Evaluation of Soil Loss and Sediment Yield Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques in a Complex Amazon Mountain Basin of Peru: Case Study Mayo River Basin, San Martin Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)
2.2.1. R Factor (Erosivity)
2.2.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.2.3. Topographic Factor (LS)
2.2.4. Factor C
2.2.5. Conservation Practices Factor
2.2.6. Application of GIS and Remote Sensing Tools
2.2.7. Sediment Rate Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Soil Loss Factors
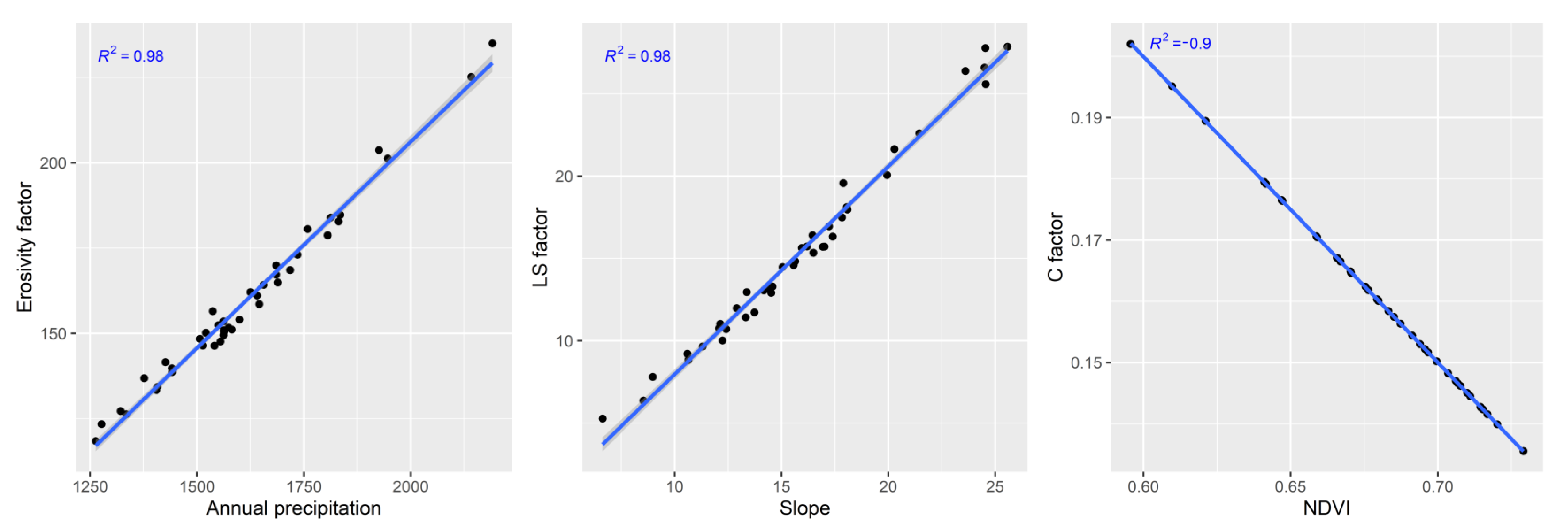
3.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor
3.1.2. Topographic Factor
3.1.3. Soil Erodibility Factor
3.1.4. Crop Management Factor
3.1.5. Conservation Practices Factor
3.2. Potential and Actual Erosion
3.3. Risk of Erosion
3.4. Sediment Rate Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poesen, J. Soil erosion in the Anthropocene: Research needs. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, A.; Cassalho, F.; Caldeira, T.L.; Oliveira, V.A.; Beskow, S.; Timm, T.C. Assessment of soil loss vulnerability in data-scarce watersheds in southern Brazil. Agric. Sci. 2018, 6, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebabu, K.; Taye, G.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Fenta, A.A.; Meshesha, D.T.; Sultan, D.; Aklog, D.; et al. Land use, management and climate effects on runoff and soil loss responses in the highlands of Ethiopia. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswaran, H.; Lal, R.; Reich, P.F. Land Degradation: An Overview. Responses to Land Degradation. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Land Degradation and Desertification, New Delhi, India, 15 March 2016; pp. 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Alkharabsheh, M.; Alexandridis, T.; Bilas, G.; Misopolinos, N.; Silleos, N. Impact of Land Cover Change on Soil Erosion Hazard in Northern Jordan Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahadur, K.C.K. Mapping soil erosion susceptibility using remote sensing and GIS: A case of the Upper Nam Wa Watershed, Nan Province, Thailand. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Meng, X. Risk assessment of soil erosion in different rainfall scenarios by RUSLE model coupled with Information Diffusion Model: A case study of Bohai Rim, China. Catena 2013, 100, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, R. Soil erosion risk assessment and spatial mapping using LANDSAT-7 ETM+, RUSLE, and GIS—A case study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Koloa, C.; Pal, D.K.; Palsamanta, B. Estimation of potential soil erosion rate using RUSLE and E30 model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Ghosh, P.; Mitra, B. GIS Based Soil Erosion Estimation Using Rusle Model: A Case Study of Upper Kangsabati Watershed, West Bengal, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2018, 13, 55871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bennett, S.J.; Li, Y. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: A case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endalew, T.; Biru, D. Soil erosion risk and sediment yield assessment with Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS: The case of Nesha watershed, Southwestern Ethiopia. Results Geophys. Sci. 2022, 12, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Burgess, M. Soil Erosion Threatens Food Production. Agriculture 2013, 3, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prashanth, M.; Kumar, A.; Dhar, S.; Verma, O.; Sharma, S. Morphometric characterization and prioritization of sub-watersheds for assessing soil erosion susceptibility in the Dehar watershed (Himachal Himalaya), Northern India. Himal. Geol. 2021, 42, 345–358. [Google Scholar]
- Prashanth, M.; Kumar, A.; Dhar, S.; Verma, O.; Gogoi, K. Hypsometric analysis for determining erosion proneness of Dehar watershed, Himachal Himalaya, North India. J. Geosci. 2022, 7, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Prashanth, M.; Kumar, A.; Dhar, S.; Verma, O.; Rai, S.K.; Kouser, B. Land use/land cover change and its implication on soil erosion in an ecologically sensitive Himachal Himalayan watershed, Northern India. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2023, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.L.; Saikia, B.K.; da Boit, K.; Pinto, D.; Tutikian, B.F.; Silva, L.F. River dynamics and nanopaticles formation: A comprehensive study on the nanoparticle geochemistry of suspended sediments in the Magdalena River, Caribbean Industrial Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelkeba, T. The Response of Sensitive LULC Changes to Runoff and Sediment Yield in a Semihumid Urban Watershed of the Upper Awash Subbasin Using the SWAT+ Model, Oromia, Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil. Sci. 2023, 2023, 6856144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggelaar, C.D.; Lal, R.; Wiebe, K.; Eswaran, H.; Breneman, V.; Reich, P. The global impact of soil erosion on productivity. II. Effects on crop yields and production over time. Adv. Agron. 2004, 81, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L. Agricultural policy: Govern our soils. Nature 2015, 528, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrelli, D.A.; Robinson, L.R.; Fleischer, E.; Lugato, C.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, K.; Meusburger, S.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe [Cepal] y Patrimonio Natural. Amazonia Posible y Sostenible. Technical Report. 2013. Available online: https://repositorio.cepal.org/handle/11362/1506 (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Silva, S.F.; Ocimar, A.; Cândido, L.A.; Nascimento, R.N.; Pauliquevis, T. Balanço de umidade na Amazônia e sua sensibilidade às mudanças na cobertura vegetal. Mudanças Clim. 2007, 59, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tiria, F.; Bonilla, C.; Bonilla, C. Transformación de las coberturas vegetales y uso del suelo en la llanura amazónica colombiana: El caso de Puerto Leguízamo, Putumayo (Colombia). Rev. Colomb. Geogr. 2018, 27, 286–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio del Ambiente [MINAM]. MINAM y MINAGRI Presentaron Datos Oficiales Sobre Cobertura y Pérdida de Bosques Húmedos Amazónicos al. 2016. Available online: https://www.minam.gob.pe/cambioclimatico/2017/09/08/minam-y-minagri-presentaron-datos-oficiales-sobre-cobertura-y-perdida-de-bosques-humedos-amazonicos-al-2016/ (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Ministerio del Ambiente [MINAM]. Mapa Nacional de Cobertura Vegetal: Memoria Descriptiva. Technical Report. 2015. Dirección General de Evaluación, Valoración y Financiamiento del Patrimonio Natural. Available online: https://www.minam.gob.pe/patrimonio-natural/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2013/10/MAPA-NACIONAL-DE-COBERTURA-VEGETAL-FINAL.compressed.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Ministerio del Ambiente [MINAM]. Mapa de Deforestación de la Amazonía Peruana 2000—MINAM. In Capítulo 3: Resultados; Ministerio del Ambiente: Lima, Peru, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Zorogastúa, K.; Gómez-Lora, J.; Gallo-Ramos, V.; Camacho-Zorogastúa, P. Guía práctica de erosión hídrica. In Casos de Estudio: Subcuenca Cumbaza y Yuracyacu—Amazonía Peruana, 1st ed.; Environmental and Hydrologic Engineering S.A.C.: Lima, Peru, 2022; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- García, L.; Veneros, J.; Pucha-Cofrep, F.; Chávez, S.; Bustamante, D.E.; Calderón, M.S.; Morales, E.; Oliva, M. Geospatial Analysis of Soil Erosion including Precipitation Scenarios in a Conservation Area of the Amazon Region in Peru. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2021, 2021, 5753942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, K.; Gomez, J.W. Erosión hídrica por lluvias máximas en diferentes periodos de retorno en la subcuenca Cumbaza. Catedra Villarreal. 2018, 6, 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Chuenchum, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, W. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Lancang–Mekong River Using the Modified Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation and GIS Techniques. Water 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montanarella, L.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Costa, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; McKenzie, N. Status o’ the World’s Soil Resources: Main Report. Technical Report. 2015. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/status-worlds-soil-resources?gclid=Cj0KCQiAx6ugBhCcARIsAGNmMbjLvYW6tjmFbykNOQzy7-ZFy8Cv6jzvjnkHqPYmVoIam1kU5l_srEEaAlUaEALw_wcB (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Pimentel, D. Soil Erosion: A Food and Environmental Threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations [FAO]. Soil Change: Impacts and Responses. Technical Report. 2015. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/c6814873-efc3-41db-b7d3-2081a10ede50/ (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Sabri, E.; Spalevic, V.; Boukdir, A.; Karaoui, I.; Ouallali, A.; Mincato, R.L.; Sestras, P. Estimation of soil losses and reservoir sedimentation: A case study in tillouguite sub-basin (high atlas—Morocco). J. Agric. For. 2022, 68, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Deshmukh, B.; Kumar, A. Using Google Earth Engine and GIS for basin scale soil erosion risk assessment: A case study of Chambal river basin, central India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 131, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.; Foster, G.; Weesies, G.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agricultural Handbook N° 703; United States Government: Washington, WA, USA, 1997; pp. 65–100.
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A Process-Based Soil Erosion Model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project Technology. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K. The European soil erosion model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf Process Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viney, N.R.; Sivapalan, M. A conceptual model of sediment transport: Application to the Avon River Basin in Western Aus-tralia. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse, L.M.; Nearing, M.A.; Laflen, J.M.; Nicks, A.D. Error Assessment in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Devrani, R.; Deshmukh, B. A Review of Remote Sensing and GIS -Based Soil Loss Models with a Comparative Study from the Upper and Marginal Ganga River Basin, 1st ed.; Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Abbasi, M.; Keesstra, S.; Cerdà, A. Assessment of soil particle erodibility and sediment trapping using check dams in small semi-arid catchments. Catena 2017, 157, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Lora, J.W.; Gallo-Ramos, V.H. Guia de Hidrologia, 1st ed.; Environmental and Hydrologic Engineering S.A.C.: Lima, Peru, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Poggio, L.; de Sousa, L.M.; Batjes, N.H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Ribeiro, E.; Rossiter, D. SoilGrids 2.0: Producing soil information for the globe with quantified spatial uncertainty. Soil 2021, 7, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhrachy, I. Vertical accuracy assessment for SRTM and ASTER Digital Elevation Models: A case study of Najran city, Saudi Arabia. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, S.; Mejía, J. Modelo autorregresivo de primer orden aplicado a la predicción anual de caudales en la Amazonía peruana: Cuenca del río Mayo. In Proceedings of the I International Congress on Water and Sustainability, Barcelona, Spain, 26–27 June 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Servicio Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología del Perú [SENAMHI]. Escenarios Climáticos del río Mayo Para el Año 2030. Technical Report. 2009. Available online: https://repositorio.senamhi.gob.pe/handle/20.500.12542/122 (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Autoridad Nacional del Agua [ANA]. Plan de Gestión de los Recursos Hídricos en la Cuenca del Río Mayo. Technical Report. 2020. Available online: https://crhc.ana.gob.pe/mayo/publicacion/plan-de-gestion-de-recursos-hidricos-en-la-cuenca-del-rio-mayo (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Ozcan, A.; Erpul, G.; Basaran, M.; Erdogan, H. Use of USLE/GIS technology integrated with geostatistics to assess soil erosion risk in different land uses of Indagi Mountain Pass-Cankiri, Turkey. Envirom. Geol. 2008, 53, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Cai, M.; Ya, L. A soil erosion assessment of the Upper Mekong River in Yunnnan Province, China. Mt. Res. Dev. 2014, 34, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organisation [FAO]; United Nations Environment Programme [PNUMA]; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization [UNESCO]. Metodología Provisional para la Evaluación de la Degradación de Los Suelos. Technical Report. 1981. Available online: https://catalogosiidca.csuca.org/Record/UCR.000142550/Description (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Lee, J.H.W.; Melching, C.S. River Dynamics and Integrated River Management, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agricultural Handbook N° 537; Science and Education Administration: Washington DC, USA, 1978; pp. 285–291.
- Arnoldus, H. An Approximation of the Rainfall Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In Assessment of Erosion; De Boodt, M., Gabriels, D., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.; Arnold, J.; Kiniry, J.; Williams, J. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical; Technical Report 2011; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. Epic “Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation”. United Stated Deparment of Agriculture Technical Bulletin. Technical Report. 1990. Available online: https://naldc.nal.usda.gov/download/CAT10698097/pdf (accessed on 24 April 2022).
- Williams, J.R. The Epic model in computer models of watershed hydrology. In Chapter 25: Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology; Singh, V.P., Ed.; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1995; pp. 909–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, P.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Fohrer, N.; Hörmann, G.; Kiesel, J. Suitability of S factor algorithms for soil loss estimation at gently sloped landscapes. Catena 2009, 77, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I. Estimación de pérdida de suelo por erosión hídrica en microcuenca de presa Madín, México. Ing. Hidráulica Y Ambiental. 2013, 34, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Knijff, J.; Jones, R.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe; Technical Report 2000; European Union, Joint Research Centre European Commission: Geel, Belgium, 2000; Available online: https://www.unisdr.org/files/1581_ereurnew2.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Patil, R.; Sharma, S. Remote Sensing and GIS based modeling of crop/cover management factor (C) of USLE in Shakker river watershed. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemical, Agricultural and Medical Sciences (CAMS-2013), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 29–30 December 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkey, C. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Durigon, V.L.; de Carvalho, D.F.; Antunes, M.A.H.; Oliveira, P.T.; Fernandes, M.M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R. Sediment-yield prediction with universal equation using runoff energy factor. In Present and Perspective Technology for Predicting Sediment Yield and Sources; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; pp. 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; de Jesus, J.M.; MacMillan, R.A.; Batjes, N.H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Ribeiro, E.; Samuel-Rosa, A.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Walsh, M.G.; et al. SoilGrids1km—Global Soil Information Based on Automated Mapping. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao-Yuan, L.; Wen-Tzu, L.; Wen-Chieh, C. Soil erosion prediction and sediment yield estimation: The Taiwan experience. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 68, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, T.N.; Rao, K.G.; Murthy, J. Fuzzy class membership approach to soil erosion modelling. Agric. Syst. 2000, 63, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzáles, C.; Llanos, R. Evaluación de los Efectos de la Deforestación en la Hidrología y Pérdida Lateral de Carbono Orgánico del Suelo de la Cuenca del Altomayo; Technical Report 2015; Infobosques: Lima, Peru, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ilbay-Yupa, M.; Zuvieta, R.; Lavado-Casimiro, W. Regionalización de la precipitación, su agresividad y concentración en la cuenca del río Guayas, Ecuador. La Granja 2019, 30, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aybar, C.; Fernández, C.; Huerta, A.; Lavado, W.; Vega, F.; Felipe-Obando, O. Construction of a high-resolution gridded rainfall dataset for Peru from 1981 to the present day. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.W.; Mello, C.R.; Chou, S.C.; Curi, N.; Norton, L.D. Soil erosion risk associated with climate change at Mantaro River basin, Peruvian Andes. Catena 2016, 147, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Aslam, B. Geospatial-based soil management analysis using novel technique for better soil conservation. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthes, J.M.; Tomazoni, J.C.; Guimarães, E.; Gomes, T.C. Uso de sistema de informação geográfica na determinação do fator topográfico da Bacia do Rio Catorze, Sudoeste do PR. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Fís. 2012, 5, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornelos, L.F.; Alves da Silva, S.M. Uso de modelos digitais de elevação (MDE) gerados a partir de imagens de radar interferométrico (SRTM) na estimativa de perdas de solo. Rev. Bras. Cartogr. 2007, 59, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.H. Evolución de la Cobertura Boscosa en la Subcuenca Yuracyacu y su Influencia la Regulación Hídrica. Bachelor’s Thesis, Ingeniero Ambiental de la Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal, Lima, Peru, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kinell, P.I.A. Geographic variation of USLE/RUSLE erosivity and erodibility factors. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, C4014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations [FAO]. A Provisional Methodology for Soil Degradation Assessment. Technical Report. 1979. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XF8108785 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
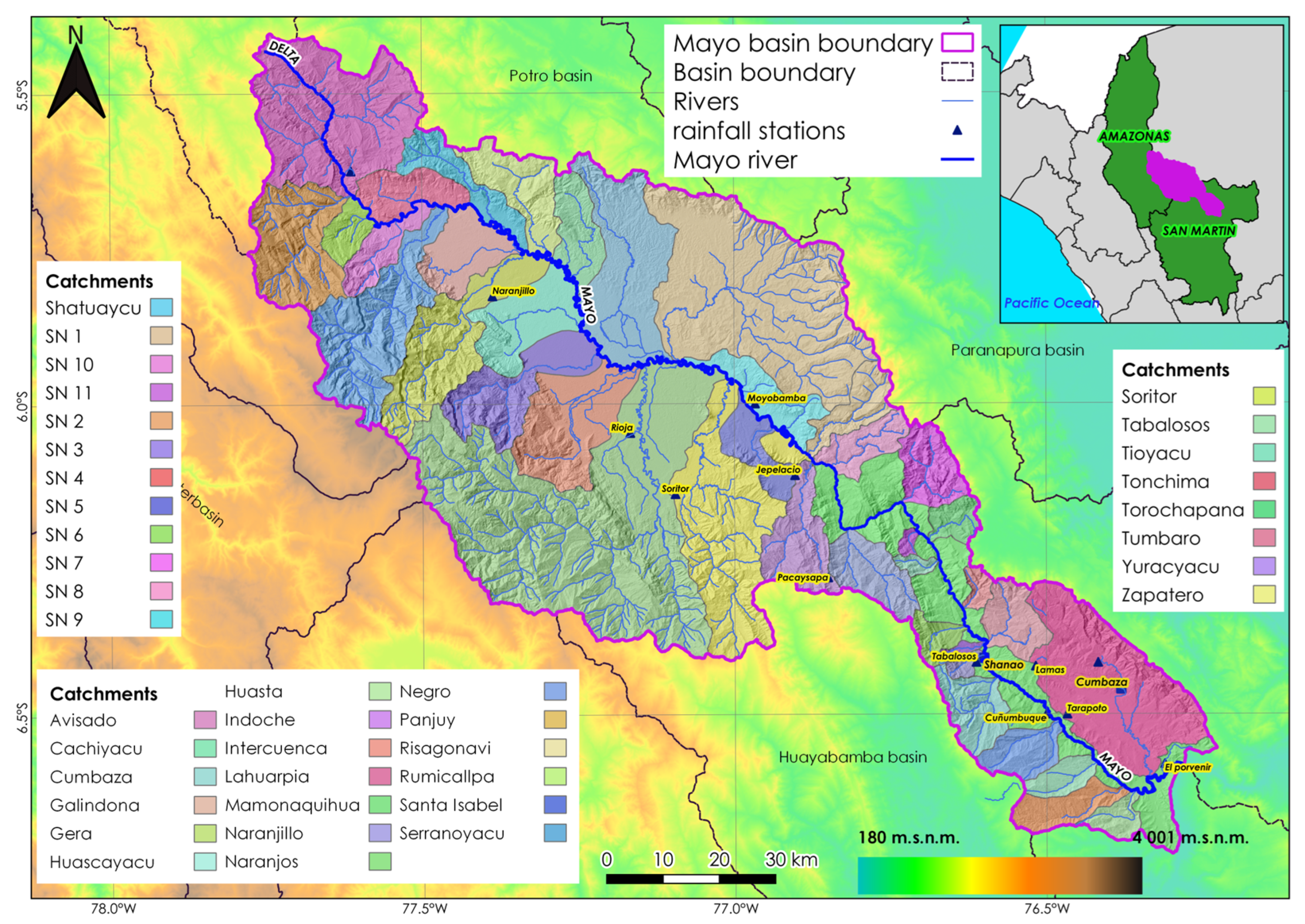


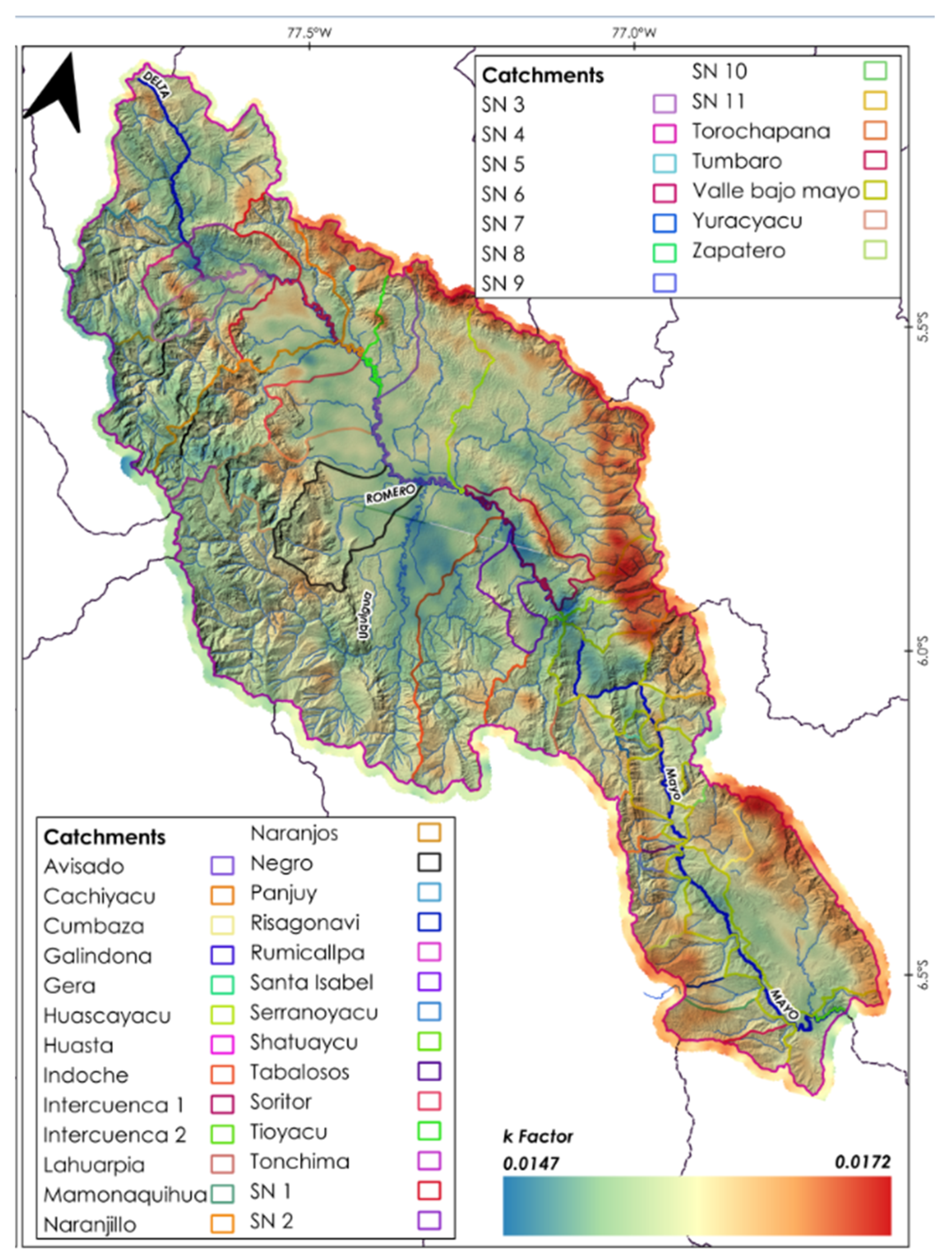


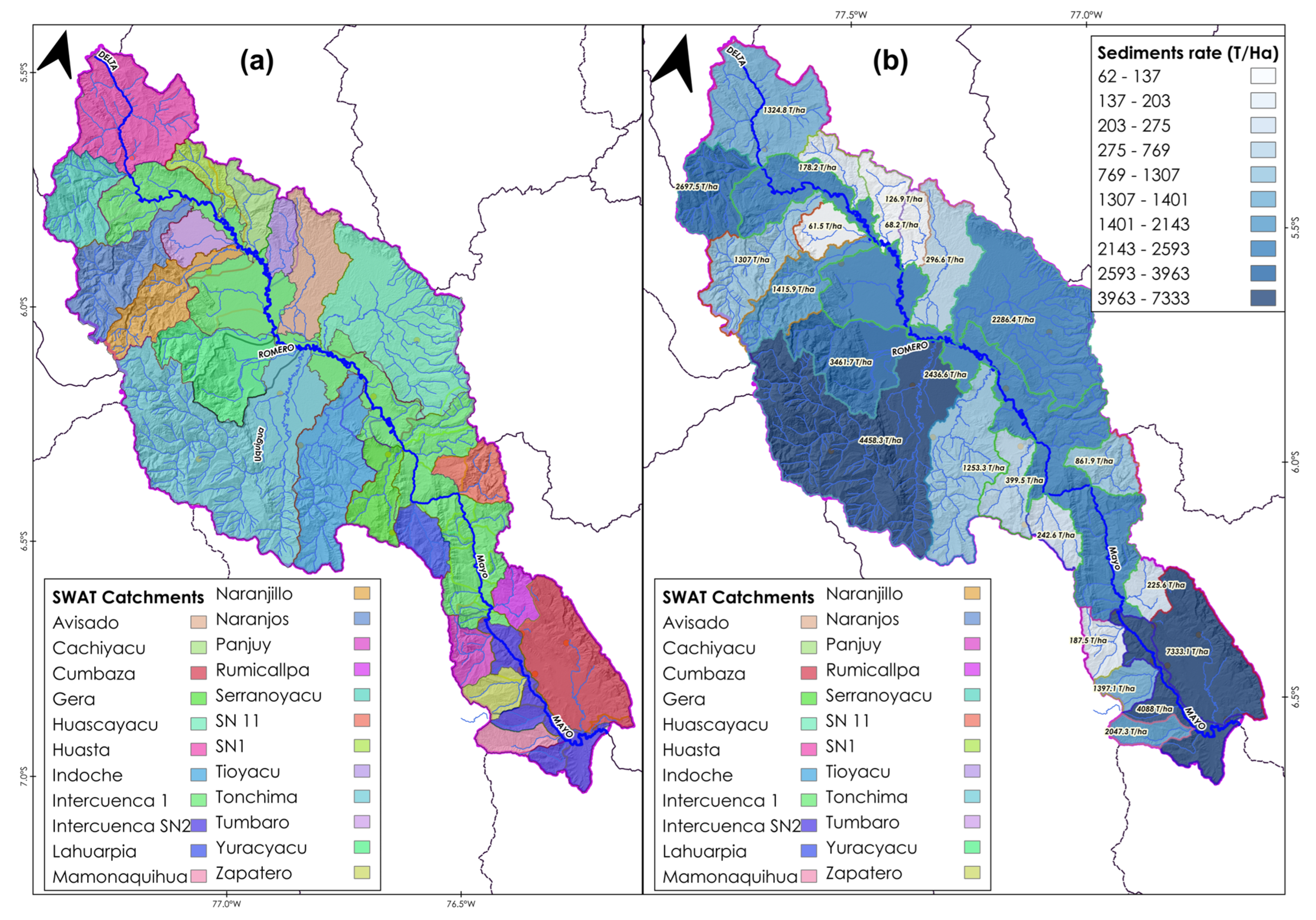

| Dataset Used | Data Source | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Departmental and district boundaries | Instituto Geográfico Nacional (IGN) | National vector information for Peru. |
| Hydrography and National basin boundaries | Autoridad Nacional del Agua (ANA) | |
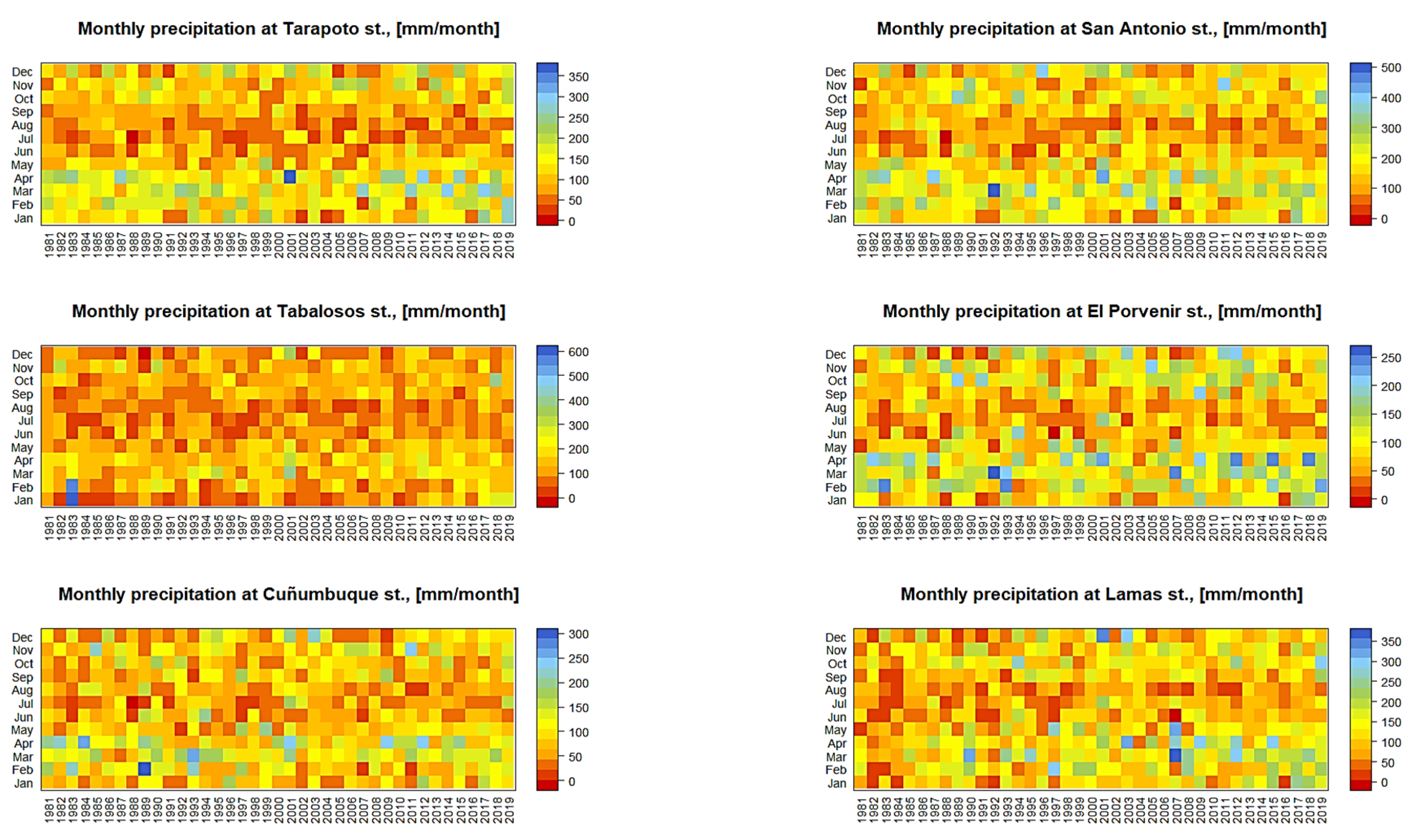
| Rainfall | Servicio Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología del Perú (SENAMHI) | 12 ground stations in the Mayo basin were used for the period 1981–2019. |
| Soil texture | SoilGrids–250m | Maps of soil properties for the entire globe at medium spatial resolution (250 m cell size) using state-of-the-art machine learning methods [45]. |
| DEM | SRTM–30m (Google Earth Engine) | 10 m spatial resolution multispectral data. |
| Remote sensing data for NDVI map | Sentinel 2–level-2A (Google Earth Engine) | Near global coverage of land elevation data at 1 arc-second generated through interferometric radar technique [46]. |
| Name | A | P | Kc | H Mean | H Min | H Max | S | L | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huasta | 607.9 | 127.2 | 1.4 | 1450.8 | 938.0 | 2337.0 | 0.03 | 51.9 | 11.7 |
| Serranoyacu | 299.6 | 89.0 | 1.4 | 2153.9 | 948.0 | 3444.0 | 0.07 | 36.2 | 8.3 |
| Naranjos | 401.9 | 131.2 | 1.8 | 2297.7 | 862.0 | 4001.0 | 0.05 | 58.8 | 6.8 |
| Tumbaro | 168.7 | 73.6 | 1.6 | 948.2 | 823.0 | 1755.0 | 0.03 | 31.5 | 5.4 |
| Cachiyacu | 179.3 | 83.4 | 1.7 | 1234.1 | 819.0 | 1750.0 | 0.03 | 36.8 | 4.9 |
| Naranjillo | 350.3 | 131.7 | 2.0 | 1823.2 | 813.0 | 3819.0 | 0.05 | 60.0 | 5.8 |
| Tonchima | 1542.1 | 265.7 | 1.9 | 1808.0 | 320.0 | 3762.0 | 0.03 | 120.0 | 12.8 |
| Soritor | 215.4 | 88.4 | 1.7 | 963.1 | 805.0 | 2092.0 | 0.03 | 38.6 | 5.6 |
| Yuracyacu | 250.9 | 101.3 | 1.8 | 1548.9 | 805.0 | 3611.0 | 0.06 | 45.1 | 5.6 |
| Negro | 315.8 | 91.9 | 1.4 | 1159.7 | 341.0 | 2831.0 | 0.07 | 37.5 | 8.4 |
| Tioyacu | 133.4 | 67.8 | 1.6 | 1017.6 | 809.0 | 1690.0 | 0.03 | 29.3 | 4.5 |
| Avisado | 419.0 | 141.1 | 1.9 | 934.4 | 801.0 | 1848.0 | 0.02 | 64.0 | 6.5 |
| Huascayacu | 962.2 | 159.9 | 1.4 | 1066.0 | 801.0 | 2266.0 | 0.02 | 65.2 | 14.8 |
| Indoche | 531.4 | 144.1 | 1.7 | 1293.8 | 800.0 | 2562.0 | 0.03 | 63.7 | 8.3 |
| Santa Isabel | 111.0 | 63.1 | 1.7 | 1012.3 | 793.0 | 1632.0 | 0.03 | 27.5 | 4.0 |
| Huascayacu | 109.1 | 64.7 | 1.7 | 1438.0 | 773.0 | 2224.0 | 0.05 | 28.5 | 3.8 |
| Panjuy | 128.6 | 55.1 | 1.4 | 1004.8 | 267.0 | 1831.0 | 0.07 | 21.6 | 6.0 |
| Gera | 179.8 | 75.9 | 1.6 | 1414.2 | 765.0 | 2136.0 | 0.04 | 32.4 | 5.5 |
| Lahuarpia | 144.6 | 55.8 | 1.3 | 1155.1 | 680.0 | 1974.0 | 0.06 | 21.1 | 6.9 |
| Galindona | 102.9 | 53.9 | 1.5 | 1317.9 | 745.0 | 1964.0 | 0.05 | 22.3 | 4.6 |
| Zapatero | 102.2 | 46.0 | 1.3 | 788.9 | 217.0 | 1560.0 | 0.08 | 17.0 | 6.0 |
| Risagonavi | 62.8 | 34.8 | 1.2 | 623.6 | 207.0 | 1366.0 | 0.09 | 12.3 | 5.1 |
| Mamonaquihua | 103.3 | 53.5 | 1.5 | 726.4 | 196.0 | 1362.0 | 0.05 | 22.1 | 4.7 |
| Shatuaycu | 27.1 | 37.4 | 2.0 | 453.8 | 180.0 | 1171.0 | 0.06 | 17.1 | 1.6 |
| Tabalosos | 16.2 | 21.4 | 1.5 | 750.4 | 283.0 | 1569.0 | 0.14 | 8.9 | 1.8 |
| Rumicallpa | 114.2 | 51.5 | 1.3 | 814.6 | 277.0 | 1644.0 | 0.07 | 20.0 | 5.7 |
| Torochapana | 53.1 | 37.6 | 1.4 | 935.8 | 304.0 | 1642.0 | 0.09 | 15.3 | 3.5 |
| Cumbaza | 573.9 | 120.9 | 1.4 | 619.5 | 193.0 | 1853.0 | 0.03 | 48.7 | 11.8 |
| Valle bajo mayo | 656.9 | 337.6 | 3.7 | 713.7 | 180.0 | 1734.0 | 0.01 | 164.8 | 4.0 |
| Intercuenca1 | 138.8 | 94.8 | 2.3 | 1042.5 | 783.0 | 1685.0 | 0.02 | 44.3 | 3.1 |
| Intercuenca 2 | 33.5 | 32.5 | 1.6 | 966.3 | 767.0 | 1636.0 | 0.06 | 13.8 | 2.4 |
| SN 1 | 135.1 | 90.2 | 2.2 | 1297.7 | 823.0 | 2187.0 | 0.03 | 41.9 | 3.2 |
| SN 2 | 130.7 | 65.4 | 1.6 | 1170.0 | 851.0 | 1921.0 | 0.04 | 28.0 | 4.7 |
| SN 3 | 100.5 | 63.3 | 1.8 | 1531.3 | 868.0 | 3439.0 | 0.09 | 28.0 | 3.6 |
| SN 4 | 68.1 | 37.4 | 1.3 | 1533.1 | 927.0 | 2794.0 | 0.14 | 13.8 | 4.9 |
| SN 5 | 13.1 | 15.8 | 1.2 | 1004.5 | 442.0 | 1408.0 | 0.17 | 5.6 | 2.4 |
| SN 6 | 53.3 | 38.0 | 1.5 | 487.7 | 197.0 | 873.0 | 0.04 | 15.6 | 3.4 |
| SN 7 | 20.6 | 22.5 | 1.4 | 972.5 | 392.0 | 1605.0 | 0.14 | 8.9 | 2.3 |
| SN 8 | 57.8 | 36.4 | 1.3 | 1129.8 | 418.0 | 1770.0 | 0.10 | 14.1 | 4.1 |
| SN 9 | 19.9 | 21.3 | 1.3 | 794.4 | 276.0 | 1560.0 | 0.16 | 8.2 | 2.4 |
| SN 10 | 29.7 | 26.9 | 1.4 | 917.6 | 319.0 | 1687.0 | 0.13 | 10.6 | 2.8 |
| SN 11 | 129.5 | 52.3 | 1.3 | 1276.8 | 516.0 | 2505.0 | 0.10 | 19.6 | 6.6 |
| Basin | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huasta | 3162.0 | 2657.5 | 4589.1 | 1917.0 | 611.4 | 616.2 | 237.6 | 332.7 | 136.1 | 892.9 | 483.4 | 261.8 | 1324.8 |
| SN1 | 432.2 | 381.3 | 621.7 | 250.7 | 78.2 | 82.6 | 32.0 | 42.3 | 15.6 | 112.1 | 58.4 | 31.7 | 178.2 |
| Tumbaro | 167.7 | 27.1 | 395.0 | 75.2 | 16.1 | 4.5 | 2.6 | 8.3 | 10.9 | 4.4 | 7.7 | 18.0 | 61.5 |
| Serranoyacu | 6088.6 | 5381.3 | 8998.5 | 4562.1 | 1473.1 | 1581.5 | 587.4 | 809.5 | 326.8 | 1542.6 | 535.4 | 482.7 | 2697.5 |
| Cachiyacu | 306.5 | 51.3 | 830.0 | 164.6 | 33.7 | 8.2 | 4.2 | 16.3 | 22.4 | 13.0 | 27.3 | 44.9 | 126.9 |
| Tioyacu | 169.5 | 28.4 | 432.7 | 84.6 | 18.7 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 9.8 | 13.6 | 8.1 | 17.2 | 28.5 | 68.2 |
| Naranjos | 3451.6 | 565.7 | 8798.6 | 1717.0 | 322.3 | 71.4 | 39.2 | 126.8 | 168.6 | 65.2 | 104.2 | 253.9 | 1307.0 |
| Avisado | 704.4 | 113.8 | 1971.4 | 394.2 | 80.1 | 18.4 | 9.0 | 36.8 | 49.0 | 27.7 | 59.1 | 95.5 | 296.6 |
| Huascayacu | 8065.1 | 7037.4 | 5169.4 | 1375.5 | 627.1 | 205.0 | 313.4 | 225.2 | 1838.9 | 279.2 | 1187.7 | 1112.6 | 2286.4 |
| Yuracyacu | 5114.5 | 9311.3 | 10,960.0 | 4564.9 | 1089.3 | 250.6 | 288.5 | 364.3 | 852.3 | 1907.4 | 2440.7 | 4396.1 | 3461.7 |
| Naranjillo | 3653.1 | 610.2 | 9257.4 | 1812.7 | 379.5 | 93.0 | 53.3 | 177.8 | 253.9 | 115.1 | 181.5 | 403.3 | 1415.9 |
| Tonchima | 2534.8 | 5838.6 | 12,337.3 | 4485.5 | 3180.2 | 960.7 | 904.0 | 2318.5 | 8439.9 | 8990.0 | 2209.6 | 1301.0 | 4458.3 |
| Indoche | 2916.7 | 3153.1 | 4241.4 | 1549.5 | 437.9 | 52.9 | 112.1 | 134.0 | 231.7 | 575.0 | 579.0 | 1056.5 | 1253.3 |
| SN 11 | 2016.8 | 1767.9 | 3171.2 | 959.7 | 270.4 | 142.3 | 93.2 | 74.1 | 278.9 | 385.3 | 414.2 | 768.8 | 861.9 |
| Gera | 504.8 | 575.7 | 2244.4 | 646.7 | 204.9 | 63.9 | 40.7 | 48.5 | 105.0 | 100.3 | 147.1 | 112.2 | 399.5 |
| Lahuarpia | 297.2 | 345.8 | 1350.8 | 408.4 | 107.2 | 45.4 | 25.3 | 31.1 | 73.8 | 64.9 | 92.6 | 68.8 | 242.6 |
| Rumicallpa | 278.6 | 1135.0 | 525.0 | 288.6 | 50.0 | 16.6 | 30.8 | 15.1 | 41.1 | 48.1 | 50.7 | 227.0 | 225.6 |
| Intercuenca 1 | 3225.1 | 3671.8 | 6523.4 | 4057.5 | 2474.2 | 1226.4 | 732.1 | 572.0 | 1264.3 | 1687.9 | 1978.9 | 1826.0 | 2436.6 |
| Panjuy | 262.5 | 501.5 | 587.5 | 361.3 | 92.7 | 16.3 | 24.2 | 12.0 | 68.3 | 118.7 | 59.9 | 145.4 | 187.5 |
| Zapatero | 3109.9 | 5456.2 | 2730.4 | 1755.1 | 514.0 | 227.7 | 201.2 | 211.4 | 207.7 | 208.8 | 342.0 | 1801.2 | 1397.1 |
| Cumbaza | 14,883.1 | 27,722.2 | 14,517.5 | 8277.3 | 2538.7 | 1496.4 | 1421.5 | 1310.4 | 1315.0 | 1709.4 | 3634.4 | 9178.5 | 7333.7 |
| Intercuenca SN2 | 5139.2 | 6314.8 | 10,271.9 | 6899.3 | 4290.8 | 2228.2 | 1409.1 | 1043.3 | 2025.6 | 2773.5 | 3444.5 | 3215.9 | 4088.0 |
| Mamonaquihua | 4883.6 | 8794.7 | 3089.8 | 1654.7 | 468.0 | 241.8 | 208.4 | 221.9 | 265.2 | 362.7 | 1273.7 | 3103.1 | 2047.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camacho-Zorogastúa, K.d.C.; Cesar Minga, J.; Gómez-Lora, J.W.; Gallo-Ramos, V.H.; Garcés Díaz, V. Evaluation of Soil Loss and Sediment Yield Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques in a Complex Amazon Mountain Basin of Peru: Case Study Mayo River Basin, San Martin Region. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119059
Camacho-Zorogastúa KdC, Cesar Minga J, Gómez-Lora JW, Gallo-Ramos VH, Garcés Díaz V. Evaluation of Soil Loss and Sediment Yield Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques in a Complex Amazon Mountain Basin of Peru: Case Study Mayo River Basin, San Martin Region. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119059
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamacho-Zorogastúa, Katherine del Carmen, Julio Cesar Minga, Jhon Walter Gómez-Lora, Víctor Hugo Gallo-Ramos, and Victor Garcés Díaz. 2023. "Evaluation of Soil Loss and Sediment Yield Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques in a Complex Amazon Mountain Basin of Peru: Case Study Mayo River Basin, San Martin Region" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119059
APA StyleCamacho-Zorogastúa, K. d. C., Cesar Minga, J., Gómez-Lora, J. W., Gallo-Ramos, V. H., & Garcés Díaz, V. (2023). Evaluation of Soil Loss and Sediment Yield Based on GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques in a Complex Amazon Mountain Basin of Peru: Case Study Mayo River Basin, San Martin Region. Sustainability, 15(11), 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119059






