Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimation of Soil Properties of Alfisols from Eastern India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
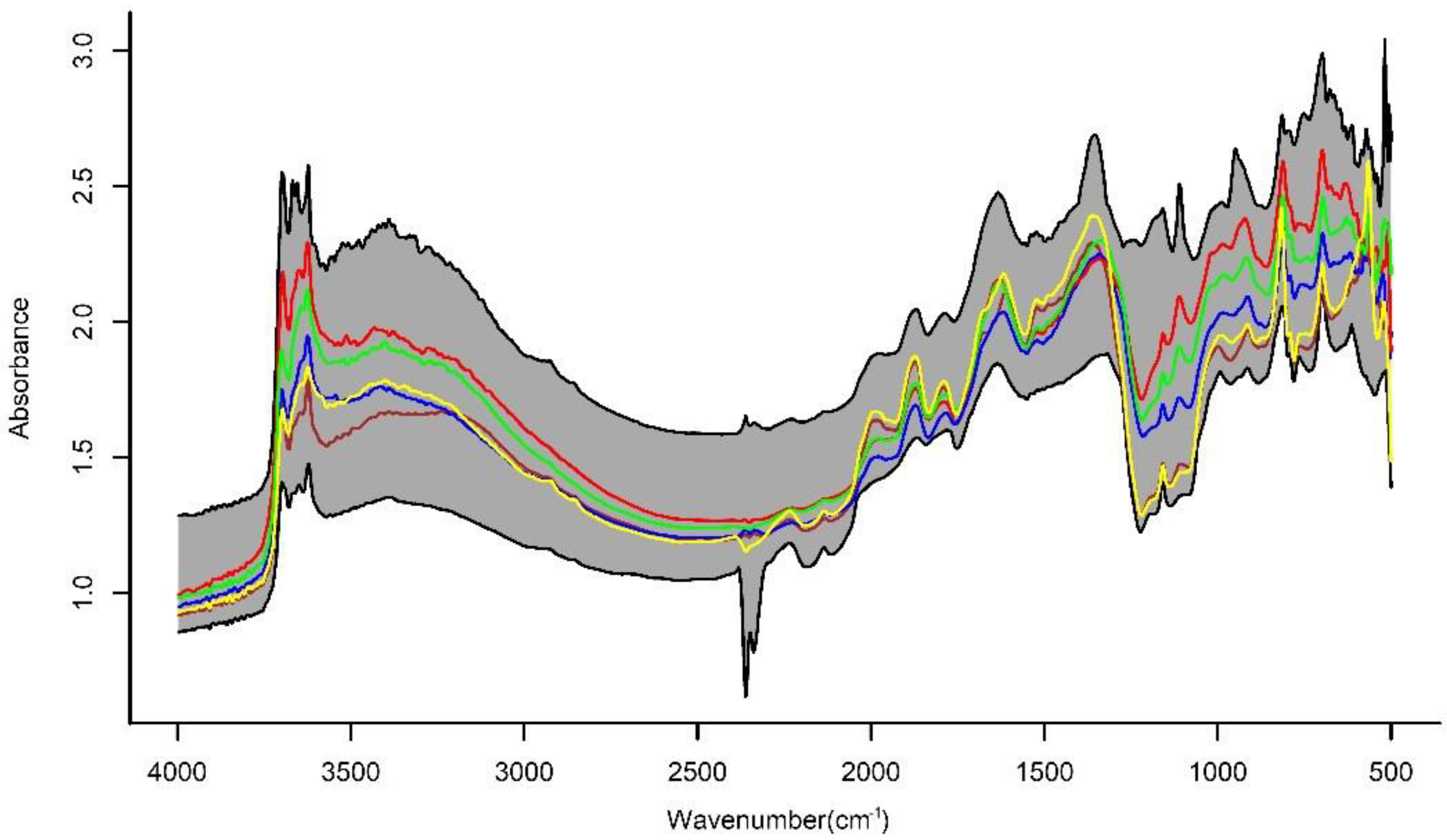
2.3. MIR Spectral Measurements and Preprocessing of Soil Spectra
2.4. Chemometric Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
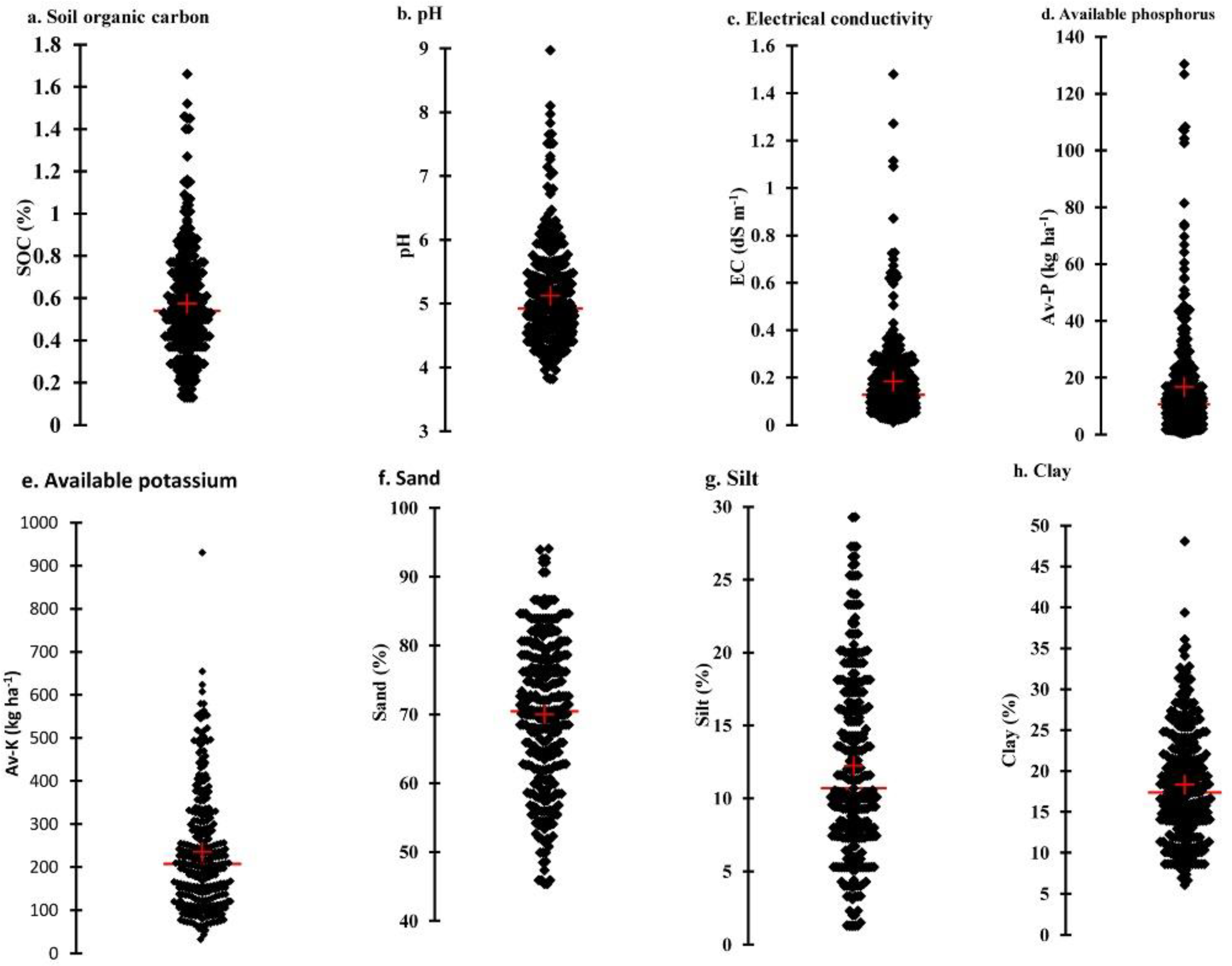
3.1. Soil and Spectral Characteristics
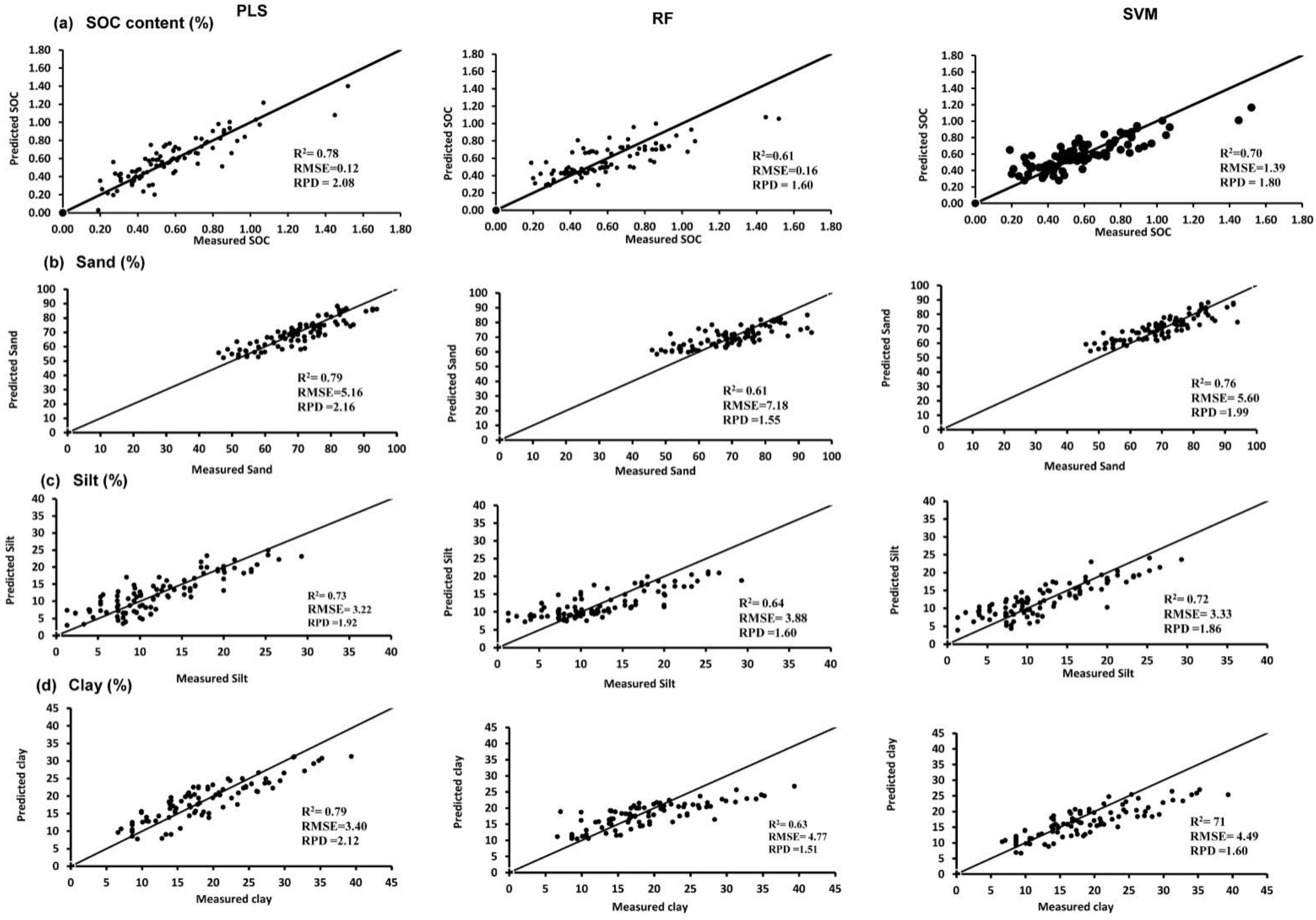
3.2. Validation of SVM, PLSR, and RF Regressions with Independent Dataset
3.3. Identifying Wavenumbers with High Explanatory Value
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez, P.A.; Ahamed, S.; Carre, F.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.; Huising, J.; Lagacherie, P.; McBratney, A.B.; McKenzie, N.J.; Mendoca-Santos, M.L.; et al. Digital soil map of the world. Science 2009, 325, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Du, C.W.; Zhou, J.M.; Shen, Y.Z. Investigation of soil properties using different techniques of mid-infrared spectroscopy. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2019, 70, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetterlind, J.; Stenberg, B.; Rossel, R.A.V. Soil analysis using visible and near infrared spectroscopy. In Plant Mineral Nutrients: Methods and Protocols; Maathuis, F.J.M., Ed.; Published in Series: Methods in molecular biology nr 953; Humana Press Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, D.; Laik, R.; Meena, V.S.; Kumari, V.; Singh, S.K.; Pramanik, B.; Sattar, A. Strategies to admittance soil quality using mid-infrared (mid-IR) spectroscopy an alternate tool for conventional lab analysis: A global perspective. Environ. Chall. 2022, 7, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, J.B.; Tavakoli, H. Application of random forest regression to spectral multivariate calibration. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonett, J.P.; Camacho-Tamayo, J.H.; Ramírez-López, L. Mid-infrared spectroscopy for the estimation of some soil properties. Agron. Colomb. 2015, 33, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, G.W.; Reeves, J.B.; Reeves, V.B.; Follett, R.F.; Kimble, J.M. Mid-infrared and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for soil carbon measurement. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, B.; Nitschke, R.; Terhoeven-Urselmans, T.; Michel, K.; Flessa, H. Use of mid-infrared spectroscopy in the diffuse-reflectance mode for the prediction of the composition of organic matter in soil and litter. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil. Sci. 2008, 171, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, A.; Singh, B.; Islam, K. Ultra-violet, visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopic techniques to predict several soil properties. Aust. J. Soil. Res. 2005, 43, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Vanlauwe, B.; Gachengo, C.N.; Palm, C.A. Decomposition and mineralization of organic residues predicted using near infrared spectroscopy. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.B., III. Near-versus mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for soil analysis emphasizing carbon and laboratory versus on-site analysis: Where are we and what needs to be done? Geoderma 2010, 158, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, K.A. Estimation of soil organic carbon using chemometrics: A comparison between mid-infrared and visible near infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Janik, L.J.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Macdonald, L.M.; McLaughlin, M.J. The performance of visible near- and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical and biological properties. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 139–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, S. An agricultural pollutant: Chemical fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, W.; Shi, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, S. In situ measurement of some soil properties in paddy soil using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wijewardane, N.K.; Ge, Y.; Wills, S.; Libohova, Z. Predicting Physical and Chemical Properties of US Soils with a Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectral Library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Ugarte, C.M.; Guan, K.; Pentrak, M.; Wander, M.M. Developing Near- and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis Methods for Rapid Assessment of Soil Quality in Illinois. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Pal, D.K.; Mandal, C.; Chandran, P.; Ray, S.K.; Sarkar, D.; Velmourougane, K.; Srivastava, A.; Sidhu, G.S.; Singh, R.S.; et al. Soils of India: Historical perspective, classification and recent advances. Curr. Sci. 2013, 104, 1308–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa Rao, C.; Lal, R.; Prasad, J.V.N.S.; Gopinath, K.A.; Singh, R.; Jakkula, V.S.; Sahrawat, K.L.; Venkateswarlu, B.; Sikka, A.K.; Virmani, S.M. Potential and Challenges of Rainfed Farming in India. Adv. Agron. 2015, 133, 113–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Huang, J. Spectral signatures of soil horizons and soil orders—An 2 exploratory study of 270 soil profiles. Geoderma 2021, 389, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau-Rewe, M.; Rasche, F.; Cobo, J.G.; Dercon, G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Cadisch, G. Generic prediction of soil organic carbon in alfisols using diffuse reflectance fourier-transform mid-infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 2358–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbial Properties. American Society of Agronomy; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America Publishers: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabaiand, M.A.; Sumner, M.E. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3: Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Publishers: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Towett, E.K.; Shepherd, K.D.; Sila, A.; Aynekulu, E.; Cadisch, G. Mid-infrared and total X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy complementarity for assessment of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennard, R.; Stone, L. Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.; Nocita, M.; Tóth, G.; Montanarella, L.; van Wesemael, B. Prediction of soil organic carbon at the European scale by visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höskuldsson, A. PLS regression methods. J. Chemom. 1988, 2, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, A.M.; Shepherd, K.D.; Pokhariyal, G.P. Evaluating the utility of mid-infrared spectral subspaces for predicting soil properties. Chemom. Lab. Syst. 2016, 153, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deiss, L.; Margenot, A.J.; Culman, S.W.; Demyan, M.S. Tuning support vector machines regression models improves prediction accuracy of soil properties in MIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Luboš, B.; Saberioon, M.; Vašát, R. Visible, near-infrared, and mid-infrared spectroscopy applications for soil assessment with emphasis on soil organic matter content and quality: State-of-the-art and key issues. Appl. Spectros. 2013, 67, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awiti, M.W.; Shepherd, K.; Kinyamario, J. Soil condition classification using infrared spectroscopy: A proposition for assessment of soil condition along a tropical forest-cropland chronosequence. Geoderma 2008, 143, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R., Jr. Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy- principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Centner, V.; Verdu-Andres, J.; Walczak, B.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Despagne, F.; Pasti, L. Comparison of multivariate calibration techniques applied to experimental NIR data sets. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Characterization and analysis of soils using Mid infrared Partial Least-Squares 2. Correlations with Some Laboratory Data. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1995, 33, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberhauer, G.; Rafferty, B.; Strebl, F.; Gerzabek, M.H. Comparison of the composition of forest soil litter derived from three different sites at various decompositional stages using FTIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 1998, 83, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberhauer, G.; Gerzabek, M.H. Drift and transmission FT-IR spectroscopy of forest soils: An approach to determine decomposition processes of forest litter. Vibrat.Spectrosc. 1999, 19, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Infrared spectroscopy: Enabling an evidence-based diagnostic surveillance approach to agricultural and environmental management in developing countries. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2007, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.T.; Aochi, Y.O. Fourier transform infrared and raman spectroscopy. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 269–322. [Google Scholar]
- Madejova, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, R.H.; Janik, L.J. Mid Infrared Spectroscopy for Rapid and Cheap Analysis of Soils.“Science and Technology: Delivering Results for Agriculture?”. In Proceedings of the 10th Australian Agronomy Conference, Hobart Tasmania, Australia, 29 January–1 February 2001; Barry, R., Danny, D., Neville, M., Eds.; Australian Society of Agronomy Inc.: Willow Grove, VIC, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guillou, F.; Wetterlind, W.; Rossel, R.V.; Hicks, W.; Grundyand, M.; Tuomi, S. How does grinding affect the mid-infrared spectra of soil and their multivariate calibrations to texture and organic carbon. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baes, A.U.; Bloom, P.R. Diffuse reflectance and transmission Fourier transform infrared (DRIFT) spectroscopy of humic and fulvic acids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Humus Chemistry—Genesis, Composition, Reactions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Mouazen, A.M. Vis/Near and Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy for Predicting Soil N and C at a Farm Scale. In Infrared Spectroscopy—Life and Biomedical Sciences; InTech Open: London, UK, 2012; pp. 185–210. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, P.M.M.; Fernandes-Filho, E.I.; Francelino, M.R.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Pereira, M.G.; Guimarães, C.C.B.; Pinto, L.A.S.R. Digital soil mapping of soil propertiesin the “Mar de Morros” environment using spectral data. Rev. Bras. de Ciência do Solo 2018, 42, e0170413. [Google Scholar]
- Minasny, B.; Tranter, G.; McBratney, A.B.; Brough, D.M.; Murphy, B.W. Regional transferability of midinfrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopic prediction for soil chemical properties. Geoderma 2009, 153, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urselmans, T.; Vagen, T.; Spaargaren, O.; Shepherd, K. Prediction of soil fertility properties from a globally distributed soil mid-infrared spectral library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, C.L.; Hernandez-Allica, J.; Dunham, S.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Haefele, S.M. A comparison of soil texture measurements using mid-infrared spectroscopy (MIRS) and laser diffraction analysis (LDA) in diverse soils. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, B.; Gupta, A.; Das, B.S. Estimation of weathering indices using spectral reflectance over visible to mid-infrared region. Geoderma 2016, 266, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Merry, R.H.; Skjemstad, J.O. Can mid infrared diffuse reflectance analysis replace soil extractions. Anim. Prod. Sci. 1998, 38, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Adamchuk, V.; Biswas, A.; Dhawale, N.; Sudarsan, B.; Zhang, Y.; ViscarraRossel, R.; Shi, Z. Assessment of soil properties in situ using a prototype portable MIR spectrometer in two agricultural fields. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 152, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Forrester, S.T.; Rawson, A. The prediction of soil chemical and physical properties from mid-infrared spectroscopy and combined partial least-squares regression and neural networks (PLS-NN) analysis. Chemom. Lab. Syst. 2009, 97, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.; Bindraban, P.; McLean, J.E.; Gatere, L.; Singh, U.; Hellums, D. Methods for rapid testing of plant and soil nutrients. In Sustainable Agricultural Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Beebe, K.R.; Kowalski, B.R. An introduction to multivariate calibration and analysis. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 1007A–1017A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil Property | Model | Calibration Set (80% of Dataset) | Validation Set (20% of Dataset) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | RPD | R2v | RMSEv | RPDv | ||
| SOC (%) | PLS | 0.88 | 0.09 | 2.85 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 2.08 |
| SVM | 0.99 | 0.02 | 10.75 | 0.70 | 1.39 | 1.80 | |
| RF | 0.95 | 0.07 | 3.71 | 0.61 | 0.16 | 1.60 | |
| pH | PLS | 0.80 | 0.36 | 2.23 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 1.82 |
| SVM | 0.98 | 0.30 | 2.71 | 0.69 | 0.44 | 1.64 | |
| RF | 0.97 | 0.30 | 2.71 | 0.37 | 0.62 | 1.68 | |
| EC * (dS m−1) | PLS | 0.70 | 0.09 | 1.81 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 1.25 |
| SVM | 0.94 | 0.05 | 3.42 | 0.47 | 0.10 | 1.34 | |
| RF | 0.98 | 0.07 | 2.20 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 1.02 | |
| Sand (%) | PLS | 0.85 | 4.0 | 2.55 | 0.79 | 5.16 | 2.16 |
| SVM | 0.99 | 0.97 | 10.47 | 0.76 | 5.60 | 1.99 | |
| RF | 0.96 | 2.73 | 3.73 | 0.61 | 7.18 | 1.55 | |
| Silt (%) | PLS | 0.82 | 2.57 | 2.36 | 0.73 | 3.22 | 1.92 |
| SVM | 0.99 | 0.58 | 10.34 | 0.72 | 3.33 | 1.86 | |
| RF | 0.96 | 1.63 | 3.72 | 0.64 | 3.88 | 1.60 | |
| Clay (%) | PLS | 0.87 | 2.32 | 2.82 | 0.79 | 3.40 | 2.12 |
| SVM | 0.99 | 0.63 | 10.35 | 0.71 | 4.49 | 1.60 | |
| RF | 0.95 | 1.82 | 3.58 | 0.63 | 4.77 | 1.31 | |
| Available P * (kg ha−1) | PLS | 0.70 | 1.00 | 1.83 | 0.38 | 1.54 | 1.26 |
| SVM | 0.85 | 0.83 | 2.20 | 0.37 | 1.60 | 1.21 | |
| RF | 0.97 | 0.68 | 2.70 | 0.28 | 1.73 | 1.13 | |
| Available K * (kg ha−1) | PLS | 0.69 | 2.38 | 1.81 | 0.22 | 3.72 | 1.12 |
| SVM | 0.98 | 0.61 | 7.07 | 0.15 | 3.83 | 1.08 | |
| RF | 0.98 | 1.62 | 2.66 | 0.05 | 4.05 | 1.03 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hati, K.M.; Sinha, N.K.; Mohanty, M.; Jha, P.; Londhe, S.; Sila, A.; Towett, E.; Chaudhary, R.S.; Jayaraman, S.; Vassanda Coumar, M.; et al. Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimation of Soil Properties of Alfisols from Eastern India. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094883
Hati KM, Sinha NK, Mohanty M, Jha P, Londhe S, Sila A, Towett E, Chaudhary RS, Jayaraman S, Vassanda Coumar M, et al. Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimation of Soil Properties of Alfisols from Eastern India. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094883
Chicago/Turabian StyleHati, Kuntal M., Nishant K. Sinha, Monoranjan Mohanty, Pramod Jha, Sunil Londhe, Andrew Sila, Erick Towett, Ranjeet S. Chaudhary, Somasundaram Jayaraman, Mounisamy Vassanda Coumar, and et al. 2022. "Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimation of Soil Properties of Alfisols from Eastern India" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094883
APA StyleHati, K. M., Sinha, N. K., Mohanty, M., Jha, P., Londhe, S., Sila, A., Towett, E., Chaudhary, R. S., Jayaraman, S., Vassanda Coumar, M., Thakur, J. K., Dey, P., Shepherd, K., Muchhala, P., Weullow, E., Singh, M., Dhyani, S. K., Biradar, C., Rizvi, J., ... Chaudhari, S. K. (2022). Mid-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Estimation of Soil Properties of Alfisols from Eastern India. Sustainability, 14(9), 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094883








