Impact of Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization and Energy Consumption on Carbon Emissions: A Study of India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Significance of the Study
- Economic growth can help to achieve S.D.G. 1 (no poverty), S.D.G. 2 (zero hunger), and S.D.G. 8 (decent work and economic growth) by raising earnings, generating jobs, and reducing hunger and poverty.
- Trade openness can help achieve S.D.G. 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure) and S.D.G. 10 (reduced inequalities) by facilitating the transfer of technology, knowledge, and resources between countries and reducing trade barriers that can impede economic growth and development.
- Urbanization can help achieve S.D.G. 11 (sustainable cities and communities) by providing essential services like water, sanitization, and healthcare access and promoting sustainable transportation, land use, and building design.
- Energy consumption can help achieve S.D.G. 7 (affordable and clean energy) and S.D.G. 13 (climate action) by increasing access to affordable and clean energy, promoting energy efficiency, and utilizing renewable energy sources.
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Relationship between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality
2.2. The Relationship between Urbanization, Industrialization, and Economic Growth
2.3. The Relationship between Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emission
2.4. The Relationship between Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization, Energy Consumption, and Carbon Emission
3. Materials and Methodology
4. Results
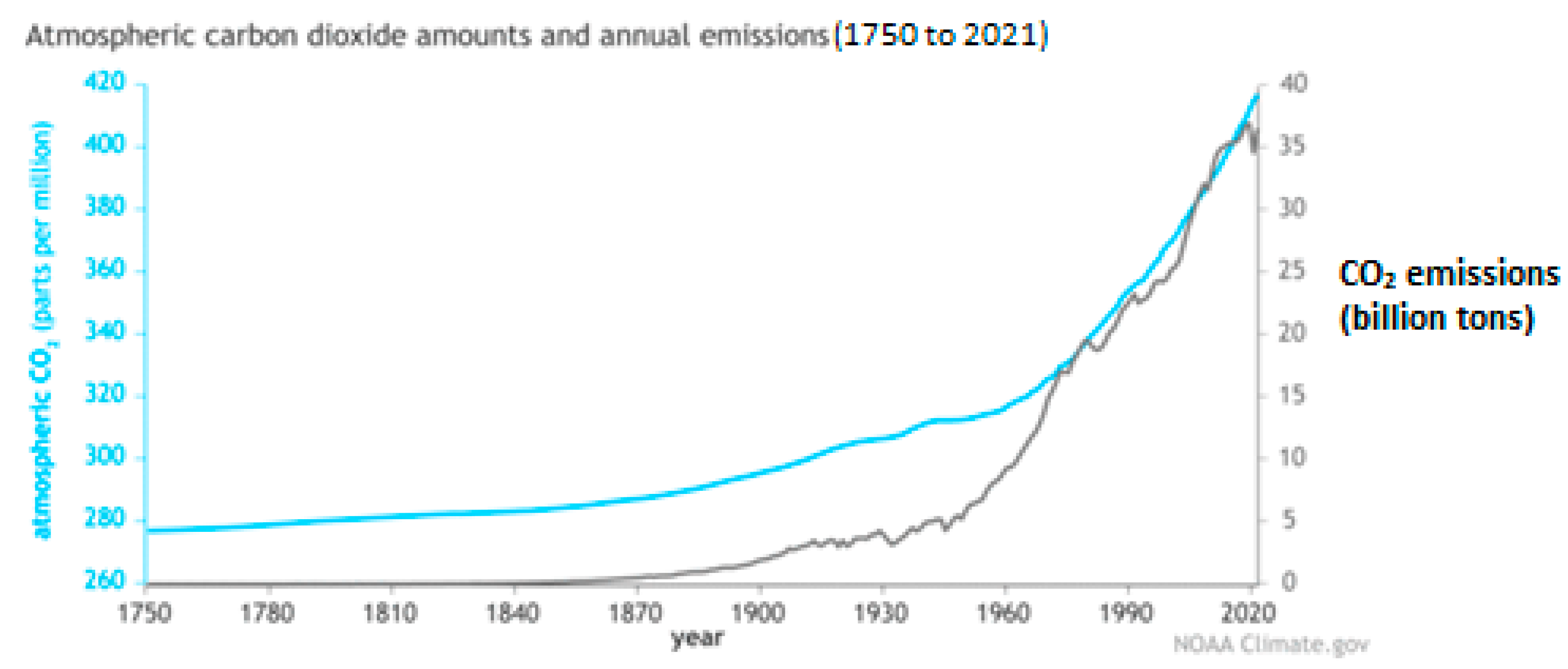
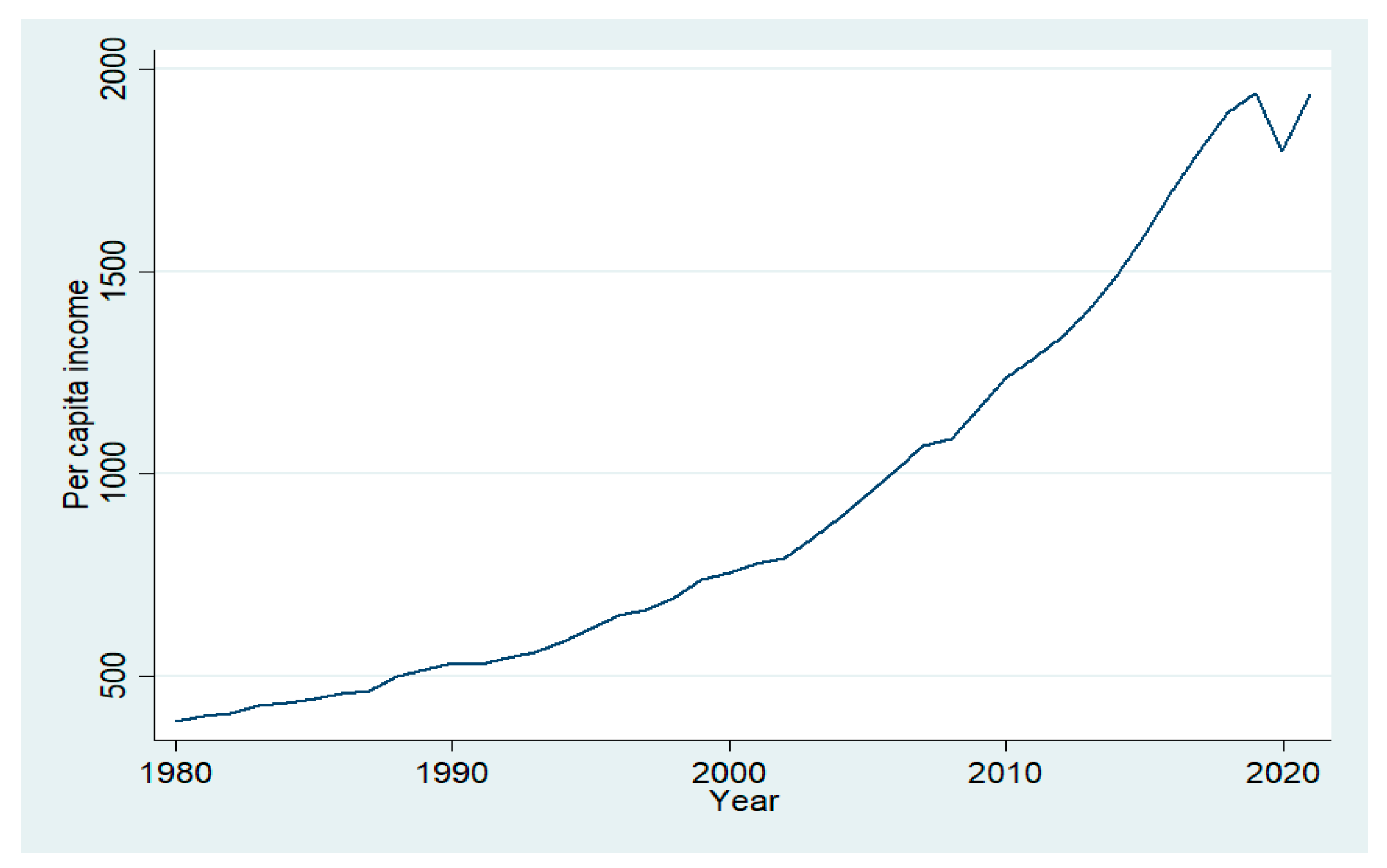
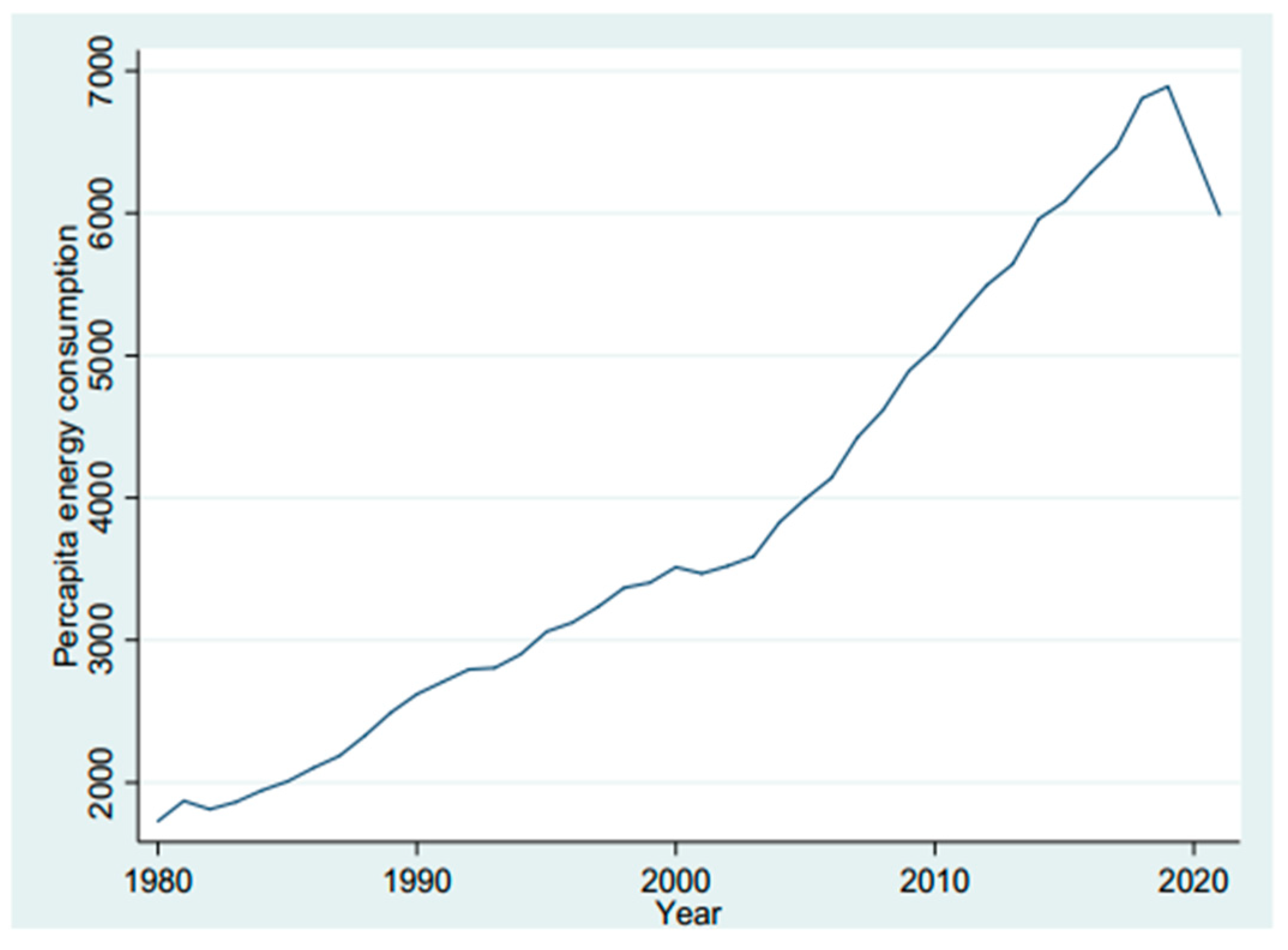
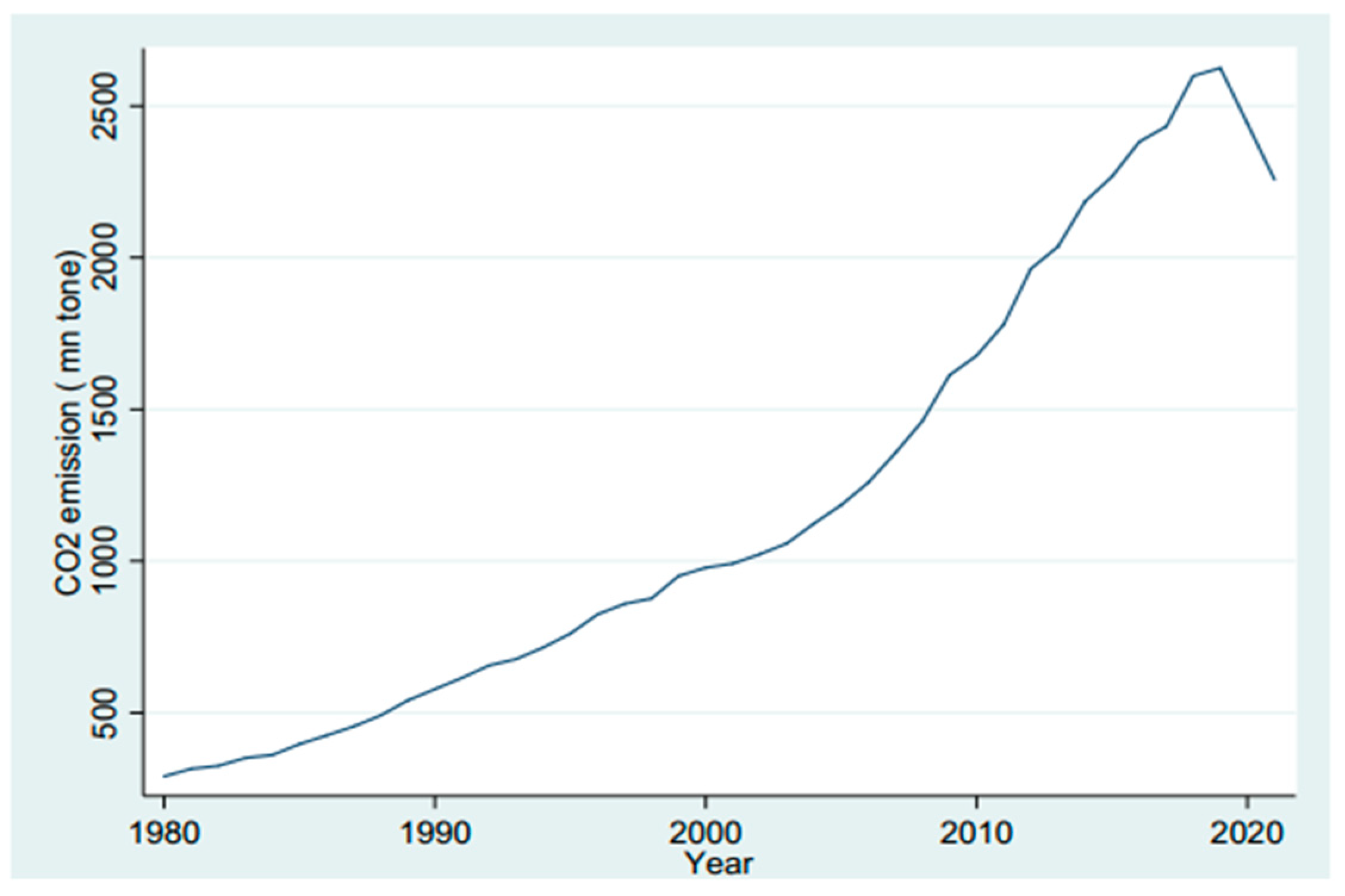
4.1. Trend of the Variables
4.2. Empirical Results of the ARDL and Random Forest Model
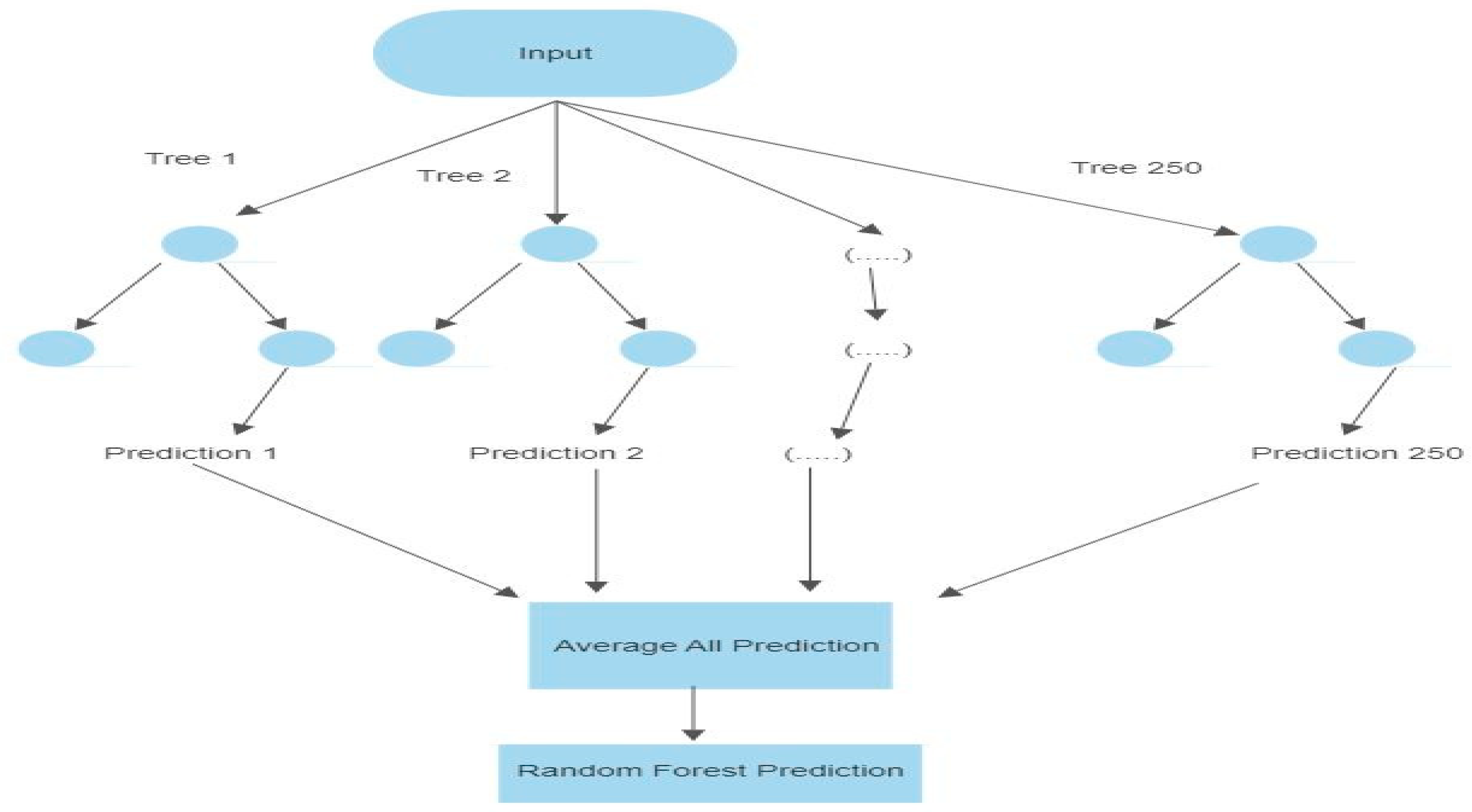
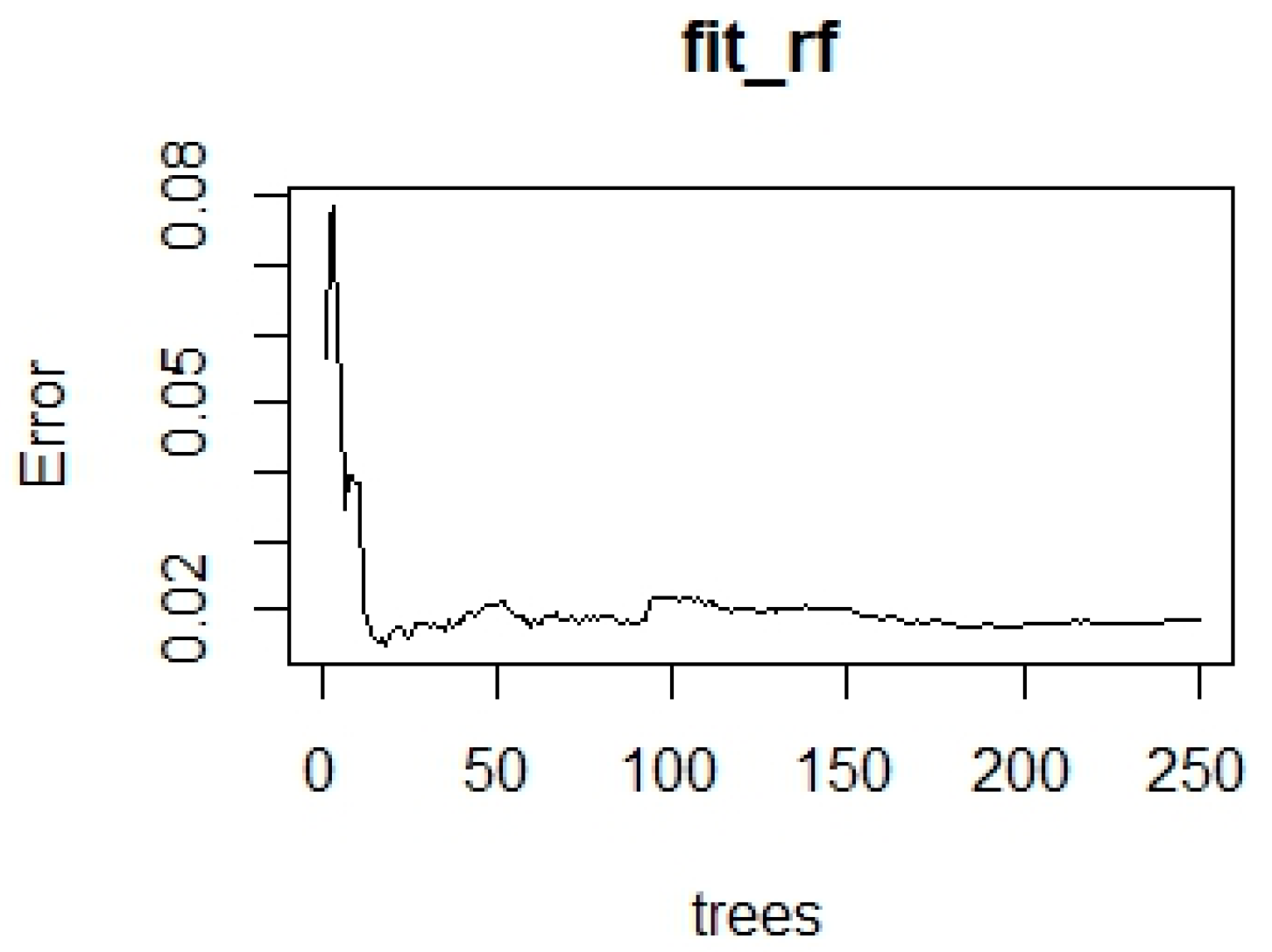
4.3. Random Forest Model
- Architecture of the Random Forest model
- Pairwise Granger causality test
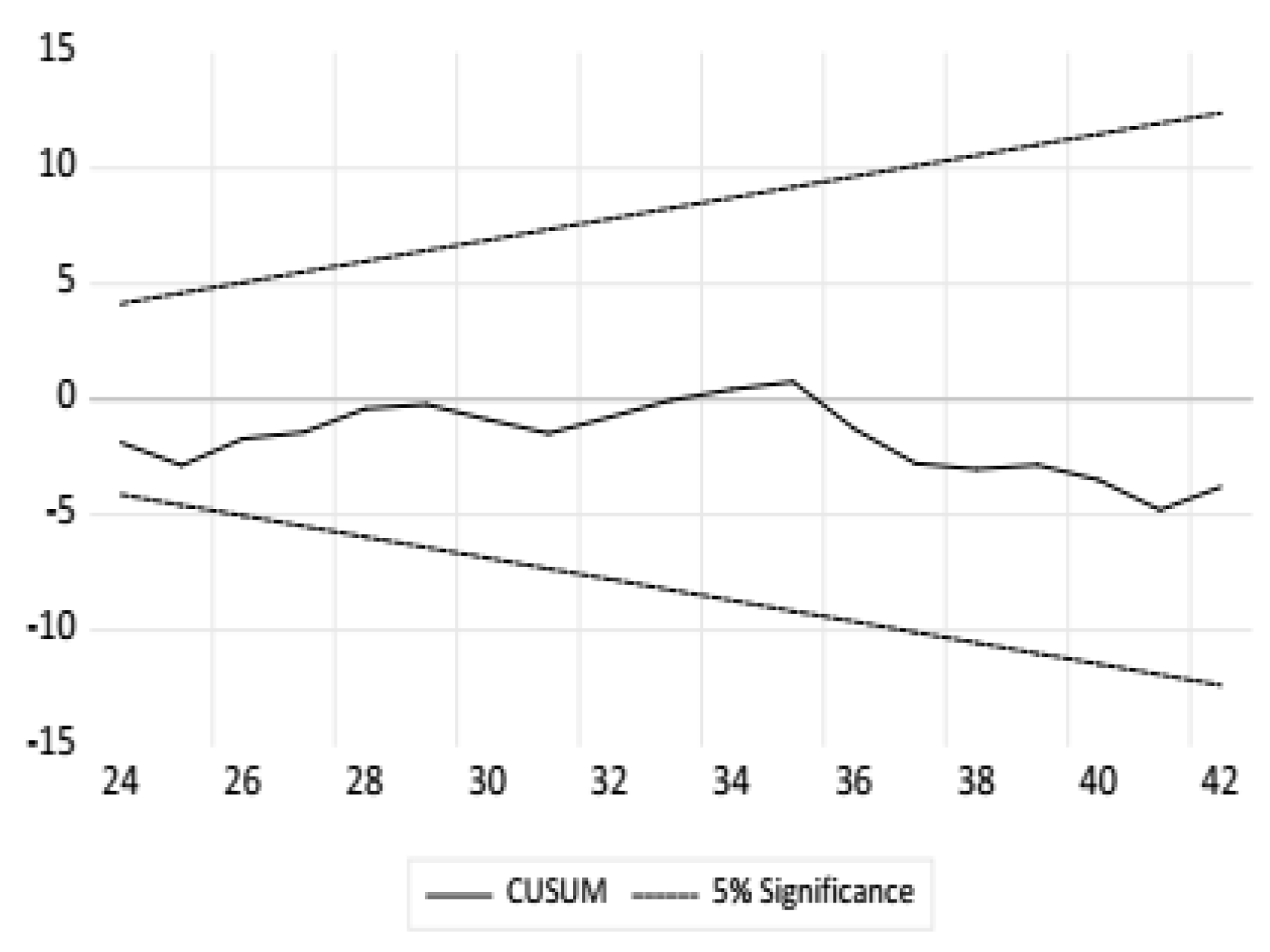
4.4. Diagnostic Tests
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Our World in Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Kivyiro, P.T. Foreign Direct Investment, Clean Development Mechanism, and Environmental Management: A case of Sub-Saharan Africa; Lappeenranta University of Technology: Lappeenranta, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Zhao, Z.Y. Empirics on linkages among industrialization, urbanization, energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: A heterogeneous panel study of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30617–30632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, K.B.; Baudelaire, D.W. Climate Variability, and Urbanization in Sub-Saharan Africa: Mitigating the Effects on Economic Growth. African Economic Research Consortium. 2021. Available online: http://3.65.68.50/bitstream/handle/123456789/2819/Working%20Paper%20Series%20CC-010.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Wang, A.; Lin, B. Assessing CO2 emissions in China’s commercial sector: Determinants and reduction strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/08/world-population-countries-india-china-2030/ (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Times of India. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/The-underage-optimist/let-this-be-indias-goal-for-this-decade-5000-per-capita-income-by-2030/ (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Lin, B.; Omoju, O.E. Does private investment in the transport sector mitigate the environmental impact of urbanization? Evidence from Asia. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- India Energy Information Enerdata. Available online: https://www.enerdata.net/estore/energymarket/india/ (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Ministry of Power, Government of India. Available online: https://powermin.gov.in/en/content/power-sector-glance-all-india (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- United Nations Development Programme. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-developmentgoals#:~:text=The%20Sustainable%20Development%20Goals%20(SDGs)%2C%20also%20known%20as%20the,people%20enjoy%20peace%20and%20prosperity (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. The effects of trade openness on decoupling carbon emissions from economic growth–evidence from 182 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Ersin, Ö. Markov-switching vector autoregressive neural networks and sensitivity analysis of environment, economic growth and petrol prices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31630–31655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. 1991. Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w3914/w3914.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Cole, M.A.; Rayner, A.J.; Bates, J.M. The environmental Kuznets curve: An empirical analysis. Environ. Dev. Econ. 1997, 2, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, J.; Levinson, A. The simple analytics of the environmental Kuznets curve. J. Public Econ. 2001, 80, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, S.; Laplante, B.; Wang, H.; Wheeler, D. Confronting the environmental Kuznets curve. J. Econ. Perspect. 2002, 16, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yandle, B.; Vijayaraghavan, M.; Bhattarai, M. The environmental Kuznets curve. A Primer PERC Res. Study 2002, 2, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dinda, S. Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: A survey. Ecol. Econ. 2004, 49, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, D.I. The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev. 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Ozturk, I.; Afza, T.; Ali, A. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in a global economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, D.I. The environmental Kuznets curve after 25 years. J. Bioeconomics 2017, 19, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Ozturk, I. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Kenya: A multivariate analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A. Re-visiting the Environmental Kuznets curve for ASEAN: A comparison between ecological footprint and carbon dioxide emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, R. Does urbanization redefine the environmental Kuznets curve? An empirical analysis of 134 Countries. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M. Using the ARDL-ECM approach to explore the nexus among urbanization, energy consumption, and economic growth in Jiangsu Province, China. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2015, 51, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. The global pattern of urbanization and economic growth: Evidence from the last three decades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frick, S.A.; Rodríguez-Pose, A. Change in urban concentration and economic growth. World Dev. 2018, 105, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniwchan, J. Economic growth, industrialization, and the environment. Resour. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 442–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttara, S.; Bhuvandas, N.; Aggarwal, V. Impacts of urbanization on environment. Int. J. Res. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impacts of urbanization and industrialization on energy consumption/CO2emissions: Does the level of development matter? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bae, J. Urbanization and industrialization impact of CO2 emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, L.; Strielkowski, W. The impact of urbanization and industrialization on energy security: A case study of China. Energies 2019, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmood, H.; Alkhateeb, T.T.Y.; Furqan, M. Industrialization, urbanization and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: Asymmetry analysis. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumik, L.C.; Sultana, T. Impact of urbanization, industrialization, electrification and renewable energy on the environment in BRICS: Fresh evidence from novel CS-ARDL model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acaravci, A.; Ozturk, I. On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 2010, 35, 5412–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Cheng, X.M. Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2706–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.; Law, S.H.; Zannah, T.I. Dynamic impact of urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and trade openness on CO2 emissions in Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12435–12443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.K.; Seyedaliakbar, S.M. Impact of energy consumption and economic growth on CO2 emissions using multivariate regression. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Raza, S.A.; Ozturk, I.; Afshan, S. The dynamic relationship of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption with carbon emissions: A global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, R.; Sarwar, S.; Wei, C. The survey of economic growth, energy consumption, and carbon emissions. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osobajo, O.A.; Otitoju, A.; Otitoju, M.A.; Oke, A. The impact of energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Guo, Q.; Kartal, M.T.; Nurgazina, Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Sharif, A. The impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on carbon emissions intensity in China: Fresh evidence from novel dynamic ARDL simulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Kanjilal, K. Long-term equilibrium relationship between urbanization, energy consumption, and economic activity: Empirical evidence from India. Energy 2014, 66, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U.; Ozturk, I.; Lean, H.H. The influence of economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, financial development, and renewable energy on pollution in Europe. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 621–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S. Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 6991–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Younis, M.; Ullah, I. Impact of urbanization and economic growth on CO2 emissions: A case of far east Asian countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurgazina, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, U.; Koondhar, M.A.; Lu, Q. The impact of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness, and financial development on carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60195–60208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ibrahim, Y. Causal nexus in industrialization, urbanization, trade openness, and carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from OPEC economies. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 13990–14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, L. Per capita renewable energy consumption in 116 countries: The effects of urbanization, industrialization, G.D.P., aging, and trade openness. Energy 2022, 254, 124289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakher, H.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Acheampong, A.O.; Nathaniel, S.P. Renewable energy, non-renewable energy, and environmental quality nexus: An investigation of the N-shaped Environmental Kuznets Curve based on six environmental indicators. Energy 2023, 263, 125660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.A.; Sohag, K.; Abdullah, S.M.S.; Jaafar, M. CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic and population growth in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Yi, W.C.; Li, B.W. The impact of urbanization on carbon emissions: Empirical evidence in Beijing. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sikder, M.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Huai, X.; Wu, L.; Kwame Yeboah, F.; Dou, X. The integrated impact of G.D.P. growth, industrialization, energy use, and urbanization on CO2 emissions in developing countries: Evidence from the panel ARDL approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Seker, F. Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: The role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2016, 94, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B. How industrialization and urbanization process impacts on CO2 emissions in China: Evidence from nonparametric additive regression models. Energy Econ. 2015, 48, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhani, S.; Chaibi, A.; Rault, C. CO2 emissions, output, energy consumption, and trade in Tunisia. Econ. Model. 2014, 38, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouri, M.E.H.; Youssef, A.B.; M’henni, H.; Rault, C. Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X. Explaining the relationship between CO2 emissions and national income—The role of energy consumption. Econ. Lett. 2005, 87, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Kannaiah, D.; Yahya Khan, G.; Shabbir, M.S.; Bilal, K.; Zamir, A. Does sustainable environmental agenda matter? The role of globalization toward energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emissions in South Asian countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 25, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y. How does urbanization affect public health? New evidence from 175 countries worldwide. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1096964. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Maiti, S. Enhancing data-driven modeling of fluoride concentration using new data mining algorithms. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country/india (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Singh, K.; Adhana, P.; Garg, V. Impact on the economy of India due to variations in climate. Int. J. Zool. Appl. Biosci. 2022, 7, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/newsroom/40556222.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Yuk, E.H.; Park, S.H.; Park, C.S.; Baek, J.G. Feature-learning-based printed circuit board inspection via speeded-up robust features and random forest. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, W.; Abdullah, A.; Azam, M. The dynamic relationship between structural change and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: A cointegrating approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12723–12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Author | Origin | Period | Method | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fakher et al., 2023 [51] | OPEC | 1994–2019 | Regression | An N-shaped relationship exists between per capita income and measures of environmental deterioration. |
| Begum et al., 2015 [52] | Malaysia | 1970–1980 | ARDL model | The negative relation between carbon emissions and per capita income. |
| Zhang et al., 2015 [53] | China | 1980–2013 | ARDL model | The positive relation between urbanization and carbon emissions. |
| Sikder et al., 2022 [54] | Developing Countries | 1995–2018 | ARDL model | Results show that economic growth, energy consumption, urbanization, and industrialization increase carbon emissions. |
| Hossain, M.S., 2011 [45] | 8 newly industrialized countries | 1971–2007 | Granger causality test | Unidirectional short-run causality from economic growth and trade openness to carbon emissions. |
| Dogan &Seker, 2016 [55] | European Union | 1980–2012 | Panel estimation techniques | There is a negative impact of renewable energy and trade on carbon emissions. |
| Xu and Lin, 2015 [56] | China | 1990–2011 | Nonparametric additive regression model | It has been found that the impact of industrialization and urbanization on carbon emissions varies across regions. |
| Farhani et al., 2014 [57] | Tunisia | 1971–2008 | ARDL model | Short-run unidirectional causality has been found, which runs from GDP, GDP square, and energy consumption to carbon emissions. |
| Arouri et al., 2012 [58] | Middle East and North African countries | 1981–2005 | Bootstrap panel unit root test and cointegration | Results depict positive relation between energy consumption and carbon emissions. There is poor support for the EKC theory. |
| Liu, X., 2005 [59] | 24 OECD countries | 1975–1990 | Regression equations | A negative relation has been found between income and carbon emissions. |
| Sadiq et al., 2022 [60] | South Asian countries | 1972–2019 | Fully modified O.L.S. | Results indicate that energy consumption, globalization, and economic growth increase carbon emissions. |
| Zhang et al., 2022 [61] | 175 countries | 2000–2018 | Coefficient stability test, GMM, instrumental variable method | Improvement in living standard can improve public health in urban areas. |
| S. No. | Variable | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CO2 emissions (mn tones) | World Development Indicators |
| 2 | Per capita energy consumption (kWh) | Our World in Data |
| 3 | Per capita income (constant 2015 U.S. USD ) | World Development Indicators |
| 4 | Trade openness (% of GDP) | World Development Indicators |
| 5 | Total urban population | World Development Indicators |
| S. No. | Assumption | Test/Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Homoscedasticity | Breusch–Pagan–Godfrey test |
| 2 | Stability | CUSUM and CUSUM Square |
| 3 | Serial Autocorrelation | Lagrange multiplier(LM) test |
| 4 | Normality | Histogram and Jarque–Bera |
| Variable | Obs. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Y) | 42 | 936.0226 | 494.5419 | 388.8227 | 1941.815 |
| (EC) | 42 | 3874.64 | 1598.356 | 1729.039 | 6889.742 |
| (CO2) | 42 | 1.20 × 109 | 7.43 × 108 | 2.92 × 108 | 2.63 × 109 |
| (TO) | 42 | 30.46358 | 14.50012 | 12.21927 | 55.79372 |
| (UB) | 42 | 2.75139 | 0.3911207 | 2.294913 | 3.889168 |
| Variables | KPSS | ADF | DF-GLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| At Level | |||
| Log(CO2) | 0.798668 *** | −1.875902 | −0.553597 |
| log(Y) | 0.752899 *** | 0.874516 | −0.075082 |
| log(TO) | 0.714984 ** | −0.668131 | 0.010759 |
| log(UB) | 0.812034 ** | −0.953089 | 0.633703 |
| log(EC) | 0.795104 *** | −1.213025 | −0.166812 |
| 1st difference | |||
| Log(CO2) | 0.406172 * | −3.648016 *** | −2.597612 ** |
| log(Y) | 0.479092 ** | −6.128427 *** | −2.211544 ** |
| log(TO) | 0.615581 ** | −5.195471 *** | −4.803803 *** |
| log(UB) | 0.776082 *** | −4.439020 *** | −1.970005 ** |
| log(EC) | 0.481169 ** | −3.297859 *** | −2.748679 *** |
| F Bounds Test | H0: No Level Relationship | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Statistics | Value | Sig. Level | I (0) | I (1) |
| Dependent variable: CO2 emissions | ||||
| F-statistics K | 9.282889 | 10% | 2.46 | 3.46 |
| 4 | 5% | 2.947 | 4.088 | |
| 1% | 4.093 | 5.532 | ||
| Dependent variable: energy consumption | ||||
| F-statistics K | 7.270500 | 10% | 2.427 | 3.395 |
| 4 | 5% | 2.893 | 4 | |
| 1% | 3.967 | 5.455 | ||
| Dependent variable: per capita income | ||||
| F-statistics K | 8.100040 | 10% | 2.427 | 3.395 |
| 4 | 5% | 2.893 | 4 | |
| 1% | 3.967 | 5.455 | ||
| Dependent variable: trade openness | ||||
| F-statistics K | 7.317451 | 10% | 2.427 | 3.395 |
| 4 | 5% | 2.893 | 4 | |
| 1% | 3.967 | 5.455 | ||
| Dependent variable: total urban population | ||||
| F-statistics K | 4.383463 | 10% | 2.427 | 3.395 |
| 4 | 5% | 2.893 | 4 | |
| 1% | 3.967 | 5.455 | ||
| Variables | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long Run | ||||
| log (CO2) | −0.691342 *** | 0.231607 | −2.984982 | 0.0073 |
| log(Y) | −0.491969 *** | 0.082263 | −5.980465 | 0.0000 |
| log (TO) | 0.133460 ** | 0.060637 | 2.200975 | 0.0396 |
| log (UB) | 0.245248 ** | 0.327734 | 2.748316 | 0.0463 |
| log (EC) | 1.839673 *** | 0.225141 | 8.171198 | 0.0000 |
| Short Run | ||||
| D(logCO2(−1)) | −0.377986 *** | 0.100887 | −3.746634 | 0.0013 |
| D(logEC) | 1.034088 *** | 0.081211 | 12.73328 | 0.0000 |
| D(logY) | −0.012747 | 0.063207 | −0.201668 | 0.8422 |
| D(logTO) | −0.051640 ** | 0.021257 | −2.429329 | 0.0247 |
| D(logUB) | 6.941345 *** | 0.779243 | 8.907808 | 0.0000 |
| ECT | −0.691342 *** | 0.077182 | −8.957236 | 0.0000 |
| R2 | RMSE | MAE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 0.988565 | 0.128052 | 0.102064 |
| Test | 0.992583 | 0.0914858 | 0.080175 |
| H0: Does Not Granger Cause | Obs. | F-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 to EC EC to CO2 | 39 | 1.36053 3.47464 | 0.2701 0.0424 ** |
| Y to CO2 CO2 to Y | 39 | 0.46512 0.64070 | 0.6320 0.5332 |
| TO to CO2 CO2 to TO | 39 | 3.46636 1.59006 | 0.0427 ** 0.2187 |
| UB to CO2 CO2 to UB | 39 | 2.43585 0.10363 | 0.1027 0.9018 |
| Y to EC EC to Y | 39 | 2.72418 0.25754 | 0.0799 * 0.7744 |
| TO to EC EC to TO | 39 | 0.32598 1.54971 | 0.7240 0.2269 |
| UB to EC EC to UB | 39 | 3.19282 0.37230 | 0.0536 ** 0.6919 |
| TO to Y Y to TO | 39 | 1.52782 1.59107 | 0.2315 0.2185 |
| UB to Y Y to UB | 39 | 0.30966 0.70914 | 0.7357 0.4992 |
| UB to TO TO to UB | 39 | 0.43255 1.01380 | 0.6524 0.3735 |
| Test | F-Statistic | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test | 1.165277 | 0.3343 |
| Breusch-Pagan-Godfrey: Heteroskedasticity Test | 0.848213 | 0.6268 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goswami, A.; Kapoor, H.S.; Jangir, R.K.; Ngigi, C.N.; Nowrouzi-Kia, B.; Chattu, V.K. Impact of Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization and Energy Consumption on Carbon Emissions: A Study of India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9025. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119025
Goswami A, Kapoor HS, Jangir RK, Ngigi CN, Nowrouzi-Kia B, Chattu VK. Impact of Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization and Energy Consumption on Carbon Emissions: A Study of India. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):9025. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoswami, Arvind, Harmanpreet Singh Kapoor, Rajesh Kumar Jangir, Caspar Njoroge Ngigi, Behdin Nowrouzi-Kia, and Vijay Kumar Chattu. 2023. "Impact of Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization and Energy Consumption on Carbon Emissions: A Study of India" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 9025. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119025
APA StyleGoswami, A., Kapoor, H. S., Jangir, R. K., Ngigi, C. N., Nowrouzi-Kia, B., & Chattu, V. K. (2023). Impact of Economic Growth, Trade Openness, Urbanization and Energy Consumption on Carbon Emissions: A Study of India. Sustainability, 15(11), 9025. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119025








