Assessment and Enhancement of Ecosystem Service Supply Efficiency Based on Production Possibility Frontier: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
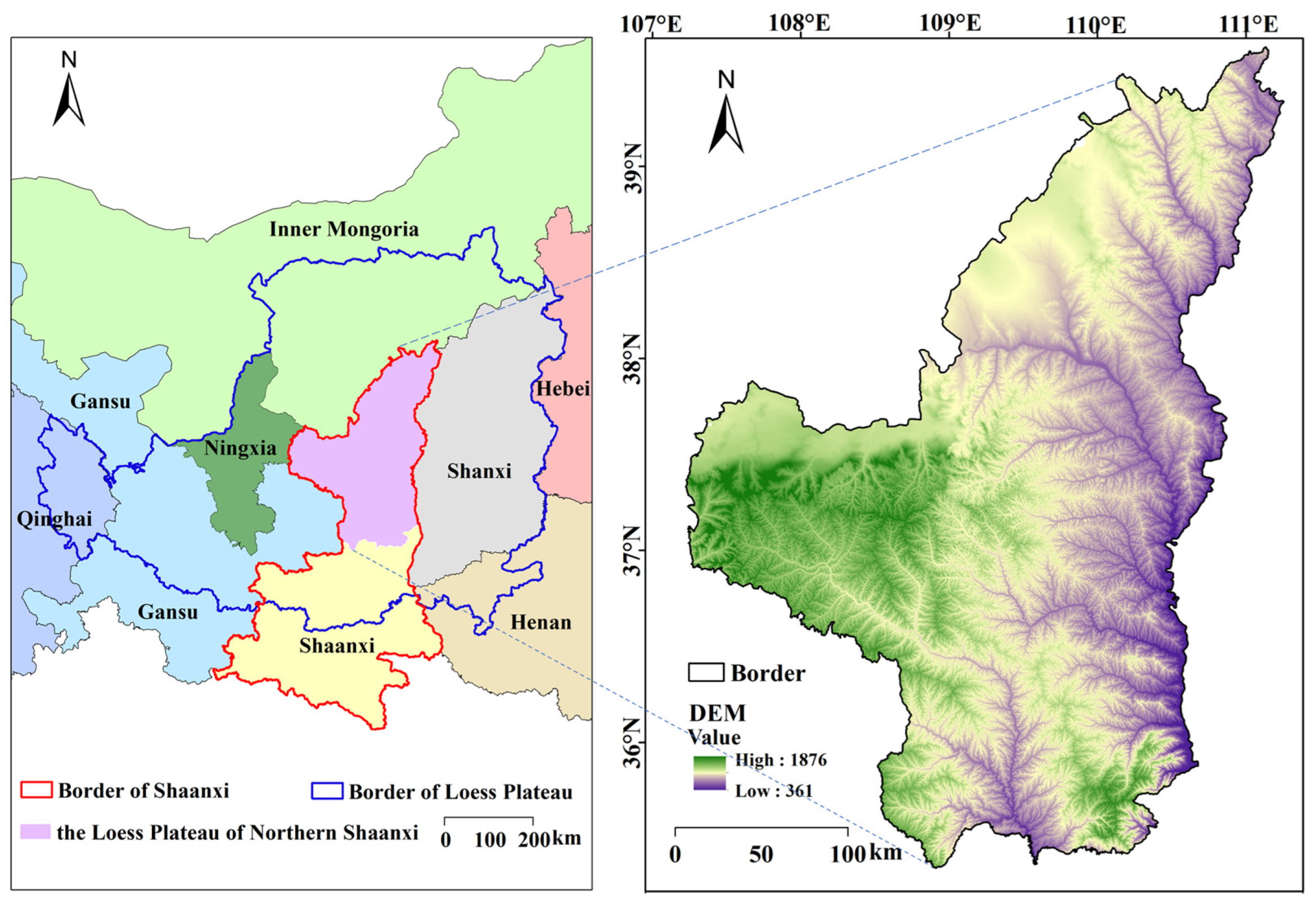
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
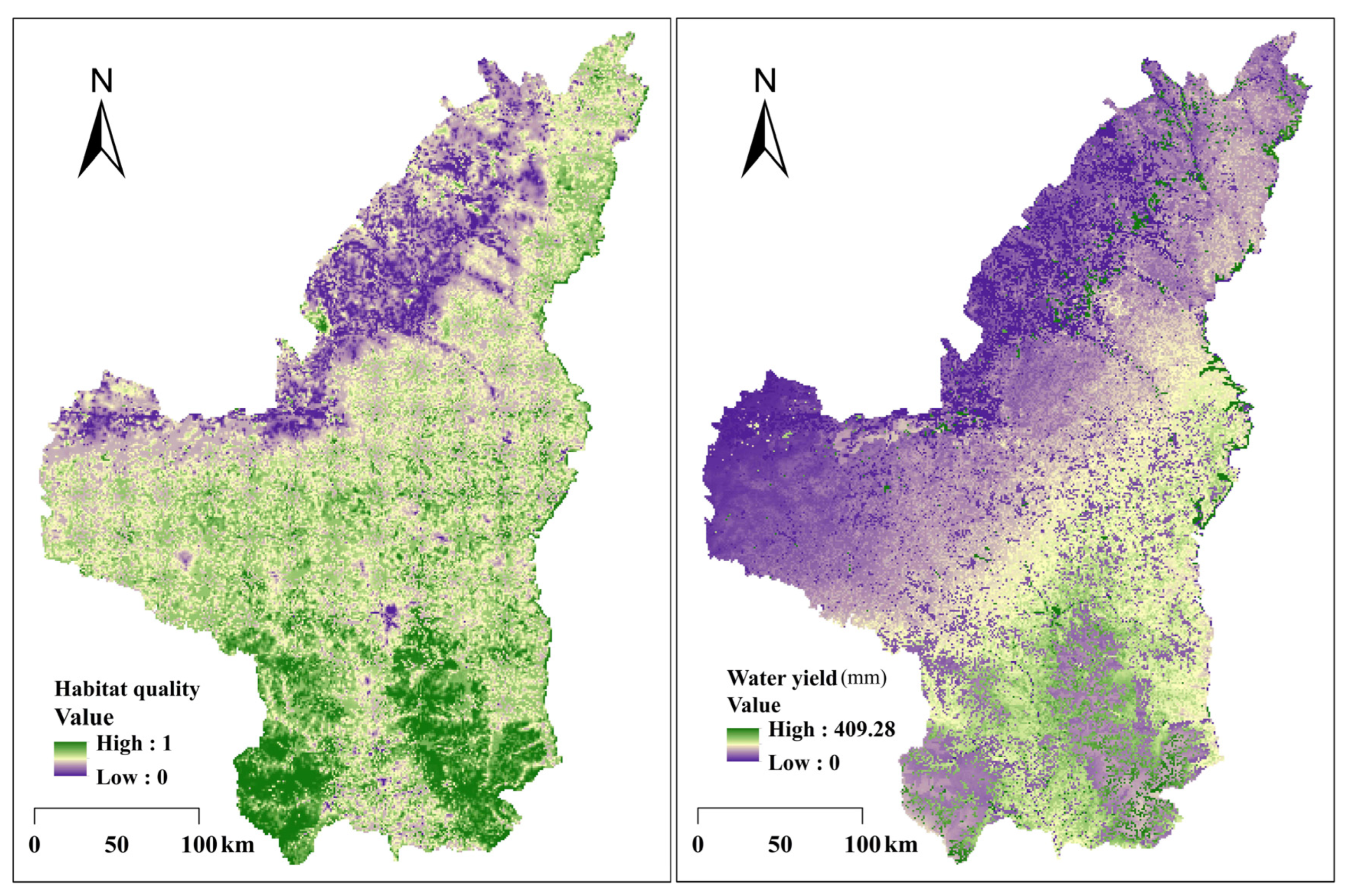
2.2.1. InVEST Model
2.2.2. Production Possibility Frontier
2.2.3. Analytical Methods for Environmental Factors
- (1)
- Selection of Environmental Factors
- (2)
- Ordinary Least Squares and Geographically Weighted Regression
2.3. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Trade-Off among Ecosystem Services
3.2. Optimal Fitting of Ecosystem Services
3.3. Analysis of Ecological Spatial Zoning and Environmental Factors
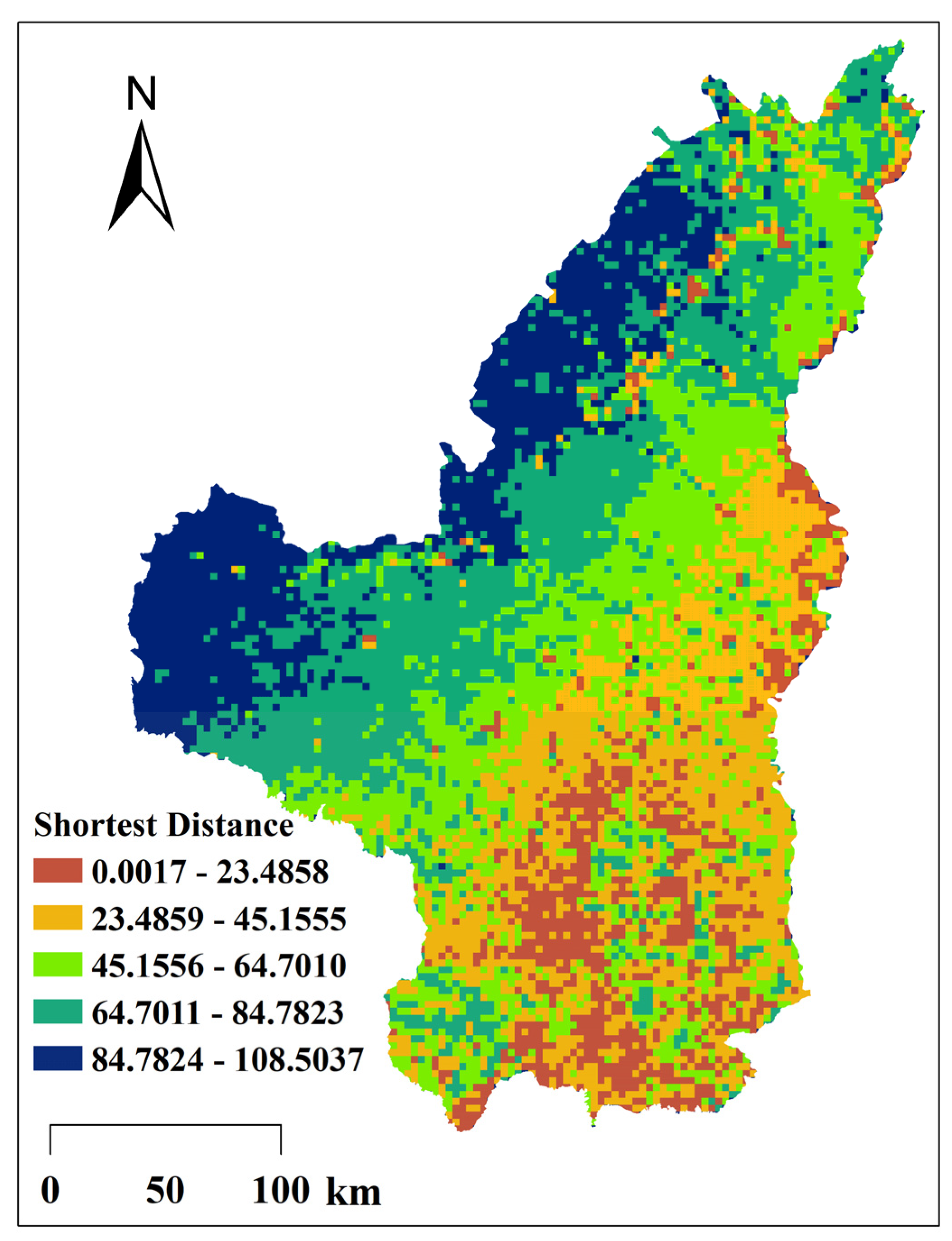
3.3.1. Analysis of Spatial Zoning
3.3.2. Comparison of Models
3.3.3. Identification of Dominant Factors
3.3.4. Spatial Characteristics of Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Supply Efficiency to Environmental Factors
4.2. Corresponding Measures for Improving the Supply Efficiency
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- There is a spatial variation in the trade-off relationship between WY and HQ in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi. Strong spatial trade-offs existed between WY and HQ in the south, west, and northeast regions. The spatial trade-off relationship between WY and HQ was weaker in the eastern and northwestern regions.
- (2)
- There is an optimal combination of WY and HQ in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, and the spatial characteristics of the supply efficiency of the two services are significant. There are eighteen optimal combination solutions for WY and HQ, and the fitted PPF curve based on the optimal combination solutions is . The supply efficiency of the two services exhibits an increasing distribution from northwest to southeast. Using the magnitude of supply efficiency, the study area is categorized into the zones of high-efficiency supply, sub-high-efficiency supply, general-efficiency supply, sub-low-efficiency supply, and low-efficiency supply.
- (3)
- The dominant factors influencing supply efficiency vary across each zone. Population, hydrology, and GDP are the dominant factors affecting supply efficiency across the entire region, as well as in the zone of general-efficiency supply, sub-low-efficiency supply, and low-efficiency supply. The dominant factors of high-efficiency supply are hydrology, NDVI, and GDP, while the dominant factors are GDP, topography, and population in the zone of high-efficiency supply.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Huang, C.; Dong, G. Integrating Land Use Management with Trade-Offs between Ecosystem Services: A Framework and Application. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlik, A.M.; Kentula, M.E.; Fennessy, M.S.; Landers, D.H. Where Is the Consensus? A Proposed Foundation for Moving Ecosystem Service Concepts into Practice. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 77, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.; Banzhaf, S. What Are Ecosystem Services? The Need for Standardized Environmental Accounting Units. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J.; Bennet, E.M. Ecosystem and Human Well-Being: A Framework for Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Luo, Y. Progress and Perspectives of Ecosystem Services Management. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.L.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, L.; Feng, C.Y.; Chen, Y.M. Research Progress and Prospect of Ecosystem Services. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, E.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D. Methods, Tools and Research Framework of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Shao, Q.; Ning, J.; Huang, H. Ecological Changes and the Tradeoff and Synergy of Ecosystem Services in Western China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pang, Q.; Hua, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, K. Linking Ecological Red Lines and Public Perceptions of Ecosystem Services to Manage the Ecological Environment: A Case Study in the Fenghe River Watershed of Xi’an. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langemeyer, J.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Haase, D.; Scheuer, S.; Elmqvist, T. Bridging the Gap between Ecosystem Service Assessments and Land-Use Planning through Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA). Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Guo, Y.; Shen, G.; Chen, W. Spatiotemporal Changes of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs under the Influence of Forest Conservation Project in Northeast China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 978145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Separating the Effects of Two Dimensions on Ecosystem Services: Environmental Variables and Net Trade-Offs. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 845–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.; Marandure, T.; Hawkins, H.J.; Mapiye, C.; Palmer, A.; Lemke, S.; Wu, L.; Moradzadeh, M. A Conceptual Framework for Understanding Ecosystem Trade-Offs and Synergies, in Communal Rangeland Systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023, 61, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.J.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-Offs across Space, Time, and Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wu, R.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, W. Spatial Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services within a Global Biodiversity Hotspot. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, G. Quantification and Driving Force Analysis of Ecosystem Services Supply, Demand and Balance in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manners, R.; Varela-Ortega, C. The Role of Decision-Making in Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs in Lowland Bolivia’s Amazonian Agricultural Systems. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 153, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Egoh, B.; Willemen, L.; Liquete, C.; Vihervaara, P.; Schägner, J.P.; Grizzetti, B.; Drakou, E.G.; La Notte, A.; Zulian, G.; et al. Mapping Ecosystem Services for Policy Support and Decision Making in the European Union. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Dai, L. Integrating Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand into Optimized Management at Different Scales: A Case Study in Hulunbuir, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Lu, N.; Fan, W.; Zhang, P.; Dong, X. Linking Ecosystem Services Supply, Social Demand and Human Well-Being in a Typical Mountain–Oasis–Desert Area, Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Hughes, A.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing China’s Ecological Redline Policy Using Ecosystem Services Assessments for Land Use Planning. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Eguskitza, N.; Martín-López, B.; Onaindia, M. A Comprehensive Assessment of Ecosystem Services: Integrating Supply, Demand and Interest in the Urdaibai Biosphere Reserve. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Meng, Q.; Lin, A.; Li, J. Trade-off Analyses and Optimization of Water-Related Ecosystem Services (WRESs) Based on Land Use Change in a Typical Agricultural Watershed, Southern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, K.; Lei, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Liang, J. Identification of Priority Areas for Water Ecosystem Services by a Techno-Economic, Social and Climate Change Modeling Framework. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Soliveres, S.; Penone, C.; Manning, P.; van der Plas, F.; Boch, S.; Prati, D.; Ammer, C.; Schall, P.; Gossner, M.M.; et al. Multiple Forest Attributes Underpin the Supply of Multiple Ecosystem Services. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, V.; Cattarino, L.; Linke, S.; Kennard, M.J. Catchment Zoning to Enhance Co-Benefits and Minimize Trade-Offs between Ecosystem Services and Freshwater Biodiversity Conservation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, F. Spatiotemporal Assessment and Trade-Offs of Multiple Ecosystem Services Based on Land Use Changes in Zengcheng, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, E.A.; Bryan, B.A.; Meijaard, E.; Mallawaarachchi, T.; Struebig, M.J.; Watts, M.E.; Wilson, K.A. Mixed Policies Give More Options in Multifunctional Tropical Forest Landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, Y. Evaluating the Effects of Carbon Prices on Trade-Offs between Carbon and Timber Management Objectives in Forest Spatial Harvest Scheduling Problems: A Case Study from Northeast China. Forests 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, T. Coordinating Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs to Achieve Win–Win Outcomes: A Review of the Approaches. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 82, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cheng, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Peng, J. Elevation Dependency of Ecosystem Services Supply Efficiency in Great Lake Watershed. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Polasky, S.; King, E.; Balvanera, P. A Sustainability Framework for Assessing Trade-Offs in Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.E.; Costello, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Gaines, S.D.; White, C.; Barth, J.A. Evaluating Tradeoffs among Ecosystem Services to Inform Marine Spatial Planning. Mar. Policy 2013, 38, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Ding, J.; Wang, S. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Their Influencing Factors: A Case Study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G.; Guo, W.Z.; Wang, W.L.; Luo, S.H.; Chen, Z.X.; Lou, Y.B.; Fei, J.P. Characteristics of Shallow Landslides under Extreme Rainfall and Their Effects on Runoff and Sediment on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7898–7909. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-M.; Jin, T.-T.; Yan, L.-L.; Gong, J. Trade-off and Synergy among Ecosystem Services and the Influencing Factors in the Ziwuling Region, Northwest China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar]
- Tallis, H.; Goldman, R.; Uhl, M.; Brosi, B. Integrating Conservation and Development in the Field: Implementing Ecosystem Service Projects. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, B.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; García-Llorente, M.; Montes, C. Trade-Offs across Value-Domains in Ecosystem Services Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lyu, Y.; Fu, B.; Yin, L.; Yu, D. The Effects of Vegetation Coverage Changes on Ecosystem Service and Their Threshold in the Loess Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 949–960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, C. Response of Ecological Service Value and Quality to Land Use Change in China’s Loess Plateau. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; Yu, C.; Gong, E.; Long, H.; Hu, H. Dynamic Monitoring of Environmental Quality in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2020 Using the Google Earth Engine Platform and the Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, T.; Zhu, B.; Li, J. Evaluation of the Importance of Ecological Regulation Function in Shaanxi Province Based on Physiographic Regions and Identification of Dominant Factors. Geogr. Res. 2023, 42, 1359–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Ding, Z.; Weng, B.; Xing, K.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Ulgiati, S.; Dong, X. Ecosystem Services and Ecological Restoration in the Northern Shaanxi Loess Plateau, China, in Relation to Climate Fluctuation and Investments in Natural Capital. Sustainability 2017, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q. Hotspot Identification and Interaction Analyses of the Provisioning of Multiple Ecosystem Services: Case Study of Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Mirghaed, F.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Mirkarimi, S.H. Decision Scenarios Using Ecosystem Services for Land Allocation Optimization across Gharehsoo Watershed in Northern Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Kang, S.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Han, L.; Xiang, X.-M.; Li, F. Spatio-Temporal Relationship between Vegetation Restoration and Ecosystem Services in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Ma, T.; Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Shen, X.; Liu, X. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Water Conservation of Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi Province by InVEST Model. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 664–676. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.X.; Liang, X.Y.; Li, H.Q.; Wei, Z. Impact of Landscape Pattern on Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Soil Protection Effect of the Grain for Green Project in Northern Shaanxi. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1835–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Yao, S. Assessing the Ecological Effectiveness of Sloping Land Conversion Programme to Identify Vegetation Restoration Types: A Case Study of Northern Shaanxi Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Y. Simulation of Biocapacity and Spatial-Temporal Evolution Analysis of Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi Based on the ca–Markov Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; He, Z.; Chen, W.; He, L.; Yang, H. Changes and Response Mechanisms of Leaf Area Index and Evapotranspiration in the Typical Natural Landscapes of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi of China under the Human Intervention. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yan, J.; Bu, Y.; Gu, L. Spatiotemporal Pattern Evolution of Forest and Grass Landscape Fragmentation in the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2022, 37, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Zheng, W.; Shi, H.; Ding, D. Ecosystem Services Assessment and Sensitivity Analysis Based on ANN Model and Spatial Data: A Case Study in Miaodao Archipelago. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Geng, J.; Bao, J.; Lin, W.; Wu, Z.; Fan, S. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Ecosystem Service Functions and Drivers in Anxi County Based on the InVEST Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cao, R. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Habitat Quality and Its Influencing Factors in Loess Plateau. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.P.; Gorddard, R.; House, A.P.N.; McIntyre, S.; Prober, S.M. Biodiversity and Agriculture: Production Frontiers as a Framework for Exploring Trade-Offs and Evaluating Policy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 23, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yu-wan, J.; Li-xin, S.; Tao, S.; Dong-dong, S. Determining the Intensity of the Trade-Offs among Ecosystem Services Based on Production-Possibility Frontiers: Model Development and a Case Study. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 2516–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Feng, D.; Lv, J. Relationship of Ecosystem Services in the Beijing–Tianjin– Hebei Region Based on the Production Possibility Frontier. Land 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Bao, B.; Zheng, K.; Li, C. Multi-Scale Spatial Differentiation and Geographic Detection Response of Ecosystem Service Value in Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier Based on the Modifiable Areal Unit Problem. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, L. Responses of Tradeoffs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services to Grain-for-Green Progect in the Red Soil Region, Sourthern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7002–7014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; He, H.; Yu, D.; Hu, H. Simulation of Maximum Light Use Efficiency for Some Typical Vegetation Types in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs in Different Climatic Regions and Its Driving Factors: A Case Study of the Sichuan-Yunnan-Loess Plateau Ecological Barrier Zone. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- QIAO, B.; FANG, C.-L. The Dynamic Coupling Model of the Harmonious Development between Urbaniza- Tion and Eco-Environment and Its Application in Arid Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 3003–3009. [Google Scholar]
- FAN, J.; ZHANG, Z.; LI, L. Mountain Demarcation and Mountainous Area Divisions of Sichuan Province. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of Climate Suitability for Human Settlement in China. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 648–653. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Shi, P.; Zhou, J.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Environmental Suitability Evaluation for Human Settlements in an Arid Inland River Basin: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhen, J. Comprehensive Suitability Evaluation and Spatial Optimization of Human Settlements Environment in Inner Mongolia. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 24, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Sylla, M.; Lasota, T.; Szewrański, S. Valuing Environmental Amenities in Peri-Urban Areas: Evidence from Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Lin, C. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and the Driving Factors in Urban Agglomerations: Evidence from 12 National Urban Agglomerations in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 804969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkin, K.; Shiode, N.; Shiode, S.; Kidd, D. Biodiversity and the Recreational Value of Green Infrastructure in England. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W.; Luan, B.; Chen, Y. On the Urban Compactness to Ecosystem Services in a Rapidly Urbanising Metropolitan Area: Highlighting Scale Effects and Spatial Non–Stationary. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, N.; Rahmonov, O. Ecosystem Services and Linkages of Naturally Managed Monotheca Buxifolia (Falc.) A. DC. Forests with Local Communities across Contiguous Mountainous Ranges in Pakistan. Biology 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, A.; Palomo, I.; González, J.A.; López, C.A.; Montes, C. Quantifying Spatial Supply-Demand Mismatches in Ecosystem Services Provides Insights for Land-Use Planning. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantz, C.A.; Manuel, J.J. Estimating Impacts of Population Growth and Land Use Policy on Ecosystem Services: A Community-Level Case Study in Virginia, USA. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Buerkert, A.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Schlecht, E.; Von Cramon-Taubadel, S.; Tscharntke, T. Implications of Agricultural Transitions and Urbanization for Ecosystem Services. Nature 2014, 515, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lee, W.K.; Choi, H.A.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S.W.; Kim, J.S. Spatial Assessment of Ecosystem Functions and Services for Air Purification of Forests in South Korea. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 63, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ding, Y. Spatial Disparity Dynamics of Ecosystem Service Values and GDP in Shaanxi Province, China in the Last 30 Years. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Song, C.; Song, C.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, H.; Polasky, S.; Polasky, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Bateman, I.J.; et al. Using Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) to Value Nature in Decision Making. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14593–14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslow, A. A Theory of Human Motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1943, 50, 370–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ma, G.; Wu, C.; Shao, J. Mapping Global Value of Terrestrial Ecosystem Services by Countries. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 52, 101361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pei, X.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, J. Understanding the Intricate Tradeoffs among Ecosystem Services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration across Spatiotemporal Features. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, N.; Khan, A.M.; Ali, K.; Abbas, F. Species Distribution Modelling of Monotheca Buxifolia (Falc.) A. DC.: Present Distribution and Impacts of Potential Climate Change. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijin, W.; Xiaoqing, P. Permafrost Degradation Services for Arctic Greening. Catena 2023, 229, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, K.M.; Bell, C.D.; McCray, J.E.; Hogue, T.S. Greening up Stormwater Infrastructure: Measuring Vegetation to Establish Context and Promote Cobenefits in a Diverse Set of US Cities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, B.; Gandini, M.; Gantes, P.; Matteucci, S.D. Regional Patterns of Ecosystem Functional Diversity in the Argentina Pampas Using MODIS Time-Series. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Xu, Y.; Guo, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, X. Study on Multi-Scale Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Trade-Offs and Synergies between Ecosystem Services in Jiangxi Province. Forests 2023, 14, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Fu, B.; Jin, T.; Chang, R. Trade-off Analyses of Multiple Ecosystem Services by Plantations along a Precipitation Gradient across Loess Plateau Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Qin, D.; Li, S. Trade-off Analyses of Multiple Mountain Ecosystem Services along Elevation, Vegetation Cover and Precipitation Gradients: A Case Study in the Taihang Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bian, J.; Liang, J.; Pan, S.; Zeng, Y. Traffic Accessibility and the Coupling Degree of Ecosystem Services Supply and Demand in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, J. Impacts of Traffic Accessibility on Ecosystem Services: An Integrated Spatial Approach. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 1816–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XU, C.; GONG, J.; LI, Y.; YAN, L.; GAO, B. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Typical Ecosystem Services Based on Terrain Gradients of Bailongjiang Watershed in Gansu. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.; Mak- Mensah, E. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Grassland Ecosystem Service Value and Its Topographic Gradient Effect in the Yellow River Basin. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, L.; Straatsma, M.W.; Wanders, N.; Verstegen, J.A.; De Jong, S.M.; Karssenberg, D. Global Ecosystem Service Values in Climate Class Transitions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, C.M.; Pelini, S.L.; Laws, A.; Rivest, E.; Woltz, M.; Bloch, C.P.; Del Toro, I.; Ho, C.K.; Kominoski, J.; Newbold, T.A.S.; et al. Invertebrates, Ecosystem Services and Climate Change. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Mou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Peng, C. Effect of Urbanization on Ecosystem Service Values in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China from 2000 to 2014. Sustainability 2020, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Data Sources |
|---|---|
| Land use, watershed, population density | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn) |
| Precipitation, evapotranspiration | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home) |
| Plant-available water content, root-restricting layer depth | Harmonized World Soil Database (http://webarchive.iiasa.ac.at/Research/LUC/External-World-soil-database/HTML/index.html?sb=1) |
| NDVI | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (https://www.nasa.gov) |
| DEM | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/home) |
| Temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, sunshine | National Meteorological Scientific Data Center (https://data.cma.cn) |
| Road network | National Catalogue Service for Geographic Information (https://www.webmap.cn/main.do?method=index) |
| Urbanization, GDP | National Bureau of Statistics (http://www.stats.gov.cn) |
| Methodology Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical Zoning | OLS | GWR | |
| first zone | 0.069 | 0.295 | |
| second zone | 0.093 | 0.279 | |
| third zone | 0.198 | 0.452 | |
| fourth zone | 0.270 | 0.537 | |
| fifth zone | 0.252 | 0.601 | |
| Environmental Factors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Efficiency | |||||||||
| 7.4 | 11.239 | −20.48 | 6.232 | 22.611 | 1.305 | 1.662 | −80.412 | ||
| −34.366 | 13.175 | −18.519 | −0.817 | −0.87 | 3.169 | 5.733 | 12.174 | ||
| −37.627 | 16.099 | −38.596 | 8.665 | 6.592 | 2.844 | 5.477 | 50.677 | ||
| −43.955 | 1.183 | −45.129 | 8.921 | 2.794 | −0.047 | 15.202 | −19.823 | ||
| −21.777 | −14.393 | −60.318 | −9.249 | −1.377 | −0.179 | 15.191 | −82.696 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, W. Assessment and Enhancement of Ecosystem Service Supply Efficiency Based on Production Possibility Frontier: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914314
Yan Z, Wang Y, Hu X, Luo W. Assessment and Enhancement of Ecosystem Service Supply Efficiency Based on Production Possibility Frontier: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914314
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Zhenjun, Yirong Wang, Xu Hu, and Wen Luo. 2023. "Assessment and Enhancement of Ecosystem Service Supply Efficiency Based on Production Possibility Frontier: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914314
APA StyleYan, Z., Wang, Y., Hu, X., & Luo, W. (2023). Assessment and Enhancement of Ecosystem Service Supply Efficiency Based on Production Possibility Frontier: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi. Sustainability, 15(19), 14314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914314







