Multi-Target Rumination Behavior Analysis Method of Cows Based on Target Detection and Optical Flow Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
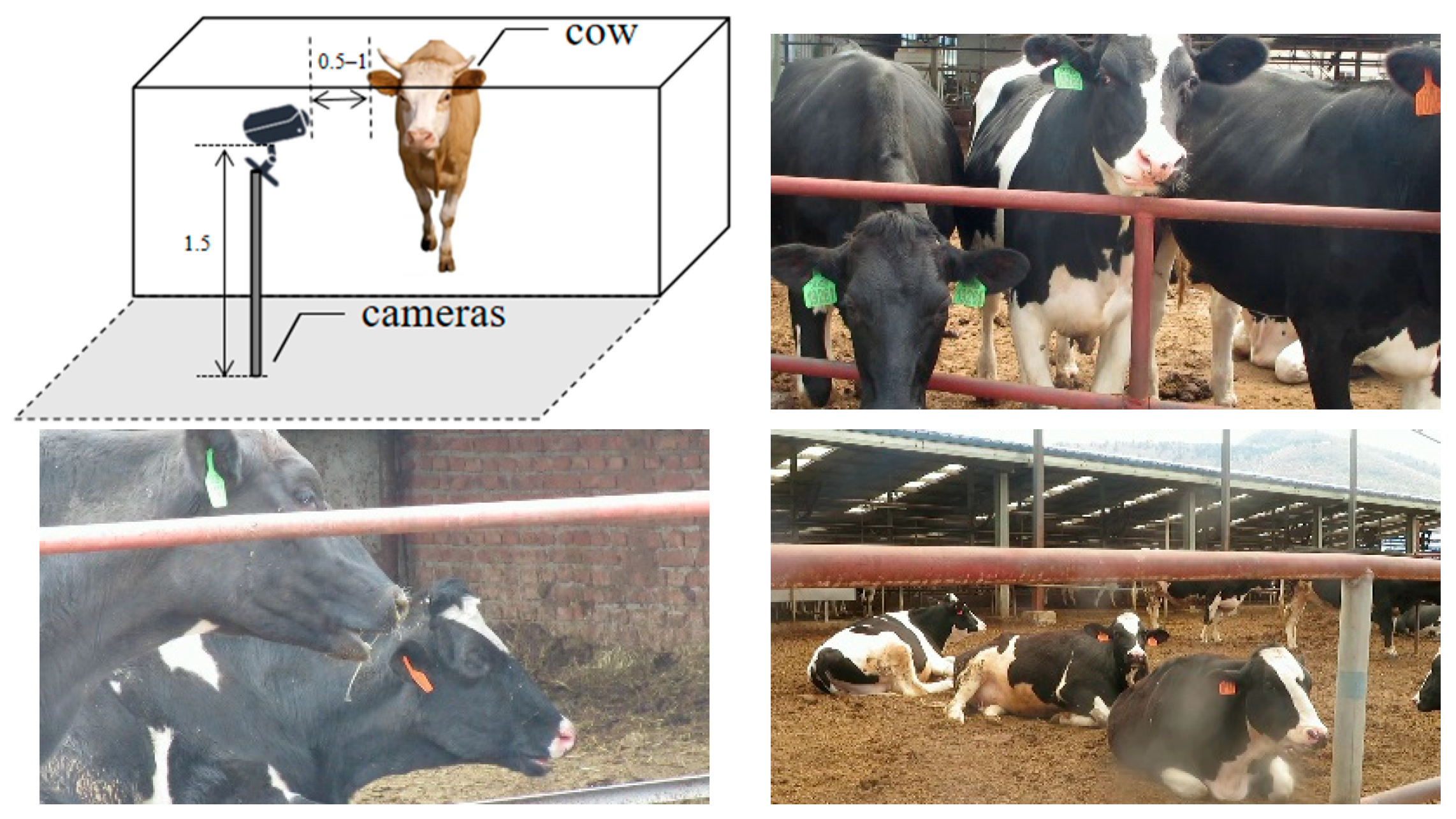
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Theoretical Approach
3. Improved Faster R-CNN Object Detection Algorithms
3.1. Fusion Feature Pyramid Network
3.2. CBAM Attention Mechanism
3.3. Fusing Optical Flow Information
4. GMFlowNet-Based Multi-Objective Analysis of Cow Ruminant Behavior
4.1. Multi-Object Cow Ruminant Optical Flow Extraction
4.2. Improved GMFlowNet Algorithm for Computing Multi-Object Optical Flow
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Dataset and Parameter Settings
5.2. Experimental Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, L.; Liu, C.Q. Development trends, challenges and policy recommendations of China’s dairy economy. China J. Anim. Husb. 2019, 55, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.X. Analysis of dairy farming patterns and their efficiency in China in the new era. China Herbiv. Sci. 2018, 38, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, K.X. Research progress on intelligent animal information perception and behavior detection in precision animal husbandry. J. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.C.; Zhai, T.C.; He, D.J. Current status and progress of research on individual information monitoring of dairy cows in precision farming. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2019, 13, 30–33+38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, F.M.; Diao, Q.Y.; Tu, Y. Research progress on the regulation mechanism of ruminant behavior in dairy cows. J. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 33, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.Q.; Tao, J.Z. Differences in rumen function and related molecular biological mechanisms in residual feed intake of ruminants. J. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 33, 3125–3131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y. Research progress on intelligent monitoring method of dairy cattle ruminant behavior and its application. China Feed 2021, 7, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauermann, F.V.; Joshi, L.R.; Mohr, K.A.; Kutish, G.F.; Meier, P.; Chase, C.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Diel, D.G. A novel bovine papillomavirus type in the genus Dyokappapapillomavirus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3225–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, Z.T.; Zheng, W.B.; Yang, Z.T.; Dong, Q. Application of machine learning for clinical disease prediction in dairy cattle. Adv. Anim. Med. 2021, 42, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, K.M.; Combs, D.K.; Beauchemin, K.A. Effects of forage particle size and grain fermentability in midlactation cows. I. Milk production and diet digestibility. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.F. A Study on the Correlation between the Change Pattern of Ruminant Behavior and Its Influencing Factors in Dairy Cows; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.F.; Li, Y.; Bai, D.N.; Sun, X.T.; Lei, X.J.; Cai, C.J.; Yao, J.H.; Cao, Y.C. Advances in ruminant starch nutrition. J. Livest. Ecol. 2021, 42, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.T.; Yan, R.; Hu, Z.Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Wang, Z.H. Effect of particle size of total mixed diets on feeding, chewing activity and production performance of dairy cows. J. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 29, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Wang, R.Y.; Shi, G.F.; Cheng, S.L.; Xin, Y.P. Effect of roughage length on chewing behavior and production performance of dairy cows. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2017, 36, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.P.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.B.; Lin, M.Q.; Wu, F.Q.; Zhou, Q.X.; Liu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.J.; Mo, F. Comparative analysis of feeding, ruminant and prolific behavior and apparent digestibility of dietary fibrous matter in lactating dairy cows. Livest. Feed Sci. 2019, 40, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.E.; Jones, B.W.; Becker, C.A.; Bewley, J. Influence of breed, milk yield, and temperature-humidity index on dairy cow lying time, neck activity. reticulorumen temperature, and rumination behavior. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.; Asselstine, V.; Leblanc, S.; Duffield, T.; DeVries, T. Association of rumination time and health status with milk yield and composition in early-lactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antanitis, R.; Zilaitis, V.; Juozaitiene, V.; Noreika, A.; Rutkauskas, A. Evaluation of rumination time, subsequent yield, and milk trait changes dependent on the period of lactation and reproductive status of dairy cows. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 21, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.R.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.X. Analysis of the correlation between milk production and rumination time, activity and somatic cell score in periparturient cows. J. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 32, 5293–5301. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, P.E.; Weber, P.S.D.; Burton, J.L.; Zanella, A. Depressed DHEA and increased sickness response behaviors in lame dairy cows with inflammatory foot lesions. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2008, 34, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.F.; Liu, Y.P.; Dong, G.F.; Zhu, K.C.; Huang, H.T. Predicting the risk of peripartum ketosis in dairy cows using prepartum ruminal rumen regurgitation time. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.T.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, L. Exploration of differential diagnosis of ruminant disorders in dairy cattle. Agric. Dev. Equip. 2016, 164, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Differential diagnosis of ruminant disorders in dairy cattle. Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2015, 5, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Tang, S.Y. Diagnosis and prevention of foregut flaccidity and related diseases in ruminant livestock. Anim. Husb. Vet. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2013, 5, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chacher, B. Evaluation of n-Carbamovlglutamate as Arginine Enhancer and Its Effect on Rumen Fermentation, Lactation Performance and Nitrogen Utilization in High Yielding Lactating Dairy Cows; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.W.; Xie, Q.J.; Liu, H.G.; Yan, L.; Xu, Z.D. Research on a wearable monitoring device for dairy cows’ rumination behavior based on multi-source information perception. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2019, 47–51, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Li, J. Research status and development analysis of wearable information monitoring technology for animal husbandry. J. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.F.; Zhang, X.Q.; Dong, X.M.; Yue, S. Multi-feature fusion correlation filter-based object extraction for sport cows. J. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, Y.F.; Li, X.J.; Pu, D. Research progress on the application of computer vision technology in pig behavior recognition. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Her. 2019, 21, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.B.; Niu, M.T.; Ji, C.H.; Li, Z.N.; Zhu, Q.M. Multi-objective monitoring of cow ruminant behavior based on video analysis. J. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- You, X.H.; Ma, Q.; Guo, H.; Wang, Q. Analysis and prospect of dairy cow identification and behavior sensing technology. Comput. Appl. 2021, 41, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Burfeind, O.; Schirmann, K.; von Keyserlingk, M.; Veira, D.; Weary, D.; Heuwieser, W. Technical note: Evaluation of a system for monitoring rumination in heifers and calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y. Research on ANT-Based Dairy Cattle Rumination Information Collection System; Donghua University: Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, U.; Trosch, L.; Nydegger, F.; Hassig, M. Evaluation of eating and rumination behaviour in cows using a noseband pressure sensor. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehner, N.; Umstaetter, C.; Niederhauser, J.J.; Schick, M. System specification and validation of a noseband pressure sensor for measurement of ruminating and eating behavior in stable-fed cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, D.; Fu, Y.; Song, H. Intelligent monitoring method of cow ruminant behavior based on video analysis technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, S.; Sattlecker, G.; Lidauer, L.; Kickinger, F.; Öhlschuster, M.; Auer, W.; Schweinzer, V.; Klein-Jöbstl, D.; Drillich, M.; Iwersen, M. Evaluation of an ear-tag-based accelerometer for monitoring rumination in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3398–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.R.; Niu, T.; Wang, P.; Song, H.B.; He, D.J. Multi-objective cow mouth tracking and regurgitation monitoring using Kalman filtering and Hungarian algorithm. J. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.X.; He, D.J.; Wang, E.Z. Video-based analysis of cow breathing frequency and abnormality detection. J. Agric. Mach. 2014, 45, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.B.; Wu, D.H.; Yin, X.Q.; Jiang, B.; He, D.J. Respiratory behavior detection of dairy cows based on Lucas-Kanade sparse optical flow algorithm. J. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 211324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Research on Multi-Objective Cow Ruminant Behavior Monitoring Method Based on Video Analysis; Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology: Yangling, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.T.; Liu, Q.H.; Gao, R.H.; Li, Q.F.; Zhao, K.X.; Bai, Q. Analysis method of cow rumination behavior based on improved flownet 2.0 optical flow algorithm. J. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Huang, Z.B.; Quan, Y.; Feng, W.L. Secondary correction method of deformable instrument image recognition based on fast regional Convolutional neural network. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 9122–9129. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.B.; Tang, R.D.; Xing, D.J.; Wang, W.; Li, S.S. Visual optical flow computing technology and its application. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2023, 45, 2710–2721. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, W.; Yu, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, X. Faster RCNN Target Detection Algorithm Integrating CBAM and FPN. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 47, 1549–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Model | Check Accuracy | Search Completeness Rate | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Model Size/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.8381 | 0.7974 | 0.7090 | 467.99 |
| Yolov3-tiny | 0.9550 | 0.9270 | 0.6020 | 24.30 |
| Ours | 0.9362 | 0.8601 | 0.7833 | 468.03 |
| Video Serial Number | Number of Actual Regurgitated Areas | Value Calculated with the Algorithm before Improvement | Regurgitation Area Accuracy/% | Improved Algorithm Calculated Values | Regurgitation Area Accuracy/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 | 639 | 42.60 | 1017 | 67.80 |
| 2 | 900 | 306 | 34.00 | 561 | 62.33 |
| 3 | 900 | 540 | 60.00 | 628 | 69.78 |
| 4 | 600 | 596 | 99.33 | 598 | 99.67 |
| 5 | 330 | 316 | 95.76 | 320 | 96.97 |
| 6 | 600 | 494 | 82.33 | 567 | 94.50 |
| 7 | 600 | 510 | 85.00 | 589 | 98.17 |
| 8 | 900 | 691 | 76.78 | 727 | 80.78 |
| 9 | 600 | 482 | 80.33 | 554 | 92.33 |
| Average | - | - | 72.90 | - | 84.70 |
| Video Serial Number | Dairy Cow Number | To Ruminate or Not to Ruminate | Actual Number of Ruminant Chews | FlowNet 2.0 Algorithm Analysis Results | GMFlowNet Algorithm Analysis Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruminant Behavior Judgement | Calculated Value of Ruminant Chewing Times | Ruminant Behavior Judgement | Calculated Value of Ruminant Chewing Times | ||||
| 1 | Cow1 | √ | 14 | √ | 14 | √ | 14 |
| Cow2 | √ | 13 | × | - | √ | 13 | |
| 2 | Cow1 | √ | 11 | √ | 11 | √ | 11 |
| Cow2 | √ | 11 | √ | 12 | √ | 11 | |
| 3 | Cow1 | √ | 11 | √ | 12 | √ | 11 |
| Cow2 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| 4 | Cow1 | √ | 13 | √ | 13 | √ | 13 |
| Cow2 | √ | 12 | × | - | √ | 12 | |
| Cow3 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| 5 | Cow1 | √ | 12 | × | - | √ | 12 |
| Cow2 | √ | 9 | √ | 6 | √ | 13 | |
| Cow3 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| 6 | Cow1 | √ | 13 | × | - | √ | 13 |
| Cow2 | √ | 13 | √ | 13 | √ | 13 | |
| Cow3 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| 7 | Cow1 | × | - | × | - | × | - |
| Cow2 | √ | 16 | √ | 16 | √ | 16 | |
| Cow3 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| Cow4 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| 8 | Cow1 | √ | 11 | √ | 12 | √ | 10 |
| Cow2 | √ | 12 | √ | 10 | √ | 12 | |
| 9 | Cow1 | √ | 14 | √ | 14 | √ | 14 |
| Cow2 | × | - | × | - | × | - | |
| Accuracy of regurgitation behavior analysis/% | 82.61 | 93.33 | 100.00 | 97.30 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Ji, J.; Bai, Q.; Zhao, K.; Yang, L. Multi-Target Rumination Behavior Analysis Method of Cows Based on Target Detection and Optical Flow Algorithm. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814015
Gao R, Liu Q, Li Q, Ji J, Bai Q, Zhao K, Yang L. Multi-Target Rumination Behavior Analysis Method of Cows Based on Target Detection and Optical Flow Algorithm. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ronghua, Qihang Liu, Qifeng Li, Jiangtao Ji, Qiang Bai, Kaixuan Zhao, and Liuyiyi Yang. 2023. "Multi-Target Rumination Behavior Analysis Method of Cows Based on Target Detection and Optical Flow Algorithm" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814015
APA StyleGao, R., Liu, Q., Li, Q., Ji, J., Bai, Q., Zhao, K., & Yang, L. (2023). Multi-Target Rumination Behavior Analysis Method of Cows Based on Target Detection and Optical Flow Algorithm. Sustainability, 15(18), 14015. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814015






