Effect of Rhizobium Inoculation on Growth of Common Bean in Low-Fertility Tropical Soil Amended with Phosphorus and Lime
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
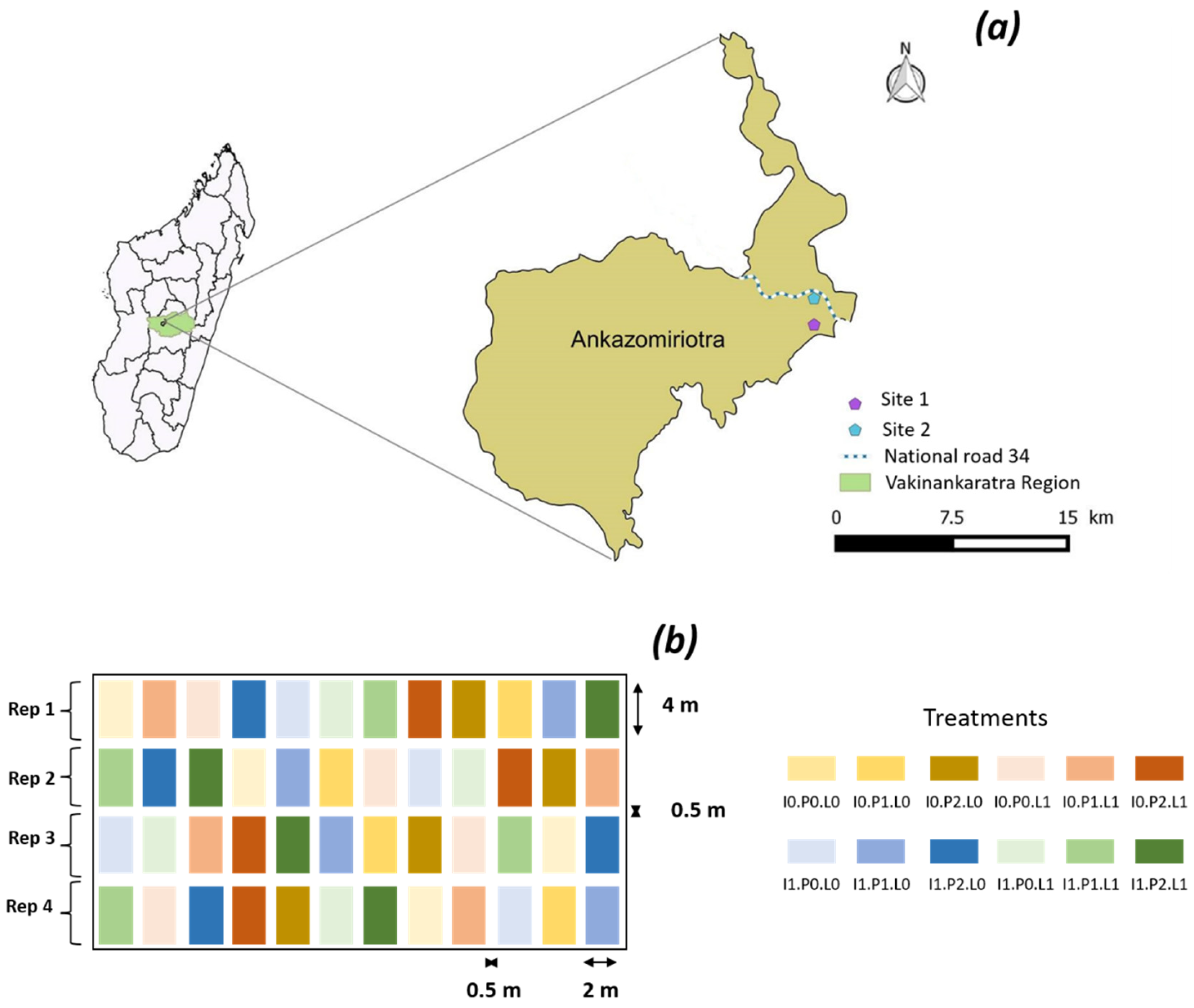
2.1. Site Location and Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant and Soil Sampling
2.4. Plant and Soil Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Legume Symbioses
3.2. Legume Growth and Biological N2 Fixation
3.3. Rhizospheric Soil
3.4. Effects of Inoculation of Bean Seed and Inputs of P and Dolomite on Common Bean and Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mudryj, A.N.; Yu, N.; Aukema, H.M. Nutritional and health benefits of pulses. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz Patto, M.C.; Amarowicz, R.; Aryee, A.N.; Boye, J.I.; Chung, H.J.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Domoney, C. Achievements and challenges in improving the nutritional quality of food legumes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbak, I.; Millar, N.; Robertson, G.P. Global metaanalysis of the nonlinear response of soil nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions to fertilizer nitrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9199–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, E.S.; Peoples, M.B.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Faba bean in cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köpke, U.; Nemecek, T. Ecological services of faba bean. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiales, D.; Mikic, A. Introduction: Legumes in sustainable agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chianu, J.N.; Chianu, J.N.; Mairura, F. Mineral fertilizers in the farming systems of sub-Saharan Africa. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 545–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augusto, L.; Delerue, F.; Gallet-Budynek, A.; Achat, D.L. Global assessment of limitation to symbiotic nitrogen fixation by phosphorus availability in terrestrial ecosystems using a meta-analysis approach. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle 2013, 27, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, M.; Tejera, N.; Iribarne, C.; Ocana, A.; Lluch, C. Growth, nitrogen fixation and ammonium assimilation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Effect of phosphorus. Physiol. Plant. 2004, 121, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimer, A.L.; Bever, J.D.; Clay, K. The interactive effects of plant microbial symbionts: A review and meta-analysis. Symbiosis 2010, 51, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Rengel, Z.; Feng, G. Soil phosphorus availability determines the preference for direct or mycorrhizal phosphorus uptake pathway in maize. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, P.H.; Vance, C.P. Nitrogen fixation in perspective: An overview of research and extension needs. Field Crop. Res. 2000, 65, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Uexküll, H.R.; Mutert, E. Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. Plant Soil 1995, 171, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndakidemi, P.A.; Bambara, S.; Makoi, J.H. Micronutrient uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by Rhizobium inoculation, and the supply of molybdenum and lime. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Romero, E. Diversity of Rhizobium-Phaseolus vulgaris symbiosis: Overview and perspectives. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, W.J. Management of the Cerrado soils of Brazil: A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlauwe, B.; Hungria, M.; Kanampiu, F.; Giller, K.E. The role of legumes in the sustainable intensification of African smallholder agriculture: Lessons learnt and challenges for the future. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 284, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports 106; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Razakatiana, A.T.E.; Trap, J.; Baohanta, R.H.; Raherimandimby, M.; Le Roux, C.; Duponnois, R.; Ramanankierana, H.; Becquer, T. Benefits of dual inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia on Phaseolus vulgaris planted in a low-fertility tropical soil. Pedobiologia 2020, 83, 150685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaroson, V.H.; Becquer, T.; Sá, S.O.; Razafimahatratra, H.; Larvy Delarivière, J.; Blavet, D.; Vendrame, P.R.S.; Rabeharisoa, L.; Rakotondrazafy, A.F.M. Mineralogical analysis of ferralitic soils in Madagascar using NIR spectroscopy. Catena 2018, 168, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.V.H.; Novais, R.D.; Dias, L.E.; Oliveira, J.D. Determinação e uso do fósforo remanescente. Bol. Inf. Soc. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2000, 25, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3. Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 869–919. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürer, J.; Rosswall, T. Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analyses Part 2, Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Weaver, R.W., Angle, S., Bottomley, P., Bezdicek, D., Smith, S., Tabatabai, A., Wollum, A., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Samago, T.Y.; Anniye, E.W.; Dakora, F.D. Grain yield of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties is markedly increased by rhizobial inoculation and phosphorus application in Ethiopia. Symbiosis 2018, 75, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, J.M.; Hayman, D.S. Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 1970, 55, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, M.; Mosse, B. An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol. 1980, 84, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ambrona, C.H.; Mínguez, M.I. Cereal–legume rotations in a Mediterranean environment: Biomass and yield production. Field Crop. Res. 2001, 70, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Kennedy, A.C. Grain legumes in northern Great Plains: Impacts on selected biological soil processes. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Lemke, R.L.; Nelson, L.M. Nitrous oxide emissions associated with nitrogen fixation by grain legumes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2283–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschuk, G.; Alberton, O.; Hungria, M. Three decades of soil microbial biomass studies in Brazilian ecosystems: Lessons learned about soil quality and indications for improving sustainability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, E.W.; Asango, A.M.; Maingi, J.; Njeru, E.M. Elucidating the potential of native rhizobial isolates to improve biological nitrogen fixation and growth of common bean and soybean in smallholder farming systems of Kenya. Int. J. Agron. 2016, 2016, 4569241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koskey, G.; Mburu, S.W.; Njeru, E.M.; Kimiti, J.M.; Ombori, O.; Maingi, J.M. Potential of native rhizobia in enhancing nitrogen fixation and yields of climbing beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in contrasting environments of Eastern Kenya. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathu, S.; Herrmann, L.; Pypers, P.; Matiru, V.; Mwirichia, R.; Lesueur, D. Potential of indigenous bradyrhizobia versus commercial inoculants to improve cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. walp.) and green gram (Vigna radiata L. wilczek.) yields in Kenya. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 58, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, J.; Dombrecht, B.; Vermeiren, N.; Xi, C.W.; Luyten, E.; Vanderleyden, J. Phaseolus vulgaris is a non-selective host for nodulation. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1998, 26, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakatiana, A.T.E. Rôle des Symbioses Mycorhizienne et Bactérienne: Biodisponibilité du Phosphore et Développement des Plantes de Haricot Sur le Sol Ferralitique de Madagascar. Doctoral Thesis, University of Antananarivo, Antananarivo, Madagascar, 26 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Catroux, G.; Hartmann, A.; Revellin, C. Trends in rhizobial inoculant production and use. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.K.; Jans, D.C.; Bremer, E.; Lupwayi, N.Z.; Rice, W.A.; Clayton, G.W.; Collins, M.M. Rhizobium population dynamics in the pea rhizosphere of rhizobial inoculant strain applied in different formulations. Can. J. Microbiol. 2001, 47, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raminoarison, M.; Razafimbelo, T.; Rakotoson, T.; Becquer, T.; Blanchart, E.; Trap, J. Multiple-nutrient limitation of upland rainfed rice in ferralsols: A greenhouse nutrient-omission trial. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeharisoa, L.; Razanakoto, O.R.; Razafimanantsoa, M.P.; Rakotoson, T.; Amery, F.; Smolders, E. Larger bioavailability of soil phosphorus for irrigated rice compared with rainfed rice in Madagascar: Results from a soil and plant survey. Soil Use Manag. 2012, 28, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribet, J.M.; Drevon, J.J. The phosphorus requirement of N2–fixing and urea-fed Acacia mangium. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amâncio, S.; Stulen, I. Nitrogen Acquisition and Assimilation in Higher Plants; Plant ecophysiology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 3, 299p. [Google Scholar]
- Neila, A.; Adnane, B.; Mustapha, F.; Manel, B.; Imen, H.; Boulbaba, L.; Cherki, G.; Bouaziz, S. Phaseolus vulgaris—Rhizobia symbiosis increases the phosphorus uptake and symbiotic N2 fixation under insoluble phosphorus. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoundji, C.C.; Houngnandan, P.; Amidou, M.H.; Kouelo, F.A.; Toukourou, F. Inoculation and phosphorus application effects on soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] productivity grown in farmers’ fields of Benin. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2015, 25, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Sa, T.M.; Israel, D.W. Energy status and functioning of phosphorus-deficient soybean nodules. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trap, J.; Blanchart, E.; Ratsiatosika, O.; Razafindrakoto, M.; Becquer, T.; Andriamananjara, A.; Morel, C. Effects of the earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus on rice P nutrition and plant-available soil P in a tropical Ferralsol. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 160, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trap, J.; Ranoarisoa, M.P.; Raharijaona, S.; Rabeharisoa, L.; Plassard, C.; Mayad, E.H.; Bernard, L.; Becquer, T.; Blanchart, E. Agricultural practices modulate the beneficial activity of bacterial-feeding nematodes on plant growth and nutrition: Evidence from an original intact soil core technique. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Ameliorating soil acidity of tropical Oxisols by liming for sustainable crop production. Adv. Agron. 2008, 99, 345–399. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, D.S.; Murphy, P.J.; Giller, K.E. The diversity of Phaseolus-nodulating rhizobial populations is altered by liming of acid soils planted with Phaseolus vulgaris L. in Brazil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4025–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vendrame, P.R.S.; Brito, O.R.; Martins, E.S.; Quantin, C.; Guimarães, M.F.; Becquer, T. Acidity control in Latosols under long-term pastures in the Cerrado region, Brazil. Soil Res. 2013, 51, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudot, J.P.; Becquer, T.; Merlet, D.; Rouiller, J. Aluminium toxicity in declining forests: A general overview with a seasonal assessment in the Vosges mountains (France). Ann. Sci. For. 1994, 51, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrow, N.J. The effects of pH on phosphate uptake from the soil. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achat, D.L.; Pousse, N.; Nicolas, M.; Brédoire, F.; Augusto, L. Soil properties controlling inorganic phosphorus availability: General results from a national forest network and a global compilation of the literature. Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledian, Y.; Quinton, J.N.; Brevik, E.C.; Pereira, P.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Developing global pedotransfer functions to estimate available soil phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.E.; Read, D.J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; 800p. [Google Scholar]
- Joner, E.J.; van Aarle, I.M.; Vosatka, M. Phosphatase activity of extra-radical arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae: A review. Plant Soil 2000, 226, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected byroot-induced chemical changes: A review. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzergue, C.; Puech-Pagès, V.; Bécard, G.; Rochange, S.F. The regulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by phosphate in pea involves early and systemic signalling events. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aryal, U.K.; Xu, H.L.; Fujita, M. Rhizobia and AM fungal inoculation improve growth and nutrient uptake of bean plants under organic fertilization. J. Sustain. Agric. 2003, 21, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Site 1 | Site 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite (g kg−1) | 312 | 294 |
| Gibbsite (g kg−1) | 147 | 67 |
| Fe2O3 (g kg−1) | 46 | 42 |
| Total N (g kg−1) | 1.41 | 1.22 |
| Total C (g kg−1) | 23.5 | 18.2 |
| Prem (mg L−1) | 23.2 | 25.6 |
| Resin P (mg kg−1) | 4.77 | 4.13 |
| pHwater | 4.68 | 4.70 |
| pHKCl | 3.98 | 3.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razafintsalama, H.; Trap, J.; Rabary, B.; Razakatiana, A.T.E.; Ramanankierana, H.; Rabeharisoa, L.; Becquer, T. Effect of Rhizobium Inoculation on Growth of Common Bean in Low-Fertility Tropical Soil Amended with Phosphorus and Lime. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094907
Razafintsalama H, Trap J, Rabary B, Razakatiana ATE, Ramanankierana H, Rabeharisoa L, Becquer T. Effect of Rhizobium Inoculation on Growth of Common Bean in Low-Fertility Tropical Soil Amended with Phosphorus and Lime. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094907
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazafintsalama, Harimenja, Jean Trap, Bodovololona Rabary, Adamson Tsoushima Ernest Razakatiana, Heriniaina Ramanankierana, Lilia Rabeharisoa, and Thierry Becquer. 2022. "Effect of Rhizobium Inoculation on Growth of Common Bean in Low-Fertility Tropical Soil Amended with Phosphorus and Lime" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094907
APA StyleRazafintsalama, H., Trap, J., Rabary, B., Razakatiana, A. T. E., Ramanankierana, H., Rabeharisoa, L., & Becquer, T. (2022). Effect of Rhizobium Inoculation on Growth of Common Bean in Low-Fertility Tropical Soil Amended with Phosphorus and Lime. Sustainability, 14(9), 4907. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094907






