Evolution and Impacting Factors of Global Renewable Energy Products Trade Network: An Empirical Investigation Based on ERGM Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- What are the macro- and micro-level characteristics of network structure evolution relating to global trade in renewable energy products? To answer this question, this paper introduces the analytical framework of complex networks in the field of renewable energy product trade and constructs a global renewable energy products trade network model.
- (2)
- What are the dependencies between network relationships, i.e., whether the occurrence of one relationship affects the probability of the occurrence of other relationships? To answer this question, the exponential random graph model (hereafter abbreviated as the ERGM model) is introduced into the formation mechanism of trade networks.
- (3)
- What are the factors that influence the evolution of renewable energy products trade networks? What are the reasons behind the evolution of the network structure comprehensively? To answer this question, the ERGM model is introduced to simultaneously take into account variables in terms of network structure and relationship at multiple levels.
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Mechanisms and Hypothesis on Influencing Factors of Renewable Energy Products Trade Network
4. Methodology
4.1. Construction of Global Trade Networks for Renewable Energy Products
4.2. Exponential Random Graph Models (ERGM)
4.3. ERGM Variables and Data
5. Results
5.1. Evolution of Structural Properties of Global Renewable Energy Products Networks
5.1.1. Global Network Analysis
5.1.2. Local Network Analysis
5.2. Influencing Factors of Renewable Energy Products Trade Network
5.2.1. Basic Results of ERGM Estimation
5.2.2. Dynamic Analysis
5.2.3. Analysis of Each Kind of Renewable Energy Product
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Description of Network Statistics
Appendix B
| Solar Energy | Wind Energy | Ocean Energy | Water Power | Biomass Energy | Geothermal Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700991 | 730820 | 850422 | 850421 | 382450 | 220710 | 730431 |
| 700992 | 841290 | 850423 | 850422 | 681091 | 220720 | 730441 |
| 711590 | 848210 | 850431 | 850423 | 841011 | 380210 | 730451 |
| 732290 | 848220 | 850432 | 850431 | 841012 | 840681 | 741121 |
| 830630 | 848230 | 850433 | 850432 | 841013 | 840682 | 741122 |
| 841280 | 848240 | 850434 | 850433 | 841090 | 841182 | 741129 |
| 841919 | 848250 | 854459 | 850434 | 850161 | 841280 | 841861 |
| 841950 | 848280 | 854460 | 854459 | 850162 | 841620 | 841950 |
| 841989 | 848340 | 890790 | 854460 | 850163 | 841931 | 850239 |
| 841990 | 850161 | 902830 | 850164 | 841940 | ||
| 850239 | 850162 | 903020 | 850421 | 847920 | ||
| 850440 | 850163 | 903031 | 850422 | 850161 | ||
| 854140 | 851064 | 903083 | 850423 | 850162 | ||
| 900190 | 850231 | 850431 | 850163 | |||
| 900290 | 850300 | 850432 | 850164 | |||
| 900580 | 850421 | 850433 | ||||
| 850434 | ||||||
Appendix C. Renewable Energy Products Network Structures

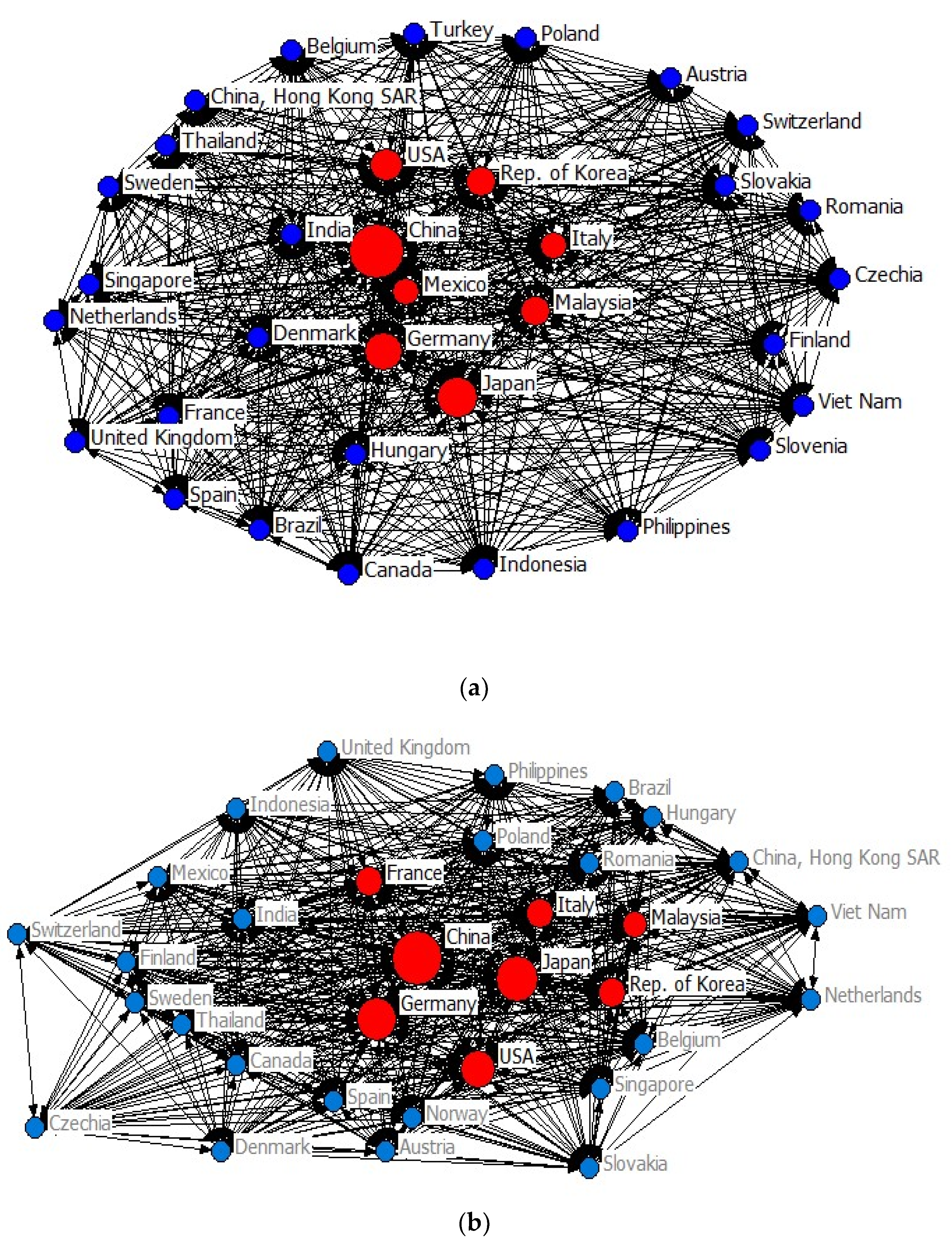
References
- Abbas, A.; Waseem, M.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, K.A.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Sensitivity analysis of greenhouse gas emissions at farm level: Case study of grain and cash crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 82559–82573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, E.; Khalid, Z. Estimating smart energy inputs packages using hybrid optimisation technique to mitigate environmental emissions of commercial fish farms. Appl. Energy 2022, 326, 119602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Zhao, C.; Waseem, M.; Khan, K.A.; Ahmad, R. Analysis of Energy Input-Output of Farms and Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Case Study of Cotton Growers. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 826838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Xue, S.; Ma, M.; Zhu, X. New energy bases and sustainable development in China: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 20, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, M.; Filipovic, S. New approach to energy intensity in the EU—Total energy and carbon cost approach. Energy Environ. 2015, 26, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B. Assessing the development of China’s new energy industry. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricic, V.K.; Danilovic, D.; Lekovic, B.; Crnogorac, M. Energy policy reforms in the Serbian oil sector: An update. Energy Policy 2018, 113, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Renwick, N.; Xue, L. The BRICS and Africa’s search for green growth, clean energy and sustainable development. Energy Policy 2018, 120, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. New Energy Development and Issues in China during the 14th Five-Year Plan. Electr. Power 2020, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ruoshui, W.; Molin, H.; Martinot, E. A study of the role played by renewable energies in China’s sustainable energy supply. Energy 2010, 35, 4392–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Y.-M.; Li, Z.-P. Role of renewable energy in China’s energy security and climate change mitigation: An index decomposition analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D. A critical review of comparative global historical energy consumption and future demand: The story told so far. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, F. The relationship amongst energy consumption (renewable and non-renewable), and GDP in Algeria. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre-Tudó, J.L.; Castelló-Cogollos, L.; Aleixandre, J.L.; Aleixandre-Benavent, R. Renewable energies: Worldwide trends in research, funding and international collaboration. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansino, J.M.; del Pablo-Romer, P.; Román, R.; Yñiguez, R. Tax incentives to promote green electricity: An overview of EU-27 countries. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6000–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoda, K.; Lonseth, R.; Lonseth, A.; Jackman, T. Development and commercialization of renewable energy technologies in Canada: An innovation system perspective. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.E.H.; Rogner, H.-H.; Gregory, K. Carbon emission and mitigation cost comparisons between fossil fuel, nuclear and renewable energy resources for electricity generation. Energy Policy 2003, 31, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C.; Ghadimi, P. Trade characteristics, competition patterns and COVID-19 related shock propagation in the global solar photovoltaic cell trade. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charters, W.W.S. Developing markets for renewable energy technologies. Renew. Energy 2001, 22, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, T.; Bloechl, F.; Brueck, T.; Theis, F.J. The Heckscher-Ohlin model and the network structure of international trade. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2011, 20, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.Z.; Zhong, W.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Li, H.J.; Gao, X.Y. Features and evolution of international crude oil trade relationships: A trading-based network analysis. Energy 2014, 74, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Evolution of international trade and investment networks. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 462, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, G.; Xu, H. Structure and formation of top networks in international trade, 2001–2010. Soc. Netw. 2016, 44, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. Structure and patterns of the international rare earths trade: A complex network analysis. Resour. Policy 2018, 55, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Poon, J.P.; Dong, W. East Asia and Solar Energy Trade Network Patterns. Geogr. Rev. 2017, 107, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; An, H.; Hao, X.; Jia, X. The Impact of Countries’ Roles on the International Photovoltaic Trade Pattern: The Complex Networks Analysis. Sustainability 2016, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, F.; Fagiolo, G.; Sornette, D.; Vega-Redondo, F.; Vespignani, A.; White, D.R.; Networks, E. Economic Networks: The New Challenges. Science 2009, 325, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivala, A.; Robins, G.; Lomi, A. Exponential random graph model parameter estimation for very large directed networks. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, G.; Pattison, P.; Kalish, Y.; Lusher, D. An introduction to exponential random graph (p*) models for social networks. Soc. Netw. 2007, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Flows, T. Barriers and Market Drivers in Renewable Energy Supply Goods. Available online: https://ictsd.iisd.org/bridges-news/biores/news/trade-flows-barriers-and-market-drivers-in-renewable-energy-supply-goods (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Jebli, M.B.; Youssef, S.B. The environmental Kuznets curve, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy, and trade in Tunisia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, L.; Centi, G.; Iaquaniello, G.; Mangiapane, A.; Perathoner, S. Trading Renewable Energy by using CO2: An Effective Option to Mitigate Climate Change and Increase the use of Renewable Energy Sources. Energy Technol. 2014, 2, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun; Prakash, R.; Prakash, R.; Bhat, I.K. Energy, economics and environmental impacts of renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2716–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilliestam, J.; Ellenbeck, S. Energy security and renewable electricity trade—Will Desertec make Europe vulnerable to the “energy weapon”? Energy Policy 2011, 39, 3380–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, C.M. China’s renewable energy development: Policy, industry and business perspectives. Asia Pac. Bus. Rev. 2015, 21, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Chou, Y.H. Overview of environmental impacts, prospects and policies for renewable energy in Taiwan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2005, 9, 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Shuai, J.; Sun, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z. Do China’s wind energy products have potentials for trade with the “Belt and Road” countries?—A gravity model approach. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, Y. Role of policy in innovation and international trade of renewable energy technology: Empirical study of solar PV and wind power technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. Trade Liberalization and China’s Exports of Renewable Energy Products: Evidence from Product Level Data. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2016, 52, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boz, D.E.; Sanli, B.; Berument, M.H. The effects of cross-border electricity trade on power production from different energy sources. Electr. J. 2021, 34, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.; Río, P.D.; Ruiz, P.; Nijs, W.; Politis, S. Analysing the influence of trade, technology learning and policy on the employment prospects of wind and solar energy deployment: The EU case. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 122, 109657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Trading wind power with barrier option. Appl. Energy 2016, 182, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinav, R.; Pindoriya, N.M. Opportunities and key challenges for wind energy trading with high penetration in Indian power market. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 47, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Caporin, M.; Paterlini, S. Dynamic network analysis of North American financial institutions. Financ. Res. Lett. 2021, 42, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Pu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, L. The influence of regional preferential trade agreements on international manufacturing trade in value-added: Based on the complex network method. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chong, Z.; Li, X.; Nie, G. Spatial patterns and determinant factors of population flow networks in China: Analysis on Tencent Location Big Data. Cities 2020, 99, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Moya, E.; Lozano, S.; Adenso-Diaz, B. Analysing the Structure of the Global Wheat Trade Network: An ERGM Approach. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, G.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Fang, G. A complex network perspective on interrelations and evolution features crossMark of international oil trade, 2002–2013. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.-B.; Ji, Q.; Fan, Y. A dynamic analysis on global natural gas trade network. Appl. Energy 2014, 132, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Moxnes, A. Networks and Trade. Annu. Rev. Econ. 2018, 10, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; Sovacool, B.K. The political economy of technological capabilities and global production networks in South Africa’s wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) industries. Political Geogr. 2017, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Duan, H. How does international trade network affect multinational diffusion of wind power technology? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Yang, Y.; Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Spatial structure, inequality and trading community of renewable energy networks: A comparative study of solar and hydro energy product trades. Energy Policy 2017, 106, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. Exploring the structure and influence factors of trade competitive advantage network along the Belt and Road. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 559, 125057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, L. The study of the influence of common humanistic relations on international services trade-from the perspective of multi-networks. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 523, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.O.; Kaku, B.K.; Vakhutinsky, A. Network-based formulations of the quadratic assignment problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 104, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.U. Reasoning about opinion dynamics in social networks. J. Log. Comput. 2019, 29, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Lee, J.W. A fuzzy inference network model for search strategy using neural logic network. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2003, 36, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brughmans, T.; Keay, S.; Earl, G. Introducing exponential random graph models for visibility networks. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 49, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, P.; Wasserman, S. Logit models and logistic regressions for social networks: II. Multivariate relations. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2019, 52, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilduff, M.; Krackhardt, D. Interpersonal Networks in Organizations; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.O.; Rogers, B.W.; Zenou, Y. The Economic Consequences of Social-Network Structure. J. Econ. Lit. 2017, 55, 49–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, D.; Koskinen, J.; Robbins, G. Exponential Random Graph Models for Social Networks; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krugman, P. Scale Economies, Product Differentiation, and the Pattern of Trade. Am. Econ. Rev. 1980, 70, 950–959. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, L.; Poncet, S. Environmental policy and exports: Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 296–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, L. Effects of Institutions and Environmental Policies on Export of Renewable Energy: A Perspective of Intensive Margin and Extensive Margin. J. Int. Trade 2015, 12, 85–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. The Mechanism and Effect of the Influence of International Humanistic Relation Network on International Trade Network. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Coase, R.H. The Nature of the Firm. Economica 1937, 4, 386–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.; Kortum, S. Technology, Geography, and Trade. Econometrica 2002, 70, 1741–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E.; van Wincoop, E. Gravity with Gravitas: A Solution to the Border Puzzle. Am. Econ. Rev. 2003, 93, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Increasing Returns and Economic-Geography. J. Political Econ. 1991, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, S.; Khasteh, S.H. A survey on exponential random graph models: An application perspective. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2020, 6, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y. Structural characteristics and correlation factors analysis of global trade Structural characteristics and correlation factors analysis of global trade network of solar energy industry. Master Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Xiong, H.; Peng, X. How to Promote International Competitiveness of China’s Renewable Energy Products?—Based on SNA Theory. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4163–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Implication | Schematic Diagram | Statistical Expression | Corresponding Hypothesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | edges |  | Is the basic tendency to generate trade in renewable energy products between national sectors stronger? Is the network denser? | |
| Reciprocity | reciprocity |  | Are countries more inclined to have reciprocal trade? | |
| Homophily(x) | homophily |  | Are national partners that all have X attributes more inclined to establish strong trade relations for renewable energy products? | |
| Sender(x) | the sender effect |  | Are national partners with X attributes more active in the trade network of renewable energy products and have more connections? | |
| Receiver(x) | the receiver effect |  | Are national partners with X attributes more popular in the trade network of renewable energy products and have more connections? | |
| NCov(g) | network covariates |  | Are countries with relationships in other networks more inclined to establish strong trade relations for renewable energy products? |
| Variables | Sources of Data | |
|---|---|---|
| actor-relational attributes | GDP | World Bank WDI database |
| RE Production | International Renewable Energy Agency Database | |
| RE Consumption | UNdata | |
| ghg emission | UNdata | |
| network covariates | Common Border Network(CBN) | CEPII (Gravdata) |
| Network of Parties to the Paris Climate Agreement (2016–2019) Kyoto Protocol State Party Network (2009–2015) | Official Document of the United Nations Paris Agreement “Kyoto Protocol”-Annex B |
| Year | Number of Nodes | Number of Edges | Density | Average Path Length | Clustering Coefficient | Reciprocity Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 222 | 37,089 | 0.268 | 1.756 | 0.733 | 0.67 |
| 2010 | 221 | 36,565 | 0.281 | 1.752 | 0.672 | 0.579 |
| 2011 | 224 | 36,788 | 0.278 | 1.743 | 0.692 | 0.668 |
| 2012 | 225 | 37,199 | 0.284 | 1.741 | 0.728 | 0.673 |
| 2013 | 225 | 36,783 | 0.291 | 1.733 | 0.656 | 0.567 |
| 2014 | 225 | 36,399 | 0.291 | 1.729 | 0.72 | 0.665 |
| 2015 | 225 | 36,092 | 0.3 | 1.716 | 0.723 | 0.668 |
| 2016 | 225 | 36,113 | 0.3 | 1.717 | 0.726 | 0.673 |
| 2017 | 225 | 35,689 | 0.304 | 1.711 | 0.725 | 0.671 |
| 2018 | 226 | 36,385 | 0.301 | 1.719 | 0.73 | 0.678 |
| 2019 | 224 | 36,676 | 0.29 | 1.728 | 0.751 | 0.692 |
| 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 212 | USA | 210 | USA | 211 | Netherlands | 209 | Germany | 210 | China | 209 |
| USA | 204 | China | 204 | Germany | 211 | Germany | 208 | Netherlands | 206 | Germany | 204 |
| China | 200 | UK | 201 | Netherlands | 207 | China | 206 | China | 205 | USA | 203 |
| Japan | 198 | France | 200 | China | 205 | France | 203 | USA | 204 | Netherlands | 203 |
| France | 195 | Japan | 197 | France | 202 | USA | 203 | France | 201 | UK | 200 |
| UK | 195 | Germany | 196 | Italy | 201 | Switzerland | 201 | UK | 201 | France | 199 |
| Italy | 190 | Netherlands | 196 | Japan | 198 | UK | 198 | Belgium | 197 | Italy | 197 |
| Canada | 189 | Italy | 192 | UK | 197 | Japan | 197 | Italy | 196 | Spain | 196 |
| Netherlands | 187 | Canada | 191 | Belgium | 194 | Italy | 197 | India | 195 | Belgium | 195 |
| Finland | 186 | Finland | 191 | Canada | 193 | Sweden | 196 | Sweden | 194 | India | 194 |
| 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 168 | France | 172 | Canada | 175 | Netherlands | 173 | Canada | 180 | Canada | 181 |
| Netherlands | 163 | Canada | 167 | Netherlands | 174 | Canada | 171 | France | 178 | France | 178 |
| Canada | 163 | USA | 163 | France | 171 | USA | 168 | USA | 172 | USA | 175 |
| USA | 161 | Netherlands | 161 | USA | 164 | France | 163 | Netherlands | 170 | Germany | 160 |
| France | 153 | Mexico | 150 | Somalia | 151 | UK | 152 | South Africa | 156 | South Africa | 159 |
| UK | 146 | UK | 147 | Mexico | 149 | China | 152 | UK | 151 | Netherlands | 158 |
| China | 145 | China | 145 | South Sudan | 148 | South Africa | 152 | China | 145 | UK | 154 |
| South Africa | 142 | Germany | 142 | UK | 146 | Germany | 149 | Spain | 144 | Singapore | 153 |
| Germany | 138 | Spain | 141 | Germany | 144 | Spain | 147 | Italy | 142 | China | 152 |
| Spain | 135 | South Africa | 138 | China | 142 | Italy | 143 | Belgium | 141 | Spain | 147 |
| Italy | 127 | Belgium | 136 | Sierra Leone | 141 | Thailand | 143 | Australia | 140 | Belgium | 147 |
| 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
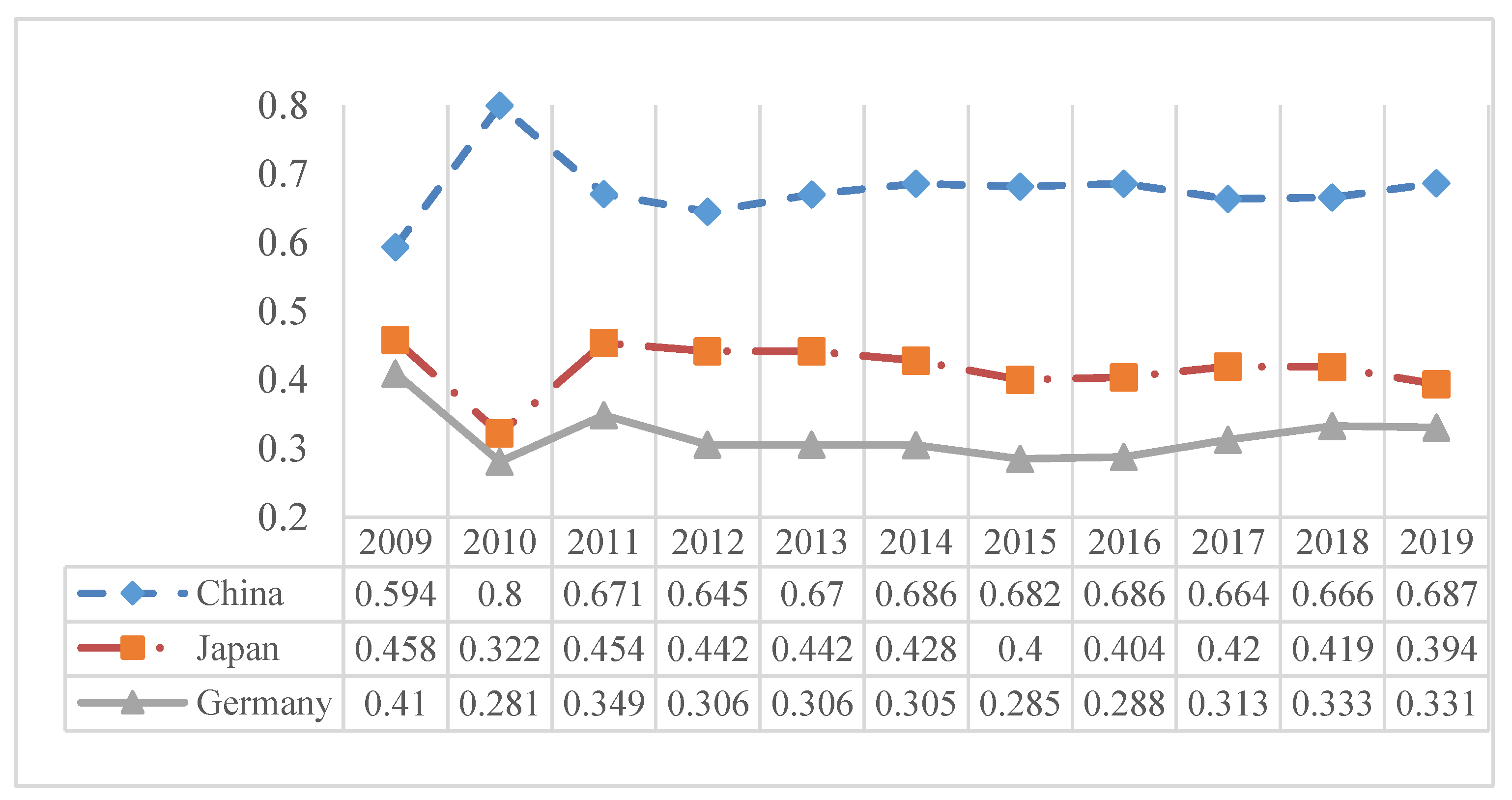
| China | 38.8 | China | 71.1 | China | 64.1 | China | 68.9 | China | 69.3 | China | 80.6 |
| Germany | 32.4 | Germany | 41.9 | Germany | 34.9 | Germany | 29.6 | Germany | 31.0 | Germany | 33.1 |
| USA | 21.8 | USA | 28.4 | USA | 28.0 | USA | 28.1 | USA | 25.5 | USA | 26.0 |
| Japan | 21.6 | Japan | 27.4 | Japan | 23.0 | Japan | 20.2 | Japan | 20.3 | Japan | 20.3 |
| Italy | 11.1 | Italy | 12.9 | Italy | 13.0 | Korea | 12.3 | Korea | 12.4 | Italy | 12.0 |
| France | 9.4 | Korea | 11.8 | Korea | 11.7 | Italy | 11.2 | Italy | 11.5 | Korea | 10.8 |
| Korea | 8.2 | France | 10.5 | France | 9.2 | Malaysia | 8.9 | Malaysia | 9.0 | Malaysia | 9.3 |
| Denmark | 6.6 | Malaysia | 7.8 | Malaysia | 7.3 | France | 8.2 | France | 8.3 | France | 8.2 |
| UK | 5.5 | Denmark | 7.2 | UK | 5.9 | Mexico | 6.4 | Mexico | 5.8 | Mexico | 7.1 |
| Netherlands | 4.9 | Netherlands | 6.9 | Netherlands | 5.9 | Spain | 5.4 | Spain | 5.7 | India | 6.5 |
| 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | 2017 | 2019 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 27.8 | China | 37.3 | China | 35.5 | China | 42.7 | China | 40.8 | USA | 46.6 |
| Germany | 25.2 | Germany | 34.3 | Germany | 23.0 | Germany | 21.7 | Germany | 22.2 | Germany | 23.1 |
| USA | 17.3 | USA | 24.4 | USA | 22.6 | USA | 19.7 | USA | 21.2 | China | 21.0 |
| Japan | 8.2 | Japan | 16.7 | Japan | 14.3 | Japan | 13.3 | Japan | 11.7 | Hong Kong, China | 11.4 |
| Italy | 8.1 | Italy | 13.2 | Italy | 13.8 | Korea | 12.8 | Korea | 11.2 | Japan | 11.1 |
| France | 8.0 | Korea | 11.8 | Korea | 11.1 | Italy | 10.0 | Italy | 9.3 | Netherlands | 10.5 |
| Korea | 7.4 | France | 10.8 | France | 9.2 | Malaysia | 9.3 | Malaysia | 9.2 | Mexico | 9.8 |
| Denmark | 6.7 | Malaysia | 10.0 | Malaysia | 8.4 | France | 9.1 | France | 8.9 | Korea | 9.4 |
| UK | 6.6 | Denmark | 9.1 | UK | 8.1 | Mexico | 7.4 | Mexico | 8.3 | France | 9.1 |
| Netherlands | 6.2 | Netherlands | 8.6 | Netherlands | 7.9 | Spain | 7.2 | Spain | 7.9 | UK | 9.0 |
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| core | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| semi-core | 25 | 24 | 26 | 29 | 29 | 28 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 27 | 26 |
| peripheral | 189 | 189 | 191 | 189 | 189 | 190 | 192 | 191 | 191 | 191 | 190 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | −1.9396 *** | −4.8100 *** | −6.8865 *** | −4.7135 *** | −4.8229 *** | −5.3275 *** | −5.4821 *** | −7.0536 *** |
| (0.0171) | (0.0605) | (0.1971) | (0.1280) | (0.1246) | (0.1456) | (0.1155) | (0.2013) | |
| Reciprocity | 2.7497 *** | 1.6119 *** | 1.5767 *** | 2.4157 *** | 2.3952 *** | 2.3531 *** | 2.2336 *** | 1.9931 *** |
| (0.0343) | (0.0392) | (0.0406) | (0.0424) | (0.0498) | (0.0480) | (0.0431) | (0.0445) | |
| nodecov.GDPhigh | 0.2099 *** | 0.2115 *** | 0.2360 *** | |||||
| (0.0028) | (0.0048) | (0.0058) | ||||||
| nodecov.GDPmid | 0.1434 *** | 0.1665 *** | 0.1322 *** | |||||
| (0.0028) | (0.0045) | (0.0058) | ||||||
| nodecov.GDPlow | 0.0712 *** | 0.3084 *** | 0.2332 *** | |||||
| (0.0068) | (0.0240) | (0.0252) | ||||||
| nodecov.RE high | −0.0044 *** | −0.0068 *** | −0.0076 *** | |||||
| (0.0003) | (0.0007) | (0.0009) | ||||||
| nodecov.RE mid | 0.0020 * | −0.0060 *** | 0.0061 *** | |||||
| (0.0008) | (0.0010) | (0.0016) | ||||||
| nodecov.RE low | −0.0149 ** | 0.0283 *** | 0.0503 *** | |||||
| (0.0052) | (0.0062) | (0.01) | ||||||
| Homophily (GDPhigh) | −0.1046 * | −2.0667 *** | −2.0568 *** | −1.9405 *** | −1.9395 *** | −0.0972 | ||
| (0.0470) | (0.0378) | (0.0485) | (0.0341) | (0.0347) | (0.0769) | |||
| Homophily (GDPmid) | 0.0363 | 0.6907 *** | 0.6784 *** | 0.6942 *** | 0.7839 *** | 0.2982 *** | ||
| (0.0343) | (0.0404) | (0.0559) | (0.0402) | (0.0345) | (0.0540) | |||
| Homophily(GDPlow) | −0.4686 ** | 1.6290 *** | 1.6054 *** | 1.5618 *** | 1.6905 *** | 1.6618 *** | ||
| (0.1439) | (0.0839) | (0.0823) | (0.0879) | (0.0809) | (0.1722) | |||
| Homophily (REhigh) | −0.2438 *** | 0.4848 *** | 0.3786 *** | 0.4062 *** | 0.4170 *** | 0.0186 | ||
| (0.0421) | (0.0392) | (0.0392) | (0.0343) | (0.0353) | (0.0531) | |||
| Homophily (REmid) | −0.1633 *** | −0.2530 *** | −0.2663 *** | −0.2680 *** | −0.2789 *** | −0.1087 ** | ||
| (0.0273) | (0.0355) | (0.0462) | (0.0368) | (0.0289) | (0.0380) | |||
| Homophily (RElow) | 0.4155 *** | 0.2998 *** | 0.3824 *** | 0.3716 *** | 0.3769 *** | 0.5389 *** | ||
| (0.0266) | (0.0394) | (0.0424) | (0.0434) | (0.0295) | (0.0367) | |||
| Receiver (GDPhigh) | 0.0807 *** | 0.0775 *** | 0.0918 *** | 0.0849 *** | −0.0841 *** | |||
| (0.0051) | (0.0052) | (0.0056) | (0.0042) | (0.0057) | ||||
| Receiver (GDPmid) | 0.2445 *** | 0.2370 *** | 0.2455 *** | 0.2325 *** | 0.0228 ** | |||
| (0.0063) | (0.0075) | (0.0079) | (0.0061) | (0.0074) | ||||
| Receiver (GDPlow) | 0.4247 *** | 0.4135 *** | 0.4170 *** | 0.4072 *** | 0.0959 *** | |||
| (0.0188) | (0.0211) | (0.0209) | (0.0184) | (0.0192) | ||||
| Receiver (RE high) | 0.0027 *** | 0.0018 * | 0.0019 * | 0.0011 | 0.0035 *** | |||
| (0.0008) | (0.0008) | (0.0009) | (0.0008) | (0.0010) | ||||
| Receiver (RE mid) | −0.0152 *** | −0.0153 *** | −0.0151 *** | −0.0185 *** | −0.0250 *** | |||
| (0.0016) | (0.0018) | (0.0018) | (0.0015) | (0.0023) | ||||
| Receiver (RE low) | 0.0120 | 0.0244 * | 0.0192 | 0.0086 | −0.0429 ** | |||
| (0.0106) | (0.0106) | (0.0109) | (0.0089) | (0.0155) | ||||
| Sender(ghg) | 0.0287 *** | 0.0305 *** | 0.0287 *** | 0.0229 *** | ||||
| (0.0020) | (0.0019) | (0.0017) | (0.0019) | |||||
| Sender(REP) | 0.0603 *** | 0.0499 *** | 0.0082 * | |||||
| (0.0048) | (0.0043) | (0.0041) | ||||||
| NCov (agreement) | 0.4991 *** | 0.2898 *** | ||||||
| (0.0237) | (0.0253) | |||||||
| NCov (CBN) | 0.6594 *** | 0.5873 *** | ||||||
| (0.1155) | (0.1134) | |||||||
| AIC | 52,935.2033 | 39,469.2773 | 39,121.8544 | 40,969.9747 | 40,635.8601 | 40,334.4190 | 39,792.9552 | 37,156.1451 |
| BIC | 52,952.859 | 39,539.8992 | 39,245.4429 | 41,093.5631 | 40,768.2763 | 40,475.6630 | 39,951.8547 | 37,368.0110 |
| Log Likelihood | −26,465.6 | −19,726.6386 | −19,546.9272 | −20,470.9873 | −20,302.9301 | −20,151.2095 | −19,878.4776 | −18,554.0726 |
| Variables | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | −7.5181 *** | −7.0474 *** | −7.7539 *** | −8.2897 *** | −5.3742 *** | −8.1608 *** |
| (0.2100) | (0.1872) | (0.2398) | (0.0060) | (0.1497) | (0.1972) | |
| Reciprocity | 1.9274 *** | 1.1840 *** | 1.7183 *** | 1.7452 *** | 2.2620 *** | 1.6777 *** |
| (0.0494) | (0.0453) | (0.0476) | (0.0011) | (0.0435) | (0.0473) | |
| nodecov.GDPhigh | 0.1995 *** | 0.2014 *** | 0.2099 *** | 0.2824 *** | 0.0962 *** | 0.2067 *** |
| (0.0078) | (0.0076) | (0.0078) | (0.0020) | (0.0062) | (0.0082) | |
| nodecov.GDPmid | 0.1385 *** | 0.1396 *** | 0.1250 *** | 0.2065 *** | 0.0350 *** | 0.1503 *** |
| (0.0081) | (0.0078) | (0.0077) | (0.0017) | (0.0059) | (0.0085) | |
| nodecov.GDPlow | 0.2510 *** | 0.2405 *** | 0.2609 *** | 0.2774 *** | 0.1161 *** | 0.1318 *** |
| (0.0241) | (0.0217) | (0.0298) | (0.0036) | (0.0179) | (0.0221) | |
| nodecov.RE high | −0.0152 *** | −0.0115 *** | −0.0139 *** | −0.0121 *** | −0.0131 *** | −0.0127 *** |
| (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0006) | (0.0008) | (0.0009) | |
| nodecov.RE mid | −0.020 *** | −0.008 *** | −0.0160 *** | −0.0032 * | −0.0096 *** | −0.0014 |
| (0.0015) | (0.0015) | (0.0016) | (0.0013) | (0.0014) | (0.0015) | |
| nodecov.RE low | −1.0871 *** | −0.4713 *** | −0.7354 *** | −0.6509 *** | −0.6893 *** | −0.7350 *** |
| (0.0721) | (0.0476) | (0.0724) | (0.0017) | (0.0436) | (0.0548) | |
| Homophily (GDPhigh) | −0.0137 | 0.0188 | −0.0129 | −0.2345 *** | −0.1830 ** | −0.2491 * |
| (0.0831) | (0.0761) | (0.0897) | (0.0035) | (0.0631) | (0.1074) | |
| Homophily (GDPmid) | 0.2154 *** | −0.0298 | 0.1342 * | 0.2965 *** | 0.0348 | 0.3849 *** |
| (0.0637) | (0.0594) | (0.0640) | (0.0019) | (0.0474) | (0.0822) | |
| Homophily(GDPlow) | 1.3452 *** | 1.3201 *** | 1.4457 *** | 1.7260 *** | 0.9433 *** | 1.4750 *** |
| (0.1704) | (0.1521) | (0.2080) | (0.0042) | (0.1244) | (0.1644) | |
| Homophily (REhigh) | 0.5258 *** | 0.5480 *** | 0.4412 *** | 0.3320 *** | 0.4955 *** | 0.4020 *** |
| (0.0595) | (0.0604 | (0.0595) | (0.0020) | (0.0507) | (0.0580) | |
| Homophily (REmid) | 0.0498 | −0.0611 | 0.0457 | −0.0670 *** | 0.2265 *** | 0.0411 |
| (0.0464) | (0.0459) | (0.0466) | (0.0015) | (0.0391) | (0.0466) | |
| Homophily (RElow) | 0.0279 | 0.0643 | 0.2204 *** | 0.2591 *** | 0.0276 | 0.0634 |
| (0.0492) | (0.0486) | (0.0504) | (0.0017) | (0.0376) | (0.0445) | |
| Receiver (GDPhigh) | −0.0115 | −0.0415 *** | −0.0059 | −0.0572 *** | 0.0175 * | 0.0152 |
| (0.0085) | (0.0078) | (0.0078) | (0.0024) | (0.0069) | (0.0081) | |
| Receiver (GDPmid) | 0.0440 *** | 0.0054 | 0.0664 *** | 0.0371 *** | 0.1033 *** | 0.0914 *** |
| (0.0101) | (0.0091) | (0.0092) | (0.0019) | (0.0081) | (0.0097) | |
| Receiver (GDPlow) | 0.0385 * | 0.0181 | 0.0526 ** | 0.1540 *** | 0.1371 *** | 0.0646 *** |
| (0.0192) | (0.0162) | (0.0187) | (0.0024) | (0.0152) | (0.0141) | |
| Receiver (RE high) | 0.0190 *** | 0.0159 *** | 0.0187 *** | 0.0164 *** | 0.0174 *** | 0.0168 *** |
| (0.0010) | (0.0009) | (0.0010) | (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0010) | |
| Receiver (RE mid) | 0.0150 *** | 0.0026 | 0.0124 *** | −0.0026 | −0.0009 | −0.0048 * |
| (0.0023) | (0.0021) | (0.0024) | (0.0021) | (0.0023) | (0.0023) | |
| Receiver (RE low) | 0.9084 *** | 0.4314 *** | 0.8892 *** | 0.6474 *** | 0.6370 *** | 0.7958 *** |
| (0.0893) | (0.0611) | (0.0953) | (0.0019) | (0.0612) | (0.0709) | |
| Sender(ghg) | 0.0052 * | 0.0137 *** | 0.0041 * | −0.0077 *** | 0.0045 * | 0.0037 |
| (0.0021) | (0.0020) | (0.0021) | (0.0019) | (0.0019) | (0.0020) | |
| Sender(REP) | 0.1927 *** | 0.1854 *** | 0.1698 *** | 0.1435 *** | 0.1590 *** | 0.1606 *** |
| (0.0067) | (0.0062) | (0.0066) | (0.0000) | (0.0065) | (0.0072) | |
| NCov (agreement) | 0.0153 | 0.4279 *** | 1.1119 *** | 0.7045 *** | 0.7885 *** | 0.7536 *** |
| (0.0703) | (0.0643) | (0.0727) | (0.0026) | (0.0560) | (0.0635) | |
| NCov (CBN) | 0.2026 | 0.1258 | 0.7830 *** | 0.8401 *** | 0.7932 *** | 0.7910 *** |
| (0.1213) | (0.1290) | (0.1226) | (0.0038) | (0.1058) | (0.1191) | |
| AIC | 32,457.5589 | 36,223.0961 | 33,046.6343 | 33,899.3276 | 39,972.4418 | 34,165.5319 |
| BIC | 32,668.5619 | 36,433.8809 | 33,258.0706 | 34,110.9792 | 40,184.0934 | 34,377.1835 |
| Variables | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | −7.5132 *** | −7.6157 *** | −7.9182 *** | −7.7598 *** |
| (0.1978) | (0.2045) | (0.2045) | (0.1980) | |
| Reciprocity | 1.6681 *** | 1.7874 *** | 1.7200 *** | 1.7640 *** |
| (0.0462) | (0.0469) | (0.0441) | (0.0447) | |
| nodecov.GDPhigh | 0.1948 *** | 0.1865 *** | 0.1435 *** | 0.1540 *** |
| (0.0079) | (0.0083) | (0.0073) | (0.0074) | |
| nodecov.GDPmid | 0.1325 *** | 0.1257 *** | 0.0864 *** | 0.1066 *** |
| (0.0078) | (0.0077) | (0.0073) | (0.0071) | |
| nodecov.GDPlow | 0.1868 *** | 0.1628 *** | 0.2359 *** | 0.2038 *** |
| (0.0248) | (0.0249) | (0.0246) | (0.0244) | |
| nodecov.RE high | −0.0126 *** | −0.0128 *** | −0.0138 *** | −0.0184 *** |
| (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0009) | (0.0007) | |
| nodecov.RE mid | −0.0042 ** | −0.0019 | −0.0064 *** | −0.0085 *** |
| (0.0015) | (0.0016) | (0.0016) | (0.0012) | |
| nodecov.RE low | −0.7387 *** | −0.4334 *** | −0.4271 *** | −0.0248 * |
| (0.0525) | (0.0372) | (0.0421) | (0.0099) | |
| Homophily (GDPhigh) | −0.0791 | −0.1347 | −0.2300 ** | −0.2213 ** |
| (0.0826) | (0.0879) | (0.0822) | (0.0826) | |
| Homophily (GDPmid) | 0.2725 *** | 0.3272 *** | 0.2952 *** | 0.3060 *** |
| (0.0595) | (0.0607) | (0.0606) | (0.0599) | |
| Homophily(GDPlow) | 0.8964 *** | 0.8880 *** | 1.8317 *** | 1.4263 *** |
| (0.1701) | (0.1729) | (0.1754) | (0.1713) | |
| Homophily (REhigh) | 0.3119 *** | 0.3727 *** | 0.2483 *** | −0.0763 |
| (0.0540) | (0.0541) | (0.0547) | (0.0390) | |
| Homophily (REmid) | 0.089 * | 0.1112 * | 0.0728 | 0.0891 * |
| (0.0441) | (0.0441) | (0.0420) | (0.0388) | |
| Homophily (RElow) | 0.0610 | 0.0921 * | 0.0781 | 0.3354 *** |
| (0.0443) | (0.0433) | (0.0437) | (0.0358) | |
| Receiver (GDPhigh) | 0.0219 ** | 0.0326 *** | 0.0437 *** | 0.0452 *** |
| (0.0081) | (0.0080) | (0.0077) | (0.0077) | |
| Receiver (GDPmid) | 0.0959 *** | 0.1103 *** | 0.1118 *** | 0.1084 *** |
| (0.0096) | (0.0095) | (0.0089) | (0.0091) | |
| Receiver (GDPlow) | 0.1423 *** | 0.1673 *** | 0.1577 *** | 0.1496 *** |
| (0.0178) | (0.0176) | (0.0180) | (0.0176) | |
| Receiver (RE high) | 0.0168 *** | 0.0189 *** | 0.0201 *** | 0.0196 *** |
| (0.0010) | (0.0010) | (0.0010) | (0.0009) | |
| Receiver (RE mid) | 0.0027 | −0.0032 | 0.0058 * | 0.0051 ** |
| (0.0023) | (0.0025) | (0.0024) | (0.0018) | |
| Receiver (RE low) | 0.7156 *** | 0.4065 *** | 0.5058 *** | 0.0605 *** |
| (0.0710) | (0.0507) | (0.0598) | (0.0149) | |
| Sender(ghg) | 0.0029 | −0.0005 | 0.0084 *** | 0.0146 *** |
| (0.0021) | (0.0021) | (0.0022) | (0.0019) | |
| Sender(REP) | 0.1963 *** | 0.1964 *** | 0.2212 *** | 0.2344 *** |
| (0.0070) | (0.0076) | (0.0076) | (0.0071) | |
| NCov (agreement) | 0.7421 *** | 0.0895 *** | 0.3025 *** | 0.0717 ** |
| (0.0657) | (0.0242) | (0.0246) | (0.0237) | |
| NCov (CBN) | 0.7546 *** | 0.3014 * | 0.7904 *** | −0.0398 |
| (0.1146) | (0.1187) | (0.1143) | (0.1173) | |
| AIC | 35,124.9615 | 34,933.5670 | 35,836.4641 | 5594.0378 |
| BIC | 35,336.6131 | 35,145.2187 | 36,048.1157 | 35,805.9037 |
| Variables | (1) Solar | (2) Wind | (3) Biomass | (4) Water | (5) Ocean | (6) Geothermal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edges | −6.2516 *** | −2.8533 *** | −6.4548 *** | −2.2559 *** | −1.0841 *** | −3.8590 *** |
| (0.2173) | (0.1456) | (0.7080) | (0.1735) | (0.2435) | (0.1856) | |
| Reciprocity | 2.1417 *** | 2.7135 *** | 1.9102 *** | 0.4659 *** | 1.1695 *** | 1.7195 *** |
| (0.0477) | (0.0406) | (0.0613) | (0.0459) | (0.0454) | (0.0923) | |
| nodecov.GDPhigh | 0.2153 *** | 0.0044 | 0.2336 *** | −0.0188 *** | 0.0365 *** | 0.0354 |
| (0.0046) | (0.0032) | (0.0074) | (0.0035) | (0.0049) | (0.0021) | |
| nodecov.GDPmid | 0.1027 *** | −0.1030 *** | 0.1177 *** | −0.0251 *** | 0.0466 *** | −0.1340 *** |
| (0.0045) | (0.0031) | (0.0100) | (0.0035) | (0.0049) | (0.0034) | |
| nodecov.GDPlow | 0.2051 *** | −0.0312 | 0.0398 | 0.0419 * | −0.3280 *** | 0.0512 |
| (0.0292) | (0.0188) | (0.0999) | (0.0212) | (0.0377) | (0.0179) | |
| nodecov.RE high | −0.0076 *** | −0.0094 *** | −0.0018 | 0.0110 *** | −0.0027 *** | −0.0086 ** |
| (0.0009) | (0.0008) | (0.0010) | (0.0007) | (0.0007) | (0.0006) | |
| nodecov.RE mid | 0.0164 *** | 0.0125 *** | −0.0120 *** | 0.0055 *** | 0.0030 * | 0.0179 *** |
| (0.0016) | (0.0012) | (0.0017) | (0.0012) | (0.0013) | (0.0012) | |
| nodecov.RE low | 0.1030 *** | 0.0774 *** | −0.0216 | 0.0842 *** | 0.0419 *** | 0.0664 *** |
| (0.0102) | (0.0089) | (0.0113) | (0.0091) | (0.0099) | (0.0084) | |
| Homophily (GDPhigh) | 0.0355 | 0.0935 * | −0.3988 *** | 0.1553 * | −0.1204 | 0.0735 * |
| (0.0658) | (0.0458) | (0.1118) | (0.0604) | (0.0673) | (0.0496) | |
| Homophily (GDPmid) | 0.1251 * | −0.0900 * | 0.5497 *** | 0.0169 | 0.0705 | −0.0972 * |
| (0.0508) | (0.0375) | (0.1069) | (0.0506) | (0.0580) | (0.0476) | |
| Homophily(GDPlow) | 1.5452 *** | 0.4127 ** | 0.6303 | 0.2285 | −1.2306 *** | 0.1235 ** |
| (0.1995) | (0.1254) | (0.6930) | (0.1466) | (0.2253) | (0.1674) | |
| Homophily (REhigh) | −0.3730 *** | −0.5420 *** | 0.0978 | 0.0439 | −0.2674 *** | −0.8450 *** |
| (0.0576) | (0.0515) | (0.0686) | (0.0541) | (0.0550) | (0.0416) | |
| Homophily (REmid) | −0.0136 | −0.1000 ** | 0.0472 | −0.1765 *** | −0.0700 | −0.1400 * |
| (0.0398) | (0.0314) | (0.0471) | (0.0421) | (0.0415) | (0.0334) | |
| Homophily (RElow) | 0.3289 *** | 0.3379 *** | 0.0645 | 0.3026 *** | 0.3177 *** | 0.3782 *** |
| (0.0371) | (0.0278) | (0.0377) | (0.0349) | (0.0355) | (0.0259) | |
| Receiver (GDPhigh) | −0.1272 *** | −0.0043 | −0.1052 *** | 0.0806 *** | −0.0318 *** | −0.0283 |
| (0.0045) | (0.0037) | (0.0088) | (0.0033) | (0.0051) | (0.0097) | |
| Receiver (GDPmid) | −0.0287 *** | 0.1320 *** | 0.0587 *** | 0.0187 *** | −0.0425 *** | 0.1020 ** |
| (0.0057) | (0.0047) | (0.0119) | (0.0038) | (0.0061) | (0.0089) | |
| Receiver (GDPlow) | −0.0268 | 0.0696 *** | 0.0900 * | 0.0340 ** | 0.1748 *** | 0.0286 *** |
| (0.0187) | (0.0146) | (0.0365) | (0.0119) | (0.0203) | (0.0144) | |
| Receiver (RE high) | −0.0001 | 0.0025 ** | 0.0050 *** | −0.0086 *** | 0.0023 ** | 0.0038 ** |
| (0.0011) | (0.0008) | (0.0010) | (0.0006) | (0.0007) | (0.0005) | |
| Receiver (RE mid) | −0.0251 *** | −0.0197 *** | 0.0154 *** | −0.0075 *** | −0.0070 *** | −0.0147 *** |
| (0.0024) | (0.0019) | (0.0022) | (0.0016) | (0.0018) | (0.0014) | |
| Receiver (RE low) | −0.0534 ** | −0.0516 *** | 0.0625 *** | −0.0317 ** | −0.0021 | −0.0346 *** |
| (0.0163) | (0.0147) | (0.0165) | (0.0115) | (0.0131) | (0.0167) | |
| Sender(ghg) | 0.0294 *** | 0.0387 *** | 0.0063 ** | 0.0013 | −0.0189 *** | 0.0667 *** |
| (0.0019) | (0.0015) | (0.0021) | (0.0019) | (0.0021) | (0.0075) | |
| Sender(REP) | 0.0319 *** | 0.0807 *** | −0.0115 * | −0.0328 *** | 0.0225 *** | 0.0567 * |
| (0.0042) | (0.0035) | (0.0050) | (0.0046) | (0.0047) | (0.0055) | |
| NCov (agreement) | 0.1940 *** | 0.3460 *** | 0.0128 | 0.0419 ** | 0.0435 *** | 0.0934 |
| (0.0237) | (0.0198) | (0.0294) | (0.0262) | (0.0255) | (0.0168) | |
| NCov (CBN) | 0.5373 *** | 0.2858 ** | −0.0818 | −0.0933 | −0.0422 | 0.2098 ** |
| (0.1138) | (0.1016) | (0.1593) | (0.1379) | (0.1330) | (0.3316) | |
| AIC | 35,000.5713 | 42,703.6925 | 23,581.2820 | 35,111.8744 | 33,045.1731 | 32,403.6025 |
| BIC | 35,212.0077 | 42,914.2581 | 23,786.7536 | 35,316.3589 | 33,250.6448 | 32,514.2981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.; Qu, Y. Evolution and Impacting Factors of Global Renewable Energy Products Trade Network: An Empirical Investigation Based on ERGM Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118701
Li J, Liu K, Yang Z, Qu Y. Evolution and Impacting Factors of Global Renewable Energy Products Trade Network: An Empirical Investigation Based on ERGM Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Juan, Keyin Liu, Zixin Yang, and Yi Qu. 2023. "Evolution and Impacting Factors of Global Renewable Energy Products Trade Network: An Empirical Investigation Based on ERGM Model" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118701
APA StyleLi, J., Liu, K., Yang, Z., & Qu, Y. (2023). Evolution and Impacting Factors of Global Renewable Energy Products Trade Network: An Empirical Investigation Based on ERGM Model. Sustainability, 15(11), 8701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118701





