Fault Prediction Recommender Model for IoT Enabled Sensors Based Workplace
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- RQ 1: What are the main ML methods for fault prediction?
- RQ 2: What various performance indicators are employed by the proposed ML algorithm?
- RQ 3: What impact does the proposed work have on the well-being of office workers?
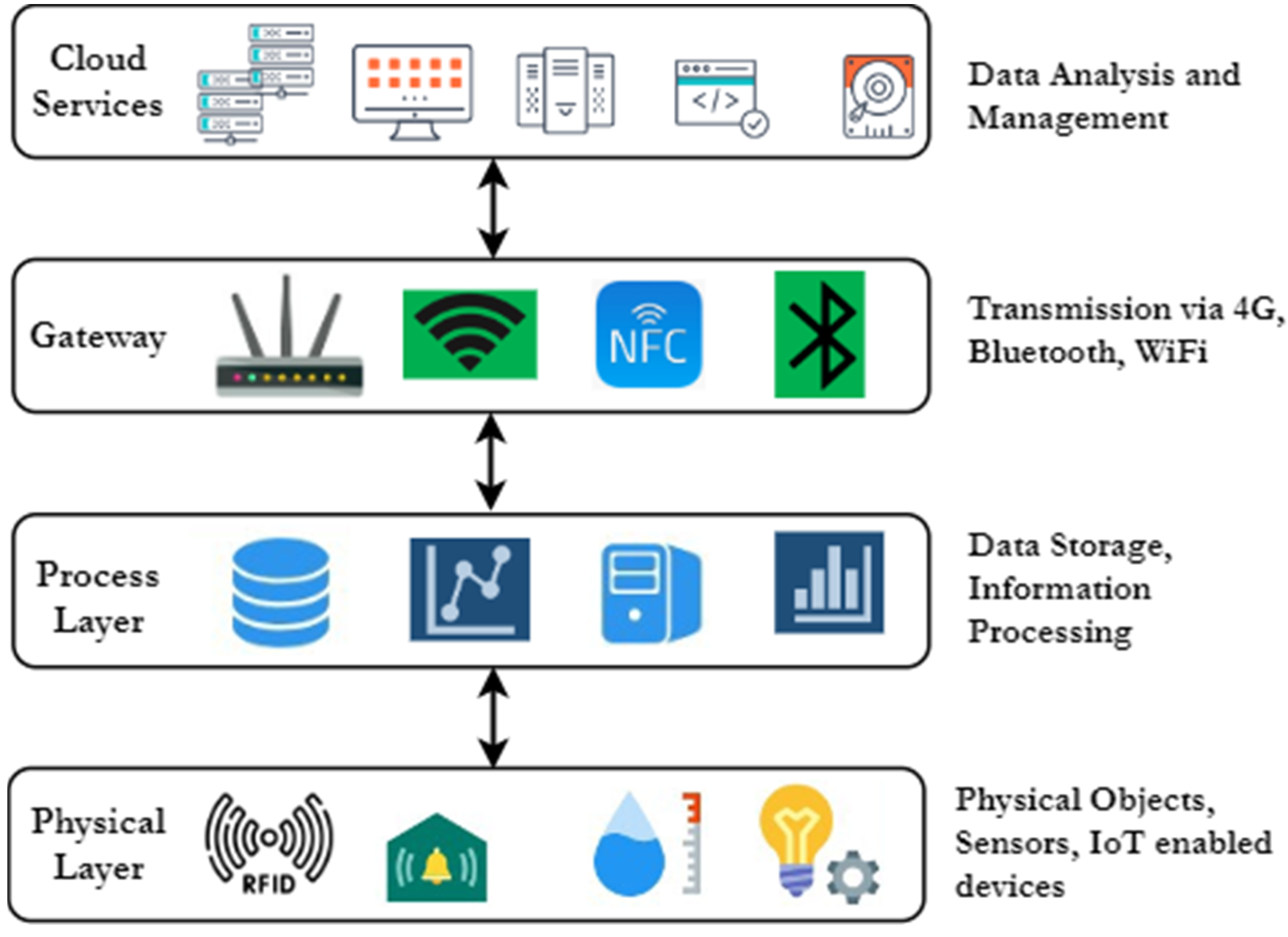
- A detailed explanation of Cloud-based IoT architecture is given which focuses on different layers and their services.
- Various sensors along with their range and distribution in the proposed model’s 3D design will also be depicted.
- This paper also discusses detailed design of a prototype of the proposed smart office along with a circuit diagram.
- A machine learning algorithm is implemented for a Fault Prediction Recommender Model (FPRM) which focuses on early prediction of faults after monitoring real-time sensor data present in an office environment.
- A web application is developed to monitor the status of sensors and devices in real-time and display the faults with recommended solutions.
2. Background and Related Works
3. System Design
Setup for Hardware Platform
4. Research Methodology
5. Experiments and Results
6. Discussions and Recommendations
7. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunchu, R.; Palli, S.; Datta, V.S.R.; Shanmugasundaram, M. Intelligent system for office environment using internet of things. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 717–721. [Google Scholar]
- Plessis, A.d.; Theron, B. Virtual World—Physical World: What is the Real World? Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Adm. 2016, 2, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rout, K.K.; Mallick, S.; Mishra, S. Design and implementation of an internet of things based prototype for smart home automation system. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Recent Innovations in Electrical, Electronics & Communication Engineering (ICRIEECE), Bhubaneswar, India, 27–28 July 2018; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Prettner, K. A note on the implications of automation for economic growth and the labor share. Macroecon. Dyn. 2019, 23, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Secular stagnation? The effect of aging on economic growth in the age of automation. Am. Econ. Rev. 2017, 107, 174-79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora, H.; Gil, D.; Terol, R.M.; Azorín, J.; Szymanski, J. An IoT-based computational framework for healthcare monitoring in mobile environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Monitoring citrus soil moisture and nutrients using an IoT based system. Sensors 2017, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, G.; Collodi, G.; Gelpi, L.; Fusco, R.; Ricci, G.; Manes, A.; Passafiume, M. Realtime gas emission monitoring at hazardous sites using a distributed point-source sensing infrastructure. Sensors 2016, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, W.F.; Lin, T.H.; Lin, Y.C. A real-time construction safety monitoring system for hazardous gas integrating wireless sensor network and building information modeling technologies. Sensors 2018, 18, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, Y.S.; Choi, H.R.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, J.W. Development of IoT-based sensor tag for smart factory. Int. Res. J. Electron. Comput. Eng. 2017, 3, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Fault diagnosis method for a mine hoist in the internet of things environment. Sensors 2018, 18, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Noh, S.D.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, Y.S. Implementation of cyber-physical production systems for quality prediction and operation control in metal casting. Sensors 2018, 18, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Shukla, S.; Majumdar, N. Machine learning techniques to reduce error in the internet of things. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 10–11 January 2019; pp. 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, B.; Su, J.; Wen, Z.; Jha, D.N.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Puthal, D.; James, P.; Yang, R.; Zomaya, A.Y.; et al. Orchestrating the development lifecycle of machine learning-based IoT applications: A taxonomy and survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2020, 53, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Fatima, I.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K. Daily life activity tracking application for smart homes using android smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2012 14th International conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT), PyeongChang, Republic of Korea, 19–22 February 2012; pp. 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Patchava, V.; Kandala, H.B.; Babu, P.R. A smart home automation technique with raspberry pi using iot. In Proceedings of the 2015 International conference on smart sensors and systems (IC-SSS), Bangalore, India, 21–23 December 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abella, C.S.; Bonina, S.; Cucuccio, A.; D’Angelo, S.; Giustolisi, G.; Grasso, A.D.; Imbruglia, A.; Mauro, G.S.; Nastasi, G.A.; Palumbo, G.; et al. Autonomous energy-efficient wireless sensor network platform for home/office automation. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3501–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Jeon, B.; Noh, J.; Kim, Y.; Park, S. An intelligent self-adjusting sensor for smart home services based on ZigBee communications. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2012, 58, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.W.; Bhatt, D.V.; Hancke, G.P.; Silva, B. A web-based office climate control system using wireless sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6104–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, S.D.T.; Suryadevara, N.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Towards the implementation of IoT for environmental condition monitoring in homes. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3846–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Y. Toward ubiquitous healthcare services with a novel efficient cloud platform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 60, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G. Cloud-assisted industrial internet of things (iiot)–enabled framework for health monitoring. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Labour Office. World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2015; International Labour Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Lao, X.Q.; Pang, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, A.; Zou, J.; Mei, L.; Yu, I.T.S. A survey of occupational health hazards among 7610 female workers in China’s electronics industry. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2013, 68, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademujimi, T.T.; Brundage, M.P.; Prabhu, V.V. A review of current machine learning techniques used in manufacturing diagnosis. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 3–7 September 2017; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, W.A.; Kian, T.K.; Ramli, R.M.; Zubir, S.N.; Zamrizaman, N.S.; Balfaqih, M.; Shepelev, V.; Alharbi, S. Design and fabrication of smart home with internet of things enabled automation system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144059–144074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A.O.; Olaniyi, O.M.; Arulogun, O.T.; Olaniyan, O.M. Development of a microcontroller-controlled security door system. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 10, 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, G.K.; Tripathi, P. A digital security system with door lock system using RFID technology. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudita Gupta, D. A comprehensive study of recommender systems for the internet of things. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1969, p. 012045. [Google Scholar]
- Uppal, M.; Gupta, D.; Juneja, S.; Dhiman, G.; Kautish, S. Cloud-based fault prediction using IoT in office automation for improvisation of health of employees. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darianian, M.; Michael, M.P. Smart home mobile RFID-based Internet-of-Things systems and services. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, 20–22 December 2008; pp. 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Gladence, L.M.; Karthi, M.; Anu, V.M. A statistical comparison of logistic regression and different Bayes classification methods for machine learning. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 10, 5947–5953. [Google Scholar]
- Mudita; Gupta, D. Prediction of Sensor Faults and Outliers in IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 3–4 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Uppal, M.; Gupta, D.; Anand, D.; SAlharithi, F.; Almotiri, J.; Ortega-Mansilla, A.; Singh, D.; Goyal, N. Fault pattern diagnosis and classification in sensor nodes using fall curve. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 1799–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuk, N.; Ku-Mahamud, K.R.; Zakaria, N.H.; Maarof, M.A. Implementation and recent progress in cloud-based smart home automation systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE), Penang, Malaysia, 28–29 April 2018; pp. 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, D.; Patel, H.; Dave, B. Development of integrated cloud-based Internet of Things (IoT) platform for asset management of elevated metro rail projects. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobinath, V.; Gladence, L.M.; Haran, S.H.; Sathiyavathi, R.; Anu, V.M. Home and office automation system-survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 Third International Conference on Science Technology Engineering & Management (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 23–24 March 2017; pp. 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Harsha, S.S.; Reddy, S.C.; Mary, S.P. Enhanced home automation system using Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 10–11 February 2017; pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, I.; Umer, M.; Majeed, R.; Mehmood, A.; Aslam, W.; Yasir, M.N.; Choi, G.S. Home automation using general purpose household electric appliances with Raspberry Pi and commercial smartphone. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, R.K.; Rath, A.K.; Sharma, S. An Energy Efficient WSN Assisted IoT Platform for Home/Office Automation to enable Green IoT. Solid State Technol. 2020, 63, 16117–16131. [Google Scholar]
- Gladence, L.M.; Sivakumar, H.H.; Venkatesan, G.; Priya, S.S. Home and office automation system using human activity recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 International conference on communication and signal processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 6–8 April 2017; pp. 0758–0762. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Gupta, K.; Turabieh, H.; Sharma, S. SWOT: A Hybrid Hardware-Based Approach for Robust Fault-Tolerant Framework in a Smart Day Care. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 2939469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, M.; Sulaiman, A.; Rajab, K.; Rajab, A.; Elmagzoub, M.A.; Shaikh, A. Cloud-Based Fault Prediction for Real-Time Monitoring of Sensor Data in Hospital Environment Using Machine Learning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, S.; Juneja, A.; Dhiman, G.; Behl, S.; Kautish, S. An approach for thoracic syndrome classification with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 3900254 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, D.; Singal, G.; Dhiman, G.; Kautish, S. Recognition of gurmukhi handwritten city names using deep learning and cloud computing. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 5945117 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Rashid, J.; Kim JViriyasitavat, W.; Gulati, K. Privacy for healthcare data using the byzantine consensus method. IETE J. Res. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, K.; Gupta, S.; Viriyasitavat, W.; Mohafez, H.; Islam, M.A. Smart-hydroponic-based framework for saffron cultivation: A precision smart agriculture perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, A.; Upadhyay, H.K. Machine Learning Algorithms for Industry Using Image Sensing. In Healthcare Solutions Using Machine Learning and Informatics; Auerbach Publications: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, C.; Upadhyay, H.K. Plant Disease Detection Using Imaging Sensors, Deep Learning and Machine Learning for Smart Farming. In Healthcare Solutions Using Machine Learning and Informatics; Auerbach Publications: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; Bhoi, A.K.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Reddy, G.T.; Bilal, M. Probabilistic deep Q network for real-time path planning in censorious robotic procedures using force sensors. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Zhu, M.; Ahanger, T.A.; Khowaja, S.A. Sparse Bayesian learning based channel estimation in FBMC/OQAM industrial IoT networks. Comput. Commun. 2021, 176, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikumar, K.S.; Prathiba, S.B.; Alazab, M.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Pandya, S.; Khan, J.M.; Moorthy, R.S. FL-PMI: Federated learning-based person movement identification through wearable devices in smart healthcare systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafea, O.; Abdul, W.; Muhammad, G.; Alsulaiman, M. Sensor-based human activity recognition with spatio-temporal deep learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaheri, H.; Muhammad, G.; Alsulaiman, M.; Amin, S.U.; Altuwaijri, G.A.; Abdul, W.; Bencherif, M.A.; Faisal, M. Deep learning techniques for classification of electroencephalogram (EEG) motor imagery (MI) signals: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Sensor Name | Specifications | Snapshot |
|---|---|---|
| DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor |
|  |
| MQ135 Air Quality Sensor |
|  |
| HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor |
|  |
| Fire/Flame Sensor |
|  |
| Sensor Name | Range | Snapshot |
|---|---|---|
| ACS712 Current Sensor |
|  |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 92.343% | 91.755% | 92.343% | 92.048% |
| Random Forest | 94.274% | 92.821% | 94.274% | 93.542% |
| K-Nearest Neighbour | 92.829% | 92.016% | 92.829% | 92.421% |
| Decision Tree | 92.115% | 92.224% | 92.115% | 92.170% |
| Appliance | Value | Recommendations | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Check for discharged battery. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Light | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Check for discharged battery. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Printer | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Appliance not responding. |
| ||
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for discharged battery. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| CCTV | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Check for discharged battery. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| LCD TV | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Check for the discharged battery. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Coffee Machine | 0 | Check for main supply (OFF). |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Check for the discharged battery. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Door Sensor | 0 | Sensor not responding. |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Fire Sensor | 0 | Sensor not responding. |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Humidity Sensor | 0 | Sensor not responding. |
|
| Check for loose wire connection. |
| ||
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Air QualitySensor | 0 | Check for loose wire connection. |
|
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| TemperatureSensor | 0 | Check for loose wire connection. |
|
| (Value < min_range) OR (Value > max_range) | If (value remain out of bound for 20 iteraions) Repair is required. |
| |
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
| ||
| Motion Sensor | 0 | Check for loose wire connection. |
|
| Check for cable wreckage. |
| ||
| Otherwise Replace the appliance. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uppal, M.; Gupta, D.; Mahmoud, A.; Elmagzoub, M.A.; Sulaiman, A.; Reshan, M.S.A.; Shaikh, A.; Juneja, S. Fault Prediction Recommender Model for IoT Enabled Sensors Based Workplace. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021060
Uppal M, Gupta D, Mahmoud A, Elmagzoub MA, Sulaiman A, Reshan MSA, Shaikh A, Juneja S. Fault Prediction Recommender Model for IoT Enabled Sensors Based Workplace. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021060
Chicago/Turabian StyleUppal, Mudita, Deepali Gupta, Amena Mahmoud, M. A. Elmagzoub, Adel Sulaiman, Mana Saleh Al Reshan, Asadullah Shaikh, and Sapna Juneja. 2023. "Fault Prediction Recommender Model for IoT Enabled Sensors Based Workplace" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021060
APA StyleUppal, M., Gupta, D., Mahmoud, A., Elmagzoub, M. A., Sulaiman, A., Reshan, M. S. A., Shaikh, A., & Juneja, S. (2023). Fault Prediction Recommender Model for IoT Enabled Sensors Based Workplace. Sustainability, 15(2), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021060











