Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
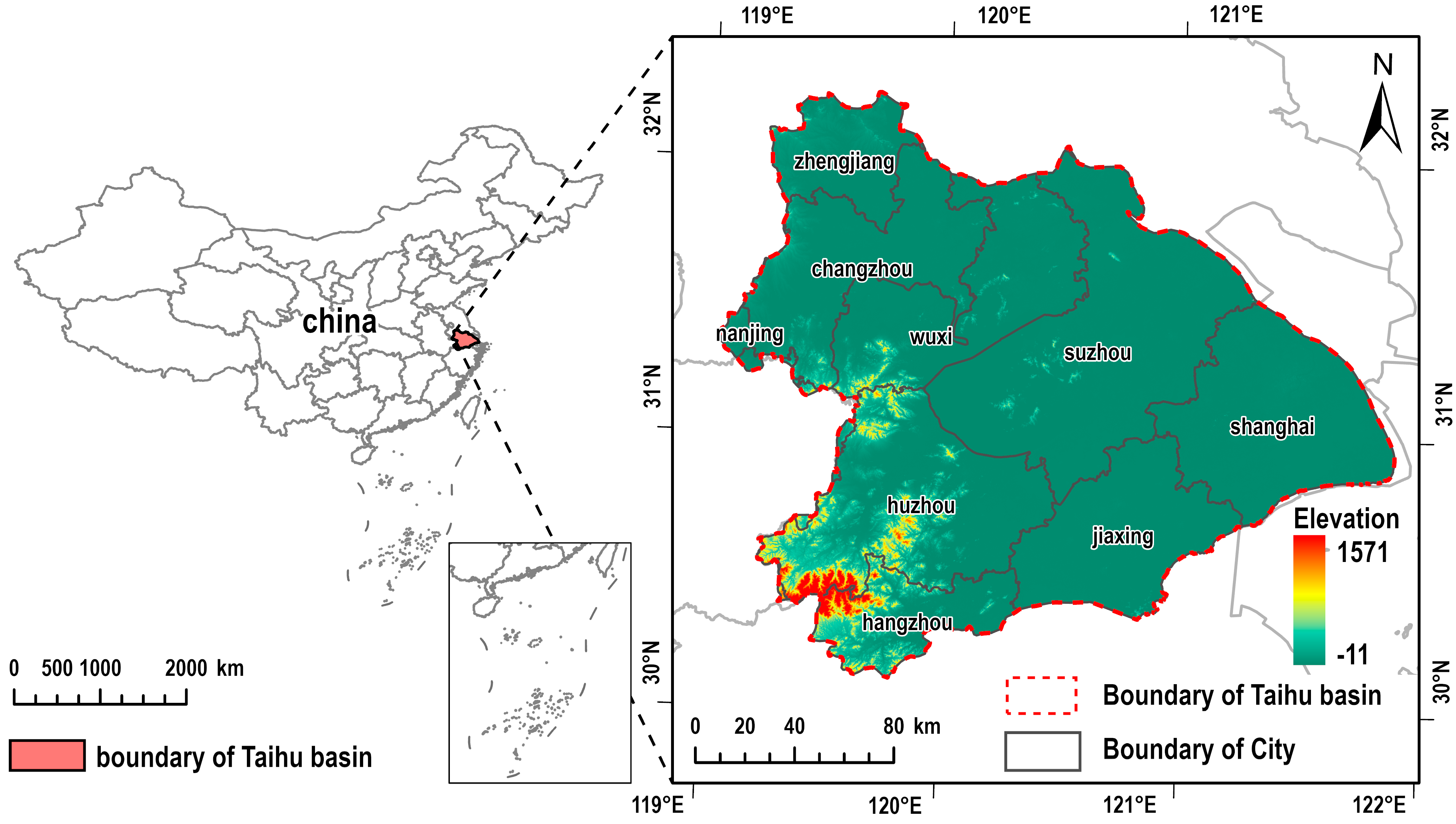
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Material
2.3. Construction of Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI)
2.3.1. Greenness
2.3.2. Wetness
2.3.3. Heat
2.3.4. Dryness
2.3.5. Calculation of Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI)
2.4. Geodetector
3. Results
3.1. RSEI Model Testing
3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in Eco-Environment Quality of Taihu Lake Basin
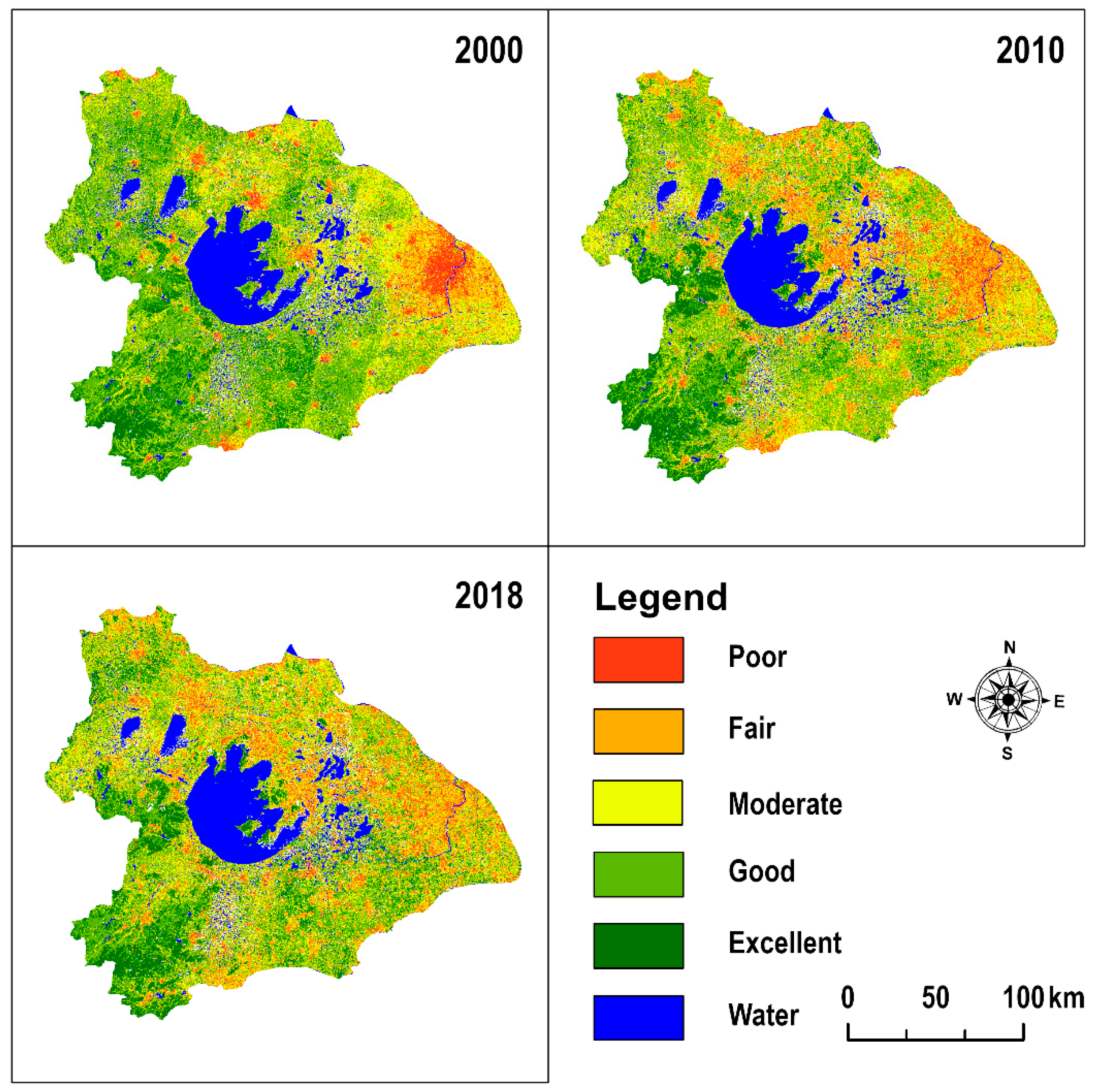
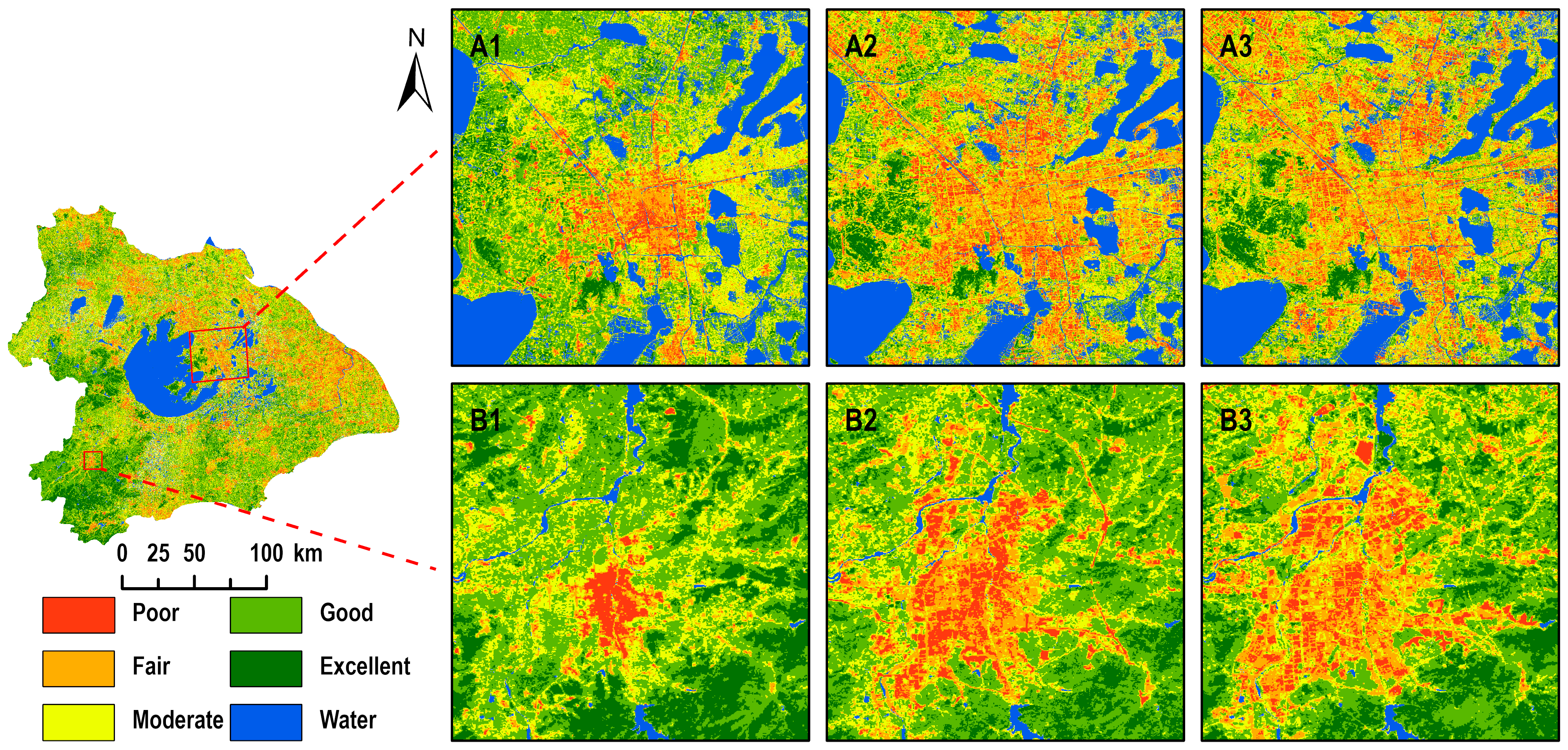
3.2.1. Grading Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality in Taihu Lake Basin
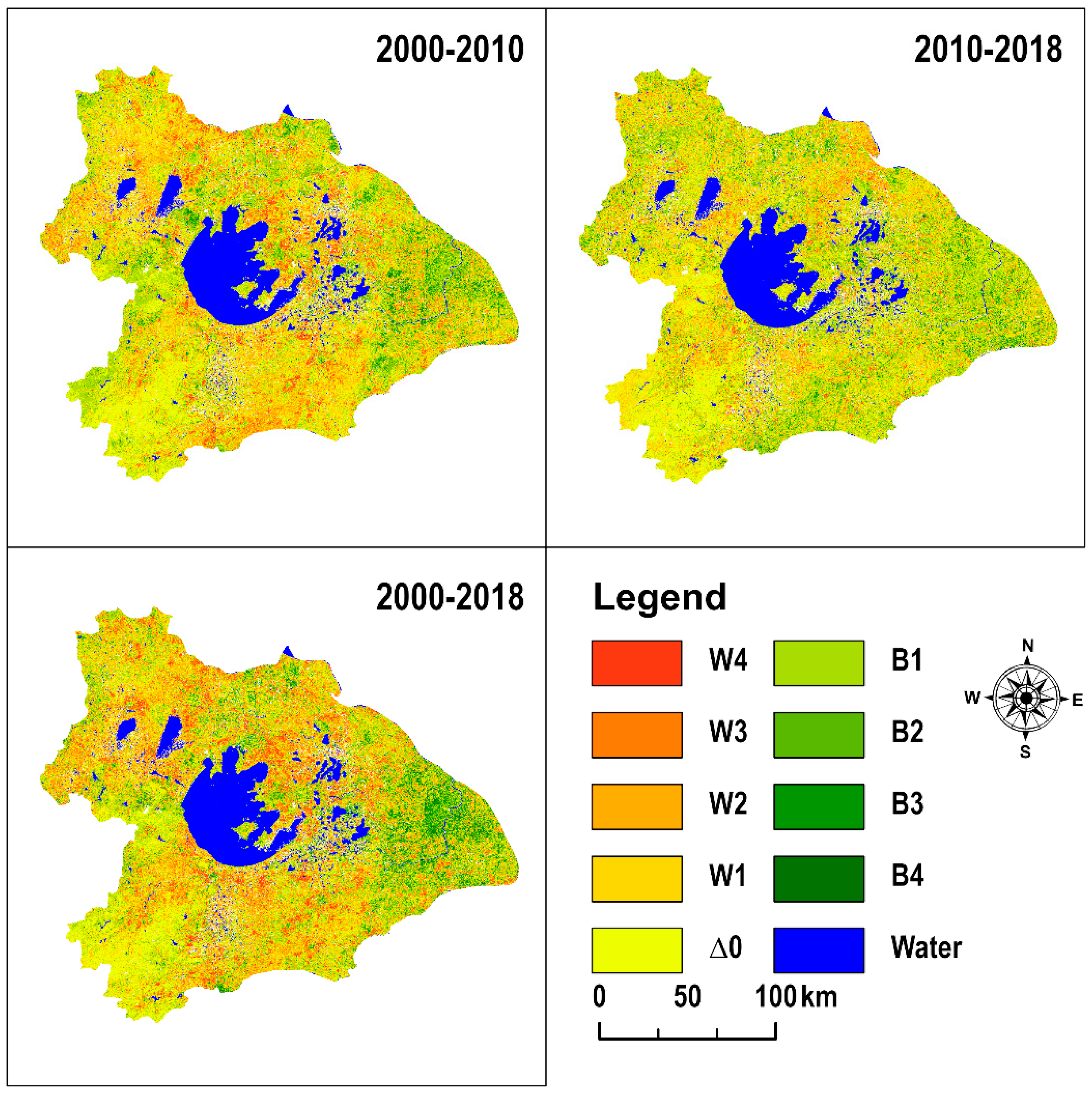
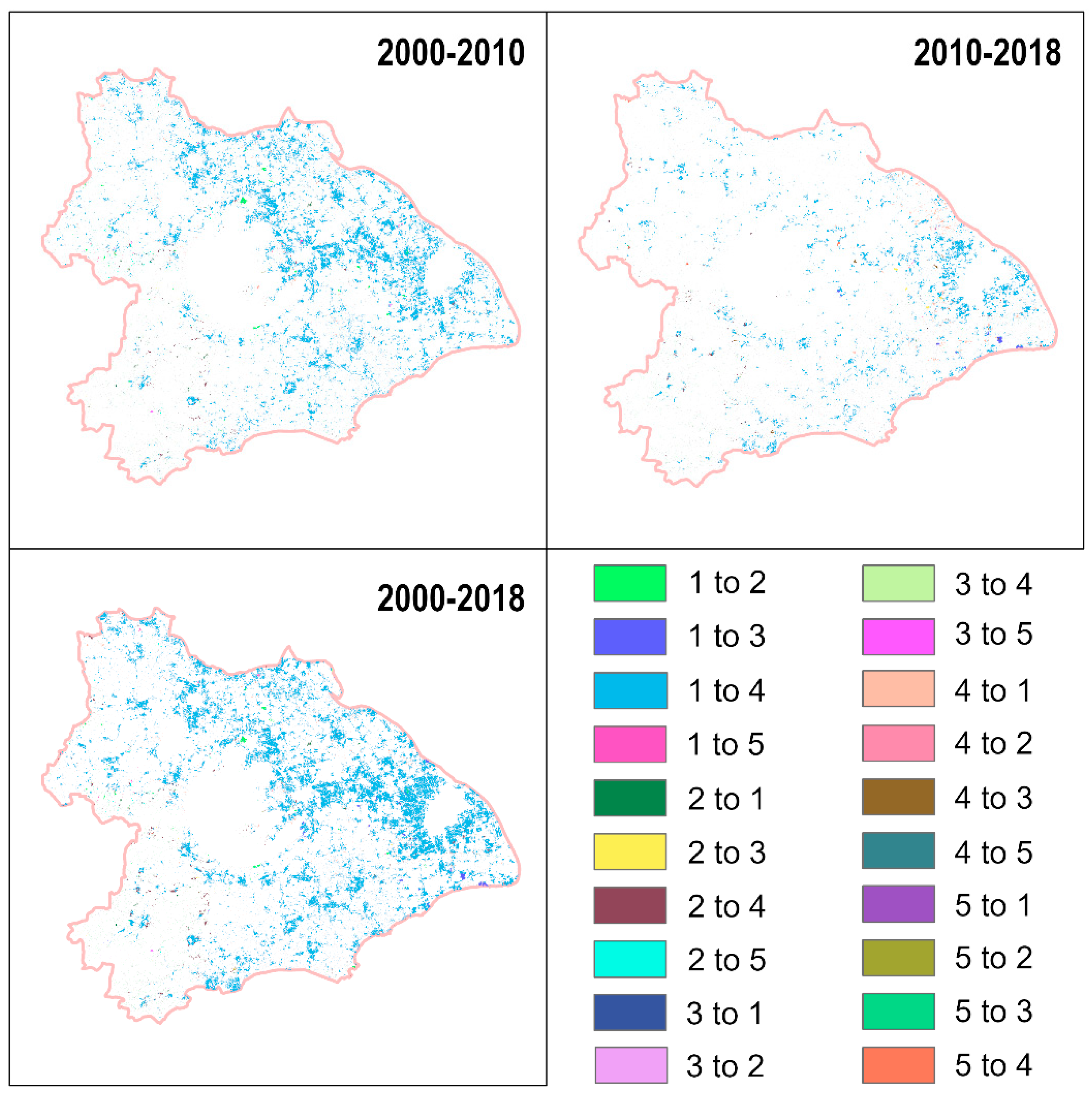
3.2.2. Detection of Eco-Environmental Quality Changes in Taihu Lake Basin
3.3. Influencing Factors of Spatial Heterogeneity in Ecological Environment Quality of Taihu Lake Basin
3.4. Relationship between Ecological Change and Land-Use Change
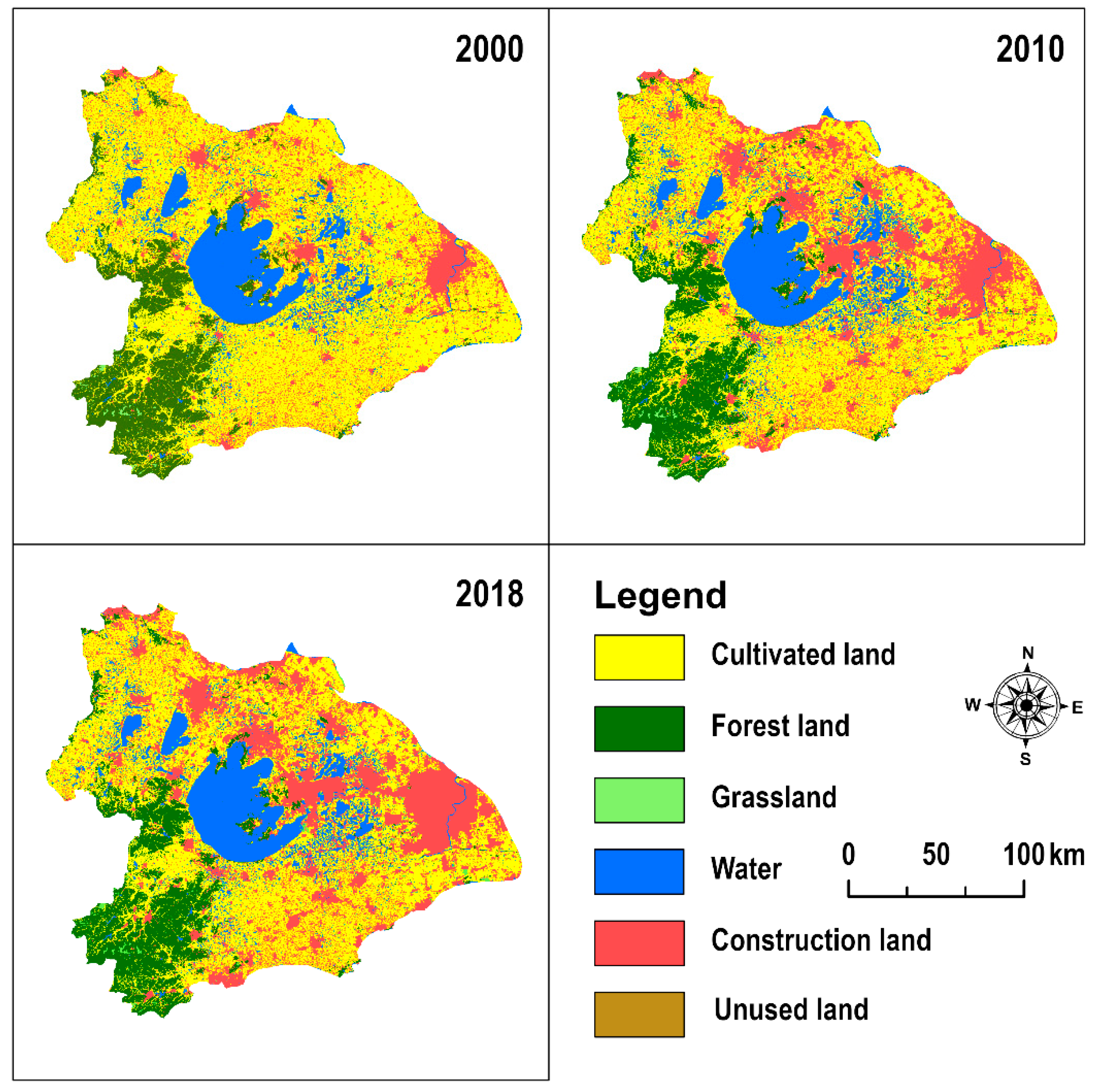
3.4.1. Characteristics of Land-Use Changes in Taihu Lake Basin
3.4.2. Relationship between Land-Use Change and Socio-Economic Indicators
3.4.3. Changes in Total RSEI for Different Land-Use Conversion Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of the Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI)
4.2. Influence Factors of RSEI Spatial Heterogeneity
4.3. Relationship between Total RSEI Changes and Land-Use Changes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sowińska-Świerkosz, B. Application of surrogate measures of ecological quality assessment: The introduction of the Indicator of Ecological Landscape Quality (IELQ). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. Catena 2016, 137, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Ma, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, S. What Has Caused Desertification in China? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Dong, Z. The relative role of climatic and human factors in desertification in semiarid China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2006, 16, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Sun, W.; Yang, K.; Zhao, L. China urbanization process induced vegetation degradation and improvement in recent 20 years. Cities 2021, 114, 103207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Li, S. The impacts of urbanization and climate change on urban vegetation dynamics in China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Coomes, D.A.; Gibson, L.; Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, M. Forest Fragmentation in China and Its Effect on Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Sun, S.; Xiao, L.; Guo, J. Ecological environment assessment based on land use simulation: A case study in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Vik, J.O.; Mysterud, A.; Gaillard, J.-M.; Tucker, C.J.; Stenseth, N.C. Using the satellite-derived NDVI to assess ecological responses to environmental change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammi, S.A.; Meng, Q. Use Time Series NDVI and EVI to Develop Dynamic Crop Growth Metrics for Yield Modeling. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Gamon, J.; Vargas, S.; Tweedie, C. Relationships of NDVI, Biomass, and Leaf Area Index (LAI) for Six Key Plant Species in Barrow, Alaska. PeerJ 2015, 3, e913v1. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhou, S.; Chen, D.; Wei, Z.; Dai, L.; Li, X. Determining the contributions of urbanisation and climate change to NPP variations over the last decade in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Yang, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Influences of urban spatial form on urban heat island effects at the community level in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarch, M.A.A.; Malekinezhad, H.; Mobin, M.H.; Dastorani, M.T.; Kousari, M.R. Drought Monitoring by Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI) in Iran. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3485–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsakiris, G. Establishing a Drought Index Incorporating Evapotranspiration. Eur. Water 2005, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Davudirad, A.A. Watershed Health Assessment Using the Pressure–State–Response (PSR) Framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A Remote Sensing Index for Assessment of Regional Ecological Changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Zan, C.; Ren, J.; Yang, L.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, L. Using the Google Earth Engine to rapidly monitor impacts of geohazards on ecological quality in highly susceptible areas. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yan, C.; Xing, X. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal change and driving factors of the Eco-Environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wu, C.; Ye, C. Effects of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on Nitrogen Transport in Northern Taihu Basin, China during 1990–2017. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, G.; Tan, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Li, H.; Wan, R.; Su, W.; Zhang, J. Ecological risk assessment of ecosystem services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Liu, J.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, K.; Deng, J. Why Lake Taihu continues to be plagued with cyanobacterial blooms through 10 years (2007–2017) efforts. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Hua, W.; Dai, X. Performance Evaluation of Watershed Environment Governance—A Case Study of Taihu Basin. Water 2022, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Tong, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y. Projection of land surface temperature considering the effects of future land change in the Taihu Lake Basin of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 167, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, D. Use of the DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Data to Study Urbanization and Its Influence on NDVI in Taihu Basin, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2016, 142, 04016018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.-F. Optimal discretization for geographical detectors-based risk assessment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; He, R.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Luo, G.; Peng, H.; Qiu, J. The Dynamic Change of Vegetation Cover and Associated Driving Forces in Nanxiong Basin, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Sader, S.A. Comparison of time series tasseled cap wetness and the normalized difference moisture index in detecting forest disturbances. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A new index for delineating built-up land features in satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han-Qiu, X.U. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Shen, J.; He, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatial-temporal analysis of ecosystem services value and research on ecological compensation in Taihu Lake Basin of Jiangsu Province in China from 2005 to 2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ming, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, X. Dynamic Monitoring and Analysis of Ecological Quality of Pingtan Comprehensive Experimental Zone, a New Type of Sea Island City, Based on RSEI. Sustainability 2019, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Guo, J.-X.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, H.; Han, Y. Spatial variation of ecological environment quality and its influencing factors in Poyang Lake area, Jiangxi, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, D. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation coverage and its associated influence factor analysis in the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32866–32879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.T.; Tian, Z.Q. Spatiotemporal Differences and Driving Factors of Land Development Degree in China Based on Geographical Detector. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.F.; Xu, J.H. Spatio-Temporal Correlation between Urbanization and Vegetation Vigor in the Delta of Yangtze River. Ecol. Sci. 2008, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Xie, C. Land use change and ecological environment evolution in Taihu Lake Basin. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Spit, T.; Jin, Z.; Bakker, M.; Wu, Q. Can the Land Use Master Plan Control Urban Expansion and Protect Farmland in China? A Case Study of Nanjing. Growth Chang. 2018, 49, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Dataset Type | Number of Images | Date Times | Path/Row |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Landsat 5 TM | 57 | 3 May 2000, 5 May 2000, 12 May 2000, 19 May 2000, 21 May 2000, 28 May 2000, | 118/038, 118/039, |
| 6 June 2000, 13 June 2000, 20 June 2000, 29 June 2000, 6 July 2000, 8 July 2000, | 119/038, 119/039, | |||
| 15 July 2000, 22 July 2000, 24 July 2000, 31 July 2000, 7 August 2000, 9 August 2000, | 120/038, 120/039 | |||
| 16 August 2000, 23 August 2000, 1 September 2000, 8 September 2000, 10 September 2000, 17 September 2000, | ||||
| 24 September 2000, 26 September 2000, 10 October 2000, 19 October 2000, 28 October 2000, 4 November 2000, | ||||
| 13 November 2000, 20 November 2000 | ||||
| 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 43 | 1 May 2010, 17 May 2010, 24 May 2010, 31 May 2010, 16 June 2010, 2 July 2010, | 118/038, 118/039, |
| 4 July 2010, 18 July 2010, 20 July 2010, 3 August 2010, 5 August 2010, 12 August 2010, | 119/038, 119/039, | |||
| 19 August 2010, 21 August 2010, 20 September 2010, 6 October 2010, 8 October 2010, 15 October 2010, | 120/038, 120/039 | |||
| 22 October 2010, 31 October 2010, 7 November 2010, 9 November 2010, 16 November 2010, 23 November 2010, | ||||
| 25 November 2010 | ||||
| 2018 | Landsat 8 OLI | 65 | 14 May 2018, 23 May 2018, 30 May 2018, 6 June 2018, 8 June 2018, 15 June 2018, | 118/038, 118/039, |
| 24 June 2018, 8 July 2018, 10 July 2018, 17 July 2018, 24 July 2018, 26 July 2018, | 119/038, 119/039, | |||
| 2 August 2018, 9 August 2018, 11 August 2018, 18 August 2018, 25 August 2018, 27 August 2018, | 120/037, 120/038, | |||
| 3 September 2018, 10 September 2018, 19 September 2018, 26 September 2018, 28 September 2018, 5 October 2018, | 120/039 | |||
| 12 October 2018, 21 October 2018, 28 October 2018, 30 October 2018, 13 November 2018, 22 November 2018, | ||||
| 29 November 2018 |
| Year | Indicator | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | NDVI | 0.525 | −0.595 | −0.305 | −0.527 |
| Wet | 0.329 | 0.798 | −0.173 | −0.474 | |
| LST | −0.474 | 0.016 | −0.880 | 0.019 | |
| NDBSI | −0.626 | −0.092 | 0.320 | −0.705 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.128 | 0.045 | 0.012 | 0.003 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 68.25% | 23.82% | 6.38% | 1.54% | |
| 2010 | NDVI | 0.612 | −0.646 | −0.147 | −0.432 |
| Wet | 0.268 | 0.711 | −0.251 | −0.600 | |
| LST | −0.372 | −0.161 | −0.914 | 0.025 | |
| NDBSI | −0.644 | −0.225 | 0.284 | −0.673 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.136 | 0.033 | 0.016 | 0.002 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 72.41% | 17.57% | 8.76% | 1.26% | |
| 2018 | NDVI | 0.598 | −0.523 | −0.333 | −0.508 |
| Wet | 0.328 | 0.370 | 0.729 | −0.474 | |
| LST | −0.383 | −0.752 | 0.536 | −0.028 | |
| NDBSI | −0.623 | 0.155 | −0.266 | −0.719 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.150 | 0.035 | 0.027 | 0.002 | |
| Percent eigenvalue | 70.60% | 16.23% | 12.46% | 0.71% |
| Year | Indicator | NDVI | WET | LST | NDBSI | RSEI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | NDVI | 1 | 0.121 | 0.667 | 0.778 | 0.838 |
| WET | 0.121 | 1 | 0.441 | 0.626 | 0.590 | |
| LST | 0.667 | 0.441 | 1 | 0.764 | 0.866 | |
| NDBSI | 0.778 | 0.626 | 0.764 | 1 | 0.972 | |
| C | 0.522 | 0.396 | 0.610 | 0.723 | 0.816 | |
| 2010 | NDVI | 1 | 0.254 | 0.561 | 0.808 | 0.897 |
| WET | 0.254 | 1 | 0.444 | 0.704 | 0.607 | |
| LST | 0.561 | 0.444 | 1 | 0.657 | 0.751 | |
| NDBSI | 0.808 | 0.704 | 0.657 | 1 | 0.970 | |
| C | 0.541 | 0.467 | 0.576 | 0.723 | 0.806 | |
| 2018 | NDVI | 1 | 0.399 | −0.472 | −0.893 | 0.913 |
| WET | 0.399 | 1 | −0.426 | −0.729 | 0.696 | |
| LST | −0.472 | −0.426 | 1 | 0.512 | −0.670 | |
| NDBSI | −0.893 | −0.729 | 0.512 | 1 | −0.974 | |
| C | 0.588 | 0.518 | 0.470 | 0.711 | 0.813 | |
| Mean of C | 0.550 | 0.460 | 0.552 | 0.719 | 0.812 |
| Year | RSEI | NDVI | WET | LST | NDBSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.594 | 0.546 | 0.543 | 0.341 | 0.388 |
| 2010 | 0.557 | 0.498 | 0.665 | 0.483 | 0.41 |
| 2018 | 0.553 | 0.535 | 0.68 | 0.512 | 0.457 |
| mean | 0.568 | 0.526 | 0.629 | 0.445 | 0.418 |
| RSEI Level | 2000 | 2010 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |
| Poor (0–0.2) | 1561.41 | 4.97 | 1826.28 | 5.81 | 1936.36 | 6.16 |
| Fair (0.2–0.4) | 3230.98 | 10.27 | 5419.73 | 17.23 | 5725.03 | 18.20 |
| Moderate (0.4–0.6) | 8862.38 | 28.18 | 9274.32 | 29.49 | 9590.00 | 30.49 |
| Good (0.4–0.6) | 14,441.47 | 45.92 | 11,687.22 | 37.16 | 10,376.92 | 32.99 |
| Excellent (0.8–1) | 3351.56 | 10.66 | 3240.26 | 10.30 | 3819.52 | 12.14 |
| Level | Change Value |
|---|---|
| Almost Unchanged | |
| Slightly Changed | |
| Moderately Changed | |
| Significantly Changed | |
| Dramatically Changed |
| Change Level | 2000–2010 | 2010–2018 | 2000–2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |
| Dramatically degraded | 1201.67 | 3.82 | 578.85 | 1.84 | 1694.02 | 5.39 |
| Significantly degraded | 2192.33 | 6.97 | 1415.53 | 4.5 | 2875.21 | 9.14 |
| Moderately degraded | 3233.05 | 10.28 | 2349.7 | 7.47 | 3498 | 11.12 |
| Slightly degraded | 6152.96 | 19.56 | 5680.15 | 18.06 | 5453.01 | 17.34 |
| Almost unchanged | 9452.71 | 30.06 | 10,663.91 | 33.91 | 8014.15 | 25.48 |
| Slightly meliorated | 5984.05 | 19.03 | 6723.36 | 21.38 | 5425.16 | 17.25 |
| Moderately meliorated | 2181.06 | 6.93 | 2740.48 | 8.71 | 2605.11 | 8.28 |
| Significantly meliorated | 875.63 | 2.78 | 1084.21 | 3.45 | 1437.85 | 4.57 |
| Dramatically meliorated | 174.34 | 0.55 | 211.61 | 0.67 | 445.29 | 1.42 |
| GDP | Population Density | Elevation | Slope | Land-Use | Precipitation | Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | 0.304 | 0.418 | 0.308 | 0.309 | 0.594 | 0.208 | 0.233 |
| Factors | GDP | Population Density | Elevation | Slope | Land-Use | Precipitation | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | 0.304 | ||||||
| Population density | 0.456 # | 0.418 | |||||
| Elevation | 0.493 # | 0.57 # | 0.308 | ||||
| Slope | 0.498 # | 0.577 # | 0.319 # | 0.309 | |||
| Land-use | 0.650 # | 0.662 # | 0.621 # | 0.622 # | 0.594 | ||
| precipitation | 0.431 # | 0.513 # | 0.334 # | 0.337 # | 0.618 # | 0.208 | |
| temperature | 0.454 # | 0.524 # | 0.384 # | 0.386 # | 0.637 # | 0.447 * | 0.233 |
| 2000–2010 | 2010–2018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | |
| Cultivated land | 17,474.54 | 71.32 | 1.00 | 3552.02 | 13.88 | 16,119.30 | 30.61 | 28.22 | 1448.72 | 1.17 |
| Forest land | 41.57 | 4782.90 | 4.15 | 67.83 | 22.37 | 31.21 | 4768.70 | 10.04 | 48.28 | 0.54 |
| Grassland | 1.32 | 4.31 | 143.68 | 3.56 | 2.62 | 1.30 | 2.96 | 144.70 | 2.84 | 0.03 |
| Construction land | 130.13 | 5.71 | 0.11 | 4970.58 | 6.39 | 176.33 | 6.27 | 10.68 | 8500.45 | 0.08 |
| Unused land | 0.05 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 10.89 | 1.30 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 11.70 | 41.64 |
| 2000–2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Forest | Grassland | Construction Land | Unused Land | Sum | |
| Cultivated land | 16,133.54 | 76.98 | 41.00 | 4865.73 | 10.03 | 21,127.26 |
| Forest | 53.32 | 4721.33 | 7.32 | 112.84 | 18.43 | 4913.24 |
| Grassland | 1.60 | 3.54 | 141.49 | 6.03 | 2.61 | 155.28 |
| Construction land | 166.13 | 6.35 | 3.40 | 4928.88 | 2.75 | 5107.51 |
| Unused land | 0.05 | 0.50 | 0.01 | 1.43 | 9.64 | 11.63 |
| Sum | 16,354.64 | 4808.70 | 193.22 | 9914.90 | 43.45 | 31,314.92 |
| Correlation Analysis | Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | r | −0.863 | 0.123 | 0.89 | 0.882 | −0.175 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.772 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.678 | |
| Population | r | −0.849 | 0.092 | 0.906 | 0.866 | −0.233 |
| p | 0.008 | 0.828 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.578 |
| 2000–2010 | 2010–2018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | |
| Cultivated land | * | - | - | −708.91 | −1.69 | * | - | 1.38 | −94.53 | - |
| Forest | −1.66 | * | - | −12.07 | −3.65 | - | * | - | −5.26 | - |
| Grassland | - | - | * | - | - | - | - | * | - | - |
| Construction land | −2.74 | - | - | * | - | 4.06 | - | 1.34 | * | - |
| Unused land | - | - | - | - | * | - | - | - | - | * |
| 2000–2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grass Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | Sum | |
| Cultivated land | * | - | 4 | −830.16 | - | −825.83 |
| Forest land | - | * | −0.2 | −21.46 | - | −23.49 |
| Grassland | - | - | * | - | - | −0.4 |
| Construction land | - | - | - | * | - | 1.05 |
| Unused land | - | - | - | - | * | 0.29 |
| Sum | −1.45 | 1.14 | 4.32 | −851.96 | −0.45 | −848.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Liu, W. Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095642
Zhou J, Liu W. Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095642
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jianbo, and Wanqing Liu. 2022. "Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095642
APA StyleZhou, J., & Liu, W. (2022). Monitoring and Evaluation of Eco-Environment Quality Based on Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI) in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sustainability, 14(9), 5642. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095642





