Abstract
At present, wastewater discharged from many industries contains a large amount of Cu (II). In this study, an O-modified activated carbon fiber (O-ACF) with high adsorption activity was prepared by oxidation modification of activated carbon fiber with 20% nitric acid. O-ACF was used to adsorb Cu (II) in water. Electrode adsorption experiments showed that O-ACF had excellent electro-adsorption performance for Cu (II), and the maximum adsorption capacity was 48.60 mg/g, which was 1.63 times that of commercial activated carbon. After optimizing and adjusting the voltage (0.6–1.2 V), pH (2–10) and electrode plate spacing (5–20 mm), it was found that the most favorable working conditions for electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF electrode were voltage of 1.0 V, solution pH of about 6, and electrode plate spacing of 10 mm. The kinetic model fitting showed that the adsorption effect of O-ACF on Cu (II) was mainly chemical adsorption. The intraparticle diffusion model further found that the adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF was influenced by membrane diffusion and internal diffusion. Adsorption regeneration experiment showed that O-ACF still maintained 95% adsorption performance for Cu (II) after 5 times of adsorption regeneration, which had good practicability. This study provides an excellent material for capacitive deionization system, which is expected to be applied in sewage treatment, seawater desalination and nutrient recovery.
1. Introduction
At present, a large amount of wastewater is produced by human industrial production, such as mining, printing and dyeing, metal smelting, power generation, etc. [1,2,3,4,5]. Among them, copper is one of the typical metals in wastewater [6,7,8]. Copper ion pollution is mainly caused by wastewater discharged from metal processing and metallurgical industry, which poses a serious risk to organisms [9]. These copper ions will enter the soil and water, and even enter the human body with the food chain, resulting in environmental pollution and human poisoning [10,11,12]. Studies have shown that copper above a certain level will inhibit the work of phagocytes in the body, cause many diseases and complications, lead to the weakening of human metabolism and cognitive ability, and even cause death in severe cases [13,14]. However, as an important resource, copper is widely used in chemical, alloy, catalysis and energy fields. It is difficult to replace or significantly reduce the use of copper [15,16]. For this reason, it is necessary to prepare a new material or technology that can efficiently extract or fix copper in wastewater to reduce the harm of copper to the ecosystem.
At present, many methods have been used to remove copper from wastewater, for example, adsorption (electro-adsorption), precipitation, membrane separation and precipitation [17,18,19,20]. Katiyar et al. examined the adsorption performance of seaweed-based biochar for Cu (II). The results showed that the highest removal rate of Cu (II) in water was more than 99% [21]. Xu et al. prepared porous nanofiber membranes and studied their performance in removing copper ions from water. The results showed that the maximum adsorption capacity for copper ions was 354 mg/g [22]. Among them, electro-adsorption technology has attracted the attention of the water treatment industry due to its simple operation, reusable materials and high separation efficiency [23,24]. It is by applying a direct current voltage to change the surface electrical properties of the material, the target ion will be moved to the target electrode by the action of the electric field force of the device, thereby enhancing the adsorption performance of the target electrode (generally the adsorption material) and achieving the removal of target pollutants in water [25,26].
The key to electro-adsorption is the choice of electrode materials. Carbon materials are usually used as electrodes and are mainly porous structures. However, there are few adsorption sites of heavy metals such as oxygen-containing groups on carbon materials, and the adsorption activity of heavy metals is not enough. It is necessary to increase its adsorption sites by artificial treatment. Activated carbon fiber is a cheap and easily available material with a large number of pore structures on the surface and excellent electrical conductivity. It is one of the excellent choices for adsorption electrodes [27,28]. Similarly, activated carbon fibers have fewer oxygen-containing functional groups, which is not conducive to adsorption. Therefore, it needs to be oxidized to increase the adsorption capacity [29,30,31]. Nitric acid oxidation modification is one of the most widely used methods, which is due to the strong oxidation of nitric acid. Different from sulfuric acid, nitric acid has low corrosion resistance to materials and will not destroy the main structure of materials. Therefore, it is more appropriate to use nitric acid as an oxidation modification solution [32,33].
In this study, nitric acid was used to oxidize the activated carbon fiber (ACF) to prepare a nitric acid modified activated carbon fiber (O-ACF) as an electrode material for electro-adsorption. The adsorption performance of Cu (II) on target pollutants was investigated. The effects of pH value, electrode plate spacing and Cu (II) concentration on the electro-adsorption capacity of O-ACF were explored. The adsorption kinetics model and intraparticle diffusion model were established for the process of electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF to explore the mechanism and properties of electro-adsorption of copper ions by O-ACF. The regeneration adsorption performance of O-ACF for Cu (II) was investigated by adsorption cycle regeneration experiment. At present, many novel methods have been studied, but complex chemical technology modification or cumbersome synthesis steps limit the application of technology or material in actual production. The acid oxidation modification method used in this study has simple steps, low cost, and is easy to be popularized and used on a large scale, and its performance has been significantly improved after modification, which is also one of the highlights of this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Adsorption Test of O-ACF
2.1.1. Preparation of O-ACF
The activated carbon fiber (ACF) is purchased from the Chinese market, the ACF was cut into a 20 cm × 20 cm square, washed with deionized water, and soaked in ethanol for 2 h to eliminate bubbles inside the material. Next rinse with deionized water for 3 times, and dry the rinsed carbon fiber at 60 °C for 4 h. The dried activated carbon fibers were put into a beaker filled with 20% (w/v) HNO3, soaked for 4 h. Then, the activated carbon fibers were washed with deionized water for about 10 times until the pH of the material was 7 and dried in a thermostat at 80 °C to obtain O-ACF.
2.1.2. Characterization of O-ACF
The Fourier infrared spectra of ACF and O-ACF were measured by FTIR-650 spectrometer in the range of 4000 cm−1–500 cm−1. The surface morphology of ACF and O-ACF samples were determined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The acceleration voltage and operating distance of the instrument are set to 10.00 kV, 6.8 mm.
2.1.3. The Electric Adsorption Device
The experimental device is shown in Figure 1 and Figure S1. The specific composition and operation of the device are described in Text S1.
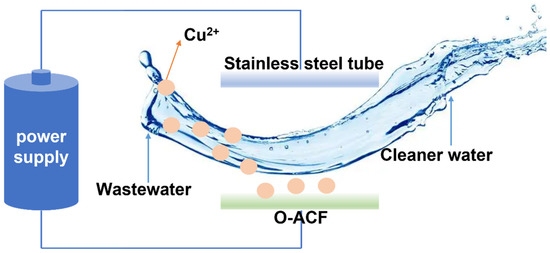
Figure 1.
Diagram of electro-adsorption device.
2.1.4. Experimental Operation and Methods
Electro-adsorption test adopts the method of single factor experiment. The effects of different pH, initial concentration of Cu (II), voltage and plate distance on the removal of Cu (II) were tested. The concentration of Cu (II) was determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Cu (II) solution was prepared from copper and nitric acid solution. In addition, the number of electrodes in the experimental electro-adsorption device is a pair.
The effect of solution pH: Under the conditions of voltage of 1.0 V, plate distance of 15 mm and original concentration of 300 mg/L, the adsorption capacity of O-ACF on Cu (II) at pH of 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 was tested. The initial concentration of target pollutants: Under the conditions of voltage of 1.0 V, plate distance of 15 mm and pH of 6, the effect of initial concentration of Cu (II) (20–300 mg/L) on the electro-adsorption capacity of O-ACF was tested. Study on the effect of voltage: Under the conditions of plate distance of 15 mm, pH of 6 and original concentration of Cu (II) of 20 mg/L, the effects of voltage of 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2 V on the electro-adsorption capacity of O-ACF were tested. Study on the effect of plate distance: Under the conditions of voltage of 1.0 V, pH of 6 and original concentration of Cu (II) of 20 mg/L, the effects of plate distance of 5, 10, 15 and 20 mm on the electro-adsorption capacity of O-ACF were studied. All experiments were repeated 3 times.
2.1.5. Model Fitting of Cu (II) Adsorption by O-ACF
In order to investigate the adsorption mechanism of O-ACF, kinetic and in-particle diffusion models were fitted to the adsorption data.
Pseudo-first-order kinetic model equation:
Pseudo-second-order kinetic model equation:
where qt (mg/g) is the adsorption capacity at time, t; t (min) is the adsorption time; qe (mg/g) is the equilibrium adsorption capacity; k1 (min−1) is the rate constant of the pseudo-first-order kinetic model; and k2 (g/(mg·min)) is the rate constant of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
The intraparticle diffusion model equation:
where qt (mg/g) is the adsorption capacity at time, t; Kid (mg/g·min0.5) is the intraparticle diffusion rate constant; and C is the model constant.
2.1.6. Backwashing Regeneration of Electro-Adsorption Reactor
Using 20% HNO3, 20% HCl and deionized water as regenerant. The backwash and regeneration effects of activated carbon (AC), ACF and O-ACF were compared. The voltage was 1.0 V, 200 mL target pollutant solution was used, and the concentration was 20 mg/L. The adsorption amount of O-ACF was determined after 12 h adsorption in a shaker. Then the voltage at both ends of the distribution board is inverted, and the activated carbon fiber is regenerated in 2 V voltage and 20% HCl for 2 h. After regeneration, the activated carbon fiber is washed with deionized water. Re-adsorption was carried out under the same conditions, the amount of re-adsorption was tested, and the regeneration rate (RA) was calculated. The RA of AC and ACF and O-ACF were calculated by the same treatment method. Each adsorption electrode was cycled 5 times. The RA calculation formula is as follows:
2.2. Main Experimental Instruments
The instruments used in the test mainly include: The surface morphology of the material was observed by scanning electron microscope (TM4000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), test sample quality was weighed by analytical balance (EX Eeries, American OHAUS, Parsippany-Troy Hills, NJ, USA), using fourier infrared spectrometer (FTIR-650, Tianjin Port East Technology, Tianjin, China) to measure the surface functional groups of materials, the content of Cu (II) in the solution was determined by ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shanghai Mepinda Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), electric blast drying oven (8401A-2, Shanghai Xuji Electric Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used to dry the test samples.
2.3. The Main Reagents of the Experiment
The main experimental materials used in the experiment are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The main experimental reagents.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influencing Factors of Cu (II) Adsorption on O-ACF in Water
The effect of pH on the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) (10 mg/L) by O-ACF is shown Figure 2a. The pH value had a remarkable effect on the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) in water by O-ACF, and the adsorption effect was the best in weak acid environment. The adsorption quantity were 7.16 and 7.12 mg/g at pH 6 and 8, respectively, and the adsorption effect decreased with the increase or decrease of pH. This may be due to the competitive adsorption of H+ and Cu (II) in the solution under acidic conditions, which consumed a lot of charge, resulting in a decrease in the amount of adsorbed Cu (II). Under alkaline conditions, Cu (II) began to precipitate again, and the colloid was negatively charged. The direction of the electric field force was opposite to that of O-ACF, so the adsorption was inhibited and the adsorption capacity of O-ACF electrode was weakened [34,35]. Based on the above results, the optimum pH for electro-adsorption of Cu (II) was 6–8.
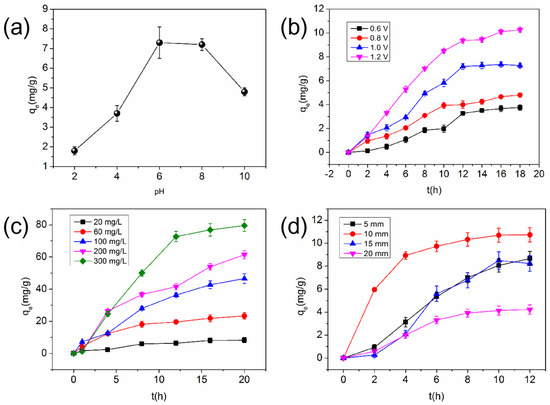
Figure 2.
Influence of operating parameters on electro-adsorption of O-ACF: (a) pH (voltage of 1.0 V, plate distance of 15 mm and original concentration of 300 mg/L); (b) voltage (plate distance of 15 mm, pH of 6 and original concentration of Cu (II) of 20 mg/L); (c) initial concentration (voltage of 1.0 V, plate distance of 15 mm and pH of 6); (d) plate spacing (voltage of 1.0 V, pH of 6 and original concentration of Cu (II) of 20 mg/L).
Figure 2b shows the effect of voltage on the adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF. The adsorption quantity of O-ACF for Cu (II) increases significantly with the increase of voltage in the voltage range of this experimental design. The higher voltage enhanced the electro-adsorption performance of O-ACF electrode for Cu (II). When the voltage increased from 0.6 V to 1.2 V, the adsorption quantity of Cu (II) increased from 3.75 mg/g to 10.27 mg/g, and the adsorption capacity increased by 170.4%. This may be because the increase of voltage will enhance the electric field strength and promote the movement of Cu (II) to the corresponding electrode, resulting in enhanced adsorption effect. But, when the voltage was greater than 1.0 V, the bubbles were observed in the water, which might be due to the high voltage resulting in weak electrolytic reaction of water. In addition, each treatment basically reached adsorption equilibrium after 12 h of point adsorption.
The effect of initial concentration on the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF is shown in Figure 2c. The adsorption capacity of O-ACF increases with the increase of initial concentration. When the original concentration was 20, 60, 100, 200 and 300 mg/L, the adsorption quantity of O-ACF for Cu (II) was 8.26, 23.37, 46.58, 61.41 and 79.56 mg/g, respectively. This was because under the condition of fixed adsorbent dosage, with the increase of pollutant concentration, the potential energy difference (concentration difference) between solution and adsorbent increased, and the mass transfer power also increased. Cu (II) in aqueous solution will move to O-ACF with the action of potential energy and electric field, which will increase the contact probability between Cu (II) and O-ACF. Under the combined action of mass transfer power and electric field force, Cu (II) was better captured by O-ACF [36,37]. However, with the increase of original concentration, the maximum adsorption quantity of Cu (II) will decrease. Therefore, when dealing with high concentration of Cu (II) solution, it was necessary to conduct a desorption experiment in time after adsorption saturation (about 4 h).
The effect of electrode plate distance on the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF is shown in Figure 2d. When the plate distance was 10 mm, the adsorption quantity of Cu (II) by O-ACF was the maximum. This was because the smaller the distance between the electrodes, the greater the thickness of the formed electric double layer, and the shorter the distance of the charged ions migrating to the electric double layer. However, due to the electrode spacing was too short will hinder the flow of water, but also may make the electrode short circuit, resulting in increased energy consumption. In addition, when the plate spacing was too small, the distinction between cations and anions is not obvious, and the freshwater area was small, so the ion content of solution decreased. When the plate spacing was too large, the ion diffusion distance between the electrodes was long, the turbulence was small. Therefore the time for ions to ion transport the electric double layer to be adsorbed became longer. And the electrode had little force on the distant ions, which cannot be adsorbed to the electrode surface. When the electrode plate spacing was 5 mm, bubbles appeared between the plates, indicating that electrolysis occurred in the water, which increased energy consumption. Consequently, 10 mm is the best electrode plate distance for adsorption.
3.2. Characterization and Adsorption Properties of ACF and O-ACF
As shown in Figure 3a, ACF had C-H, O-H, C-H, C=O, C=C, C-O, C-N and other functional groups. After modification, these functional groups are significantly enhanced, among which oxygen-containing functional groups can fix Cu2+ through complexation, and most oxygen-containing groups are in a negative form, thus enhancing the electroadsorption effect of O-ACF on Cu2+ [36,37]. Figure 3b,c are the electron scanning electron microscopy images of ACF and O-ACF, respectively. The results showed that ACF had a network structure after modification and few impurities in the network, which can promote the adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF. BET test results show that after modification, the specific surface area of O-ACF increases by 32%, confirming that acid oxidation modification can remove impurities in ACF (Table S1). In addition, Figure 3d,e are the spectral images of ACF and O-ACF, respectively. The results showed that there were C, Ca, O, Na, Al, Mg and Si elements on the surface of ACF before modification, while there were only C, N and O elements on the surface of O-ACF after modification. This was because other heteroatoms on the surface of ACF were washed off after modification with nitric acid, which increased the specific surface area of O-ACF and promoted the adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF [19].
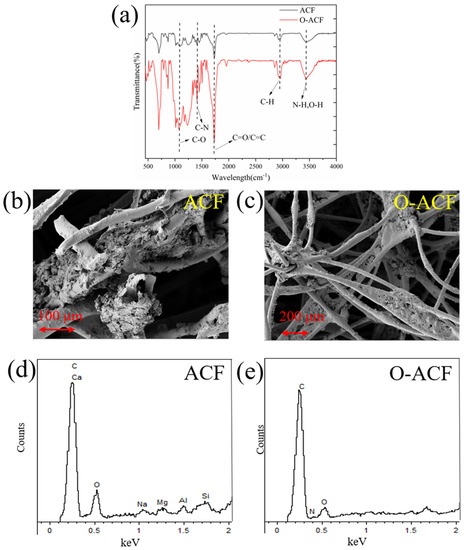
Figure 3.
(a) FTIR spectra of ACF and O-ACF; (b,c) Scanned electronic images of ACF and O-ACF; (d,e) spectral images of ACF and O-ACF.
The maximum adsorption quantity of Cu (II) on ACF and O-ACF is shown in Figure 4. The maximum adsorption quantity of commercial ACF and O-ACF as adsorption electrodes were 33.56 and 48.60 mg/g, respectively. Compared with the AC commonly used in the market, the maximum adsorption capacity of ACF and O-ACF were significantly improved. The maximum adsorption quantity of the O-ACF was also significantly higher than that of the ACF, because micropore volume and adsorption site of O-ACF were significantly improved [38,39]. This was also consistent with the conclusion obtained from the characterization above. In addition, O-ACF had excellent adsorption performance for Cu (II) compared with other materials (Table 2).
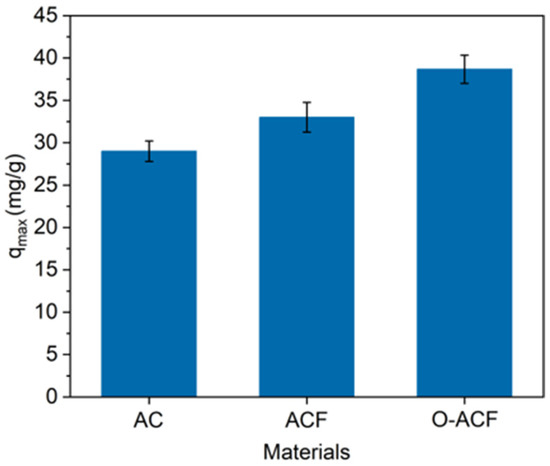
Figure 4.
Maximum adsorption of Cu (II) at optimal conditions for AC, ACF and O-ACF.

Table 2.
Comparison of adsorption properties of different adsorbents for Cu (II).
3.3. Model Fitting
3.3.1. Kinetics Model Fitting
Voltage and electrode spacing were the main factors affecting the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by activated carbon fibers (Figure 2b,d). Therefore, changing the voltage and electrode spacing played a very important role in improving the electro-adsorption effect [44]. However, compared with changing the voltage, changing the electrode plate spacing was more economical. Therefore, the adsorption data under different electrode plate spacing were fitted by pseudo-first-order kinetic model and pseudo-second-order kinetic. The fitting results are shown in Figure 5.
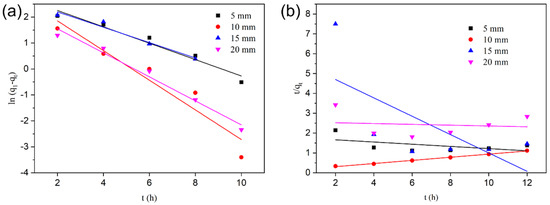
Figure 5.
Kinetic of O-ACF electro-adsorption Cu (II): (a) pseudo-first-order kinetics; (b) pseudo-second-order kinetics.
The results showed that the correlation coefficient (R2) of the fitting results of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model was higher (Figure 5a,b and Table 3 and Table 4). This indicated that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model can better react the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF, and q2 is much closer to qe. The value of qe increased with the increase of temperature (Table 3 and Table 4). And qe increased with the decrease of plate spacing. The k2 decreased with the increase of temperature, and also decreased with the increase of electrode plate spacing, that was, the longer it took to reach adsorption equilibrium. This phenomenon indicated that the adsorption of Cu (II) by O-ACF was a complex chemical adsorption process. And because the second-order model included all the adsorption processes, the pseudo-second-order kinetics can better reflect the kinetic mechanism of the adsorption of ions by O-ACF electrode [45,46].

Table 3.
Pseudo-first order kinetics parameters of Cu (II) adsorbed on O-ACF.

Table 4.
Pseudo-secondary kinetic equations of Cu (II) adsorbed on activated carbon felt.
3.3.2. Intraparticle Diffusion Model Fitting
In the first 360 min of the adsorption process, the in-particle diffusion model was used to perform piecework fitting on the adsorption curves of different initial concentrations (Table 5 and Figure 6). The linear fitting image did not cross the origin of the coordinate axis, indicating that the adsorption process was jointly controlled by internal diffusion and membrane diffusion (Figure 6) [47]. The adsorption rate was higher in the first 180 min, which was the surface diffusion stage, which was mainly controlled by the intra-particle diffusion step. Moreover, with the increase of the original concentration of pollutants, the mass transfer force also increased, and the faster the adsorption, the larger the K value (Table 5). After 180 min, adsorption sites of active carbon fibers gradually saturated, solution concentration gradually decreased, and internal diffusion resistance increased, which was jointly controlled by membrane diffusion and internal diffusion [48,49].

Table 5.
The intraparticle diffusion model of Cu (II)+ adsorption on O-ACF.
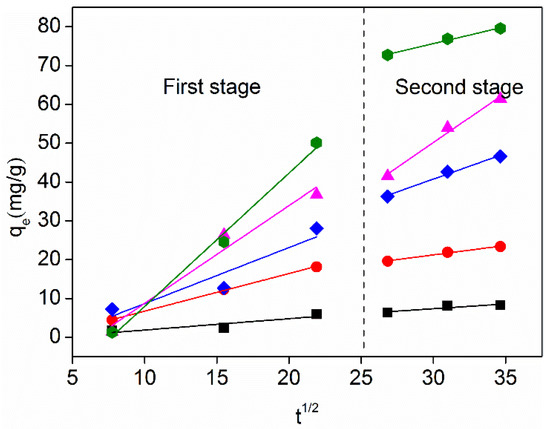
Figure 6.
The intraparticle diffusion model of Cu (II) adsorption on activated carbon fiber.
3.4. Backwashing Regeneration of Electro−Adsorption Reactor
As shown in Figure 7, O-ACF maintained a high regeneration rate in three kinds of regeneration agents. The regeneration rates of O-ACF in 20% HNO3, 20% HCl and distilled water were maintained at 95%, 87% and 74%, respectively, through 6 cycles of regeneration. The regeneration effect of 20 % HNO3 is the best. Due to the use of 20% HNO3 solution for regeneration (It is similar to the preparation method of O-ACF in this study), the specific surface area and chemical properties of the regenerated O-ACF had happened corresponding change, and the adsorption site may enhance compared with the preparation of O-ACF, resulting in the regeneration adsorption quantity is higher than the original adsorption quantity, that was, the regeneration rate exceeds 100%. With the increase of circling number, the number of adsorption sites tended to fixed value, therefore the regeneration rate decreased to some extent. Until the last regeneration rate can still reach about 95%. Compared with HNO3, the oxidation of HCl is weak, the modification intensity of O-ACF was small in the cycle process, and the increase of adsorption site was less, so the regeneration rate of HCl as the regenerant was relatively low. And using distilled water as a regenerant, because distilled water cannot increase the adsorption site of O-ACF, so there was no significant change in the regeneration rate, basically maintained at 74%.
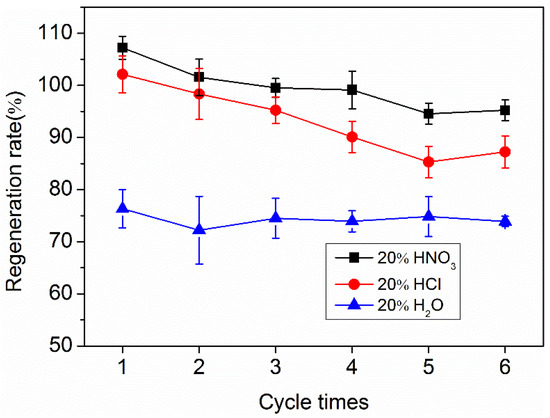
Figure 7.
The regeneration rate of O-ACF in different regenerants.
Figure 8 shows the regeneration rates of three kinds of adsorption electrodes. After 5 times of backwashing regeneration, the regeneration rates of ACF and O-ACF were maintained at about 87% and 95%, respectively (Figure 8). The regeneration rate of O-ACF was higher than that of ACF, and reached a very significant difference. After backwashing and regeneration, the electrode remained intact, no scaling, passivation and other phenomena were found, and the regeneration rate did not change much with the increase of times, indicating that the O-ACF electrode had good regeneration and adsorption performance and could meet the requirements of practical applications [50,51]. In addition, flotation is one of the effective methods to treat solid particles, so the adsorbed carbon materials can be recovered by this method in practical applications [52,53].
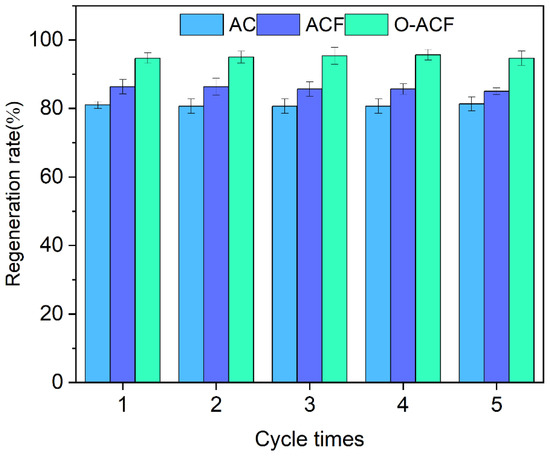
Figure 8.
Regeneration rate of different adsorption electrodes (AC: active carbon; ACF: activated carbon fiber; O-ACF: activated carbon fiber after activation).
4. Conclusions
In this work, the influence factors of O-ACF on the electro-adsorption of Cu (II) in water were investigated. The maximum adsorption capacity of AC, ACF and O-ACF under optimal electro-adsorption conditions and the regeneration of O-ACF in different regeneration fluids were studied. The adsorption test showed that the O-ACF electro-adsorption of Cu (II) in water basically reached equilibrium about 4 h. Moreover, the optimal working conditions of O-ACF electrode electro-adsorption were voltage of 1.0 V, solution pH of about 6, electrode plate spacing of 10 mm. Furthermore, the O-ACF electrode electro-adsorption process fit the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation and the particle diffusion adsorption model. The adsorption was mainly chemisorption, which was jointly controlled by a variety of factors. In addition, it was found in this study that the regeneration effect of O-ACF was the best when 20% HNO3 was used as the regeneration solution. After several adsorption-regeneration cycles, the regeneration rate of O-ACF electrode can still reach about 95% by using the inverted electrode charging method. In summary, O-ACF had good regeneration performance, which greatly reduced its application cost, it has great application prospect in the removal of Cu (II) in industrial wastewater.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su151310078/s1, Figure S1: Electroadsorption device diagram; Table S1: BET image of Carbon felt before and after modified; Text S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.X.; Methodology, Q.C.; Software, Z.X. and J.G.; Validation, Z.X., X.Z., J.G., Z.H. and H.F; Formal analysis, Z.X., Z.H. and Q.C.; Investigation, Z.H.; Resources, J.G. and H.F.; Data curation, X.Z.; Writing—original draft, Z.X. and X.Z.; Writing—review & editing, Z.X.; Supervision, Q.C.; Project administration, Q.C.; Funding acquisition, Q.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41877041; 42077051) and Taishan Scholars Young Experts of Shandong Province (TSQN201812086).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Bani-Melhem, K.; Qtaishat, M.R.; Alkasrawi, M. Heavy metal ions removal from metal plating wastewater using electrocoagulation: Kinetic study and process performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Pang, H.; Zhang, R.; Song, W.; Fu, D.; Wang, X. Boron nitride-based materials for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Cai, Z.; Fu, J.; Sun, X.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, W. Synergistic adsorption of Cu (II) and photocatalytic degradation of phenanthrene by a jaboticaba-like TiO2/titanate nanotube composite: An experimental and theoretical study. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shang, J.; Dou, B.; Lan, J.; Zhang, C.; Zou, R.; Lin, S. CO2-responsive functional cotton fibers decorated with Ag nanoparticles for “smart” selective and enhanced dye adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, P.; Zha, X.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y. Overview assessment of risk evaluation and treatment technologies for heavy metal pollution of water and soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liang, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Geng, Z.; Xu, C. A cellulose/bentonite grafted polyacrylic acid hydrogel for highly-efficient removal of Cd (II). J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 51, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Wang, X. Metal–organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Wang, X. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qian, G. Cu (II) removal from aqueous solution by Spartina alterniflora derived biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Sun, F.; Han, Z.; Han, F.; He, J.; Ou, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, X. Graphene oxide encapsulated polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate hydrogel microspheres for Cu (II) and U (VI) removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Xia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ai, Z.; Yin, W.; Xia, M.; Yue, Q. Ion-imprinted mesoporous silica/magnetic graphene oxide composites functionalized with Schiff-base for selective Cu (II) capture and simultaneously being transformed as a robust heterogeneous catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.S.; Imtiaz, M.; Zhu, J.; Yousaf, B.; Hussain, M.; Ali, L.; Hu, H. Immobilization of Pb and Cu by organic and inorganic amendments in contaminated soil. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Si, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, B.; Gao, X. Efficient removal of Tetracycline-Cu complexes from water by electrocoagulation technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, K.P.; Squitti, R. Copper imbalance in Alzheimer’s disease: Convergence of the chemistry and the clinic. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 397, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. A facile synthesis of Cu–Ni bimetallic nanoparticle supported organo functionalized graphene oxide as a catalyst for selective hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol and cinnamaldehyde. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2869–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Cao, Y.; Peng, W.; Miao, Y.; Su, S.; Fan, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Song, X. Highly efficient and selective recovery of Cu (II) from wastewater via ion flotation with amidoxime functionalized graphene oxide as nano collector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadwaj, G.B.B.; Oyetade, O.A.; Rana, S.; Martincigh, B.S.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Nyamori, V.O. Facile synthesis of three-dimensional Mg–Al layered double hydroxide/partially reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for the effective removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17290–17305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Du, X.; Hao, X.; Li, S.; An, X.; Liu, M.; Guan, G. An electrochemically-switched BPEI-CQD/PPy/PSS membrane for selective separation of dilute copper ions from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. Recovering REEs from NdFeB wastes with high purity and efficiency by leaching and selective precipitation process with modified agents. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z. Comprehensive review about methane adsorption in shale nanoporous media. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 8456–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Nguyen, T.B.; Singhania, R.R.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Adsorption of copper (II) in aqueous solution using biochars derived from Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Lv, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile-based lace nanostructures and their Cu (II) adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J. Electro-adsorption characteristics and mechanism of Sr2+ ions by capacitive deionization and CFD analysis study. Prog. Nucl. Energ. 2021, 133, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Yan, T.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Capacitive removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater via an electro-adsorption and electro-reaction coupling process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Meng, Z.; Yan, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, B.; Cai, X.; Qiao, K. Precise control of ultramicropore structure of activated carbon fiber for the application of Cu (II) adsorption/electro-adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Lei, R.; Weng, X.; Yan, C.; Fu, J.; Wei, G.; Wang, H. Uranium capture by a layered 2D/2D niobium phosphate/holey graphene architecture via an electro-adsorption and electrocatalytic reduction coupling process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Yang, Z.; Kang, F.; Inagaki, M. Carbon electrodes for capacitive deionization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 470–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Ma, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, M. A flow-through electro-Fenton process using modified activated carbon fiber cathode for orange II removal. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi, R.; Lelifajri, L.; Iqbal, M.; Fathurrahmi, F.; Jalaluddin, J.; Sembiring, R.; Farida, M.; Iqhrammullah, M. Preparation, characterization and adsorption study of PEDGE-cross-linked magnetic chitosan (PEDGE-MCh) microspheres for Cd2+ Removal. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 48, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiful; Riana, U.; Ramli, M.; Iqrammullah, M.; Raharjo, Y.; Wibisono, Y. Development of Chitosan/Rice Husk-Based Silica Composite Membranes for Biodiesel Purification. Membranes 2022, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqhrammullah, M.; Suyanto, H.; Pardede Rahmi, M.; Karnadi, I.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Chiari, W.; Abdulmadjid, S.N. Cellulose acetate-polyurethane film adsorbent with analyte enrichment for in-situ detection and analysis of aqueous Pb using LaserInduced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100516. [Google Scholar]
- Öter, Ç.; Selçuk Zorer, Ö. Adsorption behaviours of Th (IV) and U (VI) using nitric acid (HNO3) modified activated carbon: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 1950–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Shi, J.X.; Langrish, T.A. Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution using activated carbon modified with nitric acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Khaleque, M.A.; Shiekh, M.S. Treatment of cop per(II) containing wastewater by a newly developed ligand based facial conjugate materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, J. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Co (II) from aqueous solution using lignosulfonate/chitosan adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.X.; Song, B.; Peng, P.; Jiao, G.J.; Yan, X.; She, D. Preparation of three-dimensional honeycomb carbon materials and their adsorption of Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 367, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ding, W.; Zhang, H.; Peng, P.; Peng, F.; Geng, Z.; She, D.; Li, Y. A novel lignin-based hierarchical porous carbon for efficient and selective removal of Cr (VI) from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, L.; Liang, H.; Ren, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, Q.; Geng, Z.; Xu, C. Efficient removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R from water by a cellulose-based activated carbon. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Ji, H.; Xu, T.; Pan, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, D. Simultaneous adsorption of uranium (VI) and 2-chlorophenol by activated carbon fiber supported/modified titanate nanotubes (TNTs/ACF): Effectiveness and synergistic effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, S.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, H. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Pb (II) onto diethylenetriamine-bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, D.L.; He, H.; Lin, R.; Zuo, P.L. Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of Cu (II) ions on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. 2013, 23, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.R.; Ammar, N.S.; Ibrahim, H.S. Adsorption/desorption of Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) using chemically modified orange peel: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, L.V.A.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption of Cu (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) from aqueous single metal solutions by succinylated mercerized cellulose modified with triethylenetetramine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Electro-adsorption of Cs(I) ions from aqueous solution by capacitive deionization using ACC/MoO3 composite electrode. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.X.; Sun, R.R.; Song, B.; Sun, Q.Q.; Peng, P.; She, D. Preparation of nitrogen-doped porous carbon material by a hydrothermal-activation two-step method and its high-efficiency adsorption of Cr (VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.A.; Khan, A.M.; Manea, Y.K.; Salem, M.A.; Shahadat, M. Selective adsorption and ultrafast fluorescent detection of Cr (VI) in wastewater using neodymium doped polyaniline supported layered double hydroxide nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Guo, Y.N.; He, D.L.; Qu, W.; Tang, Y.N.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, R.L. A novel graphene oxide-dicationic ionic liquid composite for Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.X.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhao, P.Y.; Zhao, X.K.; Sun, H.W.; Geng, Z.C.; She, D. Synthesis of a novel three-dimensional porous carbon material and its highly selective Cr (VI) removal in wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ansari, K.B.; Danish, M.; Khatoon, A.; Rao, R.A.K.; Zaidi, S.; Aftab, R.A. A comprehensive investigation of external mass transfer and intraparticle diffusion for batch and continuous adsorption of heavy metals using pore volume and surface diffusion model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Ge, R.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X. Treatment of low-level Cu (II) wastewater and regeneration through a novel capacitive deionization-electrodeionization (CDI-EDI) technology. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Nimbhorkar, S.K. A comprehensive review on the synthesis, performance, modifications, and regeneration of activated carbon for the adsorptive removal of various water pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.C.; Wang, M.L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, W.J.; Han, G. Enhanced adsorption of sulfide and xanthate on smithsonite surfaces by lead activation and implications for flotation intensification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, W.; Wen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Han, G. Flotation of copper oxide minerals: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).