Effects of Subsurface Pipe Drainage Spacing on Soil Salinity Movement in Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Area
Abstract
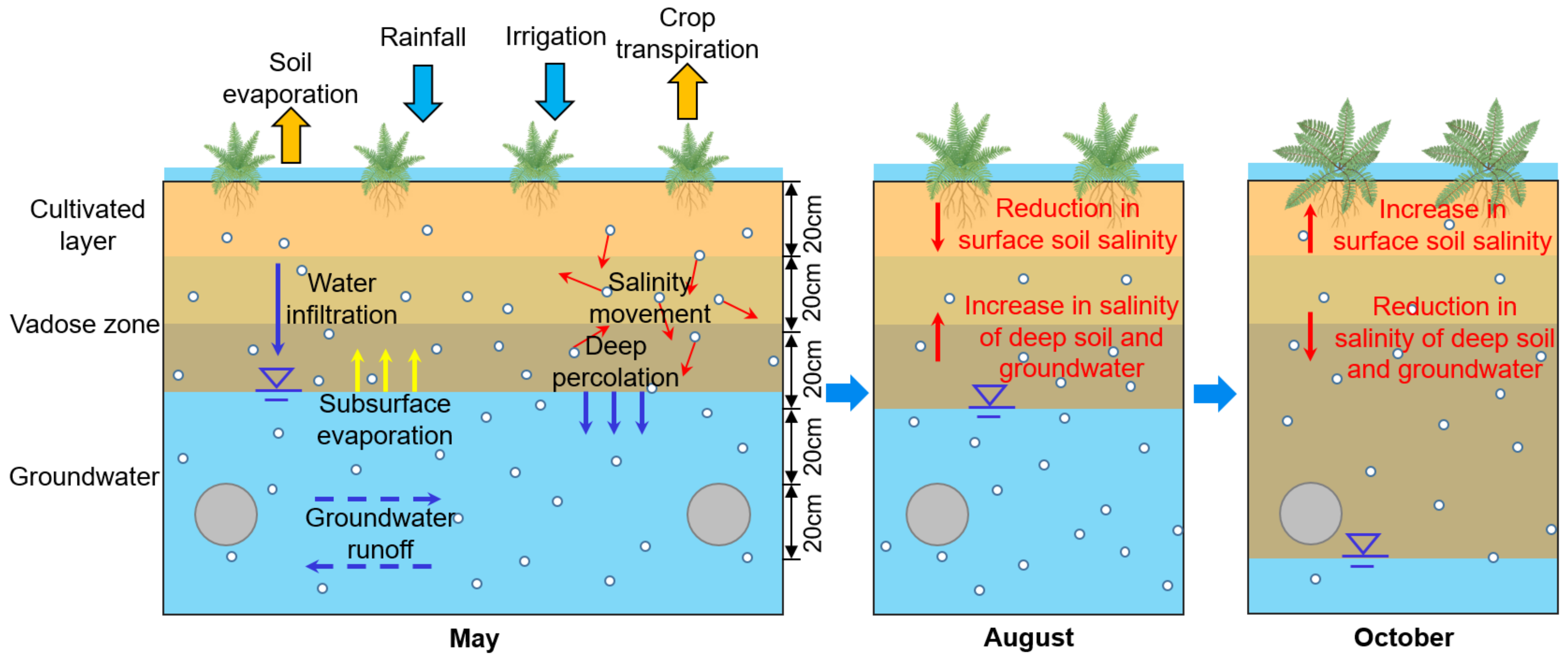
:1. Introduction
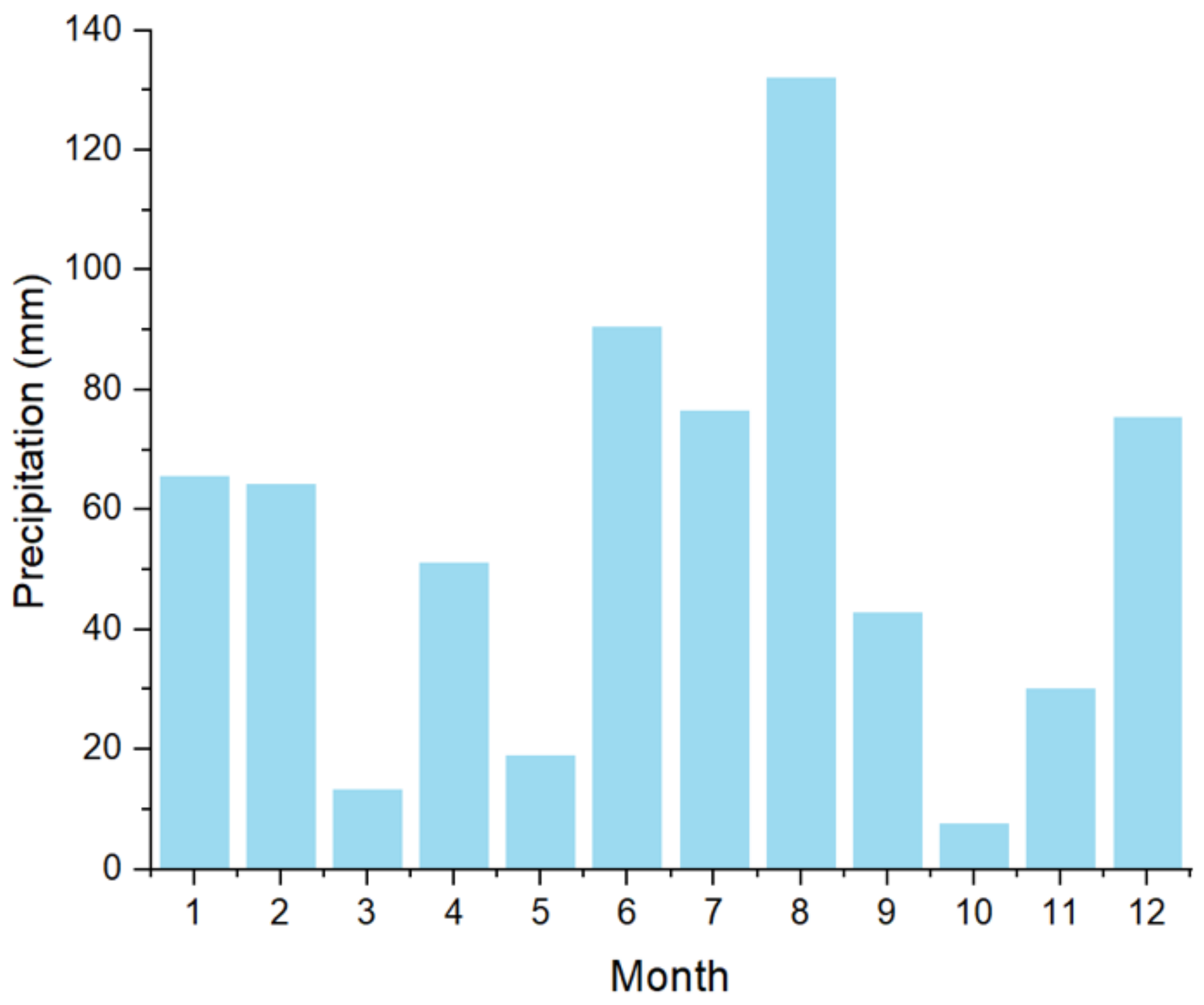
2. Materials and Methods
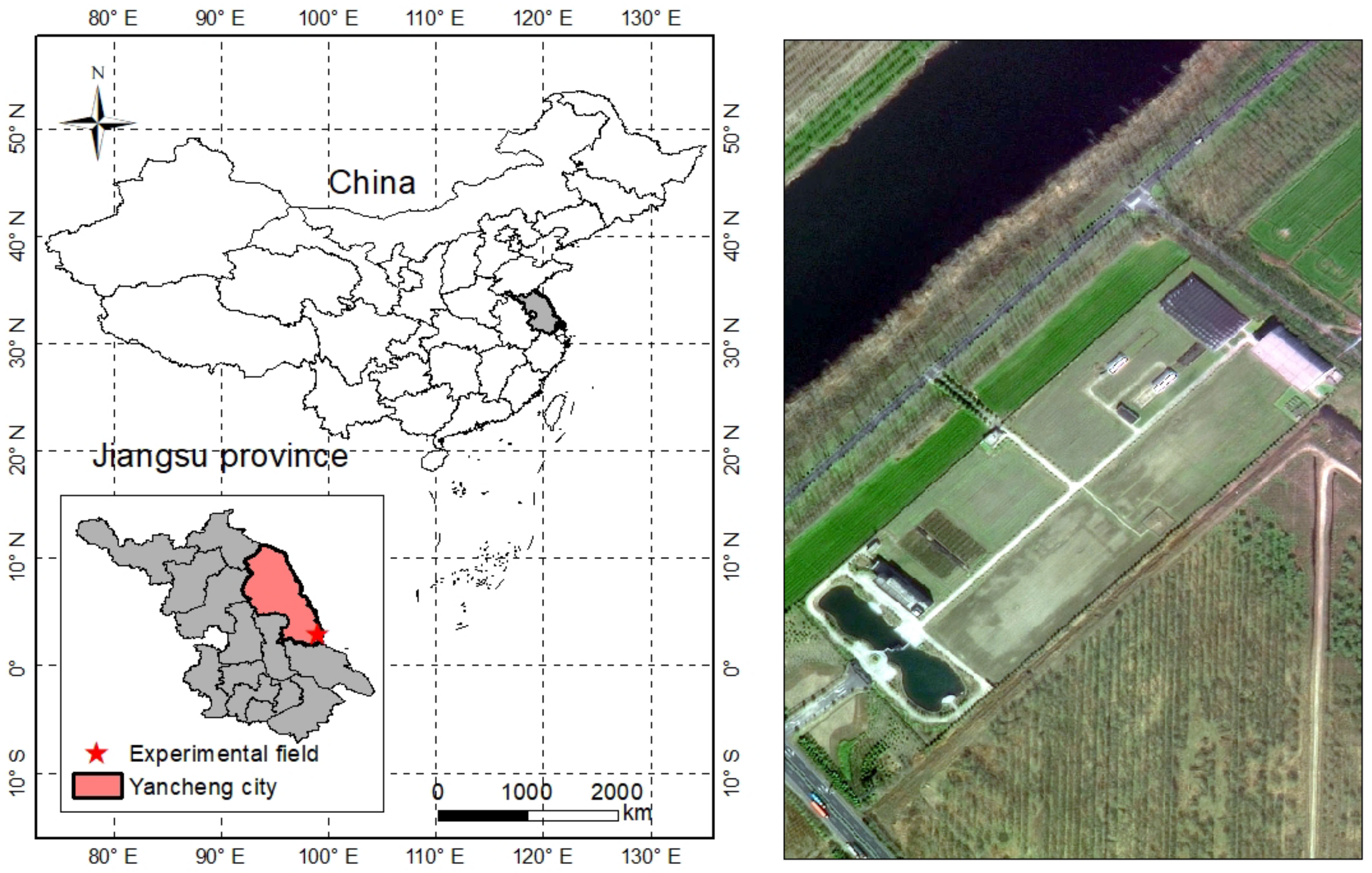
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experiment Design
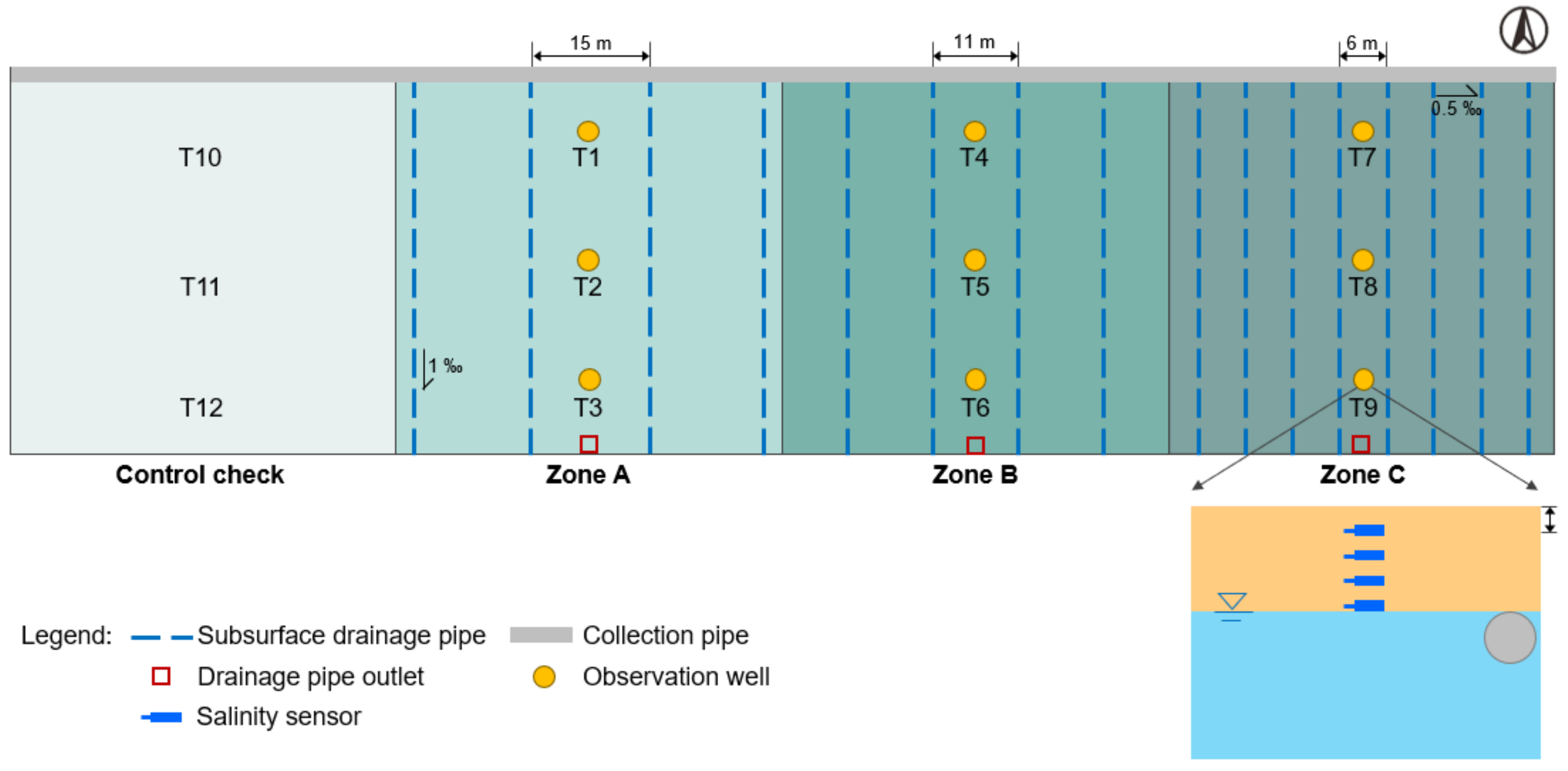
2.2.1. Subsurface Drainage Pipe Spacing
2.2.2. Distance between Observation Well and Drainage Outlet
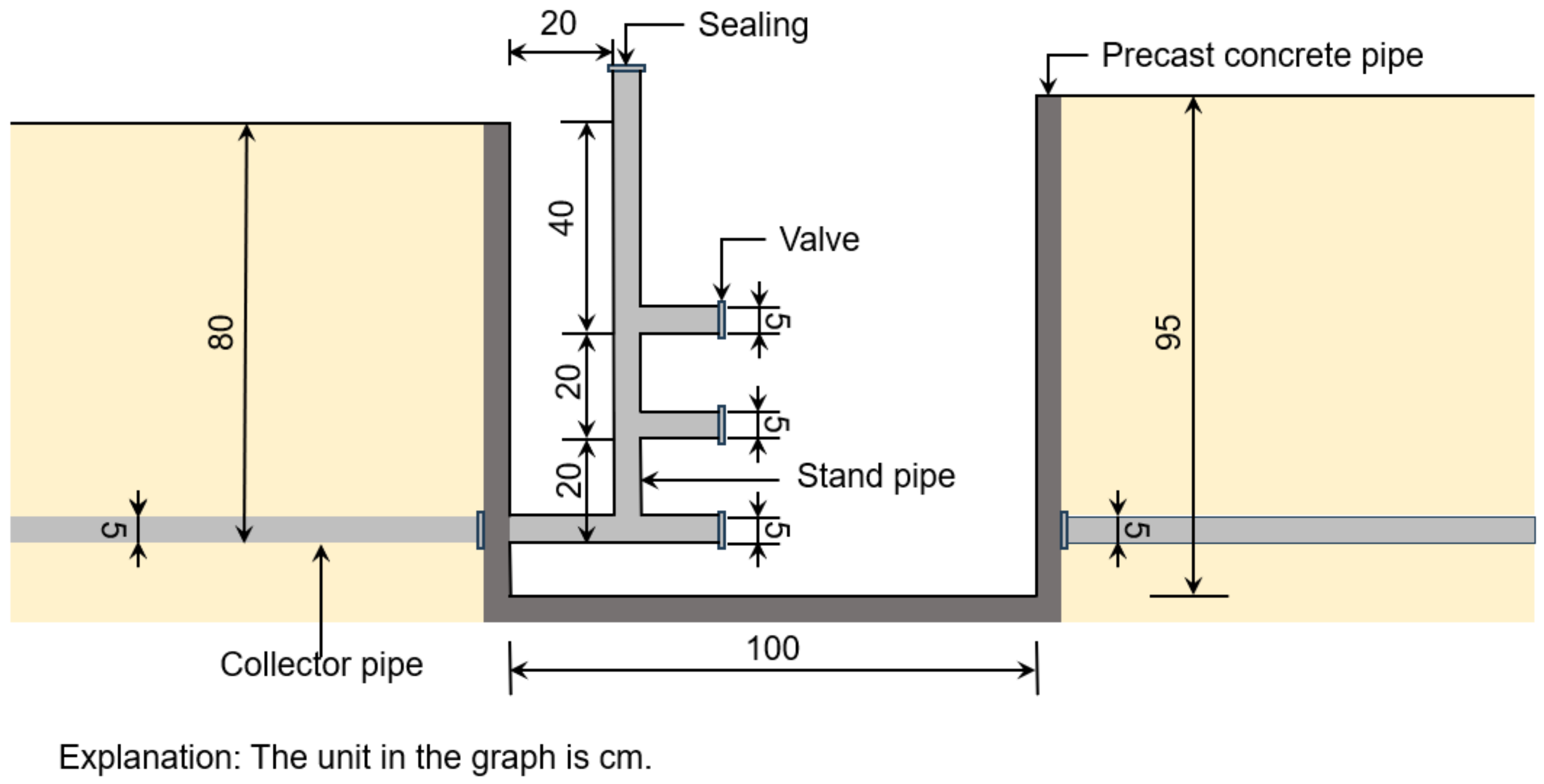
2.2.3. Buried Depth of Subsurface Pipe Outlet
2.2.4. Crop Yield
2.3. Desalination Rate
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
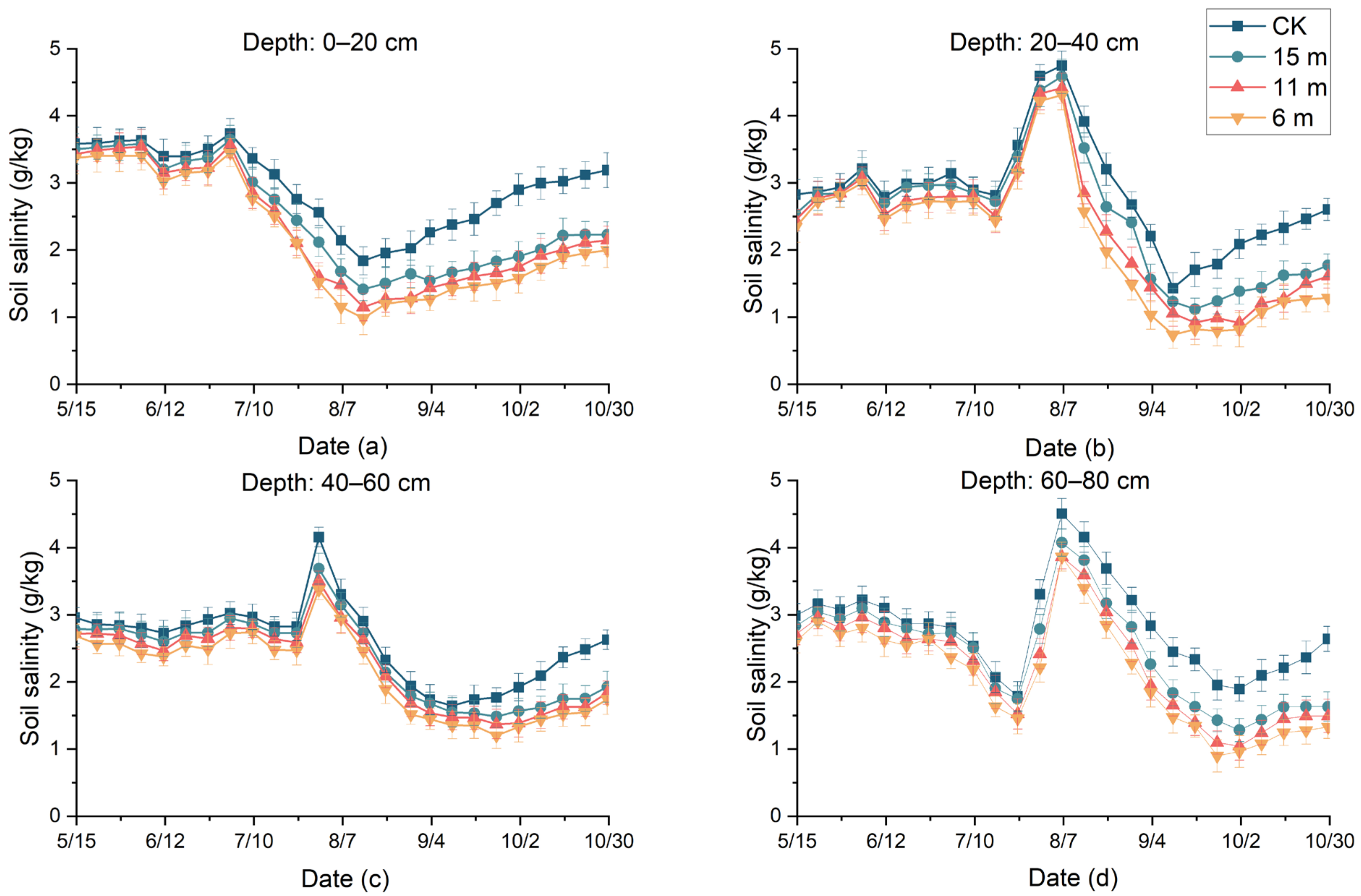
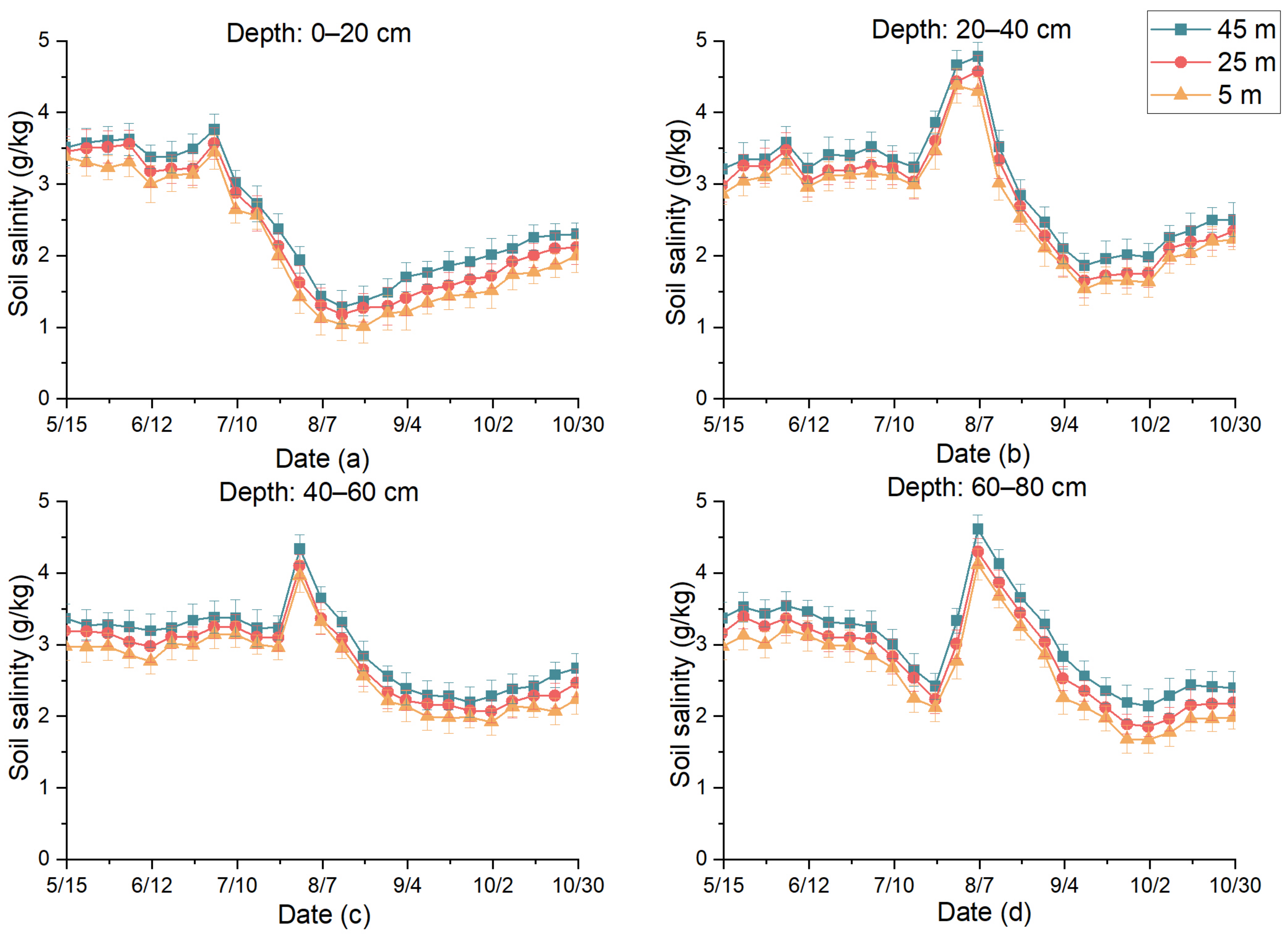
3.1. Effects of Subsurface Drainage Pipe Spacing on Soil Salinity
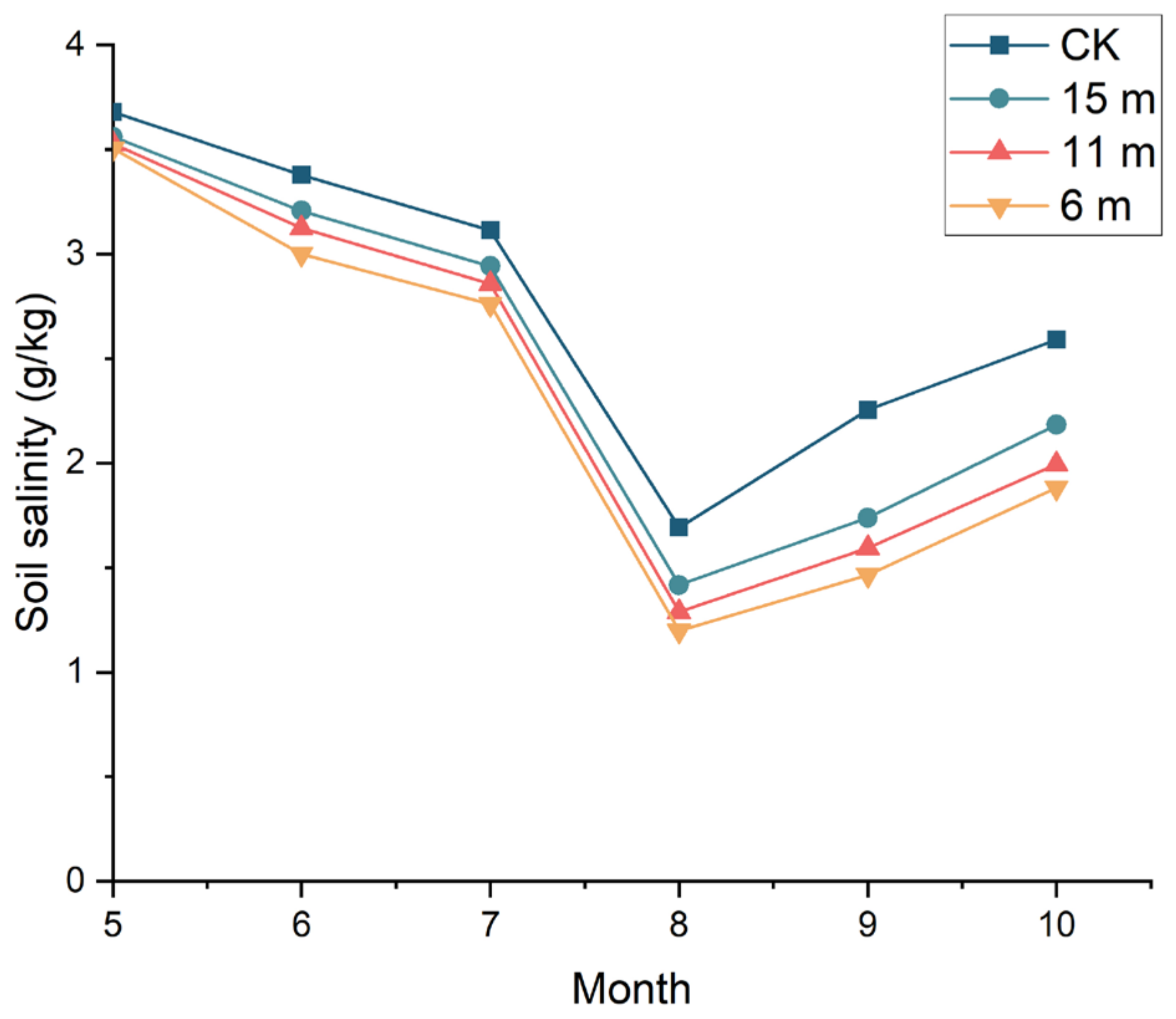
3.2. Effects of Distance between Observation Well and Drainage Outlet on Soil Salinity
3.3. Effects of Buried Depth of Subsurface Pipe outlet on Soil Salinity
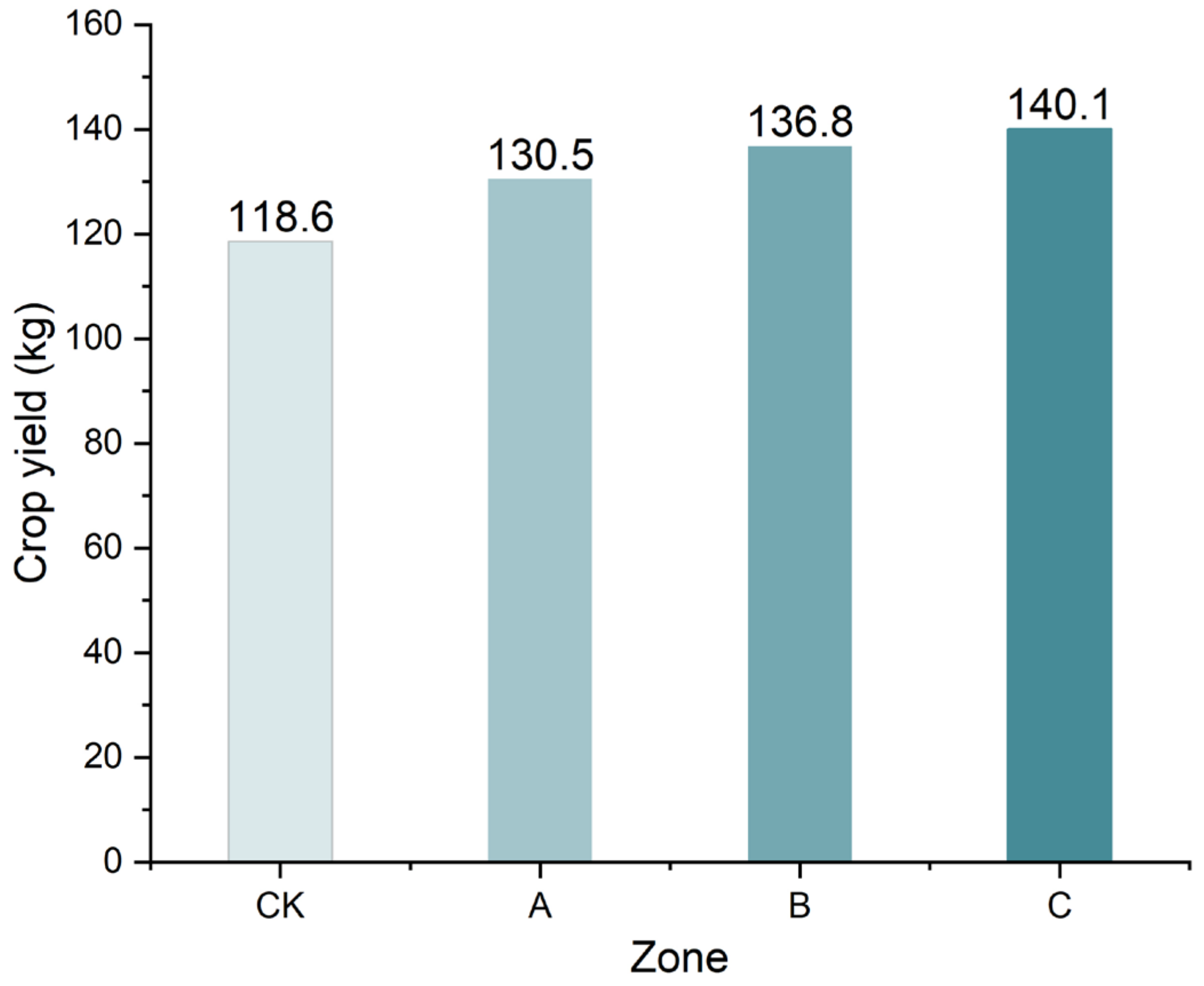
3.4. Effects of Subsurface Drainage Pipe Spacing on the Yield of a Salt-Tolerant Crop
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- With the longitudinal distance between observation wells and drainage outlets consistently maintained, soil salt content changes over time in a consistent trend with the draining of subsurface drainage pipes (with subsurface drainage pipe spacings of 6 m, 11 m, and 15 m). Subsurface drainage pipes can also effectively decrease soil salt accumulation and reduce the degree of salinization. Furthermore, subsurface drainage can significantly increase the yield of a salt-tolerant crop (Sesbania), but there is no significant difference in yield between different subsurface drainage spacings.
- When the subsurface drainage pipe spacing remains unchanged, placing subsurface drainage pipes closer to the drainage outlet leads to a better desalinization effect on the soil.
- When the subsurface drainage pipe spacing is constant, increasing the drainage outlet depth of subsurface drainage pipes can lower the groundwater level and effectively decrease soil salt accumulation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/the-state-of-food-security-and-nutrition-in-the-world-2021 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- The Total Area of Saline-Alkali Land in China Is about 99 Million Hectares. The Yellow River Delta Experimental Station Has Been Built. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1744769950363357466&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Heng, T.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Effects of combined drip irrigation and sub-surface pipe drainage on water and salt transport of saline-alkali soil in Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, X. Effects of the Salt-Tolerant Gramineous Forage Echinochloa frumentacea on Biological Improvement and Crop Productivity in Saline–Alkali Land on the Hetao Ningxia Plain in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhuo, Y.Q.; Xu, L.Z. Research on saline-alkali soil amelioration with FGD gypsum. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 121, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G. Mechanisms of straw biochar’s improvement of phosphorus bioavailability in soda saline-alkali soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47867–47872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dun, Y.; Guo, Y. Effects of land consolidation on improvement of salinity soil in Western Songnen Plain. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Heng, T.; Yang, L. Study on the farmland improvement effect of drainage measures under film mulch with drip irrigation in saline–alkali land in arid areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftchali, D.A.; Abdullah, R.H.; Karandish, F.; Bidgoli, M.A.; Nasr, M.G. Alternate wetting and drying for different subsurface drainage systems to improve paddy yield and water productivity in Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, P.; Basak, N.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, R.K.; Singh, R.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.K.; Sharma, P.C. Ameliorants and salt tolerant varieties improve rice-wheat production in soils undergoing sodification with alkali water irrigation in Indo–Gangetic Plains of India. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukolaee, M.J.; Naftchali, A.D.; Parvariji, L.Z. Investigating long−term effects of subsurface drainage on soil structure in paddy fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthin, J.N.; Luthin, J.N. Drainage Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.L.; Liu, H.G.; Ye, J.W. Comparative investigation on soil salinity leaching under subsurface drainage and ditch drainage in Xinjiang arid region. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Smedema, L.K.; Vlotman, W.F.; Rycroft, D.W. Modern Land Drainage: Planning, Design and Management of Agricultural Drainage Systems; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Azhar, A.H. Impact of Subsurface Drainage on Soil Salinity in Pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2010, 20, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Feng, G.X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, P.R. Transport Feature of Soil Water-salt by Saline Water Irrigation under Subsurface Pipe Drainage. J. Irrig. Drain 2016, 35, 37–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kladivko, E.J.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Jaynes, D.B.; Meek, D.W.; Jenkinson, B.J.; Fausey, N.R. Nitrate Leaching to Subsurface Drains as Affected by Drain Spacing and Changes in Crop Production System. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, B. Design Parameters of Underground Pipe Engineering in Saline Coastal. J. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 30, 96–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, M. Experiment and numerical simulation for designing layout parameters of subsurface drainage pipes in arid agricultural areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrakhimov, M.; Khamzina, A.; Forkutsa, I.; Paluasheva, G.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Tischbein, B.; Vlek, P.L.G.; Martius, C. Groundwater table and salinity: Spatial and temporal distribution and influence on soil salinization in Khorezm region (Uzbekistan, Aral Sea Basin). Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2007, 21, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj, A.Z.; Bouri, S. Subsurface Drainage System Performance, Soil Salinization Risk, and Shallow Groundwater Dynamic under Irrigation Practice in an Arid Land. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.R.; Ayars, J.E. Strategies for reducing subsurface drainage in irrigated agriculture through improved irrigation. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2002, 16, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, E.W.; Ayars, J.E. Subsurface Drainage System Design and Management in Irrigated Agriculture: Best Management Practices for Reducing Drainage Volume and Salt Load; CSIRO Land and Water: Clayton South, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bhattarai, R.; Cooke, R.A. Assessment of surface inlets performance on sediment transport to subsurface drainage system. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2017, 33, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Dan, H.C.; Zhou, T. An analytical solution for predicting the transient seepage from a subsurface drainage system. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Song, Q.C.; Wu, W.; Cao, S.Y. Variation law of groundwater depth and mineralization of coastal tidal flats in Jiangsu Province. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2021, 41, 52–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.J.; Cai, S.C. Simulating the effects of subsurface drainage on winter wheat yield in coastal reclamation areas of Jiangsu, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 83–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Classification and Grade of Saline-Alkali Soil for Agricultural Use (GB/T 20205107-T-326). 2020. Available online: https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/search/gbDetailed?id=A944D43C8FABBF44E05397BE0A0A276C (accessed on 24 December 2020). (In Chinese)
- Bao, S. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.P.; Singh, K.; Rao, K. Subsurface drainage for rehabilitation of waterlogged saline lands: Example of a soil in semiarid climate. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, H.; Azadi, S.; Zali, A. Experimental study of the temporal variation of drain water salinity at different drain depths and spacing in the presence of saline groundwater. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Q. Preliminary Study on High-Yielding Cultivation of Sesbania cannabina in Saline Soil. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, June 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.P.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhao, P.Y.; Li, X.P.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, M.; Tuo, D.B.; Wang, L.J.; Yang, X. Salinized soil improvement by planting 5 plant species in Hetao irrigation area. Soils Crops 2020, 9, 114–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Xiao, H.; Chen, W.J.; Yang, Y. Dynamic Changes of Soil Nutrients of Salt-tolerant Herbaceous Plants in Coastal Saline Soil. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 168–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, W.J.; Pan, J. The Characteristics of Soil Movement in Coastal Saline Soil of Four Salt-tolerant Plants. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 73–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, F.; Xiuling, C. Influence of atmospheric precipitation on soil leaching and desalinization in semi-humid region. In Proceedings of the 13th International Soil Conservation Organization Conference, Conserving Soil and Water for Society: Sharing Solutions, Brisbane, Australia, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bahceci, I.; Nacar, A.S. Subsurface drainage and salt leaching in irrigated land in south-east Turkey. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain. 2009, 58, 346–356. [Google Scholar]
- Chahar, B.R.; Vadodaria, G.P. Drainage of ponded surface by an array of ditches. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2008, 134, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, B.R.; Vadodaria, G.P. Steady subsurface drainage of homogeneous soils by ditches. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water Management; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2008; Volume 161, pp. 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ayars, J.E.; Shouse, P.; Lesch, S.M. In situ use of groundwater by alfalfa. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Christen, E.W.; Soppe, R.W.; Meyer, W.S. The resource potential of in-situ shallow ground water use in irrigated agriculture: A review. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 24, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Christen, E.W.; Hornbuckle, J.W. Controlled drainage for improved water management in arid regions irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madramootoo, C.A. Planning and design of drainage systems. Agric. Drain. 1999, 38, 871–892. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, P.; Goel, A. An overview of impact of subsurface drainage project studies on salinity management in developing countries. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, W. Effects of Subsurface Drainage on Soil Salinity and Groundwater Table in Drip Irrigated Cotton Fields in Oasis Regions of Tarim Basin. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, G.; Lu, J. Effects of controlled drainage on crop yield, drainage water quantity and quality: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classification | Salt Content (g/kg) | Alkali Content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Slight Saline-alkali | <2 | <3 |
| Moderate Saline-alkali | 2–5 | 3–8 |
| Severe Saline-alkali | 5–10 | 8–15 |
| Very Severe Saline-alkali | >10 | >15 |
| Sample | Water Content (%) | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Electric Conductivity (μs/cm) | Total Salt Content (g/kg) | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Mechanical Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | >0.05 | 0.05~0.01 | 0.01~0.005 | 0.005~0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 1 | 25.9 | 1.46 | 0.438 × 104 | 11.19 | 1.64 | 34.8 | 50.2 | 8.8 | 1.2 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 26.2 | 1.44 | 0.548 × 104 | 14.01 | 2.22 | 27.4 | 55.2 | 9.2 | 1.8 | 6.4 |
| 3 | 27.4 | 1.52 | 0.166 × 104 | 4.22 | 1.15 | 35.6 | 53.8 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 5.2 |
| 4 | 30.5 | 1.39 | 0.153 × 104 | 3.99 | 1.26 | 43.4 | 47.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 4.4 |
| Depth (cm) | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 3.581 | 0.335 | 0.228 | 0.402 | 0.987 | 0.321 | 0.057 |
| 20~40 | 3.485 | 0.204 | 0.145 | 0.125 | 1.125 | 0.258 | 0.042 |
| 40~60 | 3.468 | 0.185 | 0.165 | 0.167 | 2.254 | 0.452 | 0.051 |
| 60~80 | 3.402 | 0.214 | 0.158 | 0.148 | 3.154 | 0.345 | 0.061 |
| Measurement Point Number | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 | T11 | T12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distances between observation wells and drainage outlets (m) | 45 | 25 | 5 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 45 | 25 | 5 | 45 | 25 | 5 |
| Subsurface drainage pipe spacing (m) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Depth/cm | 40 cm Control Outlet Depth | 60 cm Control Outlet Depth | 80 cm Control Outlet Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 m Subsurface Pipe Spacing | 11 m Subsurface Pipe Spacing | 15 m Subsurface Pipe Spacing | |
| 0~20 | 90.5 | 84.9 | 80.4 |
| 20~40 | 79.9 | 65.1 | 62.4 |
| 40~60 | 30.0 | 23.2 | 16.0 |
| 60~80 | −67.9 | −59.8 | −43.2 |
| Average | 33.1 | 28.35 | 28.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, F.; Li, W.; Peng, H.; Jin, Q.; Bi, B.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A. Effects of Subsurface Pipe Drainage Spacing on Soil Salinity Movement in Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813932
Han D, Chen C, Wang F, Li W, Peng H, Jin Q, Bi B, Shaghaleh H, Hamoud YA. Effects of Subsurface Pipe Drainage Spacing on Soil Salinity Movement in Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Area. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813932
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Danni, Chao Chen, Fan Wang, Wenping Li, Hao Peng, Qiu Jin, Bo Bi, Hiba Shaghaleh, and Yousef Alhaj Hamoud. 2023. "Effects of Subsurface Pipe Drainage Spacing on Soil Salinity Movement in Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Area" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813932
APA StyleHan, D., Chen, C., Wang, F., Li, W., Peng, H., Jin, Q., Bi, B., Shaghaleh, H., & Hamoud, Y. A. (2023). Effects of Subsurface Pipe Drainage Spacing on Soil Salinity Movement in Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Area. Sustainability, 15(18), 13932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813932








