Sustainable Road Planning for Trucks in Urbanized Areas of Chinese Cities Using Deep Learning Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
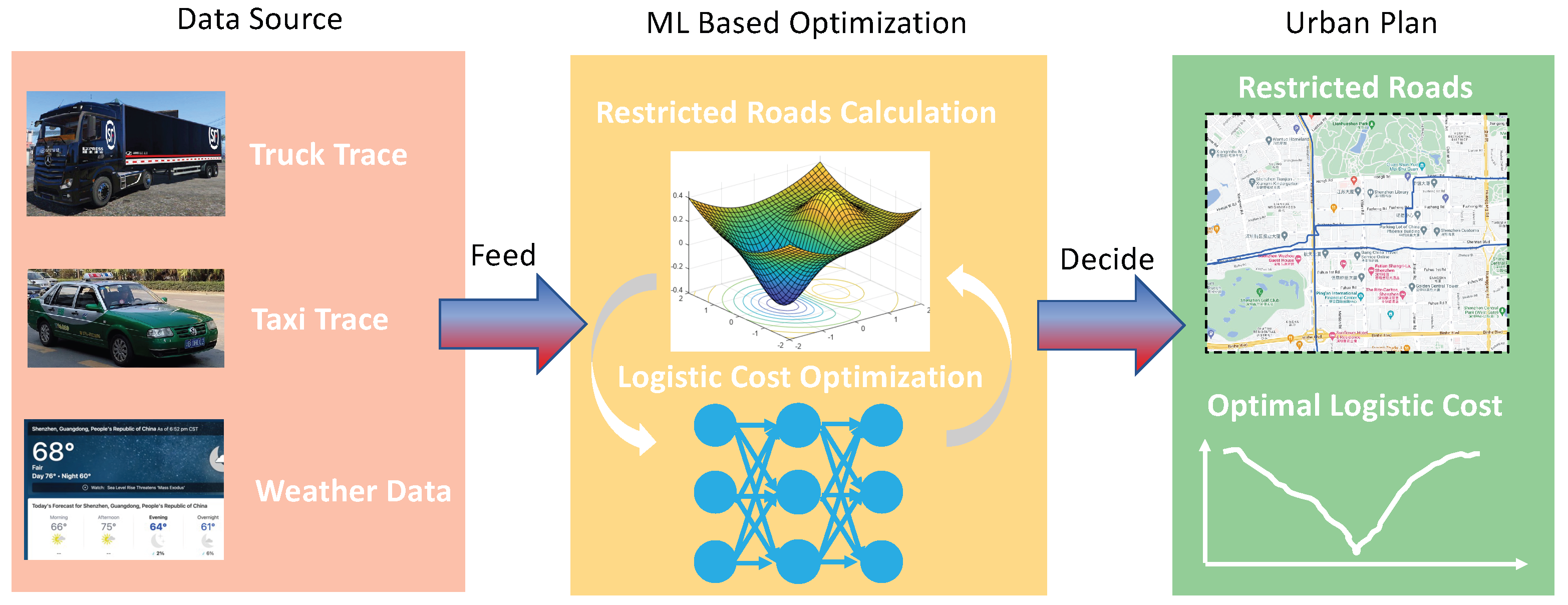
- We propose DeepPlan, a novel urban road planning tool that optimizes the logistic costs of trucks to build a sustainable road plan. DeepPlan iteratively selects the least number of roads to ban dynamically, achieving greater effectiveness and cost-efficiency compared to the existing policy.
- To obtain real-time logistic costs, DeepPlan applies deep-learning models to estimate the trucks’ logistic costs from the optimal route, learned from taxis’ trace data. This model precisely captures the driving pattern that can save logistic costs and deliver payloads in the shortest time.
- We evaluate DeepPlan with the data collected in Shenzhen, China. The experimental results show that DeepPlan outperforms the existing policy by 25% and can support real-time decisions for administrators under different weather and event conditions.
2. Literature Review
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Data and Insights
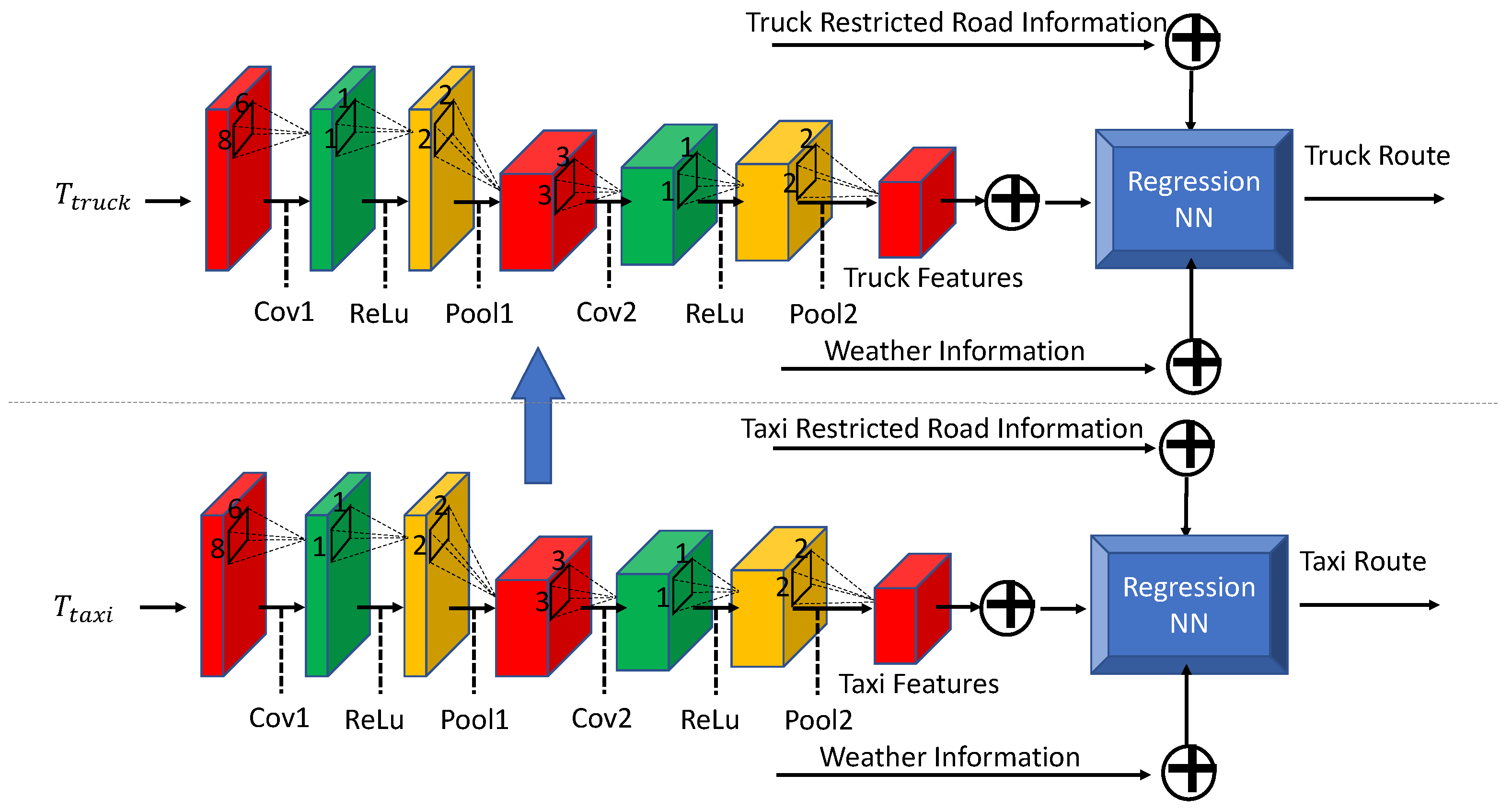
3.2. Overview of DeepPlan
3.3. Logistic Cost Optimization
3.4. Restricted Roads Calculation
| Algorithm 1 An algorithm for solving Equation (6) |
|
4. Results
4.1. Implementation
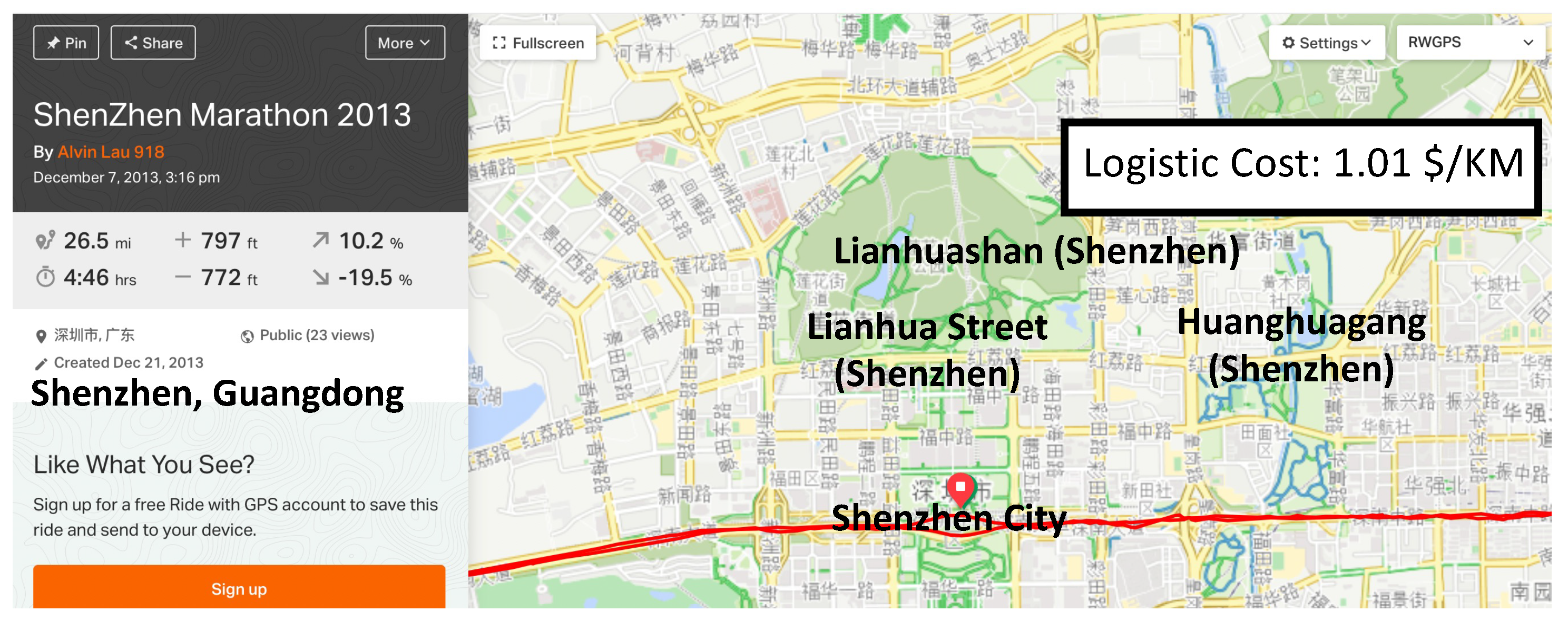
4.2. Main Results
4.3. How Update Frequency Affects Results
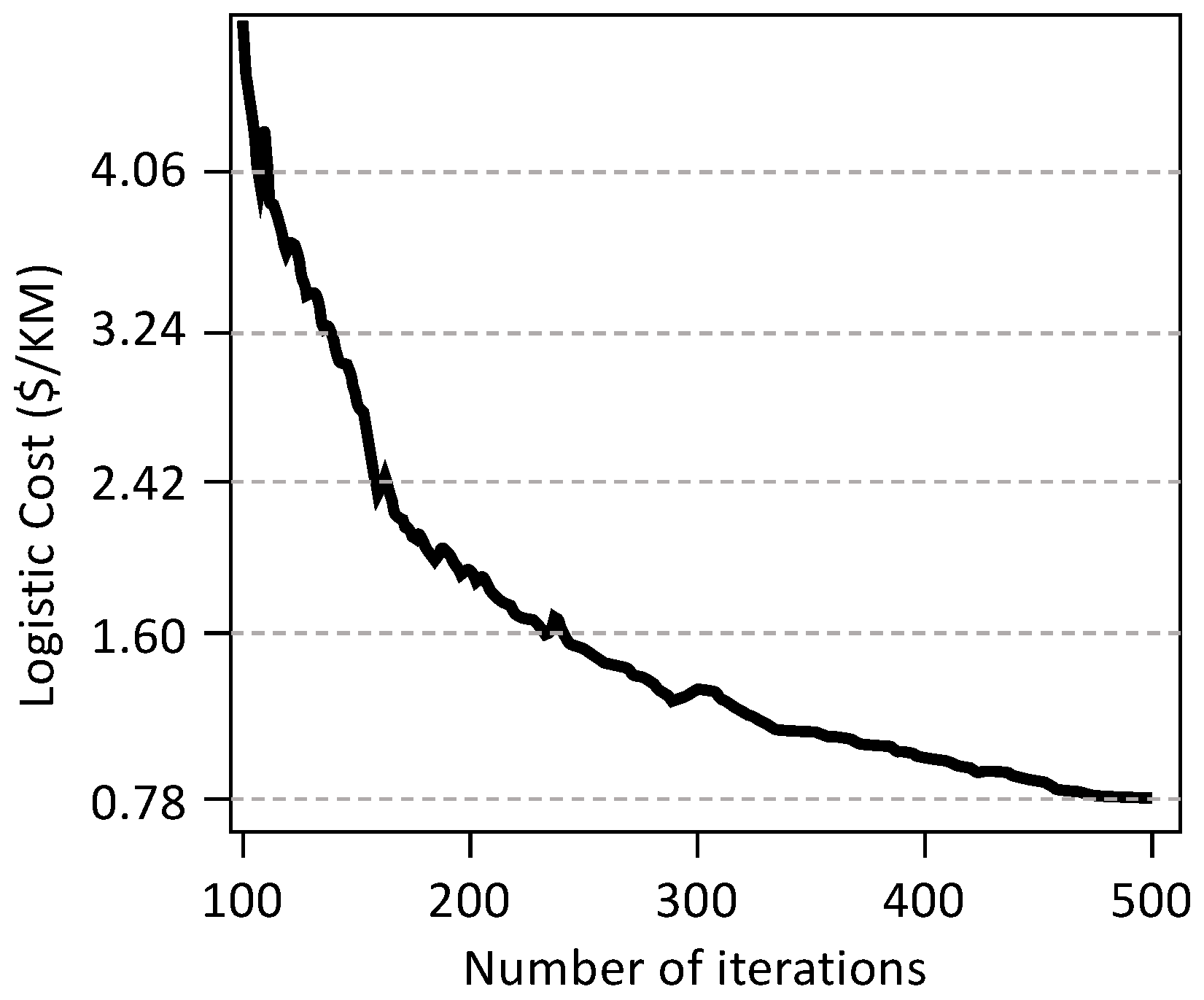
4.4. How Number of Iterations Affects Results
4.5. How Weather Affects Results
4.6. How Events Affects Results
5. Discussion
5.1. How Traffic Information Affects DeepPlan Model?
5.2. Generalizability of DeepPlan
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goh, M.; Ling, C. Logistics development in China. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2003, 33, 886–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X. Intelligent logistics cost control based on microprocessor system and sensors. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 82, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liang, Y.; Bao, X.; Qin, J.; Lim, M.K. China’s logistics development trends in the post COVID-19 era. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 25, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H. Cost Management of Logistics and Supply Chain Costs. IGI Glob. 2022, 11, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhao, H. Study on e-commerce logistics cost control methods in the context of COVID-19 prevention and control. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 11955–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdana, Y.R. Logistics information system for supply chain of agricultural commodity. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 65, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayialis, S.P.; Kechagias, E.P.; Konstantakopoulos, G.D. A city logistics system for freight transportation: Integrating information technology and operational research. Oper. Res. 2022, 22, 5953–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Cui, J. A cooperative game model of supply chain logistics information based on collaborative immune quantum particle swarm optimisation. Int. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 36, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C. Research on the Challenges and Strategies of Enterprises in Reverse Logistics Cost Control Under B2C Mode. In Advances in Smart Vehicular Technology, Transportation, Communication and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Chen, L. E-Commerce Enterprise Supply Chain Cost Control under the Background of Big Data. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6653213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, S.; Daultani, Y.; Dwivedi, A.; Zhou, F. Supplier selection and evaluation in e-commerce enterprises: A data envelopment analysis approach. Benchmarking Int. J. 2021, 29, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.H.; Yang, J.; Xiang, Z. Selection of Logistics Service Provider for the E-Commerce Companies in Pakistan Based on Integrated GRA-TOPSIS Approach. Axioms 2021, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shakeel, P.M.; Montenegro-Marin, C. Research on operational research-based financial model based on e-commerce platform. In Information Systems and e-Business Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, H.H.; Wang, M.; Johnson, L.; He, D. Projection of Chinese motor vehicle growth, oil demand, and CO2 emissions through 2050. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2038, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Ju, Y. Projection of end-of-life vehicle population and recyclable metal resources: Provincial-level gaps in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, N. Do urban motor vehicle restriction policies truly control urban air quality? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 107, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenelius, E.; Petersen, T.; Mattsson, L.G. Importance and exposure in road network vulnerability analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2006, 40, 537–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, R.J.; Watson, G.; Stuart, W.; Twentyman, C.; Kitic, C.M.; Schmidt, M. The validity, reliability, and agreement of global positioning system units—can we compare research and applied data? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 12, 3330–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kim, S.M.; He, T. Symbol-level cross-technology communication via payload encoding. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Vienna, Austria, 2–5 July 2018; pp. 500–510. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, N. Developing and analyzing eco-driving strategies for on-road emission reduction in urban transport systems-A VR-enabled digital-twin approach. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wu, M.; Chen, P.; Cao, Z.; Xie, S. Review of shared online hailing and autonomous taxi services. Transp. B Transp. Dyn. 2023, 11, 486–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamizi, M.G.; Yaghoubi, M.; Najjaran, H. A review of recent trend in motion planning of industrial robots. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2023, 1, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, T.; Tsourdos, A.; Xia, Y.; Chai, S. Deep learning-based trajectory planning and control for autonomous ground vehicle parking maneuver. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, S. Electric vehicle charging station deployment for minimizing construction cost. In Proceedings of the Big Data Analytics and Knowledge Discovery: 19th International Conference, Lyon, France, 28–31 August 2017; pp. 471–485. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Sun, C.; Tian, D.; Zhou, J.; Cao, D. Cooperative Lane-Change Motion Planning for Connected and Automated Vehicle Platoons in Multi-Lane Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.J.; Abdullah, A.H.; Mokhtar, M.; Kohar, U.H.A. The Potential of Big Data Application in Mathematics Education in Malaysia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huo, L.; Wu, J.; Bashir, A.K. Swarm Learning-Based Dynamic Optimal Management for Traffic Congestion in 6G-Driven Intelligent Transportation System. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, F.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Li, X.; Xia, J.; Lv, Z. Data information processing of traffic digital twins in smart cities using edge intelligent federation learning. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhilal, A.Y.; Finley, B.; Braud, T.; Su, D.; Hui, P. Street Smart in 5G: Vehicular Applications, Communication, and Computing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 105631–105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshayeb, S.; Stevanovic, A.; Effinger, J.R. Investigating impacts of various operational conditions on fuel consumption and stop penalty at signalized intersections. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 690–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumantri, V.N.; Rifai, A.I.; Ferial, F. Impact of inter-urban street lighting on users perception of road safety behavior: A Case of Jalan Majalengka-Rajagaluh. Citiz. J. Ilm. Multidisiplin Indones. 2022, 5, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Pu, Z.; Wang, Y. Real-time crash identification using connected electric vehicle operation data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 173, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.C.; Ma, J.; Cisco, B.; Neill, J.; Moen, B.; Jareck, C. Deriving signal performance metrics from large-scale connected vehicle system deployment. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Short-term and long-term prediction of coal consumption in Shandong Province-with ARIMA Model and Metabolism GM (1, 1) Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 227, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Optimization of Joint Decision of Transport Mode and Path in Multi-Mode Freight. Transp. Netw. 2022, 22, 4887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Qin, P. Will a driving restriction policy reduce car trips?—The case study of Beijing, China. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2014, 67, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Fang, Y. Health effects of PM2.5 emissions from on-road vehicles during weekdays and weekends in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Li, D. Efficiency measure on the truck restriction policy in China: A non-radial data envelopment model. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 129, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Hu, M.; Huang, W. A license plate recognition data to estimate and visualise the restriction policy for diesel vehicles on urban air quality: A case study of Shenzhen. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wei, N.; Sun, B.; Ni, J.; He, J.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, J.; et al. Evaluating traffic emission control policies based on large-scale and real-time data: A case study in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibeka, A.; Songchitruksa, P.; Zhang, Y. Assessing environmental impacts of ad-hoc truck platooning on multilane freeways. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 25, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkinen, T.; Hamalainen, E. Reviewing truck logistics: Solutions for achieving low emission road freight transport. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.J.; Macea, L.F.; Cantillo, V. Analysing a license plate-based vehicle restriction policy with optional exemption charge: The case in Cali, Colombia. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2023, 170, 103618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Xu, P.; Manyi, G. Logistics distribution route optimization based on genetic algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8468438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, M.; Caggiani, L.; Ottomanelli, M.; Dell’Orco, M. En route truck–drone parcel delivery for optimal vehicle routing strategies. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Ghani, M.K.A.; Hamed, R.I.; Mostafa, S.A.; Ahmad, M.S.; Ibrahim, D.A. Solving vehicle routing problem by using improved genetic algorithm for optimal solution. J. Comput. Sci. 2017, 21, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, X.; Sun, G. T-drive: Enhancing driving directions with taxi drivers’ intelligence. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2011, 1, 220–232. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, B.; Du, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Analysis of taxi drivers’ behaviors within a battle between two taxi apps. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 17, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, F.; Wu, T.; Jia, H. Taxi drivers’ cruising patterns—Insights from taxi GPS traces. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; Wang, S.; Kim, S.M. Exploiting WiFi guard band for safeguarded ZigBee. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y. COVID-GAN: Estimating Human Mobility Responses to COVID-19 Pandemic through Spatio-Temporal Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the SIGSPATIAL’20: 28th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, J.; Jia, X.; Xu, S.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Integrating Physics-Based Modeling with Machine Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04919. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Willard, J.; Karpatne, A.; Read, J.; Zwart, J.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Physics Guided RNNs for Modeling Dynamical Systems: A Case Study in Simulating Lake Temperature Profiles. In Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2 May 2019; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Publications: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yin, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kim, S.M.; He, T. Networking support for bidirectional cross-technology communication. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 20, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shekhar, S.; Li, Y. Statistically-Robust Clustering Techniques for Mapping Spatial Hotspots: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Meng, S.; Wu, H. Discover Customers’ Gender From Online Shopping Behavior. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 13954–13965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Willard, J.; Karpatne, A.; Read, J.S.; Zwart, J.A.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Physics-Guided Machine Learning for Scientific Discovery: An Application in Simulating Lake Temperature Profiles. ACM/IMS Trans. Data Sci. 2021, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bhojwani, R.; Shekhar, S.; Knight, J.F. An unsupervised augmentation framework for deep learning based geospatial object detection: A summary of results. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Bao, H.; Li, Y.; Shekhar, S. Discovering Spatial Mixture Patterns of Interest. In Proceedings of the SIGSPATIAL ’20: 28th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, J.; Jia, X.; Xu, S.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Integrating Scientific Knowledge with Machine Learning for Engineering and Environmental Systems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoglu, L.; Terzi, E.; Jia, X.; Zwart, J.; Sadler, J.; Appling, A.; Oliver, S.; Markstrom, S.; Willard, J.; Xu, S.; et al. Physics-Guided Recurrent Graph Model for Predicting Flow and Temperature in River Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Virtual Event, 29 April–1 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Gao, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S. Effectiveness of production reduction policy on improving air quality in Dongying. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 227, 052043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kotwal, P.; Wang, P.; Xie, Y.; Shekhar, S.; Northrop, W. Physics-guided Energy-efficient Path Selection Using On-board Diagnostics Data. ACM Trans. Data Sci. 2020, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.C.; Stillman, A.B.; Jia, X.; Karpatne, A.; Dugan, H.A.; Carey, C.C.; Stachelek, J.; Ward, N.K.; Zhang, Y.; Read, J.S.; et al. Predicting lake surface water phosphorus dynamics using process-guided machine learning. Ecol. Model. 2020, 420, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, P.; Shekhar, S.; Northrop, W. Significant lagrangian linear hotspot discovery. In Proceedings of the SIGSPATIAL ’20: 28th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shekhar, S. Discovering Interesting Subpaths with Statistical Significance from Spatiotemporal Datasets. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2020, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, S.; Khandelwal, A.; Nayak, G.; Karpatne, A.; Kumar, V. Spatial Context-Aware Networks for Mining Temporal Discriminative Period in Land Cover Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Calgary, AB, Canada, 2 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Karpatne, A.; Willard, J.; Steinbach, M.; Read, J.; Hanson, P.C.; Dugan, H.A.; Kumar, V. Physics Guided Recurrent Neural Networks For Modeling Dynamical Systems: Application to Monitoring Water Temperature And Quality In Lakes. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.02880. [Google Scholar]
- Number of Taxis in Shenzhen. Available online: http://jtys.sz.gov.cn/ydmh/jtzx/tzgg_1508/content/post_10540221.html (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Number of Taxis in Beijing. Available online: https://d.qianzhan.com/xdata/details/356c9d80220f0669.html (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Number of Taxis in Shanghai. Available online: https://d.qianzhan.com/xdata/details/3d4f0ca64f92f51b.html (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Restricted Area for Trucks in Shenzhen Urban Area. Available online: http://www.jipaihuanbao.cn/post/304931.html (accessed on 18 March 2023).

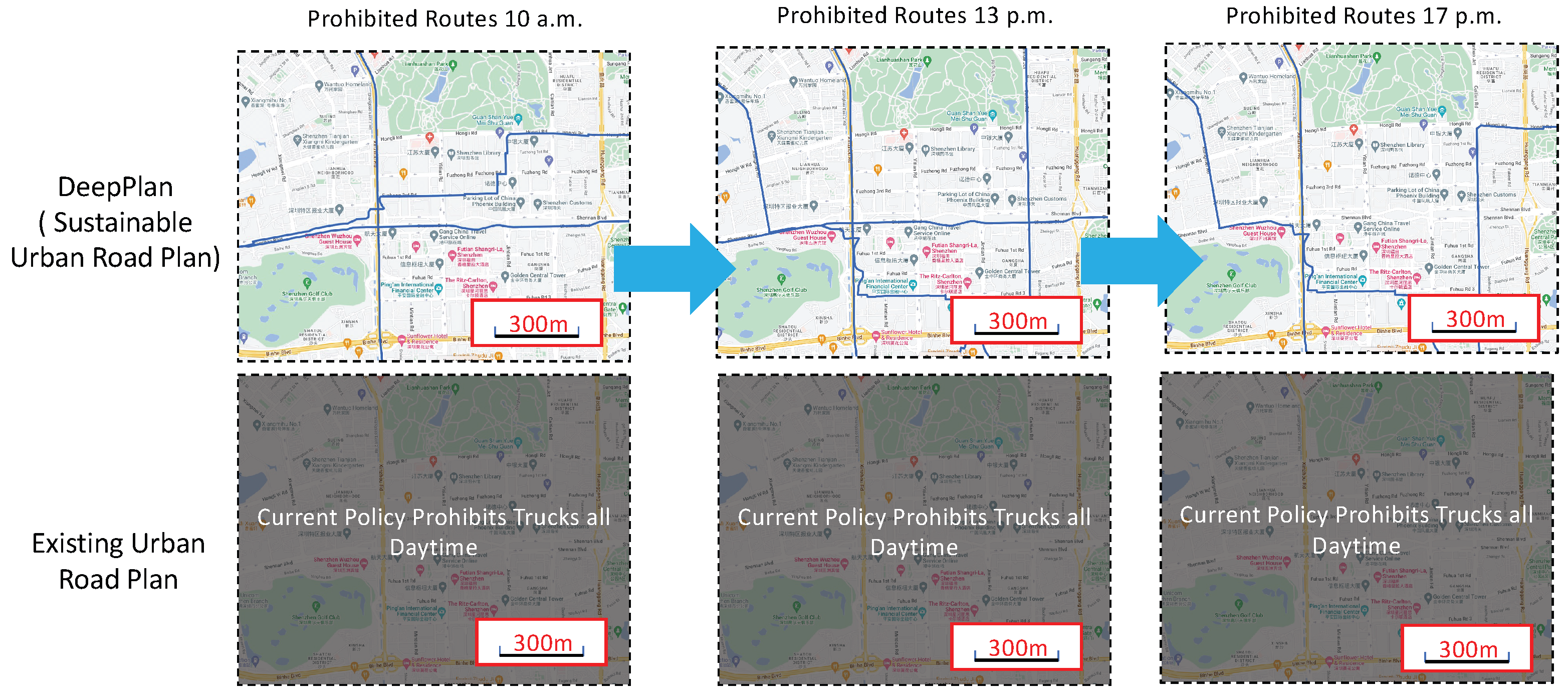

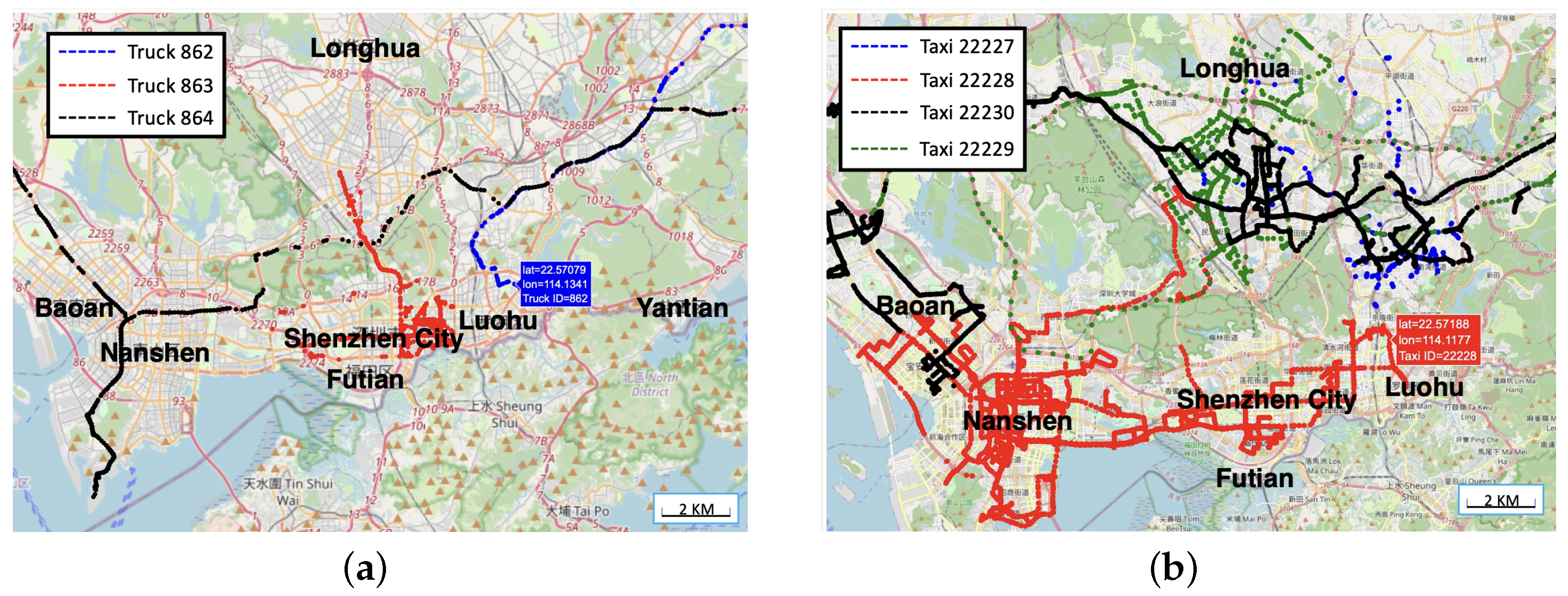
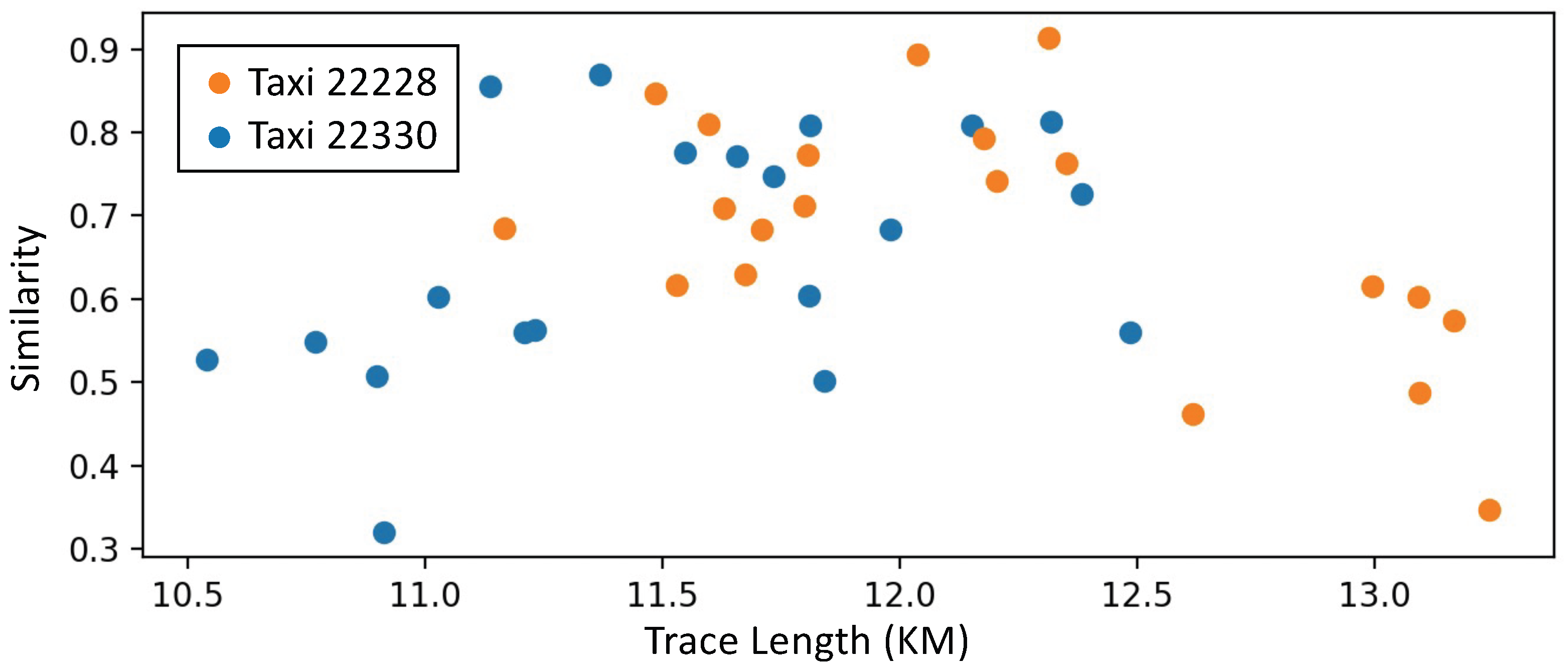






| ID | Time | Latitude | Longitude | Status | Speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxi | 22228 | 2013/06/19 13:00:07 | 113.951897 | 22.556217 | Occupied | 32 KM/s |
| Truck | 862 | 2013/06/19 20:28:28 | 113.876801 | 22.506849 | N/A | 10 KM/s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Bao, F. Sustainable Road Planning for Trucks in Urbanized Areas of Chinese Cities Using Deep Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118763
Wang H, Zhao Z, Ma Y, Wu H, Bao F. Sustainable Road Planning for Trucks in Urbanized Areas of Chinese Cities Using Deep Learning Approaches. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118763
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haopeng, Zhenzhi Zhao, Yingying Ma, Hao Wu, and Fei Bao. 2023. "Sustainable Road Planning for Trucks in Urbanized Areas of Chinese Cities Using Deep Learning Approaches" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118763
APA StyleWang, H., Zhao, Z., Ma, Y., Wu, H., & Bao, F. (2023). Sustainable Road Planning for Trucks in Urbanized Areas of Chinese Cities Using Deep Learning Approaches. Sustainability, 15(11), 8763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118763





