An Enhanced Model Using the Kano Model, QFDE, and TRIZ with a Component-Based Approach for Sustainable and Innovative Product Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Kano Model
2.2. QFDE
2.3. TRIZ
2.4. Research Gap
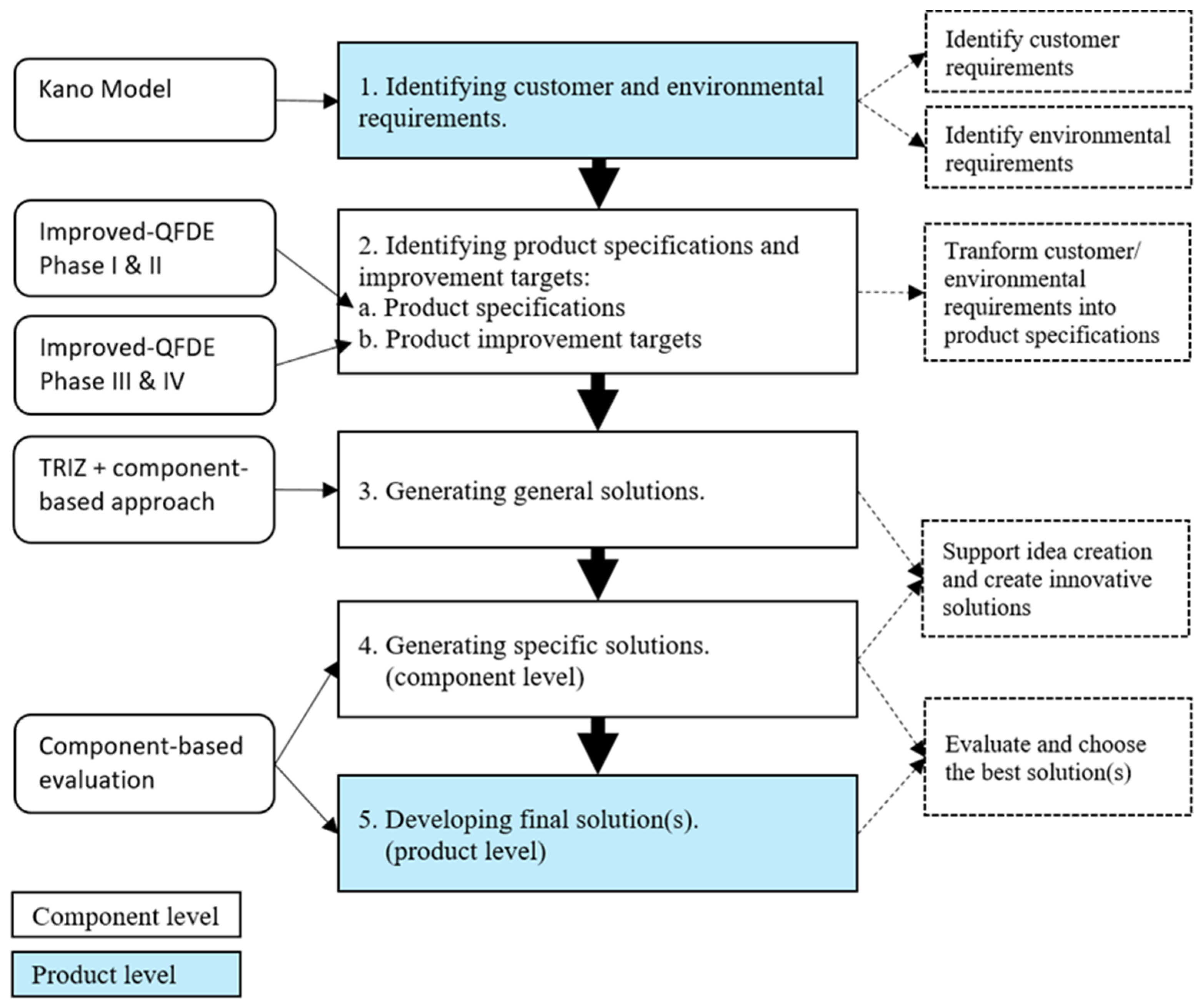
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
- Safer operation: A rubber material provides a better insulator.
- Less energy usage: The smart sensor can automatically adjust the brightness to save electricity usage.
- Longer bulb lifetime: Heat is one of the main factors that affect bulb lifetime. This new design can monitor and control the heat; thus, it can extend the lifetime of the bulb, which also reduces the cost needed to replace the bulb. This can lead to an increase in customer satisfaction.
- Less weight: Modular, wireless, and inflatable designs can reduce the overall weight significantly.
- Environmentally friendly: Composite materials with a modular/inflatable design are easy to recycle and dispose of in the end-of-life phase of the product.
- Lack of concrete methods to achieve the improvements.
- Inaccurate VOC/VOE identification.
- Inaccurate transformation of VOC/VOE to product specifications.
- Neglecting environmental issues.
5. Conclusions
- It has a more precise customer weight value in QFDE phase I, because the value reflects the degree of influence of that particular requirement on customer satisfaction.
- It uses the component-based approach to determine the right components to be included in the product’s design target, as well as which parameter (EM) needs to be improved for that particular component.
- It offers a way to thoroughly analyze the contradiction problems from the product design targets and determine the most prominent TIP to create general solutions.
- It allows the evaluation of the specific solution’s significance to the fulfilment of customer and environmental requirements.
- It can amplify the significance of the specific solutions to the product’s overall qualities by combining each component’s solutions and determining the most prominent combination.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markham, S.K.; Lee, H. Product development and management association’s 2012 comparative performance assessment study. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 30, 408–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechinhheld, F.; Sasser, W. Zero defections: Quality comes to service. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1990, 68, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mungkung, R.; Sorakon, K.; Sitthikitpanya, S.; Gheewala, S.H. Analysis of green product procurement and ecolabels towards sustainable consumption and production in Thailand. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J. From financial to sustainable profit. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2002, 9, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttropp, C.; Lagerstedt, J. EcoDesign and The Ten Golden Rules: Generic advice for merging environmental aspects into product development. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, M.; Favi, C. Eco-design teaching initiative within a manufacturing company based on LCA analysis of company product portfolio. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Germani, M.; Zamagni, A. Review of ecodesign methods and tools. Barriers and strategies for an effective implementation in industrial companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souder, W.E. Managing New Product Innovations; Lexington Books: Lexington, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Clausing, D.P. Total quality development. Mech. Eng. 1994, 116, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.-X.; Tan, K.C.; Xie, M. An integrated approach to innovative product development using Kano’s model and QFD. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2000, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Su, C.-T. A Kano-CKM model for customer knowledge discovery. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2006, 17, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, N.; Seraku, N.; Takahashi, F.; Tsuji, S. Attractive Quality and Must-be Quality, Hinshitsu. J. Jpn. Soc. Qual. Control 1984, 41, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dace, E.; Stibe, A.; Timma, L. A holistic approach to manage environmental quality by using the Kano model and social cognitive theory. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.-K.; Wu, M.-L. Quality function deployment: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 463–497. [Google Scholar]
- Masui, K.; Sakao, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Inaba, A. Applying Quality Function Deployment to environmentally conscious design. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2003, 20, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altshuller, G.; Shulyak, L. And Suddenly the Inventor Appeared: TRIZ, the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving; Technical Innovation Center, Inc.: Worcester, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Livotov, P. The Undervalued Innovation Potential. TRIZ-Journal (April. 2004); Citeseer: State College, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cherifi, A.; Dubois, M.; Gardoni, M.; Tairi, A. Methodology for innovative eco-design based on TRIZ. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2015, 9, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feniser, C.; Burz, G.; Mocan, M.; Ivascu, L.; Gherhes, V.; Otel, C.C. The Evaluation and Application of the TRIZ Method for Increasing Eco-Innovative Levels in SMEs. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreafico, C. Quantifying the advantages of TRIZ in sustainability through life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 126955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzler, K.; Hinterhuber, H.H. How to make product development projects more successful by integrating Kano’s model of customer satisfaction into quality function deployment. Technovation 1998, 18, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireli, Y.; Kauffmann, P.; Ozan, E. Integration of Kano’s model into QFD for multiple product design. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2007, 54, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontini, G. Integrating the Kano model and QFD for designing new products. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2007, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C.; Shen, X.X. Integrating Kano’s model in the planning matrix of quality function deployment. Total Qual. Manag. 2010, 11, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.M.; Dawal, S.Z.M. Kano Model and QFD integration approach for Ergonomic Design Improvement. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 57, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chung, S. User-oriented service and policy innovation in shared research equipment infrastructure: An application of the QFD and Kano’s model to the Gyeonggi Bio-Center. Asian J. Technol. Innov. 2013, 21, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-M.; Chen, H.-T.; Boger, E. Implementing City Hotel Service Quality Enhancements: Integration of Kano and QFD Analytical Models. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2015, 25, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, M. New Product Development with Kano Model to Supports Supply Chain Performance of Jewelry Industry in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering and Information Technology for Sustainable Industry, Tangerang, Indonesia, 28–29 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rampal, A.; Mehra, A.; Singh, R.; Yadav, A.; Nath, K.; Chauhan, A.S. Kano and QFD analyses for autonomous electric car: Design for enhancing customer contentment. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chang, P.-C. Developing a TRIZ-Kano model for creating attractive quality. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, WiCOM’08, Dalian, China, 12–17 October 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-C.; Lee, T.-R.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wu, H.-C. Application of TRIZ and the Kano method to home life industry innovation. Int. J. Innov. Learn. 2009, 7, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.-L.; Chang, C.-M.; Yi, C.-Y. An empirical study of applying Kano model and TRIZ business evolution trends to improve E-commerce service quality. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI), Dongguan, China, 28–30 July 2013; pp. 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, A.; Abedi, S.; Ranjbar, M.J.; Kamali, A. TRIZ and the Kano model: Proposing an integrated approach for improving product quality according to customer needs. Int. J. Product. Qual. Manag. 2017, 20, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ji, X.; Tang, X.; Li, X. Intelligent search and rescue robot design based on KANO model and TRIZ theory. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Design (ICID), Xi’an, China, 19 October 2021; pp. 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Domb, E. QFD and TIPS/TRIZ. TRIZ J. 1998. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwieqN-F2pv8AhXYaN4KHWM-CtAQFnoECAwQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.metodolog.ru%2Ftriz-journal%2Farchives%2F1998%2F06%2Fc%2Findex.htm&usg=AOvVaw2M59Z3XdmTmiWZMX73n2Xh (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Yamashina, H.; Ito, T.; Kawada, H. Innovative product development process by integrating QFD and TRIZ. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2002, 40, 1031–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, D. Software Design of Security Monitoring and Early Warning System for Electric Power Security Control. In Proceedings of the 2009 WRI World Congress on Software Engineering, Xiamen, China, 19–21 May 2009; pp. 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoqun, D. Research on application system of integrating QFD and TRIZ. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Innovation & Management, Wuhan, China, 4–5 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.H.; Huang, J.C.Y.; Yu, C.K. Integration of four-phase QFD and TRIZ in product R&D: A notebook case study. Res. Eng. Des. 2010, 22, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y. The synergy of QFD and TRIZ for solving EMC problems in electrical products–a case study for the Notebook PC. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2015, 32, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.; Iraj, E.B.; Shahrestani, H.V.; Douglas, A. Developing House of Quality by integrating top roof and side roof matrices and service TRIZ with a case study in banking services. TQM J. 2016, 28, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-T.; Cheng, H.-S. An improved grey quality function deployment approach using the grey TRIZ technique. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 92, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiana, G.; Liverani, A.; Francia, D.; Frizziero, L.; Donnici, G. Integrating QFD and TRIZ for innovative design. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2017, 11, JAMDSM0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijie, J. Research and application of mechanical product design process based on QFD and TRIZ integration. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Suzhou, China, 20–22 March 2020; p. 012088. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Cao, G.; Peng, Q.; Sun, Y. Effective radical innovations using integrated QFD and TRIZ. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 162, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakao, T. A QFD-centred design methodology for environmentally conscious product design. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 4143–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Lin, C.-S. C-Kano model: A novel approach for discovering attractive quality elements. Total Qual. Manag. 2010, 21, 1189–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-S.; Chen, L.-S.; Hsu, C.-C. An innovative approach for RFID product functions development. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 15523–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappey, A.J.C.; Ou, J.J.R.; Lin, G.Y.P.; Chen, M.Y. An eco- and inno-product design system applying integrated and intelligent qfde and triz methodology. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2011, 20, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butdee, S.; Trakunsaranakom, C. QFDE Combined with TRIZ Framework to Formulate and Respond to Functional Design for a High Temperature Machine (HTM). KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Melemez, K.; Di Gironimo, G.; Esposito, G.; Lanzotti, A. Concept design in virtual reality of a forestry trailer using a QFD-TRIZ based approach. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2013, 37, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodh, S.; Kamala, V.; Jayakrishna, K. Integration of ECQFD, TRIZ, and AHP for innovative and sustainable product development. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 2758–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; Liu, W. Using integrated quality function deployment and theory of innovation problem solving approach for ergonomic product design. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 76, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H. Incorporating the concept of systematic innovation into quality function deployment for developing multi-functional smart phones. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 107, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, F.; Niu, Y.; Xue, C. A function combined baby stroller design method developed by fusing Kano, QFD and FAST methodologies. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 75, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J. Integrating Kano model, AHP, and QFD methods for new product development based on text mining, intuitionistic fuzzy sets, and customers satisfaction. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 2349716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.; Ertas, A.; Gulbulak, U. A unique transdisciplinary engineering-based integrated approach for the design of temporary refugee housing using Kano, HOQ/QFD, TRIZ, AD, ISM and DSM Tools. Designs 2021, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwa, H.; Sapuan, S.; Mastura, M.; Zuhri, M. Conceptual design and selection of natural fibre reinforced biopolymer composite (NFBC) takeout food container. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 803–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.Z.; Kandasamy, J.; Aravind Raj, S.; Baghdadi, M.A.; Shahzad, M.A. Sustainable Product Development Using FMEA ECQFD TRIZ and Fuzzy TOPSIS. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Blauth, R.; Boger, D.; Bolster, C.; Burchill, G.; DuMouchel, W.; Pouliot, F.; Richter, R.; Rubinoff, A.; Shen, D. Kano’s methods for understanding customer-defined quality. Cent. Qual. Manag. J. 1993, 2, 3–35. [Google Scholar]
- Spreafico, C. Can TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving) strategies improve material substitution in eco-design? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 889–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups | Reference | Tools Used | C1–C5 | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||||
| Group 1: Kano + QFDE/QFD | [21] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Showed how Kano categorization can be used as a QFD input by using a case study from the ski industry. | |||
| [11] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Proposed a process model for designing and developing innovative products by integrating Kano into QFD. | ||||
| [22] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Proposed a methodology for designing multiple products simultaneously by integrating the Kano model into QFD. | ||||
| [23] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Proposed an importance weight adjustment for customer satisfaction by using a case study from beer mug design. | ||||
| [24] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Proposed an integrative approach by adjusting the traditional improvement ratio. | ||||
| [25] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Integrated Kano model–QFD based on an ergonomic approach. | ||||
| [26] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Constructed a framework for a shared research equipment service system based on integrating the Kano model and QFD. | ||||
| [27] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Integrated Kano and QFD for city hotel service quality enhancements. | ||||
| [28] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Improved the workflow for jewelry design development using Kano and QFD. | ||||
| [29] | Kano model, QFD | √ | √ | Combined Kano and QFD tools to achieve a better understanding of customer perceptions. | ||||
| Group 2: Kano + TRIZ | [30] | Kano model, TRIZ | √ | √ | Developed a TRIZ and Kano model framework to create attractive quality by using an online game as an example. | |||
| [31] | Kano model, TRIZ | √ | √ | Proposed four innovative principles to solve a problem in home-life industry innovation. | ||||
| [32] | Kano model, TRIZ | Integrated TRIZ trends of evolution with the Kano model in the E-commerce service quality strategy area. | ||||||
| [33] | Kano model, TRIZ | √ | √ | Proposed a new method that approaches TRIZand Kano as two important quality and innovation techniques. | ||||
| [34] | Kano model, TRIZ | √ | √ | √ | Integrated Kano–QFD tools to design an intelligent search-and-rescue robot for disaster rescue. | |||
| Group 3: QFDE/QFD + TRIZ | [35] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Showed which TRIZ tools are suitable for which QFD stages. | |||
| [36] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Developed a systematic product process from product planning to conceptual design. | ||||
| [37] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Integrated QFD–TRIZ by using vice tools as a case study. | ||||
| [38] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Developed an application system to settle the technical conflict between TRIZ and QFD. | ||||
| [39] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Applied a four-phase QFD–TRIZ combination to achieve a green design solution for notebook products. | ||||
| [40] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Combined QFD–TRIZ for solving EMC problems in electronic products. | ||||
| [41] | QFD, TRIZ | Integrated a TRIZ contradiction matrix with House of Quality (HOQ) side roof matrices. | ||||||
| [42] | GQFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | Proposed a grey QFD for identifying important engineering characteristics by integrating interval grey numbers into QFD–TRIZ. | ||||
| [43] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | A new method to enhance the fabrication of molds for direct open molding by using a combination of QFD and TRIZ. | ||||
| [44] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | √ | Integrated QFD–TRIZ to achieve innovative mechanical product design. | |||
| [45] | QFD, TRIZ | √ | √ | √ | Improved the success rate of radical innovations based on an integrated QFD and TRIZ framework. | |||
| Group 4: Other combinations with three or more tools | [46] | LCA, QFDE, TRIZ | √ | √ | √ | Integrated three tools for environmentally conscious product design. | ||
| [47] | Kano model, TRIZ, SCAMPER | √ | √ | Proposed a creativity-based Kano model that integrates TRIZ and SCAMPER for creating attractive quality. | ||||
| [48] | QFD, TRIZ, refined Kano model | √ | √ | √ | Created a QT–Kano model to construct new product functions of RFID products. | |||
| [49] | LCA, QFDE, TRIZ, BPN | √ | √ | √ | Proposed an integrated and intelligent eco-friendly and innovative product design to support green product development. | |||
| [50] | QFDE, TRIZ, FEM | √ | √ | √ | √ | Created a framework to formulate and respond to the functional design of a high-temperature machine (HTM). | ||
| [51] | QFD, TRIZ, AHP | √ | √ | √ | Designed a virtual reality forestry trailer using the integrated tools. | |||
| [52] | ECQFD, TRIZ, AHP | √ | √ | √ | √ | Proposed an integrated model for innovative and sustainable product development of automotive components. | ||
| [53] | CSNs, QFD, TRIZ, FGDM | √ | √ | √ | √ | Proposed a four-step integrated model to design an innovative ergonomic product and to evaluate it in the early design stages. | ||
| [54] | QFD, TRIZ, AHP, CA | √ | √ | √ | Provided a way to handle engineering conflicts in the design of smartphones by combining QFD and TRIZ. | |||
| [55] | Kano, QFD, FAST | √ | √ | √ | Proposed a function-combining design method by fusing the Kano, QFD, and FAST methodologies. | |||
| [56] | Kano, QFD, AHP | √ | √ | √ | Integrated the Kano model, AHP, and QFD with an intuitionistic fuzzy set to solve decision-making problems. | |||
| [57] | Kano, QFD, TRIZ, AD, ISM, DSM | √ | √ | √ | √ | Solved complex engineering problems involving social issues by using integrated transdisciplinary tools. | ||
| [58] | Kano, QFDE, AHP | √ | √ | √ | √ | Combined different tools to generate more conceptual designs for packaging products. | ||
| [59] | ECQFD, TRIZ, FMEA, fuzzy TOPSIS | √ | √ | √ | √ | Developed a framework for sustainable product development by integrating FMEA, ECQFD, TRIZ, and fuzzy TOPSIS. | ||
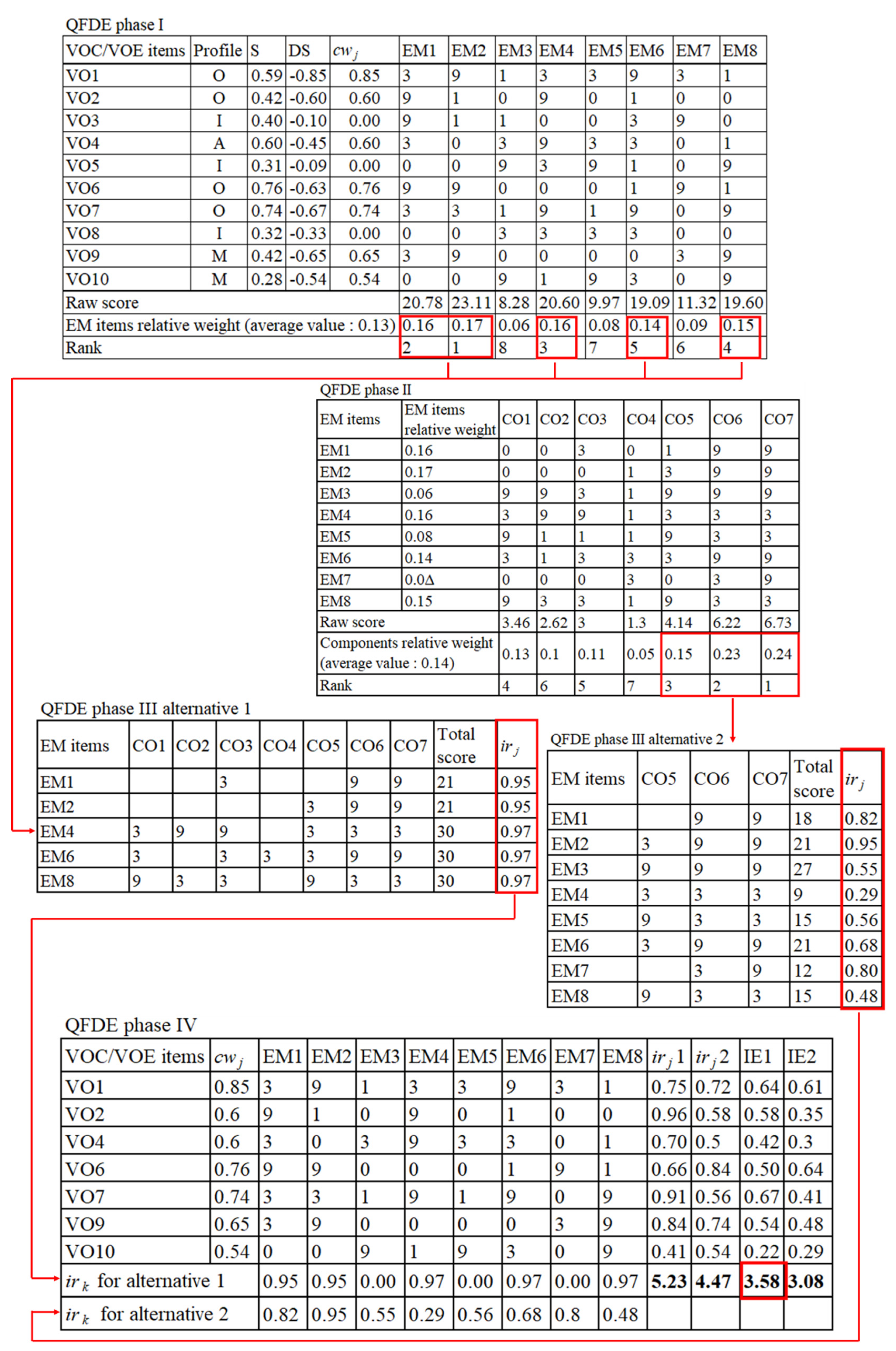
| VOC/VOE Items | M | O | A | I | R | Q | Profile | S = (A + O)/(A + O + M + I) | DS = (M + O)/((−1)∗(A + O + M + I)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO1 | 28 | 44 | 6 | 7 | 0 | 0 | O | 0.59 | −0.85 |
| VO2 | 22 | 27 | 7 | 25 | 2 | 2 | O | 0.42 | −0.60 |
| VO3 | 4 | 4 | 28 | 44 | 3 | 2 | I | 0.40 | −0.10 |
| VO4 | 16 | 22 | 29 | 18 | 0 | 0 | A | 0.60 | −0.45 |
| VO5 | 2 | 6 | 20 | 57 | 0 | 0 | I | 0.31 | −0.09 |
| VO6 | 10 | 42 | 21 | 10 | 0 | 2 | O | 0.76 | −0.63 |
| VO7 | 10 | 47 | 16 | 12 | 0 | 0 | O | 0.74 | −0.67 |
| VO8 | 16 | 12 | 15 | 42 | 0 | 0 | I | 0.32 | −0.33 |
| VO9 | 26 | 20 | 10 | 15 | 14 | 0 | M | 0.42 | −0.65 |
| VO10 | 34 | 10 | 13 | 24 | 4 | 0 | M | 0.28 | −0.54 |
| EM Items | DP | UP | TIP | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | 19 | 21 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 32 | 35 | |||
| EM1 | 18 | 17 | 9 | 9 | 9 | ||||||
| EM2 | 17 | 18 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | |||||
| EM4 | 2 | 18 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| EM6 | 16 | 18 | |||||||||
| EM8 | 26 | 32 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| ipwl′,n (average value: 9.33) | 3 | 9 | 12 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 21 | 15 | ||
| Rank | 7 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 2 | ||
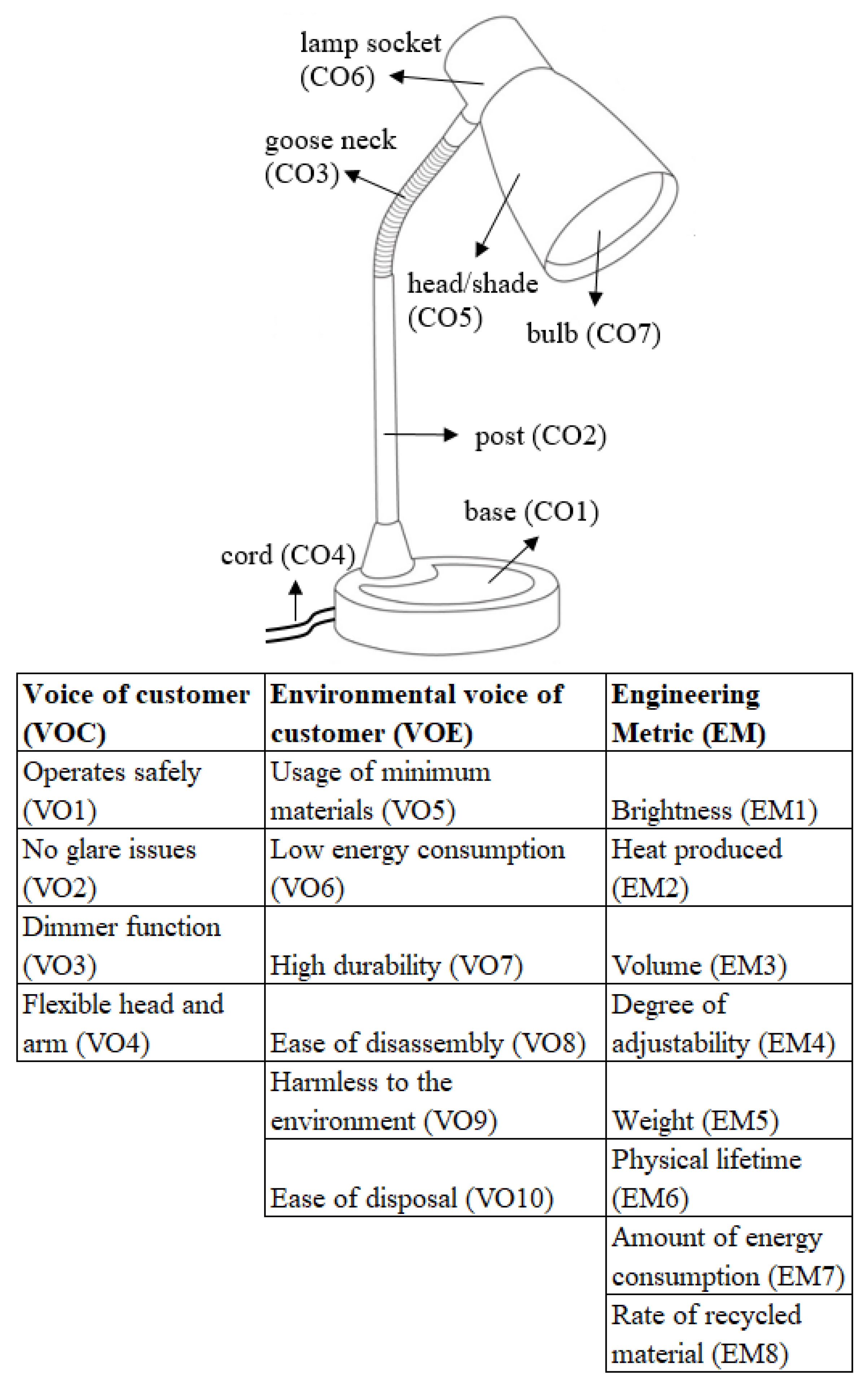
| No. | Component | TIP | Solution Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CO1 | #1 | Use modular design for base, post, head/shade | Improve the degree of adjustability and the ease of disassembly and disposal. |
| 2 | #27 | Replace solid base and post with less expensive plastic suction hook. | Reduce the weight significantly. | |
| 3 | CO2 | #1 | Same as no. 1. | Same as no. 1. |
| 4 | #27 | Same as no. 2. | Same as no. 2. | |
| 5 | #26 | This principle has a similar concept to principle #27; thus, can use the same solution as no. 2 and 4. | Same with no. 2 and 4. | |
| 6 | #40 | Use composite material instead of plastic/steel. | Lighter and easier to recycle. | |
| 7 | CO3 | #40 | Same as no. 6. | Same as no. 6. |
| 8 | CO4 | #2 | Use wireless design with rechargeable battery. | Simpler design and more portable |
| 9 | CO5 | #1 | Same as no. 1. | Same as no. 1. |
| 10 | #27 | An inexpensive black (or other color) film is used to replace the solid material. This layer of black film can be attached or detached easily. | Cheaper and easier to recycle and dispose of. | |
| 11 | #35 | Use light reflector to enhance the brightness. | Increase brightness. | |
| 12 | #29 | Use inflatable design to replace solid head/shade. | Lighter, improved degree of adjustability, and easy to dispose of. | |
| 13 | CO6 | #7 | Lamp socket with telescopic design to incorporate different bulb cap types. | More compact design. |
| 14 | #23 | Add motion sensor, heat sensor, and light sensor to automatically adjust the lamp’s brightness according to the specific condition. | Save more energy and more environmental friendly. | |
| 15 | #10 | Use better insulation material to withstand higher temperatures. | Improve the physical lifetime and the safety. | |
| 16 | #35 | Replace socket cover with rubber material. | Improved safety, lighter, easy to dispose of, and more environmentally friendly. | |
| 17 | CO7 | #32 | Bulb with color palette selection that can be personalized depending on the environmental condition or the customer’s needs. | More adaptive to customer and environmental needs. |
| 18 | #35 | Replace gas inside bulb with liquid nitrogen. | Reduce bulb’s temperature drastically. | |
| 19 | #19 | Bulb with a smart sensor that will adjust the brightness based on the surrounding brightness and the bulb’s current temperature. | Reduce energy usage and increase safety. |
| VOC/VOE Items | cwj | CO1 | CO2 | CO3 | CO4 | CO5 | CO6 | CO7 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | ||
| VO1 | 0.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 9 |
| VO2 | 0.6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| VO4 | 0.6 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| VO6 | 0.76 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| VO7 | 0.74 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 3 |
| VO9 | 0.65 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| VO10 | 0.54 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| srp | 12.99 | 10.00 | 12.99 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 13.54 | 14.74 | 4.93 | 12.99 | 7.68 | 11.25 | 13.84 | 9.37 | 12.55 | 12.55 | 11.94 | 5.44 | 11.74 | 14.07 | |
| Solution No. | Combination srp Value | Rank No. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO1 | CO2 | CO3 | CO4 | CO5 | CO6 | CO7 | ||
| 1 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 14 | 19 | 86.66 | 1 |
| 1 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 19 | 86.66 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 14 | 19 | 86.11 | 3 |
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 19 | 86.11 | 3 |
| 1 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 19 | 86.05 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tandiono, Y.; Rau, H. An Enhanced Model Using the Kano Model, QFDE, and TRIZ with a Component-Based Approach for Sustainable and Innovative Product Design. Sustainability 2023, 15, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010527
Tandiono Y, Rau H. An Enhanced Model Using the Kano Model, QFDE, and TRIZ with a Component-Based Approach for Sustainable and Innovative Product Design. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010527
Chicago/Turabian StyleTandiono, Yauwseph, and Hsin Rau. 2023. "An Enhanced Model Using the Kano Model, QFDE, and TRIZ with a Component-Based Approach for Sustainable and Innovative Product Design" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010527
APA StyleTandiono, Y., & Rau, H. (2023). An Enhanced Model Using the Kano Model, QFDE, and TRIZ with a Component-Based Approach for Sustainable and Innovative Product Design. Sustainability, 15(1), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010527





