Integrated Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Biochar Adsorption for the Efficient Removal of Organic Matter and Nutrients from Brazilian Landfill Leachate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
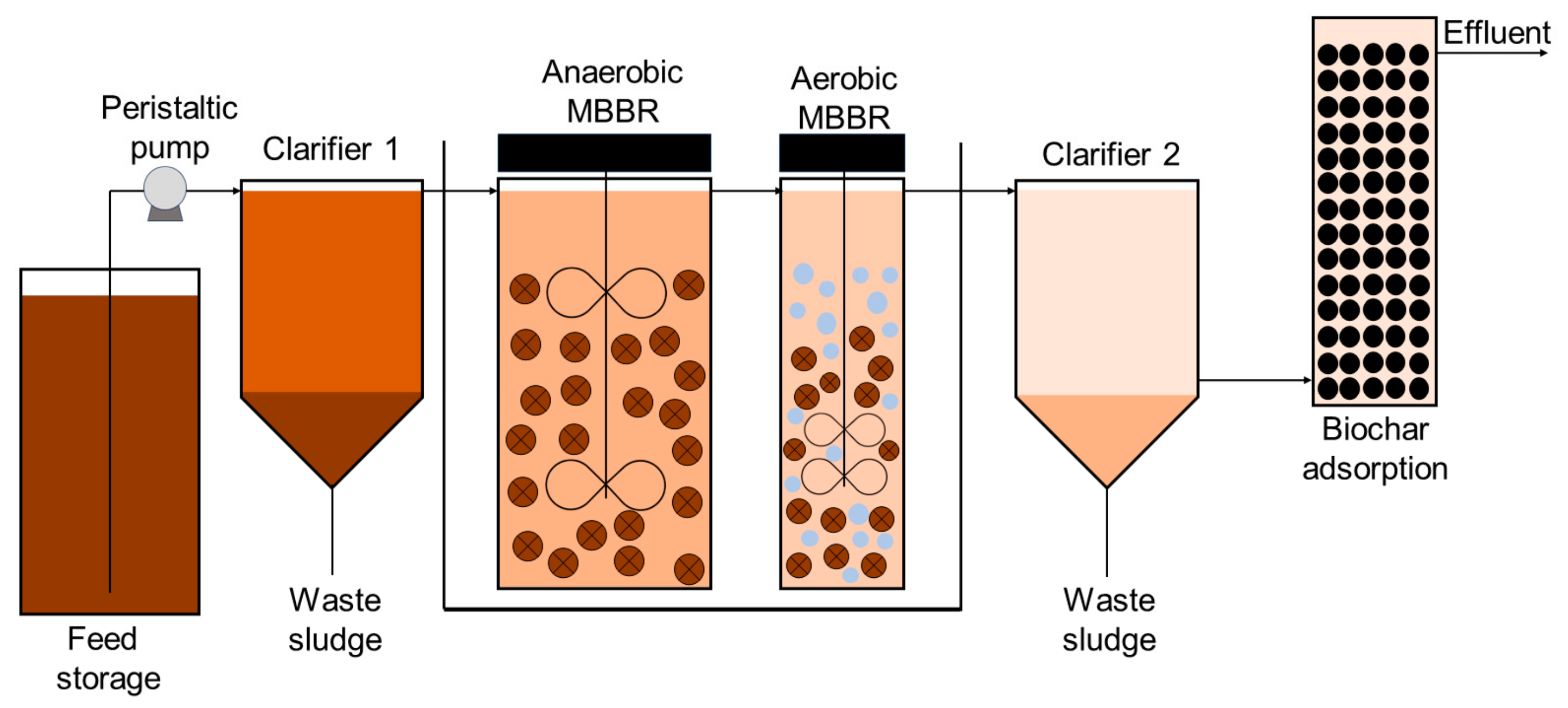
2.1. Experimental Setup and LL Samples
2.2. Operating Procedures
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Biochar Characterization
2.5. Kinetic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biochar Characterization
- 3445 cm−1: The presence of a broad peak at 3445 cm−1 suggests the presence of O-H or N-H functional groups, indicative of potential hydrogen bonding or the presence of hydroxyl or amine groups.
- 2920 cm−1 and 2850 cm−1: Peaks at 2920 cm−1 and 2850 cm−1 are associated with C-H stretching vibrations in aliphatic chains, indicating the presence of methyl or methylene groups within the biochar structure.
- 1625 cm−1: The peak at 1625 cm−1 may correspond to carbonyl (C=O) groups, which could be associated with ketonic/aldehydic functionalities within the biochar.
- 1380 cm−1: A peak at 1380 cm−1 may correspond to C-H bending vibrations, possibly indicating the presence of methyl or methylene groups, similar to the peaks at 2920 cm−1 and 2850 cm−1. They can be also associated with the C=C unsaturated bonds of the aromatic structure of biochar.
- 880 cm−1: The peak at 880 cm−1 is generally associated with C-H bending vibrations in cyclic or aromatic structures.

3.2. COD Removal
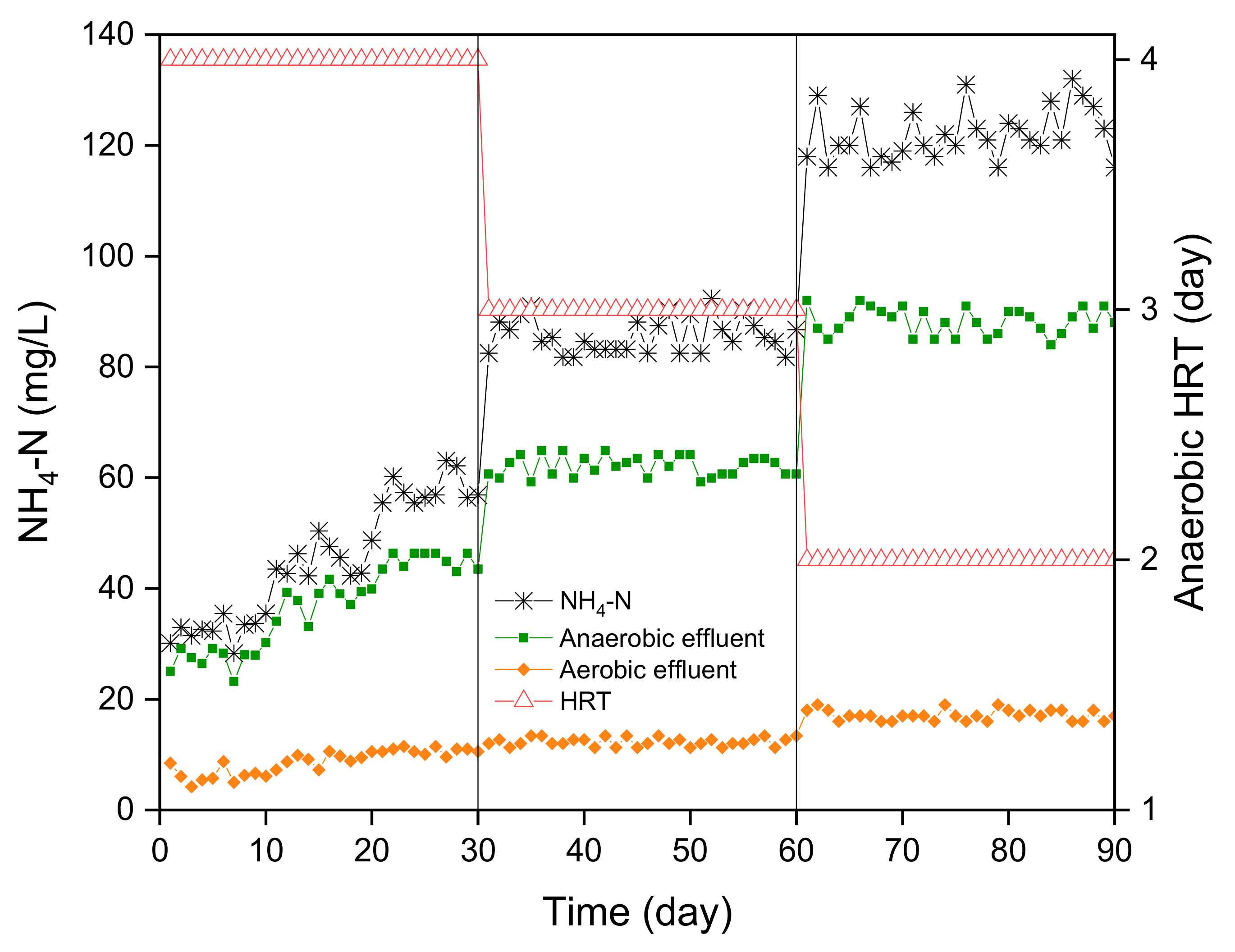
3.3. NH4-N Removal
3.4. TP Removal
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Al-Sulaiman, A.M.; Okasha, R.A. Landfill Leachate: Sources, Nature, Organic Composition, and Treatment: An Environmental Overview. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Land Infiltration for Wastewater Treatment As Efficient, Simple, And Low-Cost Techniques: An Overview. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Oloibiri, V.; Chys, M.; Audenaert, W.; Decostere, B.; He, Y.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S. The Present Status of Landfill Leachate Treatment and Its Development Trend from a Technological Point of View. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2015, 14, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Recent Advances in Municipal Landfill Leachate: A Review Focusing on Its Characteristics, Treatment, and Toxicity Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowczyk, A.; Szymańska-Pulikowska, A. Differences in the Composition of Leachate from Active and Non-Operational Municipal Waste Landfills in Poland. Water 2020, 12, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anqi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Suhua, H.; Xia, L. Review on Landfill Leachate Treatment Methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 565, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, S.M.; Zhao, R.; Pathak, A.; Gupta, A.; Pruden, A.; Novak, J.T.; He, Z. A Review of Landfill Leachate Induced Ultraviolet Quenching Substances: Sources, Characteristics, and Treatment. Water Res. 2018, 145, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; De Carluccio, M.; Cerrato, F.; Garcia Junior, C.A.; Proto, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Rizzo, L. Improving Organic Matter and Nutrients Removal and Minimizing Sludge Production in Landfill Leachate Pre-Treatment by Fenton Process through a Comprehensive Response Surface Methodology Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Fiorentino, A.; Proto, A. Greywater Treatment for Reuse: Effect of Combined Foam Fractionation and Persulfate-Iron Based Fenton Process in the Bacterial Removal and Degradation of Organic Matter and Surfactants. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, D.; Chung, J.-S. Simultaneous Removal of COD and Ammonium from Landfill Leachate Using an Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving-Bed Biofilm Reactor System. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanavarotai, K.; Kamyab, H.; Nor Anuar, A.; Khademi, T.; Yuzir, A.; Ashokkumar, V.; Rezania, S. Storage and Reactivation of Aerobic Granular Sludge: A Review. Fuel 2022, 330, 125536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jery, A.; Aldrdery, M.; Shirode, U.R.; Gavilán, J.C.O.; Elkhaleefa, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Sammen, S.S.; Tizkam, H.H. An Efficient Investigation and Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Decolorization of Wastewater by Using Zeolite Catalyst in Electro-Fenton Reaction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Cucciniello, R.; Motta, O.; Rizzo, L.; Proto, A. Combination of Foam Fractionation and Photo-Fenton like Processes for Greywater Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; Soriano-Molina, P.; Abeledo-Lameiro, M.J.; de la Obra, I.; Proto, A.; Polo-López, M.I.; Pérez, J.A.S.; Rizzo, L. Neutral (Fe3+-NTA) and Acidic (Fe2+) pH Solar Photo-Fenton Vs Chlorination: Effective Urban Wastewater Disinfection Does Not Mean Control of Antibiotic Resistance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliapan, S.; Arumugam, N.; Md Din, M.F.; Kamyab, H.; Ebrahimi, S.S. Chapter 11—Anaerobic Treatment of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Leachate. In Bioreactors; Singh, L., Yousuf, A., Mahapatra, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 175–193. ISBN 978-0-12-821264-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, A.M.; Abd-El-Mageed, H.; Ghanem, N. Biological Treatment of Hazardous Heavy Metals by Streptomyces Rochei ANH for Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Airoldi, M. Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; El-Wafai, N.A.; Abou-Aly, H.E.; Salem, H.M.; Soliman, S.M.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Elrys, A.S.; Selim, S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; et al. Hazardous Wastes and Management Strategies of Landfill Leachates: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jery, A.E.; Noreen, A.; Isam, M.; Arias-Gonzáles, J.L.; Younas, T.; Al-Ansari, N.; Sammen, S.S. A Novel Experimental and Machine Learning Model to Remove COD in a Batch Reactor Equipped with Microalgae. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-Y.; Zeng, G.-M.; Yang, Z.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, M.; Sun, H.-S.; Ji, L.-L.; Chen, Y. Biological Treatment of Landfill Leachate with the Integration of Partial Nitrification, Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation and Heterotrophic Denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.; Yanowitz, J.; Ratcliff, M.; McCormick, R.L. Renewable Oxygenate Blending Effects on Gasoline Properties. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4723–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helness, H.; Ødegaard, H. Biological Phosphorus Removal in a Sequencing Batch Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahren, S.J.; Rintala, J.A.; Ødegaard, H. Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor Treating Thermomechanical Pulping Whitewater under Thermophilic Conditions. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusten, B.; Siljudalen, J.G.; Strand, H. Upgrading of a Biological-Chemical Treatment Plant for Cheese Factory Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, B.; Siljudalen, J.G.; Wien, A.; Eidem, D. Biological Pretreatment of Poultry Processing Wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghei, S.M.; Hosseini, S.H. The Treatment of Phenolic Wastewater Using a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Page, M.W.; Blaha, L. Full Scale Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor Results from Refinery and Slaughter House Treatment Facilities. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Faggiano, A.; De Carluccio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Cucciniello, R.; Proto, A.; Rizzo, L. Photo-Fenton like Process as Polishing Step of Biologically Co-Treated Olive Mill Wastewater for Phenols Removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; Rizzo, L.; Guilloteau, H.; Bellanger, X.; Merlin, C. Comparing TiO2 Photocatalysis and UV-C Radiation for Inactivation and Mutant Formation of Salmonella Typhimurium TA102. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, A.; Kargı, F. Biological Nutrient Removal from Pre-Treated Landfill Leachate in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qin, L.; Meng, Q.; Fan, Z.; Wu, D. Aerobic SMBR/Reverse Osmosis System Enhanced by Fenton Oxidation for Advanced Treatment of Old Municipal Landfill Leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Hou, H.; Du, C.; Ma, P.-C.; Kadier, A. Application of Biochar for Wastewater Treatment. In Biochar and Its Application in Bioremediation; Thapar Kapoor, R., Treichel, H., Shah, M.P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 67–90. ISBN 9789811640599. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Biochar Technology in Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Kipkemoi Kirui, W.; Lei, M.; Lu, Q.; Bah, H.; Dong, R. Evaluation of Slow Pyrolyzed Wood and Rice Husks Biochar for Adsorption of Ammonium Nitrogen from Piggery Manure Anaerobic Digestate Slurry. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, W.; Lu, L.; Yan, L.; Yu, D. Utilization of Biochar for the Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi Shariat Panahi, H.; Dehhaghi, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Nizami, A.-S.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Mussatto, S.I.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Lam, S.S. A Comprehensive Review of Engineered Biochar: Production, Characteristics, and Environmental Applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.M.; Alfaia, R.G.d.S.M.; Campos, J.C. Landfill Leachate Treatment in Brazil—An Overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An Overview of Landfill Leachate Treatment via Activated Carbon Adsorption Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill Leachate Treatment: Review and Opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chian, E.S.K.; DeWalle, F.B. Sanitary Landfill Leachates and Their Treatment. J. Environ. Eng. Div. 1976, 102, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Vazquez, H.; Jefferson, B.; Judd, S.J. Membrane Bioreactors vs Conventional Biological Treatment of Landfill Leachate: A Brief Review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRSA-CNR, APAT. Metodi Analitici per le Acque; I.G.E.R. srl: Rome, Italy, 2003; ISBN 88-448-0083-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.; Hongwei, J.; Huizhen, X.; Li, L. A New Spectrophotometric Method for Measuring COD of Seawater. J. Ocean Univ. China 2006, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, 301. Available online: https://www.ibacon.com/your-study-type/chemistry/oecd-301310-ready-biodegradability-tests (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Lin, J.; Wang, L. Comparison between Linear and Non-Linear Forms of Pseudo-First-Order and Pseudo-Second-Order Adsorption Kinetic Models for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Activated Carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohamy, H.-A.S.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Kamel, S. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Amphoteric Fluorescence Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Chromium Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Feng, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Gielen, G.; Wu, W. Rice (Oryza sativa L) Plantation Affects the Stability of Biochar in Paddy Soil. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, C.H.; Gong, B.; Joseph, S.D.; Marjo, C.E.; Munroe, P.; Rich, A.M. Imaging of Mineral-Enriched Biochar by FTIR, Raman and SEM–EDX. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janu, R.; Mrlik, V.; Ribitsch, D.; Hofman, J.; Sedláček, P.; Bielská, L.; Soja, G. Biochar Surface Functional Groups as Affected by Biomass Feedstock, Biochar Composition and Pyrolysis Temperature. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2021, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Maruyama, K.; Yoshizawa, N.; Yamada, Y.; Sato, Y. XRD Analysis of Carbon Stacking Structure in Coal during Heat Treatment. Fuel 2004, 83, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Ma, D.; Han, R. Characterization of Bio-Char from Pyrolysis of Wheat Straw and Its Evaluation on Methylene Blue Adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 46, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, E.; Leiknes, T.; Helness, H.; Rasmussen, V.; Ødegaard, H. Effect of Organic Loading Rate on a Wastewater Treatment Process Combining Moving Bed Biofilm and Membrane Reactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zeng, W.; Meng, Q.; Liu, H.; Ma, C.; Peng, Y. Achieving Partial Nitrification, Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal and in-Situ Fermentation (PNPRF) in Continuous-Flow System and Mechanism Analysis at Transcriptional Level. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, Y. Phosphorus Removal and Recovery from Domestic Wastewater in a Novel Process of Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Coupled with Crystallization. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Enhanced Denitrifying Phosphorous Removal in a Novel Anaerobic/Aerobic/Anoxic (AOA) Process with the Diversion of Internal Carbon Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10340–10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Qian, Y.; Xi, P.; Cao, R.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Chai, G.; Huang, M.; Li, K.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Partial Nitrification and Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal in a Sequencing Batch Reactor Treating High-Strength Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, C.W.; Chapin, R.W. Acetic Acid Inhibition of Biological Phosphorus Removal. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, B.F.; de Araujo, C.M.B.; do Nascimento, A.C.; da Costa, G.R.B.; Gomes, B.F.M.L.; da Silva, M.P.; da Silva Santos, R.K.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A. Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 and Basic Blue 12 Using Biochar from Gasification Residues: Batch Tests and Fixed-Bed Breakthrough Predictions for Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ahmad, T.; Hashim, R.; Said, N.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mohamad-Saleh, J.; Sulaiman, O. Comparison of Surface Properties of Wood Biomass Activated Carbons and Their Application against Rhodamine B and Methylene Blue Dye. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | Range | Average ± SD | Value from Literature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 4523–4792 | 4698 ± 67 | 4000–1000 | [39] |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 1659–2067 | 1659 ± 102 | 1000–4000 | [37] |
| TP (mg/L) | 17–27 | 22 ± 3 | 10–100 | [37] |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 117–132 | 123 ± 4 | 250–700 | [39] |
| BOD5/COD | 0.37–0.43 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | - | - |
| NH4-N/COD | 0.02–0.03 | 0.025 ± 0.001 | - | - |
| pH | 7.2–8.4 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 6.5–7.5 | [39] |
| Model | Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH4-N | TP | ||
| PFO | Qmax | 4.39 | 0.16 | 0.075 |
| k1 | 3.7 | 2.39 | 2.16 | |
| R2 | 0.977 | 0.982 | 0.984 | |
| RMSE | 0.24 | 0.010 | 0.005 | |
| PSO | Qmax | 4.61 | 0.17 | 0.079 |
| k2 | 4.8 | 0.19 | 0.09 | |
| R2 | 0.946 | 0.953 | 0.949 | |
| RMSE | 0.36 | 0.014 | 0.006 | |
| Elovich | α | 4.90 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| β | 72.7 | 20.13 | 16.17 | |
| R2 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.91 | |
| RMSE | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| Parameter | Raw LL | MBBR Effluent | Biochar Effluent |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 4698 | 514 | 75 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 1659 | 240 | 13.7 |
| TP (mg/L) | 22 | 8.2 | 0.68 |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 123 | 17 | 0.97 |
| BOD5/COD | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| NH4-N/COD | 0.025 | 0.03 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faggiano, A.; Motta, O.; Ricciardi, M.; Cerrato, F.; Garcia Junior, C.A.; Fiorentino, A.; Proto, A. Integrated Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Biochar Adsorption for the Efficient Removal of Organic Matter and Nutrients from Brazilian Landfill Leachate. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813914
Faggiano A, Motta O, Ricciardi M, Cerrato F, Garcia Junior CA, Fiorentino A, Proto A. Integrated Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Biochar Adsorption for the Efficient Removal of Organic Matter and Nutrients from Brazilian Landfill Leachate. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813914
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaggiano, Antonio, Oriana Motta, Maria Ricciardi, Francesco Cerrato, Carlos Augusto Garcia Junior, Antonino Fiorentino, and Antonio Proto. 2023. "Integrated Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Biochar Adsorption for the Efficient Removal of Organic Matter and Nutrients from Brazilian Landfill Leachate" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813914
APA StyleFaggiano, A., Motta, O., Ricciardi, M., Cerrato, F., Garcia Junior, C. A., Fiorentino, A., & Proto, A. (2023). Integrated Anaerobic–Aerobic Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Biochar Adsorption for the Efficient Removal of Organic Matter and Nutrients from Brazilian Landfill Leachate. Sustainability, 15(18), 13914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813914










