Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We review the existing work to assess the environmental impacts of AI and show their limitations (Section 2.1 and Section 2.2).
- We present life cycle assessment (Section 2.3) and examine how it can comprehensively evaluate the direct environmental impacts of an AI service (Section 3).
- We discuss how to assess the environmental value of an AI service designed for environmental purposes (Section 4).
- We argue that although improving the state of the art, the proposed methodology can only show the technical potential of a service, which may not fully realize in a real-life context (Section 5).
2. Related Work
2.1. Carbon Footprint of AI
- Integrated tools, such as Experiment Impact Tracker (https://github.com/Breakend/experiment-impact-tracker, accessed on 27 February 2022) [4], Carbon Tracker (https://github.com/lfwa/carbontracker, accessed on 27 February 2022) [3], and CodeCarbon (https://codecarbon.io/, accessed on 27 February 2022), which are all Python packages reporting measured energy consumption and the associated carbon footprint.
- Online tools, such as Green Algorithms (http://www.green-algorithms.org/, accessed on 27 February 2022) [6] and ML CO2 impact (https://mlco2.github.io/impact/#compute, accessed on 27 February 2022) [5], which require only a few parameters, such as the training duration, the material, and the location but are less accurate.
2.2. AI for Green Benefits
2.3. Life Cycle Assessment
- Economic flows are the directed links between the unit processes or said differently exchanges inside the technosphere.
- Environmental flows are the links from the biosphere to the technosphere or vice versa.
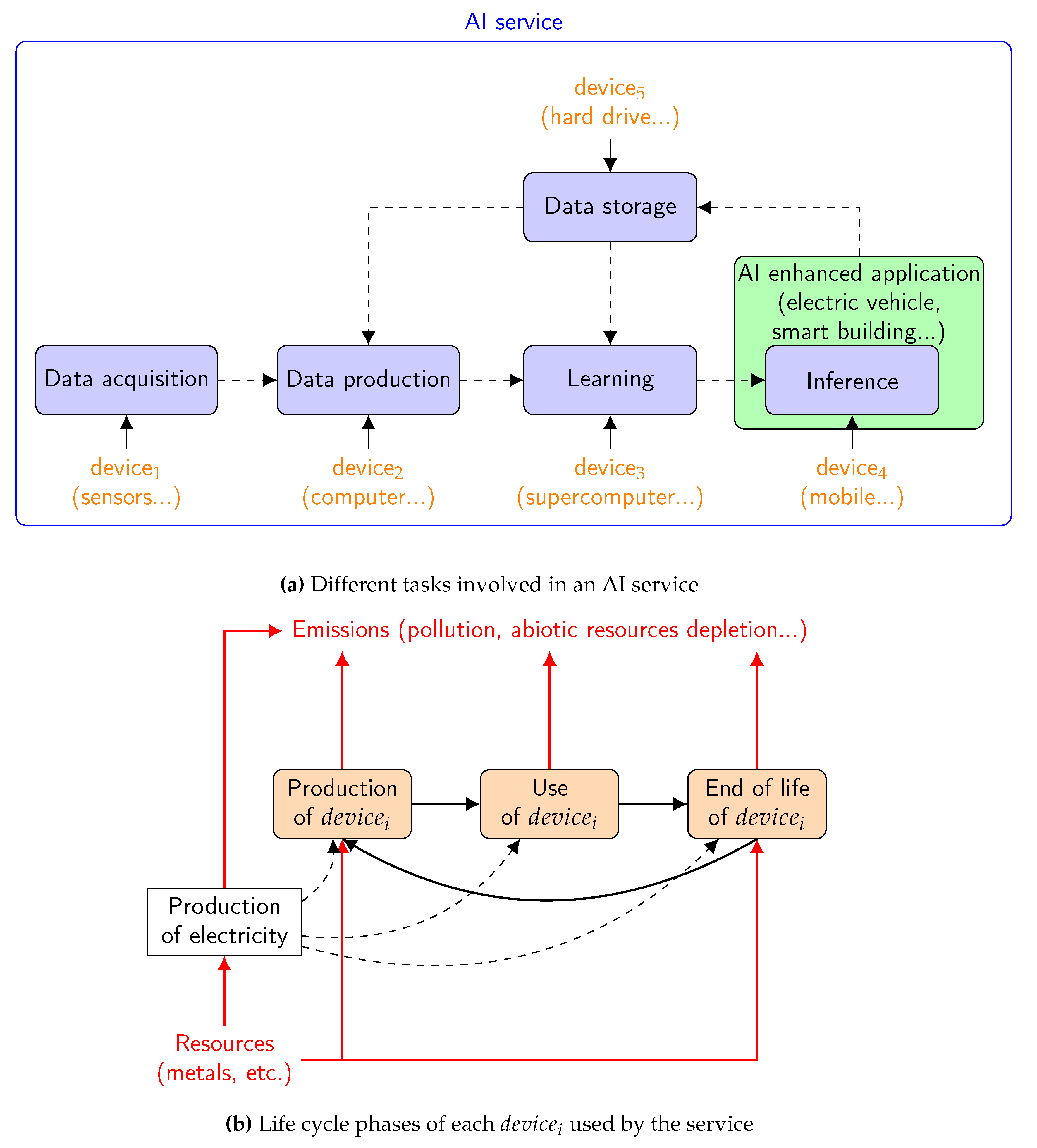
3. Life Cycle Assessment of an AI Solution
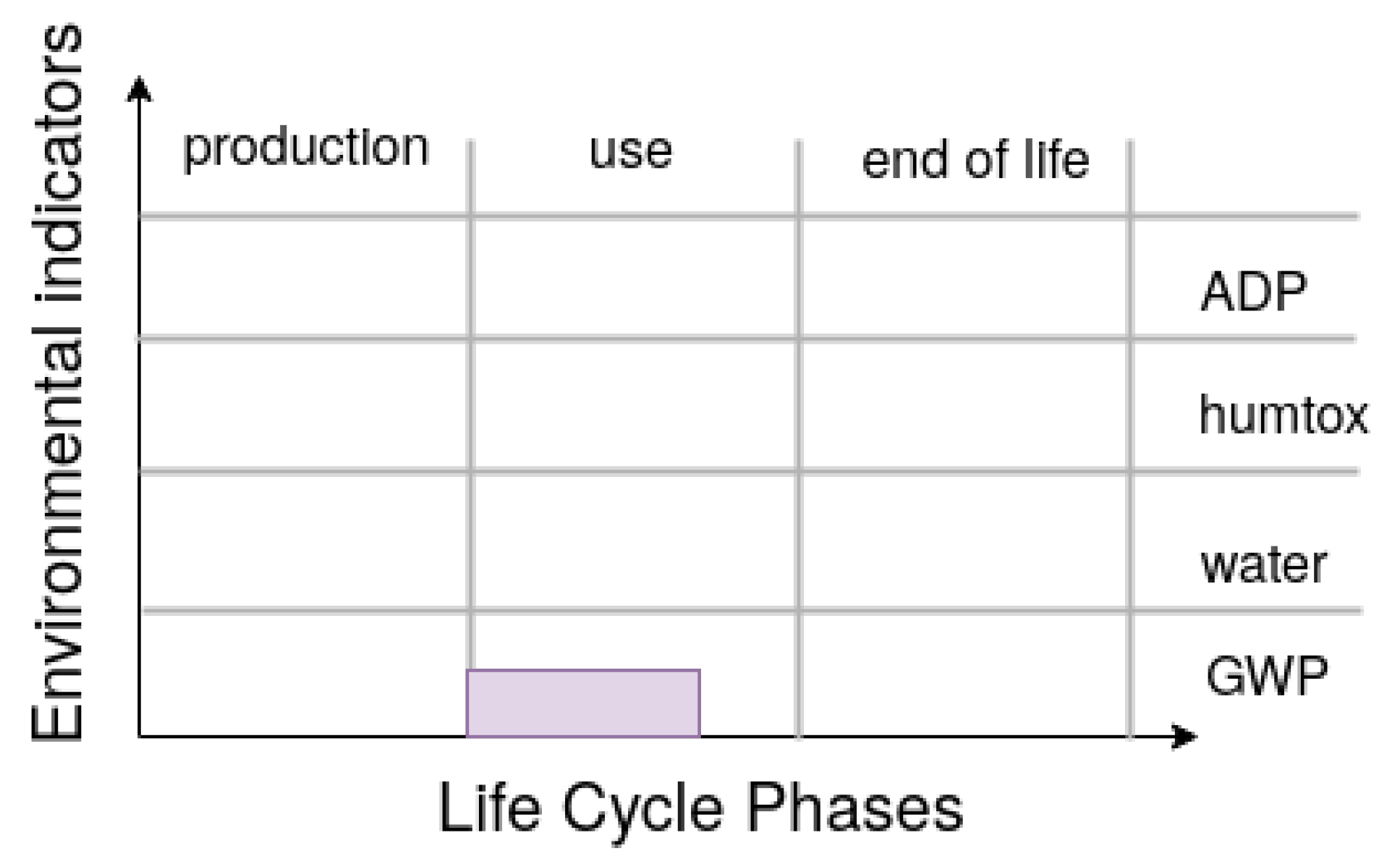
3.1. First-Order Impacts of an AI Service
- Raw material extraction, which encompasses all the industrial processes involved in the transformation from ore to metals;
- Manufacturing, which includes the processes that create the equipment from the raw material;
- Transport, which includes all transport processes involved, including product distribution;
- Use, which includes mostly the energy consumption of equipment while it is being used;
- and End of life, which refers to the processes to dismantle, recycle, and/or dispose of the equipment.
3.2. Life Cycle Assessment Methodology for AI
- terminals. In the case of the smart building, this can include: user terminals used to develop, train, and use the AI service; terminals in the facility where the AI service is trained and dedicated to IT support; and smart thermostats.
- network. For the smart building case, this includes network equipment used for training the AI model in the facility and network equipment in the buildings where the thermostats are used.
- data center/server. For the smart building case, this includes servers on which the model is trained and used; training and inference can be done on the same server or not.
- For equipment that is dedicated to the application, such as the smart thermostats: Production, Use, and End of life.
- For the servers on which the AI service is trained and used and their environment (network devices, storage servers, backup servers, user terminal, HVAC, and other potential equipment not dedicated to the application):
- -
- Production and End of life with an allocation of the impacts, with respect to the execution time, for instance.
- -
- Part of the use phase corresponding to the dynamic energy consumption, i.e., raise of consumption due to the execution of the program.
- -
- Part of the use phase corresponding to the static consumption, with an allocation (for example, if n programs are run simultaneously, of this consumption) “since equipment is switched on in part to address the computing needs of the (Machine Learning) model” [18].
4. Assessing the Usefulness of an AI for Green Service
- A reference application that corresponds to the application without AI. If the application is a smart building, for example, will be the building without smart capabilities.
- An AI-enhanced application that corresponds to the application with an AI service that is supposed to have a positive impact on the environment. In the previous case, it would be the smart building.
4.1. Theoretical Aspects
- the reference application without using the AI service,
- the application enhanced by AI,
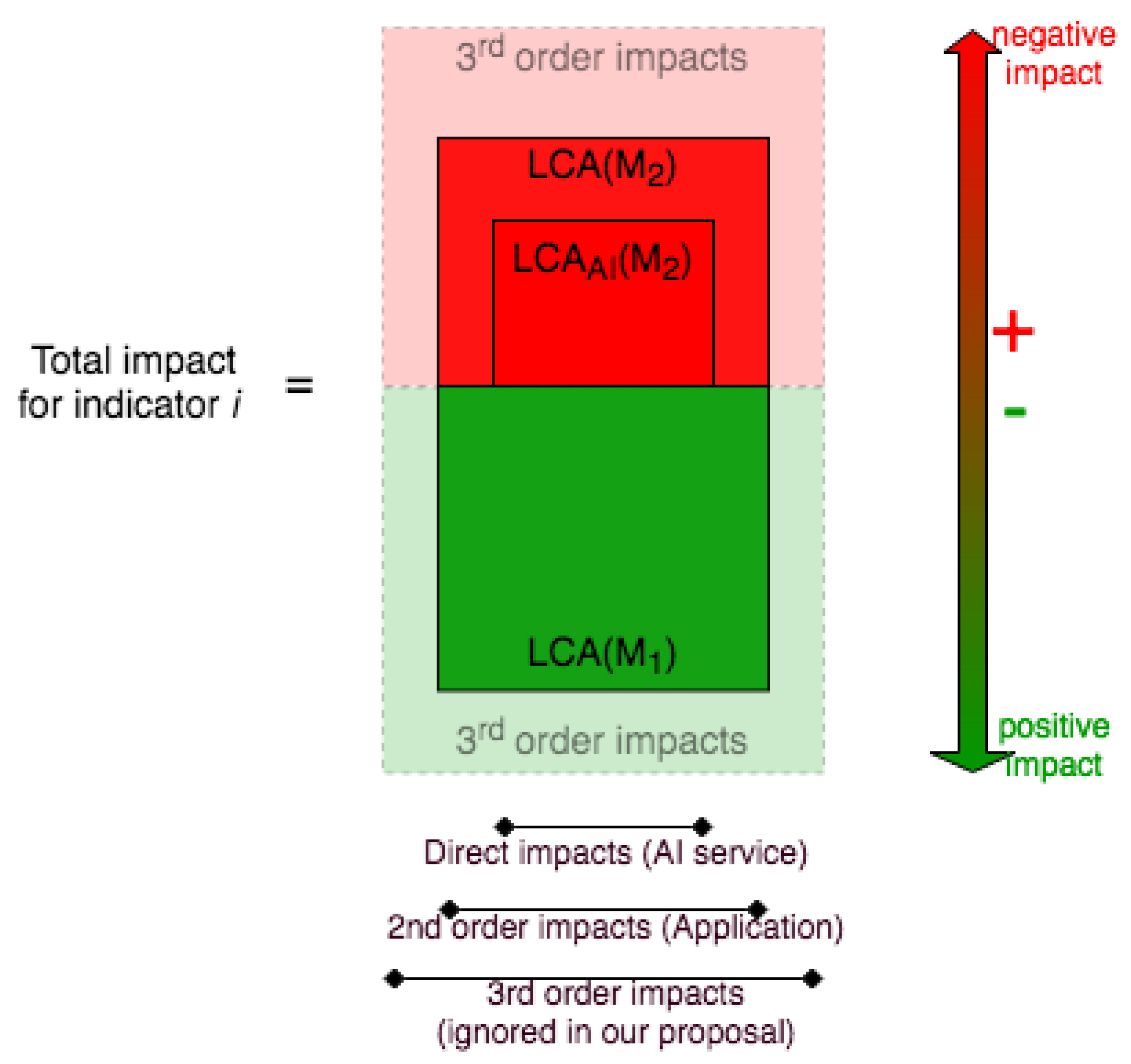
- a quantification of d types of environmental impacts (e.g., GHG emissions, water footprint, etc.). The LCA methodology is described in Section 3.2. Note that includes the impacts of the AI service itself, i.e., .
- the value of using the model, i.e., the environmental gain induced by its use in the practical application considered
- the environmental benefit that can be interpreted as the difference between the initial impact of the application and its final impact (not taking into account the AI solution, i.e., the Learning and Inference task in the top part of Figure 2)
- the energy cost of the model
- all other impacts, including chip production, waste, risks for biodiversity, and third-order impacts (which are not discussed here).
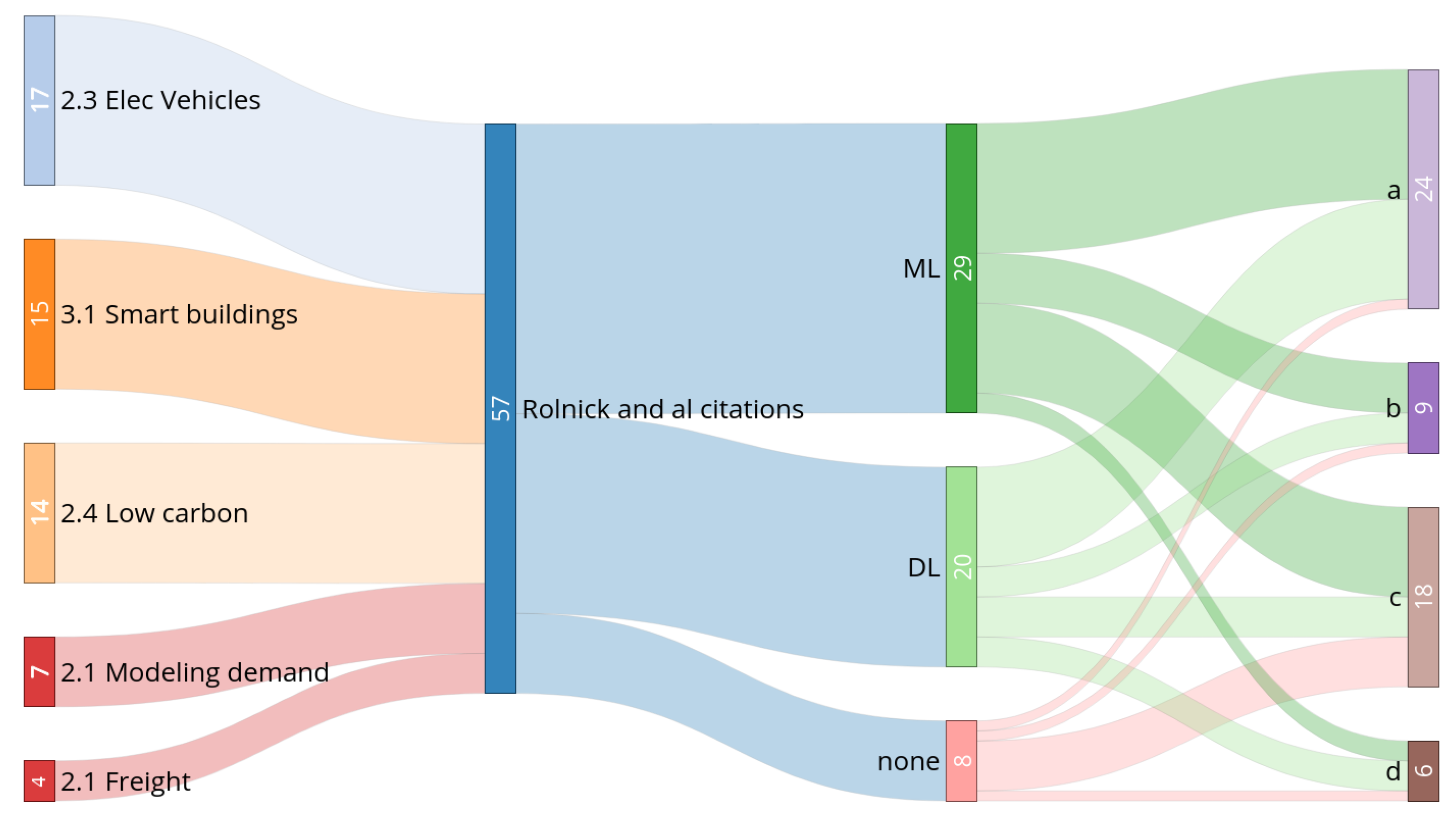
4.2. Case Studies
- No mention of the environmental gain.
- General mention of the environmental gain.
- A few words about the environmental gain but no quantitative evaluation or only indirect estimation.
- Evaluation of the energy gain without taking the AI service into account.
- Evaluation of the energy gain taking the use phase of the AI service into account.
- Comprehensive evaluation of the environmental gain (comparison of LCAs).
5. Discussion
5.1. Current Environmental Evaluation of AI Services Is Under-Estimated
5.2. AI Research should Use Life Cycle Assessment to Assess the usefulness of an AI Service
5.3. AI for Green Gains Are Only Potential
5.4. AI Services and Large Deployment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| HVAC | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning |
| ICT | Information and Communications Technology |
| LCA | Life cycle Assessment or Analysis |
| LCI | Life Cycle Inventory |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| TPU | Tensor Processing Unit |
References
- Strubell, E.; Ganesh, A.; McCallum, A. Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02243. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, R.; Dodge, J.; Smith, N.A.; Etzioni, O. Green AI. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, L.F.W.; Kanding, B.; Selvan, R. Carbontracker: Tracking and Predicting the Carbon Footprint of Training Deep Learning Models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.03051. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, P.; Hu, J.; Romoff, J.; Brunskill, E.; Jurafsky, D.; Pineau, J. Towards the Systematic Reporting of the Energy and Carbon Footprints of Machine Learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste, A.; Luccioni, A.; Schmidt, V.; Dandres, T. Quantifying the Carbon Emissions of Machine Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.09700. [Google Scholar]
- Lannelongue, L.; Grealey, J.; Inouye, M. Green Algorithms: Quantifying the carbon emissions of computation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.07610. [Google Scholar]
- Abrassart, C.; Bengio, Y.; Chicoisne, G.; De Marcellis-Warin, N.; Dilhac, M.-A.; Gambs, S.; Gautrais, V.; Gibert, M.; Langlois, L.; Laviolette, F.; et al. Montréal Declaration for A Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence—2018 Report. Technical Report, IA Responsable. 2018. Available online: https://www.montrealdeclaration-responsibleai.com/the-declaration (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Walsh, T.; Evatt, A.; de Witt, C.S. Artificial Intelligence & Climate Change: Supplementary Impact Report; Technical Report; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rolnick, D.; Donti, P.L.; Kaack, L.H.; Kochanski, K.; Lacoste, A.; Sankaran, K.; Ross, A.S.; Milojevic-Dupont, N.; Jaques, N.; Waldman-Brown, A.; et al. Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S.D.; Tegmark, M.; Fuso Nerini, F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gailhofer, P.; Herold, A.; Schemmel, J.P.; Scherf, C.U.; Köhler, A.R.; Braungardt, S. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the European Green Deal. Technical Report, Study for The Special Committee on Artificial Intelligence in a Digital Age (AIDA), Policy Department for Economic, Scientific and Quality of Life Policies, European Parliament. 2021. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2021/662906/IPOL_STU(2021)662906_EN.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Wu, C.; Raghavendra, R.; Gupta, U.; Acun, B.; Ardalani, N.; Maeng, K.; Chang, G.; Behram, F.A.; Huang, J.; Bai, C.; et al. Sustainable AI: Environmental Implications, Challenges and Opportunities. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00364. [Google Scholar]
- Cardon, D.; Cointet, J.P.; Mazières, A.; Libbrecht, E. Neurons spike back. Reseaux 2018, 211, 173–220. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, X.; Becchi, M.; Zong, Z. Evaluating the Energy Efficiency of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks on CPUs and GPUs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conferences on Big Data and Cloud Computing (BDCloud), Social Computing and Networking (SocialCom), Sustainable Computing and Communications (SustainCom)(BDCloud-SocialCom-SustainCom), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martín, E.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Riley, G.; Grahn, H. Estimation of energy consumption in machine learning. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2019, 134, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-T. Methodology for Environmental Life Cycle Assessments of Information and Communication Technology Goods, Networks and Services. Technical Report, ITU-T. 2014. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-L.1410-201412-I/fr (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Gupta, U.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, S.; Tse, J.; Lee, H.H.S.; Wei, G.Y.; Brooks, D.; Wu, C.J. Chasing Carbon: The Elusive Environmental Footprint of Computing. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.02839 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ligozat, A.L.; Luccioni, A. A Practical Guide to Quantifying Carbon Emissions for Machine Learning Researchers and Practitioners. Technical Report, Bigscience Project, LISN and MILA. 2021. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03376391/document (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Kaack, L.H.; Donti, P.L.; Strubell, E.; Kamiya, G.; Creutzig, F.; Rolnick, D. Aligning Artificial Intelligence with Climate Change Mitigation. Working Paper or Preprint. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03368037/document (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Patterson, D.; Gonzalez, J.; Le, Q.; Liang, C.; Munguia, L.M.; Rothchild, D.; So, D.; Texier, M.; Dean, J. Carbon emissions and large neural network training. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.10350. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild, M.Z.; Rosenbaum, R.K.; Olsen, S.I. Life Cycle Assessment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heijungs, R.; Suh, S. The Computational Structure of Life Cycle Assessment; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Hilty, L.M.; Hercheui, M.D. ICT and sustainable development. In What Kind of Information Society? Governance, Virtuality, Surveillance, Sustainability, Resilience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Horner, N.C.; Shehabi, A.; Azevedo, I.L. Known unknowns: Indirect energy effects of information and communication technology. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADEME. General Principles for The Environmental Labelling of Consumer Products, Methodological Standard for the Environmental Assessment of Digital Services. Technical Report, ADEME. 2021. Available online: http://www.base-impacts.ademe.fr/documents/Numerique.zip (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Berthoud, F.; Bzeznik, B.; Gibelin, N.; Laurens, M.; Bonamy, C.; Morel, M.; Schwindenhammer, X. Estimation de I’empreinte Carbone D’une Heure.coeur De Calcul. Research Report, UGA—Université Grenoble Alpes; CNRS; INP Grenoble; INRIA. 2020. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02549565v4/document (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global e-Waste Monitor 2017: Quantities, Flows and Resources; United Nations University (UNU), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and International Solid Waste Association (ISWA). 2017. Available online: https://ewastemonitor.info/gem-2017/ (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Berkhout, P.H.; Muskens, J.C.; Velthuijsen, J.W. Defining the rebound effect. Energy Policy 2000, 28, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Hinterberger, F.; Mesicek, R.H.; Luks, F. ECO-INFO-SOCIETY: Strategies for an Ecological Information Society. In Sustainability in the Information Society; Metropolis: Marburg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Villard, A.; Lelah, A.; Brissaud, D. Drawing a chip environmental profile: Environmental indicators for the semiconductor industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiebat, M.; Brown, A.L.; Safford, H.R.; Qu, S.; Xu, M. A Review on Energy, Environmental, and Sustainability Implications of Connected and Automated Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11449–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracquené, E.; De Bock, Y.; Duflou, J. Sustainability impact assessment of an intelligent control system for residential heating. Procedia Cirp Life Cycle Eng. (Lce) Conf. 2020, 90, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, D.; Pirson, T.; Dekimpe, R. Moore’s Law and ICT Innovation in the Anthropocene. In Proceedings of the IEEE Design and Test in Europe Conference, Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Coroamă, V.C.; Pargman, D. Skill Rebound: On an Unintended Effect of Digitalization. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on ICT for Sustainability, Bristol, UK, 21–26 June 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Life Cycle Id | Life Cycle Stage and Unit Processes | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| A—Raw material acquisition | Mandatory | |
| B—Production | ||
| Device production and assembly | Mandatory | |
| Manufacturer support activities | Recommended | |
| Production of support equipment | Mandatory | |
| ICT-specific site construction | Recommended | |
| C—Use | ||
| Use of ICT equipment | Mandatory | |
| Use of support equipment | Mandatory | |
| Operator support activities | Recommended | |
| Service provider support activities | Recommended | |
| D—End of life | ||
| Preparation of ICT goods for reuse | Mandatory | |
| Storage/disassembly/dismantling/crushing | Mandatory | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ligozat, A.-L.; Lefevre, J.; Bugeau, A.; Combaz, J. Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095172
Ligozat A-L, Lefevre J, Bugeau A, Combaz J. Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095172
Chicago/Turabian StyleLigozat, Anne-Laure, Julien Lefevre, Aurélie Bugeau, and Jacques Combaz. 2022. "Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095172
APA StyleLigozat, A.-L., Lefevre, J., Bugeau, A., & Combaz, J. (2022). Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions. Sustainability, 14(9), 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095172






