An Exploration of the Relationship between Sustainability-Related Involvement and Learning in Higher Education
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What is the relationship between students’ sustainability-related co-curricular involvement and key sustainability learning outcomes?
- To what extent are demographic characteristics significant predictors of students’ sustainability competencies?
- What is the relationship between key sustainability learning outcomes and students’ engagement in public sustainability-related behaviors, such as climate change leadership behaviors?
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainability
2.2. Higher Education Sustainability Education
2.3. Competencies
3. Conceptual Framework
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site
4.2. Instrument Design
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Measures
4.5. Student Inputs
Demographic Data
4.6. Collegiate Environment Variables (Environment)
Sustainability-Related Involvement
4.7. Behavioral Outcomes (Outputs)
4.7.1. Sustainability-Related Activism
4.7.2. Climate Change Leadership Practices
4.8. Cognitive Learning Outcomes (Outputs)
4.8.1. Systems Thinking
4.8.2. Futures Thinking
4.8.3. Contextual Competence
4.8.4. Sustainability Literacy
4.9. Analytical Procedure
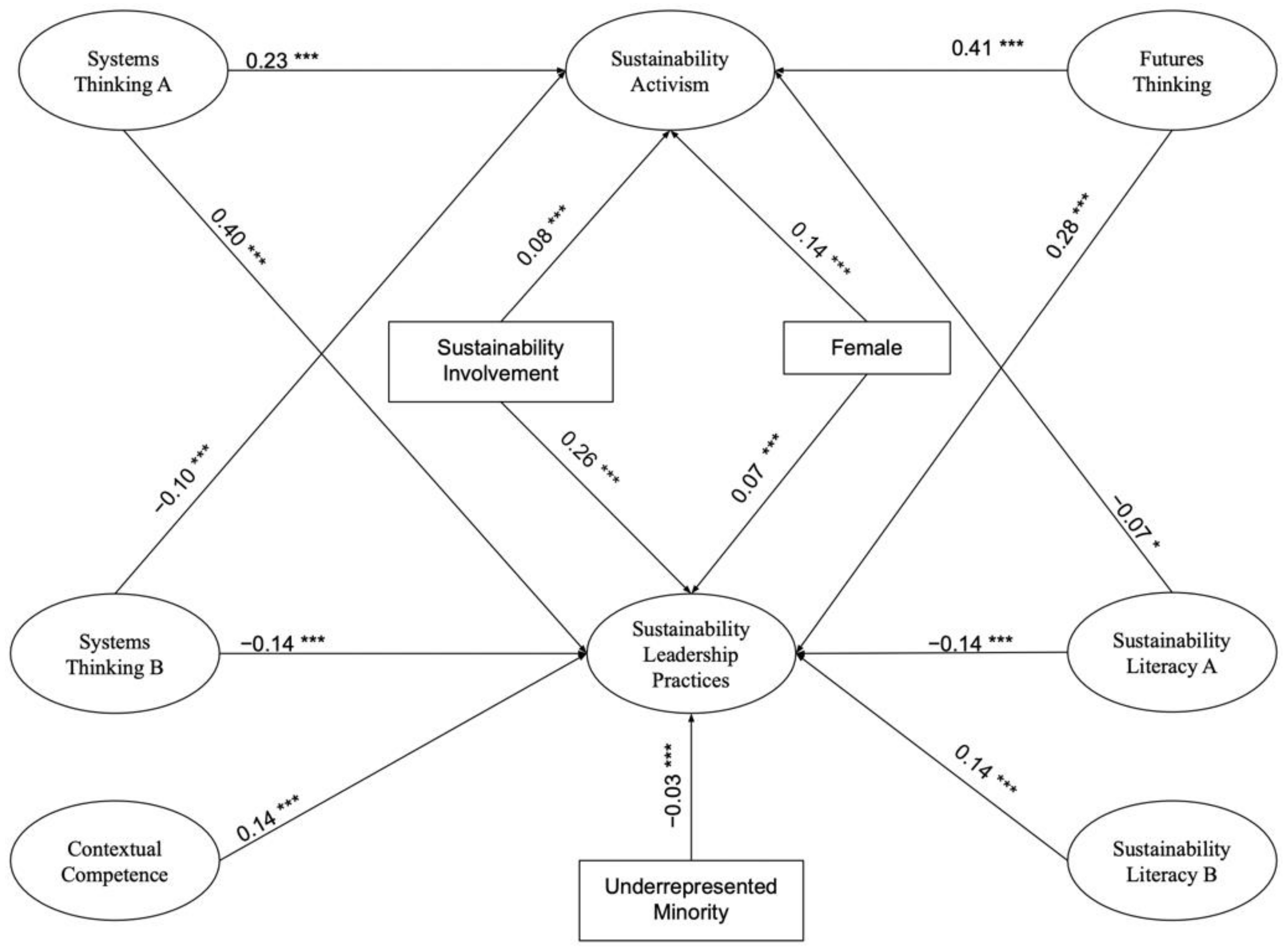
5. Results
5.1. Measurement Model
5.2. MIMIC Models
5.3. Structural Model
6. Limitations
7. Discussion
7.1. The Role of Participation
7.2. Demographic Differences
7.3. Sustainability Learning Outcomes, Activism, and Leadership
7.4. Implications for Teaching about Climate Change
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The National Task Force on Civic Learning and Democratic Engagement. A Crucible Moment: College Learning and Democracy’s Future; Association of American Colleges and Universities: Washington, DC, US, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Astin, A.W.; Astin, H.S. Leadership Reconsidered: Engaging Higher Education in Social Change; Kellogg Foundation: Battle Creek, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, J.B.; Michel, J.O. An examination of higher education institutional level learning outcomes related to sustainability. Innov. High. Educ. 2020, 45, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, K. Higher education for sustainability: Seeking affective learning outcomes. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2008, 9, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipos, Y.; Battisti, B.; Grimm, K. Achieving transformative sustainability learning: Engaging head, hands and heart. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2008, 9, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, D. Social movement theory and the prospects for climate change activism in the United State. Annu. Rev. Political Sci. 2017, 20, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, B.; Davidson, O.R.; Bosch, P.R.; Dave, R.; Meyer, L. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2007. Available online: https://archive.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/publications_ipcc_fourth_assessment_report_wg3_report_mitigation_of_climate_change.htm (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- The President’s Commission on Carbon Neutrality: University of Michigan. Draft Report and Recommendations. 2020. Available online: http://sustainability.umich.edu/media/files/pccn/pccn_draft_final_report.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Glasser, H.; Hirsh, J. Toward the development of robust learning for sustainability core competencies. Sustain. J. Rec. 2016, 9, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterling, S.; Glasser, H.; Rieckmann, M.; Warwick, P. “More than Scaling Up”: A Critical and Practical Inquiry into Operationalizing Sustainability Competencies. In Envisioning Futures for Environmental and Sustainability Education; Corcoran, P.B., Weakland, J.P., Wals, A.E.J., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Crick, R.D. Key competencies for education in a European context: Narratives of accountability or care. Eur. Educ. Res. J. 2008, 7, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arbuthnott, K.D. Sustainable consumption: Attitudes, actions, and well-being. Anal. Soc. Issues Public Policy 2012, 12, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanström, M.; Lozano-García, F.J.; Rowe, D. Learning outcomes for sustainable development in higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2008, 9, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brundtland Commission. Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development Goals: Learning Objectives; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mohai, P.; Pellow, D.; Roberts, J.T. Environmental justice. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kessel, C. Teaching the climate crisis: Existential considerations. J. Curric. Stud. Res. 2020, 2, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, T.A.; Gillig, B.; Hanson, J.M.; Pascarella, E.T.; Blaich, C.F. The conditional nature of high impact/good practices on student learning outcomes. J. High. Educ. 2014, 85, 531–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besong, F.; Holland, C. The dispositions, abilities and behaviours (DAB) framework for profiling learners’ sustainability competencies in higher education. J. Teach. Educ. Sustain. 2015, 17, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal Filho, W.; Pace, P. Teaching Education for Sustainable Development at University Level; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J. Environmental Education in the 21st Century: Theory, Practice, Progress and Promise; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, D.; Winter, J. ‘It’s Not Just Bits of Paper and Light Bulbs’: A Review of Sustainability Pedagogies and their Potential for Use in Higher Education. In Sustainability Education: Perspectives and Practice Across Higher Education; Jones, P., Selby, D., Sterling, S., Eds.; Earthscan: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, J.O. Charting students’ exposure to promising practices of teaching about sustainability across the higher education curriculum. Teach. High. Educ. 2020, 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astin, A. Student involvement: A developmental theory for higher education. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 1984, 25, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kuh, G.D. Assessing what really matters to student learning inside the national survey of student engagement. Chang. Mag. High. Learn. 2001, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G.D. What student affairs professionals need to know about student engagement. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2009, 50, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber-Curan, P. Co-curricular involvement and student leadership as catalysts for student learning. New Dir. High. Educ. 2019, 188, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G.D. High Impact Educational Practices: What They Are, Who Has Access to Them, and Why They Matter. Association of American Colleges and Universities. 2008. Available online: http://provost.tufts.edu/celt/files/High-Impact-Ed-Practices1.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Kwon, R.; Brint, S.; Curwin, K.; Cantwell, A. Co-curricular learning at research universities: Results from the SERU Survey. J. Stud. Aff. Res. Pract. 2020, 57, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, T.S. Exploring the Post-Graduation Benefits of High-Impact Practices in Engineering: Implications for Retention and Advancement in Industry. In Proceedings of the American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference and Exposition, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.; Bridgstock, R. What actually works to enhance graduate employability? The relative value of curricular, co-curricular, and extra-curricular learning and paid work. High. Educ. 2021, 81, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beringer, A.; Wright, T.; Malone, L. Sustainability in higher education in Atlantic Canada. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2008, 9, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.O.; Zwickle, A. The effect of information source on higher education students’ sustainability knowledge. Environ. Educ. Res. 2021, 27, 1080–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.; Helferty, A.; Clarke, A. Student-led campus climate change initiatives in Canada. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2009, 10, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, K.G.; Hart-Steffes, J.S. Sustainability, student affairs, and students. New Dir. Stud. Serv. 2012, 2012, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, D.W. Foreword: Shallow Versus Deep Environmental Education. In Teaching Sustainability: Perspectives from the Humanities and Social Sciences; Peterson Boring, W., Forbes, W., Stephen, F., Eds.; Austin State University Press: Nacogdoches, TX, USA, 2013; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Blewitt, J. Deschooling society? A lifelong learning network for sustainable communities, urban regeneration and environmental technologies. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3465–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, J.O. Toward conceptualizing education for sustainability in higher education. New Dir. Teach. Learn. 2020, 2020, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, I.; Day, T. Sustainability capabilities, graduate capabilities, and Australian universities. Int. J. Sustain. High. Education. 2014, 15, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiek, A.; Withycombe, L.; Redman, C.L. Key competencies in sustainability: A reference framework for academic program development. Sustain. Sci. 2011, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brundiers, K.; Barth, M.; Cebrián, G.; Cohen, M.; Diaz, L.; Doucette-Remington, S.; Zint, M. Key competencies in sustainability in higher education—Toward an agreed-upon reference framework. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwickle, A.M.; Koontz, T.M.; Slagle, K.T.; Bruskotter, J. Assessing sustainability knowledge of a student population: Developing a tool to measure knowledge in the environmental, economic and social domains. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2014, 15, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiserowitz, A.; Kates, R.W.; Parris, T.M. Sustainability values, attitudes, and behaviors: A review of multinational and global trends. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2006, 31, 413–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peattie, K. Green consumption: Behavior and norms. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 195–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Manzanal, R.; Rodríguez-Barreiro, L.; Carrasquer, J. Evaluation of environmental attitudes: Analysis and results of a scale applied to university students. Sci. Educ. 2007, 91, 988–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdig, M.A. Sustainability leadership: Co-creating a sustainable future. J. Chang. Manag. 2007, 7, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astin, A.W. The methodology of research on college impact, part one. Sociol. Educ. 1970, 43, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, K.S.; Head, B.W. Determinants of young Australians’ environmental actions: The role of responsibility attributions, locus of control, knowledge and attitudes. Environ. Educ. Res. 2012, 18, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.S.; Strube, M.J. Environmental attitudes, knowledge, intentions and behaviors among college students. J. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 152, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.; Nilsson, A. Personal and social factors that influence pro-environmental concern and behaviour: A review. Int. J. Psychol. 2014, 49, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, J.; Kollmuss, A. Mind the gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behaviour? Environ. Educ. Res. 2010, 8, 239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Agyeman, J.; Crouch, C. The Contribution of Environmental Justice to Sustainability in Higher Education. In Higher Education and the Challenge of Sustainability; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Décamps, A.; Barbat, G.; Carteron, J.C.; Hands, V.; Parkes, C. Sulitest: A collaborative initiative to support and assess sustainability literacy in higher education. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2017, 15, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugksch, R.C. Scientific literacy: A conceptual overview. Sci. Educ. 2000, 84, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.D.; Wade, J.P. A definition of systems thinking: A systems approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 44, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godfrey, P.; Crick, R.D.; Huang, S. Systems thinking, systems design and learning power in engineering education. Int. J. Eng. Education. 2014, 30, 112–127. [Google Scholar]
- Dyehouse, M.; Bennett, D.; Harbor, J.; Childress, A.; Dark, M. A comparison of linear and systems thinking approaches for program evaluation illustrated using the Indiana Interdisciplinary GK-12. Eval. Program Plan. 2009, 32, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller Connell, K.Y.; Remington, S.M.; Armstrong, C.M. Assessing systems thinking skills in two undergraduate sustainability courses: A comparison of teaching strategies. J. Sustain. Educ. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Futures Thinking in Brief. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/education/school/schoolingfortomorrow-thestarterpackfuturesthinkinginaction.htm (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Ro, H.K.; Merson, D.; Lattuca, L.R.; Terenzini, P.T. Validity of the contextual competence scale for engineering students. J. Eng. Educ. 2015, 104, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Justice. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/environmentaljustice (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Strayhorn, T.L. College Students’ Sense of Belonging: A Key to Educational Success for All; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, L.M.; Hatch, A.; Johnson, A. Cross-national gender variation in environmental behaviors. Soc. Sci. Q. 2004, 85, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, A.; Luo, Y.; Mobley, C.; Shealy, E. Changes in public and private environmentally responsible behaviors by gender: Findings from the 1994 and 2010 general social survey. Sociol. Inq. 2015, 85, 503–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, C.; Quaye, S.J.; Lange, A.C.; Roberts, R.E.; Lacy, M.C.; Wilson, K.O. A student should have the privilege of just being a student: Student activism as labor. Rev. High. Educ. 2019, 42, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barndhardt, C.L. The Promise and Struggles of Campus-Based Student Activism. In Student Activism in the Academy: Its Struggles and Promise; Sasso, P.A., DeVitis, J.L., Eds.; Myers Education Press: Gorham, ME, USA, 2019; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Osagie, E.R.; Wesselink, R.; Blok, V.; Lans, T.; Mulder, M. Individual competencies for corporate social responsibility: A literature and practice perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 135, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.; Nicolazzo, Z. High impact of [Whiteness] on Trans* students in postsecondary education. Equity Excell. Educ. 2018, 51, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgo, C.A.; Linley, J.L.; Renn, K.A.; Woodford, M.R. High impact for whom? The influence of environment and identity on lesbian, gay, bisexual, and queer college students’ participation in high-impact practices. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2019, 60, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayhorn, T.L. How college students’ engagement affects personal and social learning outcomes. J. Coll. Character. 2008, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Registrar, University of Michigan. Enrollment Reports. 2020. Available online: https://ro.umich.edu/reports/enrollment (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- University of Michigan. Facts and Figures. 2020. Available online: https://umich.edu/facts-figures/ (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Graham Sustainability Institute, University of Michigan. U-M Sustainability Course Database. 2020. Available online: http://graham.umich.edu/course-search (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Shephard, K.; Harraway, J.; Lovelock, B.; Skeaff, S.; Slooten, L.; Strack, M.; Jowett, T. Is the environmental literacy of university students measurable? Environ. Educ. Res. 2014, 20, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cadenas, G.A.; Bernstein, B.L. Measuring college students’ leadership engagement in advocacy. J. Divers. High. Educ. 2020, 13, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgraft, R.G.; Carew, A.L.; Therese, S.A.; Blundell, D.L. Teaching and assessing systems thinking in engineering. Res. Eng. Educ. Symp. 2008, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Tonn, B.; MacGregor, D. Individual approaches to futures thinking and decision making. Futures 2009, 41, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.; Evans, E.B.; Knight, R.; Ruehr, T. Interdisciplinary Team Teaching: Lessons for Engineering Instructors from a Capstone Course in Environmental Studies. In Proceedings of the 2007 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–27 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Guildford: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Modeling 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemer, M.A.; Li, C. Critical consciousness development and political participation among marginalized youth. Child Dev. 2011, 82, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington-Doucette, S.; Musgrove, S. Variation in sustainability competency development according to age, gender, and disciplinary affiliation: Implications for teaching practice and overall program structure. Int. J. Sustain. High. Ed. 2015, 16, 537–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education. Salaries and Status of Sustainability Professionals in Higher Education. 2020. Available online: https://www.aashe.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/2020-staffing-survey-report-1.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Taylor, D.E. Gender and racial diversity in environmental organizations: Uneven accomplishments and cause for concern. Environ. Justice 2015, 8, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craps, S. Introduction: Ecological grief. Am. Imago 2020, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macy, J. Working Through Environmental Despair. In Ecopsychology: Restoring the Earth, Healing the Mind, Roszak, T.E., Gomes, M.E., Kanner, A.D., Eds.; Sierra Club Books: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, M. Eco-anxiety. RSA J. 2018, 164, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A. Eco-anxiety at university: Student experiences and academic perspectives on cultivating healthy emotional responses to the climate crisis. Indep. Study Proj. Collect. 2017, 2642. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, L.; Rocque, R.; Desmarais, M.É. Enabling students to face the environmental crisis and climate change with resilience: Inclusive environmental and sustainability education approaches and strategies for coping with eco-anxiety. Int. J. High. Educ. Sustain. 2020, 3, 112–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nisiforou, O.; Charalambides, A.G. Assessing undergraduate university students’ level of knowledge, attitudes and behaviour towards biodiversity: A case study in Cyprus. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2012, 34, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habron, G.; Goralnik, L. Embracing the learning paradigm to foster systems thinking. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2012, 13, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Competency | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Learning Outcomes | |
| Sustainability Literacy | Sustainability literacy can be defined similarly to competencies, as “the knowledge, skills, and mindsets that help compel an individual to become deeply committed to building a sustainable future and allow him or her to make informed and effective decisions to this end.” [53] (p. 141). It can also be understood as an outgrowth of scientific literacy whereby it is implicit concerning what students ought to know about science [54] and thus can represent what knowledge students ought to understand about sustainability. |
| Systems Thinking | Systems thinking represents “a set of synergistic analytic skills used to improve the capability of identifying and understanding systems, predicting their behaviors, and devising modifications to them in order to produce desired effects” [55] (p. 675). It is an interdisciplinary construct often taught in engineering [56], economics [57], and sustainability [58]. |
| Futures Thinking | Futures thinking is “a method for informed reflection on the major changes that will occur in the next 10, 20 or more years in all areas of social life, including education. Futures Thinking uses a multidisciplinary approach to pierce the veil of received opinion and identify the dynamics that are creating the future” [59]. Given the uncertainty around climate change and sustainability, students ought to be equipped to navigate sustainability issues in this interdisciplinary way. |
| Contextual Competence | Contextual competence refers to the “ability to anticipate and understand the constraints and impacts of social, cultural, environmental, political, and other contexts on engineering solutions” [60] (p. 36). In the context of sustainability, Contextual Competence represents students’ “ability to anticipate and understand the constraints and impacts of social, cultural, environmental, political, and other contexts on engineering solutions” within sustainability. |
| Affective Learning Outcomes | |
| Environmental Justice | Scholarship on environmental justice comes from “an interdisciplinary body of literature, in which researchers were documenting the unequal impacts of environmental pollution on different social classes and racial/ethnic groups ….. known variously as environmental racism, environmental inequality” [16]. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), environmental justice is “the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people regardless of race, color, national origin, or income, with respect to the development, implementation, and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies,” [61]. |
| Sense of Belonging | Sense of belonging is a college student’s “perceived social support on campus, a feeling or sensation of connectedness, the experience of mattering or feeling cared about, accepted, respected, valued by, and important to the group” [62] (p. 3). In the context of sustainability, sense of belonging is a students’ perceived feeling of connectedness, mattering, acceptance within the sustainability learning space. |
| Behavioral Learning Outcomes | |
| Public Behaviors | Sustainability-related, society-oriented behaviors are often referred to as “public” behaviors. Public behaviors include collective activism in the form of protest/demonstration. While private behaviors are less political and reflect a form of consumer behaviors, public behaviors are more political and reflect a form of active citizenship [63,64]. Public behaviors are distinguished as visible forms of support for the environment—such as joining an environmental group or participating in a protest. Public behaviors have been understood by the literature to be the ultimate evidence of one’s commitment to the environment [64]. |
| Activism | Activism in the context of sustainability includes efforts to effect positive sustainability-related change. To be classified as activism, these efforts must extend beyond individual actions (e.g., lifestyle changes) to include collective or public behaviors. Linder et al. [65] use the term activism to broadly refer to “students’ efforts to interrupt power and dominance to create more just campuses” (p. 39). Whether applicable to campus or beyond, student activism has been described as “discourse in action—a form of praxis, a profound effort toward social, economic, and political progress,” [66]. |
| Sustainability Leadership | Sustainability leadership “reflects an emerging consciousness among people who are choosing to live their lives and lead their organizations in ways that account for their impact on the earth, society, and the health of local and global economies” [46] Sustainability leaders must be able to develop a vision and being prepared to take risks all while thinking about the future [67]. |
| Survey Sample N (%) | Sampling Frame N (%) | University Statistics N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Female | 2786 (65.1) | 9516 (52.1) | 24,087 (50.3) |
| Male | 1495 (34.9) | 8764 (47.9) | 23,820 (49.7) |
| Unknown | - | 1 (0.01) | - |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||
| Asian America/Pacific Islander | 848 (19.8) | 3560 (19.5) | 6755 (14.1) |
| Black/African American | 139 (3.3) | 773 (4.2) | 2079 (4.3) |
| Latino/a | 313 (7.3) | 1307 (7.3) | 3258 (6.8) |
| Native American/Native Alaskan | 7 (0.2) | 31 (0.2) | 81 (0.2) |
| White | 2361 (55.2) | 10,014 (54.8) | 24,819 (51.8) |
| Other | 613 (14.3) | 2596 (14.2) | 4235 (8.8) |
| URM Status | 510 (11.9) | 2392 (13.1) | 6318 (13.2) |
| International Student Status | 333 (7.8) | 1762 (9.6) | 6680 (13.9) |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Organize a local group to pass out leaflets to inform the public about sustainability issues in your community. | 3.41 | 1.14 |
| Organize a local group of people who want to increase awareness about climate change. | 3.28 | 1.16 |
| Organize a local group who are concerned about climate change and connect with other organizations. | 3.24 | 1.18 |
| Contact your local government about climate-related concerns. | 3.16 | 1.20 |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Persuade others to take action to help mitigate climate change. | 2.93 | 1.16 |
| Teach new concepts about climate change to others. | 2.61 | 1.22 |
| Take a role within a team addressing climate change in our work. | 2.31 | 1.18 |
| Establish and use networks in a community for addressing climate change. | 2.22 | 1.13 |
| Create innovative solutions for mitigating climate change. | 2.05 | 1.08 |
| Give a presentation about climate change. | 1.96 | 1.05 |
| Organize a project, event, etc. related to climate change initiatives. | 1.94 | 1.00 |
| Attend leadership training to develop skills for addressing climate change. | 1.88 | 1.09 |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Systems Thinking (Factor A) | ||
| Designing systems and/or processes for addressing sustainability problems according to specified criteria. | 3.28 | 1.24 |
| Managing sustainability projects. | 3.25 | 1.26 |
| Documenting, analyzing and reflecting on sustainability outcomes. | 3.02 | 1.25 |
| Using a holistic approach for designing sustainability solutions. | 3.01 | 1.23 |
| Working according to the principles of sustainable development. | 2.63 | 1.15 |
| Systems Thinking (Factor B) | ||
| Communicating with the wider community. | 2.33 | 1.11 |
| Operating professionally within a business environment. | 2.21 | 1.20 |
| Meeting legal, professional, and ethical responsibilities. | 2.07 | 1.07 |
| Communicating with others in teams. | 1.74 | 0.89 |
| Working with people from other disciplines and cultures. | 1.73 | 0.91 |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| I spend time thinking about how climate change will affect future generations. | 1.99 | 1.03 |
| I spend time thinking about how climate change will affect my personal future. | 1.91 | 1.06 |
| Thinking about the impact of climate change solutions on future generations is interesting to me. | 1.88 | 0.94 |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Ability to recognize how different contexts change a solution. | 3.65 | 0.99 |
| Knowledge of the connections between climate change solutions and their implications for whom it benefits. | 3.30 | 1.07 |
| Knowledge of contexts that might affect the solution to a climate change problem. | 3.24 | 1.04 |
| Ability to apply knowledge about different cultures, social values, or political systems when addressing climate change challenges. | 3.03 | 1.07 |
| Item | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability Literacy (Factor A) | ||
| I understand the value of scientific evidence for addressing climate change. | 4.75 | 0.60 |
| I understand why climate change is a critical focus of scientists, businesses, communities, and organizations. | 4.65 | 0.66 |
| I understand the value of local/community knowledge for addressing climate change. | 4.59 | 0.73 |
| I understand how climate change impacts people, the planet and our economy. | 4.37 | 0.73 |
| Sustainability Literacy (Factor B) | ||
| I understand strategies for achieving sustainability. | 4.16 | 0.85 |
| I can explain the consequences of climate change to suit various audiences/stakeholders. | 3.95 | 1.01 |
| I can explain what climate change is to suit various audiences/stakeholders. | 3.79 | 1.05 |
| I can explain the causes of climate change to suit various audiences/stakeholders. | 3.79 | 1.04 |
| Construct | Std. Estimate | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activism | |||
| Female | 0.15 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.53 |
| Participation | 0.23 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Leadership Practices | |||
| Female | 0.05 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.42 |
| Participation | 0.43 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Systems Thinking A | |||
| Female | −0.09 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Participation | 0.29 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Systems Thinking B | |||
| Female | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.005 |
| URM | 0.08 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Participation | 0.15 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Futures Thinking | |||
| Female | 0.13 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.15 |
| Participation | 0.28 | 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Contextual Competence | |||
| Female | −0.003 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.938 |
| Participation | 0.233 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Literacy A | |||
| Female | 0.10 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | −0.002 | 0.02 | 0.89 |
| Participation | 0.20 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| Literacy B | |||
| Female | −0.06 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
| URM | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.94 |
| Participation | 0.23 | 0.02 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henderson, T.S.; Michel, J.O.; Bryan, A.; Canosa, E.; Gamalski, C.; Jones, K.; Moghtader, J. An Exploration of the Relationship between Sustainability-Related Involvement and Learning in Higher Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095506
Henderson TS, Michel JO, Bryan A, Canosa E, Gamalski C, Jones K, Moghtader J. An Exploration of the Relationship between Sustainability-Related Involvement and Learning in Higher Education. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095506
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenderson, Trevion S., Jessica O. Michel, Alex Bryan, Emily Canosa, Clara Gamalski, Kelly Jones, and Jeremy Moghtader. 2022. "An Exploration of the Relationship between Sustainability-Related Involvement and Learning in Higher Education" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095506
APA StyleHenderson, T. S., Michel, J. O., Bryan, A., Canosa, E., Gamalski, C., Jones, K., & Moghtader, J. (2022). An Exploration of the Relationship between Sustainability-Related Involvement and Learning in Higher Education. Sustainability, 14(9), 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095506






