An Experimental Study of Operating Range, Combustion and Emission Characteristics in an RCCI Engine Fueled with Iso-Propanol/n-Heptane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
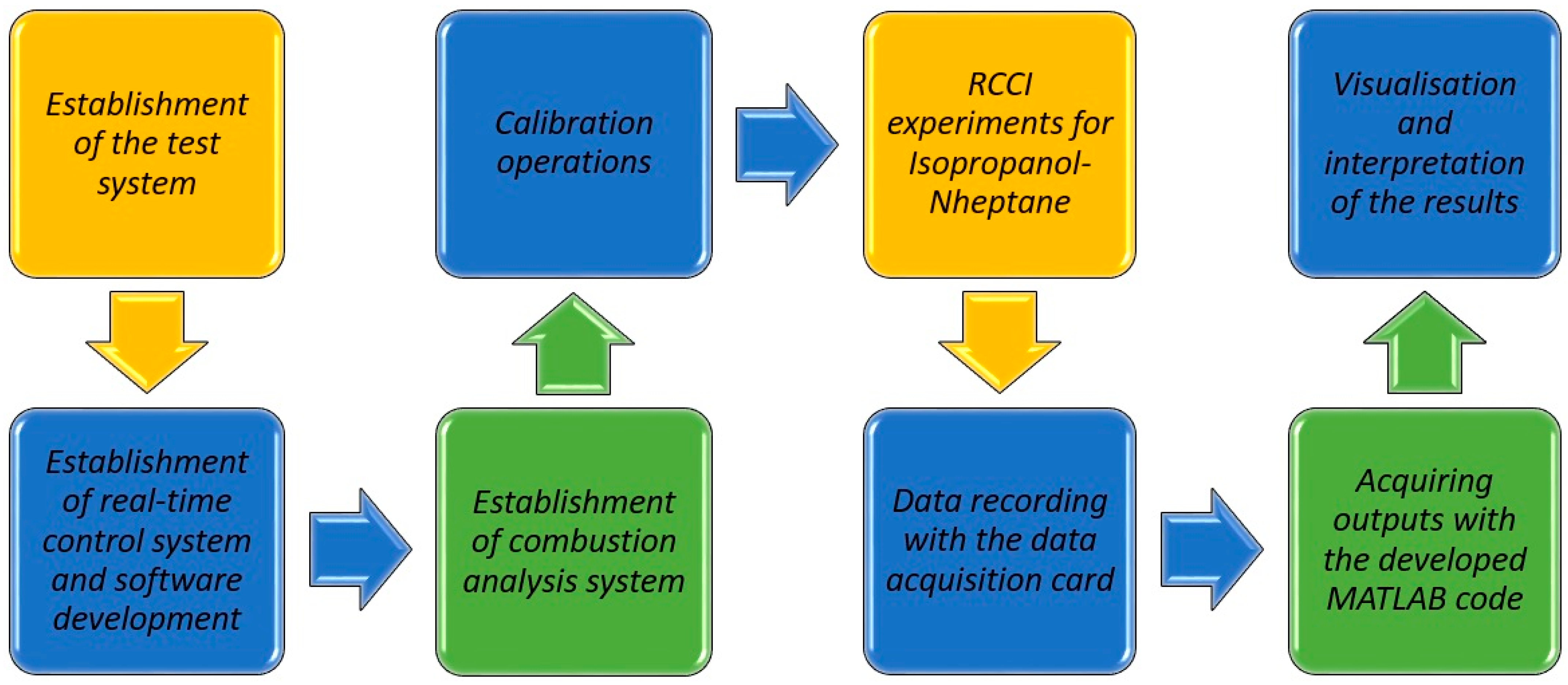
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
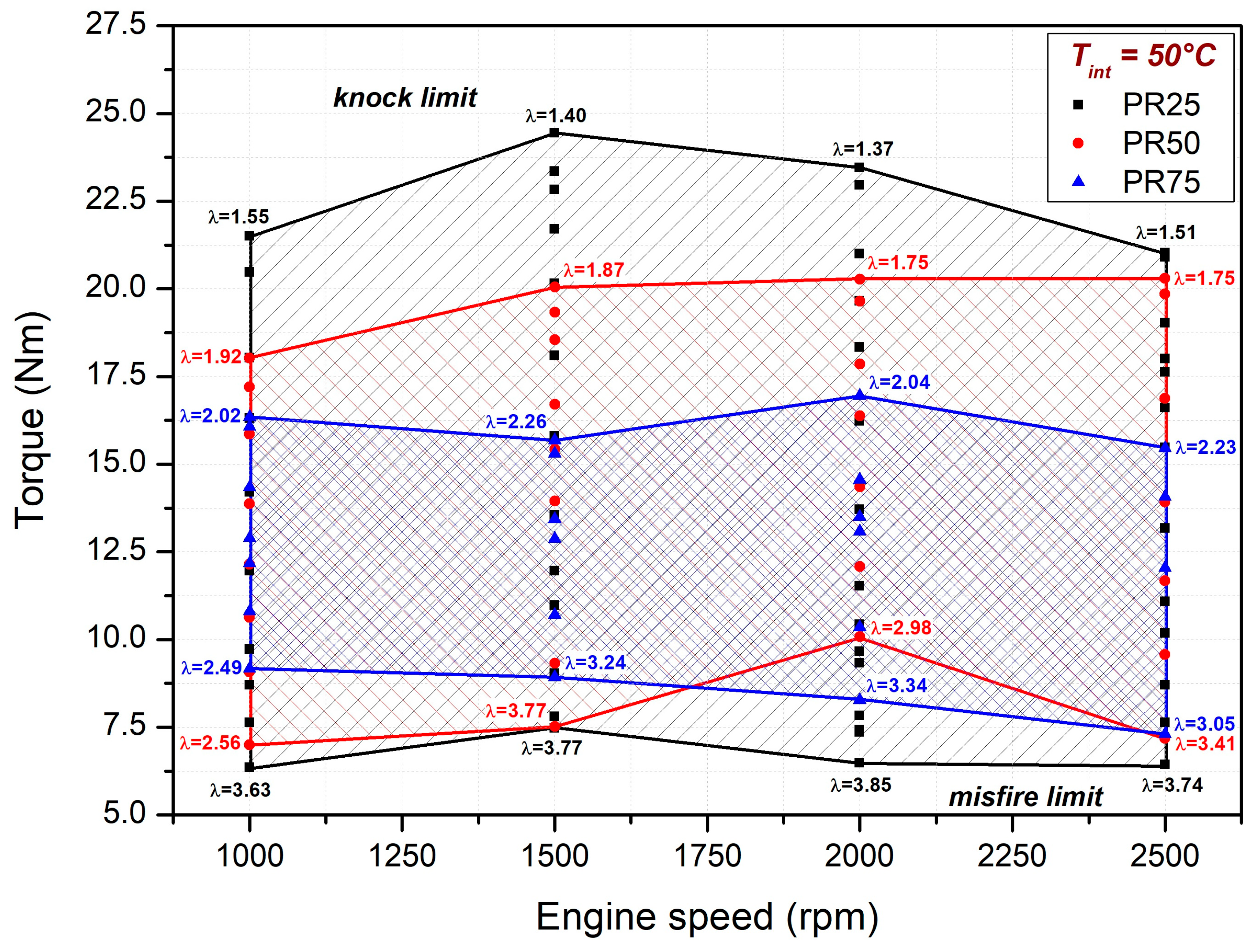
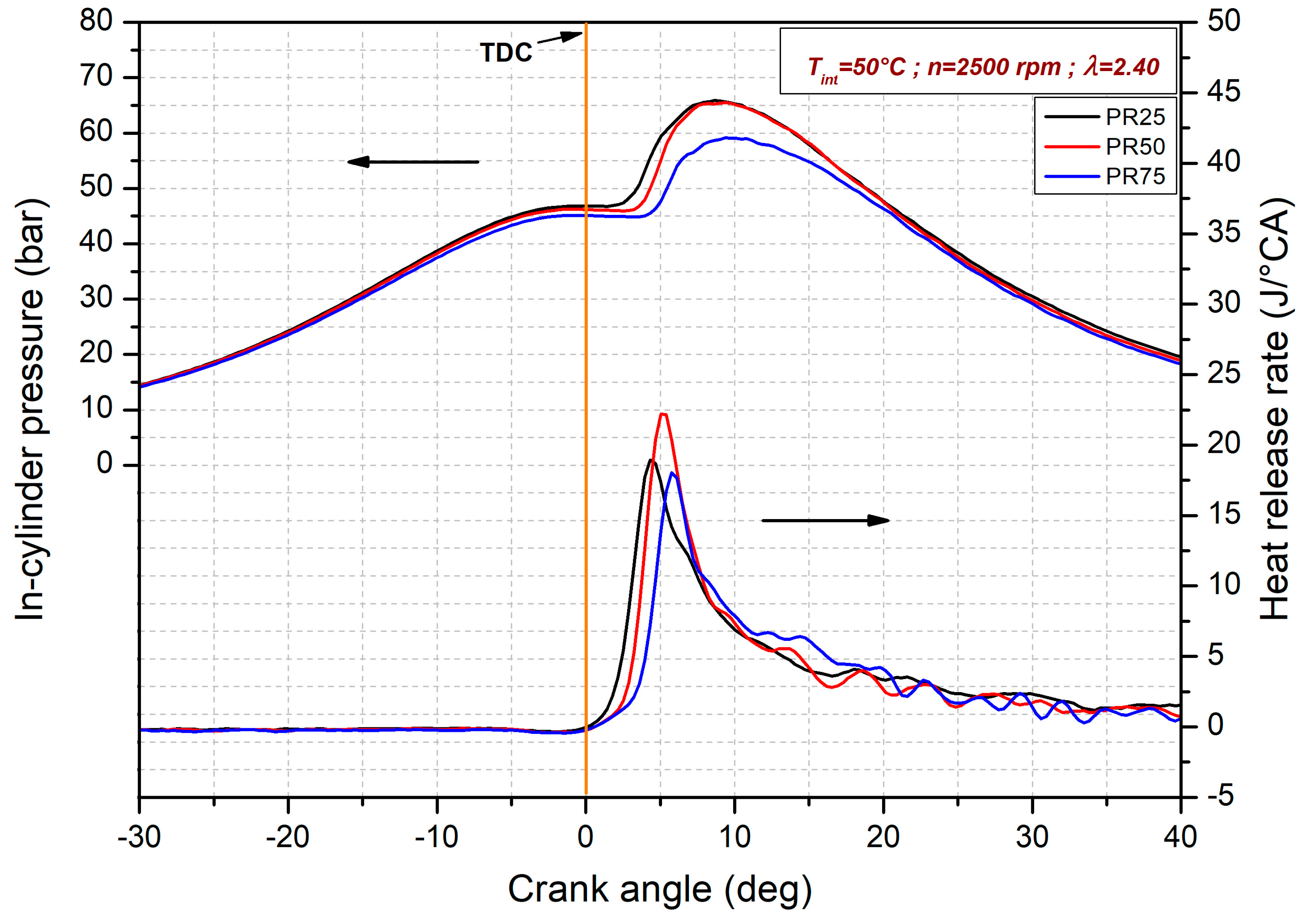
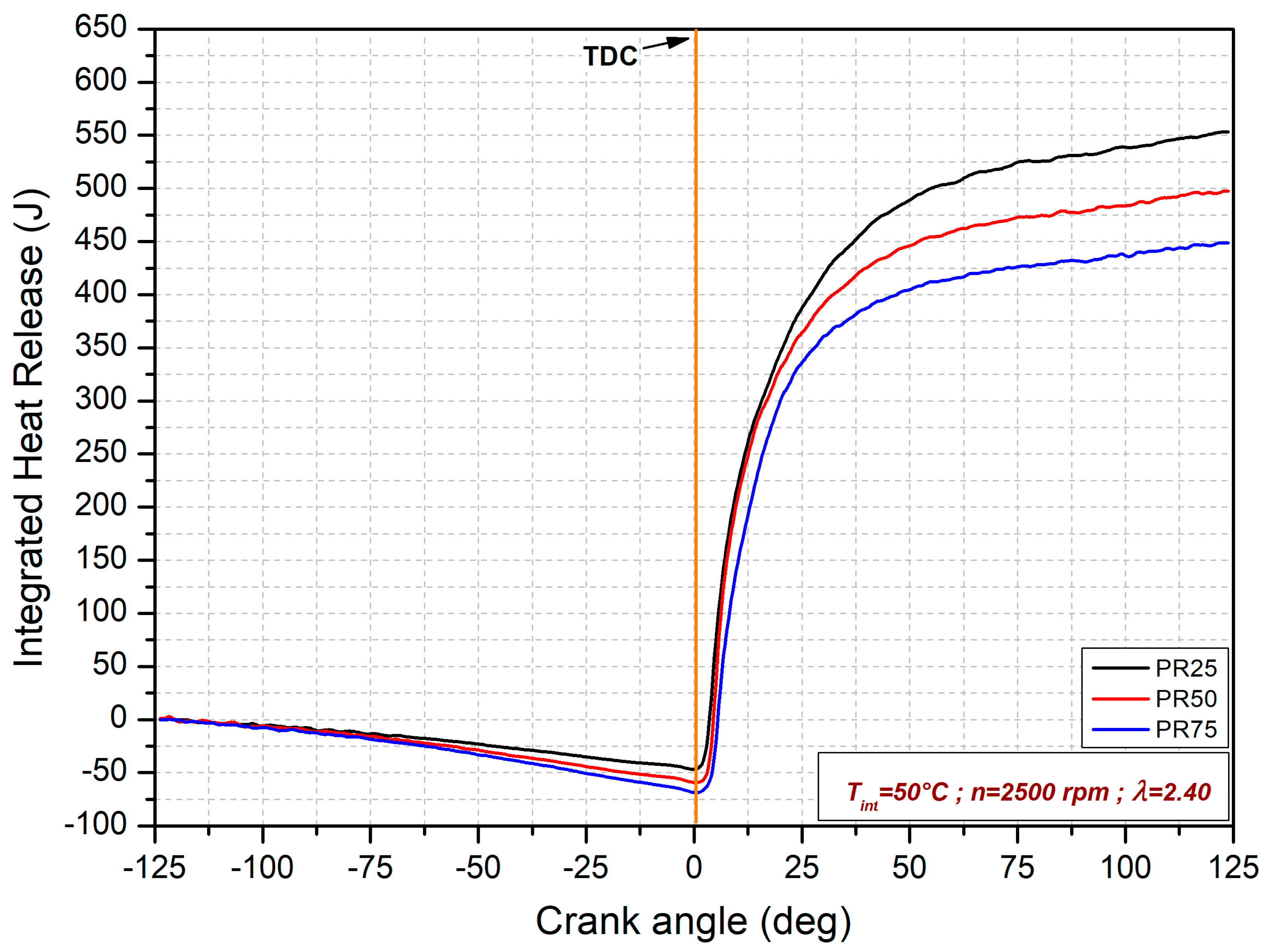
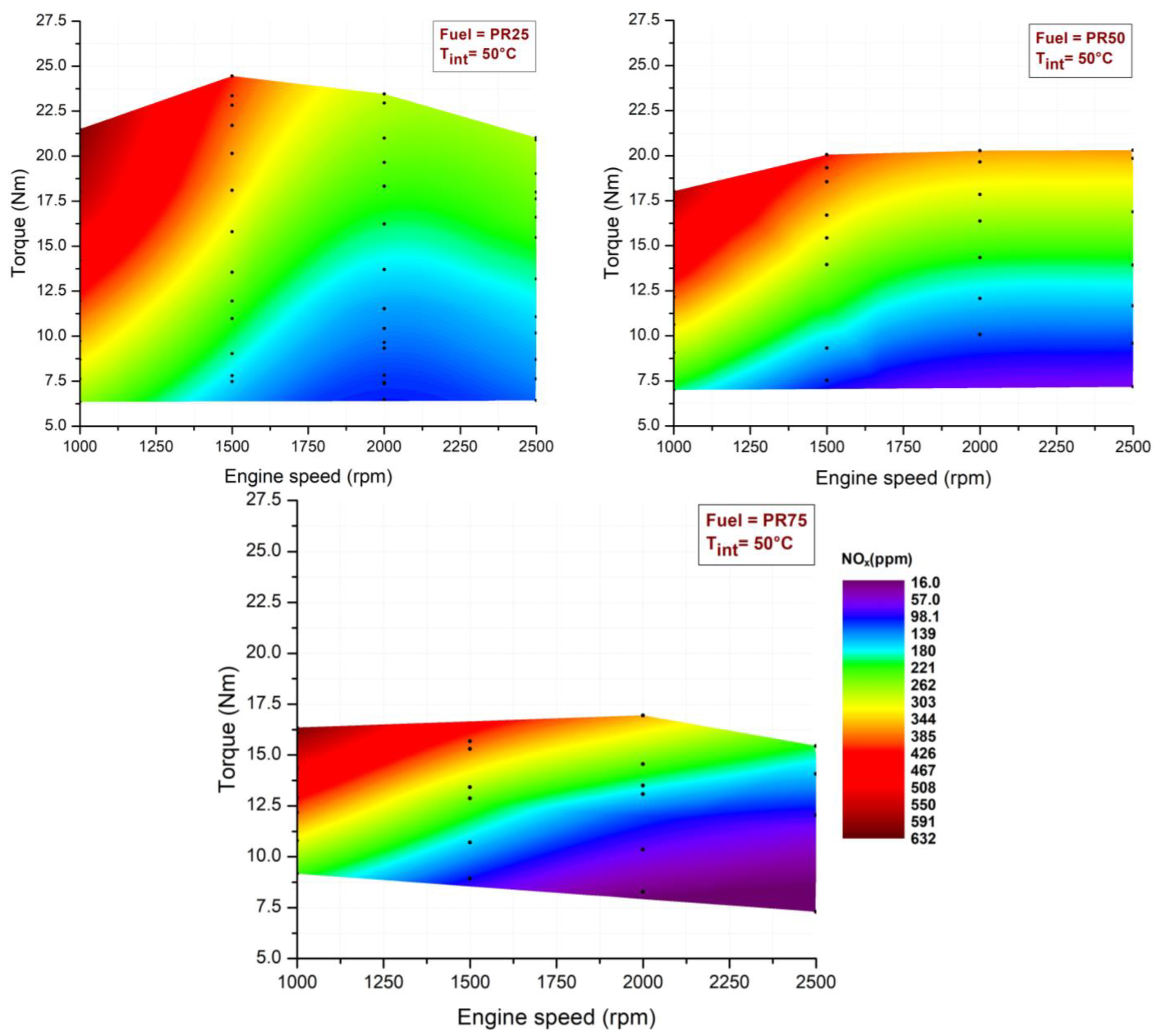
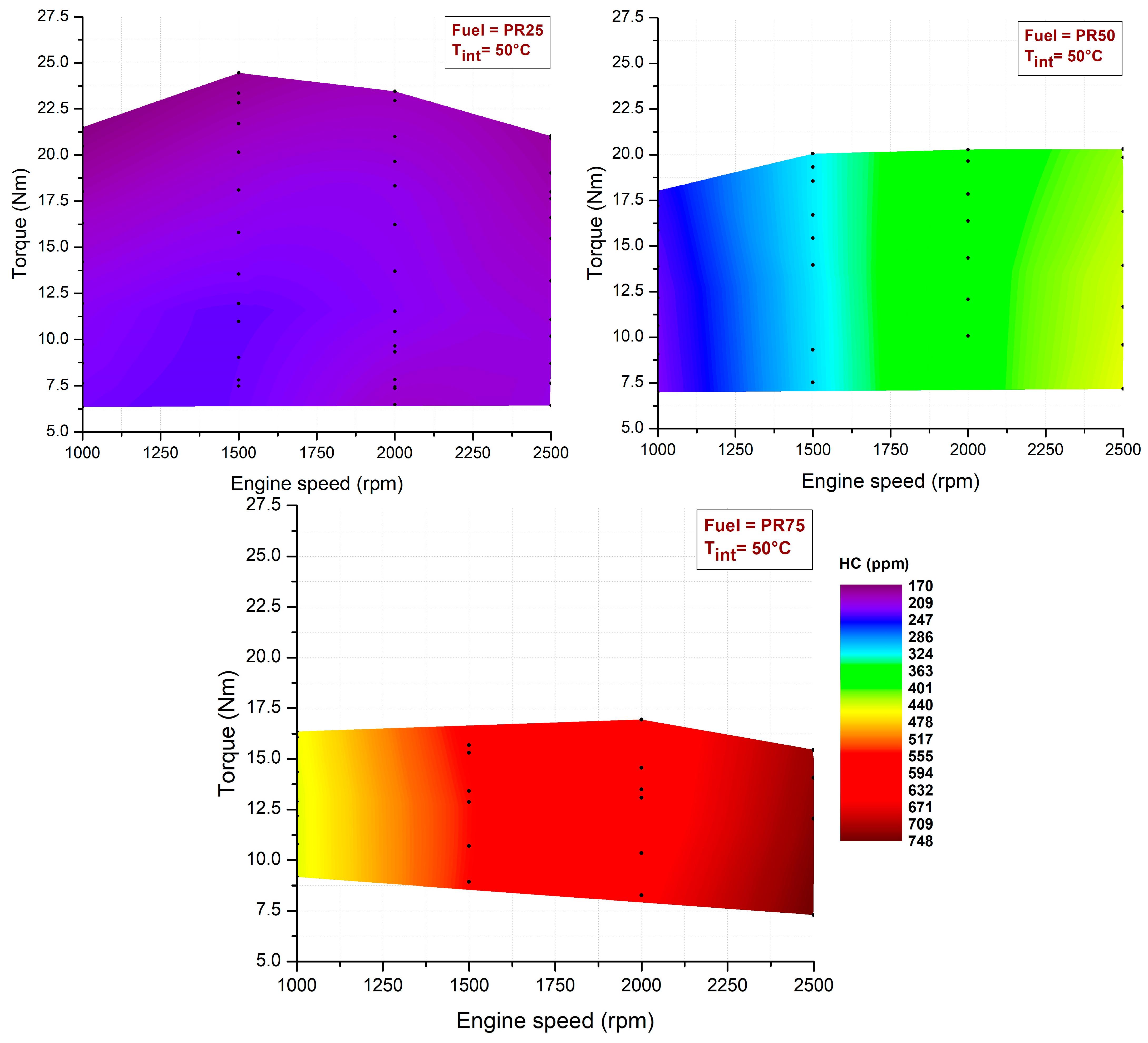
3.1. Premixed Ratio Effects
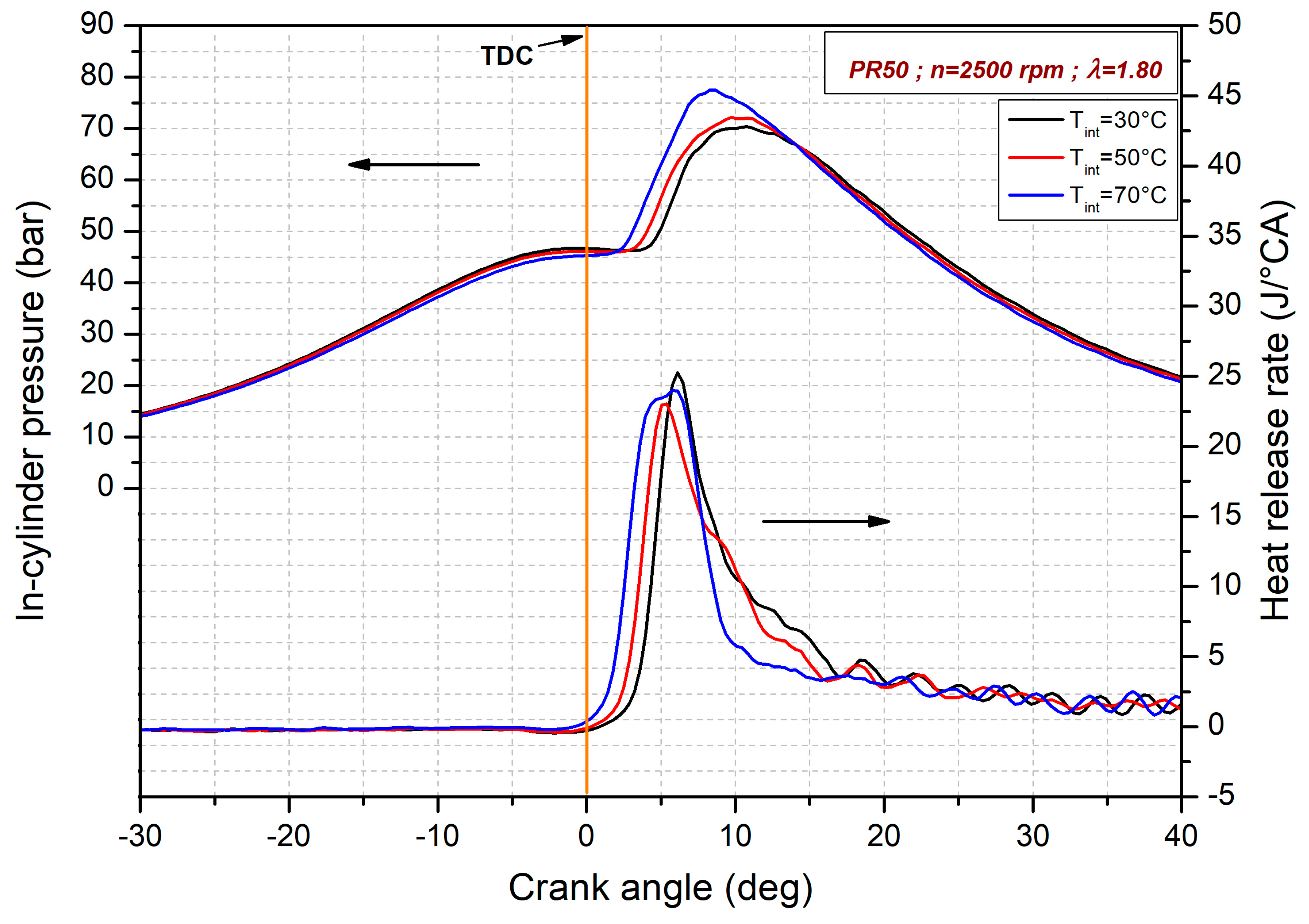
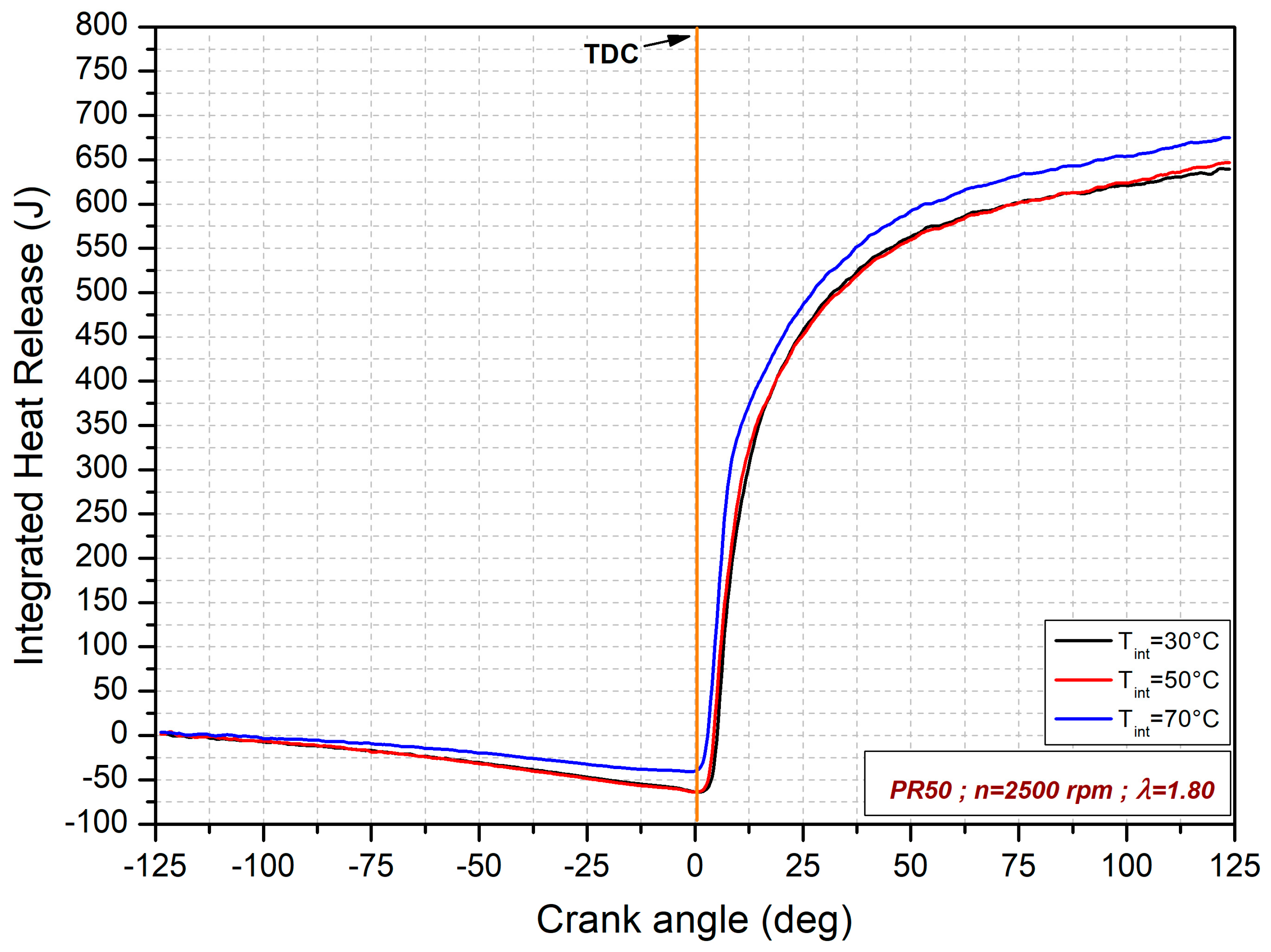
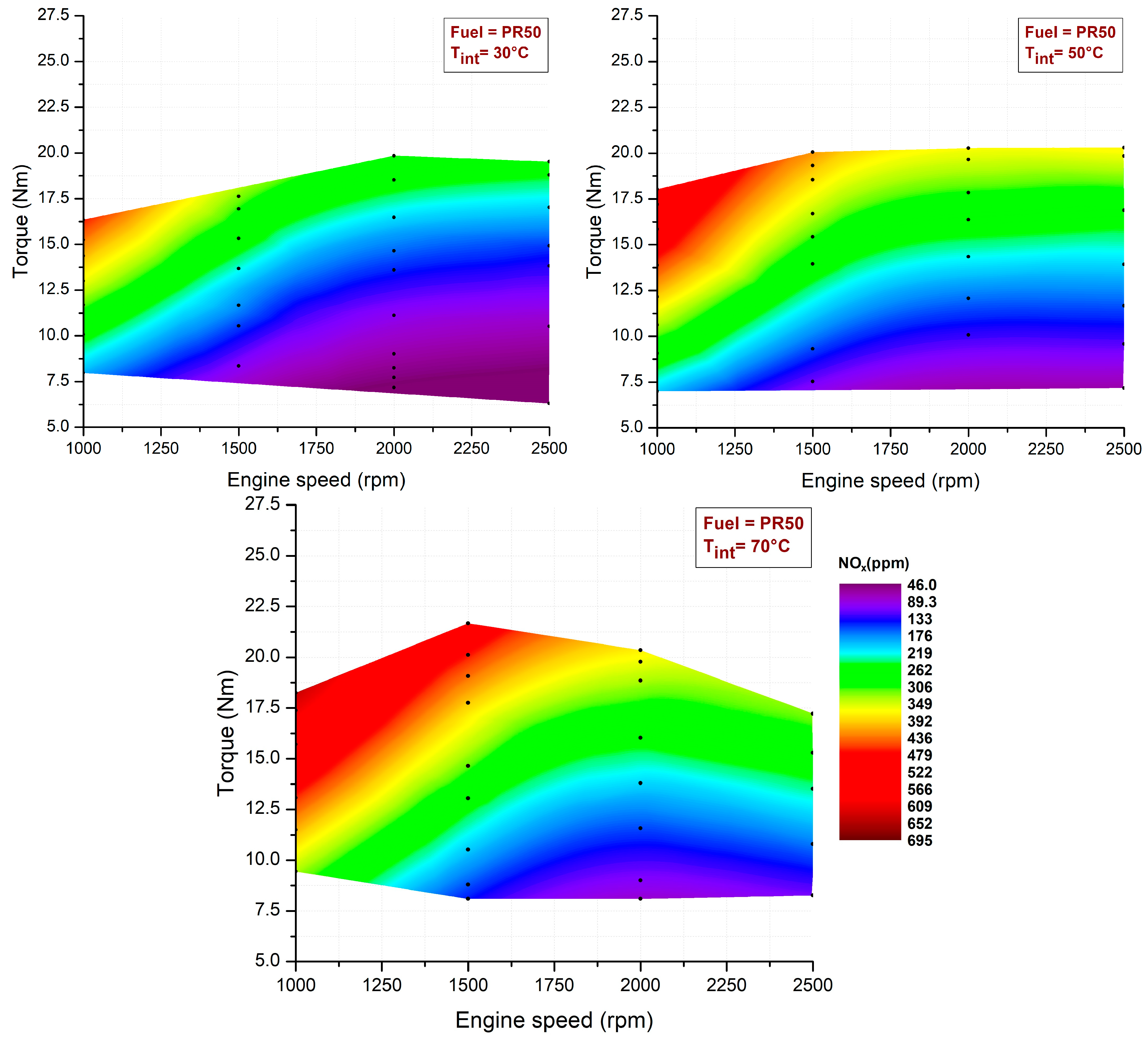
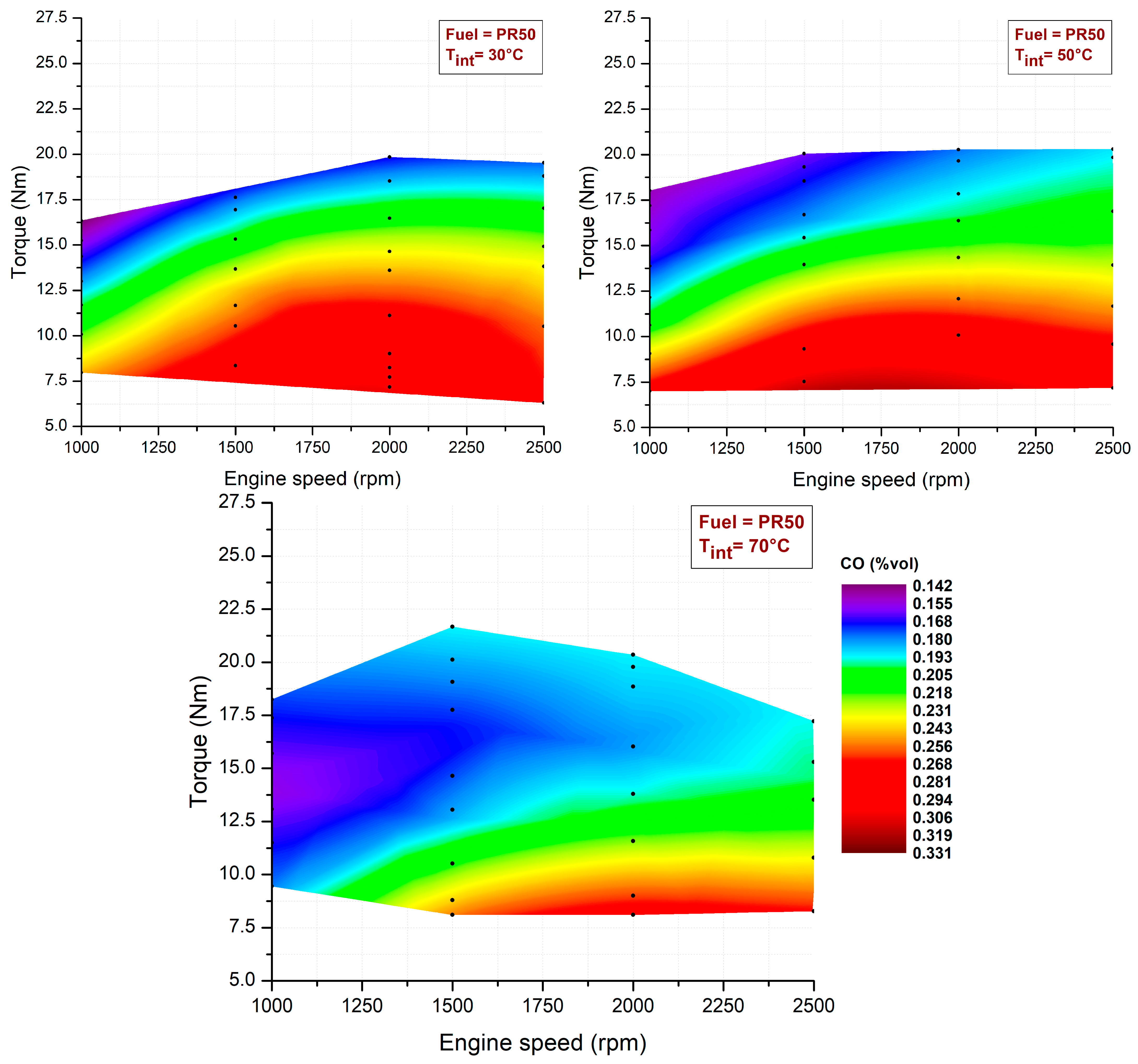
3.2. Intake Air Temperature Effects
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| aTDC | After Top Dead Center |
| BSFC | Brake-Specific Fuel Consumption |
| bTDC | Before Top Dead Center |
| CA | Crank Angle |
| CA50 | Crank Angle Corresponding to 50% of the Total Heat Release |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CI | Compression Ignition |
| CNG | Compressed Natural Gas |
| CO | Carbon Monoxides |
| COVIMEP | Coefficient of Variation of IMEP |
| CR | Compression Ratio |
| DI | Direct Injection |
| DPF | Diesel Particulate Filter |
| EGR | Exhaust Gas Recirculation |
| HC | Hydrocarbon |
| HCCI | Homogeneous Charged Compression Ignition |
| HRF | High-Reactivity Fuel |
| HRR | Heat Release Rate |
| IAT | Intake Air Temperature |
| ICEs | Internal Combustion Engines |
| IHR | Integrated Heat Release |
| IMEP | Indicated Mean Effective Pressure |
| ITE | Indicated Thermal Efficiency |
| LTC | Low-Temperature Combustion |
| LHV | Low Heat Value |
| LRF | Low-Reactivity Fuel |
| MPRR | Maximum Pressure Rise Rate |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| PCCI | Premixed Charge Compression Ignition |
| PFI | Port Fuel Injection |
| PR | Premixed Ratio |
| RCCI | Reactivity-Controlled Compression Ignition |
| SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction |
| SI | Spark Ignition |
| SOC | Start of Combustion |
| SOI | Start of Injection |
| UHC | Unburned Hydrocarbons |
References
- Agarwal, A.K. Biofuels (alcohols and biodiesel) applications as fuels for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; Molina, S.; García, A.; Belarte, E.; Vanvolsem, M. An investigation on RCCI combustion in a heavy duty diesel engine using in-cylinder blending of diesel and gasoline fuels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 63, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyumaz, A. An experimental investigation into combustion and performance characteristics of an HCCI gasoline engine fueled with n-heptane, isopropanol and n-butanol fuel blends at different inlet air temperatures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 98, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, H. A comparative study on the usage of fusel oil and reference fuels in an HCCI engine at different compression ratios. Fuel 2020, 273, 117775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, F.; Halis, S.; Yıldırım, E.; Altın, M.; Balaban, F.; Solmaz, H.; Yücesu, H.S. Effects of premixed ratio on engine operation range and emissions of a reactivity controlled compression ignition engine. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2022, 16, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.; Hu, X.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Ye, M.; Deng, B. Exploration on the emissions and catalytic reactors interactions of a non-road diesel engine through experiment and system level simulation. Fuel 2023, 342, 127746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyumaz, A.; Solmaz, H.; Yılmaz, E.; Yamık, H.; Polat, S. Experimental examination of the effects of military aviation fuel JP-8 and biodiesel fuel blends on the engine performance, exhaust emissions and combustion in a direct injection engine. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardebili, S.M.S.; Calam, A.; Yılmaz, E.; Solmaz, H. A comparative analysis of the engine performance and exhaust emissions characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with Mono ethylene glycol supported emulsion. Fuel 2021, 288, 119723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halis, S.; Nacak, Ç.; Solmaz, H.; Yilmaz, E.; Yücesu, H. Investigation of the effects of octane number on combustion characteristics and engine performance in a HCCI engine. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Calam, A.; Aydoğan, B.; Halis, S. The comparison of combustion, engine performance and emission characteristics of ethanol, methanol, fusel oil, butanol, isopropanol and naphtha with n-heptane blends on HCCI engine. Fuel 2020, 266, 117071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S.; Solmaz, H.; Yılmaz, E.; Calam, A.; Uyumaz, A.; Yücesu, H.S. Mapping of an HCCI engine using negative valve overlap strategy. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, H.; Calam, A.; Halis, S.; İpci, D.; Yilmaz, E. Investigation of the effects of intake manifold pressure on performance and combustion characteristics in an HCCI engine. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2022, 37, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H. Progress and recent trends in homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2009, 35, 398–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.M.; Kokjohn, S.L.; Splitter, D.A.; Reitz, R.D. An experimental investigation of fuel reactivity controlled PCCI combustion in a heavy-duty engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2010, 3, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiplimo, R.; Tomita, E.; Kawahara, N.; Yokobe, S. Effects of spray impingement, injection parameters, and EGR on the combustion and emission characteristics of a PCCI diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 37, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T. Critical review on the characteristics of performance, combustion and emissions of PCCI engine controlled by early injection strategy based on narrow-angle direct injection (NADI). Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Kumar, V.; Agarwal, A.K. Evaluation of comparative engine combustion, performance and emission characteristics of low temperature combustion (PCCI and RCCI) modes. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, E.; Park, H.; Bae, C. Comparisons of advanced combustion technologies (HCCI, PCCI, and dual-fuel PCCI) on engine performance and emission characteristics in a heavy-duty diesel engine. Fuel 2020, 262, 116436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokjohn, S.L.; Hanson, R.M.; Splitter, D.A.; Reitz, R.D. Fuel reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI): A pathway to controlled high-efficiency clean combustion. Int. J. Engine Res. 2011, 12, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, D. Review on the management of RCCI engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, H.; Ipci, D. Control of combustion phase with direct injection timing for different inlet temperatures in an RCCI engine. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Elkelawy, M.; El Shenawy, E.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Elarabi, M.M.; Bastawissi, H.A.E. Impacts of EGR on RCCI engines management: A comprehensive review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 14, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepanraj, B.; Ashok, A.; Gugulothu, S.K.; Reddy, R.V.; Senthilkumar, N.; Said, Z.; Bhowmik, M. Enhancement of RCCI engine characteristics of Jatropha oil biodiesel as high reactivity fuel and 1-pentanol as low reactivity fuel with variable injection timing. Fuel 2023, 348, 128390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S.; Yücesu, H.S.; Kannan, K.; Uyumaz, A.; Solmaz, H.; Shahbakhthi, M. Experimental comparison of different injection timings in an HCCI engine fueled with n-heptane. Int. J. Automot. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Calam, A.; Halis, S.; Aydoğan, B.; Haşimoğlu, C. Combustion characteristics of naphtha and n-heptane fuels in an auto-ignited HCCI engine at different lambda values and engine loads. Fuel 2022, 327, 125183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, R.D.; Duraisamy, G. Review of high efficiency and clean reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI) combustion in internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 46, 12–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halis, S.; Solmaz, H.; Polat, S.; Yücesu, H.S. Numerical study of the effects of lambda and injection timing on RCCI combustion mode. Int. J. Automot. Sci. Technol. 2022, 6, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, S.; Calam, A.; Ardebili, S.M.S.; Şahin, F.; Boroiu, A.A.; Solmaz, H. Operating range, performance and emissions of an HCCI engine fueled with fusel oil/diethyl ether: An experimental study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, R.D.; Hanson, R.M.; Splitter, D.A.; Kokjohn, S.L. Engine Combustion Control via Reactivity Stratification. U.S. Patent No. 8616177 B2, 28 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kakoee, A.; Bakhshan, Y.; Aval, S.M.; Gharehghani, A. An improvement of a lean burning condition of natural gas/diesel RCCI engine with a pre-chamber by using hydrogen. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoee, A.; Bakhshan, Y.; Gharehghani, A.; Salahi, M.M. Numerical comparative study of hydrogen addition on combustion and emission characteristics of a natural-gas/dimethyl-ether RCCI engine with pre-chamber. Energy 2019, 186, 115878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, M.; Okcu, M.; Altun, Ş.; Varol, Y. Numerical investigation of natural gas (NG) as low reactivity fuel in a reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI) engine model. Fuel 2023, 343, 127949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calam, A. Study on the combustion characteristics of acetone/n-heptane blend and RON50 reference fuels in an HCCI engine at different compression ratios. Fuel 2020, 271, 117646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.R.; Maurya, R.K. Effect of Diesel Injection Timing on Peak Pressure Rise Rate and Combustion Stability in RCCI Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, S.; Poorghasemi, K.; Solmaz, H.; Calam, A.; Ipci, D. Effect of nitrogen and hydrogen addition on performance and emissions in reactivity controlled compression ignition. Fuel 2021, 292, 120330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Jia, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. A comparative study on the performance of partially premixed combustion (PPC), reactivity-controlled compression ignition (RCCI), and RCCI with reverse reactivity stratification (R-RCCI) fueled with gasoline and polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODEn). Fuel 2021, 298, 120838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; Pastor, J.V.; García, A.; Monsalve-Serrano, J. The potential of RCCI concept to meet EURO VI NOx limitation and ultra-low soot emissions in a heavy-duty engine over the whole engine map. Fuel 2015, 159, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, M.; Chang, Y.; Xie, M.; Reitz, R.D. Towards a comprehensive understanding of the influence of fuel properties on the combustion characteristics of a RCCI (reactivity controlled compression ignition) engine. Energy 2016, 99, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; García, A.; Monsalve-Serrano, J.; Balloul, I.; Pradel, G. An assessment of the dual-mode reactivity controlled compression ignition/conventional diesel combustion capabilities in a EURO VI medium-duty diesel engine fueled with an intermediate ethanol-gasoline blend and biodiesel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 123, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, V.D.; Deshmukh, D. Fuel flexibility study of various fuels with charge dilution and high compression ratio for medium-load operating RCCI engine. Fuel 2022, 310, 122163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyumaz, A.; Solmaz, H.; Boz, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Polat, S. The effects of lambda on combustion characteristics in a reactive controlled compression ignition engine. Afyon Kocatepe Univ. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 17, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, C.F.; Zhang, C. Effects of dilute gas on combustion and emission characteristics of a common-rail diesel engine fueled with isopropanol-butanol-ethanol and diesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 165, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, M.; Altun, Ş.; Okcu, M.; Varol, Y. Experimental investigation on combustion and emission characteristics of reactivity controlled compression ignition engine powered with iso-propanol/biodiesel blends. Propuls. Power Res. 2022, 11, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisirirat, P.; Togbé, C.; Chanchaona, S.; Foucher, F.; Mounaïm-Rousselle, C.; Dagaut, P. Auto-ignition and combustion characteristics in HCCI and JSR using 1-butanol/n-heptane and ethanol/n-heptane blends. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Guralp, O.; Filipi, Z.; Assanis, D.; Kuo, T.W.; Najt, P.; Rask, R. New heat transfer correlation for an HCCI engine derived from measurements of instantaneous surface heat flux. SAE Tech. Pap. 2004, 2004, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. HCCI and CAI Engines for the Automotive Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Yao, M. Combustion mode design with high efficiency and low emissions controlled by mixtures stratification and fuel reactivity. Front. Mech. Eng. 2015, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.; Kokjohn, S.; Splitter, D.; Reitz, R. Fuel effects on reactivity controlled compression ignition (RCCI) combustion at low load. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 394–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yue, Y. Experimental study of n-butanol additive and multi-injection on HD diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2010, 89, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Jia, J.; Wu, J.; Shang, W.; Ma, Z. Experimental investigation on performance of a turbocharged DI diesel engine using isopropanol-diesel fuel blends. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advanced Electronic Science and Technology (AEST 2016), Shenzhen, China, 19–21 August 2016; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, G.A.; Heywood, J.B.; Keck, J.C. Experimental and theoretical study of nitric oxide formation in internal combustion engines. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1970, 1, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calam, A.; Solmaz, H.; Yilmaz, E.; Icingur, Y. Investigation of effect of compression ratio on combustion and exhaust emissions in a HCCI engine. Energy 2019, 168, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Mulenga, M.C.; Reader, G.T.; Wang, M.; Ting, D.S.; Tjong, J. Biodiesel engine performance and emissions in low temperature combustion. Fuel 2008, 87, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.A. On the emissions from internal-combustion engines: A review. Int. J. Energy Res. 1998, 22, 483–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Battista, D.; Vittorini, D.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Cipollone, R. Optimization of the Engine Intake Air Temperature through the Air Conditioning Unit; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, R.; Reitz, R. Transient RCCI operation in a light-duty multi-cylinder engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Engine | Compression Ignition (4-Stroke, Water-Cooled) |
|---|---|
| Combustion strategy | RCCI |
| Stroke × bore | 90 mm × 85 mm |
| Number of cylinders | 1 |
| Compression ratio | 17.5:1 |
| Cylinder volume | 510 cm3 |
| Length of connecting rod | 118 mm |
| Power | 12 HP |
| Max. engine speed | 3000 rpm |
| Max. torque | 32.8 Nm @1800 rpm |
| Oil consumption | 8 g/h |
| Oil reservoir capacity | 1.75 lt |
| Fuel | Octane Number | Density (kg/m3) | Boiling Point (°C) | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Lower Heating Value (kJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iso-propanol C3H8O | 107 | 809 | 82 | 60.10 | 30447 |
| n-heptane C7H16 | - | 679.5 | 98 | 100.16 | 44560 |
| Measurement Range | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|
| Lambda | 0.5 to 9.999 | 0.001 |
| NO (ppm vol) | 0 to 5000 | 1 |
| HC (ppm vol) | 0 to 9999 | 1 |
| CO (% vol) | 0 to 10 | 0.001 |
| CO2 (% vol) | 0–18 | 0.01 |
| O2 (% vol) | 0 to 22 | 0.01 |
| Parameters | Case-1 | Case-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion mode | RCCI | RCCI |
| Fuel | PR25-PR50-PR75 | PR50 |
| Intake air temperature (°C) | 50 | 30–50–70 |
| Engine speed (rpm) | 1000–2500 | 1000–2500 |
| Lambda | 1.40–4.00 | 1.40–4.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halis, S. An Experimental Study of Operating Range, Combustion and Emission Characteristics in an RCCI Engine Fueled with Iso-Propanol/n-Heptane. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410897
Halis S. An Experimental Study of Operating Range, Combustion and Emission Characteristics in an RCCI Engine Fueled with Iso-Propanol/n-Heptane. Sustainability. 2023; 15(14):10897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410897
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalis, Serdar. 2023. "An Experimental Study of Operating Range, Combustion and Emission Characteristics in an RCCI Engine Fueled with Iso-Propanol/n-Heptane" Sustainability 15, no. 14: 10897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410897
APA StyleHalis, S. (2023). An Experimental Study of Operating Range, Combustion and Emission Characteristics in an RCCI Engine Fueled with Iso-Propanol/n-Heptane. Sustainability, 15(14), 10897. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151410897






