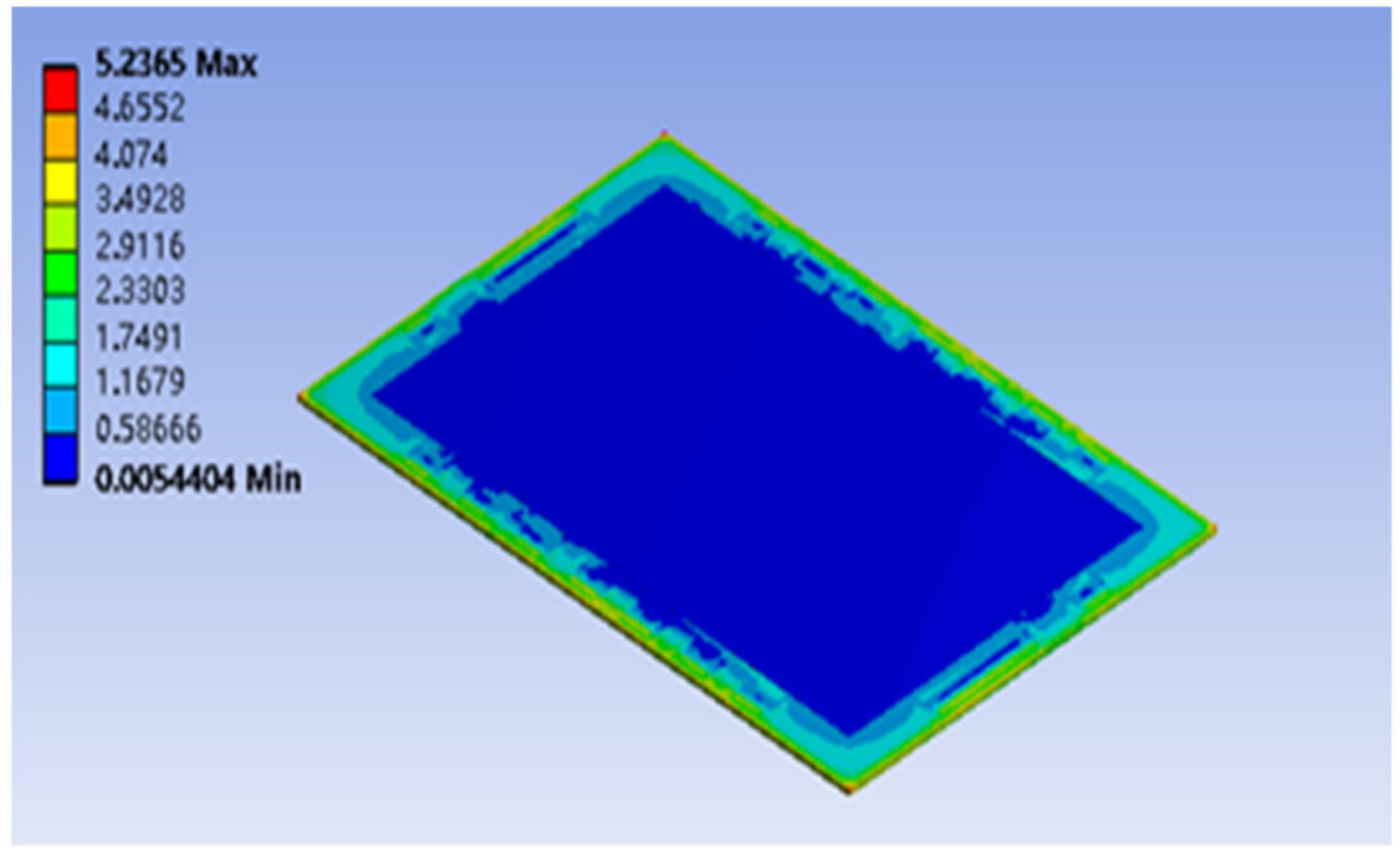
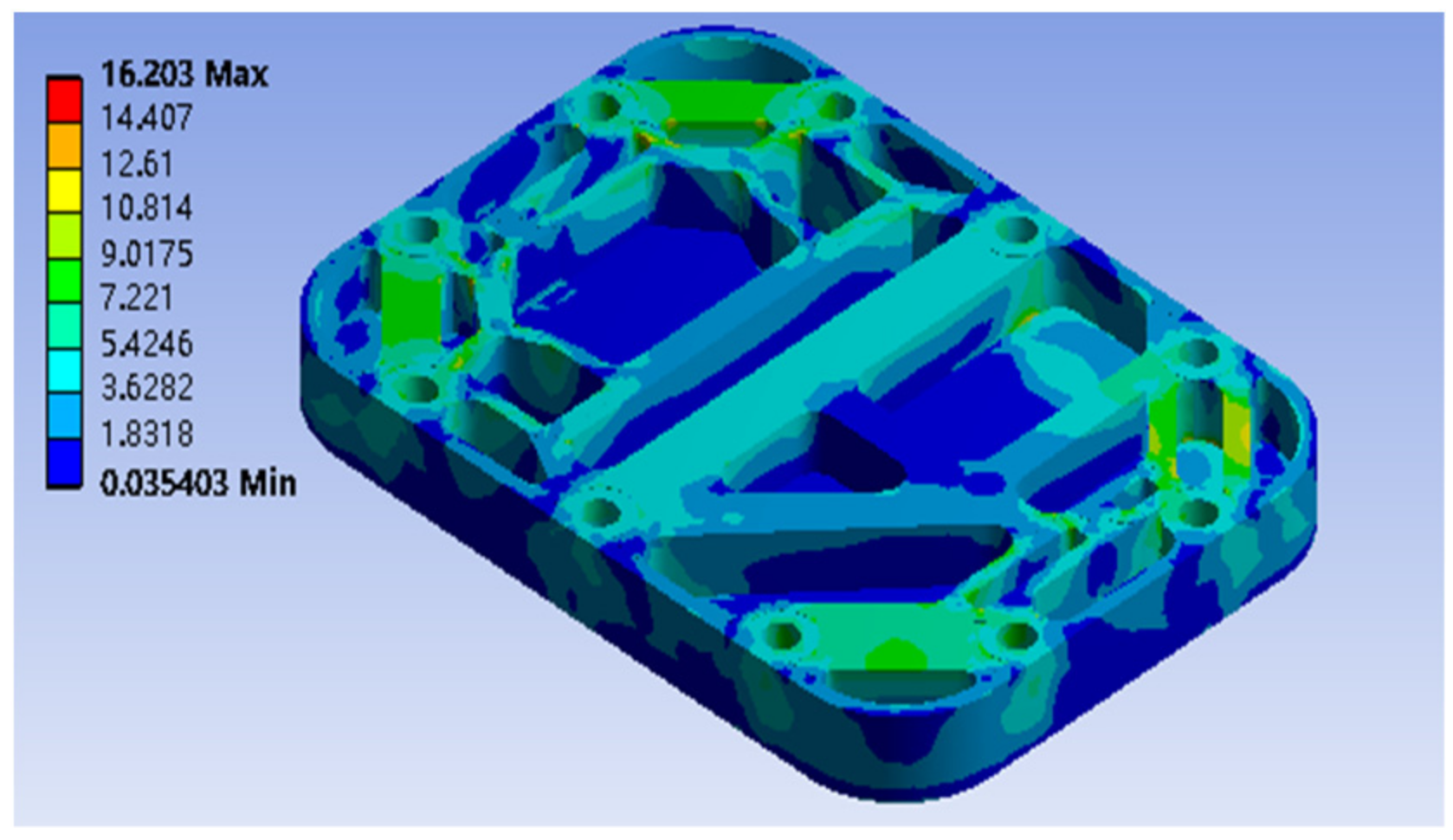
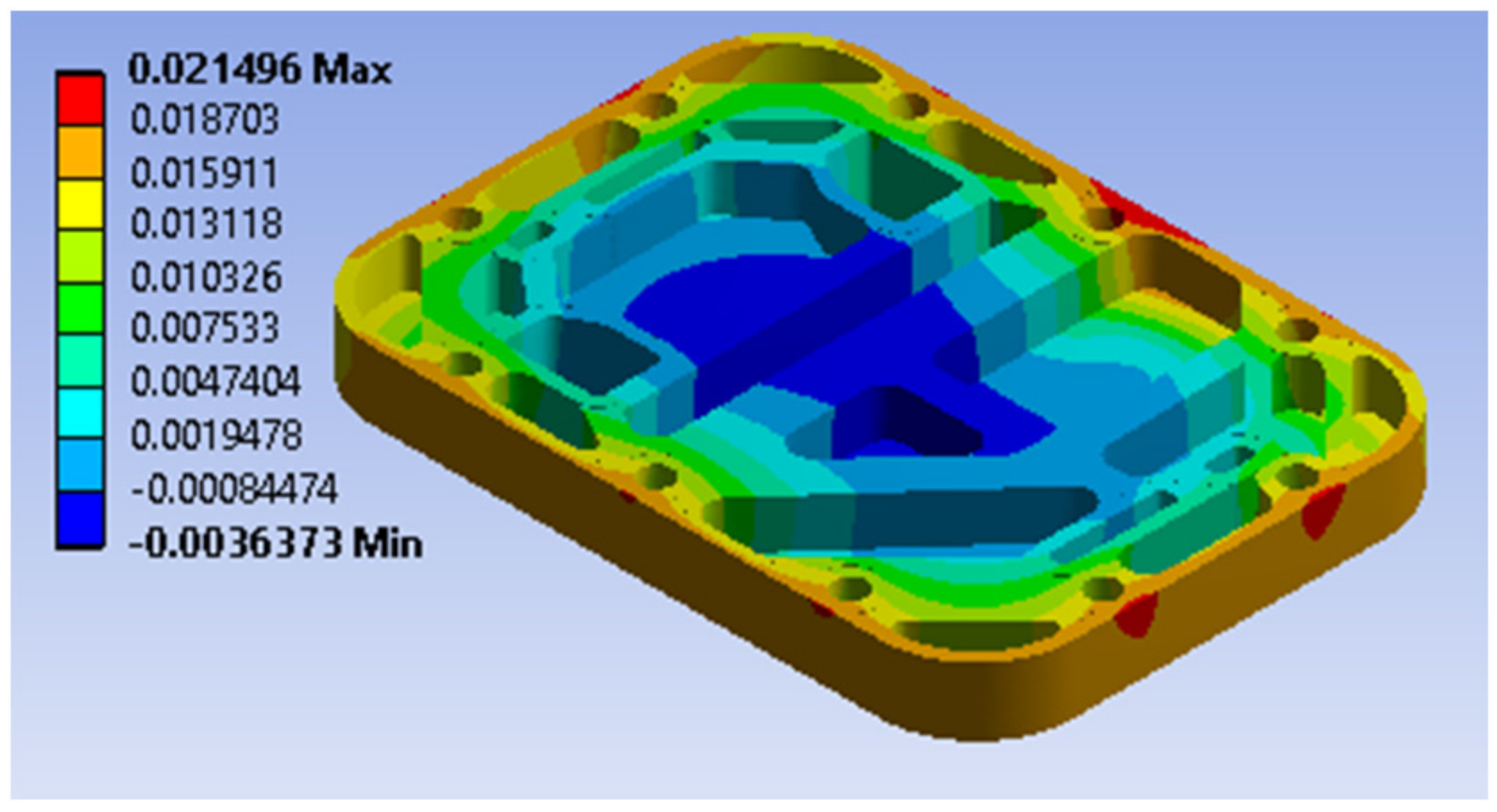
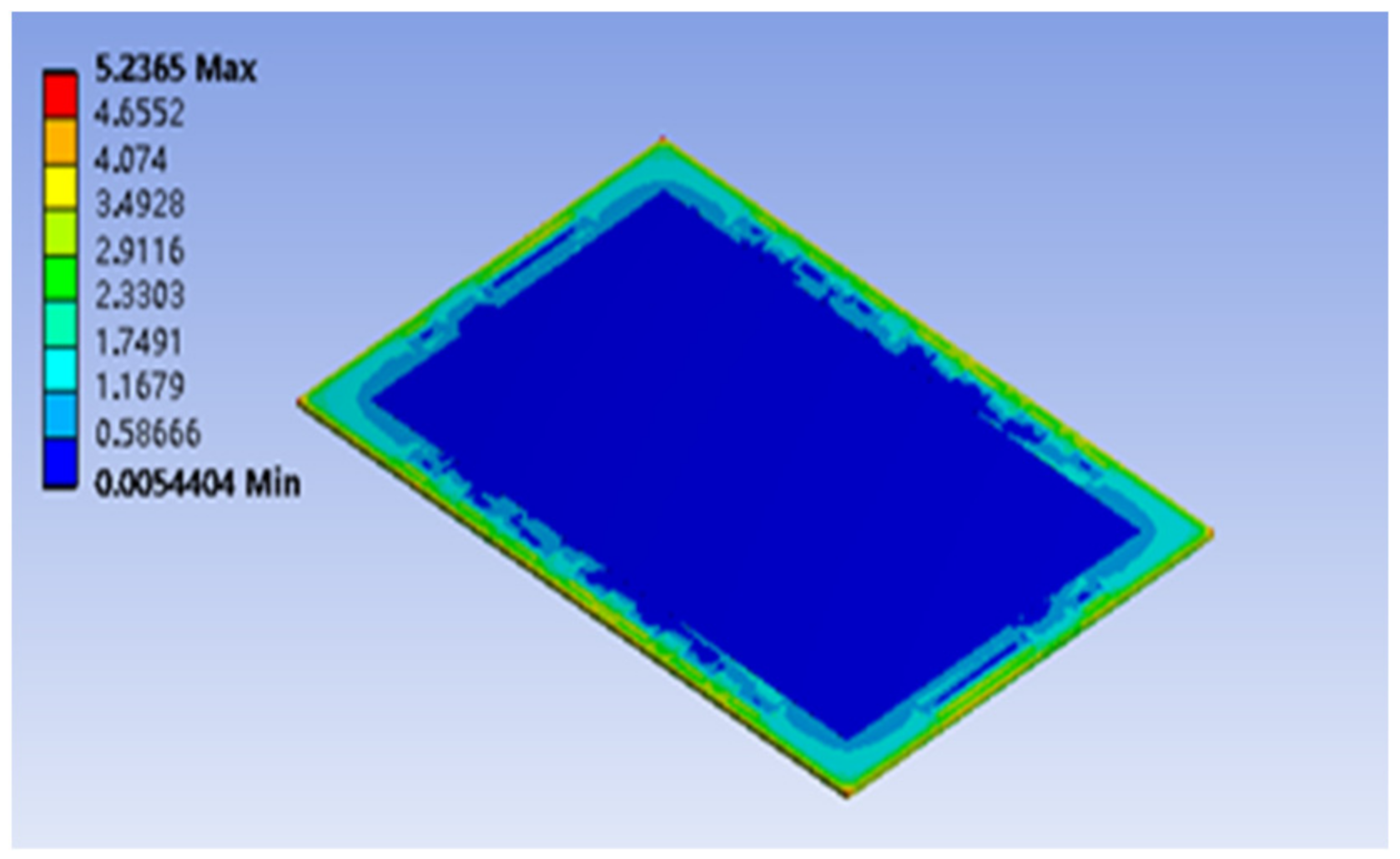
3.1. Static Results of Endplates
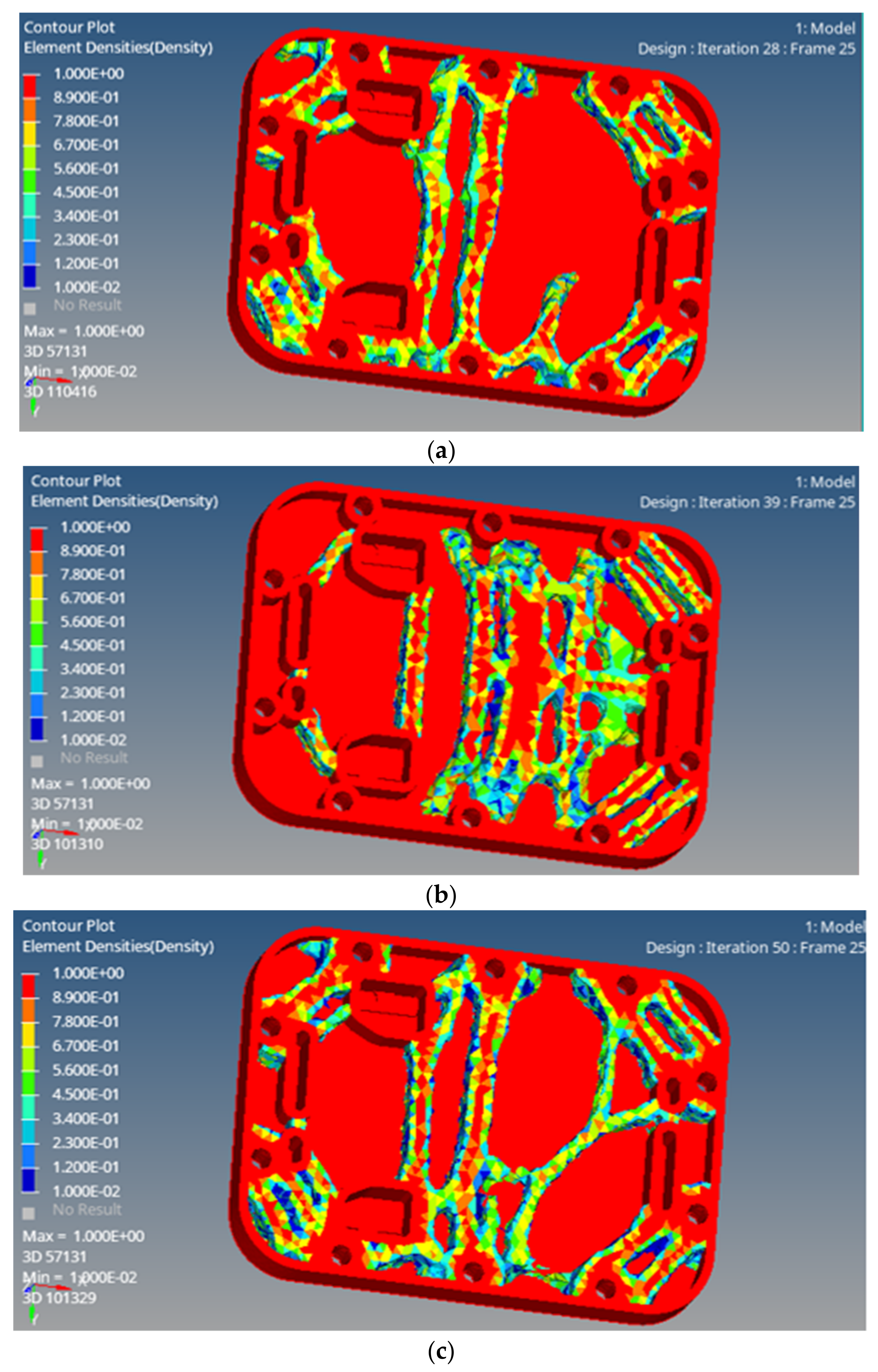
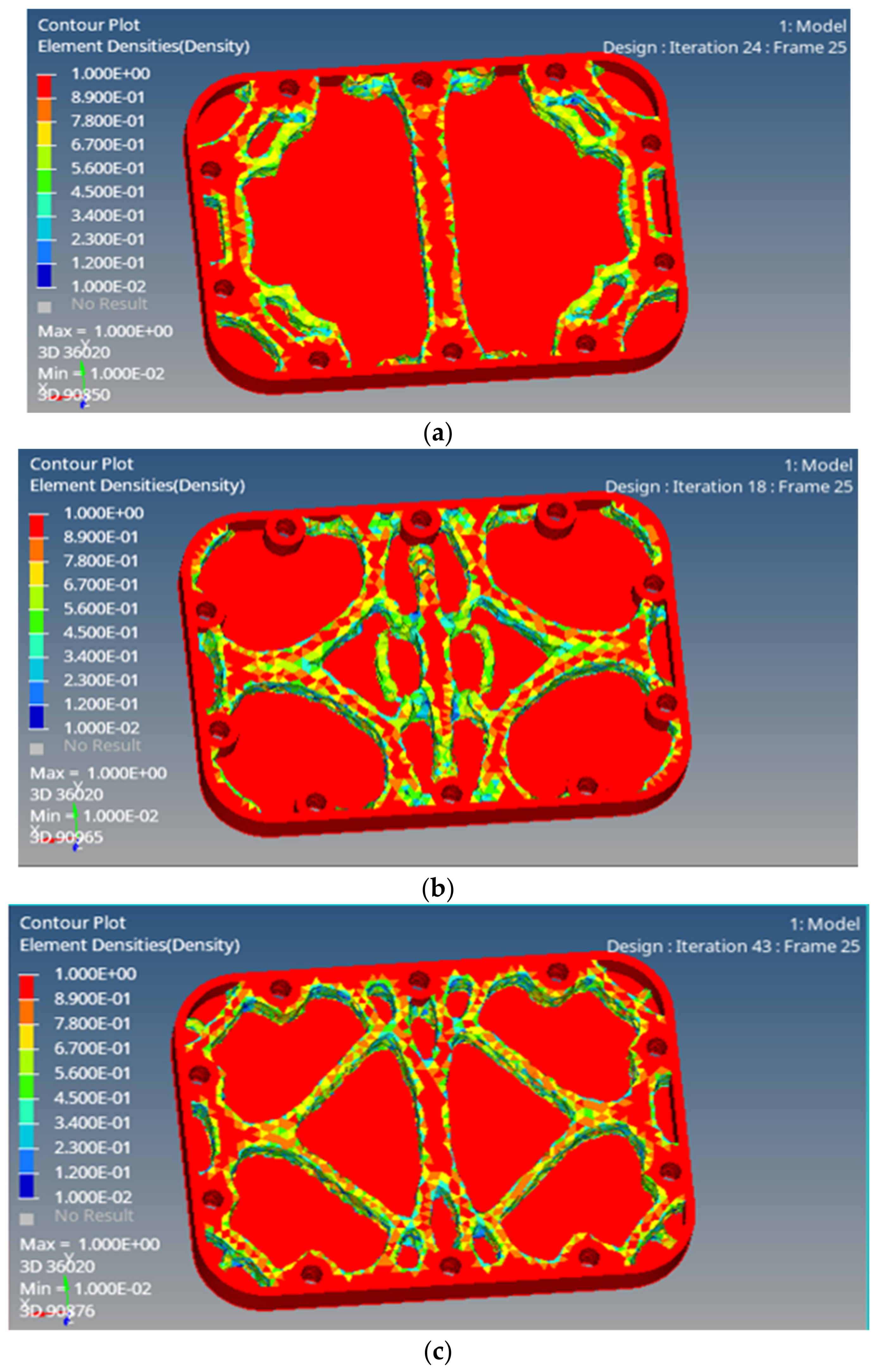
3.2. Topology Optimization
4. Conclusions
- Under the clamping force, the endplate presents a shape with a relatively convex center and a relatively concave around the corners. The stresses at the supply and discharge ports are relatively large due to stress concentration.
- After the topology optimization of the endplate, the mass of the intake endplate can be reduced by 35%, and the mass of the blind endplate can be reduced by 46%, while maintaining the stress distribution uniformity of the endplates, the goal of a lightweight endplate is achieved.
- Due to the difference in structure between the intake endplate and the blind endplate, there are also obvious differences in topology results, which need to be designed separately.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajanovic, A.; Haasa, R. Prospects and impediments for hydrogen and fuel cell vehicles in the transport sector. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 46, 10049–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Wilberforce, T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Fuel cell application in the automotive industry and future perspective. Energy 2021, 214, 118955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Martinez, A.; Hong, P.; Xu, H.; Bockmillera, F.R. Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Station Network for Automobiles: Status, Technology, and Perspectives. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millichamp, J.; Mason, T.J.; Neville, T.P.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Jervis, R.; Shearing, P.R.; Brett, D.J.L. Mechanisms and effects of mechanical compression and dimensional change in polymer electrolyte fuel cells—A review. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Shao, H.; Qiu, D.; Yi, P.; Lai, X. Investigation of the non-uniform distribution of current density in commercial-size proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2020, 453, 227836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Peng, L.; Yi, P.; Lehnert, W.; Lai, X. Review on proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack assembly: Quality evaluation, assembly method, contact behavior and process design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oualid, S.E.; Lachat, R.; Candusso, D.; Meyer, Y. Characterization process to measure the electrical contact resistance of gas diffusion layers under mechanical static compressive loads. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 23920–23931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Investigation of optimal operating temperature for the PEMFC and its tracking control for energy saving in vehicle applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 29, 114842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Su, S.C. Effects of assembly torque on a proton exchange membrane fuel cell with stamped metallic bipolar plates. Energy 2018, 159, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qin, Y.; Du, Q.; Peng, J. Effects of Clamping Force on the Operating Behavior of PEM Fuel Cell. SAE Tech. Pap. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Lin, C.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, G.; Zhang, J. Effect of clamping pressure on liquid-cooled PEMFC stack performance considering inhomogeneous gas diffusion layer compression. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, G.J. A systematic review for structure optimization and clamping load design of large proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2020, 476, 228724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibnia, M.; Shirkhani, M.; Tamami, P.G. Optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell’s end plates. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Shahsamandi, M.H.; Khorasani, M.R.A. Design and manufacturing of end plates of a 5kW PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 9291–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carral, C.; Charvin, N.; Trouve, H.; Mele, P. An experimental analysis of PEMFC stack assembly using strain gage sensors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 4493–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Hu, Y.Y. Fuel cell stack mechanical structure research and end plate design optimization. Dongfang Electr. Rev. 2015, 29, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, E.; Barzegari, M.M.; Momenifar, M.; Ghadimi, M.; Saadat, S.H.M. Investigation of contact pressure distribution over the active area of PEM fuel cell stack. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 3062–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzundurukan, A.; Bilgili, M.; Devrim, Y. Examination of compression effects on PEMFC performance by numerical and experimental analyses. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 35085–35096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, J. Optimization of the size and shape of the end plate of the fuel cell stack with steel straps. J. Tongji Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 45, 575–581. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Tan, J.; Yang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, C. Better electrochemical performance of PEMFC under a novel pneumatic clamping mechanism. Energy 2021, 229, 120796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, E.; Ghadimi, M.; Barzegari, M.M.; Momenifar, M.; Saadat, S.H.M. Development of contact pressure distribution of PEM fuel cell’s MEA using novel clamping mechanism. Energy 2017, 131, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wu, P.; Miao, T.; Liang, J.; Jiao, K.; Li, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J. An Intelligent Approach for Contact Pressure Optimization of PEM Fuel Cell Gas Diffusion Layers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhou, P.; Wu, C.W. Multi-objective topology optimization of end plates of proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.N. Research on the Optimization Design and Impact Resistance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell End Plates. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.Y. Optimum Design of End Plate for Steel Tape Encapsulated Fuel Cell. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Hao, Y.; Li, B.; Ming, P.; Zhang, C. Topology optimization design for the lightweight endplate of proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack clamped with bolts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 9680–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
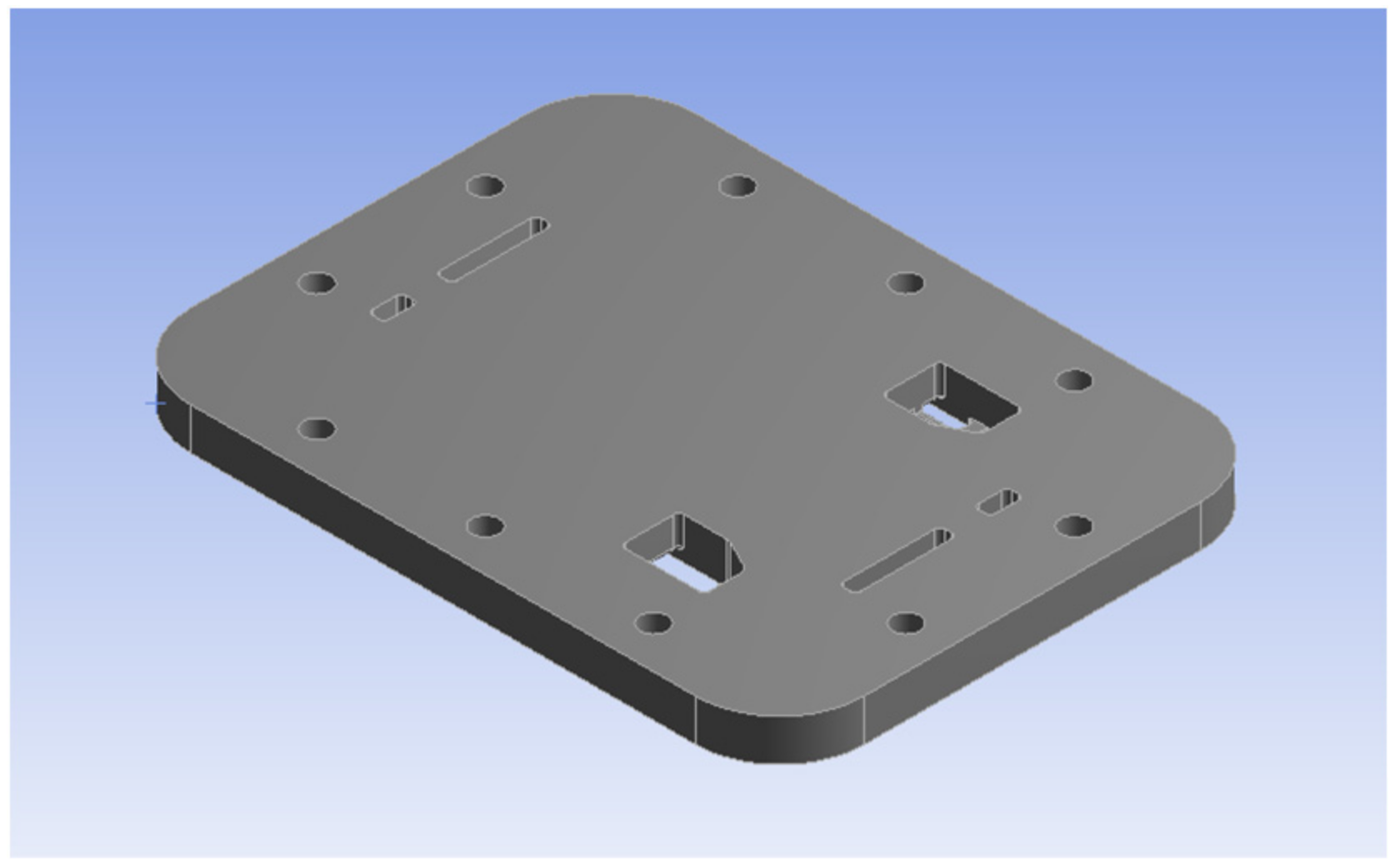
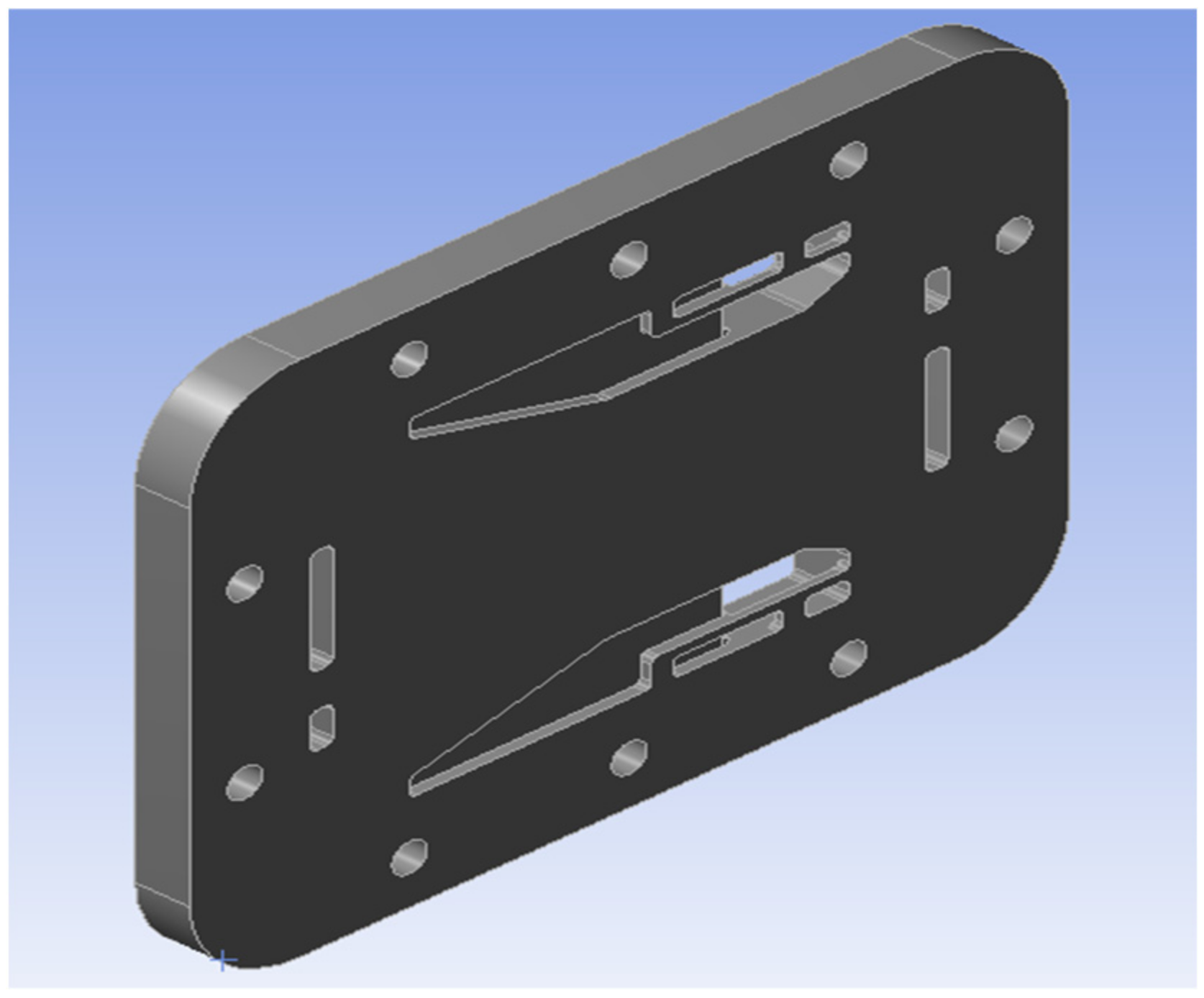

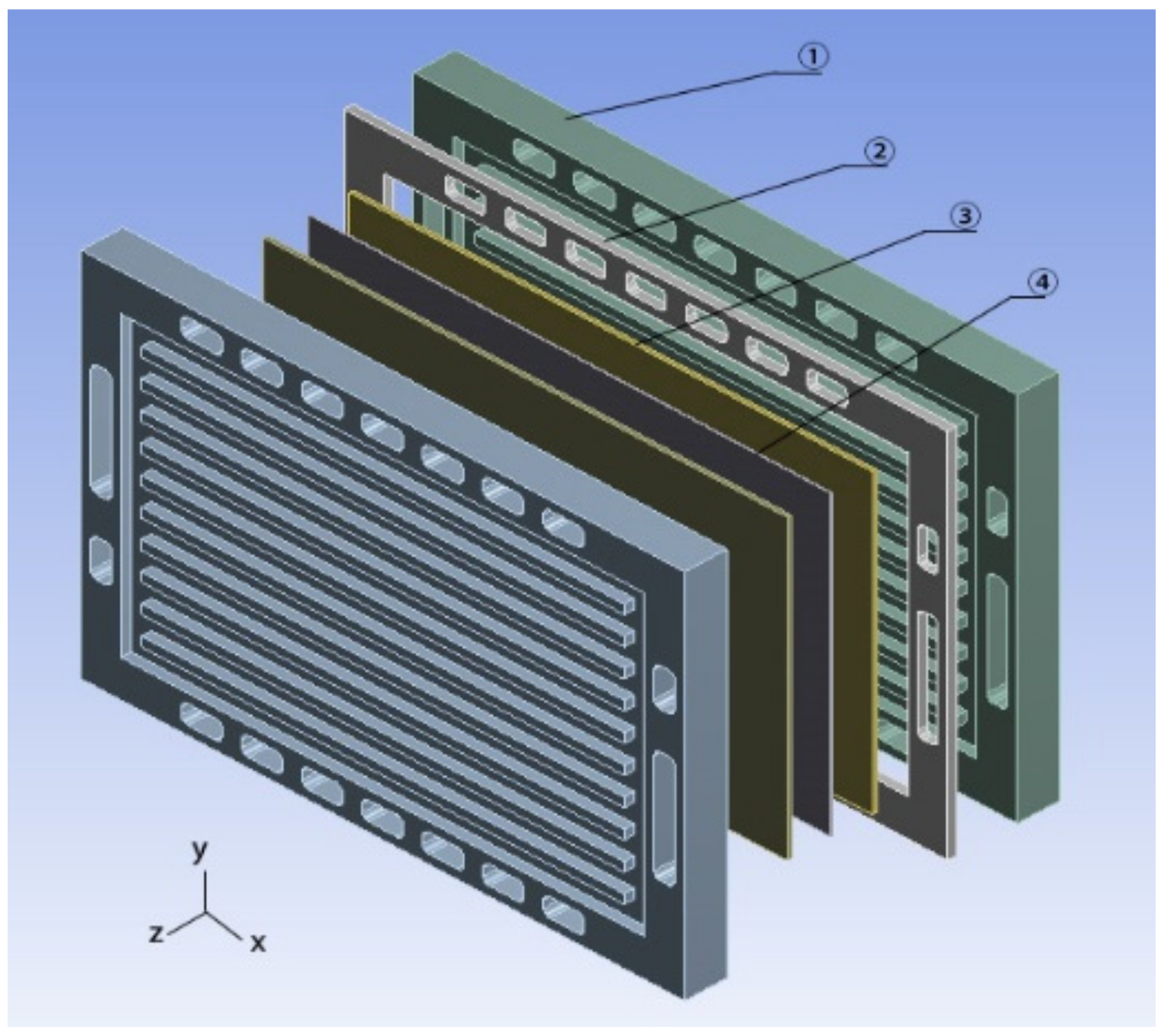
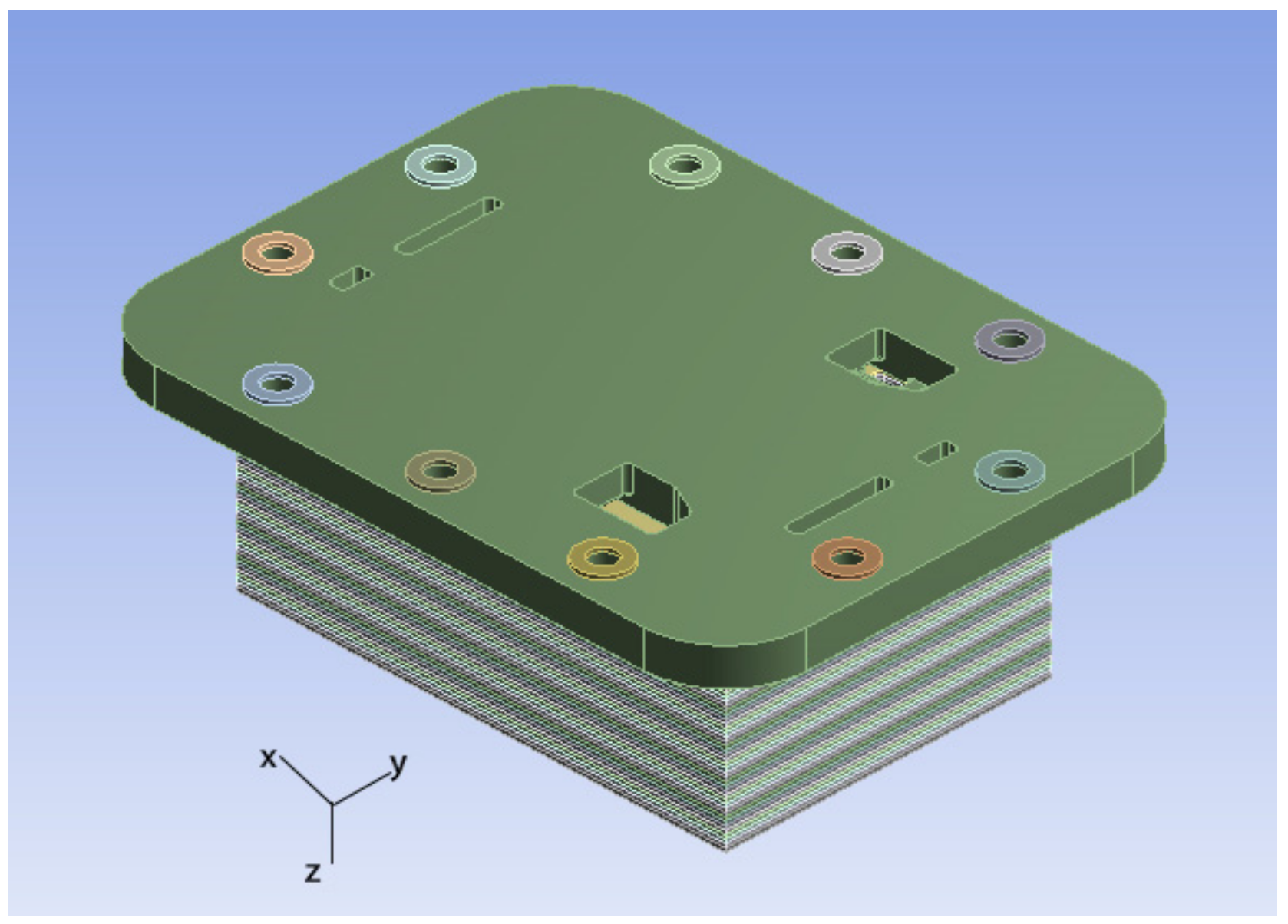
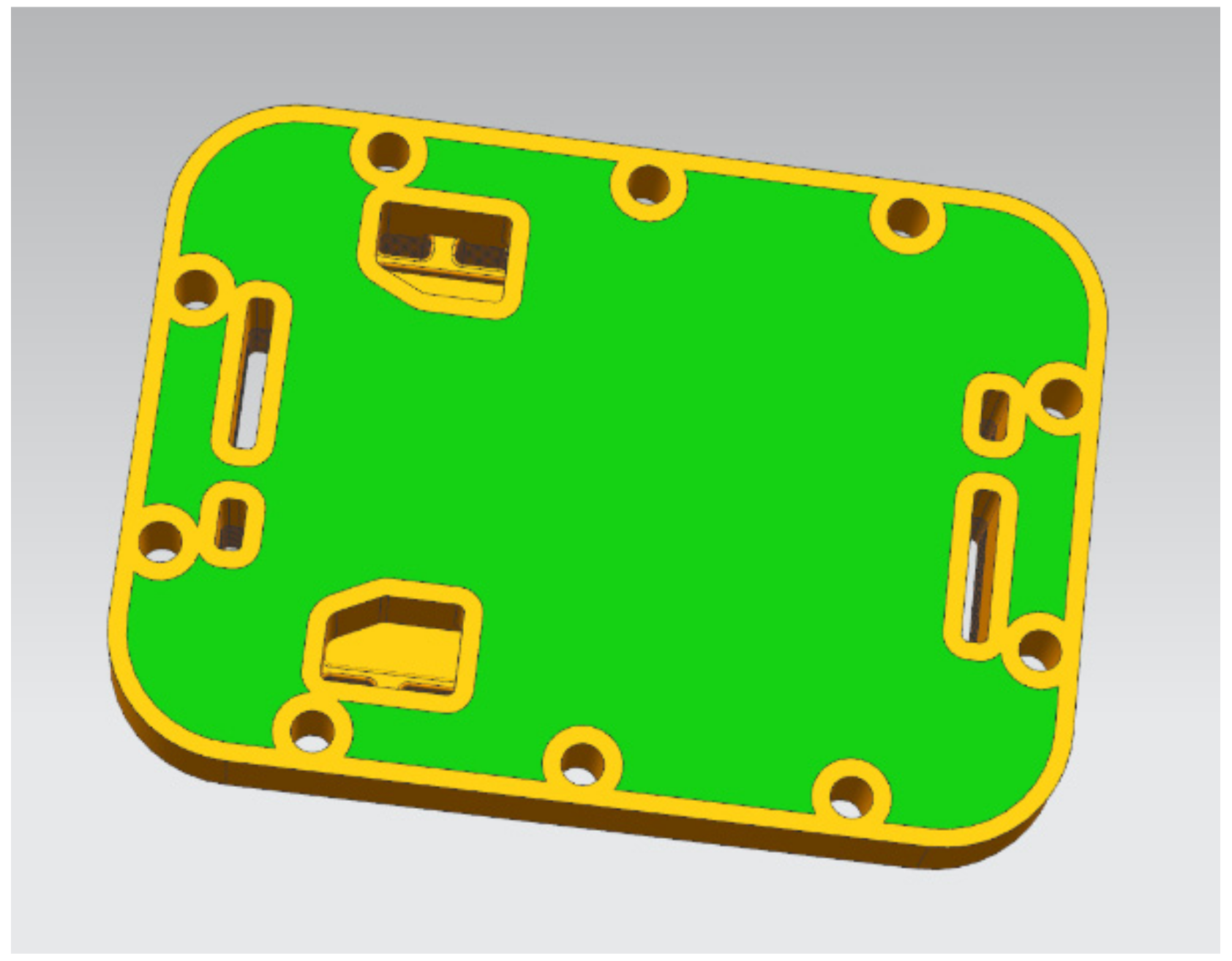




| Components | Material | Elastic Modulus/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Density/kg/m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEM | Nafion®112 | 0.32 | 0.4 | 500 |
| GDL | TGP-H-90 | 0.06 (thickness) 10 (in-plane) | 0.33 | 440 |
| Gasket | VMQ | 5.5 | 0.3 | 1700 |
| Bipolar plate | Graphite | 10 | 0.25 | 2160 |
| Current collector | Copper | 100 | 0.33 | 8940 |
| Insulator | POM | 2.6 | 0.386 | 1420 |
| Endplate | Aluminum alloy | 69 | 0.33 | 2800 |
| Components | Length/mm | Width/mm | Thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEM | 260 | 160 | 0.2 |
| GDL | 260 | 160 | 0.05 |
| Gasket | 300 (outer) 260 (inner) | 200 (outer) 160 (inner) | 0.45 |
| Bipolar plate | 300 | 200 | 2.09 |
| Current collector | 300 | 200 | 2 |
| Insulator | 300 | 200 | 3 |
| Endplate | 400 | 300 | 35 |
| Bolt gasket | D = 30 mm, d = 17 mm, H = 3 mm | ||
| Mass/kg | Maximum Stress/MPa | Average Stress/MPa | Coefficient of Variation of the First Cell Next to the Endplate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original endplate | 8.019 | 12.711 | 2.321 | 1.454 |
| Optimized endplate | 5.103 | 16.203 | 2.783 | 1.467 |
| Change | Decrease 35% | Increase 27% | Increase 20% | Increase 1% |
| Mass/kg | Maximum Stress/MPa | Average Stress/MPa | Stress Value Coefficient of Variation of the First Single Cell Next to the Endplate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original endplate | 8.451 | 5.855 | 1.556 | 1.274 |
| Optimized endplate | 4.590 | 19.009 | 3.506 | 1.353 |
| Change | Decrease 46% | Increase 224% | Increase 125% | Increase 6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Endplate Design and Topology Optimization of Fuel Cell Stack Clamped with Bolts. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4730. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084730
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhang T. Endplate Design and Topology Optimization of Fuel Cell Stack Clamped with Bolts. Sustainability. 2022; 14(8):4730. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084730
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiming, Jun Zhang, and Tong Zhang. 2022. "Endplate Design and Topology Optimization of Fuel Cell Stack Clamped with Bolts" Sustainability 14, no. 8: 4730. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084730
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhang, J., & Zhang, T. (2022). Endplate Design and Topology Optimization of Fuel Cell Stack Clamped with Bolts. Sustainability, 14(8), 4730. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084730






