Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Organic Matter Content in Farmland Soil in the Arid Zone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
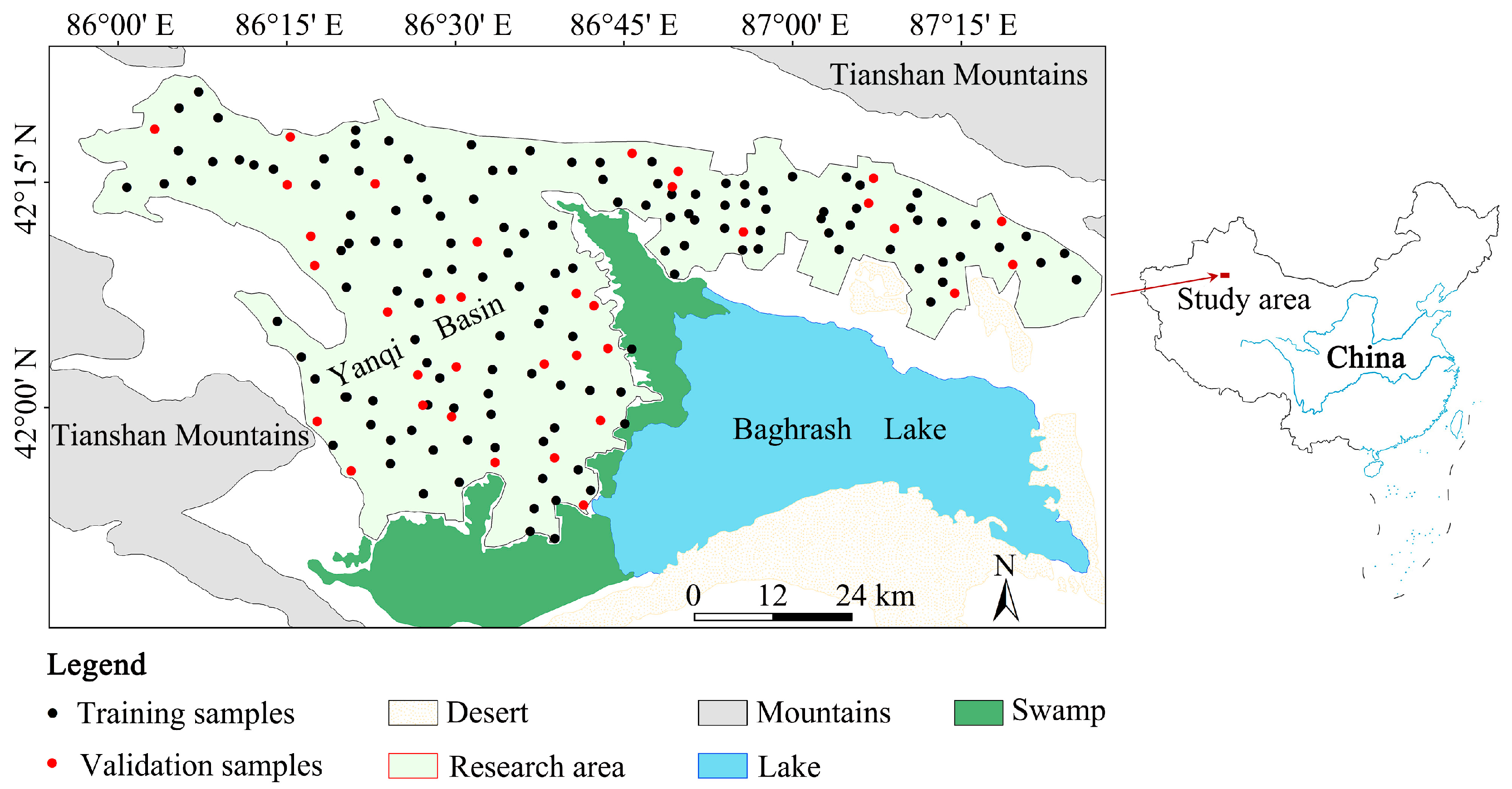
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Indexes Measurement
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3.1. Algorithm Construction
2.3.2. Algorithm Assessment Approach
3. Results
3.1. Statistics of SOM Content
3.2. Analysis of Soil Spectral Reflectivity
3.3. Correlation between SOM Content and Reflectance Data
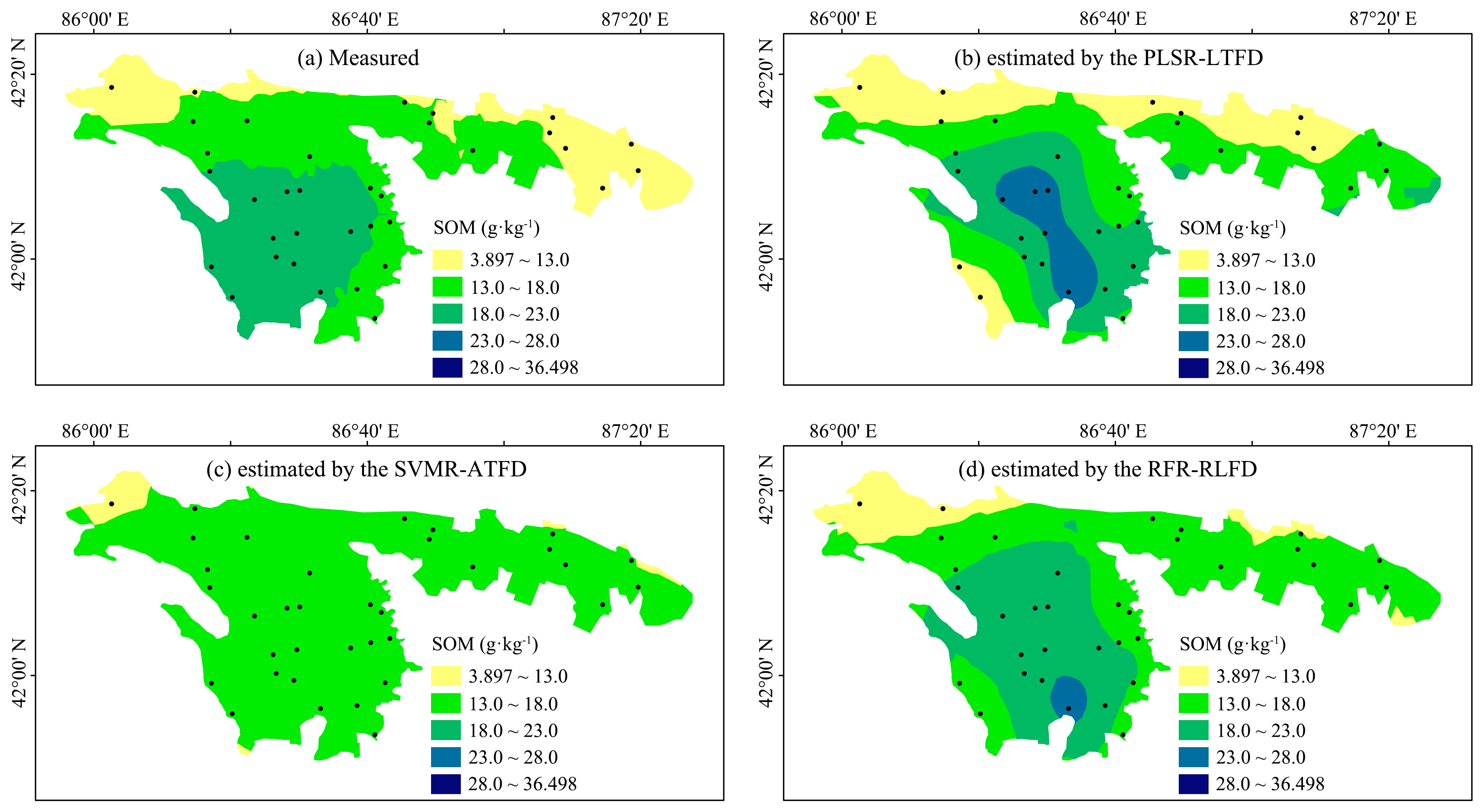
3.4. Modeling and Validation of SOM Content
3.4.1. Estimation of SOM Content with PLSR
3.4.2. Estimation of SOM Content with SVMR
3.4.3. Estimation of SOM Content with RFR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Six, J.; Paustian, K. Aggregate-associated soil organic matter as an ecosystem property and a measurement tool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, A4–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Z.; Ga, M.F.; Yan, J.W.; Li, Z.L.; Leng, P.; Yang, Q.; Duan, S.B. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter content using different spectral preprocessing techniques and PLSR method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Simpson, M.J. Molecular-level methods for monitoring soil organic matter responses to global climate change. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 13, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Lavallee, J.M. Soil organic matter formation, persistence, and functioning: A synthesis of current understanding to inform its conservation and regeneration. Adv. Agron. 2022, 172, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Schillaci, C.; Acutis, M.; Lombardo, L.; Lipani, A.; Fantappie, M.; Märker, M.; Saia, S. Spatio-temporal topsoil organic carbon mapping of a semi-arid Mediterranean region: The role of land use, soil texture, topographic indices and the influence of remote sensing data to modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.T.; Chen, S.B.; Xu, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, R. Exploring appropriate preprocessing techniques for hyperspectral soil organic matter content estimation in black soil area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W. Soil organic matter in major pedogenic soil groups. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, S.C.; Arnoud, B.; Brian, M.C.; Michael, E.M.; Zoë, E.R.; Matthew, N.B.; Alex, M.J.C. Biome-scale characterization and differentiation of semi-arid and arid zone soil organic matter compositions using pyrolysis–GC/MS analysis. Geoderma 2013, 200, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, M.S.; Vernon, F.H. Copper complexation by dissolved organic matter in arid soils: A voltametric study. Environments 2018, 5, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.X.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.C.; Yang, W.; Ding, G.W.; Sun, H.; Liang, Z.Y.; Shi, C.C. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter based on different spectral preprocessing techniques. Spectrosc. Lett. 2017, 50, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.M.; Li, M.W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Q.H.; Huang, D.Y. Soil organic matter detection based on pyrolysis and electronic nose combined with multi-feature data fusion optimization. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jia, C.H.; Zhang, K.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.X.; Cui, T.; He, X.T. A rapid detection method for soil organic matter using a carbon dioxide sensor in situ. Measurement 2023, 208, 112471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Q.; Luo, S.J.; Ye, Q.; Li, X.C.; Jiao, W.H. Hyperspectral estimates of soil moisture content incorporating harmonic indicators and machine learning. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Duan, H.C.; Liao, J.; Guo, P.L.; Huang, C.H.; Xue, X.A. Estimation of soil salinization by machine learning algorithms in different arid regions of northwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasenjiang, K.; Yang, S.T.; Nigara, T.; Zhang, F. Hyperspectral estimation of soil electrical conductivity based on fractional order differentially optimized spectral indices. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7237–7248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.C.; Wang, J.N.; Ding, S.T.; Liu, S.H. Effects of hyperspectral data with different spectral resolutions on the estimation of soil heavy metal content: From ground-based and airborne data to satellite-simulated data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.J.; Ke, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, B.B.; Yu, H.L.; Li, H.; Feng, H. Estimation of the soil arsenic concentration using a geographically weighted XGBoost model based on hyperspectral data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.B.; Feng, M.C.; Song, L.F.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.D.; Xie, Y.K.; Jing, B.H.; Xiao, L.J.; Zhang, M.J.; Song, X.Y.; et al. Study on hyperspectral estimation model of soil organic carbon content in the wheat field under different water treatments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18582–18590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Estimation of soil organic matter content using selected spectral subset of hyperspectral data. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, G.J.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Deng, H. Hyperspectral estimation model of forest soil organic matter in northwest Yunnan Province, China. Forests 2019, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, Y.M.; He, J.; Jin, G.; Xie, Y.; Chai, D.; He, L. Response of soil hyperspectral characteristics of different particle sizes to soil organic matter. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2014, 22, 266–270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vašát, R.; Kodešová, R.; Klement, A.; Borůvka, L. Simple but efficient signal pre-processing in soil organic carbon spectroscopic estimation. Geoderma 2017, 298, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C. Hyperspectral retrieval of soil organic matter for different soil types in the Three-river Headwaters Region. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2015, 31, 186–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y. Combining multi-temporal sentinel-2A spectral imaging and Random Forest to improve the accuracy of soil organic matter estimates in the plough layer for cultivated land. Agriculture 2022, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X. Soil organic matter prediction model with satellite hyperspectral image based on optimized denoising method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xie, L.J.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Li, H.R.; Yang, M. Hyperspectral inversion of soil organic matter content in the Three-Rivers source region. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 564–574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Xie, L.; Li, H.; Yue, T. Hyperspectral inversion of soil heavy metals in Three-River Source Region based on random forest model. Catena 2021, 202, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamattursun, E.; Anwar, M.; Ajigul, M.; Gulbanu, H. A human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Yanqi Basin, Silk Road Economic Belt, China. Human Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 9834-88; Methods for Determination of Soil Organic Matter. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
- Askari, M.S.; Cui, J.F.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Holden, N.M. Evaluation of soil structural quality using VIS–NIR spectra. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Yumiti, M.M.; Mao, D.L.; Liang, T. Hyperspectral estimation of heavy metal chromium content in arable soil of arid area oasis. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 2076–2084. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vohland, M.; Besold, J.; Hill, J.; Heinz-Christian, F. Comparing different multivariate calibration methods for the determination of soil organic carbon pools with visible to near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 2011, 166, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, R.; Lin, G.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhao, L. Estimate of soil heavy metal in a mining region using PCC-SVM-RFECV-AdaBoost combined with reflectance spectroscopy. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Deng, F.; He, J.L.; Wei, W. Hyperspectral estimation model for heavy metal arsenic in soil. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 2872–2878. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Ren, H.; Zhuang, D.; Shi, X.; Yu, X. Effects on application of spectroscopy in estimating of soil organic matter content. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2012, 14, 258–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, J.W.; Sudduth, K.A.; Hollinger, S.E. Soil moisture and organic matter prediction of surface and subsurface soils using an NIR soil sensor. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 32, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.S.; Li, X.C.; Ren, W.J.; Wu, Y.A.; Liu, J.Y. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter content using grey relational local regression model. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2021, 11, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiao, X.X.; Li, G.X.; Feng, M.C.; Xie, Y.K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, M.J.; Song, X.Y.; Xiao, L.J.; Anwar, S.; et al. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter and clay content in loess plateau of China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2506–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, Q.; Jiang, X.; Ye, T.; Li, X.; Niu, B. Estimation of soil salt content and organic matter on arable land in the Yellow River Delta by combining UAV hyperspectral and Landsat-8 multispectral imagery. Sensors 2022, 22, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.W.; Li, M.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Long, S.Y.; Guo, Z.L.; Wang, H.N.; Li, W.; Wang, D.A.; Hu, Y.K.; Wei, Y.Y.; et al. Hyperspectral inversion of mercury in reed leaves under different levels of soil mercury contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22935–22945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Bai, Y.L.; Yang, L.P.; Wang, H.J. Application of hyperspectral data for soil organic matter estimation based on principle components regression analysis. Plant Nut. Fert. Sci. 2008, 14, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar]



| Sample Type | n | SOM Content (g·kg−1) | CV (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | SD | |||
| Total | 173 | 43.338 | 1.120 | 16.597 | 7.803 | 47% |
| Training dataset | 138 | 43.338 | 1.120 | 16.667 | 7.997 | 48% |
| Validation dataset | 35 | 36.498 | 3.897 | 16.322 | 6.980 | 43% |
| Spectral Transformation | R | lgR | 1/lgR | Lg(1/R) | FD | SD | RTFD | RTSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum correlation band/nm | 611 | 611 | 611 | 611 | 441 | 2351 | 1045 | 2351 |
| Correlation coefficient | −0.385 * | −0.393 * | 0.366 * | 0.409 * | −0.561 * | −0.434 * | −0.522 * | 0.475 * |
| Spectral Transformation | LTFD | LTSD | RMSFD | RMSSD | ATFD | ATSD | RLFD | RLSD |
| Maximum correlation band/nm | 1014 | 2351 | 421 | 2351 | 1014 | 2351 | 441 | 2351 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.505 * | −0.457 * | −0.532 * | −0.446 * | −0.505 * | 0.457 * | 0.549 * | 0.404 * |
| Spectral Transformation | PLSR | SVMR | RFR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE (%) | MAE | R2 | RMSE (%) | MAE | R2 | RMSE (%) | MAE | |
| R | 0.176 | 10.355 | 4.825 | 0.224 | 6.312 | 4.926 | 0.232 | 6.224 | 5.146 |
| lgR | 0.177 | 10.206 | 4.846 | 0.315 | 5.876 | 4.456 | 0.141 | 6.513 | 5.068 |
| 1/lgR | 0.435 | 5.339 | 4.073 | 0.293 | 6.089 | 4.723 | 0.188 | 6.368 | 5.263 |
| Lg(1/R) | 0.444 | 6.036 | 4.023 | 0.301 | 6.038 | 4.659 | 0.274 | 5.950 | 4.746 |
| FD | 0.647 | 4.496 | 3.853 | 0.331 | 5.915 | 4.735 | 0.712 | 3.996 | 3.227 |
| SD | 0.280 | 6.383 | 5.413 | 0.176 | 6.509 | 5.188 | 0.354 | 5.623 | 4.551 |
| RTFD | 0.664 | 4.158 | 3.318 | 0.316 | 6.399 | 5.037 | 0.625 | 4.376 | 3.683 |
| RTSD | 0.268 | 5.992 | 4.801 | 0.176 | 6.535 | 5.224 | 0.358 | 5.635 | 4.460 |
| LTFD | 0.700 | 4.278 | 3.481 | 0.349 | 5.991 | 4.735 | 0.722 | 3.892 | 3.335 |
| LTSD | 0.166 | 6.435 | 5.112 | 0.184 | 6.498 | 5.210 | 0.349 | 5.648 | 4.478 |
| RMSFD | 0.657 | 4.448 | 3.693 | 0.364 | 5.876 | 4.667 | 0.725 | 3.801 | 3.029 |
| RMSSD | 0.271 | 6.446 | 5.531 | 0.221 | 6.441 | 5.184 | 0.316 | 5.832 | 4.783 |
| ATFD | 0.658 | 4.262 | 3.455 | 0.350 | 5.988 | 4.735 | 0.742 | 3.668 | 2.900 |
| ATSD | 0.166 | 6.435 | 5.112 | 0.184 | 6.498 | 5.210 | 0.381 | 5.555 | 4.324 |
| RLFD | 0.655 | 4.484 | 3.891 | 0.339 | 5.959 | 4.757 | 0.884 | 2.817 | 2.222 |
| RLSD | 0.340 | 6.239 | 5.213 | 0.118 | 6.633 | 5.271 | 0.318 | 5.817 | 4.843 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subi, X.; Eziz, M.; Zhong, Q. Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Organic Matter Content in Farmland Soil in the Arid Zone. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813719
Subi X, Eziz M, Zhong Q. Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Organic Matter Content in Farmland Soil in the Arid Zone. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813719
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubi, Xayida, Mamattursun Eziz, and Qing Zhong. 2023. "Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Organic Matter Content in Farmland Soil in the Arid Zone" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813719
APA StyleSubi, X., Eziz, M., & Zhong, Q. (2023). Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Organic Matter Content in Farmland Soil in the Arid Zone. Sustainability, 15(18), 13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813719





