Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
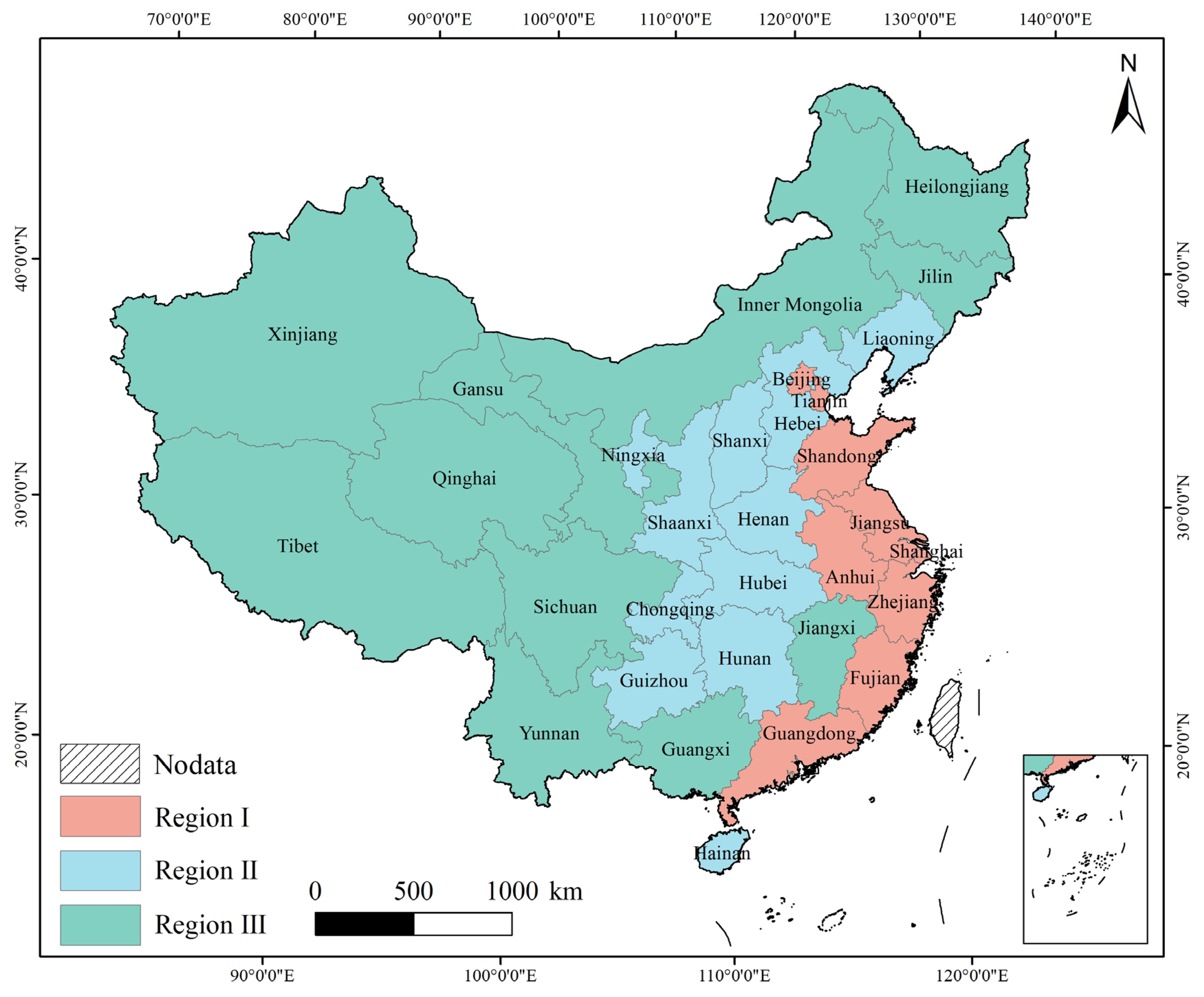
2. Study Area and Datasets
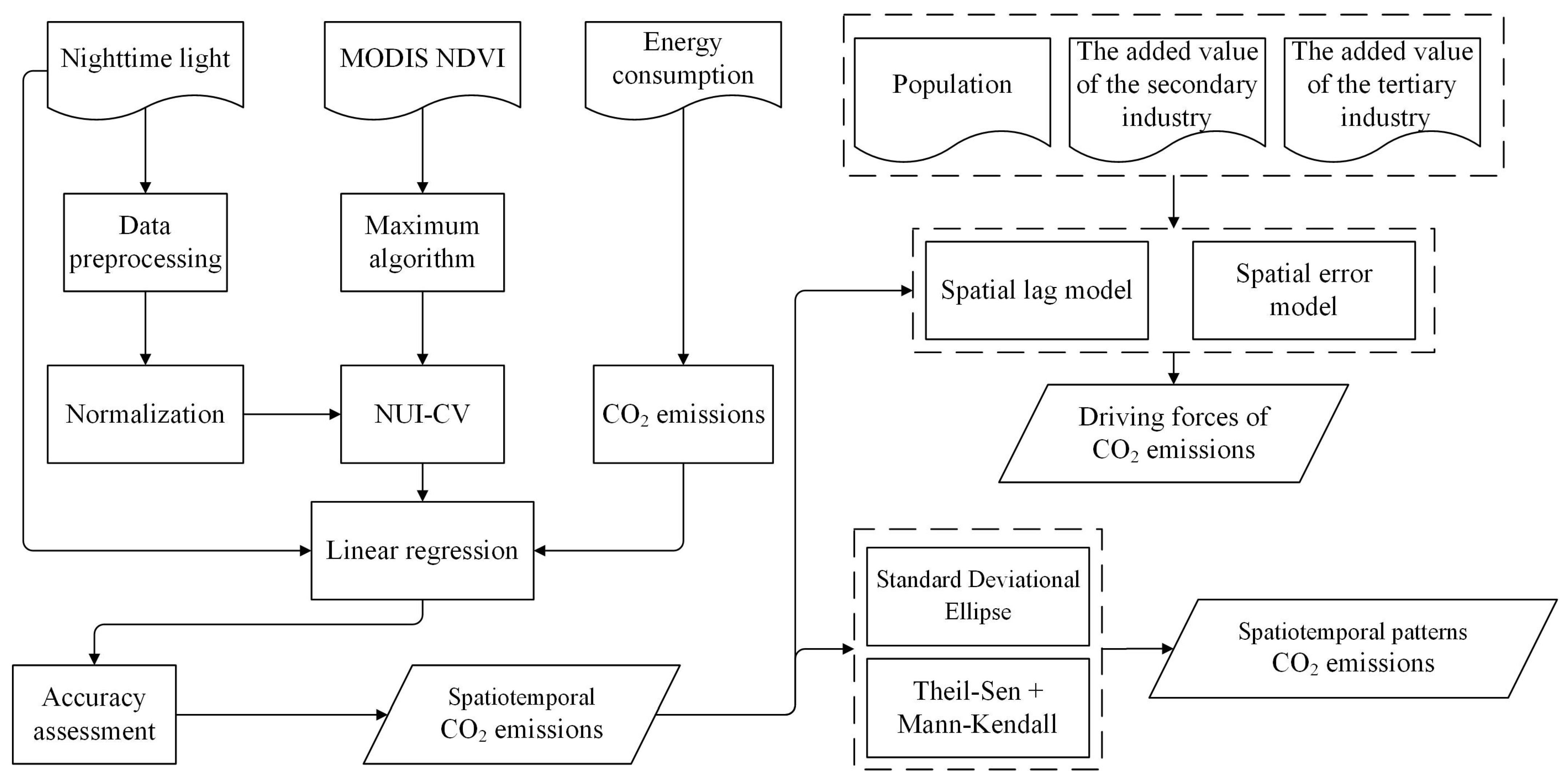
3. Methods
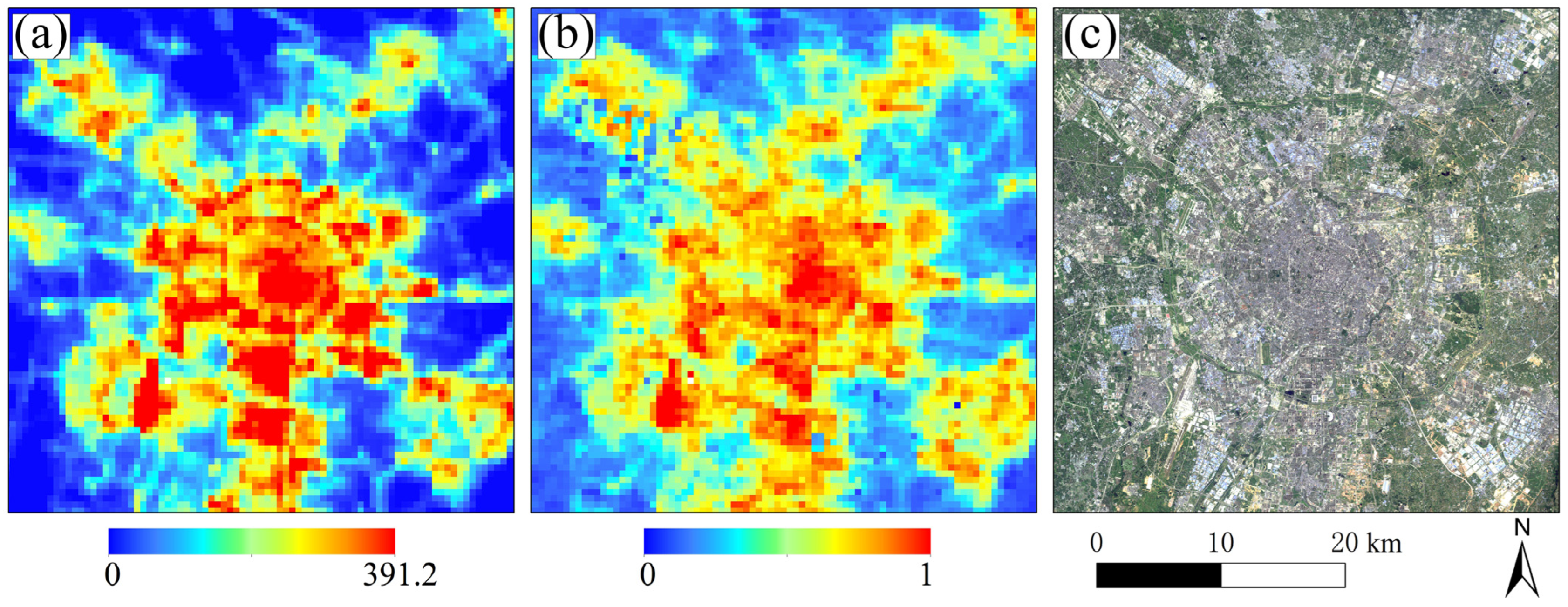
3.1. Preprocessing of Remote Sensing Data
3.2. Estimation of CO2 Emissions
3.3. Assessment of Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions
3.3.1. Analysis of CO2 Emissions Trend
3.3.2. CO2 Emissions Evolution Direction
3.4. Driving Force Analysis of CO2 Emissions
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Variables and Models
4.2. Spatiotemporal CO2 Emissions Dynamics
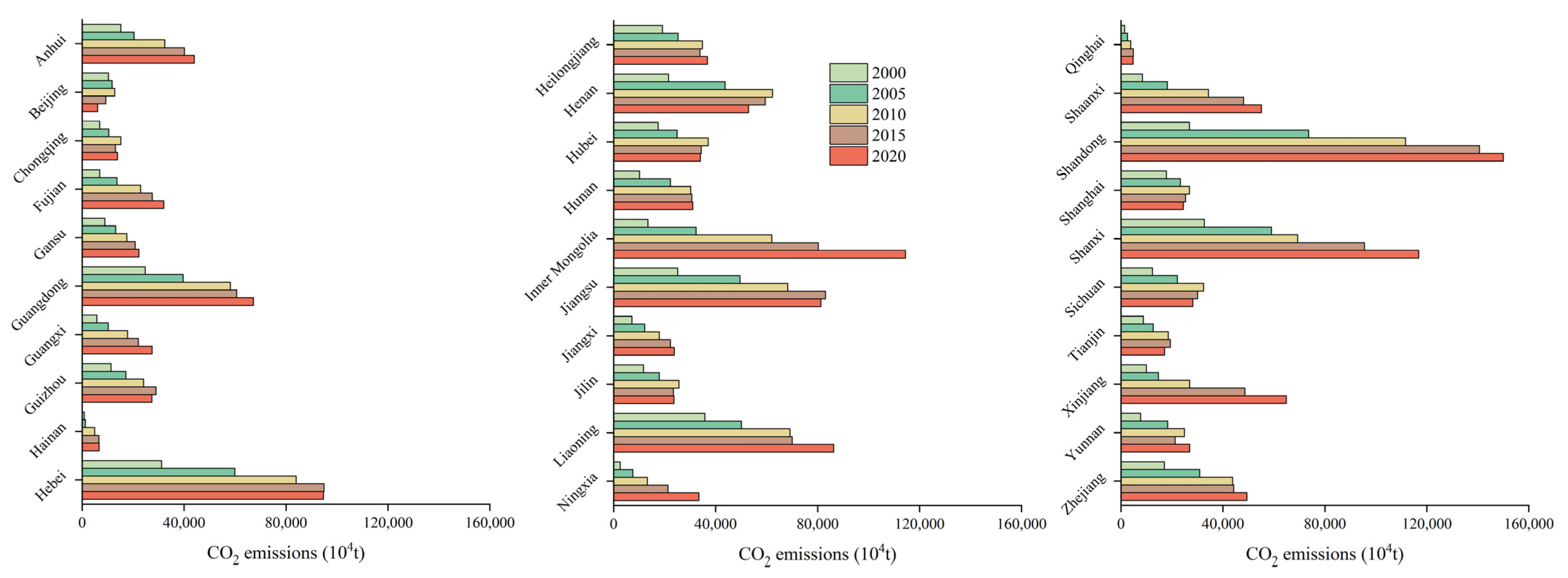
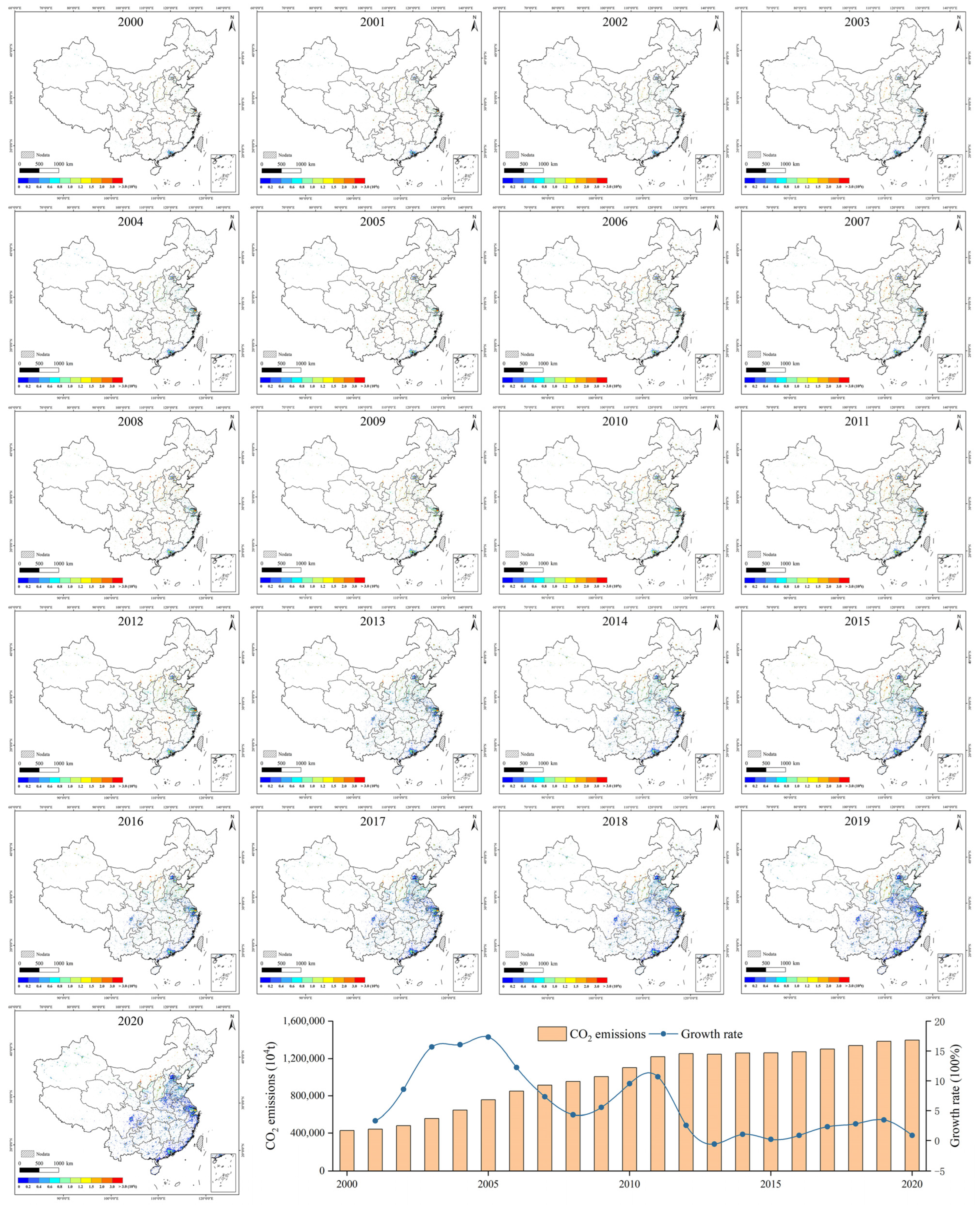
4.2.1. Variations at National and Provincial Scales
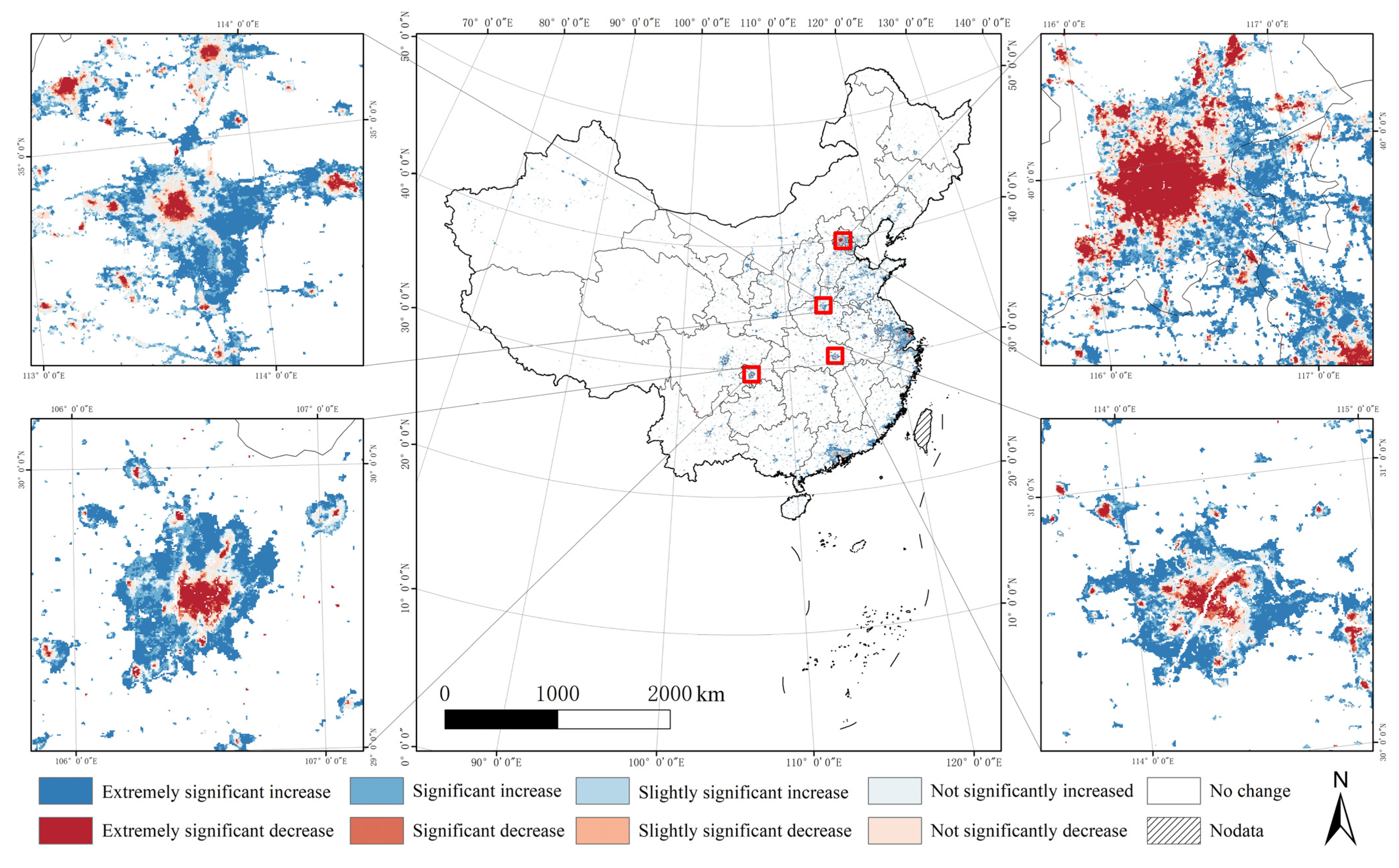
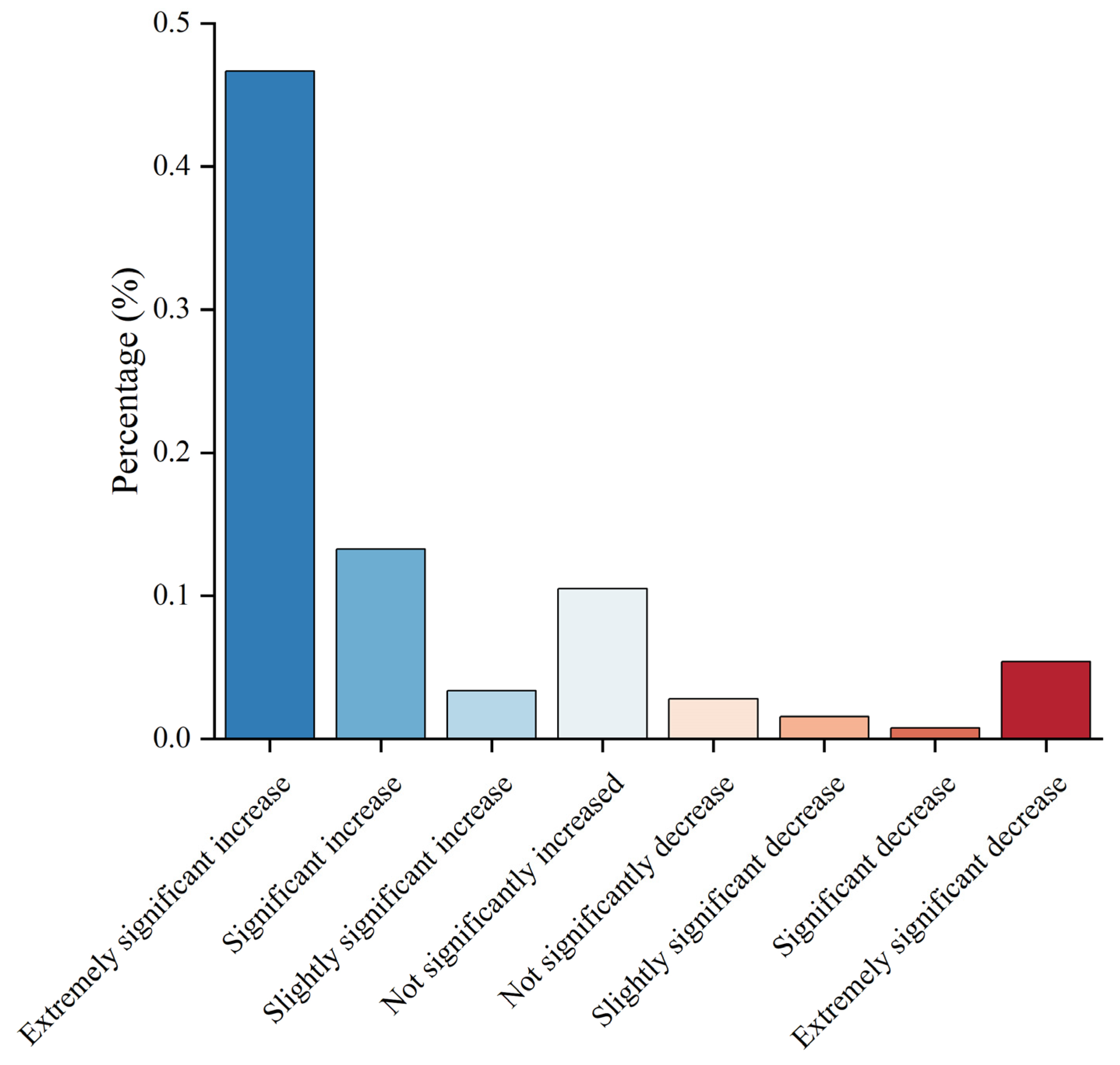
4.2.2. Study of Variation Trends at Pixel Scale
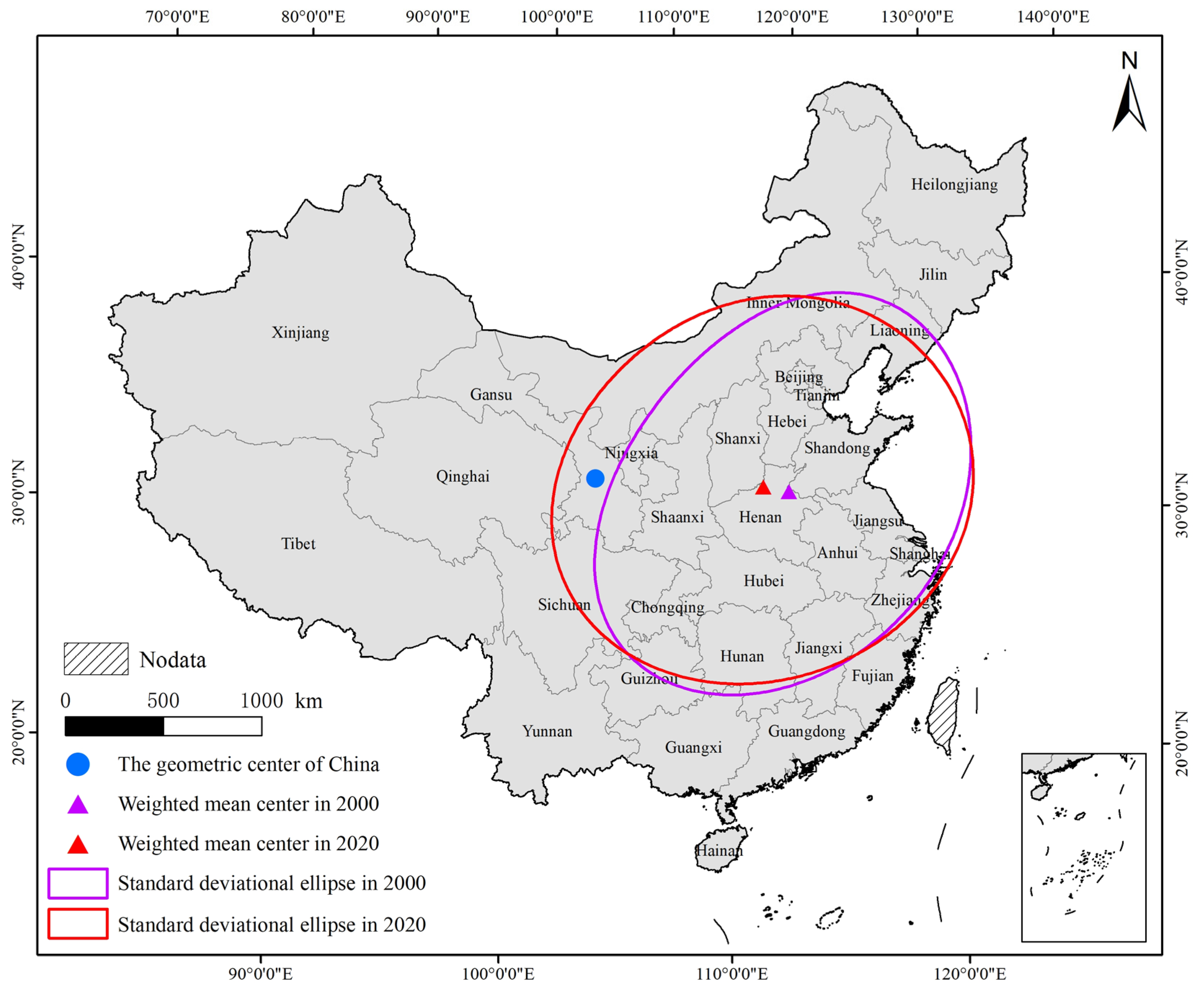
4.2.3. Evaluation of The SDE Results
4.3. Driving Forces of CO2 Emissions
5. Conclusions
6. Policy Implications
7. Limitations and Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhan, P. The effects of urbanization on CO2 emissions in the Pearl River Delta: A comprehensive assessment and panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, R.; Li, X. Investigating the differentiated impacts of socioeconomic factors and urban forms on CO2 emissions: Empirical evidence from Chinese cities of different developmental levels. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, R. Does urbanization redefine the environmental Kuznets curve? An empirical analysis of 134 Countries. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 76, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, R. Trade openness helps move towards carbon neutrality—Insight from 114 countries. Sustain. Dev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Does renewable energy reduce ecological footprint at the expense of economic growth? An empirical analysis of 120 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-C.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, L.-T.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C. Investigating the significant variation of coal consumption in China in 2002–2017. Energy 2020, 207, 118307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Shang, Y. Multiscale analysis on spatiotemporal dynamics of energy consumption CO2 emissions in China: Utilizing the integrated of DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 703, 134394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Pata, U.K.; Li, R.; Kartal, M.T. Digital economy and carbon dioxide emissions: Examining the role of threshold variables. Geosci. Front. 2023, 101644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koondhar, M.A.; Tan, Z.; Alam, G.M.; Khan, Z.A.; Wang, L.; Kong, R. Bioenergy consumption, carbon emissions, and agricultural bioeconomic growth: A systematic approach to carbon neutrality in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal variations of CO2 emissions and their impact factors in China: A comparative analysis between the provincial and prefectural levels. Appl. Energy 2019, 233, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, S.; Tan, X. Decomposition and prediction of China’s carbon emission intensity towards carbon neutrality: From perspectives of national, regional and sectoral level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Pang, B.; Ma, H. Urbanisation, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Y. County-level CO2 emissions and sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Meng, X.; Zhou, X.; Yi, B.; Liu, M.; Xiang, W.-N. A long-term analysis of urbanization process, landscape change, and carbon sources and sinks: A case study in China’s Yangtze River Delta region. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, X. Mapping and evaluating cultivated land fallow in Southwest China using multisource data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 654, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C. A new method for extracting built-up urban areas using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable lights: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, southern China. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Ghosh, T.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.E.; Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E. A global poverty map derived from satellite data. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping Impervious Surface Distribution with Integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, G.; Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, D. Exploring improvement of impervious surface estimation at national scale through integration of nighttime light and Proba-V data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Huang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, W. Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5541–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aegerter, C.; Xu, X.; Szykman, J.J. Potential application of VIIRS Day/Night Band for monitoring nighttime surface PM 2.5 air quality from space. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Tian, L.; Zhao, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, Z. Detecting spatiotemporal dynamics of PM2.5 emission data in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W. Dasymetric mapping of urban population in China based on radiance corrected DMSP-OLS nighttime light and land cover data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Yang, J.; Xue, B.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Jin, C.; Li, X. Spatial evolution of population change in Northeast China during 1992–2018. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 776, 146023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Huang, X. A novel locally adaptive method for modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption based on DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, J. Detecting spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gibson, J. Using Multi-Source Nighttime Lights Data to Proxy for County-Level Economic Activity in China from 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sutton, P.C.; Qi, B. Global Mapping of GDP at 1 km2 Using VIIRS Nighttime Satellite Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z. GDP spatialization in Ningbo City based on NPP/VIIRS night-time light and auxiliary data using random forest regression. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the service industry, traffic, and secondary industry as revealed by the remotely sensed nighttime light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.; Muller, J.P.; Elvidge, C. Night-time Imagery as a Tool for Global Mapping of Socioeconomic Parameters and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ziskin, D.; Tuttle, B.T. Creating a Global Grid of Distributed Fossil Fuel CO2 Emissions from Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Energies 2010, 3, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Xie, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. How does spatiotemporal variations and impact factors in CO2 emissions differ across cities in China? Investigation on grid scale and geographic detection method. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ou, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Jiao, L.; Liu, Y. Estimating spatiotemporal variations of city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: An improved disaggregating model based on vegetation adjusted nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Dietz, J.B.; Bland, T.; Sutton, P.C.; Kroehl, H.W. Radiance Calibration of DMSP-OLS Low-Light Imaging Data of Human Settlements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Samson, E.L.; Currit, N.A. Nighttime-Lights-Derived Fossil Fuel Carbon Dioxide Emission Maps and Their Limitations. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X. A harmonized global nighttime light dataset 1992–2018. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F. A Saturated Light Correction Method for DMSP/OLS Nighttime Satellite Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ji, G.; Yue, Y.; Lai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z. Spatio-temporal dynamics of urban residential CO2 emissions and their driving forces in China using the integrated two nighttime light datasets. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.-C.; Taneja, J. Annual Time Series of Global VIIRS Nighttime Lights Derived from Monthly Averages: 2012 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of npp-viirs nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Kuang, W.; Moran, E. Methods to extract impervious surface areas from satellite images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Using a combination of nighttime light and MODIS data to estimate spatiotemporal patterns of CO2 emissions at multiple scales. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 848, 157630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Kuang, W. Improving Fractional Impervious Surface Mapping Performance through Combination of DMSP-OLS and MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Han, J.; Huang, C. An Improved Vegetation Adjusted Nighttime Light Urban Index and Its Application in Quantifying Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Carbon Emissions in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Li, R.; Pata, U.K. Linking trade openness to load capacity factor: The threshold effects of natural resource rent and corruption control. Gondwana Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, R. Free trade and carbon emissions revisited: The asymmetric impacts of trade diversification and trade openness. Sustain. Dev. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. The effects of trade openness on decoupling carbon emissions from economic growth–Evidence from 182 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L. An improved method of night-time light saturation reduction based on EVI. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2015, 36, 4114–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007 the Fourth Assessment Report of IPCC; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, K.; Yao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, W. Trends in Forest Greening and Its Spatial Correlation with Bioclimatic and Environmental Factors in the Greater Mekong Subregion from 2001 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ye, B.; Bai, Z.; Feng, Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra, P.; Rojas, C.; Ohno, R.; Xue, M.; Gómez, K. A GIS-base exploration of the relationships between open space systems and urban form for the adaptive capacity of cities after an earthquake: The cases of two Chilean cities. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 48, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of electric power consumption in countries along the Belt and Road. Energy 2018, 150, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, F. Analyzing the impact factors of energy-related CO2 emissions in China: What can spatial panel regressions tell us? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, T.; Yang, Y.-Y. Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in China: A spatial panel data approach. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, D.; Li, J. Does foreign direct investment affect environmental pollution in China’s cities? A spatial econometric perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ye, B.; Liu, J. Peak of CO2 emissions in various sectors and provinces of China: Recent progress and avenues for further research. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ma, A.; Wang, H. Lanzhou urban growth prediction based on Cellular Automata. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, D.; Chalvatzis, K.J.; Guan, D.; Ioannidis, A. Energy and carbon intensity: A study on the cross-country industrial shift from China to India and SE Asia. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, C. Spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China: A multiscale perspective. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Description | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nighttime light (DMSP-OLS, VIIRS-DNB) | Long time series of global nighttime light data. | 2000–2020 | https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/YGIVCD (accessed on 13 August 2023) |
| MODIS NDVI (MOD13A1) | Global 500 m spatial resolution 16-day product. | 2000–2020 | Google Earth Engine platform (https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 13 August 2023) |
| Energy consumption data | Energy statistics for 30 provinces (104 t). | 2000–2020 | China Energy Statistics Yearbook |
| Socioeconomic data | Three types of socio-economic indicators: population, AVSI, and AVTI. | 2000, 2010, 2020 | China National Bureau of Statistics |
| Trend Category | ||
|---|---|---|
| Extremely significant increase | ||
| Significant increase | ||
| Slightly significant increase | ||
| Not significantly increased | ||
| Any value | No change | |
| Not significantly decrease | ||
| Slightly significant decrease | ||
| Significant decrease | ||
| Extremely significant decrease |
| Year | NTL | NUI-CV | Year | NTL | NUI-CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.5794 | 0.6461 | 2011 | 0.725 | 0.7718 |
| 2001 | 0.5336 | 0.6312 | 2012 | 0.6069 | 0.7035 |
| 2002 | 0.7525 | 0.7547 | 2013 | 0.7519 | 0.8251 |
| 2003 | 0.7706 | 0.7772 | 2014 | 0.7436 | 0.7907 |
| 2004 | 0.7643 | 0.7848 | 2015 | 0.6644 | 0.7716 |
| 2005 | 0.7096 | 0.7373 | 2016 | 0.6698 | 0.7554 |
| 2006 | 0.6908 | 0.7429 | 2017 | 0.679 | 0.7719 |
| 2007 | 0.763 | 0.7887 | 2018 | 0.6328 | 0.7259 |
| 2008 | 0.7148 | 0.7481 | 2019 | 0.616 | 0.7117 |
| 2009 | 0.5992 | 0.7075 | 2020 | 0.5829 | 0.6754 |
| 2010 | 0.7211 | 0.7666 | Average | 0.6796 | 0.7423 |
| Variables | SLM | SEM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | |
| Population | 0.1335 | 0.1838 | 0.6918 ** | 0.2162 | 0.2395 | 0.6985 ** |
| AVSI | 1.2972 *** | 1.1154 *** | 0.9205 ** | 0.8983 *** | 0.9851 *** | 0.9275 *** |
| AVTI | −0.6465 * | −0.579 ** | −0.9178 *** | −0.1862 | −0.4202 * | −0.8458 *** |
| R2 | 0.8199 | 0.8141 | 0.6258 | 0.8472 | 0.8612 | 0.7072 |
| Log likelihood | −21.4209 | −18.1811 | −27.5137 | −19.7957 | −14.758 | −24.8366 |
| AIC | 52.8418 | 46.3623 | 65.0273 | 47.5915 | 37.5161 | 57.6733 |
| SC | 60.0117 | 53.5322 | 72.1973 | 53.3274 | 43.252 | 63.4093 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713143
Li Y, Guo W, Li P, Zhao X, Liu J. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data. Sustainability. 2023; 15(17):13143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713143
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongxing, Wei Guo, Peixian Li, Xuesheng Zhao, and Jinke Liu. 2023. "Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data" Sustainability 15, no. 17: 13143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713143
APA StyleLi, Y., Guo, W., Li, P., Zhao, X., & Liu, J. (2023). Exploring the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions through a Combination of Nighttime Light and MODIS NDVI Data. Sustainability, 15(17), 13143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713143







