Pollution Characteristics and Health Exposure Risks of Heavy Metals in River Water Affected by Human Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
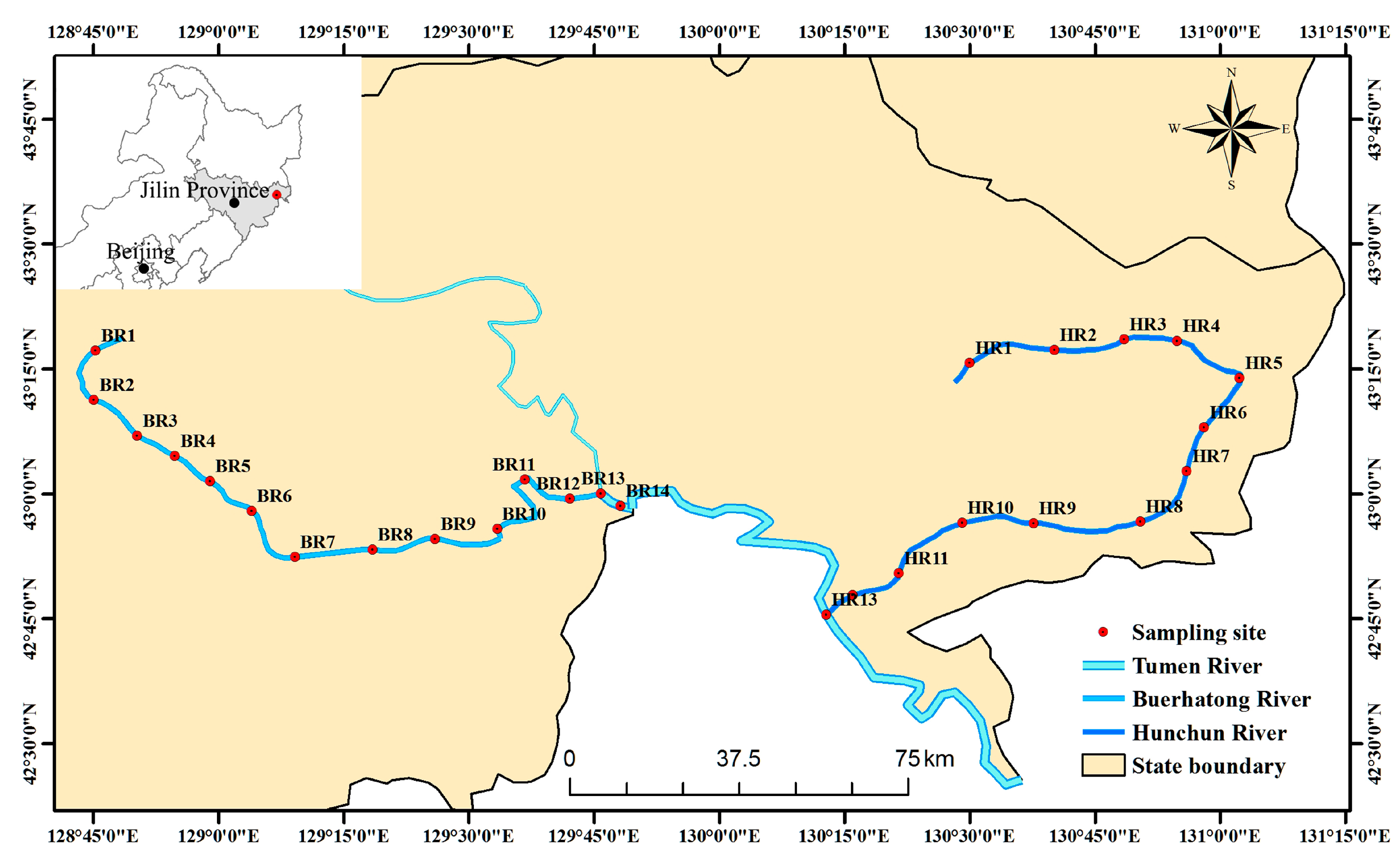
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Chemical Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Contents and Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Surface Water of BR and HR
3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in BR and HR
4. Discussion
| River Metal (μg L−1) | Cr | Cu | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beiyun River | 0.77 | 1.34 | 2.98 | 0.01 | - | 0.07 | [16] |
| Han River | 8.00 | 14.00 | - | 2.00 | - | 9.00 | [23] |
| Liuyang River | 0.73 | 2.90 | 2.41 | 0.07 | - | 1.20 | [19] |
| Wen-Rui Tang River | 5.32 | 20.90 | - | 0.98 | 0.03 | 4.23 | [18] |
| Pearl River Delta | 12.20 | 28.40 | 39.00 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 31.80 | [21] |
| Yangtze River | - | 2.86 | - | 0.96 | - | 4.69 | [17] |
| Yangtze River | 1.30 | 2.80 | 0.97 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 2.00 | [22] |
| Yongding River | 9.90 | 1.50 | - | - | - | 0.20 | [20] |
| Houjing River | 10.50 | 105.40 | 3.20 | 1.50 | 2.80 | 51.30 | [13] |
| Gomti River | - | 20.00 | - | 100.00 | - | 20.00 | [57] |
| Beas River | 31.00 | 4.00 | - | 5.00 | - | 81.00 | [58] |
| Kali River | 60.00 | - | - | 60.00 | - | 130.00 | [24] |
| Brahmani River | 24.70 | 7.60 | - | 5.60 | - | 10.80 | [59] |
| Buriganga River | 114.00 | 239.00 | - | 59.00 | - | 119.00 | [25] |
| Korotoa River | 73.00 | 61.00 | - | 8.00 | - | 27.00 | [60] |
| Pardo River | 1.88 | 3.28 | 2.14 | 0.05 | - | 1.80 | [61] |
| Guadaira River | 20.00 | 10.00 | - | 1.00 | - | 8.00 | [62] |
| Tigris River | 5.00 | 32.00 | - | 0.10 | - | 0.30 | [63] |
| Soan River | 10.00 | 20.00 | - | - | - | 650.00 | [26] |
| Mississippi River | 0.20 | 2.10 | - | 0.57 | - | 0.31 | [64] |
| To Lich River | 2.90 | 4.50 | - | - | - | 8.10 | [65] |
| Ismailia Canal | - | 7.00 | - | 0.45 | - | 18.00 | [66] |
| Ajay River | - | 80.00 | - | 30.00 | - | 50.00 | [31] |
| Bogacayi | 3.20 | 0.92 | 0.43 | 0.23 | - | 0.48 | [67] |
| Coruh River | 1.68 | 670.90 | - | 1.87 | - | 67.38 | [68] |
| Upper Ganga River | 33.00 | - | - | - | - | 5.00 | [69] |
| Hazar River | - | 13.50 | 55.35 | 2.65 | - | 4.40 | [45] |
| Sirsa | 35.50 | 27.00 | 5.50 | 2.60 | - | 17.90 | [70] |
| Euphrates | 0.07 | 2.48 | - | 2.14 | - | 0.10 | [71] |
| Mashavera River | 0.80 | 210.00 | 0.10 | 4.60 | - | 2.80 | [72] |
| Mean | 18.63 | 56.98 | 11.21 | 11.17 | 0.94 | 44.23 | |
| Mean value of BR and HR | 3.23 | 10.48 | 34.73 | 1.46 | 0.59 | 9.86 | In this study |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, P.; Raju, N.J.; Bcsr, R.; Suresh, U.; Sankar, D.B.; Tvk, R. Heavy metal contamination in river water and sediments of the Swarnamukhi river basin, India: Risk assessment and environmental implications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 40, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Luo, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in seawater and sediments from Meishan bay, Zhejiang coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Ponnusamy, S.K.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohain, S.B.; Bordoloi, S. Impact of municipal solid waste disposal on the surface water and sediment of adjoining wetland Deepor Beel in Guwahati, assam, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Karki, K.; Zhang, F. Heavy metals in surface sediments in the trans-Himalayan Koshi river catchment: Distribution, source identification and pollution assessment. Chemosphere 2019, 244, 125410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebi, L.; Sobhanardakani, S. Analysis of heavy metal contents and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment through consumption of tilapia fish (oreochromis niloticus). Pollution 2020, 6, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, M.S.; Desai, K.P.; Lynch, H.N.; Rhomberg, L.R.; Beck, B.D.; Venditti, F.J. Mechanisms of action for arsenic in cardiovascular toxicity and implications for risk assessment. Toxicology 2015, 331, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffman, L.C. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Sachdeva, M.; Gupta, N.; Mishra, P.; Yadav, M.; Tiwari, A. Lead exposure in different organs of mammals and prevention by curcumin–nanocurcumin: A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M. Use of water quality index and multivariate statistical methods for the evaluation of water quality of a stream affected by multiple stressors: A case study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, H.-G.; Chiang, C.-F.; Lin, C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-W.; Cheruiyot, N.K.; Tran, H.-T.; Bui, X.-T. Human health risk simulation and assessment of heavy metal contamination in a river affected by industrial activities. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.; Durães, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Serrano, A.; Alcaraz, C.; Ibanez, C.; Trobajo, R.; Barata, C. Procambarus clarkii as a bioindicator of heavy metal pollution sources in the lower Ebro river and delta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, M.; Qie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, R.; Li, L.; Lin, A. Health risk assessment based on source identification of heavy metals: A case study of Beiyun river, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tang, X.; Guo, W.; Lin, L.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal distribution dynamics of heavy metals in water, sediment, and zoobenthos in mainstream sections of the middle and lower Changjiang river. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Huang, H.; Xia, F.; Liu, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K. Risk analysis of heavy metal concentration in surface waters across the rural-urban interface of the Wen-Rui Tang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Qu, Z.; Yang, Z. Distribution, contamination and accumulation of heavy metals in water, sediments, and freshwater shellfish from Liuyang river, southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7012–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Gao, Y.; Xing, Y. Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in overlying water, porewater, and sediments of Yongding river in a coal mine brownfield. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.-P.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhu, X.-P.; Chen, K.-C.; Pan, D.-B.; Hong, X.-Y.; Yin, Y. Residues and potential ecological risk assessment of metal in water and sediments from freshwater fish pond of pearl river delta. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper Han river, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.; Singhal, K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in water of kali river using principle component and cluster analysis, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Dampare, S.B.; Islam, M.; Suzuki, S. Source apportionment and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in water and sediments of Buriganga river, Bangladesh, using multivariate analysis and pollution evaluation indices. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, S.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N. Heavy metals distribution, risk assessment and water quality characterization by water quality index of the river Soan, Pakistan. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Kwon, E.; Song, H.; Wang, S.-L.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Rinklebe, J. Soil contamination by potentially toxic elements and the associated human health risk in geo-and anthropogenic contaminated soils: A case study from the temperate region (Germany) and the arid region (Egypt). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Levizou, E.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment?—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 819–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.-P.; Hsu, H.-T.; Shie, R.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Hong, Y.-S. Health risk of consuming heavy metals in farmed tilapia in central taiwan. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinklebe, J.; Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rosche, O.; Altermann, M. Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils along the central Elbe River, Germany. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.K.; Kumar, B. Pathways of heavy metals contamination and associated human health risk in Ajay river basin, India. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Jinping, Z.; Zhongling, G.; Chunnan, F. Sources and health risk of organochlorine pesticides in surface water from Buerhatong river and Hunchun river in northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.T.; Lin, C.; Yeh, G.; Villanueva, M.C. Bioaccumulation and potential sources of heavy metal contamination in fish species in taiwan: Assessment and possible human health implications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19422–19434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in freshwater fish in the central and eastern north China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Nutrition Association. Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents 2022; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2022; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Duh, J.-M.; Chou, W.-S.; Hsu, H.-T. Development of a multi-pathway probabilistic health risk assessment model for swimmers exposed to chloroform in indoor swimming pools. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response (OSWER). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (Rags), Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) Interim; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, C. Estimation of skin exposure area of Chinese people in health risk assessment. J. Saf. Environ. 2008, 8, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination of Land for Construction; Hj 25.3-2019; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences. Technical Specification for Environmental Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals; T/Cses 38-2021; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response; 9355/4-24; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Abarike, G.A.; Wang, S.; Xing Xing, C.; Yaoqian, L.; Han, Y.; Bin, W.; Song, Z. Heavy metal concentrations in the surface water of a crater lake in southern China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, E.J. Quality assessment for shatt al-arab river using heavy metal pollution index and metal index. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, M.; Patgiri, A.D. Metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Dikrong river, ne India. J. Hum. Ecol. 2009, 27, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T. An index approach to metallic pollution in river waters. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghi, R.; Kaushal, N. Our National River Ganga: Lifeline of Millions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; An, Z.; Wang, S. Analysis and evaluation of the source of heavy metals in water of the river changjiang. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.I.; Zheng, J.P.; Fan, C.N.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.L. Analyzing on landscape patterns of land-use in Tumenjiang watershed. J. Beihua Univ. 2013, 14, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Yu, S. Spatio-temporal variational characteristics analysis of heavy metals pollution in water of the typical northern rivers, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, S.; Moore, F. Assessment of heavy metal concentration in the Khoshk river water and sediment, shiraz, southwest Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Ansari, A.; Müller, G.; Singh, I. Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of the Gomati river (a tributary of the ganga river): Effects of human activities. Environ. Geol. 1997, 29, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, M.; Kadriu, S.; Kelmendi, M.; Latifi, L. Impact of artana mine on heavy metal pollution of the marec river in kosovo. Dnipro University of Technology. Min. Miner. Depos. 2021, 15, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadriu, S.; Sadiku, M.; Kelmendi, M.; Sadriu, E. Studying the Heavy Metals Concentration in Discharged Water from the Trepa Mine and Flotation, Kosovo; Dnipro University of Technology: Dnipro, Ukraine, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Skrobala, V.; Popovych, V.; Tyndyk, O.; Voloshchyshyn, A. Chemical pollution peculiarities of the nadiya mine rock dumps in the chervonohrad mining district, Ukraine. Min. Miner. Depos. 2022, 16, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, D.; Kozielska, B.; Abramowicz, A.; Fabiańska, M.; Krzykawski, T. Heavy metal- and organic-matter pollution due to self-heating coal-waste dumps in the upper Silesian coal basin (Poland). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlychenko, A.; Kovalenko, A. The Investigation of Rock Dumps Influence to the Levels of Heavy Metals Contamination of Soil; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.K.; Chabukdhara, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, J.; Bux, F. Evaluation of ecological risk of metal contamination in river Gomti, India: A biomonitoring approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar Thukral, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, R.; Sahoo, B. Mapping of heavy metal pollution in river water at daily time-scale using spatio-temporal fusion of modis-aqua and landsat satellite imageries. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.I.; Sampaio, C.F.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Segura-Muñoz, S.I. Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo river, Brazil: Human health risks. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enguix González, A.; Ternero Rodríguez, M.; Jiménez Sá, J.; Fernández Espinosa, A.; Barragán De La Rosa, F. Assessment of metals in sediments in a tributary of Guadalquiver river (Spain). Heavy metal partitioning and relation between the water and sediment system. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 121, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Şen, B. Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris river, Turkey. Catena 2012, 92, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussan, D.D.; Ochs, C.A.; Jackson, C.R.; Anumol, T.; Snyder, S.A.; Cizdziel, J.V. Concentrations of select dissolved trace elements and anthropogenic organic compounds in the Mississippi river and major tributaries during the summer of 2012 and 2013. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuong, N.T.; Yoneda, M.; Ikegami, M.; Takakura, M. Source discrimination of heavy metals in sediment and water of to lich river in hanoi city using multivariate statistical approaches. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8065–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.E.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Moniem, I.A.; Fahmy, A.H.; El-sayed, S.M. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia canal, Nile river, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, M.F.; Kilic, S.; Yalcin, F.; Kilic, M.; Gurhan Yalcin, M. Evaluation of heavy metal risk potential in Bogacayi river water (Antalya, Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, A.; Konanç, M.U. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal pollution of Coruh river basin (Turkey) by multivariate statistical methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Saluja, R.; Joshi, V.; Garg, J. Heavy metal pollution in surface water of the upper ganga river, India: Human health risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herojeet, R.; Rishi, M.S.; Kishore, N. Integrated approach of heavy metal pollution indices and complexity quantification using chemometric models in the sirsa basin, nalagarh valley, Himachal Pradesh, India. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.M.; Saleh, M.M.; Salman, J.M. A study of physicochemical parameters and nine heavy metals in the Euphrates river, iraq. E-J. Chem. 2010, 7, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanachchi, S.S.; Ghambashidze, G.; Kunchulia, I.; Urushadze, T.; Ploeger, A. Water quality in surface water: A preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination of the Mashavera river, Georgia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, T.; Stevenson, H.; Pieters, M.N.; Rennen, M.; Slob, W.; Hakkert, B.C. Assessment factors for human health risk assessment: A discussion paper. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1999, 29, 439–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, M.; Houdart, S.; Oberli, M.; Kalonji, E.; Huneau, J.-F.; Margaritis, I. Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 35, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jia, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, D.; Xia, F.; Li, Y. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze river delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourieh Fallah, S.; Bakaeian, M.; Parsian, H.; Amouei, A.; Asgharnia, H.; Ghanbarian, M.; Mousapour, A.; Tabarinai, H.; Oskoei, V.; Miri, S.A. Potentially harmful heavy metal contamination in Babolrood river: Evaluation for risk assessment in the Mazandaran province, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 7209–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.; Dong, H. Contamination characteristics, source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil in Shi river basin in China based on high density sampling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Fisher, S.; Suk, W.A.; Sly, P.; Chiles, T.C.; Bose-O’Reilly, S. Pollution and children’s health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2389–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Adult | Children | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Fish ingestion rate | 0.0457 kg/d | [35] | |||||
| EFfish | Exposure frequency | 365 d | [34] | |||||
| EDfish | Exposure duration | 70 y | 6 y | [34] | ||||
| ETder/ETing | Daily exposure time for swimming | 0.5 h/d | [13] | |||||
| EFder/EFing | Exposure frequency for swimming | 15 d/y | [13] | |||||
| EDder/EDing | Exposure duration for swimming | 30 y | 4 y | [36,37] | ||||
| IngR | Incidental water ingestion rate | 0.044 L/h | [13] | |||||
| SA | Exposed skin area | 16,106 cm2 | 8640 cm2 | [38] | ||||
| BW | Body weight | 60 kg | 30 kg | [34] | ||||
| AT | 365 d y−1 × ED | |||||||
| Cr | Cu | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | |||
| BCF | Bioconcentration factor (L kg−1) | 24.22 | 18.60 | 3.00 | 1.78 | 7.62 | 5.77 | [33,34] |
| k | Permeability constant of heavy metals (cm h−1) | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | [37] |
| RfDfish | Reference doses of heavy metals (mg kg−1 d−1) | 0.003 | 0.04 | 0.0003 | 0.001 | 0.0003 | - | [39,40] |
| RfDder | Reference doses of heavy metals (mg kg−1 d−1) | 7.5 × 10−5 | 0.04 | 0.0003 | 2.5 × 10−5 | 2.1 × 10−5 | - | [39,40] |
| RfDing | Reference doses of heavy metals (mg kg−1 d−1) | 0.003 | 0.04 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.0003 | - | [39,40] |
| SFfish | Cancer slope factors ((mg kg−1 d−1)−1) | 0.012 | - | 1.5 | - | - | 0.0085 | [39,40] |
| SFder | Cancer slope factor ((mg kg−1 d−1)−1) | 0.48 | - | 1.5 | - | - | - | [39,40] |
| SFing | Cancer slope factor ((mg kg−1 d−1)−1) | 0.012 | - | 1.5 | - | - | 0.0085 | [39,40] |
| ADDfish | Average daily exposure dose of heavy metals through fish ingestion | |||||||
| ADDder | Average daily exposure dose of metals through dermal contact | |||||||
| ADDing | Average daily exposure dose of metals through ingestion | |||||||
| HQfish/CRfish | Non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through fish ingestion | |||||||
| HQder/CRder | Non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through dermal contact | |||||||
| HQing/CCRing | Non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through incidental water ingestion | |||||||
| HIfish/CCRfish | The cumulative non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through fish ingestion | |||||||
| HIder/CCRder | The cumulative non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through dermal contact | |||||||
| HIing/CCRing | The cumulative non-carcinogenic/carcinogenic risk of heavy metals through incidental water ingestion | |||||||
| Elements | BR | HR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mg L−1) | Range (mg L−1) | Mean (mg L−1) | Range (mg L−1) | |
| Cr | 0.00456 | 0.00035–0.01470 | 0.00191 | 0.00079–0.00520 |
| Cu | 0.01344 | 0.00382–0.03204 | 0.00752 | 0.00311–0.02052 |
| As | 0.03527 | 0.02678–0.08050 | 0.03420 | 0.02675–0.04618 |
| Cd | 0.00151 | 0.00112–0.00197 | 0.00140 | 0.00097–0.00241 |
| Hg | 0.00108 | 0.00033–0.00470 | 0.00011 | 0.00007–0.00016 |
| Pb | 0.00820 | 0.00206–0.01900 | 0.01153 | 0.00719–0.02048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, C. Pollution Characteristics and Health Exposure Risks of Heavy Metals in River Water Affected by Human Activities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108389
Liu Q, Cheng Y, Fan C. Pollution Characteristics and Health Exposure Risks of Heavy Metals in River Water Affected by Human Activities. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108389
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiang, Yan Cheng, and Chunnan Fan. 2023. "Pollution Characteristics and Health Exposure Risks of Heavy Metals in River Water Affected by Human Activities" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108389
APA StyleLiu, Q., Cheng, Y., & Fan, C. (2023). Pollution Characteristics and Health Exposure Risks of Heavy Metals in River Water Affected by Human Activities. Sustainability, 15(10), 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108389





