Gyttja as a Soil Conditioner: Changes in Some Properties of Agricultural Soils Formed on Different Parent Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soils
2.2. Gyttja
2.3. Experimental
2.4. Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pH | soil reaction |
| EC | electrical conductivity |
| CaCO3 | total lime |
| SOM | soil organic matter |
| WSA | wet stability of aggregates |
| SSI | structural stability index |
| DR | dispersion ratio |
| K-ex | Potassium that can be extracted by 1N Ammonium acetate |
| Ca-ex | Calcium that can be extracted by 1N Ammonium acetate |
| Mg-ex | Magnesium that can be extracted by 1N Ammonium acetate |
| P-av | available phosphorus content extracted by NaHCO3 extraction |
| Fe-ex | Iron that can be extracted by DTPA |
| Zn-ex | Zinc that can be extracted by DTPA |
| Cu-ex | Cupper that can be extracted by DTPA |
| Mn-ex | Manganese that can be extracted by DTPA |
| Ni-ex | Nickel that can be extracted by DTPA |
| Cd-ex | Cadmium that can be extracted by DTPA |
References
- Lal, R. Soils and sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekşen, A.; Yakupoglu, G.; Yakupoglu, T.; Gülser, C.; Öztürk, E.; Özdemir, N. Changes in chemical compositions of substrates before and after Ganoderma lucidum cultivation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 27, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Malone, B.P.; McBratney, A.B.; Angers, D.A.; Arrouays, D.; Chambers, A.; Chaplot, V.; Chen, Z.S.; Cheng, K.; Winowiecki, L.; et al. Soil carbon 4 per mille. Geoderma 2017, 292, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Hansel, C.M.; Kaiser, C.; Kleber, M.; Maher, K.; Manzoni, S.; Nunan, N.; Reichstein, M.; Schimel, J.P.; Torn, M.S.; et al. Persistence of soil organic carbon caused by functional complexity. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.H.; Lehmann, J.; Van Zwieten, L.; Joseph, S.; Archanjo, B.S.; Cowie, B.; Thomsen, L.; Tobin, M.J.; Vongsvivut, J.; Klein, A.; et al. Probing the nature of soil organic matter. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 4072–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembiring, M.; Sabrina, T.; Mukhlis, M. Effect of soil conditioner enriched with biofertilizers to improve soil fertility and maize (Zea mays L.) growth on andisols Sinabung area. Acta Agric. Slov. 2020, 116, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutoyo, W.; Karamina, H.; Fikrinda, W. Soil amendment impact to soil organic matter and physical properties on the three soil types after second corn cultivation. AIMS Agric. Food 2020, 5, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, R.; Arjumend, T.; Ekinci, M.; Yildirim, E.; Turan, M.; Argin, S. Biochar as an organic soil conditioner for mitigating salinity stress in tomato. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, P.; Nurmi, E.; Haikarainen, I.; Savikurki, R.; Kaseva, J.; Hakala, K.; Valkama, E. Crushed bark as a novel soil conditioner for organic plant production. Ital. J. Agron. 2021, 16, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulia, M.; Kontezaki, E.; Kalogeropoulos, N.; Chassapis, K. One step bioremediation of olive-oil-mill waste by organoinorganic catalyst for humics-rich soil conditioner production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Song, W.; Yang, J.; Ren, C.; Du, H.; Tang, T.; Qin, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, H. The role and mechanism of commercial macroalgae for soil conditioner and nutrient uptake catalyzer. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 97, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakupoglu, T.; Durmus, M.; Kara, Z.; Kızılkaya, R. Changes in properties of a clayey soil after adding composted and uncomposted gyttja. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 3259–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevica, K.; Burlakovs, J.; Klavins, M. Organic rich freshwater sediments (sapropel) as potential soil amendment for recultivation of areas contaminated with heavy metals. In Proceedings of the 13th SGEM GeoConference on Water Resources, Forest, Marine and Ocean Ecosystems, Albena, Bulgaria, 16–22 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saltalı, K.; Nedirli, A. Phosphorus sorption by gyttja and its effect on the pH value and phosphorus in acidic soils. Turk J. Agric. For. 2021, 45, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülser, F.; Yılmaz, C.; Sönmez, F. Effects of gyttja and chemical fertilizer applications on growing media and pomologic and biochemical properties in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) fruit. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. J. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Torun, B. The effect of gyttja application on cereal grain yield and soil physicalchemical properties in field conditions. HRU Fac. Agric. J. 2009, 13, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yuce, G.; Yakupoglu, T. Effects of gyttja and polyacrylamide applications on some physical properties of soils with different texture. Soil Water J. 2017, 6, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Saltalı, K.; Yıldırım, Ö.F. Effect of gyttja application on some plant and soil properties in confectionary sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) cultivation at dry condition. KSU J. Agric. Nat. 2015, 19, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karaca, S.; Gülser, F.; Sönmez, F.; Gökkaya, T.H. The effects of gyttja on soil properties in nickel-contaminated soils. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltalı, K.; Kara, Z. Effects of gyttja applications on some chemical properties of acidic soils. KSU J. Agric. Nat. 2022, 25, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, A.; Turgay, O.C.; Tamer, N. Effects of a humic deposit (gyttja) on soil chemical and microbiological properties and heavy metal availability. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 42, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, N.; Karaca, A. Effects of gyttja and lignite on some enzyme activities of soil. Selcuk J. Agric. Food Sci. 2006, 20, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Torun, B.; Yazici, A.; Gultekin, I.; Cakmak, I. Influence of gyttja on shoot growth and shoot concentrations of zinc and boron of wheat cultivars grown on zinc-deficient and boron-toxic soils. J. Plant Nut. 2003, 26, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkiran, A.R.; Cengiz, M.C. Effects of different organic materials and chemical fertilizers on nutrition of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) inorganic arboriculture. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6320–6328. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, O.F.; Dikici, H.; Yılmaz, K. Effect of gyttja and nitrogen applications on plant growth of red pepper (Capsicum annum L.) in the soils formed on the different parent materials. TURJAF 2017, 5, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namli, A.; Akca, M.O.; Akca, H. Determination of the impacts of organic and organomineral fertilizers developed from the organic materials of Afşin-Elbistan basin lignite pit on the yield and yield components of wheat and on some soil characteristics. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. J. 2019, 7, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ditzler, C.; Scheffe, C.K.; Monger, H.C. (Eds.) Soil Science Division Staff, Soil Survey Manual; USDA Handbook 18; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Borie, F.; Rubio, R. Total and organic phosphorus in Chilean volcanic soils. Gayana Bot. 2003, 60, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümsavaş, Z. Determination of the fertility levels of the soils of Vertisol great soil group by soil analysis in Bursa province. Uludağ. Univ. Fac. Agric. J. 2003, 17, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sağlam, C. Heavy metal accumulation in the edible parts of some cultivated plants and media samples from a volcanic region in southern Turkey. Ekoloji 2013, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duygu, N. The Morphological, Physical and Chemical Properties of the Soils Formed on Parent Materials Erupted from the Erciyes Strato Volcano. Master’s Thesis, Gaziosmanpasa University, Tokat, Turkey, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kılıç, K.; Yalçın, H.; Durak, A.; Doğan, H.M. Andisols of Turkey: An example from the Cappadocian Volcanic Province. Geoderma 2018, 313, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Hochwimmer, B.; Brearley, F.Q. Geochemical assessment of metal transfer from rock and soil to water in serpentine areas of Sabah (Malaysia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, Z.; Rızaoğlu, T.; Saltalı, K. Total heavy metal contents in serpentinite soils from Türkoğlu-Kahramanmaraş/Turkey. In Proceedings of the 18th International Multidisciplinary SGEM Conference, Albena, Bulgaria, 2–8 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rajakaruna, N.; Harris, T.B.; Alexander, E.B. Serpentine geoecology of eastern North America: A review. RHODORA 2009, 111, 21–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yılmaz, K.; Çelik, İ.; Kapur, S.; Ryan, J. Clay minerals, Ca/Mg ratio and Fe-Al-oxides in relation to structural stability, hydrolic conductivity and soil erosion in Southeastern Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2005, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Özdoğan, A. Effects of Gyttja Application on Some Soil Properties of Soils Formed Volcanic Main Materials. Master’s Thesis, Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Kahramanmaras, Turkey, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Solak, S. Effects of Gyttja Applications on Physicochemical Properties of Soils Formed on Serpentine Parent Material. Master’s Thesis, Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Kahramanmaras, Turkey, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kacar, B. Chemical Analysis of Plant and Soil-III. Soil Analysis, 705; Ankara University Faculty of Agriculture Publications: Ankara, Turkey, 1994; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregates Stability and Size Distribution. In Methods of Soil Analysis, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Erosion Research Methods; Soil and Water Conservation Society: Ankeny, IA, USA, 1988; pp. 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.I.; Bonilla, C.A. Predicting soil aggregate stability using readily available soil properties and machine learning techniques. Catena 2020, 187, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; De Gryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, B.L.M.; Herath, H.M.S.K.; Sleutel, S.; De Neve, S.; Gabriels, D.; Reheul, D.; Moens, M. The quality of exogenous organic matter: Short-term effects on soil physical properties and soil organic matter fractions. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jing, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q. Effects of biochar amendment on rapeseed and sweet potato yields and water stable aggregate in upland red soil. Catena 2014, 123, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagea, I.S.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Schwilch, G. Evaluation of promising technologies for soil salinity amelioration in Timpaki (Crete): A participatory approach. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Sun, Z. Responses of saline soil properties and cotton growth to different organic amendments. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakupoğlu, G.; Saltalı, K.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Yakupoğlu, T.; Cerda, A. Manure effect on soil–plant interactions in capia pepper crops under semiarid climate conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwite, J.N. Assessment of soil structural stability under different land uses using some predictive indices in Abakaliki, Southeastern Nigeria. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 2015, 3, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, M.W.M. A rapid method for estimating structural stability of soils. Soil Sci. 1963, 96, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşkın, T. An Investigation on Determining Structural Stability and Erodibility of Ordu Soils. Master’s Thesis, Ondokuz Mayis University, Samsun, Turkey, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Nisar, S.; Choudhary, O.P. Structural stability and organic matter stabilization in soils: Differential impacts of soil salinity and sodicity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.-J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuria, D.; Hazarika, S.; Krishnappa, R. Soil acidity and management options. Indian J. Fertil. 2016, 12, 40–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, S.; Nabam, A.; Thakuria, D.; Kataki, S.; Krishnappa, R. Lime equivalence of organic manures and scope of their utilization as acid soil amendments. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 67, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, K.; Ergin, M.N.; Akgün, M.; Saltalı, K. The influence of humic deposit (gyttja) application on some selected soil properties and yield-quality of hazelnut in acid conditions. Agrochimica 2021, 65, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.A.; Bingham, F.T.; Pratt, P.F. Redistribution of Exchangeable Calcium, Magnesium, and Aluminum following lime or gypsum applications to a Brazilian Oxisol. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Pavan, M.A.; Ziglio, C.O.; Franchini, J.C. Reduction of Exchangeable Calcium and Magnesium in Soil with Increasing pH. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2001, 44, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Jdrgensen, S.S.; Moberg, J.P.; Raben-Lange, B. Influence of organic matter on phosphate adsorption by aluminium and iron oxides in sandy soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 41, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wandruszka, R. Phosphorus retention in calcareous soils and the effect of organic matter on its mobility. Geochem. Trans. 2006, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, A.; Madrid, A.; Kassem, S.; Andreu, L.; Campillo, M. Phosphorus fertilizer recovery from calcareous soils amended with humic and fulvic acids. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, Z. Investigation of the Asbest Mineral Content and Geochemical Characteristics of Different Areas Representing Rocks and the Soil Formed on Them of Ophiolitic Assemblage in Kahramanmaras Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Kahramanmaras, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, R.L. Allophane and imogolite: Role in soil biogeochemical processes. Clay Miner. 2009, 44, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusterhues, K.; Hädrich, A.; Neidhardt, J.; Küsel, K.; Keller, T.F.; Jandt, K.D.; Totsche, K.U. Reduction of ferrihydrite with adsorbed and coprecipitated organic matter: Microbial reduction by Geobacter bremensis vs. abiotic reduction by Na-dithionite. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4953–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Adsorption of heavy metals on kaolinite and ontmorillonite: A review. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 6698–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, I.M.; Igbokwe, O.A. Sorption of heavy metals on clay minerals and oxides: A review. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; Edebali, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dikici, H.; Saltali, K.; Bingölbalı, S. Equilibrium and Kinetics Characteristics of Copper (II) Sorption onto Gyttja. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010, 84, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Stromvall, A.M.; Steenari, B.M. Adsorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn on Sphagnum peat from solutions with low metal concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
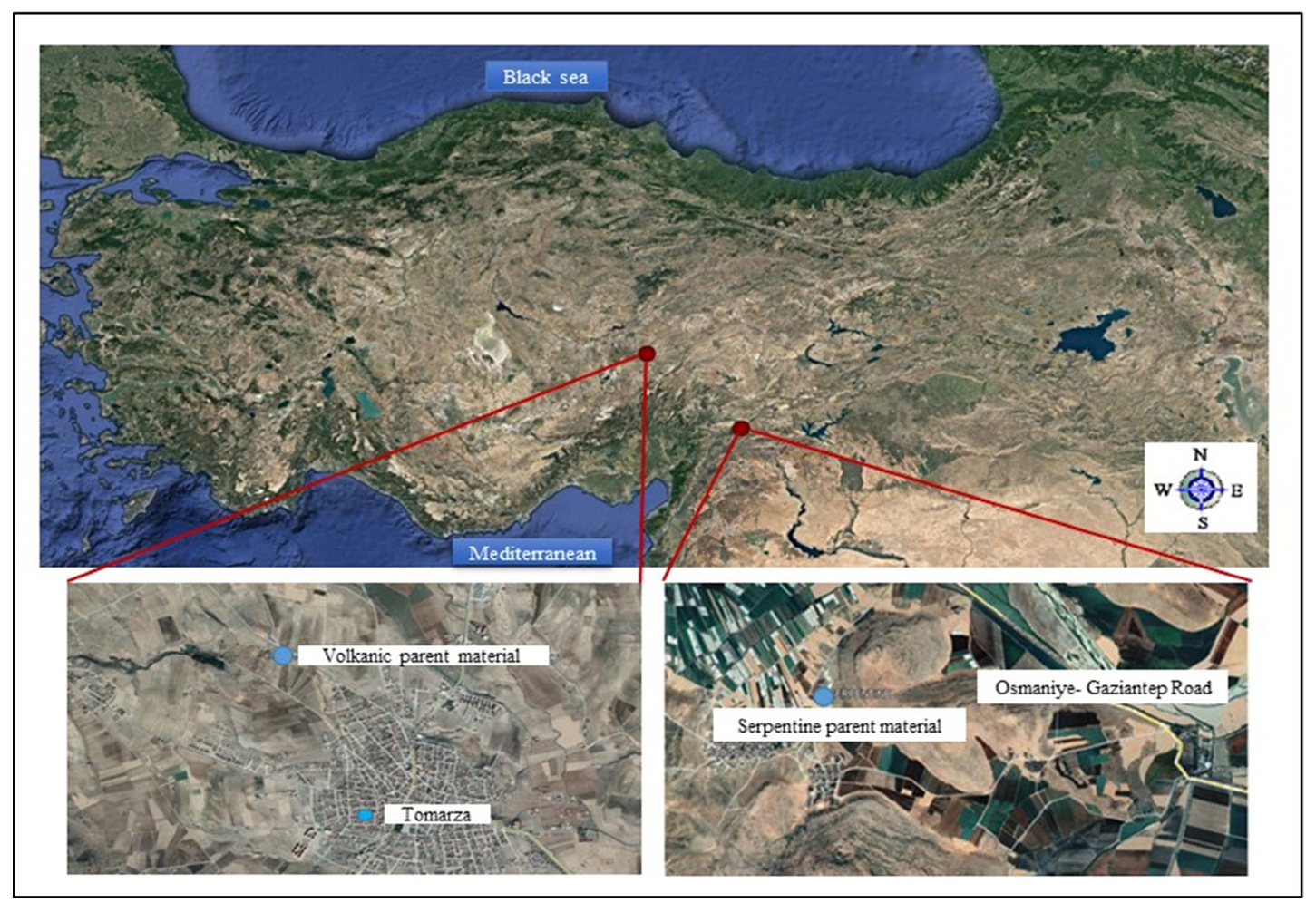


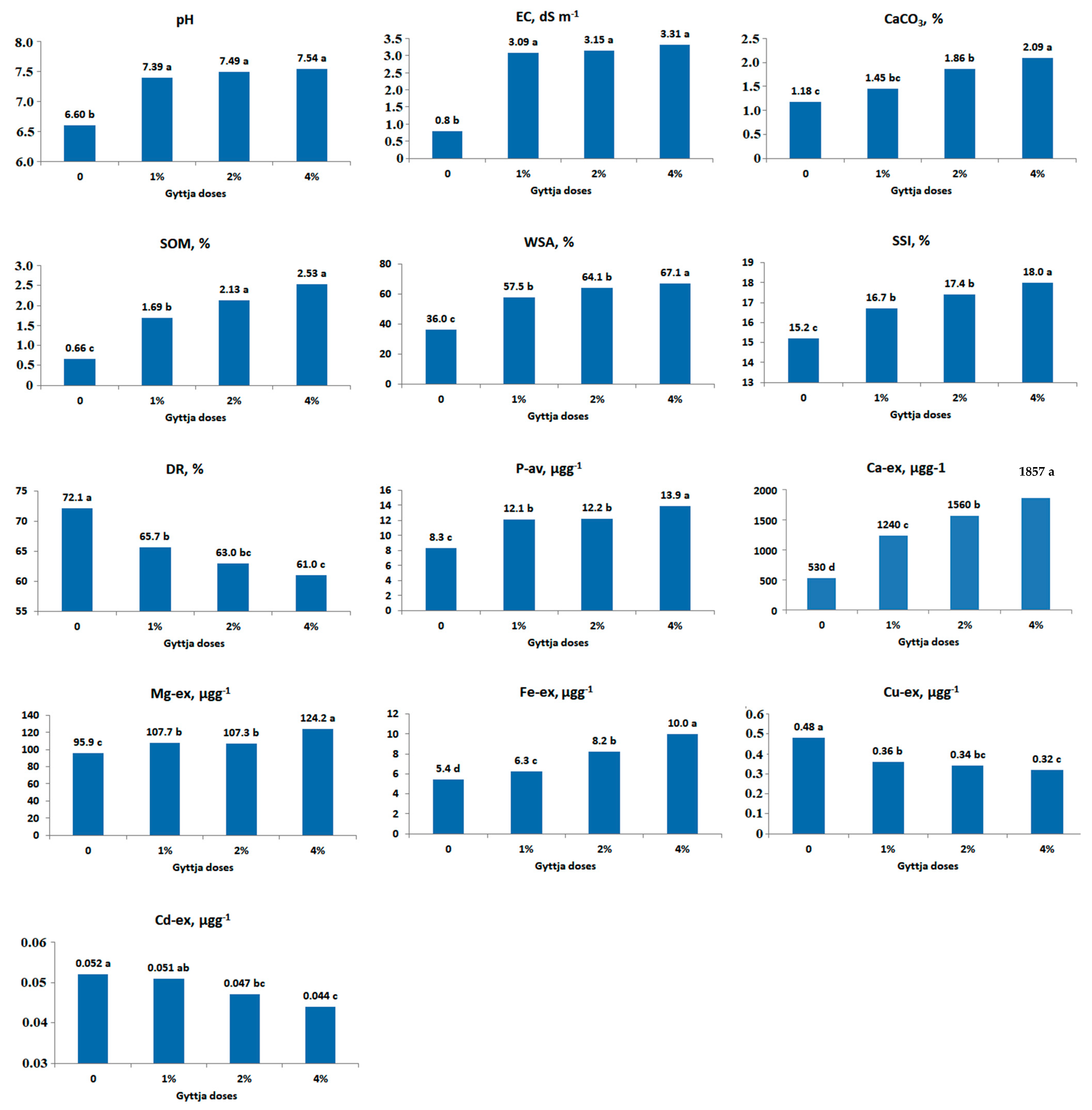
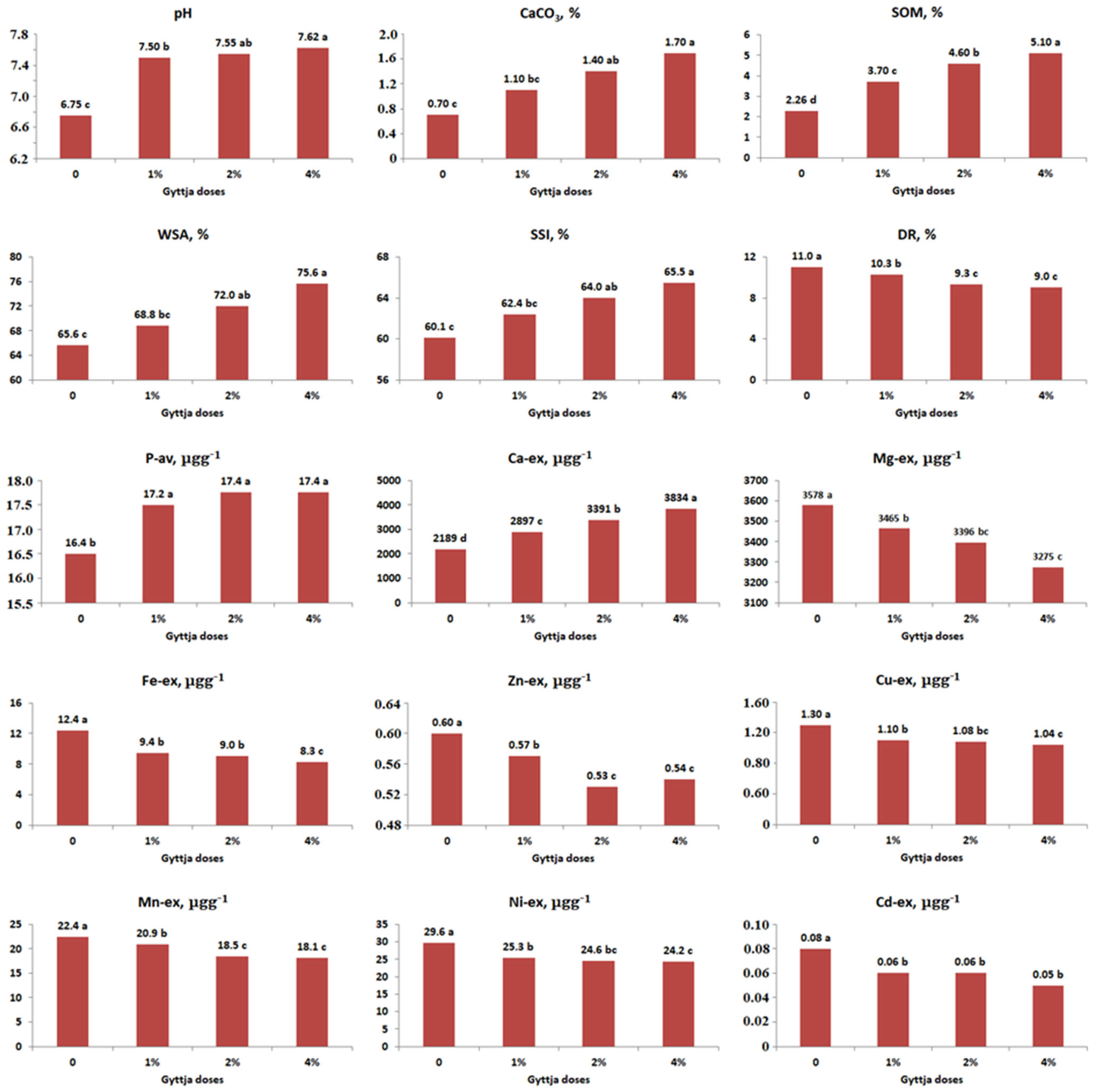
| Soil Property | Parent Material | |
|---|---|---|
| Volcanic | Serpentine | |
| Sand, % | 54.5 | 38.0 |
| Silt, % | 27.2 | 23.6 |
| Clay, % | 18.3 | 38.4 |
| Textural class | SL | CL |
| WSA, % | 36.0 | 65.6 |
| SSI | 15.2 | 60.1 |
| DR | 72.1 | 11.0 |
| pH | 6.60 | 6.75 |
| EC, dSm−1 | 0.802 | 0.971 |
| SOM, % | 0.66 | 2.26 |
| CaCO3, % | 1.18 | 0.70 |
| P-av, μgg−1 | 8.3 | 16.4 |
| Ca-ex, μgg−1 | 559.7 | 2189 |
| Mg-ex, μgg−1 | 95.9 | 3578 |
| K-ex, μgg−1 | 217.8 | 209 |
| Fe-ex, μgg−1 | 5.41 | 12.4 |
| Cu-ex, μgg−1 | 0.48 | 1.30 |
| Zn-ex, μgg−1 | 0.88 | 0.60 |
| Mn-ex, μgg−1 | 6.8 | 22.40 |
| Ni-ex, μgg−1 | 0.41 | 29.6 |
| Cd-ex, μgg−1 | 0.052 | 0.080 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.22 |
| EC, dSm−1 | 1.13 |
| OM, % | 41.3 |
| CaCO3, % | 53.2 |
| P-av, μgg−1 | 12.0 |
| Ca-ex, μgg−1 | 6697 |
| Mg-ex, μgg−1 | 745 |
| K-ex, μgg−1 | 103 |
| Fe-ex, μgg−1 | 128 |
| Cu-ex, μgg−1 | 0.24 |
| Zn-ex, μgg−1 | 1.58 |
| Mn-ex, μgg−1 | 3.74 |
| Ni-ex, μgg−1 | 1.32 |
| Cd-ex, μgg−1 | 0.38 |
| Parent Material | Soil Properties | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volcanic | pH ** | EC * | CaCO3 ** | SOM *** | WSA *** | SSI * | DR * | K-ex ns | Ca-ex * |
| Mg-ex ** | P-av * | Fe-ex ** | Zn-ex ns | Cu-ex * | Mn-ex ns | Ni-ex ns | Cd-ex * | ||
| Serpentine | pH ** | EC ns | CaCO3 * | SOM *** | WSA ** | SSI * | DR * | K-ex ns | Ca-ex *** |
| Mg-ex ** | P-av * | Fe-ex ** | Zn-ex ** | Cu-ex ** | Mn-ex ** | Ni-ex * | Cd-ex * | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saltalı, K.; Solak, S.; Özdoğan, A.; Kara, Z.; Yakupoğlu, T. Gyttja as a Soil Conditioner: Changes in Some Properties of Agricultural Soils Formed on Different Parent Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9329. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129329
Saltalı K, Solak S, Özdoğan A, Kara Z, Yakupoğlu T. Gyttja as a Soil Conditioner: Changes in Some Properties of Agricultural Soils Formed on Different Parent Materials. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9329. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129329
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaltalı, Kadir, Serdar Solak, Ali Özdoğan, Zekeriya Kara, and Tuğrul Yakupoğlu. 2023. "Gyttja as a Soil Conditioner: Changes in Some Properties of Agricultural Soils Formed on Different Parent Materials" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9329. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129329
APA StyleSaltalı, K., Solak, S., Özdoğan, A., Kara, Z., & Yakupoğlu, T. (2023). Gyttja as a Soil Conditioner: Changes in Some Properties of Agricultural Soils Formed on Different Parent Materials. Sustainability, 15(12), 9329. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129329







