Abstract
Clarifying service demands is a necessary prerequisite for promoting high-quality service development and sustainable supply. According to the charm quality theory and the logical system and basic viewpoints of the Kano model, a questionnaire survey was conducted on the needs of 241 elderly people (aged 60 and above) in the Dabei Quhou community, Chengyang District, Qingdao City, to understand the needs and willingness of elderly people in the community to integrate health promotion services. Statistical survey results on the division of the service demand level attribution, the level of satisfaction coefficient and dissatisfaction coefficient, the priority sequence of community sports, and medical integration health promotion service projects were addressed. Among the nineteen service demand items, there are four essential elements (M), three expected elements (O), eleven attractive elements (A), and one irrelevant element (I). Its service demand as a whole presents low dependence. On the basis of the hierarchical division of the health promotion service needs of physical and medical integration, based on the safety and convenience of maintaining a daily healthy life, the composition of each demand level presents the demand tendency that spans from basic function demand satisfaction to service function development and content-rich expansion. Secondly, given the convenience of service supply, there is a tendency for social public health promotion services to reach the community level.
1. Introduction
With the increasingly aging population, health problems in the elderly caused by chronic diseases such as hypertension have become increasingly prominent, causing social and public health concerns around the world. The United States advocated for the concept of “sports are good doctors”; formulated and implemented sports, healthcare, and other multi-subject participation mechanisms for the “integration of physical and medical services”; and actively addressed elderly health problems. The Chinese government has responded to the aging population by implementing a “Healthy China 2030” plan that calls for the wider integration of sports, medical services, and non-medical health interventions, with a specific focus on addressing the health problems of key populations (such as the elderly). China’s Medium- and Long-term Plan for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases (2017–2025) calls for health promotion strategies to reduce disease risk among high-risk groups and promote the integration of sports and medical services. The National Plan for Medium- and Long-term Active Responses to Population Aging proposes the implementation of a comprehensive prevention and control strategy for chronic diseases to improve the health of the elderly. Integrating sports and medical care is a key measure to accelerate the prevention and control of chronic diseases and health promotion among the elderly in China. The community is the basic unit of social governance and the cut-in point for the primary prevention of diseases. Therefore, there has been a consensus to promote the mixed health model on the health coverage of community-based medical integration services for the elderly [1]. However, China’s community health service centers provide less support for sports rehabilitation and health management. There are certain problems in the integration of community sports and medicine, such as unclear service content, a lack of pertinence, and a lack of precision. This results in an unreasonable supply structure, the low efficiency of coordinated supply, and a contradiction between supply and demand [2], which inhibits the integration service and leads to the insufficient expression of potential service demands among the elderly. Therefore, there is an urgent need to accurately identify the elderly’s health service needs in order to develop community sports and medicine integration services in China.
With the advancements in theoretical and practical research, research on the elderly’s health service needs has become the focus of discussion. For example, a survey shows that approximately 80% of the elderly have a demand for medical services. The study shows that factors such as household registration, health status, family income, and government living allowance significantly affect the demand for community-based medical services among the elderly [3]. In addition, regional and national surveys on the need for community-based care for the elderly have shown that there is a strong and comprehensive need for integrated community-based sports and medical health services [4,5], and a high demand for home-based services such as family doctors, with close attention paid to spiritual needs and life care needs. Moreover, the whole predicament of “big service demand, weak intergenerational support” exists in the elderly’s economic, healthcare, and spiritual needs, as well as in professional medical and daily care, showing a higher demand for the regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood glucose levels, household sanitation, and daycare services [6,7].
Previous studies have focused on the main service supply, supply mechanism, factors, and other aspects of the demand itself. However, studies on the level of demand and the importance of analysis are lacking. From a macro perspective, some studies have used national statistical data to explore differences [8,9] and provided a holistic description of the demand for health promotion services for the elderly. However, there are regional differences in the elderly’s service needs, particularly affected by economic development levels, health status, cognitive levels, as well as other needs of the elderly in different areas (that differ in degree, content, and emphasis). Even in the same region, the elderly’s needs differ based on living and physical conditions [10,11]. Therefore, national and non-differential needs should be analyzed instead of regional and differential needs. In practice, the convergence and disparity of supply content, quantity, structure, and quality will occur.
In addition, through a summary of the literature of domestic and foreign research, it is found that there is a certain simplification in the research on the demand for sports and medical integration services. Although there are many studies on the demand for health services for the elderly at this stage, this study focuses on the supply subject, supply mechanism, influencing factors, and other aspects of service demand. Demand is more widely used as a preliminary cover. For the demand itself, demand levels and priority satisfaction analyses have not been studied in detail.
Based on this, as well as the theory of charm quality and the Kano model, this study aims to improve the rationality, science, comprehensiveness, and sustainability of the supply of physical and medical integration health promotion services for the elderly community in China, as well as the elderly’s satisfaction and identity in relation to the service; clarify the demands for physical and medical integration health promotion services for the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community; propose priority areas to meet the sequence; improve the accuracy and effectiveness of the supply of physical and medical integration services; and provide theoretical support and practical reference for the main body of service supply.
2. Research Method and Theoretical Basis
The theory of attractive quality and the Kano model [12] was proposed by Professor Noriaki Kano of the Tokyo Institute of Technology, and his team was inspired by the two-factor theory. Based on the analysis of the demands of the service audience, a nonlinear relationship between service quality and the satisfaction of participants was observed, i.e., “not every service supply (lack) could increase (decrease) the satisfaction of the consumer, and the effect of satisfaction with each service content element (increase or decrease) also differs”. See Figure 1.
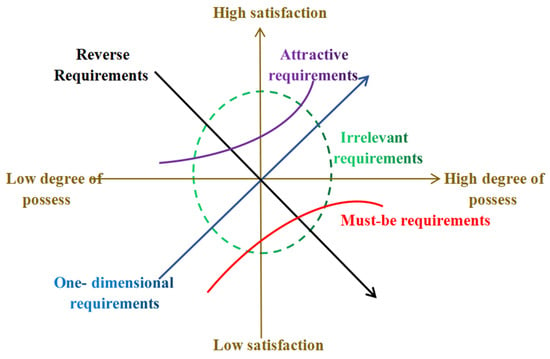
Figure 1.
Element hierarchy of the Kano model.
The theory of attractive quality and Kano’s model can accurately show the relationship between service availability and the elderly’s satisfaction in the urban community. Based on the two dimensions of service, i.e., “ability degree” and “satisfaction”, according to the importance of service elements, the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community can be divided into five groups, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Kano model service requirement hierarchy types and parsing.
The Kano model analysis method mainly aims to cover the “positive/negative” aspect of each service demand and the elderly’s degree of satisfaction with health promotion services on the integration of community physical medicine. Based on the results of “positive/negative” interaction options, the corresponding service requirement level is determined, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Requirements hierarchy attribution classification of Kano model problem options.
The traditional model determines the hierarchy of requirements and the priority sequence of M > O > A, according to the option with the highest frequency of every single factor. However, there are drawbacks to the level of demand and priority sequence determined in this manner. For example, the impact of various service elements on satisfaction is still different, even within the same demand level. Therefore, Berger et al. introduced a comparison method by calculating the customer satisfaction coefficient [13]. Because of the positive and negative effects between the provision of service demand factors and the satisfaction of the consumer, the coefficient of customer satisfaction can be divided into dissatisfaction (DSI) and satisfaction coefficients (SI) (Table 3), which are calculated as follows:

Table 3.
Dissatisfactory coefficient (DS) and satisfactory coefficient (CS) analysis.
According to the theory of attractive quality, the identification and ranking of the demand for health promotion services for the integration of sports and medical care for the elderly in our community should be based on the determination of the levels of demand for various services. The satisfaction and dissatisfaction coefficients of each service demand factor were compared, following the order of M > O > A, and the demand factors with significant DS and CS coefficients were given priority supply.
3. Empirical Analysis
The data used in this study were derived from a questionnaire survey completed by elderly (aged 60 years and above) members of the Dabei Quhou community, Chengyang District, Qingdao, in 2022. A total of 267 questionnaires were distributed and 241 valid responses were obtained with an effective rate of 90.3%. The questionnaire on the service demands of the elderly, which aimed to explore two forms of home service in the Dabei Quhou community and the unified organization service, was designed according to the performance, scope, and practice of the health promotion service model on the integration of sports and medical services in the Dabei Quhou community. A total of 19 service items were divided into facilities, professional services, organized activities, and health education and management (Table 4). The Kano model is designed for the “positive/negative” aspects of each service demand, i.e., “when you provide (do not provide) a certain service item, your satisfaction (dissatisfaction) degree changes”.

Table 4.
Content design of sports and medicine integration services for the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community.
3.1. Sample Description
Among the 241 elderly people surveyed, 38.6% were men and 61.4% were women, and the sex gap was significant. The average age was 64.15 years, among which people aged 75 years and above accounted for 12.86% of the total sample size. More than half of the participants had a middle-school education or less.
Due to the characteristics of the region and time, most elderly people were non-public-sector workers. However, due to the late development of urban planning, limited land resources will be integrated and revitalized after the transformation of the community. The community collectively owned 53,000 m2 of commercial real estate. The community had many operational assets, and its annual income exceeded CNY 20 million. As a result, it can be argued that most elderly people have a stable community welfare income. The average monthly income of 88.1% of the elderly ranged from CNY 1001 to 4000, and the monthly income of 5.3% of elderly people was more than CNY 4001. Due to their old age and the improvement in community welfare treatment, the elderly’s desire for material consumption and the demand for subsidies for their children decreased, reflecting that they are able to afford services.
Regarding family status, 78% of the elderly were married and 20% were widowed; five elderly participants had no children. Many elderly people choose to live separately from their children because of different living habits and limited housing conditions.
3.2. Demand Division of Sports and Medicine Integration into Health Promotion Services for the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
According to the traditional model demand level attribution classification reference table (Table 2), combined with the questionnaire results, the frequency of each service level was counted, and each service demand level was determined according to the highest frequency (Table 5).

Table 5.
Hierarchical classification table of health promotion service demands for physical and medical integration.
3.3. Better–Worse Coefficient Analysis
Analyzing the dependence and expectation of the service project, which reflects the effect of each service project on the satisfaction of the service object and the degree of dependence and expectation of the service object on each service intuitively and quantitatively, can avoid the lack of any detailed distinction of the importance of services under the single demand hierarchy. Combined with the above analysis and Table 3 results, the calculation results of the better–worse coefficients in this survey are shown in Table 6 and Figure 2.

Table 6.
Better–Worse coefficient values of different service items.
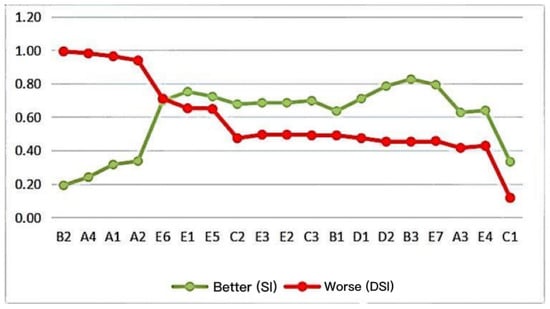
Figure 2.
The expectation and dependence trends of different service projects.
As shown in Figure 2, the SI value of most service items was higher than the | DSI | value. In addition to B2 professional medical staff, A4 basic medical facilities, A1 sports venues, A2 sports facilities, and E6 health monitoring, the five projects showed a trend of dependence greater than expectation, and other service projects showed a strong SI > | DIS | expectation.
This survey shows that the elderly′s dependence on community health promotion service needs is generally low. Based on the average dependence coefficient of 0.59 as the standard, only 7 items had more than 0.59 demand items. Among them, the dissatisfaction coefficients of B2 professional medical staff, A4 basic medical facilities, A1 sports venues, and A2 sports facilities were larger, and the values were all greater than 0.9, showing a strong dependence on the above four service items.
Secondly, the overall expectation of the health promotion service project for the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community was relatively high, with an average value of 0.6 as the standard, and the number of projects higher than the average value was 15, among which the satisfaction coefficient of B3 exercise prescription was the highest, and its value was greater than 0.8.
In order to make the data more intuitive, the data results of Table 6 were graphically analyzed, and the coordinate axis was established according to the composition principle of the four-quadrant diagram, and the better–worse coefficient diagram on the health promotion service demands of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community was drawn, as shown in Figure 3.
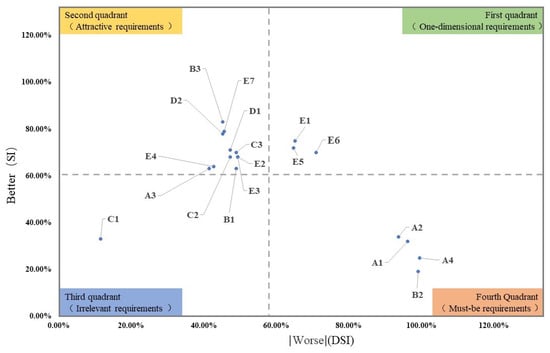
Figure 3.
Service requirements of the better–worse coefficient matrix.
In the first quadrant, the | better–worse | coefficient, which belongs to the expected attribute, was high. When the service demand items were satisfied, the satisfaction levels of elderly members of the Dabei Quhou community will be greatly improved. When the service demand items were not satisfied, satisfaction levels among the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community were expected to decrease slightly. The specific services in this quadrant were E1 volunteer service, E6 health monitoring, and E5 health records.
In the second quadrant, the better coefficient was high and the | worse | coefficient was low, indicating that when the service items in the quadrant are provided, satisfaction levels among the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community can be greatly improved. When such services were not provided, the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community had less impact on the satisfaction of the service, and the degree of impact was lower than the expected attribute service items in the first quadrant. This feature was consistent with the characteristics of the charismatic attribute, i.e., the potential demands of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community for a health promotion service demand project. The service items in this quadrant included C2 daily physical exercise, E3 chronic disease intervention, E2 pain injury prevention, and D2 scientific exercise guidance, among others.
The absolute value of the better–worse coefficient of the physical and medical integration health promotion service project in the third quadrant was lower, indicating that the satisfaction of such service projects has less impact on the satisfaction of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community, which is consistent with the characteristics of the indifference attribute, and the service projects in this quadrant were the only interesting sports activities. Because the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community had no obvious attitude towards this type of service demand, in the case of limited resources, this part of time and energy could be transferred to other projects.
In the fourth quadrant, the worse coefficient of the traditional Chinese-medicine-integrated health promotion service project was higher, and its better coefficient was lower, which is consistent with the essential attribute. This shows that when this kind of health promotion service project is met, it has little effect on the satisfaction level of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community. However, when such services are not met, the satisfaction levels of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community with the community health promotion service will be greatly reduced. Therefore, the service demand project in this quadrant was the basic demand of the health promotion service demand of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community. The service items in this quadrant were B2 professional medical staff, A4 basic medical facilities, A1 sports venues, and A2 sports facilities.
3.4. Ranking Results Based on ASC Coefficients
Based on the comparison of | SI | and | DIS |, Jang et al. proposed the average satisfaction coefficient (ASC) [14], which was used to compare the importance of each service element under the same category. Therefore, the ASC coefficient was introduced to prioritize the health promotion services of community medical integration under the same category. Its calculation formula is shown below.
The ASC coefficient is an important reference for comparing service demands in the KANO model. The larger the value, the higher the demand for a health promotion service. Therefore, after calculating the ASC coefficient combined with the characteristics of the demand hierarchy category and the service priority satisfaction sequence of the KANO model, that is, the order of M > O > A, the indifference demand items were removed, and the final demand priority satisfaction order is shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Service requirements for ASC analysis.
According to the research results, this study used 18 service projects with high demand, including four necessary elements, three expected elements, and eleven attractive elements. First of all, the elderly believe that the necessary needs must be met and should be met in the health promotion services of community sports and medical integration, including B2 professional medical staff, A4 basic medical facilities, A1 sports venues, and A2 sports facilities, which meet the most basic expectations of the elderly. Priority should be given to ensuring that the elderly have a basic recognition of community health promotion services. Secondly, it is a service project that raises expectations for the elderly and has certain requirements for the quality of service supply, including E1 volunteer service, E6 health monitoring, and E5 health records. Finally, it offers charismatic demands, including C2 organization daily physical exercise, E3 chronic disease intervention, E2 pain injury prevention, C3 physical fitness tests, B1 social sports instructor, D1 health knowledge lectures, D2 scientific exercise guidance, B2 exercise prescription, E7 psychological counseling, A3 intelligent equipment, and E4 exercise prescription. Satisfying the needs of this kind of service project will greatly improve satisfaction levels among the elderly with the health promotion service of community physical and medical integration. It is the service demand that should be implemented in the process of policy implementation and service supply to meet basic needs. According to the sorting results mentioned above, combined with the characteristics of the demand-level category and the service priority satisfaction sequence of the KANO model, as well as the existing service resources of the community (according to the satisfaction order of M > O > A), the specific service items in each level were sorted first to supply the top service items.
3.5. Analysis of the Physical and Medical Integration Service Demands of the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
3.5.1. Essential Requirements of the Demand of Health Promotion Services for the Integration of Physical Medicine for the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
The M requirements were the most important service demands subjectively determined by the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community. The M requirements included one professional staff member and three facilities, as well as the specific content of services for professional medical staff, basic medical facilities, sports venues, and sports facilities. According to the theory of attractive quality, the lack of the above-mentioned service content has a significant impact on the satisfaction of the health promotion service of the integration of physical medicine for the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community and the identification and utilization of integration services of physical medicine.
At the same time, there were also differences in the impact of various service contents on the essential needs of the satisfaction of the elderly. Among them, sports venues and sports facilities ranked at the top of the ASC coefficient ranking of essential elements. Therefore, the importance of the above two services was more prominent. In terms of sports, the elderly′s demand for physical exercise was more focused on the provision of daily basic sports facilities. Due to the elderly’s fixed living environment and their lack of mutual assistance ability and function, the elderly were found to have deficiencies in maintaining health, daily life, and anti-risk ability, and the service demand was more inclined to guarantee basic living needs [15]. Professional medical staff and basic medical facilities were ranked as the third and fourth most necessary elements. In contrast, some elderly people′s physical mobility was limited, the practical ability of intelligent equipment was weak, and the frequency of regular fun sports activities and intelligent sports facilities selected as irrelevant elements (I) was more frequent [16].
3.5.2. O Requirements of the Demand for Health Promotion Services for the Integration of Physical Medicine for the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
The O requirement of the health promotion service demand was the service content which directly affected the elderly’s satisfaction levels with the health care integration service, which needs to be improved urgently. The supply or lack of expectation factors was positively correlated with the increase or decrease in satisfaction. O requirements included health monitoring, free clinic services, and health records. Due to the relative increase in the frequency of expected requirements classified as O and I requirements, the importance of O requirements was relatively reduced.
Compared with M requirements, the O requirements reflected the extended comprehensive demand for health, medical treatment, and convenient services [17,18]. For example, along with the need for medical professionals and basic medical facilities, the need for free medical services, health records, and health monitoring is also important for health management and disease prevention in the elderly. Studies in other countries have shown that collaborative governance among intersectoral data systems for integrated medical and physical services improved population health information infrastructure for the benefit of community residents [19]. The health monitoring and provision of free medical services in O requirements effectively increased the health threshold of the elderly, which is in accordance with the strategic requirements of the “Health China 2030 for the National Health Strategic Planning”. Due to the shortage of medical resources and the inconvenience experienced by the elderly when they go out, there were delays in medical treatment, which is a significant problem [20]. The elderly’s demand for free medical services not only reflects the demand for basic medical facilities but also the need for social care and spiritual satisfaction. Health monitoring ranked first in the O requirements, and its DSI coefficient was closer to 1 compared with that of the other two services. In addition, the health monitoring service was the first service requirement item with positive SI and DSI values. It was also critical in service satisfaction, ranking from dissatisfaction-oriented to satisfaction-oriented services. In the service content below, the impact of service delivery on satisfaction levels was greater than the level of dissatisfaction caused by a lack of service.
3.5.3. A Requirement of the Demand for Health Promotion Services for the Integration of Physical Medicine for the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
In this survey, a total of 11 services were classified as A requirements, including health management (n = 5), organizational activities (n = 2), professionals (n = 2), and health education (n = 2). Compared with the first two requirements, the A requirements had a lower degree of demand importance and dissatisfaction, but their SI was the highest. It is difficult to meet the needs of the A requirements at the level of family, which shows a strong need for external social services [21]. Therefore, more service needs are to be fulfilled at the level of community services. Conducting physical tests, delivering health awareness lectures, and increasing the awareness of physical exercise can partly meet the needs of healthy life for the elderly. Exercise intervention and injury prevention and treatment for chronic diseases can not only reduce inconvenience for the elderly to seek medical treatment but also allow hospital treatment to extend to grassroots communities and facilitate the diversification of contents of social medical care. In contrast, requirements for advanced sports facilities and prescription were the lowest, and their ID, SI, and DSI values were lower than those of the same services in the essential and expected factors. Through content comparison, we observed that advanced sports facilities and prescriptions emphasized active acceptance among the elderly, which reflected their efforts to enhance their cognitive level [22].
3.5.4. Priority Satisfaction Sequence Analysis of Health Promotion Services for the Integration of Physical Medicine for the Elderly in the Dabei Quhou Community
According to the empirical results of the study, the sequence of priority was obtained based on the guidance of social benefit and the service supply efficiency of health promotion services. In the service priority satisfaction sequence, there were three service items in the health management category: health monitoring, free medical services, and establishing health records. The elderly’s demand for health promotion services represents a long-term demand for social services. For example, health monitoring and establishing health record services suggest that regular, real-time, and dynamic attention should be paid to the physical condition of the elderly, and stage-by-stage analysis should be conducted to improve their health status. We should actively conduct disease prevention programs and ensure timely diagnosis and treatment. In this regard, the United States government has instructed healthcare practitioners to provide information to residents, set up referral systems and community projects, and use health information technology to screen residents with unhealthy exercise habits or provide exercise intervention services [23]. In comparison, the health promotion service demands of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community effectively promote the deep integration of sports, medical, and health services; extend the platform to grassroots communities; and involve multiple attributes of community services to promote the integration of resources among various departments [24].
To conclude, there are some similarities and differences between the outcomes of this study and other relevant studies. The results of this study highlight the need for basic health promotion services [25], such as health professionals, basic medical facilities, sports venues, and sports facilities. Moreover, lectures on health, injury prevention, treatment, and exercise intervention for chronic diseases are also popular. Other studies have shown that the elderly had a high demand for health management services [26], but it was more likely to be associated with “expectations” of service provision. This is similar to the classification of expected factors in this study, such as health monitoring, free medical service, and establishing health records. In addition, there are some differences between the outcomes of this study and those of some regional studies with respect to the demand degree of individual service items. For example, exercise intervention for chronic diseases, health lectures, and regular physical examinations was not as demanding, as shown in previous studies [27,28,29]. This may be due to differences in the survey area or sample characteristics, as Qingdao is the first pilot city in China dedicated to the health promotion of physical medicine integration, and the cognition of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community to the integration of physical medicine service is different from that of elderly populations in other areas. Therefore, this study focused on the priority of service supply rather than an analysis of demands for services.
4. Conclusions and Suggestions
4.1. Research Conclusions
The purpose of this study is to improve the satisfaction and identity of the elderly in relation to the health promotion service of community sports and medical integration and to improve the accuracy of the matching between service supply and demand. Based on the theory of charm quality and the Kano model, through a random survey completed by elderly (over 60 years old) members of the Chengyang District of Qingdao City, the elderly’s demand levels and priority sequences to the health promotion service project of different community sports and medical integration were identified, and the following conclusions can therefore be drawn.
From the division of each demand level and its content composition, the overall demand for sports and medical integration services shows a low dependence rate. In the expansion sequence from the essential elements to the expected elements and the charm elements, the following demand tendencies are shown. First, based on the supplement of the community health promotion service function and the maintenance of the order of daily healthy life, the demand tendency that spans from the basic function of demand satisfaction to service function development and content-rich expansion is presented. Secondly, based on the convenience of service supply, social public health promotion services are shown to reach the community level.
According to the order of importance of each service item, the needs of the elderly in the Dabei Quhou community for the health promotion service of the integration of physical medicine should prioritize basic medical facilities and sports venues. The facilities were complementary to the basic functions of daily family life in the aspects of health education and management and professionals. This highlights the service demand tendency and the elderly’s functional orientation to maintain their physical health.
4.2. Research Suggestion
- (1)
- Clarifying government functions and promoting the orderliness of multi-subject participation
In order to meet the demands of integrated health promotion services for the elderly and improve the precision of integrated health promotion service supply in the Dabei Quhou community, we should gradually improve the convenience of facilities and basic professional services, health management, and education services on disease prevention and treatment; the provision of an active health promotion service platform; and the efficacy of emergency services. Multi-subject participation should be promoted and service supply capacity should be improved. Government functions should be gradually optimized, the talent training mechanism should be gradually improved, the construction of the community elderly self-service platform should be strengthened, and the order and sustainability of multi-subject participation in service supply should be enhanced.
- (2)
- Improve the professional ability of service personnel and promote the sustainability of the service supply
The elderly’s effective acceptance of service needs in the Dabei Quhou community should be based on existing service resources and service capabilities; should strengthen informal services; should facilitate the feedback channels of normalized service needs; and should implement menu-based service supply to ensure that the community is subject to existing conditions.
4.3. Research Insufficiency and Prospect
Advantages and limitations: This study takes the first pilot city in China as the research focus. The respondents had a high level of awareness of the sports and medical integration service project, which can reflect the current situation of the elderly′s demand for sports and medical integration services in China to a certain extent, and can provide theoretical support and experience on the formulation and implementation of sports and medical integration policies at national and local levels in China. However, due to the large differences in economic levels and demographic characteristics among different regions in China, this study has certain limitations, namely in the selection of survey areas and survey objects, so the practical generalization of research results is limited.
Therefore, in a follow-up study, we should expand the research scope and size of the research groups, explore the needs of different people in different regions of China on the integration of physical and medical health promotion services, improve and perfect the supply system of the integration of physical and medical services, and improve the people′s recognition of the integration of physical and medical services.
Author Contributions
B.W. and Q.L. conceived the study. Y.W., B.W. and X.Z. were involved in the data collection and analysis. B.W. wrote the manuscript. J.Y. and H.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Fund Project “Research on the realization mechanism and path of the precise supply of the sports and medicine integration public services driven by digital economy” (Grant No. 21BTY093).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represent a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
References
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.W. Research on the connotation, realistic dilemma and multi-dimensional path of the deep integration of national fitness and national health. J. Shenyang Inst. Phys. Educ. 2021, 40, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. Conflict and Equilibrium: Stakeholder co-governance study of Community Medical Integrated Health Services. China Health Serv. Manag. 2022, 39, 736–741 + 800. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.H.; Ling, W.H. Research on the needs of the elderly for community door-to-door health care services from the perspective of demand spillover theory. Med. Soc. 2022, 35, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, W.X.; Xiao, L.Y.; Wu, P.X. A qualitative study on the needs for integrated medical care for the elderly in Jinan. J. Nurs. 2021, 28, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Wang, G.Z. Demand-oriented elderly health service model in China. J. Hebei Univ. 2021, 46, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Z.; Hu, Z.L.; Wang, J.J. Study on the needs of community support services and influencing factors for the disabled elderly under the combination of medical and nursing care. J. Nurs. Manag. 2018, 18, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Guo, J.Z.; Hu, S.J.; An, H.Q.; Zhuang, L.H. Corresponding analysis of health service project needs for the elderly with different self-care abilities in urban communities. Health Stat. Chin. 2017, 34, 951–953. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.P.; Wei, H.Y.; Yang, G.M.; Liang, X.X.; Dong, H.Y.; He, Y. Analysis of the combined service needs of community-based elderly people based on the EQ-5D scale. J. Zhengzhou Univ. Italy 2022, 57, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Dai, W.W.; Su, B.B.; Fan, H.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zheng, X.Y. Evaluation of rehabilitation service demand and reason analysis of supply and demand gap in China. Rehabil. Theory Pract. Chin. 2022, 28, 725–729. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, J.R. The pension willingness, health status and health service needs of the elderly people in rural areas in southern Ningxia. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2018, 38, 3519–3520. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Shen, Q.; Chen, G.L.; Xu, J. Study on the integrated service demand and influencing factors of family medical care for the elderly in Hangzhou. Nurs. Manag. Chin. 2018, 18, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, N.; Seraku, N.; Takahashi, F.; Tsuji, S. Attractive quality and must-be quality. J. Jpn. Soc. Qual. Control 1984, 14, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C. Kano’s Methods for Understanding Customer—Defined Quality. Cent. Qual. Manag. J. 1993, 2, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Song, H.; Park, Y.T. Determining the Importance Values of Quality Attributes Using ASC. J. Korean Soc. Qual. Manag. 2012, 40, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liang, S.Y.; Wang, W.R.; Xu, Y.Y. Research on the development model of medical and nursing integrated nursing under the background of “Internet +”. Development 2023, 3, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B. Research on the Problems and Countermeasures of Community Home Care Service in Y Town. Ph.D. Thesis, Yangzhou University, Gaoyou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Zhong, L.P.; Fan, C.W.; Zhan, B. A study on the practice of health promotion service model combining health care, medical care and nursing care in China. J. Cap. Inst. Phys. Educ. 2022, 34, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.F.; Li, H.; Chen, J.X.; Yang, T.T. Evaluation of the practice effect of intelligent medical care for the elderly in the community. J. Nurs. 2022, 37, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, L.; Tobey, R.; Cantor, J.; Hessler, D.; Adler, N.E. Integrating Social And Medical Data To Improve Population Health: Opportunities And Barriers. Heal. Aff. 2016, 35, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.Q.; Zhou, Y.S.; Liao, C.F.; Du, Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, R.Q.; Cai, Z.J.; Zhou, H. Status quo and influencing factors of delayed medical treatment behavior of residents in rural areas of Sichuan Province. J. Chin. Acad. Med. Sci. 2023, 45, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.Z.; Gong, H.R.; Huang, F.J.; Sun, S.Y.; Jing, B.; Zhang, T.L. Analysis of hypertension screening and compliance of residents aged 35–85 years in Linqu County in 2019. Forum Prev. Med. 2020, 26, 778–779 + 799. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J. To build a “happy station” for the elderly. Bazhong Daily 2022, 03–31, 006. [Google Scholar]
- Galaviz, K.I.; Narayan, K.M.V.; Lobelo, F.; Weber, M.B. Lifestyle and the prevention of type 2 diabetes status report. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2015, 12, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Kou, X.J. Diabetes prevention and treatment in the context of medical integration: Amer-can experience and enlightenment. Gen. Pract. Chin. 2022, 25, 3089–3096. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.G.; Jin, X.L.; Zeng, S.j.; Cui, Z.H. Study on health promotion needs of residents aged 60 and above in Xuhui District, Shanghai. Health Educ. Health Promot. 2018, 13, 448–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.T.; Zhao, Y.W.; Wang, X.S.; Ling, Y.H.; Jiang, G.; Wang, H. The integration of social adaptation concept into the health management of the elderly in the community. Med. Philos. 2022, 43, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Cheng, X.R. Survey on the health status, pension willingness, and health service demand of the elderly in Yongchuan District, Chongqing. Mod. Med. Health 2022, 38, 4042–4045. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Su, J.K.; Shang, L. Standardized management mode and effect evaluation of elderly chronic diseases in the community. J. Hebei Med. Univ. 2019, 40, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Fu, Y.X.; Lin, L.; Chen, S. Research on the current situation and demand of community health care services for the elderly in Chengdu. China 2022, 20, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).