Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Water Usage in Typical Industrial Enterprises
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methodology
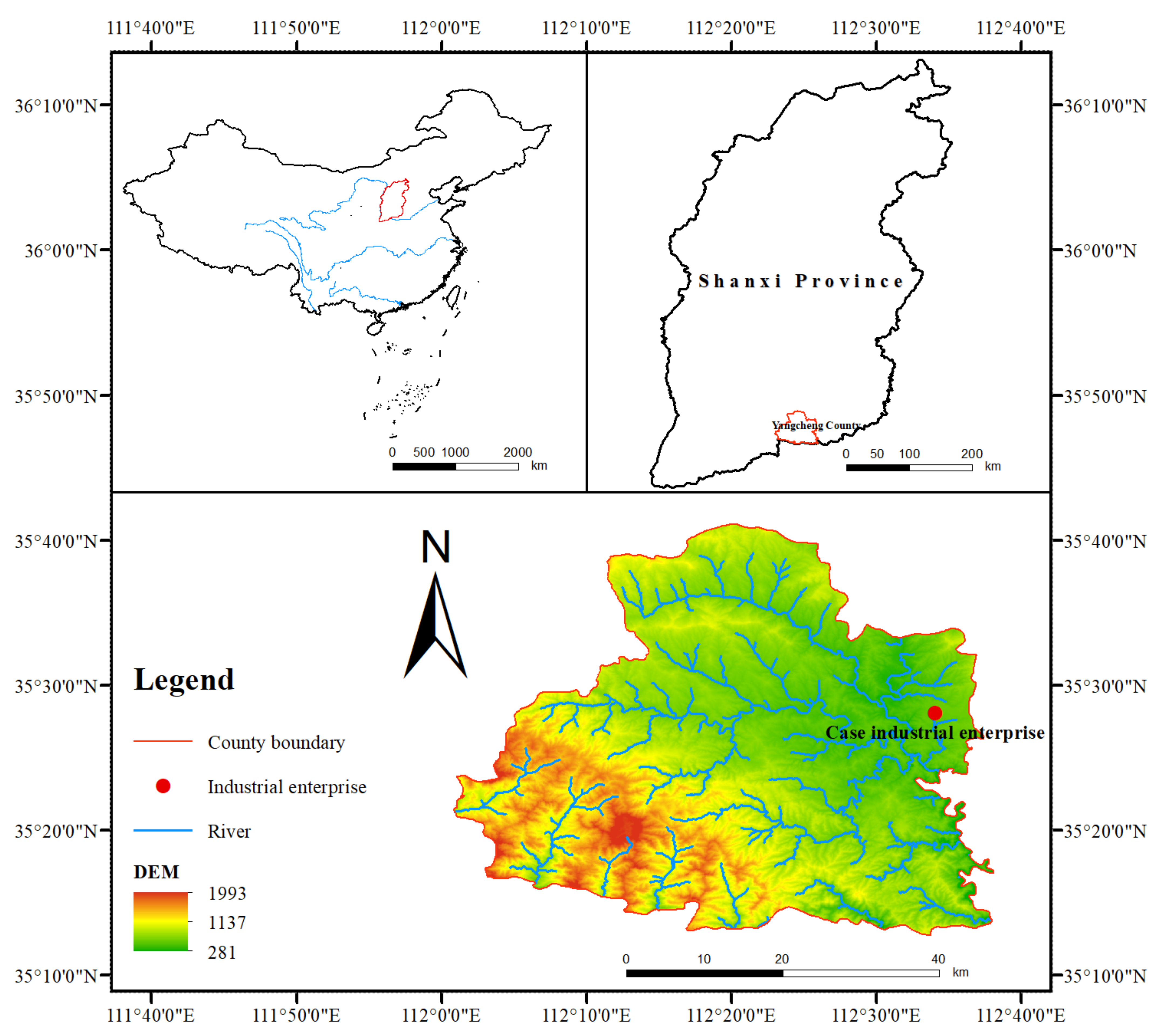
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Framework
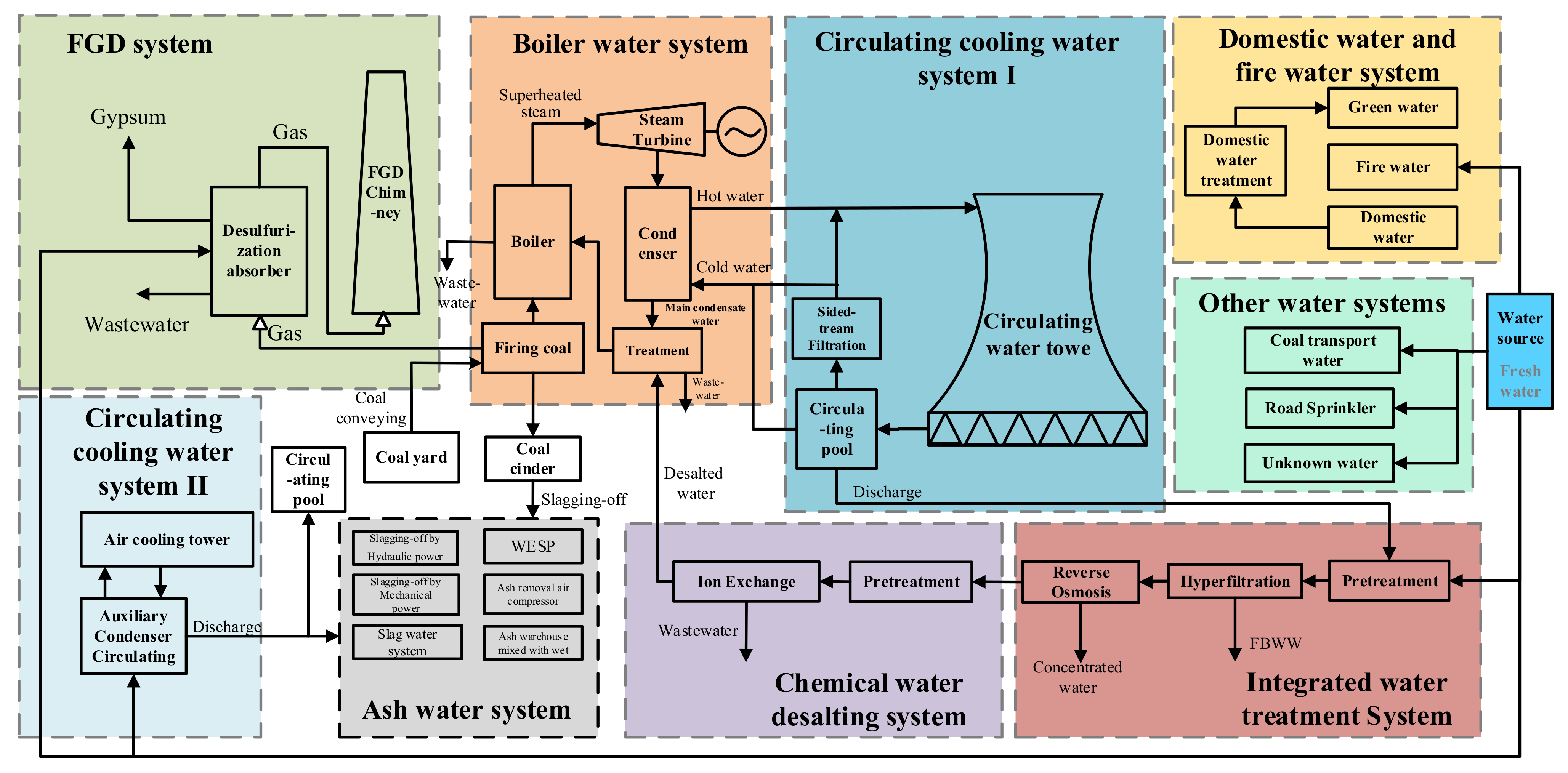
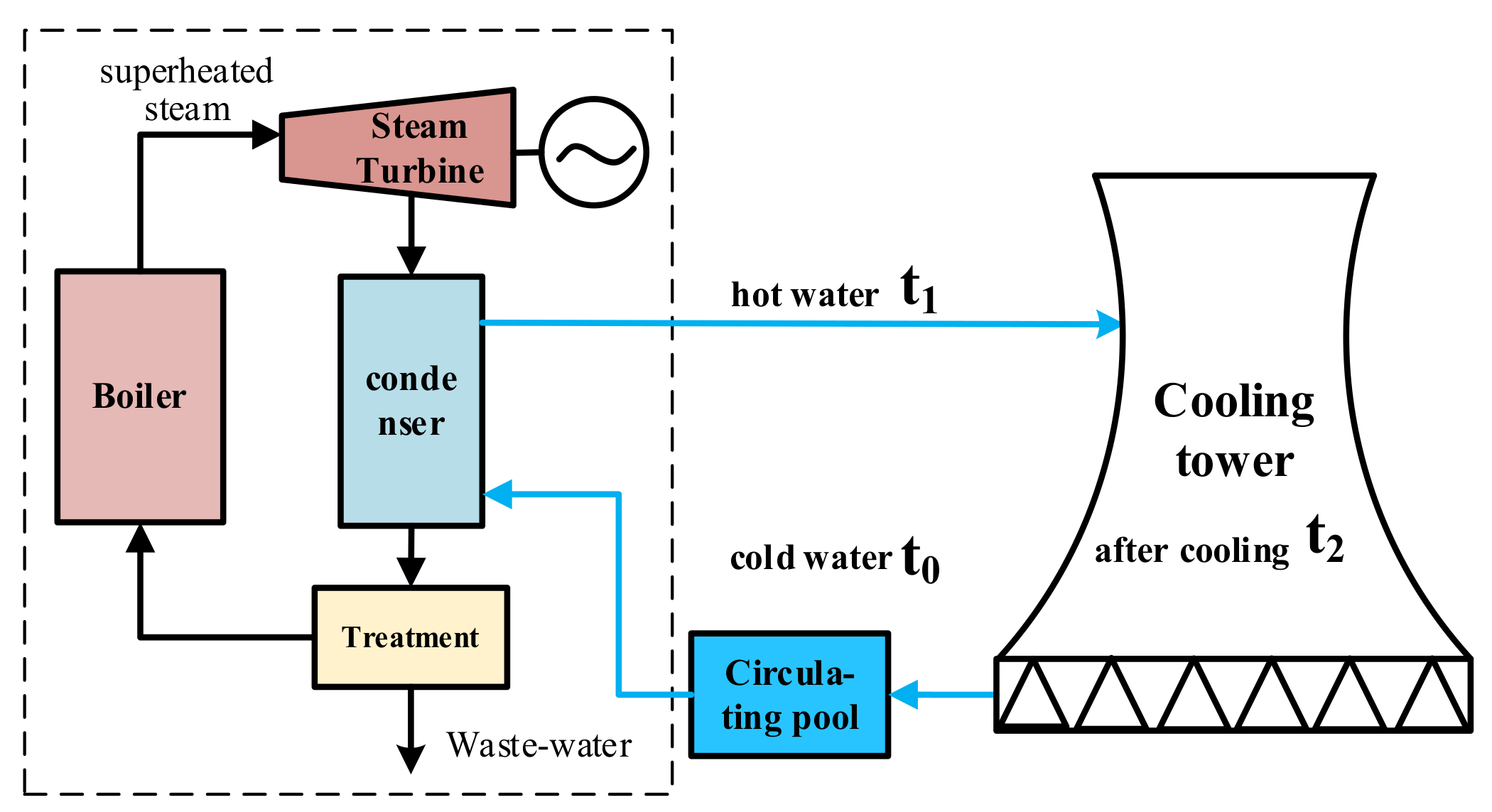
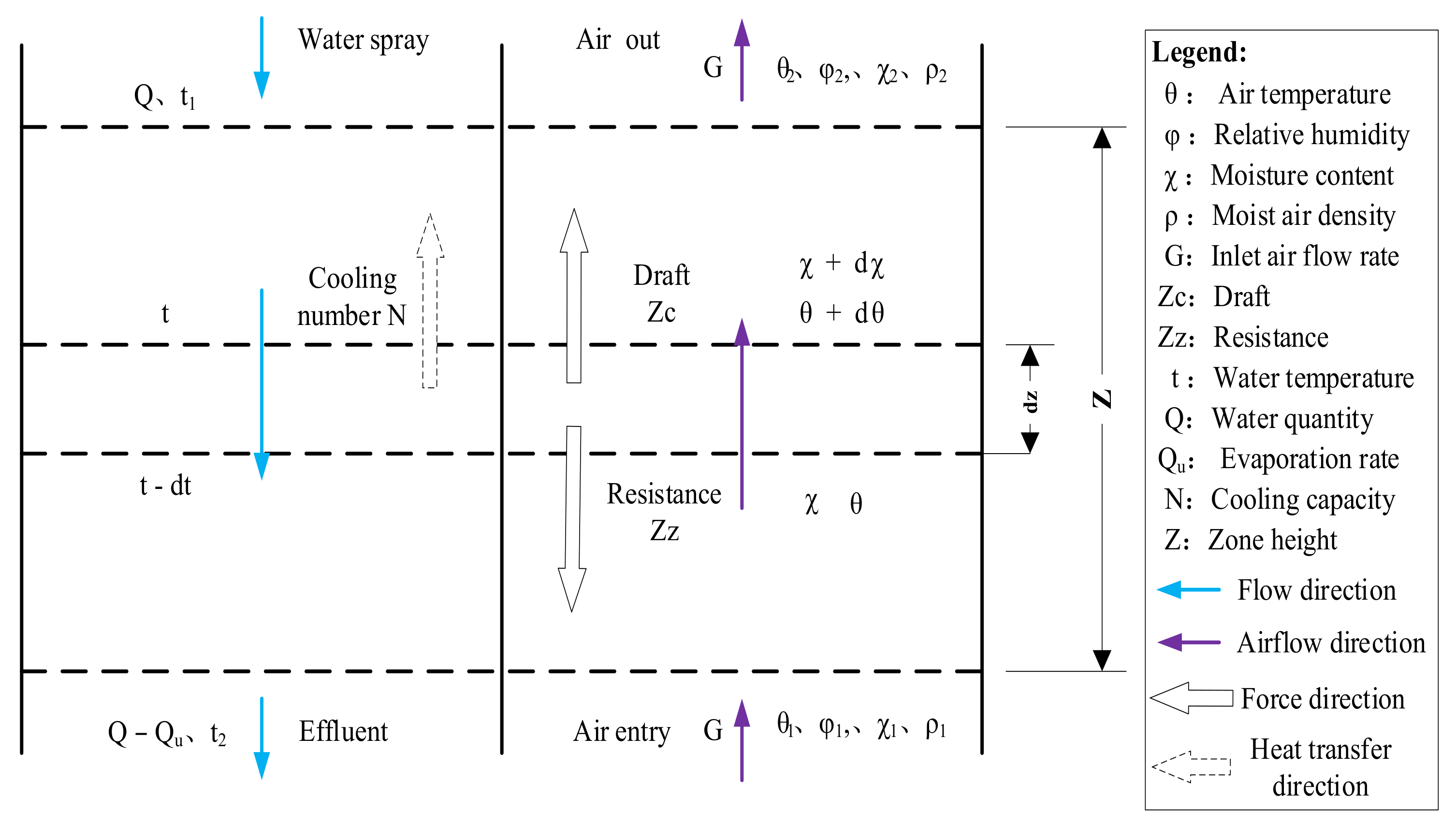
2.3. Simulation of Primary Water Usages
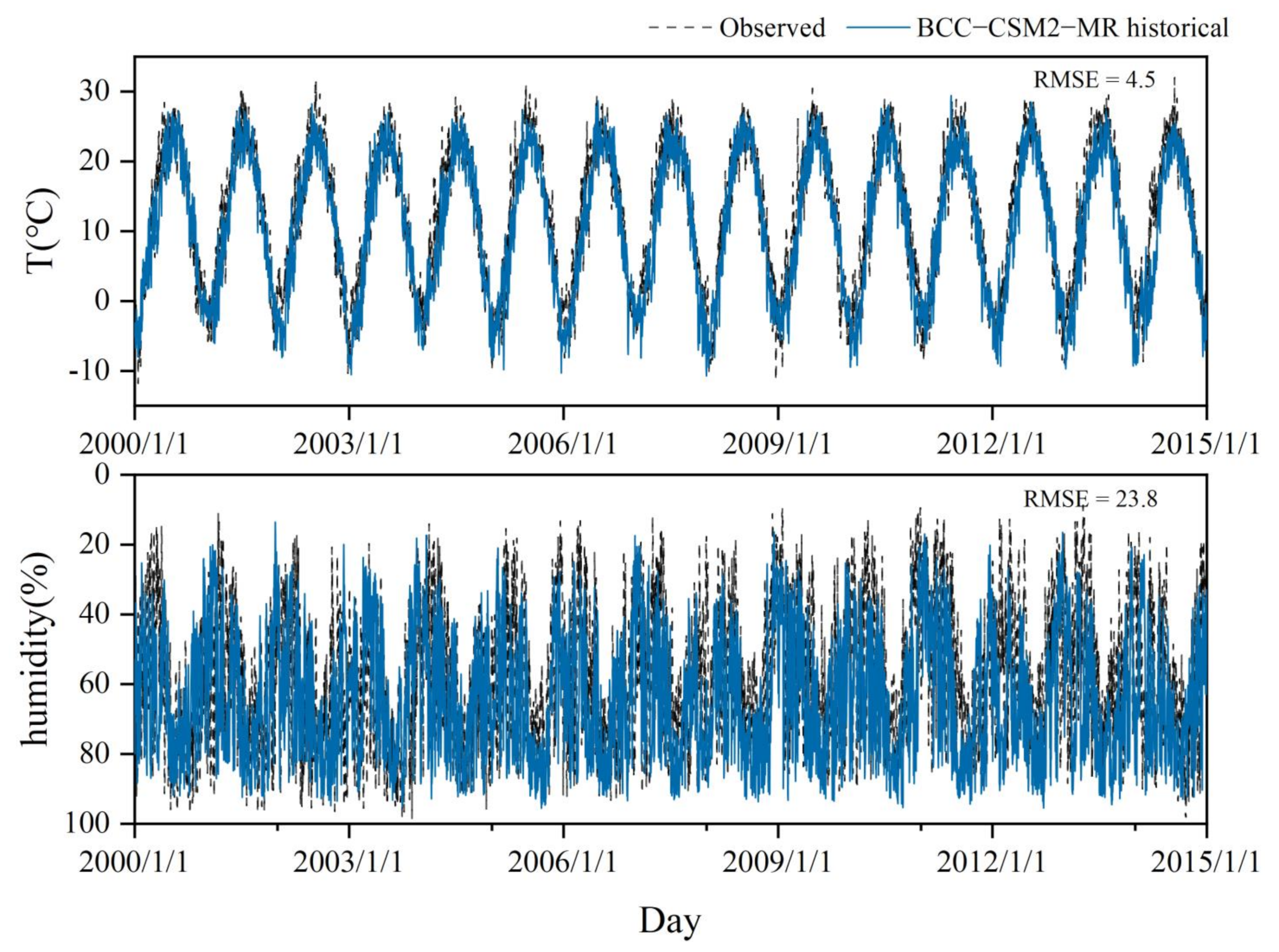
2.4. Climate Change Impact Research Methods
3. Results
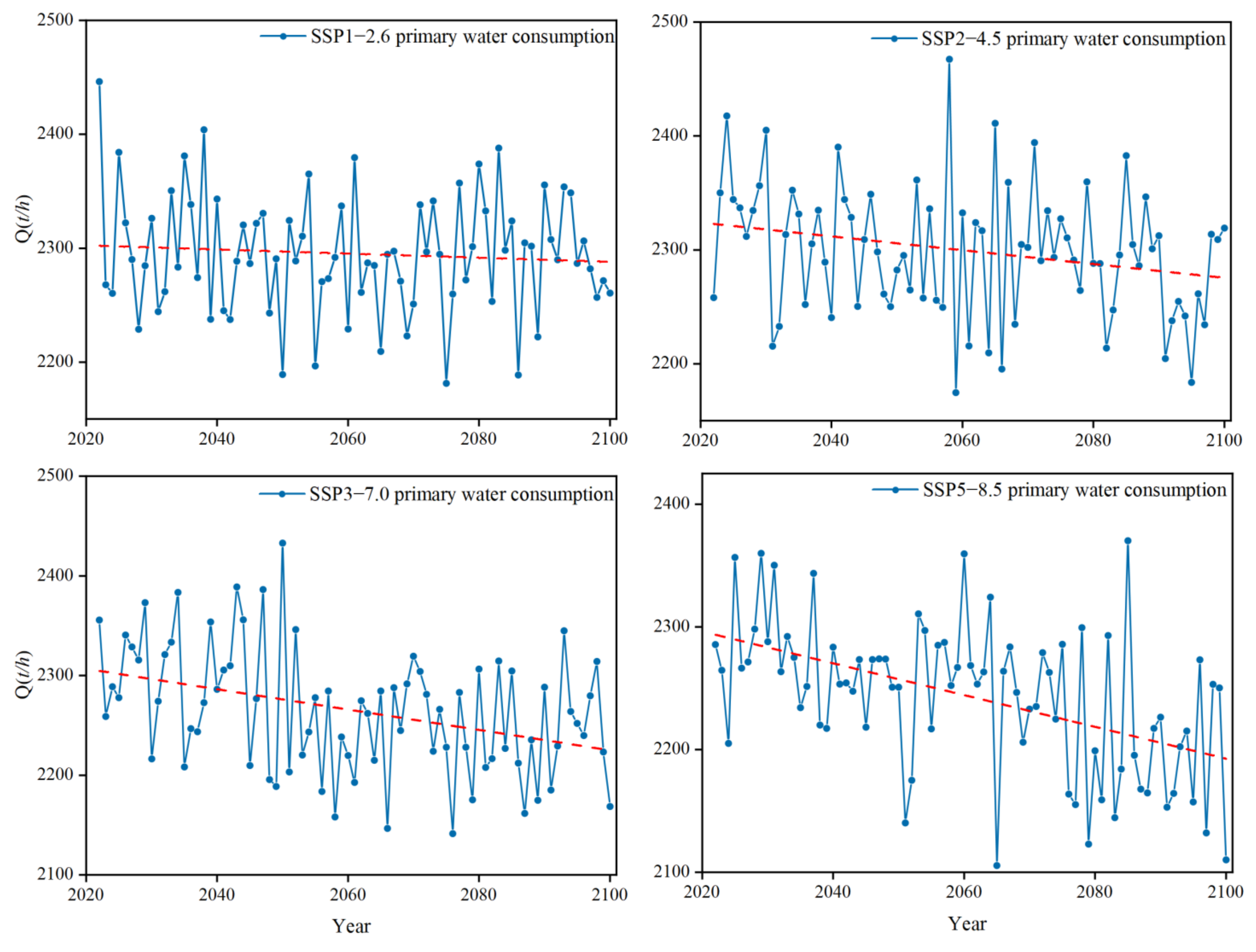
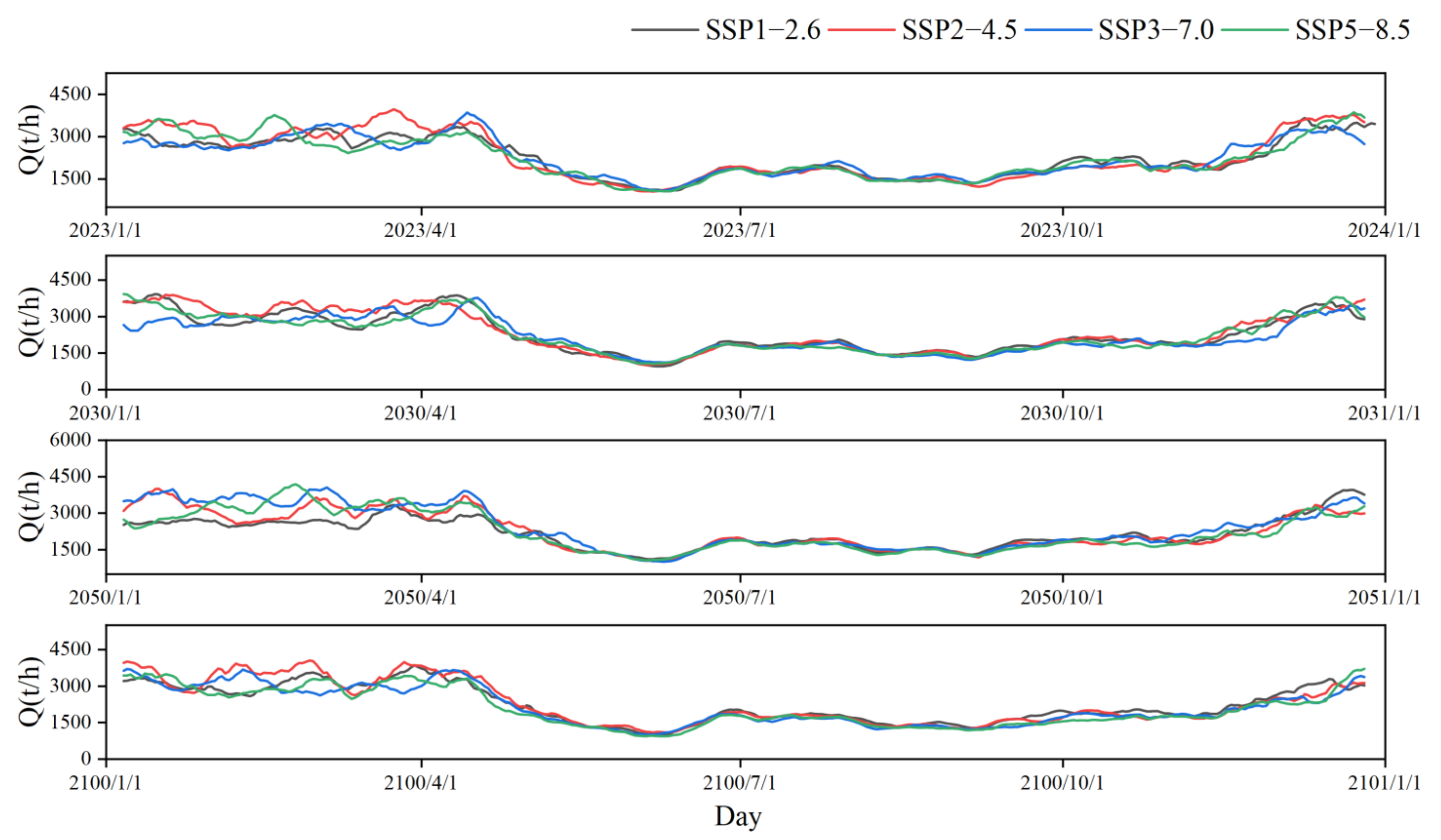
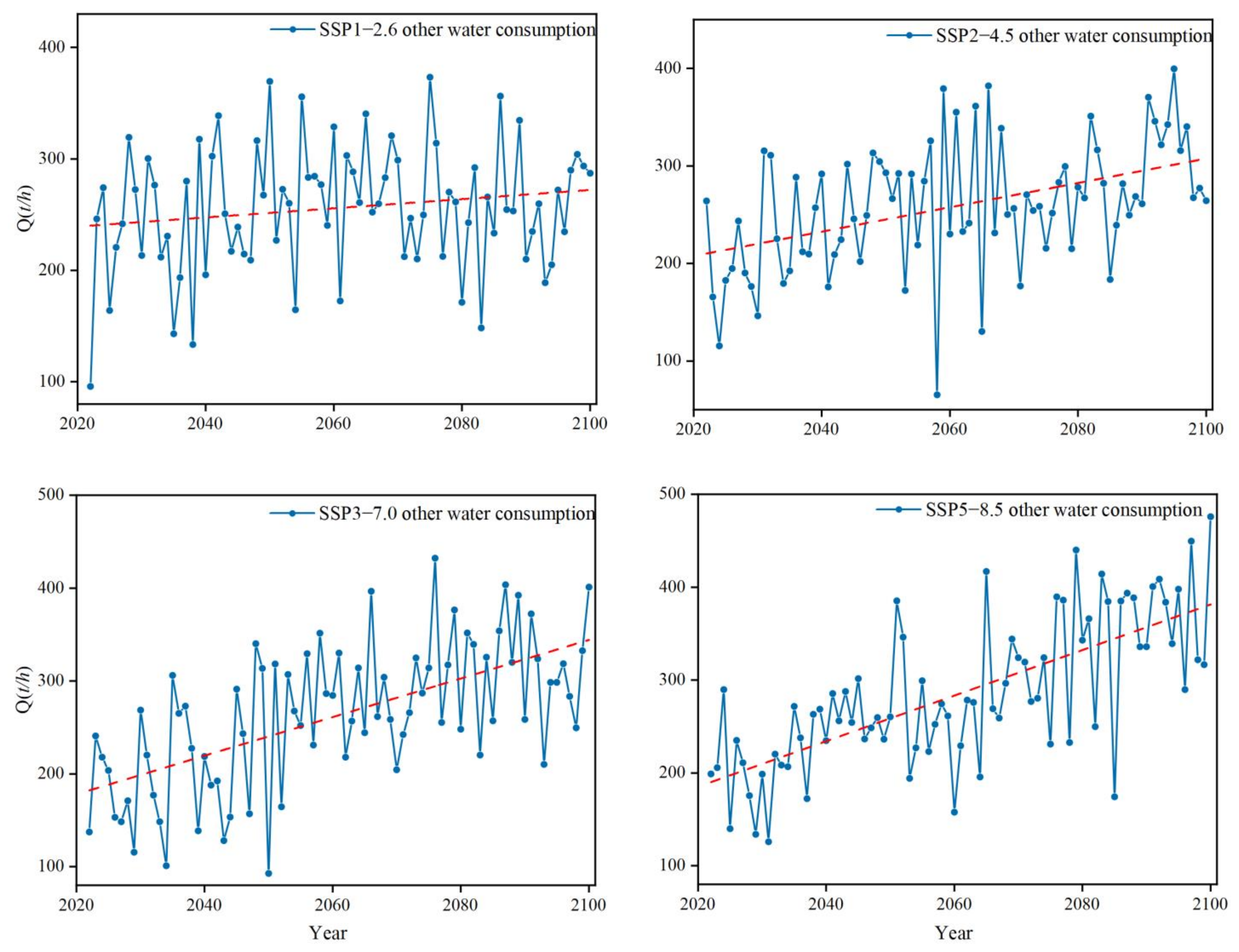
3.1. Impact of Climate Change on Water Consumption
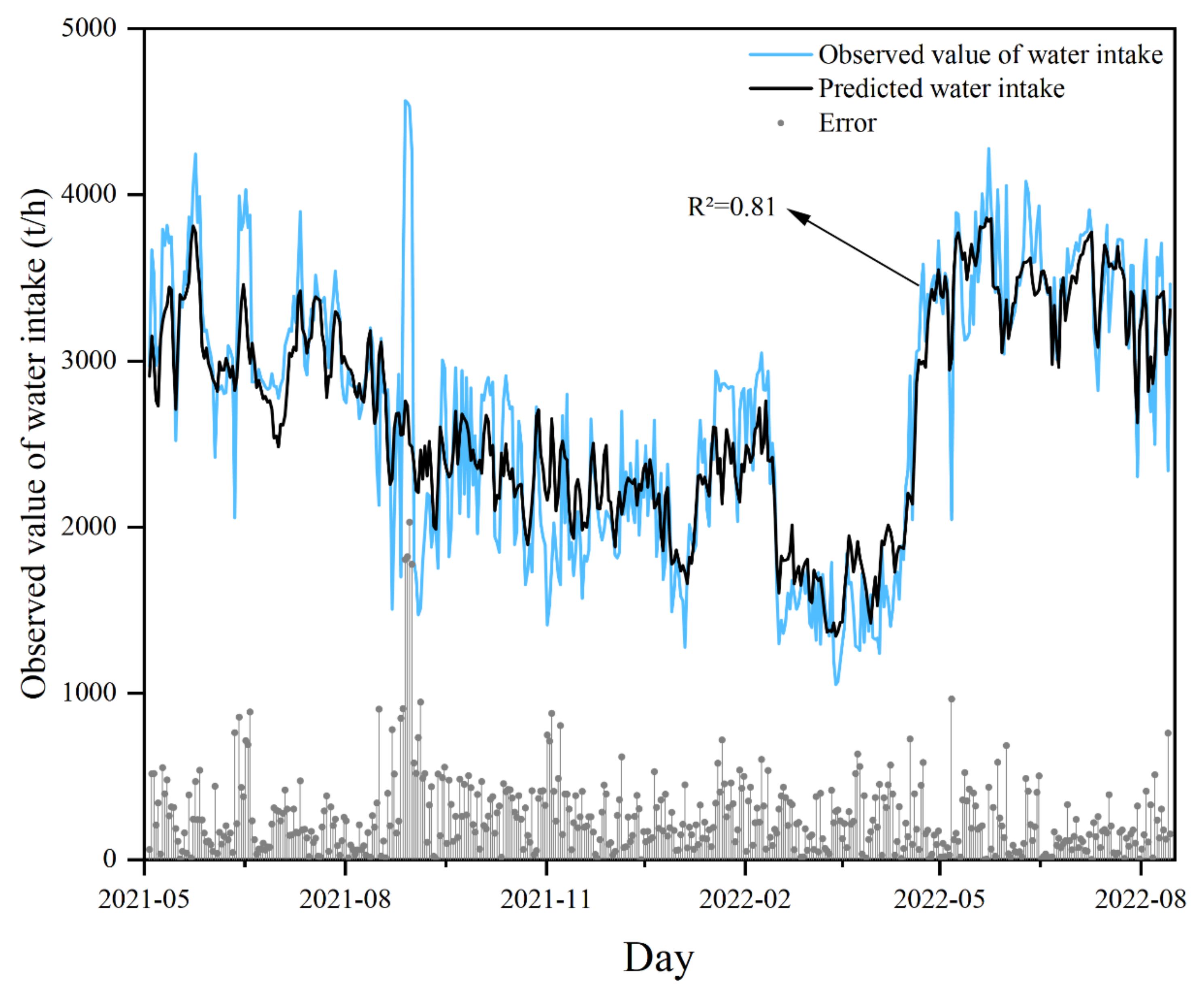
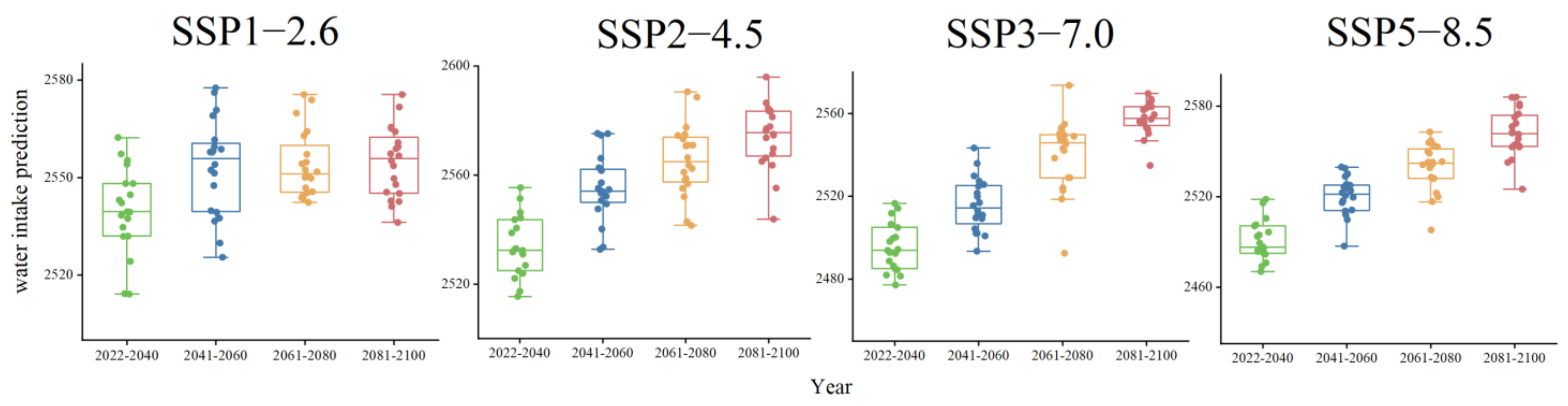
3.2. Impact of Climate Change on Water Intake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.X.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, X. An Empirical Research on Influence Factors of Industrial Water Use. Water 2019, 11, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggen, B.; Boussu, K.; De Vreese, I.; Van Baelen, G.; Willemse, F.; Goedeme, D.; Colen, W. Industrial Process Water Recycling: Principles and Examples. Environ. Prog. 2005, 24, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Du, Z.; Cao, H.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, W.; Tang, S.; Wang, P. Development of a novel mobile industrial-scale fluidized adsorption process for emergency treatment of water polluted by aniline: CFD simulation and experiments. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q. Simulation and prediction of electrooxidation removal of ammonia and its application in industrial wastewater effluent. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echi, S.; Bouabidi, A.; Driss, Z.; Abid, M.S. CFD simulation and optimization of industrial boiler. Energy 2019, 169, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, E.; Shafiei, S.; Abdollahnezhad, A. Reducing water consumption of an industrial plant cooling unit using hybrid cooling tower. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mujtaba, I.M. Modeling and simulation of VMD desalination process by ANN. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 84, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdalski, J.; Dróżdż, B.; Piechocki, J.; Gaworski, M.; Zander, Z.; Marjanowski, J. Determinants of water consumption in the dairy industry. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Liang, L.; Zhou, K.L.; Yang, M.; Wei, Y.Q. Water-energy nexus: The origin, development and prospect. Ecol. Model. 2020, 419, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Tebaldi, C.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Eyring, V.; Friedlingstein, P.; Hurtt, G.; Knutti, R.; Kriegler, E.; Lamarque, J.F.; Lowe, J.; et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3461–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ao, T.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Chen, T.; Wang, B.X. Evaluating the impacts of climate change on industrial water demand by sector. Clim. Res. 2021, 84, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shahid, S.; Bi, S.H.; Elmahdi, A.; Liao, C.H.; Li, Y.D. Forecasting industrial water demand in Huaihe River Basin due to environmental changes. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2018, 23, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemeš, J.J. Industrial water recycle/reuse. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguniewicz-Zablocka, J.; Klosok-Bazan, I.; Naddeo, V. Water quality and resource management in the dairy industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.W.; Mao, G.Z.; Wang, Y. Operational Water Withdrawal and Consumption Factors for Electricity Generation Technology in China-A Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Sun, F.Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, X.Y. A sensitivity-coefficients method for predicting thermal performance of natural draft wet cooling towers under crosswinds. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 206, 118105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; Yu, B. Numerical simulation of heat transfer performance of an air-cooled steam condenser in a thermal power plant. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 45, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, J.S.; Ma, W.; Gurgenci, H.; Guan, Z.Q.; Wang, P. Water Consumption Comparison Between a Natural Draft Wet Cooling Tower and a Natural Draft Hybrid Cooling TowerAn Annual Simulation for Luoyang Conditions. Heat Transf. Eng. 2017, 38, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Sun, F.Z.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, R.Q. Effect of Thermal Load on Evaporation Loss of Natural Draft Counter-Flow Wet Cooling Towers. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2020, 12, 051019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Gao, S.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y. Effect of cooling water salinity on the cooling performance of natural draft wet cooling tower. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 161, 120257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.J.; Qi, X.N.; Sun, P.; Guo, P.J. New explicit analytical solutions of equations for heat and mass transfer in a cooling tower energy system. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019896147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Sun, F.Z.; Liu, R.Q.; Chen, X.H.; Li, Y. Effect of change factors on evaporation loss based on cold end system in natural draft counter-flow wet cooling towers. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, JTST0015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Xue, K.; Zhang, G.L.; Chen, W.X.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, G.Z. Development and assessment of a novel air/water hybrid cooling system coupling two units for energy and water saving. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102330. [Google Scholar]
- Milosavljevic, N.; Heikkilä, P. A comprehensive approach to cooling tower design. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Wang, M.W.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, S.; He, S.Y.; Zhao, J.F.; Zhan, J.W.; Liu, Z.L.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; et al. Investigation on the cooling performance of mechanical draft dry-wet hybrid cooling tower. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 228, 120473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospolita, J.; Kuczuk, A.; Widera, K.; Buryn, Z.; Cholewa, R.; Drajczyk, A.; Pietrucha, M.; Smejda, R. Water Losses in the Condenser Cooling System at the 905 MWe Power Unit. Energies 2022, 15, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; He, S.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, S. Comparison on cooling performance of pre-cooled natural draft dry cooling towers using nozzles spray and wet medium. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Fang, X. Accuracy of Hourly Water Temperatures in Rivers Calculated from Air Temperatures. Water 2015, 7, 1068–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, P. Status of Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) systems from coal-fired power plants: Overview of the physic-chemical control processes of wet limestone FGDs. Fuel 2015, 144, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Xie, B.; Cheng, Y. Analysis of Carbon Emissions and Emission Reduction from Coal-Fired Power Plants Based on Dual Carbon Targets. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliauskas, G.; Puida, E.; Poškas, R.; Poškas, P. The Influence of Droplet Dispersity on Droplet Vaporization in the High-Temperature Wet Gas Flow in the Case of Combined Heating. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Debeire, K.; Eyring, V.; Fischer, E.; Fyfe, J.; Friedlingstein, P.; Knutti, R.; Lowe, J.; O’Neill, B.; Sanderson, B.; et al. Climate model projections from the Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) of CMIP6. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 253–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yu, R.; Lu, Y.; Jie, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. BCC-CSM2-HR: A high-resolution version of the Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 2977–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.W.; Lu, Y.X.; Fang, Y.J.; Xin, X.G.; Li, L.; Li, W.P.; Jie, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model (BCC-CSM): The main progress from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1573–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, L.F. Using Fractional Order Grey Seasonal Model to Predict the Power Generation in China. Environ. Process. Int. J. 2021, 8, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A Review of Recurrent Neural Networks: LSTM Cells and Network Architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahi, Y.; Dilcan, C.C.; Koksal, D.D.; Gultas, H.T. Reservoir Evaporation Forecasting Based on Climate Change Scenarios Using Artificial Neural Network Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 2607–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhomayoon, Z.; Naghizadeh, F.; Malekpoor, M.; Azar, N.A.; Ball, J.; Milan, S.G. Prediction of evaporation from dam reservoirs under climate change using soft computing techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 27912–27935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.W.; Chen, B.Y.; Shang, Y.P.; Song, M.L. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Low-carbon transformation planning of China’s power energy system under the goal of carbon neutrality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44367–44377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.P.; Fu, Y.H.; Ren, D.F.; Zhang, X.Y. Dynamic changes in provincial exhaust emissions in China in the carbon peak and neutrality setting: Based on the effects of energy consumption and economic growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 5161–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Value | |
| Property parameter | Tower height (m) | 105 |
| Air intake height (m) | 7.8 | |
| Distance from bottom of packing to top of sprinkler (m) | 10.9 | |
| Distance from sprinkler to tower top outlet (m) | 103.75 | |
| Average diameter of tower air inlet (m) | 79.69 | |
| Average diameter of tower outlet (m) | 47.024 | |
| water distribution media surface area (m2) | 4500 | |
| Resistance parameter | ||
| Thermal parameter | ||
| Variable parameter | circulation water flow rate (m3/h) | Tower #1: 42,500, Tower #2: 42,500, Tower #3: 40,000, Tower #4: 41,000, Tower #5: 41,500, Tower #6: 40,500 |
| Parameter | Value |
| thermal efficiency | 0.4 |
| unit quantity of coal flue gas | 6 m3/kg |
| sulfur content percentage in coal | 1.7% |
| inlet flue gas humidity | 20% |
| desulfurization efficiency | 99% |
| Coeff | Generating Load | Water Consumption | Air Temperature | Relative Humidity |
| SSP1–2.6 | 0.7271 | 0.3885 | −0.0094 | −0.0088 |
| SSP2–4.5 | 0.7418 | 0.3042 | −0.0074 | −0.0043 |
| SSP3–7.0 | 0.7293 | 0.3075 | 0.0031 | −0.0073 |
| SSP5–8.5 | 0.7158 | 0.3133 | −0.0015 | −0.0035 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, L. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Water Usage in Typical Industrial Enterprises. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310141
Liu J, Zhou Y, Chen L, Wang L. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Water Usage in Typical Industrial Enterprises. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jun, Yuyan Zhou, Lihua Chen, and Lichuan Wang. 2023. "Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Water Usage in Typical Industrial Enterprises" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310141
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhou, Y., Chen, L., & Wang, L. (2023). Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Water Usage in Typical Industrial Enterprises. Sustainability, 15(13), 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310141







