Exploring the Relationships between Land Surface Temperature and Its Influencing Determinants Using Local Spatial Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
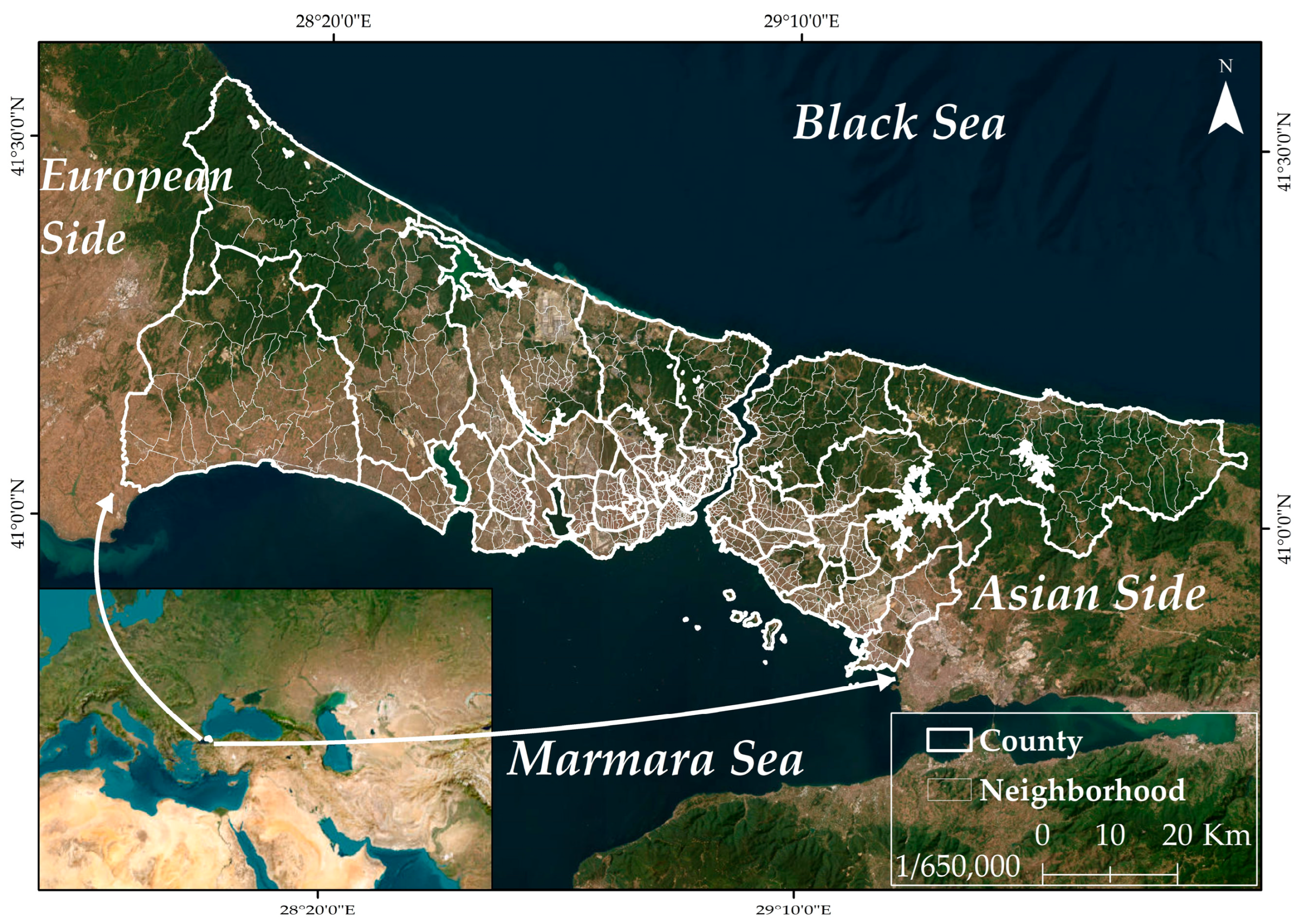
2.1. Study Area
2.2. LST as the Outcome Variable
2.3. Covariates


2.4. Spatial Analysis
3. Results
3.1. OLS Model Results
3.2. Spatial Model Results









4. Discussion
4.1. Social Determinants Association with LST
4.2. Environmental Determinants Association with LST
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Correlation | Positive/Negative | Chart |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LST | Mean NDVI | 0.76 | Negative |  |
| LST | Ratio of Built Environment | 0.58 | Positive |  |
| LST | Population Density | 0.42 | Positive |  |
| LST | Total Number of Residences | 0.18 | Positive |  |
| Total Number of Residences | Mean NDVI | 0.22 | Negative |  |
| Ratio of Built Environment | Mean NDVI | 0.71 | Negative |  |
| Ratio of Built Env. | Population Density | 0.61 | Positive |  |
| Population Density | Total Number of Residences | 0.26 | Positive |  |
| Socioeco. Index | Mean Elevation | 0.11 | Negative |  |
| Socioeco. Index | Ratio of 65 and older | 0.17 | Positive |  |
| Ratio of Children | Mean Age | 0.18 | Negative |  |
| Ratio of Children | Mean Household Size | 0.17 | Positive |  |
References
- Oke, T.R. Street design and urban canopy layer climate. Energy Build. 1988, 11, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Luo, X.; Jin, C.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of vegetation phenology along the urban–rural gradient in Coastal Dalian, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Columbia Coroners Service. Extreme Heat and Human Mortality: A Review of Heat-Related Deaths in B.C. in Summer 2021; British Columbia Coroners Service. 2022. Available online: https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/birth-adoption-death-marriage-and-divorce/deaths/coroners-service/death-review-panel/extreme_heat_death_review_panel_report.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Simon, F.; Lopez-Abente, G.; Ballester, E.; Martinez, F. Mortality in Spain during the heat waves of summer 2003. Eurosurveillance 2005, 10, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobías, A.; Dominic, R.; Carmen, I. Heat-attributable Mortality in the Summer of 2022 in Spain. Epidemiology 2023, 34, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellis, F.P.; Princé, H.P.; Lovatt, G.; Whittington, R.M. Mortality and Morbidity in Birmingham during the 1976 Heatwave. Qjm Int. J. Med. 1980, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, K. Spatiotemporal analysis of heat and heat wave effects on elderly mortality in Texas, 2006–2011. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Gürkan, H.; Eskioğlu, O.; Yazıcı, B.; Şensoy, S.; Kömüşçü, A.Ü.; Çalık, Y. Projected Trends in Heat and Cold Waves under Effect of Climate Change. In Proceedings of the 8th Atmospheric Sciences Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Erlat, E.; Türkeş, M.; Aydin-Kandemir, F. Observed changes and trends in heatwave characteristics in Turkey since 1950. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2021, 145, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, Y.S.; Tan, E.; Mentes, S.S. Summer heat waves over western Turkey between 1965 and 2006. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2013, 112, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, A.; Homar, V.; Romero, R.; Brooks, H.; Ramis, C.; Gordaliza, M.; Alonso, S. Projections of heat waves with high impact on human health in Europe. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 119, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.E.; Alexander, L.V.; Nairn, J.R. Increasing frequency, intensity and duration of observed global heatwaves and warm spells. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, K.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, B.; Hu, W.; Shu, R. High ambient temperatures are associated with urban crime risk in Chicago. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 856, 158846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.A.; Delisi, M. Implications of Global Climate Change for Violence in Developed and Developing Countries. In The Psychology of Social Conflict and Aggression; Forgas, J., Kruglanski, A., Williams, K., Eds.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 249–265. [Google Scholar]
- McDowall, D.; Loftin, C.; Pate, M. Seasonal cycles in crime, and their variability. J. Quant. Criminol. 2012, 28, 389–410. [Google Scholar]
- Zander, K.K.; Botzen, W.J.W.; Oppermann, E.; Kjellstrom, T.; Garnett, S.T. Heat stress causes substantial labour productivity loss in Australia. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, K.; Kuklane, K.; Gao, C.; Holmer, I. Effects of heat stress on working populations when facing climate change. Ind. Health 2013, 51, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mashhoodi, B. Environmental justice and surface temperature: Income, ethnic, gender, and age inequalities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 68, 102810. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, G.; Crane, M. An analysis of urban thermal characteristics and associated land cover in Tampa Bay and Las Vegas using Landsat satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Miaomiao, X.; Wang, Y. Investigating spatial non-stationary and scale-dependent relationships between urban surface temperature and environmental factors using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Ivajnšič, D.; Kaligarič, M.; Žiberna, I. Geographically weighted regression of the urban heat island of a small city. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokaie, M.; Zarkesh, M.K.; Arasteh, P.D.; Hosseini, A. Assessment of Urban Heat Island based on the relationship between land surface temperature and Land Use/Land Cover in Tehran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Zhou, W.; Cadenasso, M.L. Is everyone hot in the city? Spatial pattern of land surface temperatures, land cover and neighborhood socioeconomic characteristics in Baltimore, MD. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Wen, F.; Yu, D. The impact of the terrain effect on land surface temperature variation based on Landsat-8 observations in mountainous districts. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 1808–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Cecilia, J.X.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Impact of urban morphology and landscape characteristics on spatiotemporal heterogeneity of land surface temperature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, C.; Liu, H. The Diversified Impacts of Urban Morphology on Land Surface Temperature among Urban Functional Zones. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Li, R. Impacts of the evolving urban development on intra-urban surface thermal environment: Evidence from 323 Chinese cities. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 771, 144810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Weng, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, W.; Schienke, E.W.; Zhang, Z. Land Surface Temperature Variation and Major Factors in Beijing, China. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, K.; Ai, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Dominant Factors and Spatial Heterogeneity of Land Surface Temperatures in Urban Areas: A Case Study in Fuzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1266. [Google Scholar]
- Toros, H.; Abbasnia, M.; Sagdic, M.; Tayanç, M. Long-Term Variations of Temperature and Precipitation in the Megacity of Istanbul for the Development of Adaptation Strategies to Climate Change. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 6519856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, T.; Hanel, M.; Oğuz, K.; Demircan, M. Assessment of The Urban Heat Island Effect Under Current and Climate Change Conditions in Istanbul. In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference, Albena, Bulgaria, 28 June–7 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank Group. Türkiye Country Climate and Development Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Çulpan, H.C.; Şahin; Can, G. A Step to Develop Heat-Health Action Plan: Assessing Heat Waves’ Impacts on Mortality. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2126. [Google Scholar]
- Can, G.; Şahin, Ü.; Sayılı, U.; Dubé, M.; Kara, B.; Acar, H.C.; İnan, B.; Sayman, A.; Lebel, G.; Bustinza, R.; et al. Excess Mortality in Istanbul during Extreme Heat Waves between 2013 and 2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4348. [Google Scholar]
- Karaca, M.; Tayanç, M.; Toros, H. Effects of urbanization on climate of İstanbul and Ankara. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3411–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Karaca, M.; Anteplioğlu, Ü.; Karsan, H. Detection of urban heat island in Istanbul, Turkey. II Nuovo C. C 1995, 18, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dihkan, M.; Karsli, F.; Guneroglu, A.; Guneroglu, N. Evaluation of surface urban heat island (SUHI) effect on coastal zone: The case of Istanbul Megacity. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 118, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ünal, Y.S.; Sonuç, C.Y.; İncecik, S.; Topçu, H.S.; Diren-Üstün, D.H.; Temizöz, H.P. Investigating urban heat island intensity in Istanbul. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 139, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Khorrami, B.; Gunduz, O. Spatio-temporal interactions of surface urban heat island and its spectral indicators: A case study from Istanbul metropolitan area, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 386. [Google Scholar]
- Aksak, P.; Öztürk, Ş.K.; Ünsal, Ö. Investigation of Urban Heat Island Effect on Climate Parameters and Remote Sensing: The Case of Istanbul City. Aegean Geogr. J. 2023, 32, 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Okumus, D.E.; Terzi, F. Reconsidering Urban Densification for Microclimatic Improvement: Planning and Design Strategies for Istanbul. Iconarp Int. J. Arch. Plan. 2022, 10, 660–687. [Google Scholar]
- Okumus, D.E.; Terzi, F. Evaluating the role of urban fabric on surface urban heat island: The case of Istanbul. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 73, 103128. [Google Scholar]
- Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality. Istanbul Climate Vision; Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality: Istanbul, Turkey, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality. Istanbul Climate Change Action Plan; Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality: Istanbul, Turkey, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bölen, F.; Türkeroğlu, H.E.; Ergün, N.; Yirmibeşoğlu, F.; Terzi, F.; Kaya, S.; Kundak, S. Quality of Residential Environment in a City Facing Unsustainable Growth Problems: Istanbul. In Proceedings of the New Approaches in Urban and Regional Planning, Istanbul, Turkey, 28–29 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Turkish Statistical Institute. Central Dissemination System. 2023. Available online: https://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/medas/?locale=en (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UN. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality. 2023. Available online: https://www.ibb.istanbul/en (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Avcı, S. Population Characteristics of Istanbul and Vulnerability to Disasters. In Proceedings of the Istanbul’s Disaster Vulnerability Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 4–5 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, F.; Bölen, F. The Potential Effects of Spatial Strategies on Urban Sprawl in Istanbul. Urban Stud. 2011, 49, 1229–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, F.; Bolen, F. Urban Sprawl Measurement of Istanbul. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Geymen, A.; Baz, I. Monitoring urban growth and detecting land-cover changes on the Istanbul metropolitan area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 136, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Dereli, M.A. Monitoring and prediction of urban expansion using multilayer perceptron neural network by remote sensing and GIS technologies: A case study from Istanbul Metropolitan City. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 9336–9344. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, M.Z.; Çetinkaya, G.; Aydın, S. Climate Types of Turkey According to Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification. J. Geogr. 2017, 35, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, E.; Çiçek, İ. Türkiye’nin detaylandırılmış Köppen-Geiger iklim bölgeleri. J. Hum. Sci. 2018, 15, 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Türkeş, M. Climate and Drought in Turkey. In Water Resources of Turkey; Harmancıoğlu, N.B., Altınbilek, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 85–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turoğlu, H. Detection of Changes on Temperature and Precipitation Features in Istanbul (Turkey). Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2014, 4, 549–562. [Google Scholar]
- Ezber, Y.; Şen, Ö.L.; Kındap, T.; Karaca, M. Climatic effects of urbanization in Istanbul: A statistical and modeling analysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 27, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Avdan, U.; Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for Automated Mapping of Land Surface Temperature Using LANDSAT 8 Satellite Data. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1480307. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B. Revised landsat-5 tm radiometric calibration procedures and postcalibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, C.; Galve, J.M.; Sánchez, J.M.; Caselles, V. Alidation of Landsat-7/ETM+ thermal band calibration and atmospheric correction with ground-based measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 547–555. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Using the USGS Landsat Level-1 Data Product. 2021. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/using-usgs-landsat-level-1-data-product (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Soria, G.; Romaguera, M.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Plaza, A.; Martinez, P. Land Surface Emissivity Retrieval from Different VNIR and TIR Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, W.D. On Grouping for Maximum Homogeneity. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.; Caspall, F. Error on Choropleth Maps: Definition, Measurement, Reduction. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1971, 61, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.T.; Shyy, T.-K. Integrating attribute and space characteristics in choropleth display and spatial data mining. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2000, 14, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smith, M.J.; Goodchild, M.F.; Longley, P.A. Geospatial Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Principles, Techniques and Software Tools, 6th ed.; The Winchelsea Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.; Liu, H.; Liang, B.; Lu, D. The Spatial Variations of Urban Land Surface Temperatures: Pertinent Factors, Zoning Effect, and Seasonal Variability. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2008, 1, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, R.; Surawar, M. Land Use, Land Cover, and Population Density Impact on the Formation of Canopy Urban Heat Islands through Traverse Survey in the Nagpur Urban Area, India. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2016, 142, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Cadenasso, M.L. People, landscape, and urban heat island: Dynamics among neighborhood social conditions, land cover and surface temperatures. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.; Shivers, S.; Wetherley, E.; Cudd, R. New ECOSTRESS and MODIS Land Surface Temperature Data Reveal Fine-Scale Heat Vulnerability in Cities: A Case Study for Los Angeles County, California. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, G.P.; Yardley, J.; Brown, C.; Sigal, R.J.; Jay, O. Heat stress in older individuals and patients with common chronic diseases. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 182, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.P.; Wilson, J.S. The socio-spatial dynamics of extreme urban heat events: The case of heat-related deaths in Philadelphia. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerette, G.D.; Harlan, S.L.; Brazel, A.; Jones, N.; Larsen, L.; Stefanov, W.L. Regional relationships between surface temperature, vegetation, and human settlement in a rapidly urbanizing ecosystem. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhoodi, B.; Stead, D.; van Timmeren, A. Land surface temperature and households’ energy consumption: Who is affected and where? Appl. Geogr. 2019, 114, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şeker, M.; Ersöz, H.Y.; Kazan, H.; Saldanlı, A.; Akman, S.U.; Bektaş, H.; Şişmanoğlu, E.; Yurduer, Y.; Uzun, S. Mahallem Istanbul Project; Istanbul University: Istanbul, Turkey, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- GEE. Google Earth Engine. 2023. Available online: https://earthengine.google.com (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Copernicus, EU-DEM. 2016. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/imagery-in-situ/eu-dem/eu-dem-v1.1 (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- DB, Urban Atlas. Available online: https://www.csb.gov.tr (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Rogerson, P.A. Data reduction: Factor analysis and cluster analysis. Stat. Methods Geogr. 2001, 2001, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Haining, R.P. Spatial Sampling. Int. Encycl. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2001, 14822–14827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Voss, K.J.; Curtis, W.; Roger, B.H. Explorations in Spatial Demography. In Population Change and Rural Society; Kandel, W.A., Brown, D.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 407–429. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfata, A. Using Geographically Weighted Models to Explore Obesity Prevalence Association with Air Temperature, Socioeconomic Factors, and Unhealthy Behavior in the USA. J. Geovisualization Spat. Anal. 2022, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Fotheringham, A.S. A Comparison of Spatially Varying Regression Coefficient Estimates Using Geographically Weighted and Spatial-Filter-Based Techniques. Geogr. Anal. 2017, 50, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Hamurcu, A.U. Relationships between socio-demographic structure and spatio-temporal distribution patterns of COVID-19 cases in Istanbul, Turkey. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2022, 26, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. mgwr: A Python Implementation of Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression for Investigating Process Spatial Heterogeneity and Scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.; Tiefelsdorf, M. Multicollinearity and correlation among local regression coefficients in geographically weighted regression. J. Geogr. Syst. 2005, 7, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollini, I.; Lu, B.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C.; Harris, P. GWmodel: An R package for exploring spatial heterogeneity using geographically weighted models. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünsal; Avci, V. Determining the Relationship Between Land Surface Temperatures and Urban Land Use: The Example of Şanlıurfa, Diyarbakır and Mardin. Turk. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2023, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ünsal; Kuzulugil, A.C.; Aytatlı, B.; Demircioğlu Yıldız, N. Determining the Change of Land Use Types by Years with Land Surface Temperature Data (Erzurum City Case Study). J. Urban Cult. Manag. 2023, 16, 1334–1361. [Google Scholar]

| Covariate | Unit | Source | Calculation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Elevation | Meter | EU DEM v1.1 | Downloaded from EU DEM v1.1, used zonal statistics by neighborhood |
| Mean NDVI | Index | GEE | Downloaded from GEE, used zonal statistics by neighborhood |
| Ratio of 65 and Older | % | TSI + IMM | Divided +65 aged population to total population by neighborhood |
| Population Density | Person/km2 | TSI + IMM | Divided total population into neighborhood area |
| Mean Age | Value | TSI + IMM | Obtained from IMM by neighborhood directly |
| Dependent Population | Index | TSI + IMM | Divided +65 and 0–15 aged population to total population by neighborhood |
| Ratio of Children | % | TSI + IMM | Divided 0–18 aged population to total population by neighborhood |
| Mean Household Size | Index | TSI + IMM | Obtained from IMM by neighborhood directly |
| Socioeconomic Index | Index | Mahallem Istanbul Project | Obtained from Mahallem Istanbul Project report file by neighborhood directly |
| Ratio of Built Environment | % | Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change | The total area of impermeable surfaces of urban atlas by neighborhood |
| Total Number of Residences | Value | IMM | Obtained from IMM by neighborhood directly |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | p-Value | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 33.89 | 0.48 | 69.85 | 0.00 | - |
| Mean Elevation | 0.01 | 0.00 | 18.98 | 0.00 | 1.39 |
| Mean NDVI | −22.98 | 0.69 | −33.20 | 0.00 | 4.84 |
| Ratio of 65 and older | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 1.46 |
| Population Density | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.73 | 0.00 | 3.36 |
| Mean Age | 0.01 | 0.00 | 2.44 | 0.03 | 1.58 |
| Dependent Population | 0.50 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.00 | 1.39 |
| Ratio of Children | 0.08 | 0.02 | 4.00 | 0.00 | 1.81 |
| Mean Household Size | 1.43 | 0.31 | 4.50 | 0.02 | 1.43 |
| Socioeconomic Index | −0.01 | 0.00 | −5.49 | 0.00 | 1.64 |
| Ratio of Built Environment | 0.01 | 0.00 | 3.18 | 0.00 | 6.40 |
| Total Number of Residences | −0.01 | 0.00 | −1.96 | 0.00 | 1.58 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.86 | ||||
| AICc | 2978.60 |
| Statistic | GWR Results | MGWR Results |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted R2 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| AICc | 2210.98 | −242.32 |
| Sigma-squared | 0.42 | 0.03 |
| Sigma-squared MLE | 0.29 | 0.02 |
| Effective degrees of freedom | 671.88 | 759.26 |
| Bandwidth (% of Features) | Significant (% of Features) | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Median | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 31 (3.18) | 274 (28.07) | 0.06 | 0.16 | −0.44 | 0.06 | 0.43 |
| Mean Elevation | 30 (3.01) | 343 (35.14) | 0.12 | 0.15 | −0.23 | 0.11 | 0.74 |
| Mean NDVI | 30 (3.07) | 950 (97.34) | −0.69 | 0.17 | −1.05 | −0.71 | −0.05 |
| Ratio of 65 and older | 391 (40.06) | 235 (24.08) | −0.04 | 0.03 | −0.11 | −0.32 | 0.02 |
| Population Density | 306 (31.35) | 976 (100) | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| Mean Age | 391 (40.06) | 62 (6.35) | −0.02 | 0.02 | −0.13 | −0.03 | 0.02 |
| Dependent Population | 306 (31.35) | 112 (11.48) | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
| Ratio of Children | 976 (100) | 462 (47.34) | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Mean Household Size | 173 (17.73) | 420 (43.03) | 0.04 | 0.06 | −0.08 | 0.04 | 0.17 |
| Socioeconomic Index | 201 (20.59) | 400 (40.98) | −0.03 | 0.05 | −0.13 | −0.03 | 0.05 |
| Ratio of Built Environment | 165 (16.91) | 863 (88.42) | 0.21 | 0.09 | −0.07 | 0.22 | 0.36 |
| Total Number of Residences | 976 (100) | 16 (1.64) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ünsal, Ö.; Lotfata, A.; Avcı, S. Exploring the Relationships between Land Surface Temperature and Its Influencing Determinants Using Local Spatial Modeling. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511594
Ünsal Ö, Lotfata A, Avcı S. Exploring the Relationships between Land Surface Temperature and Its Influencing Determinants Using Local Spatial Modeling. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511594
Chicago/Turabian StyleÜnsal, Ömer, Aynaz Lotfata, and Sedat Avcı. 2023. "Exploring the Relationships between Land Surface Temperature and Its Influencing Determinants Using Local Spatial Modeling" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511594
APA StyleÜnsal, Ö., Lotfata, A., & Avcı, S. (2023). Exploring the Relationships between Land Surface Temperature and Its Influencing Determinants Using Local Spatial Modeling. Sustainability, 15(15), 11594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511594







