GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Method
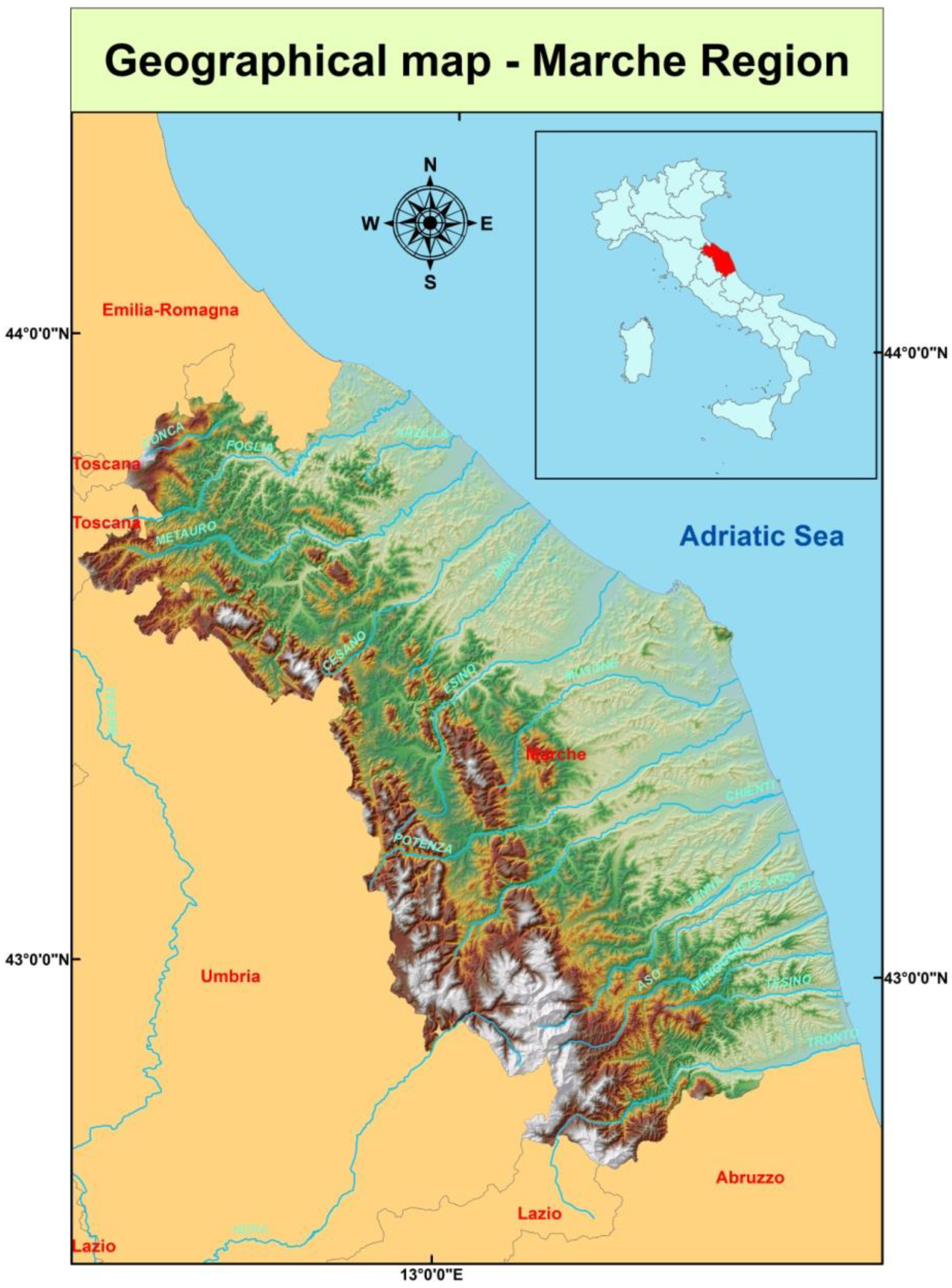
2.1. Study Area
- Continental arctic cold: It develops in northern Russia in the area of Siberia; this air mass can affect Italy from late October to April, and it represents the coldest air mass, which can affect the Italian territory.
- Continental polar cold: Cold, dry air mass from southern Russia originating in the Balkan area.
- Continental tropical warm: Hot, dry mass of air originating from arid and desert areas from the southern belt; it represents the warmest air mass affecting Italy.
- Maritime tropical warm: Air mass from the southwest in the Atlantic Ocean; in winter, it is mild and humid, while in summer, it becomes hot and muggy.
2.2. Weather Stations
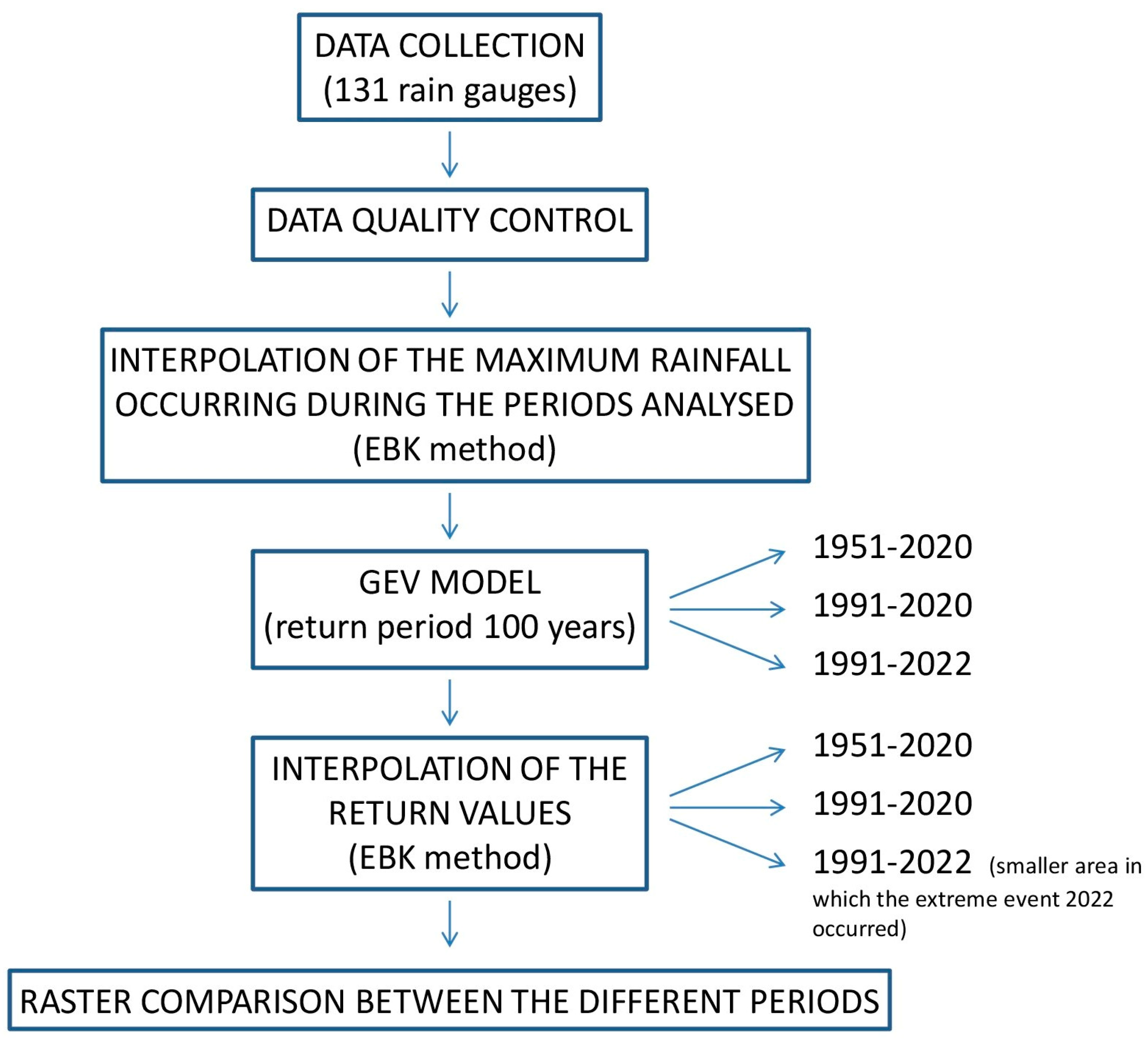
2.3. Flow Chart of the Analysis
2.4. Software
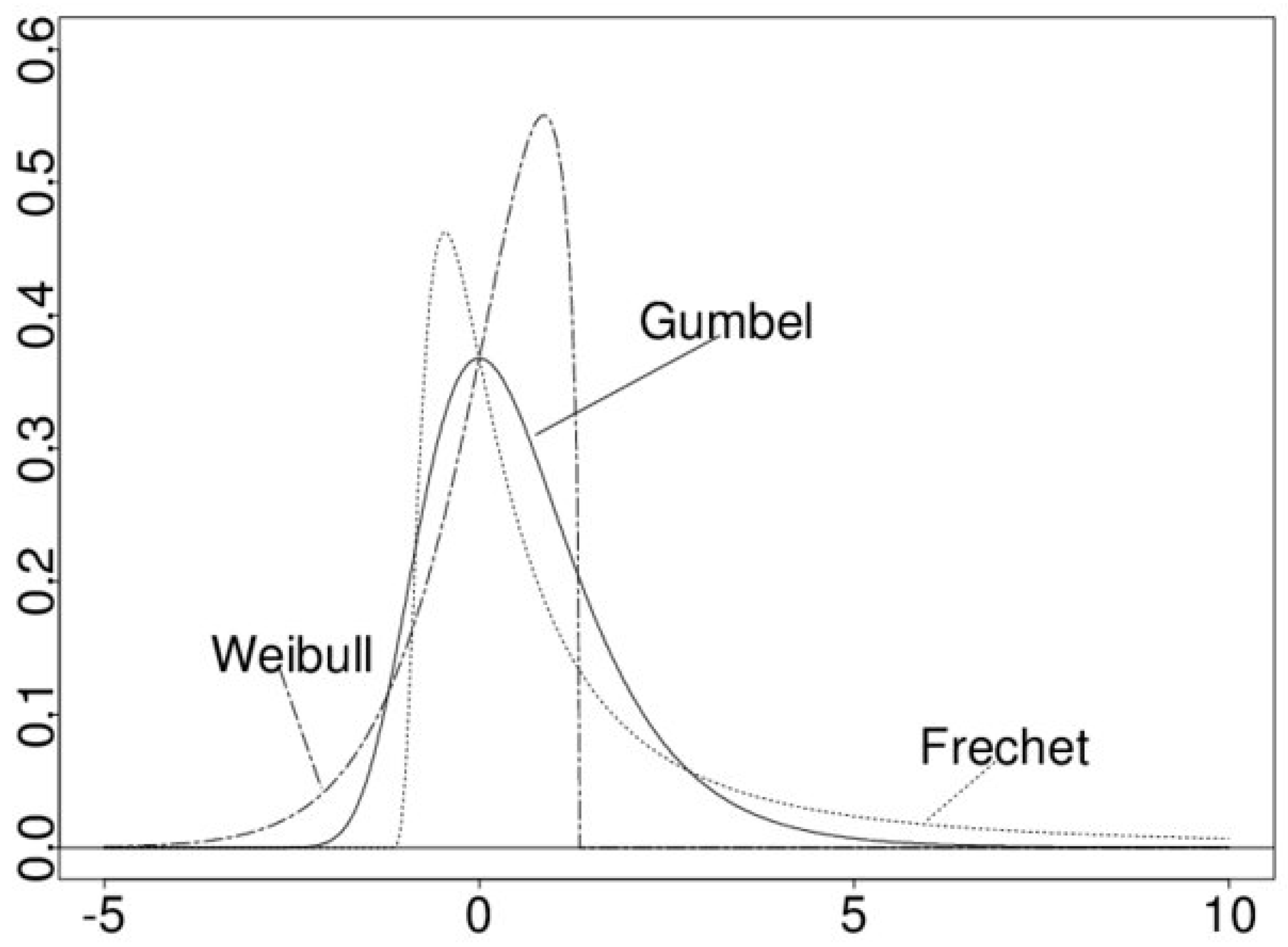
2.5. GEV Model and Statistical Interpolation Techniques
- Range: This is the point at which the semivariogram flattens out and consequently signals the end of autocorrelation between pairs of values.
- Nugget: This is the value of y (other than zero) when x is zero. It often indicates measurement error or variations at distances smaller than the sampling distances.
- Sill: This is the value of the y-axis when the range flattens out.
3. Results
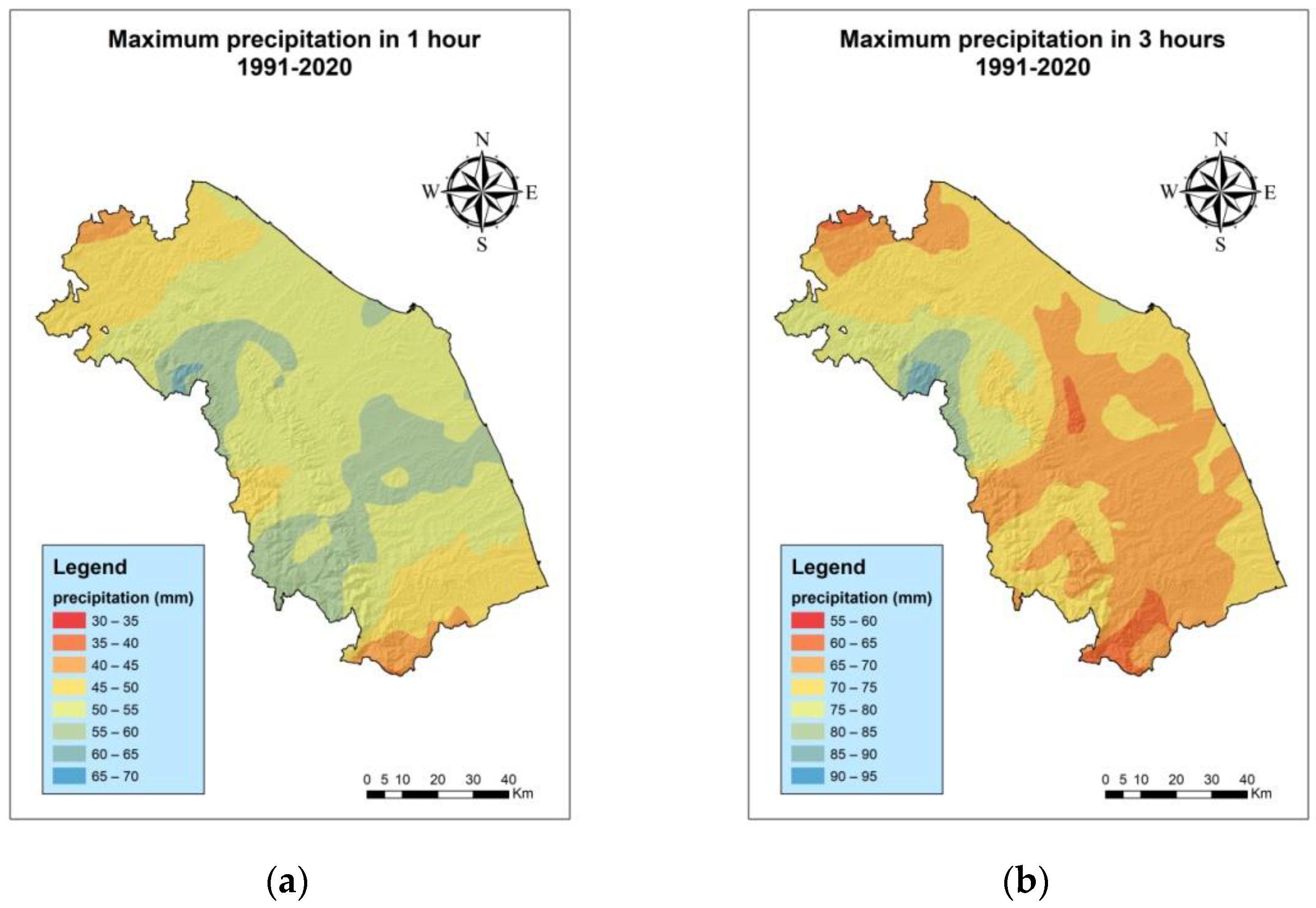
3.1. Analysis of Maximum Extreme Events for the Periods 1991–2020 and 1951–2020
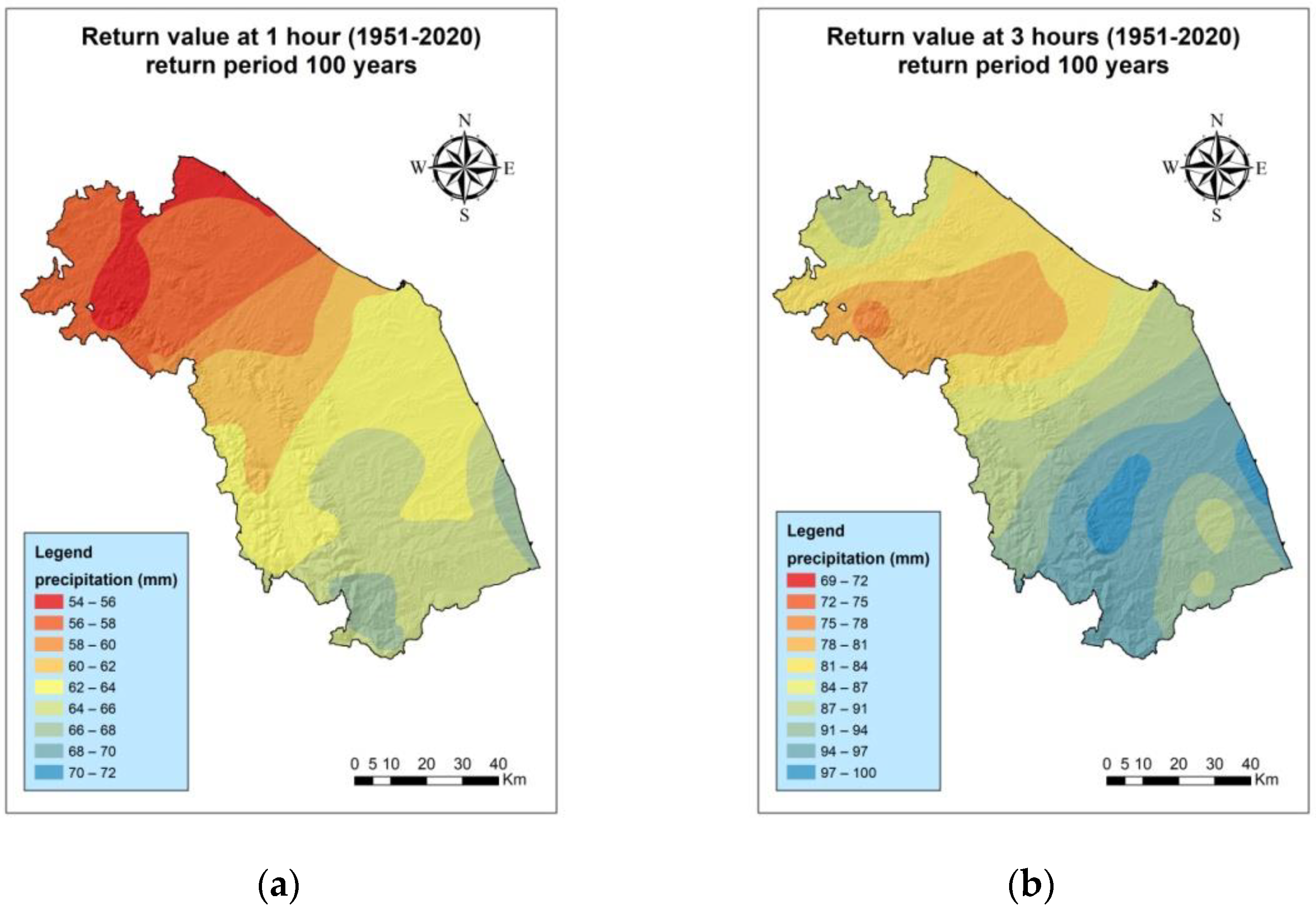
3.2. 100-Year Return Levels for the Periods 1991–2020 and 1951–2020
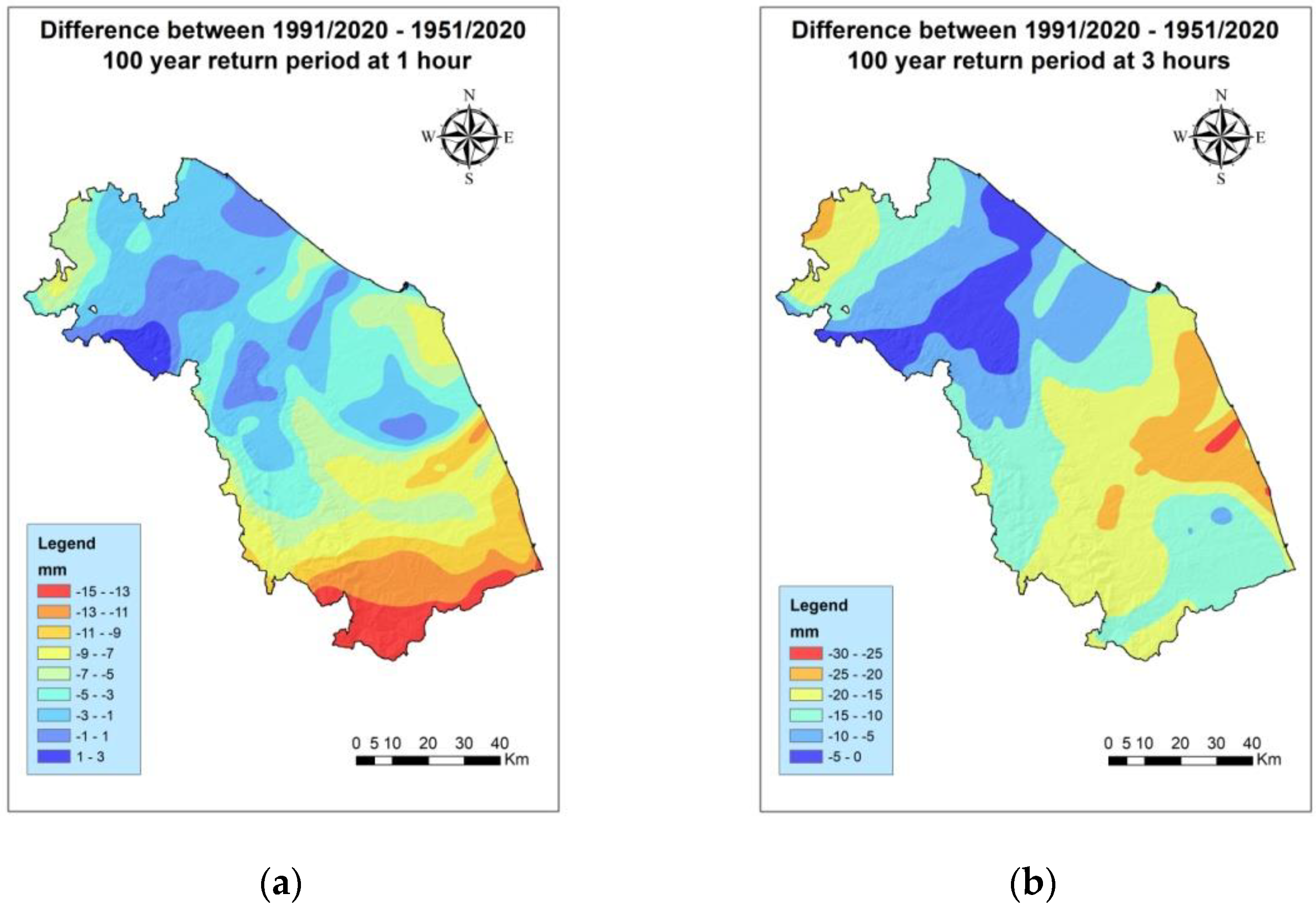
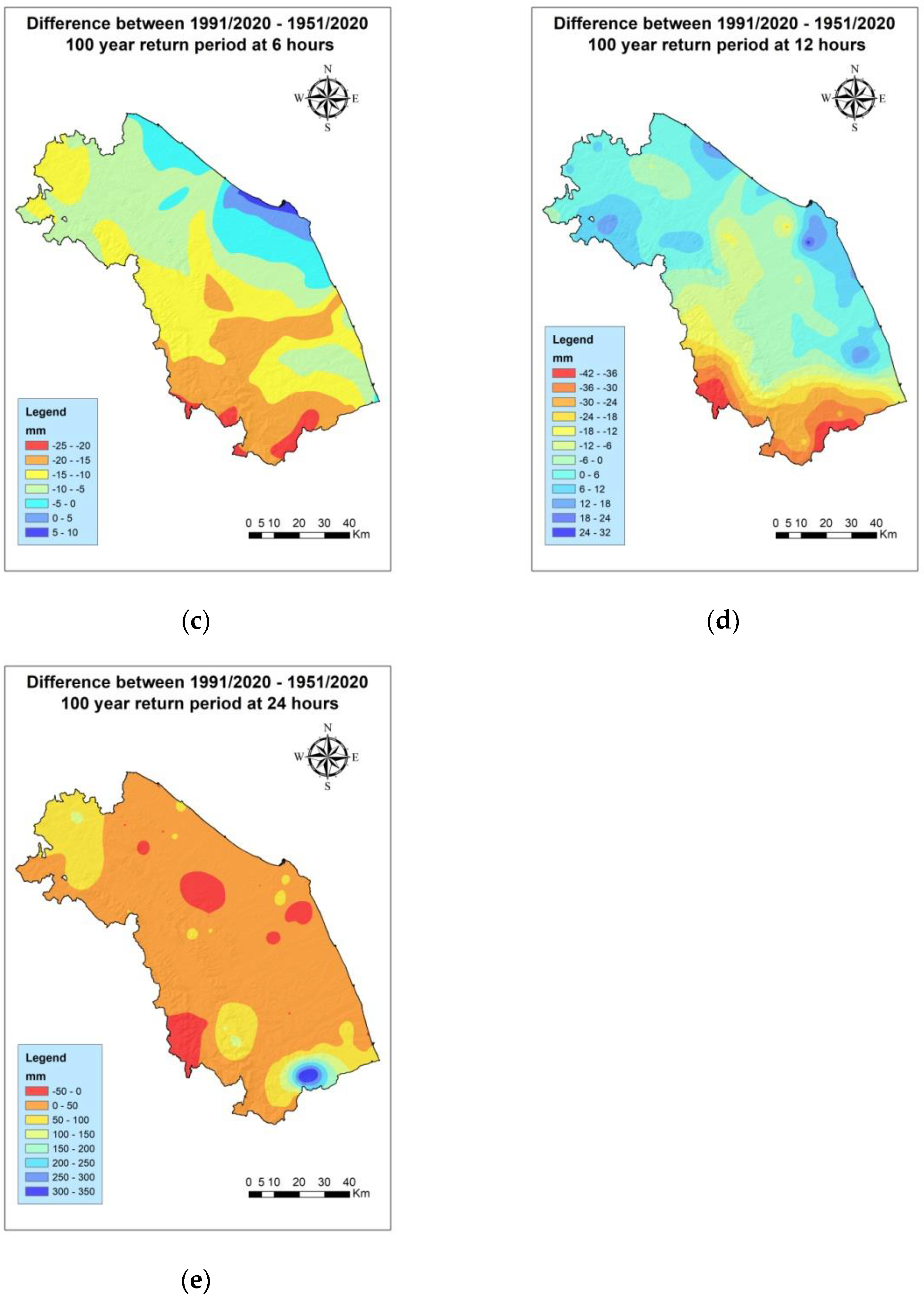
3.3. Analysis of the Differences between the Periods 1991–2020 and 1951–2020
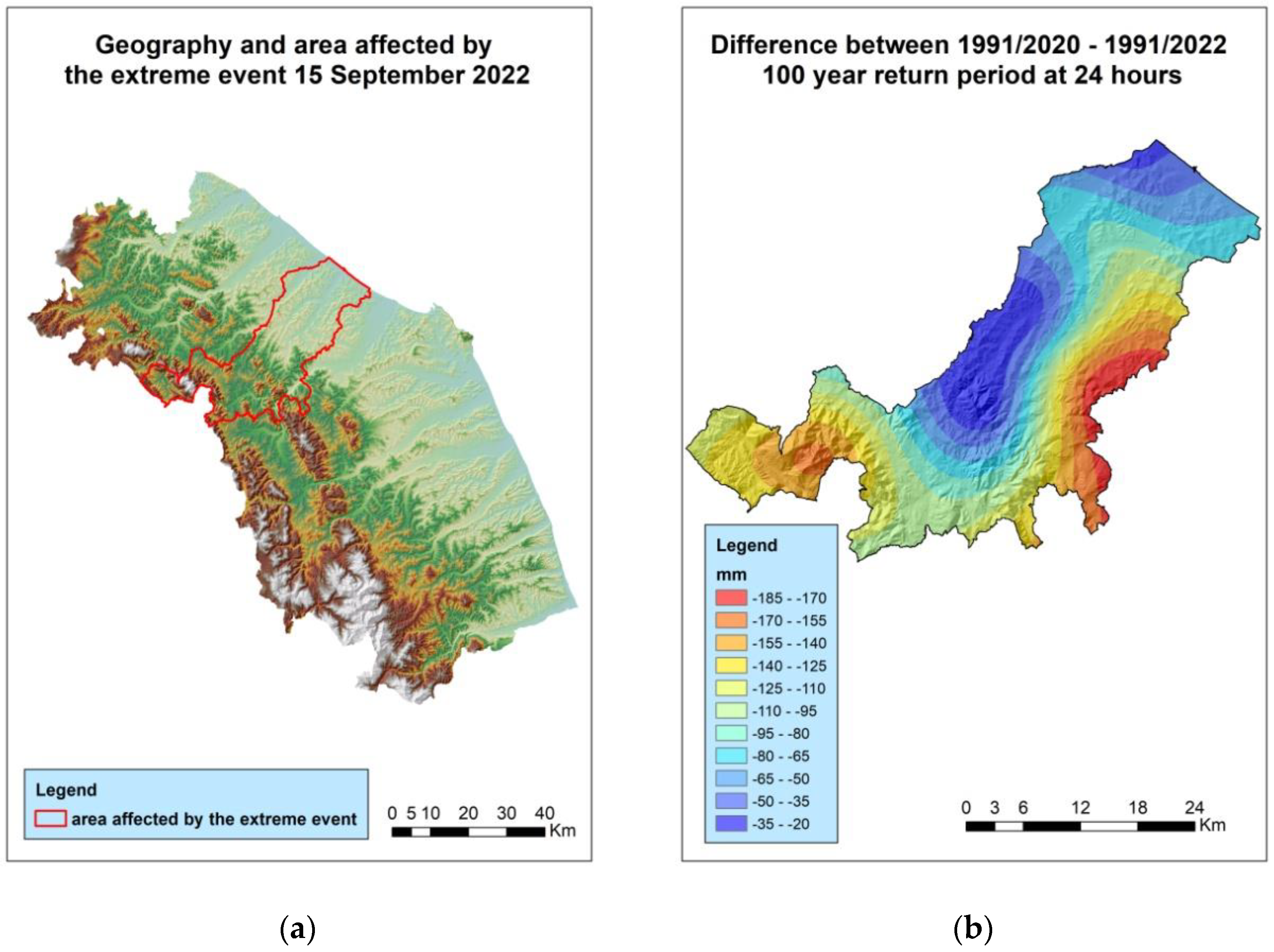
3.4. Effect of the Introduction of an Extreme Event on the 100-Year Return Value Evaluated over 24 h
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Y.; Achberger, C.; Linderholm, H.W. Rain-season trends in precipitation and their effect in different climate regions of China during 1961–2008. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, T. Climate Change: Observed Impacts on Planet Earth; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jubb, I.; Canadell, P.; Dix, M. Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs); Australian Government, Department of the Environment: Canberra, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guhathakurta, P.; Sreejith, O.P.; Menon, P.A. Impact of climate change on extreme rainfall events and flood risk in India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 120, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.B.; Mechem, D.B.; Brunsell, N.A. The effects of Great Plains irrigation on the surface energy balance, regional circulation, and precipitation. Climate 2014, 2, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmith, T.; Thejll, P.; Berg, P.; Boberg, F.; Christensen, O.B.; Christiansen, B.; Christensen, J.H.; Madsen, M.S.; Steger, C. Identifying robust bias adjustment methods for European extreme precipitation in a multi-model pseudo-reality setting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rootzén, H.; Katz, R.W. Design life level: Quantifying risk in a changing climate. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5964–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Ismail, K.; Meng, X. Freeway safety estimation using extreme value theory approaches: A comparative study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 62, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malevergne, Y.; Pisarenko, V.; Sornette, D. On the power of generalized extreme value (GEV) and generalized Pareto distribution (GPD) estimators for empirical distributions of stock returns. Appl. Financ. Econ. 2006, 16, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, J.; Ceresetti, D.; Molinié, G.; Creutin, J.D. A regional GEV scale-invariant framework for Intensity–Duration–Frequency analysis. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Shin, H.; Heo, J.H. Appropriate model selection methods for nonstationary generalized extreme value models. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabson, B.B.; Palutikof, J.P. Tests of the generalized Pareto distribution for predicting extreme wind speeds. JAMC 2000, 39, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Stein, M.L.; Kotamarthi, V.R.; Huang, W.K. Evaluation of dynamically downscaled extreme temperature using a spatially-aggregated generalized extreme value (GEV) model. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alentorn, A.; Markose, S. Generalized extreme value distribution and extreme economic value at risk (EE-VaR). In Computational Methods in Financial Engineering: Essays in Honour of Manfred Gilli; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Jiang, S.; Liu, G.L. Generalized extreme value-pareto distribution function and its applications in ocean engineering. China Ocean Eng. 2019, 33, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, M.C. Bias correction to gev shape parameters used to predict precipitation extremes. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04016035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Barbieri, M.; Pambianchi, G. Reliability of the IMERG product through reference rain gauges in Central Italy. Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGaetano, A.T. Time-dependent changes in extreme-precipitation return-period amounts in the continental United States. JAMC 2009, 48, 2086–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Baloutsos, G. Analysis of a long record of annual maximum rainfall in Athens, Greece, and design rainfall inferences. Nat. Hazards 2000, 22, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Barbieri, M.; D’Aprile, F.; Zardi, D. Analysis of extreme precipitation indices in the Marche region (central Italy), combined with the assessment of energy implications and hydrogeological risk. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, G.; Gentilucci, M.; Aringoli, D.; Pambianchi, G. Analysis of landslide Susceptibility and Tree Felling Due to an Extreme Event at Mid-Latitudes: Case Study of Storm Vaia, Italy. Land 2022, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Djouohou, S.I.; Barbieri, M.; Hamed, Y.; Pambianchi, G. Trend Analysis of Streamflows in Relation to Precipitation: A Case Study in Central Italy. Water 2023, 15, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Jian, J. Environmental prediction, risk assessment and extreme events: Adaptation strategies for the developing world. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4768–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, G.; Grifoni, D.; Torrigiani, T.; Vallorani, R.; Meneguzzo, F.; Gozzini, B. Precipitation changes from two long-term hourly datasets in Tuscany, Italy. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, M.; Pambianchi, G. Prediction of Snowmelt Days Using Binary Logistic Regression in the Umbria-Marche Apennines (Central Italy). Water 2022, 14, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleland, E.; Katz, R.W. extRemes 2.0: An Extreme Value Analysis Package in R. J. Stat. Soft. 2016, 72, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggag, A.M.; Alharbi, A. Spatial Analysis of Soil Properties and Site-Specific Management Zone Delineation for the South Hail Region, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, K.; Gribov, A. Evaluation of empirical Bayesian kriging. Spat. Stat. 2019, 32, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrechts, P.; Resnick, S.I.; Samorodnitsky, G. Extreme value theory as a risk management tool. N. Am. Actuar. J. 1999, 3, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleland, E.; Katz, R. In2extRemes: Into the R Package ExtRemes. Extreme Value Analysis for Weather and Climate Applications, 2016 (No. NCAR/TN-523+STR). Available online: https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/technotes:534 (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Crisci, A.; Gozzini, B.; Meneguzzo, F.; Pagliara, S.; Maracchi, G. Extreme rainfall in a changing climate: Regional analysis and hydrological implications in Tuscany. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Extreme rainfall nonstationarity investigation and intensity–frequency–duration relationship. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Diodato, N.; Meo, M. Reconstruction of a storm map and new approach in the definition of categories of the extreme rainfall, northeastern Sicily. Water 2016, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persiano, S.; Ferri, E.; Antolini, G.; Domeneghetti, A.; Pavan, V.; Castellarin, A. Changes in seasonality and magnitude of sub-daily rainfall extremes in Emilia-Romagna (Italy) and potential influence on regional rainfall frequency estimation. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, V.; Hutchinson, S.L.; Hutchinson, J.S.; Anandhi, A. Extreme daily rainfall event distribution patterns in Kansas. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.K.; Stein, M.L.; McInerney, D.J.; Sun, S.; Moyer, E.J. Estimating changes in temperature extremes from millennial-scale climate simulations using generalized extreme value (GEV) distributions. Adv. Stat. Climatol. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2016, 2, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Aerts JC, J.H.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Baldi, M.; Becker, A.; Bichet, A.; Blöschl, G.; Bouwer, L.M.; Brauer, A.; Cioffi, F.; et al. Floods and climate: Emerging perspectives for flood risk assessment and management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1921–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




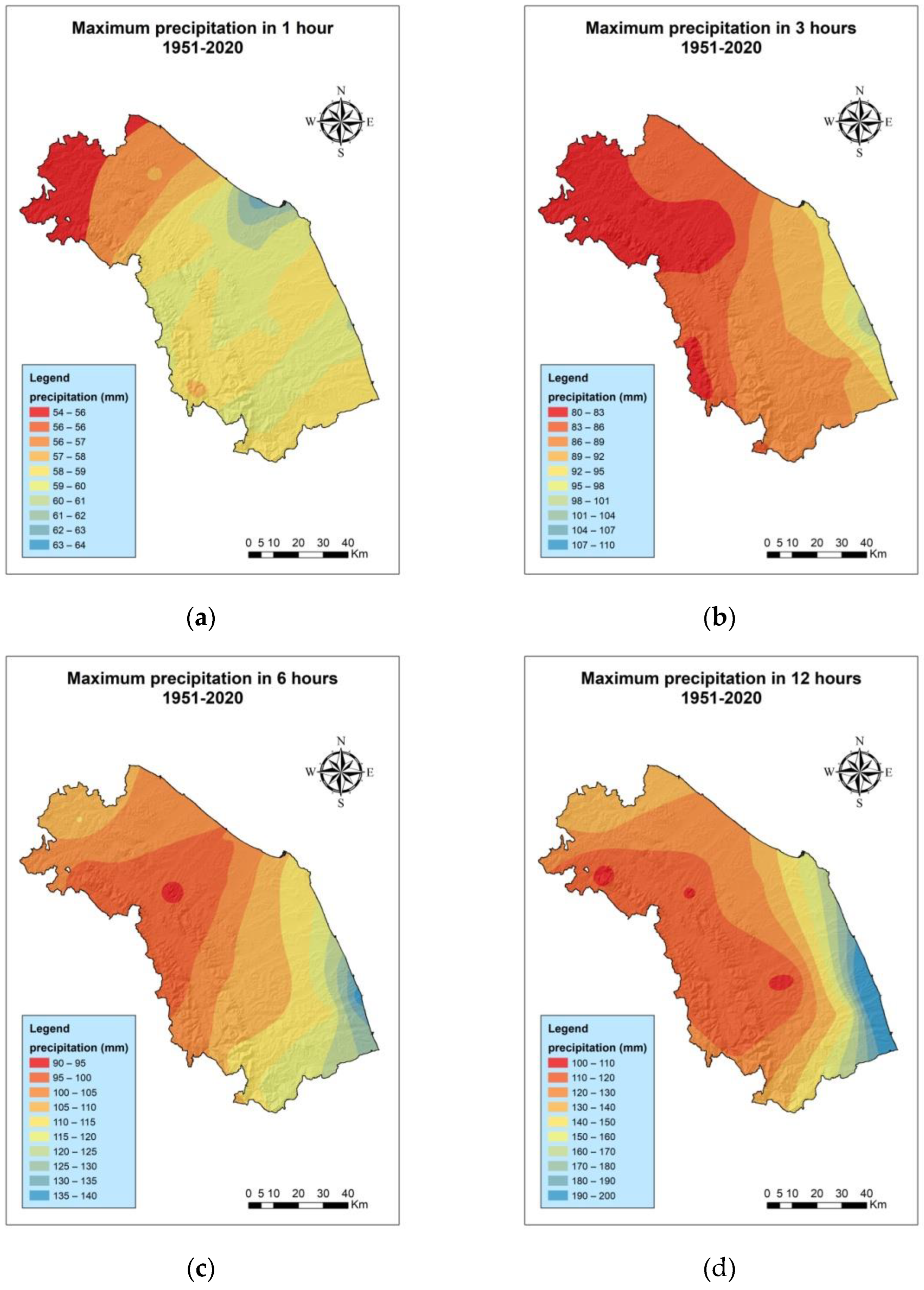
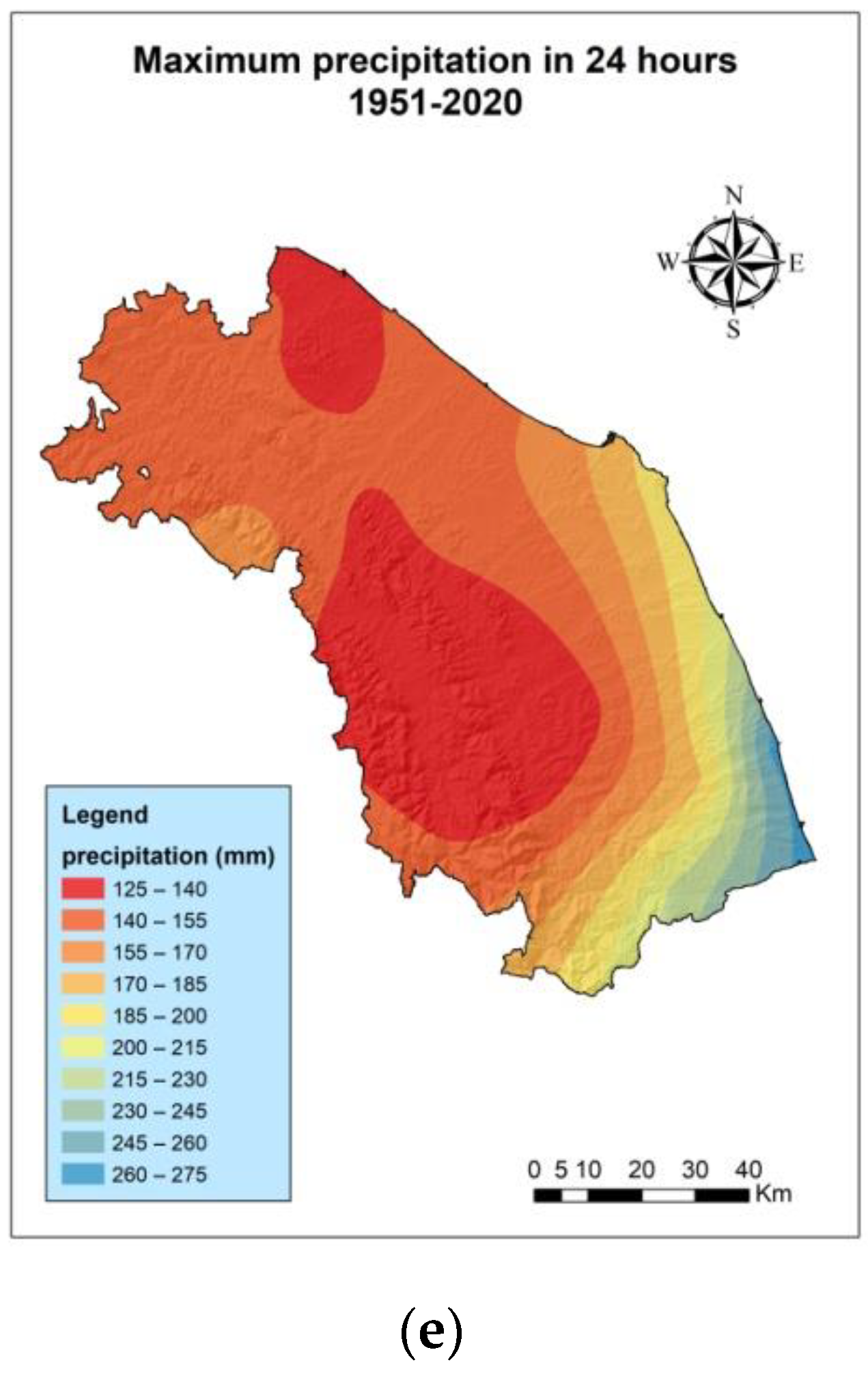

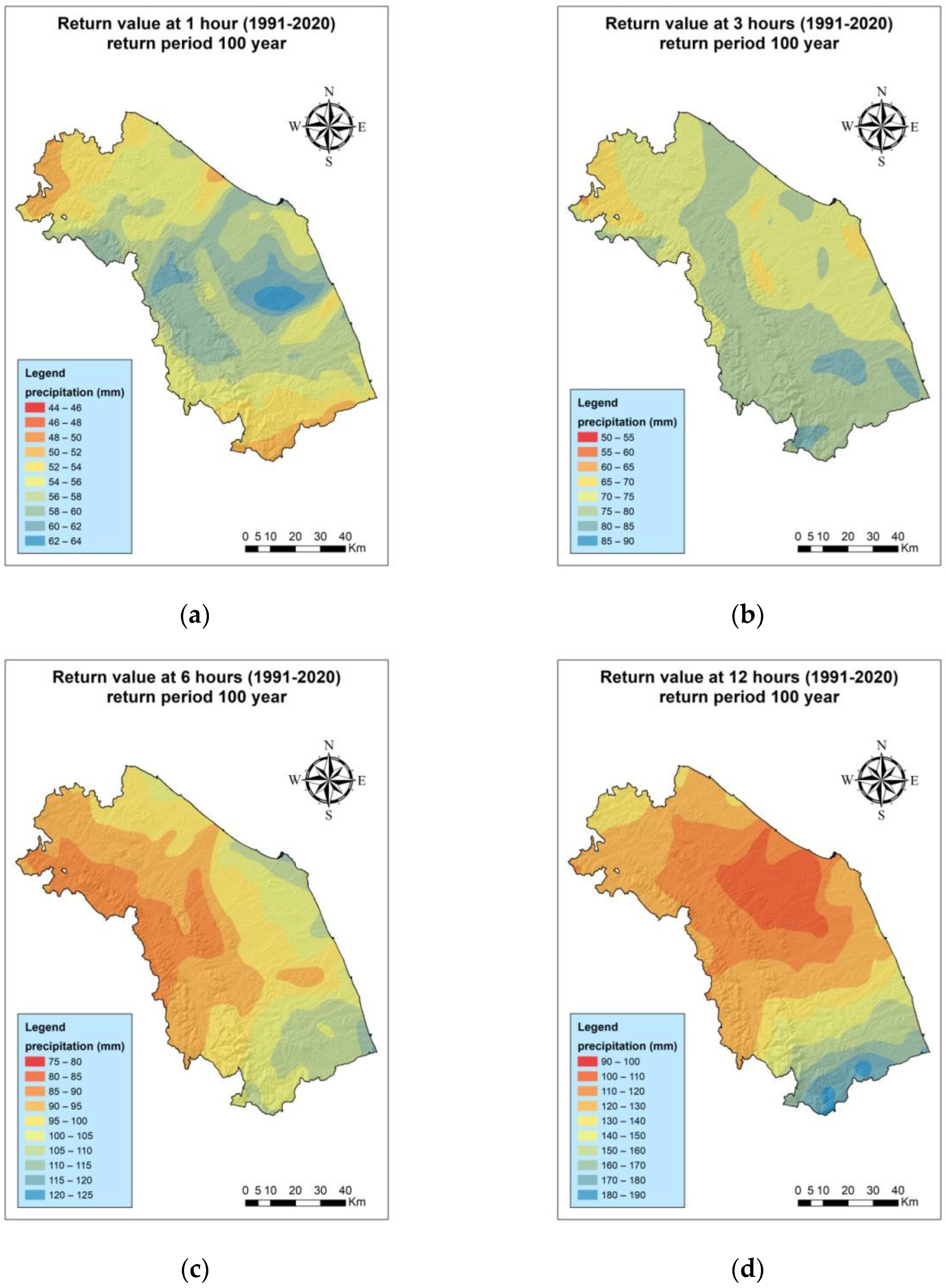
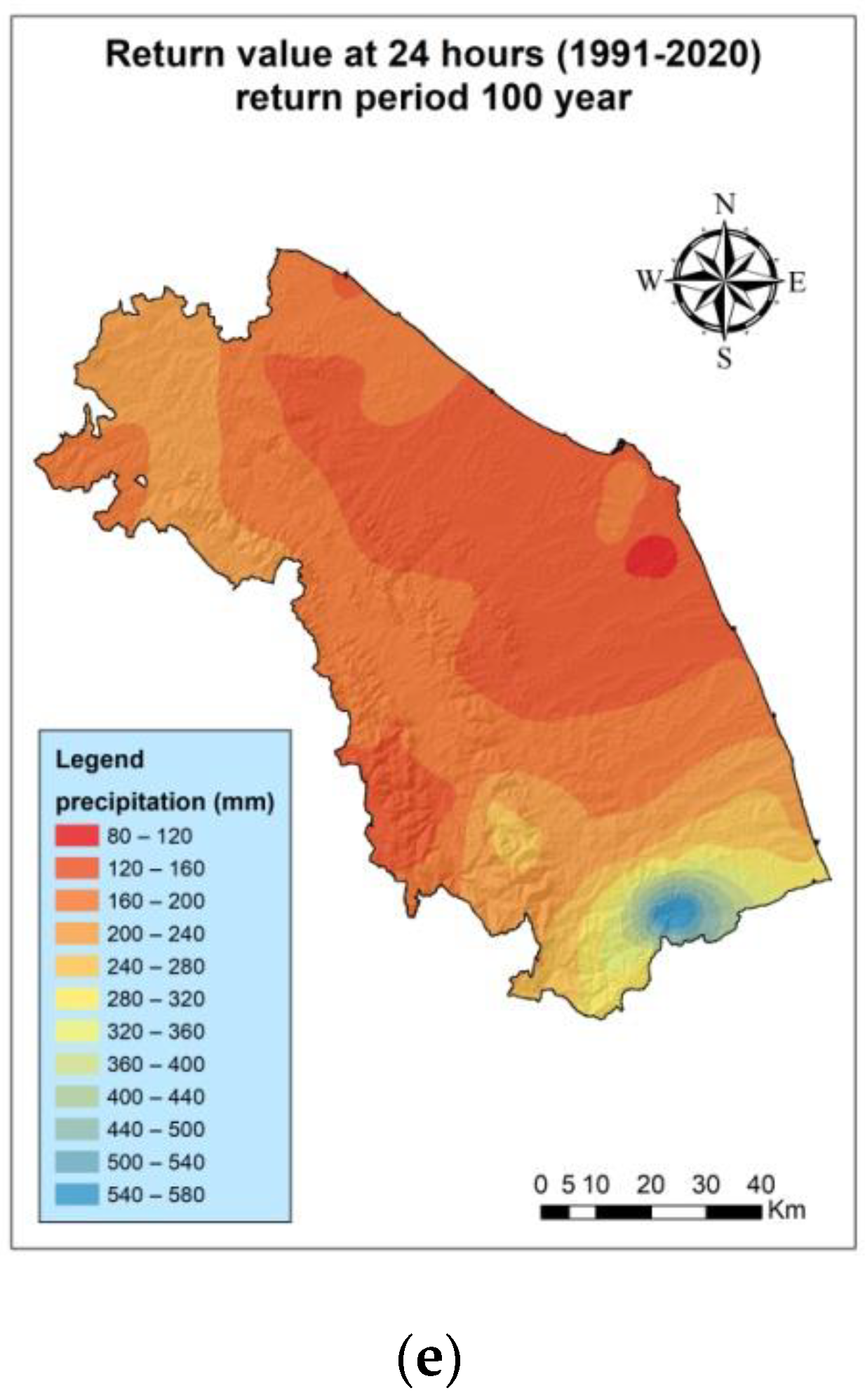

| Code | W.S. | Lifetime |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acqualagna | 1991–2005/2007–2020 |
| 2 | Acquasanta | 1991–2007/2012–2020 |
| 3 | Agugliano | 2008–2020 |
| 4 | Amandola | 1991–2014/2016–2020 |
| 5 | Ancona Regione | 2008–2020 |
| 6 | Ancona Torrette | 1991–2020 |
| 7 | Apecchio | 2008–2020 |
| 8 | Apiro | 1991–2008 |
| 9 | Appignano | 2008–2020 |
| 10 | Arcevia | 1951–2020/2022 |
| 11 | Arquata del Tronto | 1991–2014/2016–2020 |
| 12 | Ascoli Piceno | 1951–2003/2006–2014 |
| 13 | Baraccola | 1991–2007/2010–2020 |
| 14 | Barbara | 1991–2020/2022 |
| 15 | Barchi | 1991–2007 |
| 16 | Bargni | 1951–1959/1961/1964–1971/1973–2007 |
| 17 | Bettolelle | 2008–2020 |
| 18 | Bolognola | 1991–2020 |
| 19 | Bronzo | 2008–2020 |
| 20 | Ca’ Mazzasette | 2008–2018 |
| 21 | Cagli | 1991–2014/2019–2020 |
| 22 | Calcinelli | 1991–2014 |
| 23 | Camerino | 1991–1996/2008–2020 |
| 24 | Campodiegoli | 1991–2020 |
| 25 | Cantiano | 1951–2020/2022 |
| 26 | Capo di Colle | 1991–2007 |
| 27 | Capodacqua | 1991–2005/2007/2009–2020 |
| 28 | Carpegna | 1991–2020 |
| 29 | Cingoli | 1991–2008/2010–2020 |
| 30 | Colle | 2008/2010–2020/2022 |
| 31 | Colleponi | 2008–2020 |
| 32 | Corinaldo | 1991–2020 |
| 33 | Croce di Casale | 1991–2014 |
| 34 | Cupramontana | 1991–2020 |
| 35 | Diga di Carassai | 1951–1965/1968/1984–2007 |
| 36 | Diga di Talvacchia | 1991–2007 |
| 37 | Endesa | 2008–2020 |
| 38 | Esanatoglia convento | 2008/2010–2020 |
| 39 | Fabriano | 1952–2009/2011/2014–2020 |
| 40 | Fano | 1991–2014 |
| 41 | Fermo | 1991–1999/2001–2020 |
| 42 | Filottrano | 1991–2008/2010–2012/2016–2020 |
| 43 | Fiume di Fiastra | 1991–2020 |
| 44 | Fonte Avellana | 1991–2004/2008–2020/2022 |
| 45 | Force | 2008–2020 |
| 46 | Foresta della Cesana | 1991–2006/2010–2020 |
| 47 | Fossombrone | 1991–2017/2019–2020 |
| 48 | Gallo | 2008–2020 |
| 49 | Gelagna Alta | 1993/1996–2015/2018–2020 |
| 50 | Grottammare | 2008–2020 |
| 51 | Grottazzolina | 2008–2020 |
| 52 | Jesi | 1953–1961/1963–2020 |
| 53 | Lamoli | 1991/1993–2007 |
| 54 | Loreto | 1991–2020 |
| 55 | Lornano | 1991–2016 |
| 56 | Loro Piceno | 1951–1962/1964/1966–1967/1969–1972/1991–2020 |
| 57 | Lucrezia | 2008–2020 |
| 58 | Macerata Montalbano | 2009–2020 |
| 59 | Marotta Cesano | 2008–2020 |
| 60 | Mercatello | 1991–2010 |
| 61 | Metaurilia | 2008–2014/2017–2020 |
| 62 | Moie | 1951–2020 |
| 63 | Mondolfo | 1991–2007 |
| 64 | Monte Bove Sud | 2008–2020 |
| 65 | Monte Cavallo | 2008–2020 |
| 66 | Monte Grimano Terme | 2008–2020 |
| 67 | Monte Paganuccio | 2009–2020 |
| 68 | Monte Prata | 2008–2020 |
| 69 | Montecarotto | 1991–2007 |
| 70 | Montecassiano | 1991–2007 |
| 71 | Montecchio | 2011–2020 |
| 72 | Montefano | 2008–2020 |
| 73 | Montelabbate | 2008–2020 |
| 74 | Montemonaco | 1991–2020 |
| 75 | Montepolesco | 2009–2020 |
| 76 | Monterubbiano | 1992–2007 |
| 77 | Morrovalle | 1998–2014 |
| 78 | Mozzano | 2008–2020 |
| 79 | Offida | 1991–2002 |
| 80 | Osimo | 1991–2013 |
| 81 | Osimo Monteragolo | 2008–2020 |
| 82 | Ostra | 1991/1993–2007 |
| 83 | Pedaso | 1951–1969/1971–2007 |
| 84 | Pergola | 1991–2020 |
| 85 | Pesaro | 1991–2001/2008–2020 |
| 86 | Petriano | 1991–2007 |
| 87 | Piagge | 1991–1994/1996–2020 |
| 88 | Pianello di Cagli | 1991–2020 |
| 89 | Pie’ del Sasso | 1991–2007 |
| 90 | Pieve Bovigliana | 1991–1994/1996–2020 |
| 91 | Piobbico | 1952–1961/1963–1973/1991–2014/2016–2020 |
| 92 | Pioraco | 1991–2020 |
| 93 | Poggio S. Romualdo | 1991–2007 |
| 94 | Poggio San Vicino | 2010–2020 |
| 95 | Ponte Tavola | 2008–2020 |
| 96 | Porto S. Elpidio | 1951–1964/1967–1978/1980/2020 |
| 97 | Recanati | 1991–2020 |
| 98 | Ripatransone | 1991–2020 |
| 99 | Rostighello | 2010–2020 |
| 100 | Rotella | 2008–2020 |
| 101 | S. Maria Goretti | 2010–2020 |
| 102 | S. Maria in Arzilla | 2008–2020 |
| 103 | San Benedetto | 2008–2020 |
| 104 | San Giovanni | 2008–2020 |
| 105 | San Lorenzo in Campo | 1991–2008/2010–2020 |
| 106 | San Severino Marche | 2008–2020 |
| 107 | Santa Maria di Pieca | 1999–2020 |
| 108 | Sant’Angelo in Pontano | 1999–2020 |
| 109 | Sant’Angelo in Vado | 1991–2020 |
| 110 | Sarnano | 1954–1973/1991–2007 |
| 111 | Sassocorvaro | 1951–1963/1965–1966/1968–1972/1991–2007 |
| 112 | Sassofeltrio | 2008–2016/2018–2020 |
| 113 | Sassoferrato | 1991–2020 |
| 114 | Sassotetto | 2008–2020 |
| 115 | Sefro | 2010–2020 |
| 116 | Senigallia | 1991–2020 |
| 117 | Serralta | 1991–2001/2008–2020 |
| 118 | Serravalle di Chienti | 1991–2013/2015–2020 |
| 119 | Servigliano | 1991–2014/2016–2020 |
| 120 | Sorti | 1992–2020 |
| 121 | Spindoli | 2010–2020 |
| 122 | Spinetoli | 1991–2020 |
| 123 | Svarchi | 2010–2020 |
| 124 | Tavoleto | 1991–2008/2010–2020 |
| 125 | Tolentino | 1991–1996/1998–2008/2010–2020 |
| 126 | Umito | 2008–2020 |
| 127 | Urbania | 1991–2016/2018–2020 |
| 128 | Urbino | 1991–2020 |
| 129 | Ussita | 2008–2020 |
| 130 | Villa Fastiggi | 2008–2020 |
| 131 | Villa Potenza | 2008–2020 |
| Code | Period | 1 h | 3 h | 6 h | 12 h | 24 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1951–2020 | 53.6 | 72 | 78.8 | 95.5 | 125 |
| 10 | 1991–2020 | 128.3 | 163.2 | 172.5 | 176.2 | 184.1 |
| 39 | 1951–2020 | 63.3 | 88.8 | 100 | 131.8 | 141 |
| 39 | 1991–2020 | 115.4 | 119.6 | 122.5 | 133.8 | 159 |
| 52 | 1951–2020 | 54.7 | 75.7 | 96 | 101.3 | 124.6 |
| 52 | 1991–2020 | 106.2 | 110 | 120 | 126.6 | 148 |
| 83 | 1951–2020 | 75 | 104.5 | 119.2 | 142.8 | 165.4 |
| 83 | 1991–2020 | 90 | 115.2 | 122.2 | 159.3 | 170.8 |
| 110 | 1951–2020 | 75 | 110 | 114.3 | 141.6 | 150 |
| 110 | 1991–2020 | 81.2 | 145.8 | 223.5 | 258.8 | 263.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gentilucci, M.; Rossi, A.; Pelagagge, N.; Aringoli, D.; Barbieri, M.; Pambianchi, G. GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511656
Gentilucci M, Rossi A, Pelagagge N, Aringoli D, Barbieri M, Pambianchi G. GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511656
Chicago/Turabian StyleGentilucci, Matteo, Alessandro Rossi, Niccolò Pelagagge, Domenico Aringoli, Maurizio Barbieri, and Gilberto Pambianchi. 2023. "GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511656
APA StyleGentilucci, M., Rossi, A., Pelagagge, N., Aringoli, D., Barbieri, M., & Pambianchi, G. (2023). GEV Analysis of Extreme Rainfall: Comparing Different Time Intervals to Analyse Model Response in Terms of Return Levels in the Study Area of Central Italy. Sustainability, 15(15), 11656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511656









