Abstract
The Volta Grande do Xingu (VGX) in the Amazon Forest of Brazil was chosen to analyze the land use and land cover changes (LULCC) from 2000 to 2017, with the aim of assessing the most suitable classification method for the area. Three parametric (Mahalanobis distance, maximum likelihood and minimum distance) and three non-parametric (neural net, random forest and support vector machine) classification algorithms were tested in two Landsat scenes. The accuracy assessment was evaluated through a confusion matrix. Change detection of the landscape was analyzed through the post-classification comparison method. While maximum likelihood was more capable of highlighting errors in individual classes, support vector machine was slightly superior when compared with the other non-parametric options, these being the most suitable classifiers within the scope of this study. The main changes detected in the landscape were from forest to agro-pasture, from forest/agro-pasture to river, and from river to non-river, resulting in rock exposure. The methodology outlined in this research highlights the usefulness of remote sensing tools in follow-up observations of LULCC in the study area (with the possibility of application to the entire Amazon rainforest). Thus, it is possible to carry out adaptive management that aims to minimize unforeseen or underestimated impacts in previous stages of environmental licensing.
1. Introduction
The Amazon Forest is a megadiverse biome, distributed across nine countries, mostly in Brazil. Since the 1970s, unprecedented tropical deforestation rates have been transforming the Brazilian Amazon into a mosaic of agriculture, pasture and different stages of successional vegetation patches [1,2,3]. In the past 20 years, many anthropogenic activities have pressured this biome, such as the construction of hydroelectric dams since the 1990s [4,5]. Until 2022, seven of the largest existing hydroelectric dams (Tucuruí, Balbina, Samuel, Santo Antônio, Jirau, Teles Pires and Belo Monte) have been in full operation in the legal Brazilian Amazon [6,7].
Regional environmental changes caused by hydropower development can lead to non-trivial implications in climate, hydrological and biodiversity regimes in all Amazon regions. The magnitude of the plans and impacts caused by such development projects makes it extremely important to learn all possible lessons from hits and misses in the planning and construction of hydroelectric dams in the Amazon Forest [6].
Former experiences in the area indicate the need to improve the systems of development planning, impact analysis and environmental licensing. Furthermore, the role of climate and land cover change in energy planning in emergent economies remains a critical issue that could play a major role in the sustainability of hydropower projects [8,9,10].
Dams’ impacts in large tropical rivers have been generally assessed belatedly or are underestimated in terms of their socio-environmental changes, affecting socio-ecological sustainability [11,12]. This is the case of the Belo Monte Hydroelectric Complex (BMHC) in the Volta Grande do Xingu (VGX), where the presence of dams has resulted in changes within habitats and biomes [13]. Although it is very common to find in the literature studies that debate the pros and cons of this mega operation [6], a search on indexed journal databases reveals that the VGX is a much lesser explored and studied area compared with the rivers and floodplain environments where the other largest Amazon hydroelectric dams are installed.
Land use and land cover changes (LULCC) have been important tools for the assessment of the impacts of large dams on the environment [14]. This is especially essential for the Amazon Forest due to its high cultural and biodiversity values. LULCC evaluation, classification and accuracy are some of the most important applications in remote sensing, and its applicability and enhancement are major concerns in Earth observation sciences [15,16]. Classification methods in remote sensing are the basis for several LULCC environmental applications [17].
There is no consensus on which classification algorithms are the best for LULCC analysis [17]. The individualities of each study, such as their aims and objectives, the dataset used or the area under study, make the choice for a classification method very particular for each case [18]. A better comprehension of the use of different classifiers, aiming to gather most relevant and reliable land cover information, is a continuous demand, and this is the reason why the selection of a suitable classifier is so unique and requires the consideration of factors that include algorithm performance, accuracy results, computational resources and limitations inherent to the methodology [17,19].
Some of the most important and susceptible aspects that can bring uncertainty to a final product happen during the image acquisition process and during the different stages of the classification procedures. These can, in turn, affect the spatial and radiometric resolutions, generating position and interpretation errors [20]. The poor quality of training samples, which affect the area estimation of land-cover classes and the interaction between the instrument resolution and the scale of processes being analyzed on the ground, is also an issue of concern [18]. For tropical forests in particular, atmospheric conditions (clouds are often a problem for remote sensing in tropical areas, due to the difficulty of collecting cloud-free orbital imagery), complex vegetation composition and the lack of reliable reference data that can be used for validation must be considered when assessing classification quality [21]. To overcome challenges related to the intrinsic complexity of the landscape and elaborate image processing techniques, research has been developed in the LULC classification methods and comparative studies of different classifiers are frequent in literature [17].
As important as the debates around the advantages and disadvantages of a mega operation such as the BMHC are the measurements of the imbalances caused to such a fragile ecosystem, an issue much less explored in the literature. A better understanding of the relationships between a dam’s construction, its operation and the resulting land-cover changes on the part of decision makers and public policy makers is essential for effective land management that promotes both economic development and a conceivable level of sustainability and environmental wholeness. Therefore, it is fundamental to make available the most suitable and straightforward methodologies and data sources, embracing even users outside the remote sensing community.
Considering all of the arguments above, this study seeks to compare the applications and accuracy assessment of supervised parametric (Mahalanobis distance, maximum likelihood, and minimum distance) and non-parametric (neural net, random forest, and support vector machine) classification algorithms, which are very popular in image processing software, in the VGX field.
To do so, we analyzed the land use and land cover change using Landsat images from 2000 and 2017. This study discusses which classification algorithms might be more suitable to evaluate LULCC in VGX and identifies potential alterations in land use and land cover that might be related to the construction of the BMHC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
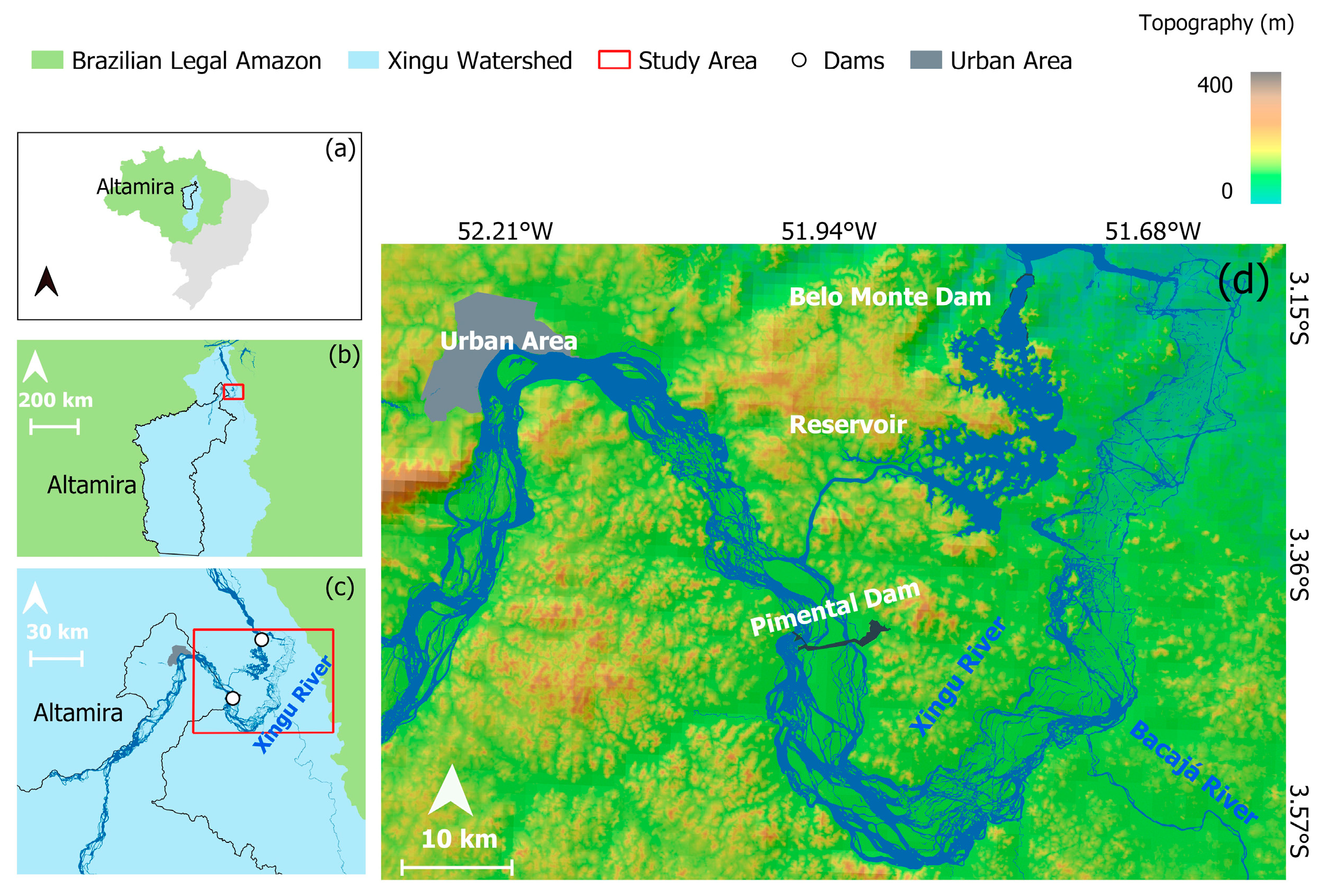
The Amazon is mainly covered by evergreen forest, wetlands and water surface. The main land uses of the biome are cattle ranching, agriculture, mining, logging, non-timber forestry production and uses related to occupation processes, such as road building [4,22]. The watershed of the Xingu River is located in the Brazilian states of Pará and Mato Grosso (Figure 1). The lowest part of the middle Xingu is known as The Volta Grande do Xingu, located totally in Pará.
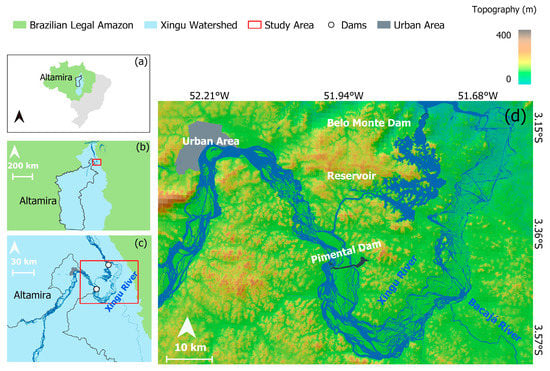
Figure 1.
(a) The Xingu watershed and the municipality of Altamira (Pará state, Brazil) within the Brazilian legal Amazon. (b) Location of the VGX, northward of the municipality of Altamira (red square) and the Xingu watershed. (c) The VGX area comprising the Belo Monte and Pimental dams (white dots) in the study area (red square). (d) The study area and its topography in detail.
Cattle have been present in the Xingu floodplains for at least the last 100 years [23]. More recently, cattle ranches have been replaced by large-scale agriculture, increasing deforestation rates [24]. Indeed, mega-scale soy plantations are a dangerous threat to the environment in the Amazon Forest—the Xingu basin alone provides 8% of global soy production [25]. In the VGX, most of the land cover and land use include primary forest, secondary forest, agriculture (such as cocoa and açaí plantations and other kinds of crops), pasture, exposed soil, and alluvial forests under the influence of flood pulses [12,26]. The local economy is based on familiar agriculture, and has riverside agriculture and traditional extractive activities, such as rubber and Brazilian nuts [27].
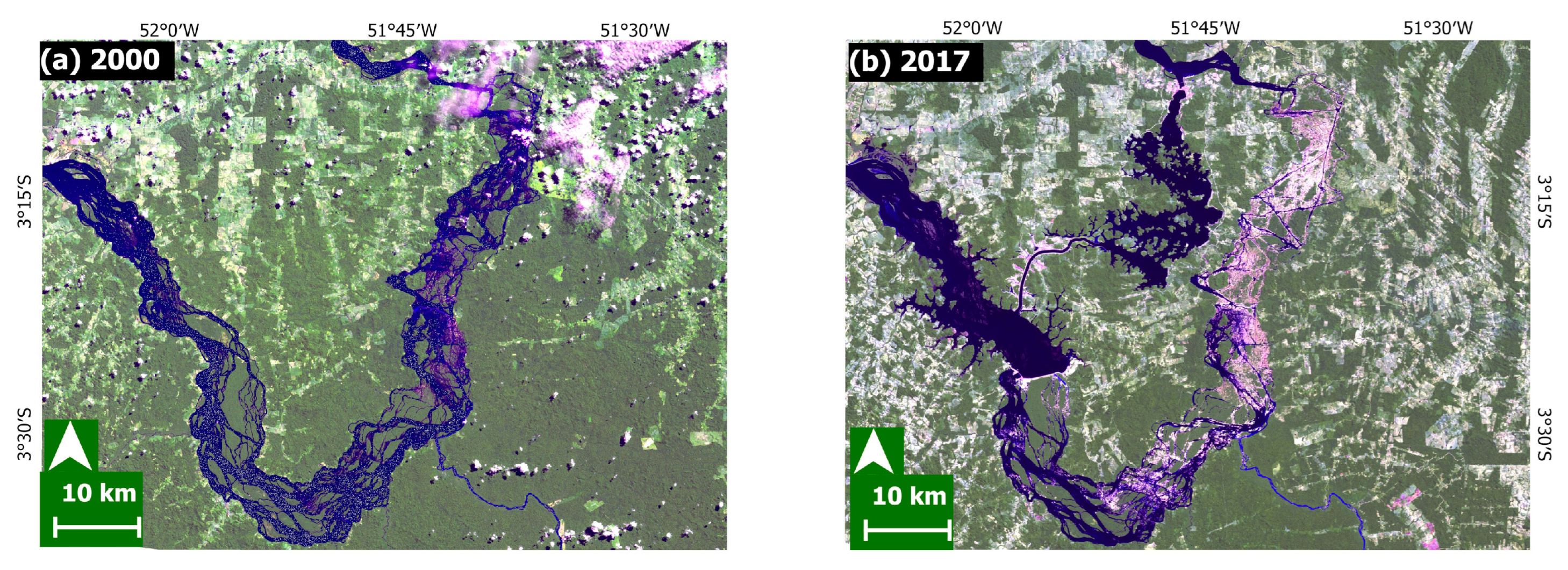
The construction of BMHC began in 2001 and was completed in 2016. BMHC is the third-largest hydroelectric plant in the world, with 11.2 GW of capacity [28]. The major alteration caused to the Xingu River was the inundation of an extensive area of vegetation (as can be seen from Figure 2a,b). It has drained approximately 130 km of the river channel between Pimental and the outlet of the BMHC dam (downstream—the focus of this study). From there, the water is returned to the Xingu’s main channel [29,30,31].
The BMHC has two dams (Pimental and Belo Monte). The main dam of Belo Monte, which resulted in the Xingu reservoir, is 40 km downstream of the municipality of Altamira, which is the largest Brazilian municipality and concentrates the core urban area nearby (Figure 1) [32].
The geomorphology of the Xingu watershed is complex, with large boulders of rock in the Xingu River channel with associated vegetation, mainly downstream of its encounter with the Bacajá River and close to its encounter with the Iriri River [29,33]. This configuration promotes abundance and diversity in fauna and flora, with about 174 species of fish, 440 species of birds, 259 species of mammals, as well as endemic and endangered species [34]. Surrounding the VGX, there are different conservation units and indigenous lands [35].
Tropical rivers, such as the Xingu River, are ruled by a well-pronounced flood pulse [36]. Its peak is from March to May, while the dry season is from September to November. The BMHC altered the natural flood pulse in an extreme way when the river flow was diverted for the construction of the reservoir [27]. The average flow, able to reach 20,000 m³/s during its peak, was reduced to 4000 m³/s yearly, rotating with an 8000 m³/s flow every two years, a reduction of 80% of the river flow in the VGX area [37]. This new hydrological regime imposed by the dam operators has been implemented since the end of 2019, with some occasional interruptions due to judicial interferences caused by the proven unsustainable conditions to keep healthy riverine ecosystems [38,39]. Indeed, some studies already indicated that the artificial regulation of the Xingu water flow level is failing to simulate the natural flood pulse and specialized vegetation and aquatic organisms are not able to survive the new conditions [27,30,31,37].
2.2. Dataset
Two Landsat (Landsat sensor products are commonly used for local and regional scales—the case of this work—and have been one of the most frequent sources of data for LULC classification and analysis due to the benefits associated with being free of charge and having registered the Earth’s surface for decades. Despite the cloud-free issue, Landsat 7 and 8 are able to distinguish many different kinds of surface targets, mainly when supported by good quality field survey data [28].) multispectral products were analyzed: a Landsat 7 image from 26 May 2000 (Figure 2a) and a Landsat 8 image from 20 July 2017 (Figure 2b). The year 2000 represents a scenario before the dam’s construction, and 2017 represents a scenario the year right after the dam’s full operation. This long time interval was chosen mainly due to the sparse availability of cloud-free images for the VGX, since frequent observations in the Brazilian Amazon are highly improbable using optical images [21]. Both images were acquired from the USGS Landsat Image Gallery platform [40] and have spatial resolution of 30 meters. The bands used for the image classification and analysis were the visible, near and short-wave infrared for both. The two images were radiometric calibrated, stacked and mosaicked.
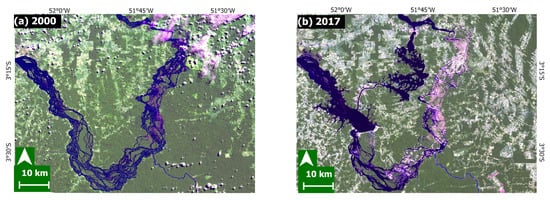
Figure 2.
(a) Landsat 7 image from 26 May 2000; (b) Landsat 8 image from 20 July 2017. Source: Landsat-7 and 8 images courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey.
Figure 2.
(a) Landsat 7 image from 26 May 2000; (b) Landsat 8 image from 20 July 2017. Source: Landsat-7 and 8 images courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey.
2.3. Class Selection and Spectral Signatures
Based on the Amazon landscape, in a first attempt of class selection, primary and secondary forest, crops, exposed soils, agricultural lands, pasture, river, rocks and clouds were chosen based on a thematic vegetation map from the area [41]. It was not possible to completely remove clouds and their shadows from the 2000-year Landsat image using a mask, so it was determined that clouds/shadows would be considered a single class, one that was easier to disregard on the post-classification analysis and other quantitative approaches.
To avoid misinterpretations during the classification process, a prior selection of classes was performed that considering spectral signatures, based on the analysts’ previous knowledge. Using the function “Statistics” in ENVI 5.5.3, a spectral profile for both Landsat images (2000 and 2017) for each class was created. The spectral information is the mean spectral signature, or reflectance, of the targets, in digital numbers (DN), for all the bands in the image, collected through polygons represented as region of interest (ROIs) for each of the classes.
A significant overlapping of spectral signatures (primary and secondary forests and agricultural lands) was observed, indicating that the algorithms would misinterpret some of the classes. This might occur due to the heterogeneity and complexity in vegetation structure in tropical forests. Remote sensors primarily capture canopy information and structures between different vegetation stages (e.g., secondary succession and mature forest). This way, different vegetation species may look similar. Besides that, a single pixel might contain more than one vegetation type, forest stage or land-cover class in a 30 m resolution Landsat imagery, resulting in confusion between classes [15].
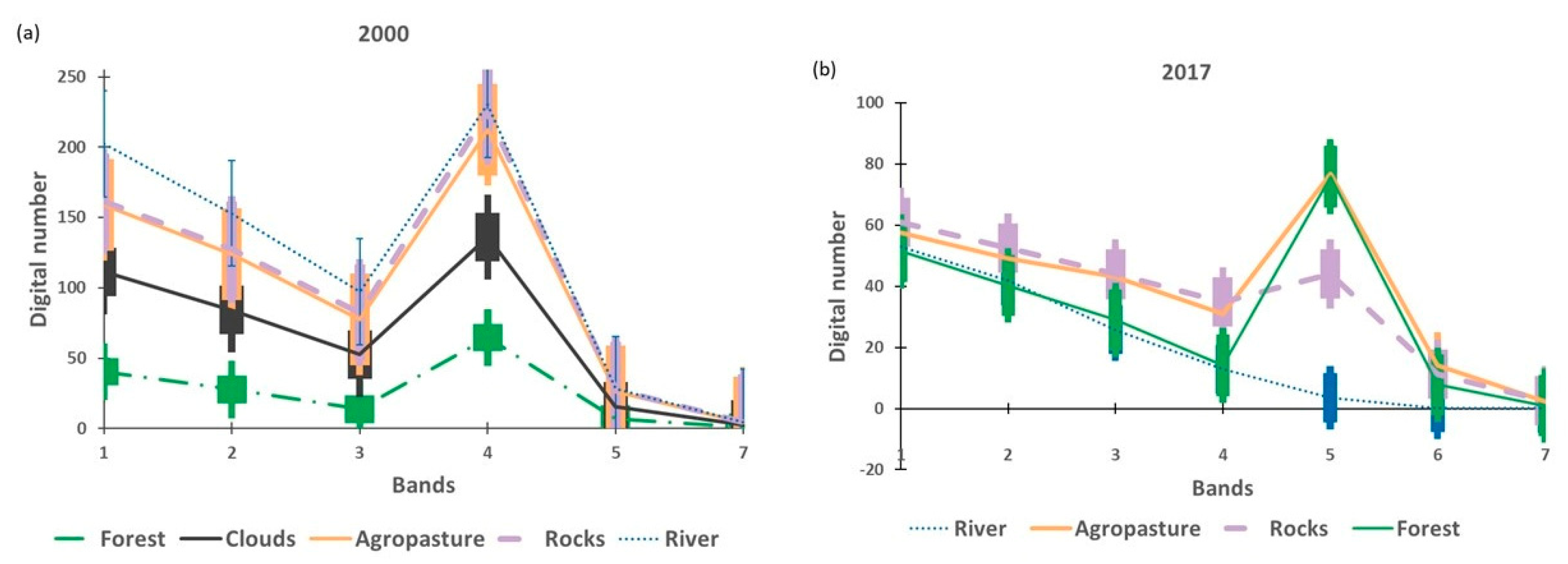
Therefore, intermediate stages of vegetation and different kinds of crops and bare soil environments were merged in unique classes: primary and secondary forest and developed mature crops were grouped into “vegetation” and agricultural lands; and fresh crops and pasture were grouped into “agro-pasture”. Ultimately, this study considered five classes: clouds (which were disregarded on the quantitative analysis); forest (which included different types of vegetation, such as alluvial forest, inland forest, primary and secondary vegetation); agro-pasture (including different types of crops, pasture areas, exposed soil and logging areas); river (comprising different depths of the water column); and rocks (large exposed boulders of gneiss rock covered by low vegetation and ferruginous crusts, eventually crossed by the watercourse) (Figure 3). Examples of these classes in the ground are shown in Figure 4e–g.
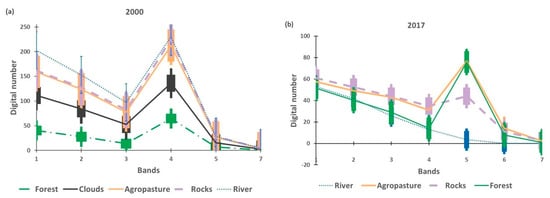
Figure 3.
Spectral profiles and their respective error bars for each class selected for the classification of the images of the VGX area extracted from Landsat 7, May 2000 (a) and Landsat 8, July 2017 (b).
The fusion of classes worked well for vegetation, but it was observed that, for agro-pasture and rocks in the year 2000 (Figure 3a), the reflectance still has overlaps, corroborating the spectral confusion already reported in the literature between bare soils and non-vegetated wetlands [42] in the study area. For the year 2017 (Figure 3b), although river and rocks are well distinguished from other classes in band 5, there is a superposition of rocks and agro-pasture and forest and rivers at the visible band, exhibiting a pattern of two spectral signature clusters in the visible band. Although there are some distinctions between the classes, mainly in the NIR bands, at no wavelength was the separation of spectral signatures complete, including overlapping of error bars.
2.4. Reference Data
Good classification results strongly depend on the selection of reliable training datasets for each class [18] and field visits are important to improve the quality of the reference data [43]. To support and guide the selection of more accurate sample plots to be used in the training stage and improve the accuracy assessment of the final products, very-high resolution orthomosaics, at the order of centimeters and capable of revealing great details of the landscape, were employed. These orthomosaics represent interest zones in the scope of the study, are small compared to the VGX and are therefore not representative of the whole area. These were created through orthophotos collected using a Phantom 4 Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPA) (examples of orthophotos are in Figure 4b–d). The images generated by the flights were processed on Agisoft Metashape Pro version 1.8.3. For more information on this methodology, the reader can refer to [44,45]. The flights occurred between 07–14 November 2021 in a field trip to the study area, mainly over the floodplain, where different environments (such as wetlands, forests, river, bare soil, and rocks) could be detected. Agro-pasture areas could not be reached by the RPA from where the flights took place and were not imaged. The training sample polygons were then drawn with consideration of the analyst’s knowledge of the area, of the imagery dataset acquired from the RPA flights during the field trip, of the high-resolution imagery set used as reference of the ground and of the spectral signatures of each class.
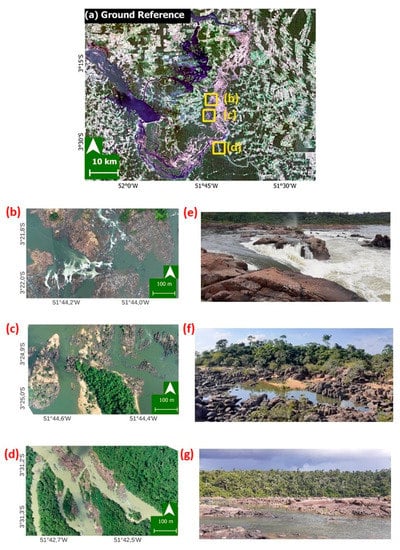
Figure 4.
(a) Ground reference dataset based on the Planet Labs platform (4.77 m resolution) and used in the accuracy assessment step. The yellow squares are the location from orthophotos (b–d). (b) Orthophoto and (e) field example from a rocky environment among narrow river channels and rapids. (c) Orthophoto and (f) field example from exposed soil, rocks and associated rock vegetation. (d) Orthophoto and (g) field example from dense wetland and upland forest vegetation being crossed by the Xingu River (which has its main course diverted into channels) and blocks of rocks. (e–g) are not georeferenced and are examples of interest zones within environments (b–d).
Figure 4.
(a) Ground reference dataset based on the Planet Labs platform (4.77 m resolution) and used in the accuracy assessment step. The yellow squares are the location from orthophotos (b–d). (b) Orthophoto and (e) field example from a rocky environment among narrow river channels and rapids. (c) Orthophoto and (f) field example from exposed soil, rocks and associated rock vegetation. (d) Orthophoto and (g) field example from dense wetland and upland forest vegetation being crossed by the Xingu River (which has its main course diverted into channels) and blocks of rocks. (e–g) are not georeferenced and are examples of interest zones within environments (b–d).
The last step of the process is the accuracy assessment of the map generated through the classification process using a confusion (or error) matrix. High-resolution aerial or satellite imagery is often used to assess the accuracy of maps made from moderate-resolution satellite imagery, such as Landsat. Simple classification schemes (from two to eight classes) can be reliably assessed from the interpretation of high-resolution imagery [43].
Due to the small coverage of the orthomosaics generated by the RPA, this dataset could not be used in the accuracy assessment stage as a ground reference. This is why, for this study, a 4.77 m resolution image, able to cover the entire study area, was created. The imagery was generated by calculating the median of all reflectance values by each pixel, from all imagery products made available for November 2021 by the Planet Labs platform (Figure 4a), in the Planet Labs Catalog for Google Earth Engine (Planet and NICFI Basemap for Tropical Forest Monitoring Collection). This image was used as a ground reference in the assessment of the classification performances, comparing the classes of the sample training areas on the map with the samples representing the same classes in the reference data set, which were confirmed through field validation, to generate the error matrix [43].
2.5. Complementary Data
A long time series analysis might not capture some important land cover changes. Land cover change at different detection periods (long and short) can provide different conclusions regarding the processes that induce transformations [46]. In a long detection interval, the general trends may be observable, but the intermediate change processes will not necessarily be detected, especially for a land cover in continuous transformation, such as the VGX area.
That is why the dataset from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre Global Surface Water (JRC GSW) initiative was also used for the LULCC analysis. The JRC GSW dataset is an initiative from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre in the framework of the Copernicus Programme which maps the location and temporal distribution of water surfaces at the global scale. These freely available data allow the mapping occurrence, intensity, seasonality, recurrence and transition of water bodies all around the world over the last four decades, providing statistics on the extent and change of water surfaces. The dataset is produced from Landsat imagery, where each pixel is individually classified into water/non-water using an expert system, and the results are combined into monthly history maps for change detection [47]. Data are available from both the GSW website [48] and from the Google Earth Engine (GEE) catalog.
For this work, the JRC GSW dataset was handled on GEE using the “JRC Yearly Water Classification History”, a dataset containing maps of the location and temporal distribution of surface water from 1984 until the present. The interval used was from 2000 to 2017. The collection offers a year-by-year classification of the seasonality of water based on the occurrence values detected throughout the year. The dataset’s original classes are “no data”, “not water”, “seasonal water” and “permanent water”. The yearly images were downloaded from GEE and the ground surface water maps were treated in QGIS 3.16.14 (Hannover) using the post-classification comparison method through SCP plugin tool “Land Cover Change” [49]. Thus, it was possible to quantify how much of the permanent/seasonal/no water turned into emerged or submerged habitats or remained unchanged.
Table 1 presents a summary of all the dataset sources and where they can be reached.

Table 1.
Summary of dataset sources used in the present study.
2.6. Image Classification
Image classification methods are divided into many different categories: supervised and unsupervised, parametric and non-parametric, hard and soft (fuzzy), per-pixel, subpixel and per-field and object-based, each of which has many algorithms to suit them (the reader is referred to [51,52] for in-depth reviews on the subject). For this work, we focused on the supervised (where the algorithm is trained to learn characteristics of the image), parametric, and non-parametric pixel-based (where each pixel stores the spectral information as digital numbers) classifications. While parametric classification assumes that a normally distributed dataset exists and the statistical parameters from the training samples are representative, for non-parametric models, the assumption of a normal distribution of the dataset is not demanded and the statistical parameters do not necessarily split the images into classes [17].
Six different classification algorithms were tested in the VGX area. Three of these are parametric: Mahalanobis distance (MH), maximum likelihood (ML) and minimum distance (MD). The other three are non-parametric: neural net (NN), random forest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM). MH, ML, MD, SVM [53,54] and NN [55] (pp. 419–421) algorithms were performed on ENVI 5.5.3. RF classification algorithm was performed on the European Spatial Agency’s (ESA) SentiNel Application Platform (SNAP) 8.0 toolbox [56]. All of these were performed using the standard configurations of the software. These classification algorithms were chosen because they are very popular in image processing software and are extensively used in the already available literature, allowing for a good basis of comparison [15,17,20].
The MD classifier characterizes each class by its mean reflectance in each band from the training site with unknown pixels assigned to the class with the nearest mean value. In other words, the candidate pixels are assigned to the class that is spectrally closer to the sample mean. In the ML classification, the probability assumes a normal spectral distribution for each class and an equal probability that the pixel belongs to a particular class, taking the variability of classes into account. The MH classification is a direction-induced distance classifier where a probability statistics calculation is used for each class, but assuming that all covariance is equal [51,52].
NN is a pixel segmentation technique trained to recognize patterns. It has a non-parametric advantage of taking arbitrary decisions, since it does not make assumptions on a feature’s distribution. No prior knowledge about any statistical parameters of a class is required, ensuring an easy adaptation to different types of data [15,17]. The RF algorithm is a technique that randomly and iteratively samples the data to generate a large group of classification trees (the so-called forest) at the training stage. This represents the statistical mode of many decision trees, where the outputs are the classes selected by most trees. This usually gets a more robust classification than a single model run [57].
Lastly, the SVM algorithm, which is a method derived from statistical learning theory, separates the classes based on a decision surface that maximizes the margin between those classes. The closest points to these surfaces are the support vectors, which are the critical elements of the training set. This algorithm has become a popular classification method due to its excellent empirical performance [58].
The sampling strategy was designed to select a large number of sample polygons for each land cover or land use class in different areas of the image, aiming to capture the greatest possible spectral variability of the classes. Samples were located where there was certainty that the land cover/use did not change between 2000, 2017 and 2021. This strategy was chosen since there were no available reference images obtained in the field from years 2000 and 2017. Training samples were overlaid on the 2000, 2017 and 2021 images separately to adjust the land cover classes based on visual interpretation. The same strategy was adopted to select test samples in the reference image for the accuracy assessment step, making sure that they were different from the training polygons. Table 2 describes the number of pixels within the training and test sample polygons used for each class for the years 2000, 2017 and 2021 respectively.

Table 2.
Number of pixels within the ROIs for training and testing polygons used for each class, for all classifications, for 2000, 2017 and 2021.
It is notable that forest, agro-pasture and river classes have more training pixels than rocks. This approach was used because, in addition to being less frequent in the landscape, the rocky environment in the Landsat images could easily be visually confused with other environments (such as water or vegetation associated with the rocks), even when using NIR bands or the reference image to select them. Rock training classes were chosen considering only emerging areas in both 2000 and 2017 images, in the reference image from 2021 and on orthophotos acquired in the field. Therefore, considering the other classes, many less samples labeled as rocks were available to be selected as training samples.
2.7. Accuracy Assessment
Quantitative accuracy assessment of maps relies on the comparison of the area represented on the map against reference information for the same site. A common method for classification accuracy assessment is through the use of confusion (or error) matrices. The reader is referred to [43] (pp. 74–76) and [59] for mathematical representation and examples of confusion matrices. In this work, they were calculated using ENVI 5.5.3 post classification tool “Confusion Matrix Using Ground Truth ROIs”. This pairs ground truth reference ROIs with the classes of the classified image, to show what percentage of the ROI pixels were or were not contained in the resulting classes. It also provides a specific evaluation of the agreement between the classified result and the reference data, giving details even on misclassification [15]. The report generated when a confusion matrix is calculated contains the following diagonal elements:
- Overall Accuracy (OA): calculated by summing the number of reliable classified pixels divided by the total number of training pixels.
- Errors of Commission (Comm): are the fraction of sample pixels that were predicted to be in a class but do not belong to that class (false positives).
- Errors of Omission (Om): are the fraction of pixels that belong to a class but were predicted to be in a different class (false negatives).
- Producer Accuracy (PA): a measure of the probability that a pixel in a given class was classified properly.
- User Accuracy (UA): a measure of the probability that a pixel predicted to be in a certain class really belongs to that class.
- Kappa Coefficient (Kappa): takes non-diagonal elements into account and measures how equivalent classification and reference values are. A kappa value of 1 represents a perfect match, while a value of 0 represents no equivalence. Despite the criticism by some authors, the kappa coefficient is considered a powerful tool when analyzing a single error matrix and for comparing the differences between various error matrices [43,60].
Although the literature recommends accuracies of 85% as acceptable, for contemporary mapping this suggestion may be inappropriate and unrealistic [61,62]. In fact, there are no agreements in the scientific community about limits on how accurate a classification must be to be considered reliable [63]. The approach usually used in the literature follows the selection of the most accurate classifier, either among the simultaneously evaluated classifiers or the comparison with classifiers from other studies. With this in mind, for this study, a range of values were defined to categorize the performance of the classification algorithms (Table 3):

Table 3.
Accuracy assessment performance categories considered for this study. OA: Overall Accuracy; Comm: Commission; Om: Omission.
2.8. Detecting Land Cover Change
A great number of change detection techniques have been developed, but many are able to detect only binary transformations on the landscape (change/non-change categories). A “from–to” change track strategy, otherwise, provides a superior comprehensive understanding of LULCC patterns and rates [20].
The post-classification comparison is a very popular change detection analysis, and was the method chosen for this work. It was performed using QGIS 3.16.14 (Hannover) through the Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin (SCP) post processing tools “Cross Classification” and “Land Cover Change” [45]. Studies have shown that this method offers good accuracy in representing changes in land use [64,65].
The classification results from years 2000 and 2017 were cross-tabulated on a pixel-to-pixel comparison, where each pixel represents a class transforming into a different class between the dates (i.e., the direction of transformation). Then, maps regarding these changes (or tracks) were generated for forest/non-forest and for river/non-river transformation categories.
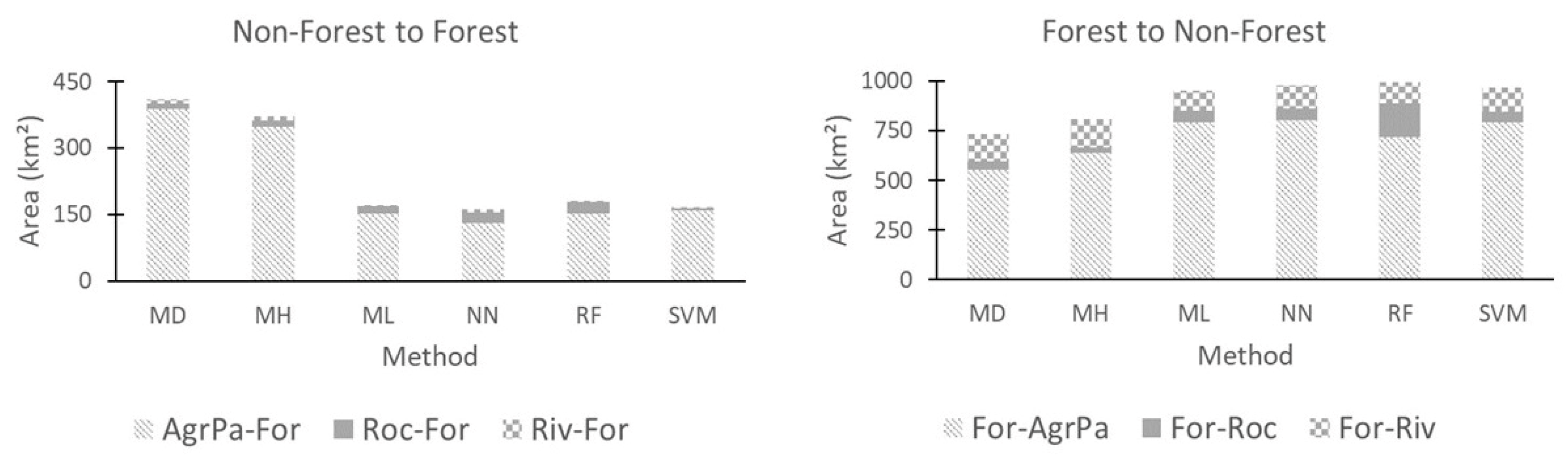
The directions of changes were also tabulated and represented as graphics, in which transformations were estimated through ten change tracks: agro-pasture to forest (AgrPa-For), rock to forest (Roc-For), river to forest (Riv-For), forest to agro-pasture (For-AgrPa), forest to rock (For-Roc), forest to river (For-Riv), river to agro-pasture (Riv-AgrPa), river to rock (Riv-Roc), agro-pasture to river (AgrPa-Riv), and rock to river (Roc-Riv).
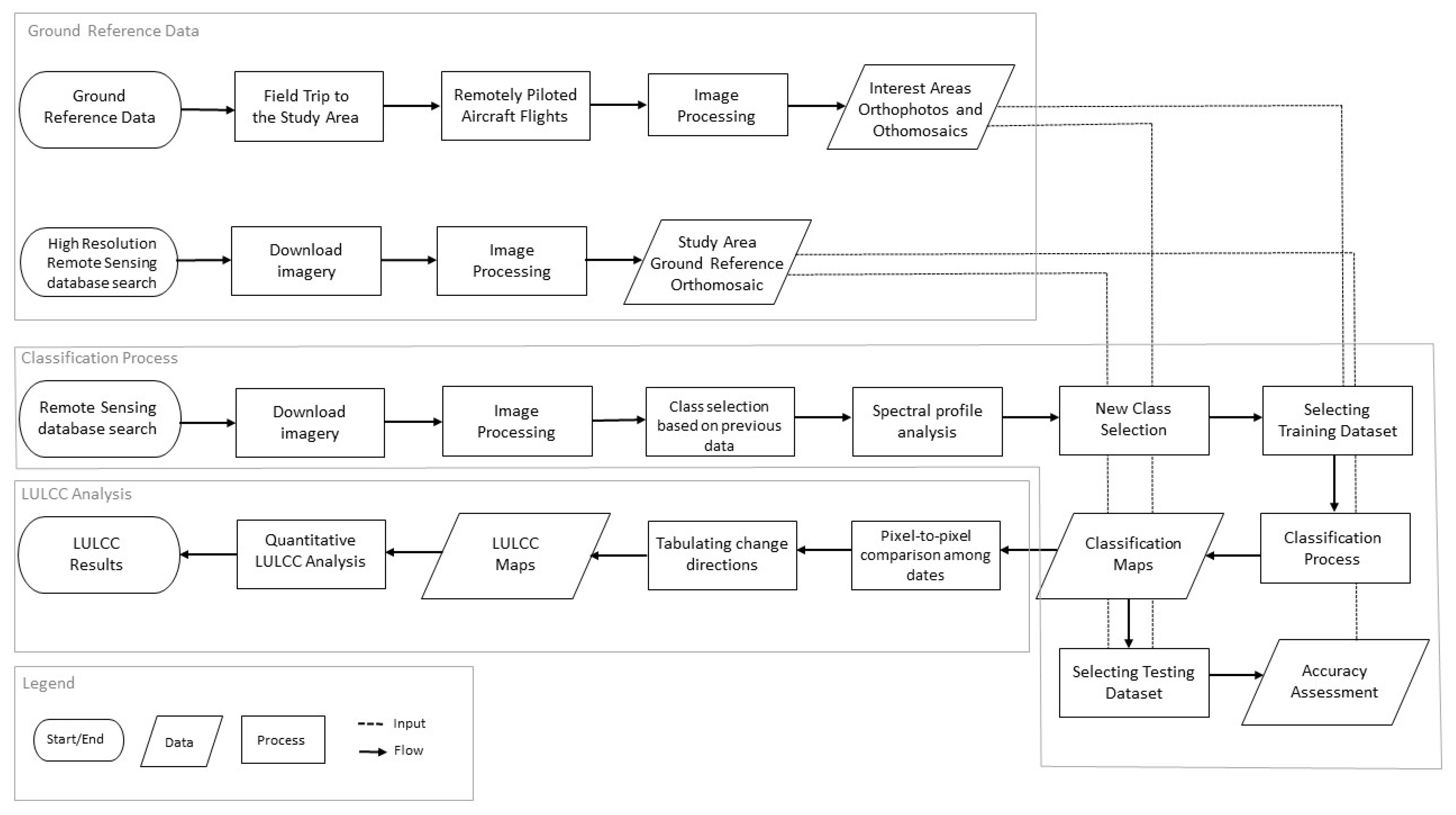
Since the classification process and LULCC analysis are complex and involve many different steps, Figure 5 summarizes all the methodology described above in a comprehensive workflow.
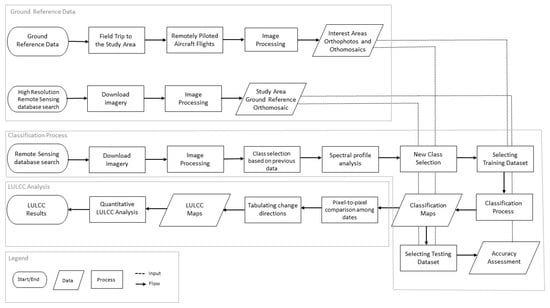
Figure 5.
Classification process and LULCC analysis workflow.
3. Results
3.1. Classification Accuracy Assessment
Map accuracy assessment assumes that the information contained within the error matrix is a true characterization of the classified map being assessed. Analysis of the causes of its differences might be one of the most important steps in the construction of a thematic map [43]. Table 4 shows a summary of all accuracy metrics calculated for river, forest, agro-pasture, and rock classes. Columns represent true classes, while rows represent the classifier’s predictions.

Table 4.
Confusion matrices containing overall accuracy, kappa coefficient, commission and omission errors and producer and user accuracies calculated for all classification methods, for 2000 and 2017. OA: Overall Accuracy; Comm: Errors of Commission; Om: Errors of Omission; PA: Producer Accuracy; UA: User Accuracy; Kappa: Kappa Coefficient; MH: Mahalanobis distance, ML: maximum likelihood; MD: minimum distance; NN: neural net; RF: random forest; SVM: support vector machine.
According to Table 3, regarding Overall Accuracy and Kappa Coefficient, all the classifiers were considered satisfactory, which means that all the classifications are in good agreement with the reference data. All values were above 0.9, except Kappa for MD in 2017 (0.88) (Table 4). However, these two measures alone are not enough to point to misclassifications of individual map classes. Although some authors consider the Kappa Coefficient a more meaningful statistic when compared to Overall Accuracy, the similarity between them in this study makes Kappa less efficient as an assessment parameter [43].
All the algorithms had good performances for the forest class, for both years, with Comm and Om errors and PA and UA considered satisfactory in all cases, which was expected due to its homogeneity, major area coverage in the image and distinct spectral signature from the other land classes. Major omission errors happened in the rock class for both MH (32.70%) and MD (41.21%) in 2000, and for MD in 2017 (41.14%) (Table 4). This means that an elevated percentage of the area predicted to be classified as rocks was excluded (omitted) from the rock category. Commission errors were unsatisfactory only for RF in 2000 (32.11%) and 2017 (25.23%—a border value) (Table 4), which means that for both, the algorithm included pixels predicted to be classified as rocks in other categories. There were also regular performances for Comm and Om errors for agro-pasture (MH in 2000 and 2017 and MD in 2017), river (MH, MD and RF in 2000) and rocks (MD in 2000 and for all the algorithms in 2017) (Table 4).
For both years, and for parametric and non-parametric classification algorithms, user and producer accuracies were predominantly above 80% for forest, river and agro-pasture. Nevertheless, the rock class had lower rates mainly when compared with other classes, for almost all algorithms and both years. The only exception is for ML and SVM in 2000. The matrices reveal especially high Comm and Om errors for MH, MD and RF algorithms in both years. PA is much lower than 80% for Maha and MD in the year 2000. RF and MD also have higher errors in the year 2017. For the other classifiers, Comm and Om errors and PA and UA, although still adequate, had their performances below other classes, such as forest and agro-pasture.
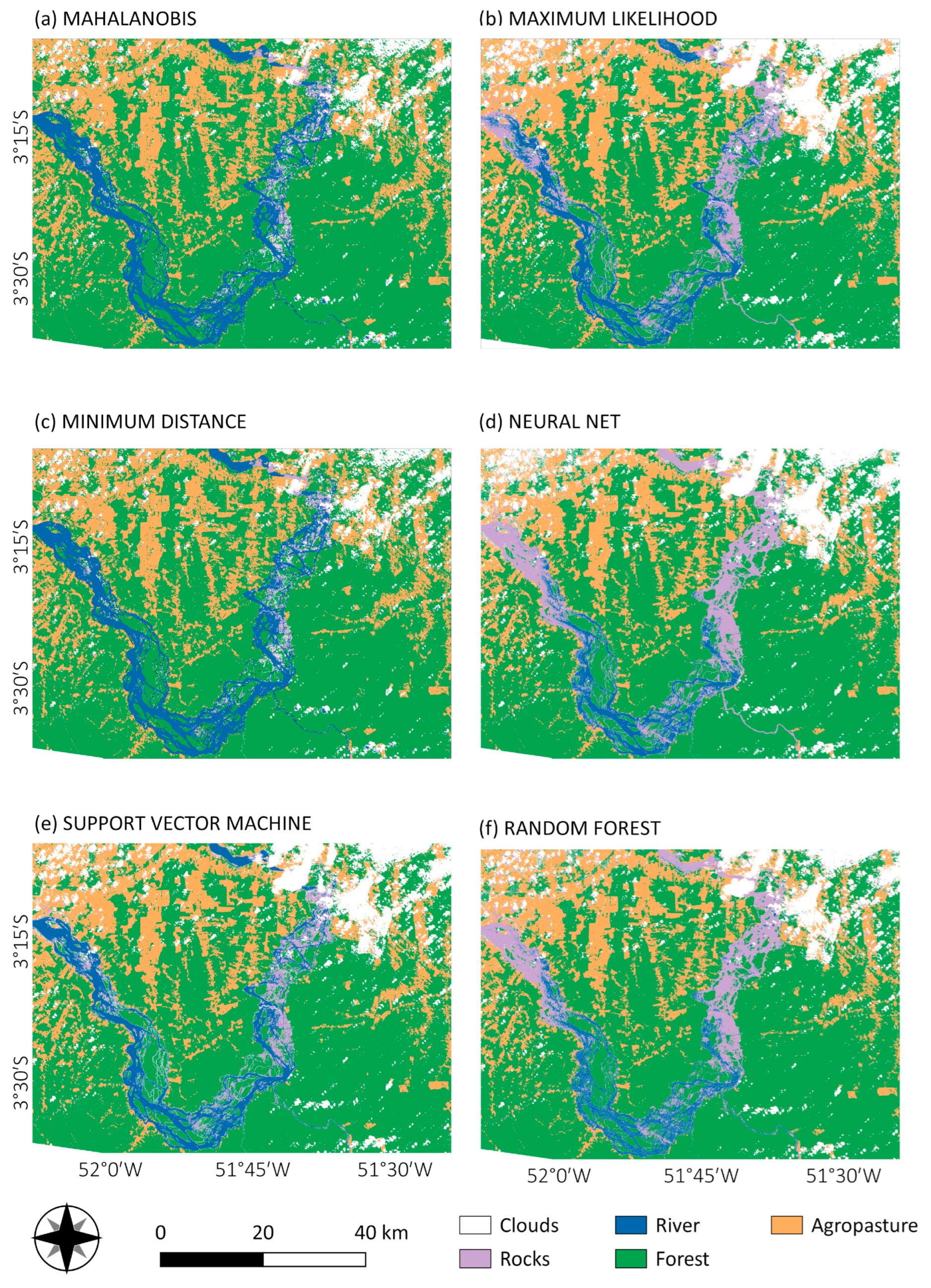
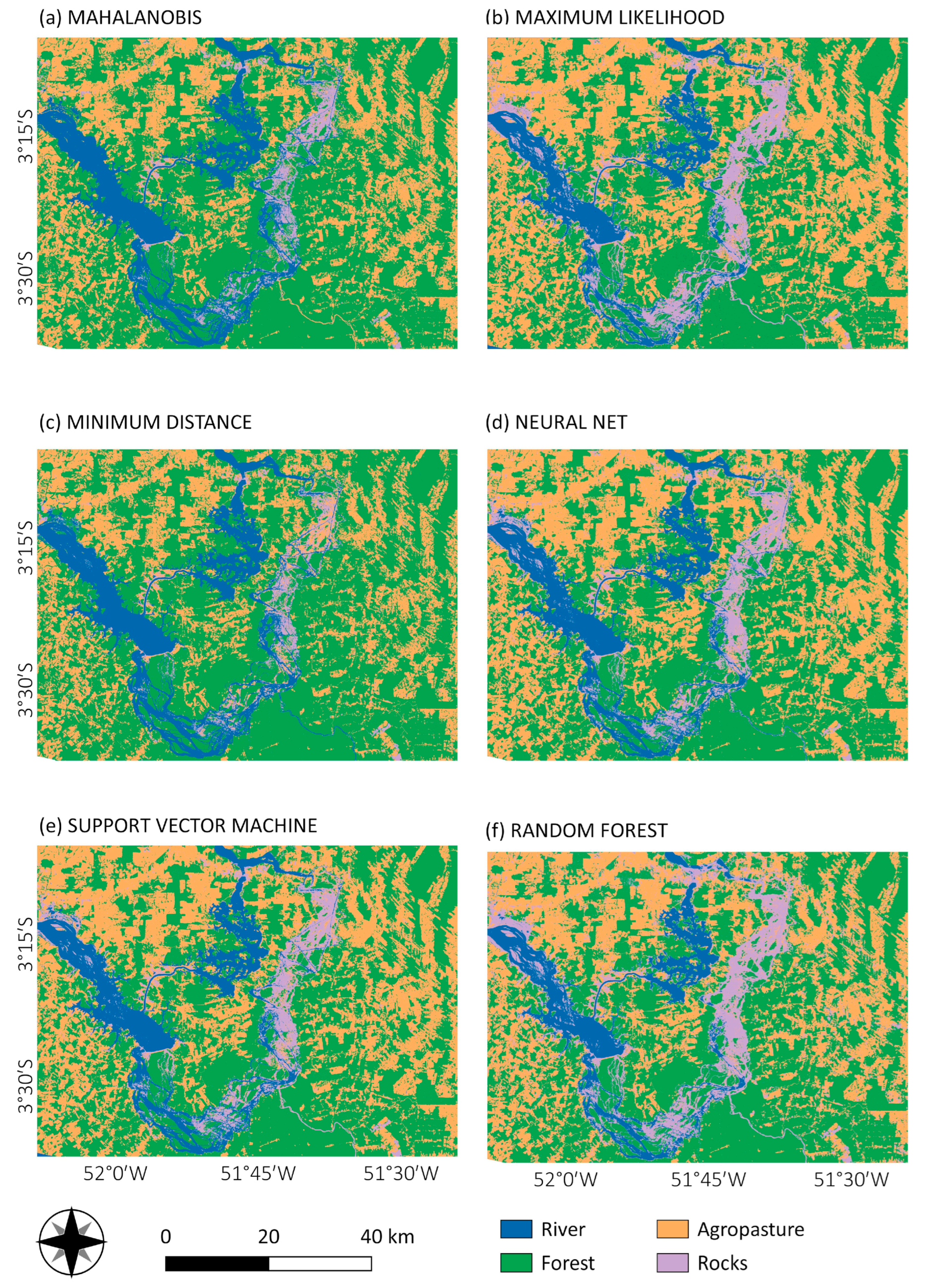
The performance of the parametric algorithms in the rock class is more accurate than the non-parametric algorithms, mainly for MD and MH classifiers, in both years. The visualization of the classification maps of all the methods are presented in Figure 6 and Figure 7 for 2000 and 2017 respectively.
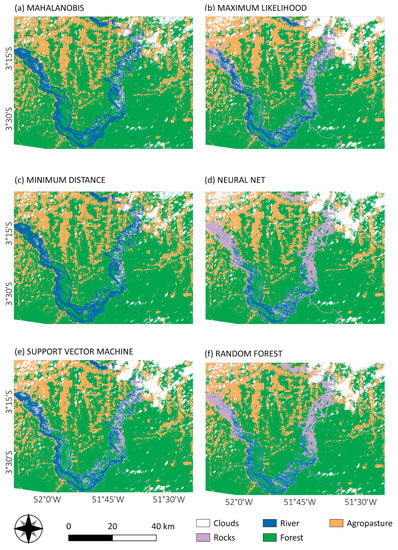
Figure 6.
Pixel-based classification from Mahalanobis distance (a), maximum likelihood (b), minimum distance (c), neural net (d), SVM (e) and random forest (f) for the year 2000.
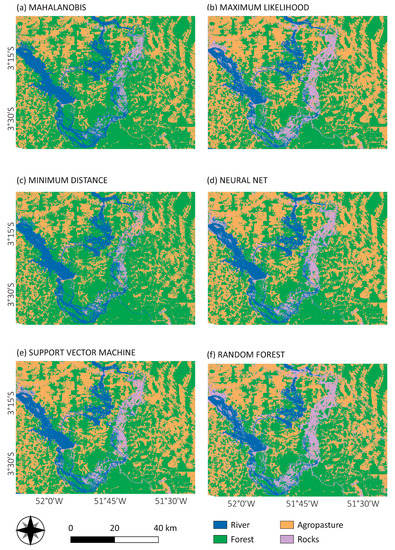
Figure 7.
Pixel-based classification from Mahalanobis distance (a), maximum likelihood (b), minimum distance (c), neural net (d), SVM (e) and random forest (f) for the year 2017.
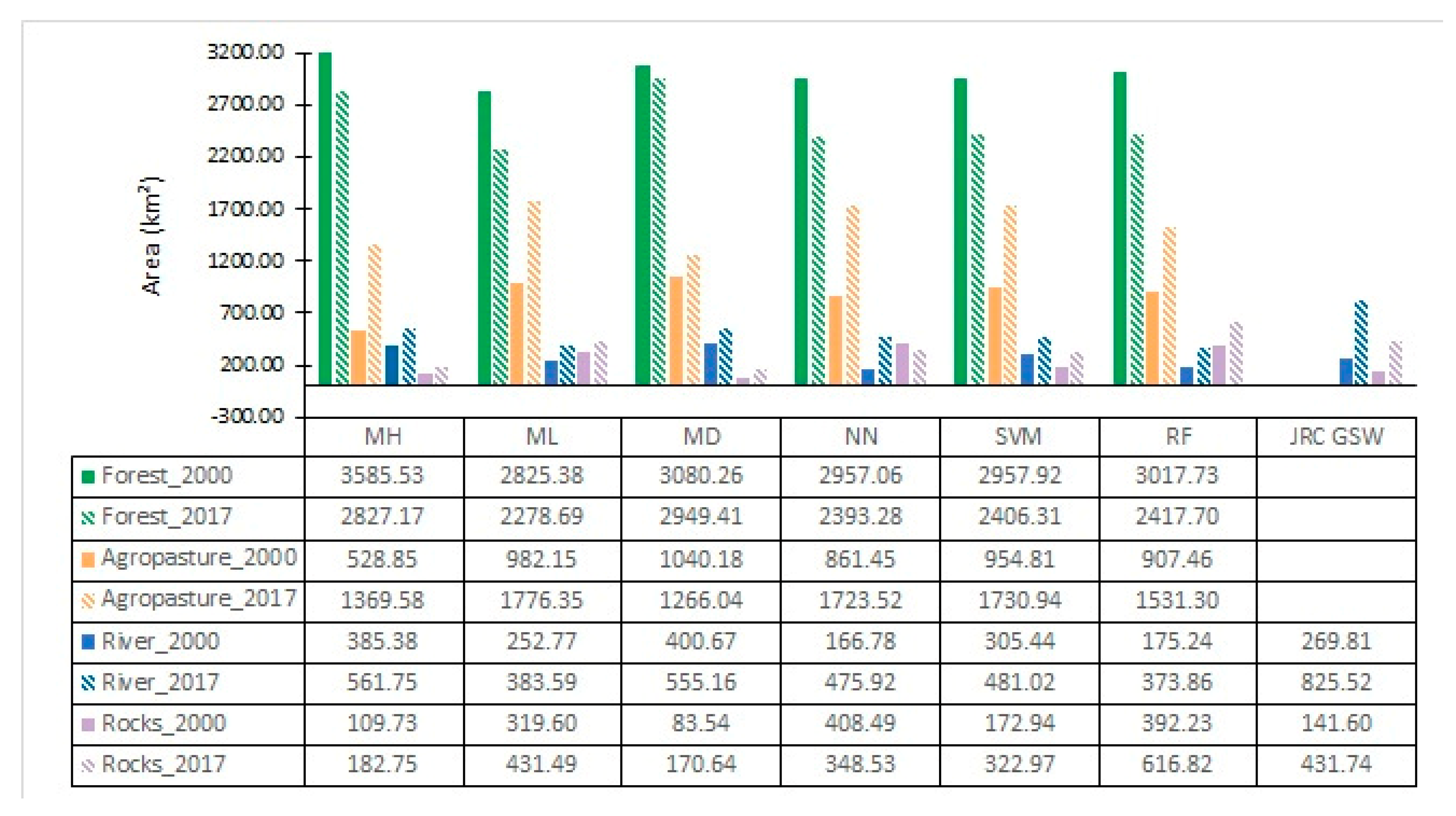
Class area estimation for each classification algorithm for both years are shown in Figure 8, revealing the variation of the classified area between classification outputs. Forest and agro-pasture were the most homogeneous classes (less variation between all classifications), with emphasis on the year 2000, where there was only an 8% difference in area between the algorithms which classified the smaller (ML) and greater (MH) forest area. In opposition, rock and river classes had more than a 50% difference in the classified areas, for both years, between the algorithms. Rock class, as expected, was the most heterogeneous class, with a more than 70% difference between the areas classified using MD—which detected the smaller rock area—and NN (79% for the year 2000) and RF (72% for 2017), which classified the larger rock areas.
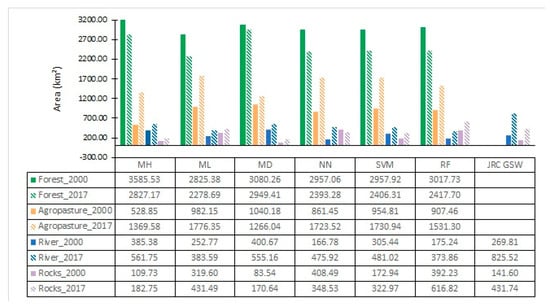
Figure 8.
Variation of classified areas, for each different class and for each classification algorithm, for 2000 and 2017.
3.2. Land Cover Change
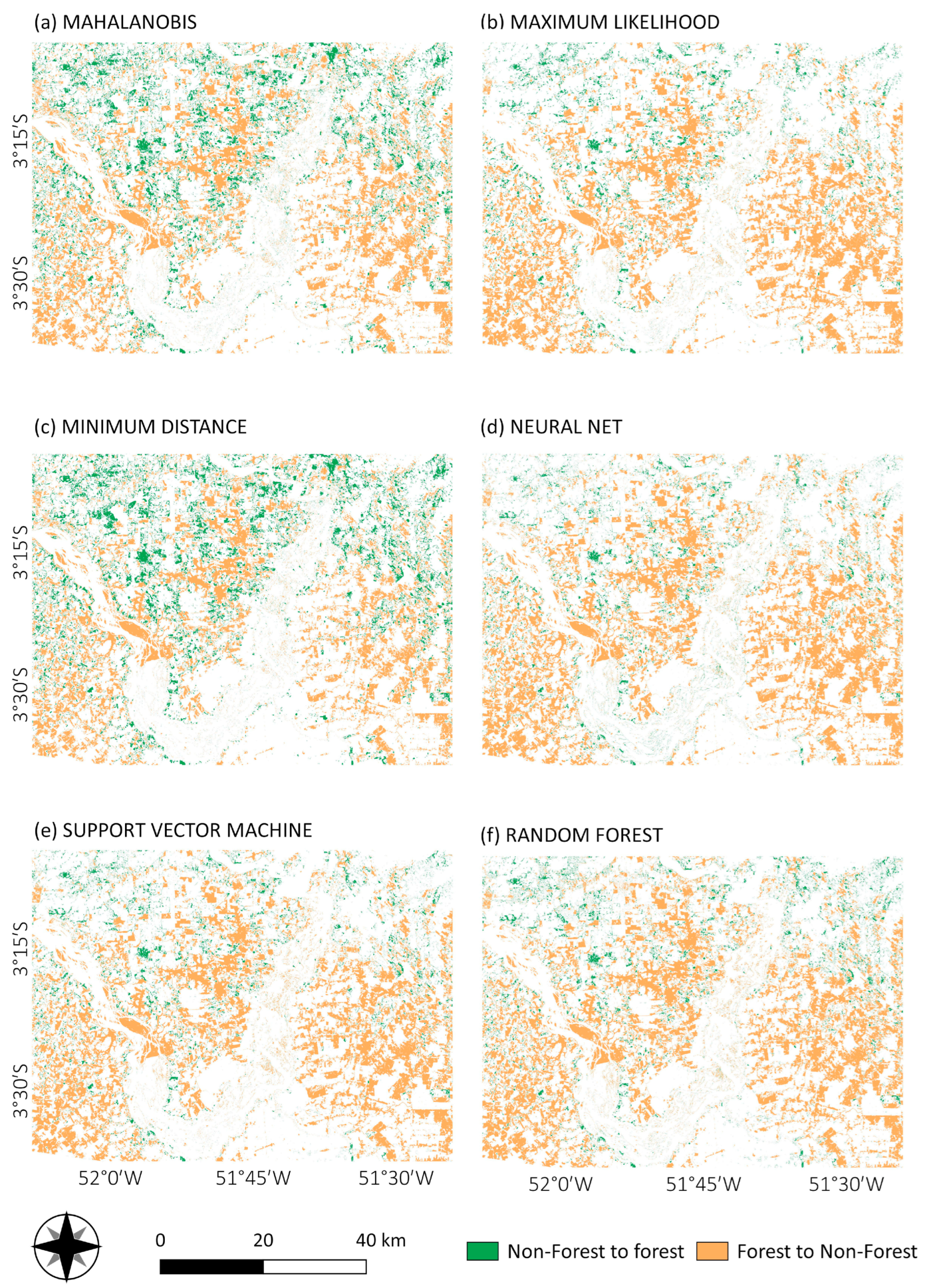
Due to the land flooding necessary for the reservoir construction and the expansion and installation of secondary economic activities triggered by the power plant construction, the most significant transformation was from forest to non-forest classes. For instance, the conversion from forest to agro-pasture in all classification methods (Figure 9). A few agro-pasture areas have been converted to forest, mainly in the north of the study area, similar to what is observed in Figure 10 (non-forest to forest class). Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the land cover transformation for forest and non-forest classes in the VGX area.
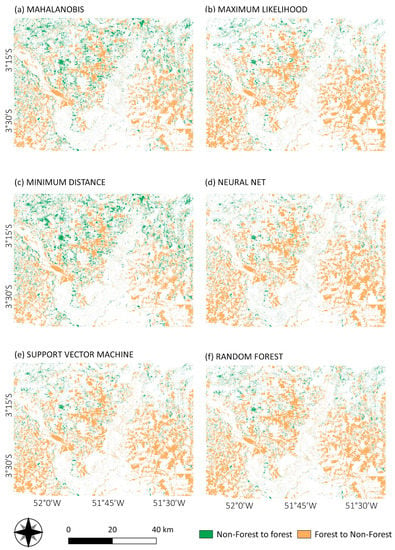
Figure 9.
Land cover change for forest and non-forest transitions from 2000 to 2017, derived from Mahalanobis distance (a), maximum likelihood (b), minimum distance (c), neural net (d), SVM (e) and random forest (f) classifications.
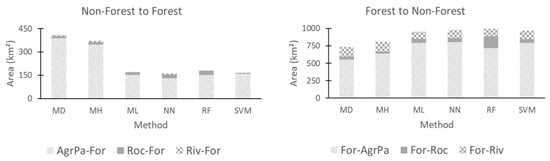
Figure 10.
Land use and land cover change from 2000 to 2017 for forest to non-forest areas using minimum distance (MD), Mahalanobis distance (MH), maximum likelihood (ML), neural net (NN), random forest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM) classifiers. Trajectories: forest to agro-pasture (For-AgrPa), forest to rocks (For-Roc), forest to river (For-Riv), agro-pasture to forest (AgrPa-For), rock to forest (Roc-For) and river to forest (Riv-For).
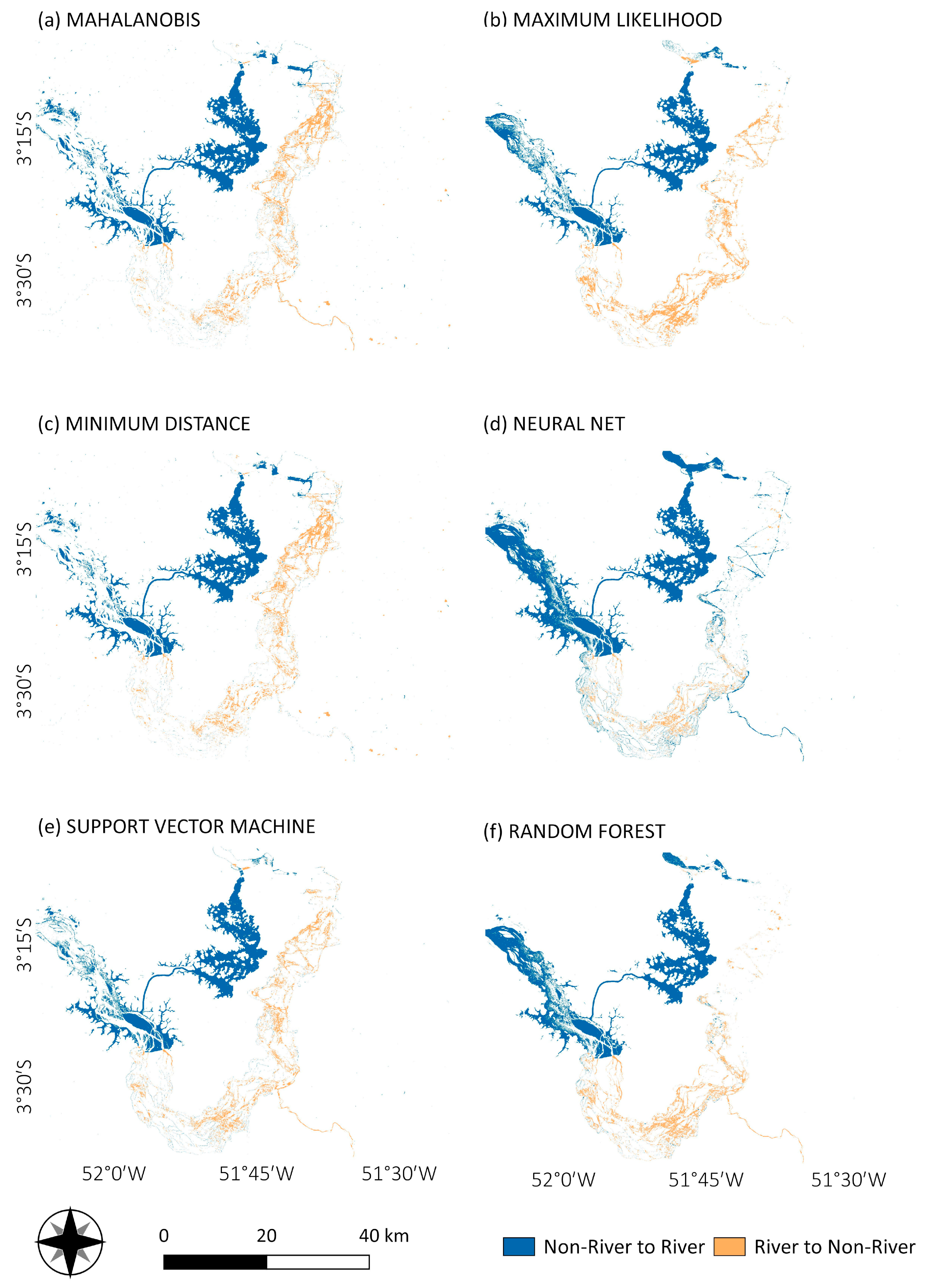
Figure 11 and Figure 12 show the land cover transformation for river and non-river classes. Downstream of the Xingu River, the main alteration is the conversion from river to non-river areas, while upstream and in a channel area northward, there is an increase in the river area (non-river to river classes). Both changes are associated with the construction of the reservoir. In the first case, the reduction of the water flow caused by the river damming exposed environments that were previously submerged, mainly rocks, but also soil that ultimately turned into agro-pasture areas and even recovered forest (Figure 12). Upstream, due to the flooding of land areas, mainly forest areas, but also crops, were transformed into water (the Belo Monte reservoir) (Figure 11).
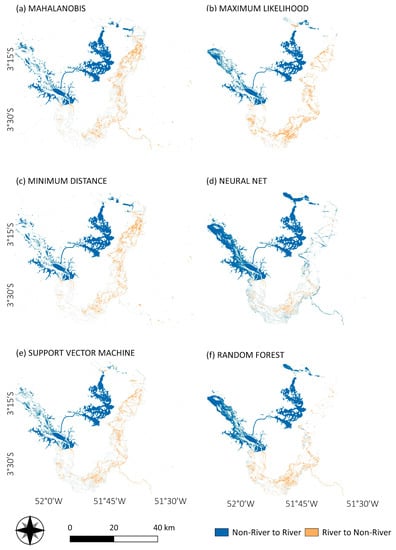
Figure 11.
Land cover change for river and non-river transitions from 2000 to 2017, derived from Mahalanobis distance (a), maximum likelihood (b), minimum distance (c), neural net (d), SVM (e) and random forest (f) classifications.
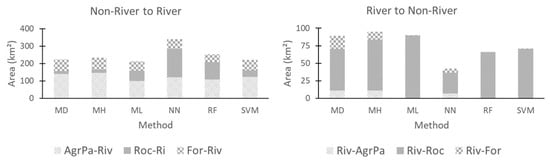
Figure 12.
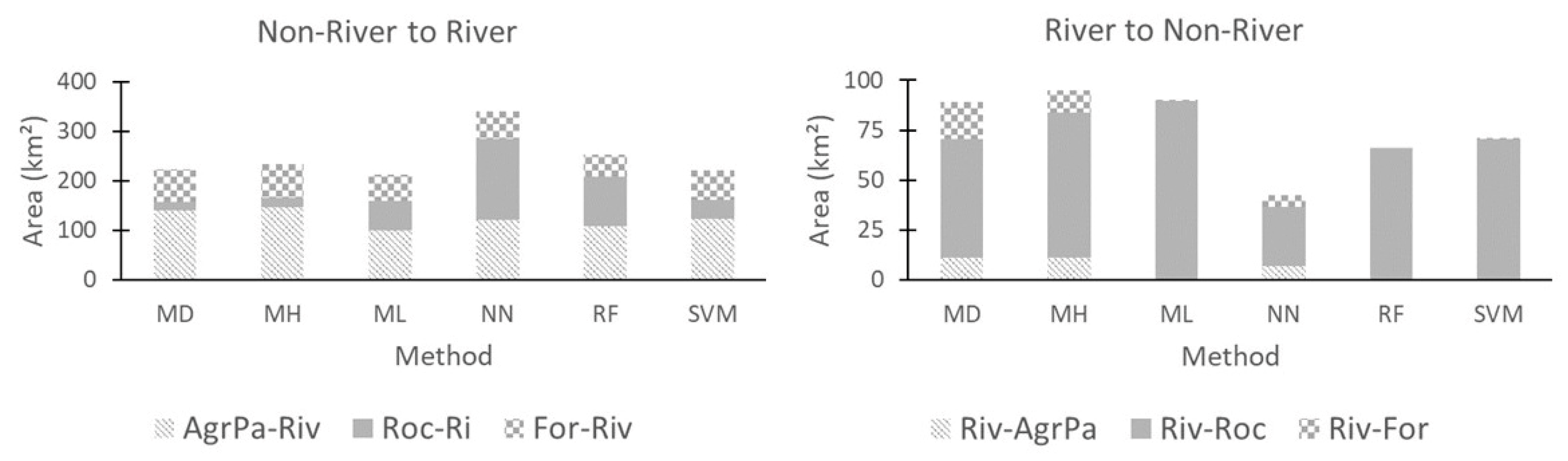
Land use and land cover change from 2000 to 2017 for river to non-river areas using minimum distance (MD) Mahalanobis distance (MH), maximum likelihood (ML), neural net (NN), random forest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM) classifiers. Trajectories: river to agro-pasture (Riv-AgrPa), river to rocks (Riv-Roc), river to forest (Riv-For), agro-pasture to river (AgrPa-Riv), rock to river (Roc-Riv) and forest to river (For-Riv).
Table 5 gives a summary of the areas of LULCC for each classifier in both years shown in Figure 9 and Figure 11.

Table 5.
LULCC areas from forest to non-forest and river to non-river areas, for each year, using minimum distance (MD) Mahalanobis distance (MH), maximum likelihood (ML), neural net (NN), random forest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM) classifiers.
3.3. JRC Ground Surface Water Dataset
Figure 13 shows yearly changes in the water availability during the analyzed period. Quantifying this information is important since the different performances of the algorithms, mainly regarding river and rock classes, could have biased the analysis in relation to the impacts caused in these environments when the river was dammed. This could have led to a misinterpretation in which the classifier would be responsible for the difference between the areas, and not the impact caused by the dam. Figure 14 shows the alteration in key years (the year when the dam construction was concluded, one year before and one year after the river damming).
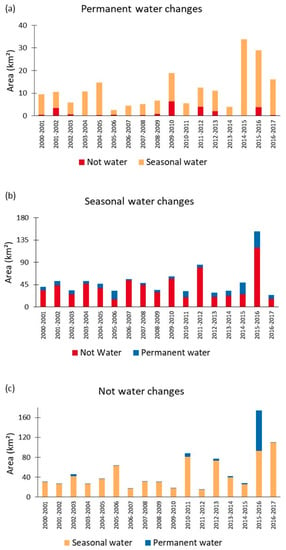
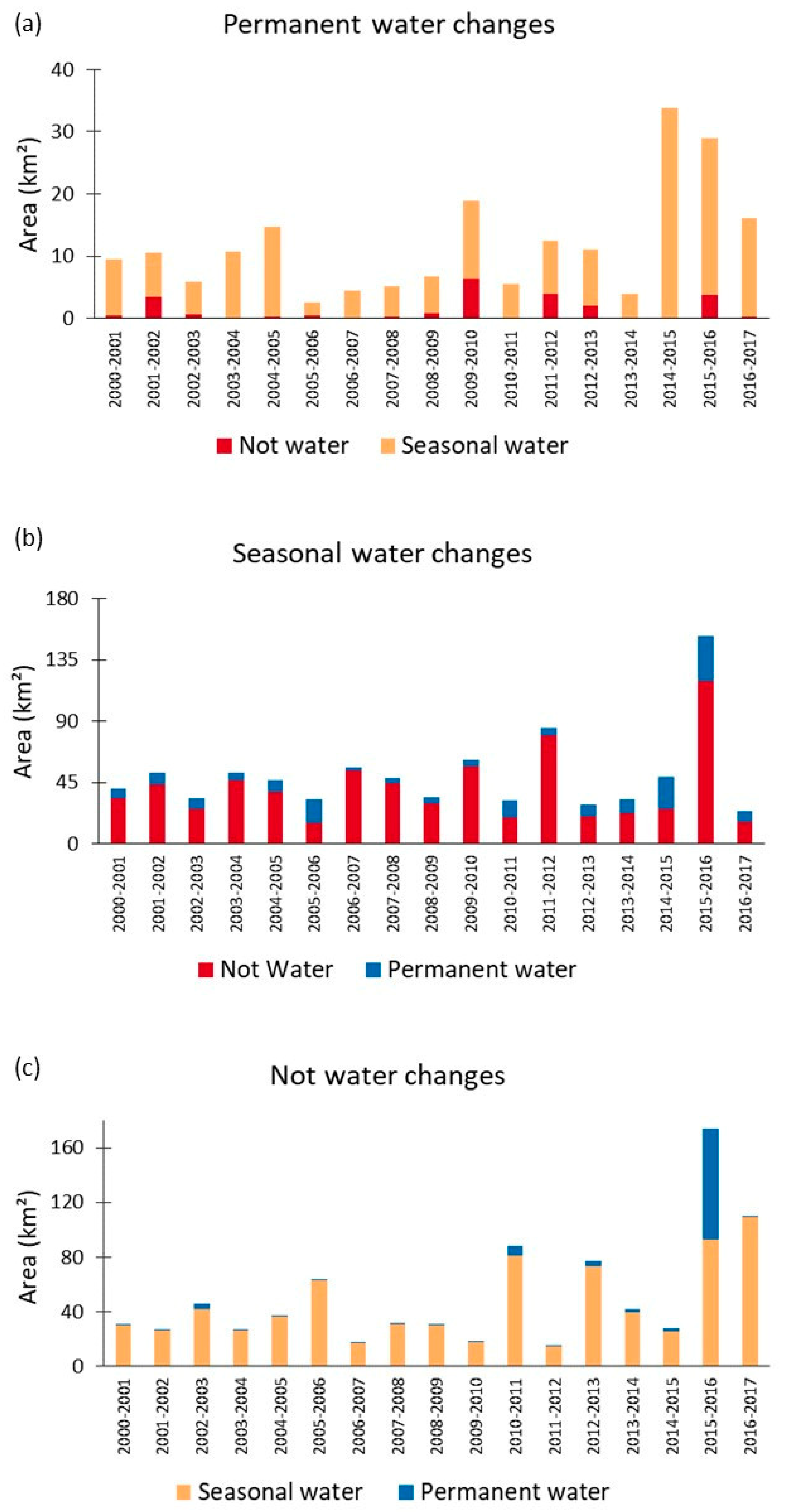
Figure 13.
Products from JRC ground surface water data. The graphics represent (a) permanent water turned into not water (red) and seasonal water (orange), (b) seasonal water turned into not water (red) and permanent water (blue), and (c) not water turned into seasonal water (orange) and permanent water (blue).
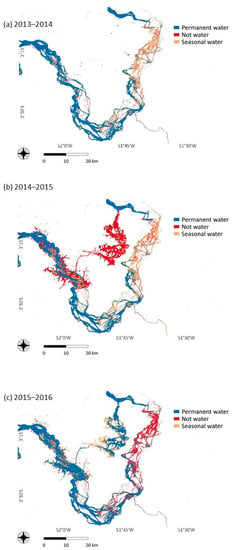
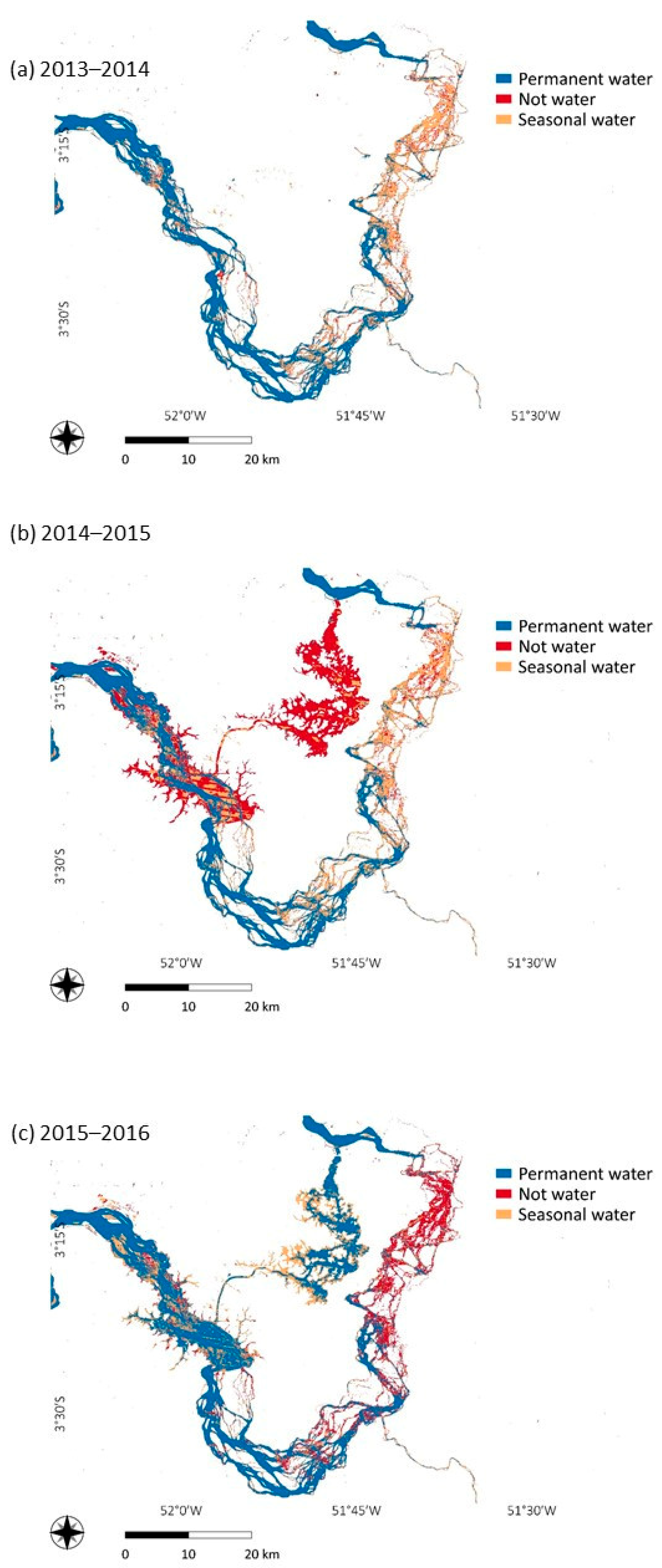
Figure 14.
Ground surface water transformations in three key periods: (a) before the river damming (2013–2014), (b) the year of the dam’s conclusion (2014–2015), and (c) one year after the conclusion (2015 to 2016).
For the years prior to the damming of the river, the pattern of alterations is induced by natural phenomena, such as the ones caused by the El Niño South Oscillation (ENSO), that can influence the natural hydrological cycles through the rainfall regime [8]. From Figure 13, it is very clear to see that the natural pattern of flooding was substantially altered from 2015 onwards.
4. Discussion
Due to the importance of a comprehensive comparison of different algorithms for LULC classification, aiming to improve knowledge on issues such as accuracy assessment and the selection of suitable algorithms for a historical remote sensing analysis for the VGX, the discussion section intends to sum with other previous initiatives that sought to measure and evaluate manmade transformations in study areas using remote sensing [3,12,15,28,30,31,42,46,66,67].
4.1. Accuracy Assessment of Classification Methods
Regarding general statistics (Table 4), Overall Accuracy and Kappa Coefficients were very similar among all classifications, both higher than 80%, which was expected for results which are highly correlated. The parameters also corroborate with other results already described in the literature for the area [3,12,28,46]. A previous study [28] achieved overall accuracies (90–92%) and kappa coefficients (0.85–0.90) using ancillary data and more than one orbital sensor product. Another study [46] obtained an overall accuracy of 84.3% and a kappa coefficient of 0.79 in their classification for the VGX area using six Landsat images between 1991 and 2017. Ref. [12] applied the ML classification on multi-temporal Landsat imagery of the VGX, achieving overall classification accuracies of 89.7% (2011) and 92.3% (2017).
Commission (Comm) and Omission (Om) errors and Producer’s (PA) and User’s Accuracies (UA) were determinative to better understand what the map represents and what is actually on the ground, so that potential confusion between classes can be understood. It is expected that commission and omission errors have the lowest possible values (since they represent percentage errors of inclusion and exclusion of classified pixels in the correct class or different classes), and PA and UA to be as close as possible to 100% (since they are used to determine the probability of a predicted pixel to be in the correct or different class) [68].
Three major possibilities might be associated with the misclassifications revealed by the Om and Comm errors: (1) the overlapping of spectral signatures, since the algorithm understands a class as a different one; (2) the resolution of the image, since a unique pixel might contain more than one class; and (3) the heterogeneity of the class.
The Om errors associated with agro-pasture can be related primarily with its spectral signature, mainly for the year 2017 where agro-pasture and forest reflectances are overlapped in all bands of the image (Figure 3). Additionally, agro-pasture areas are more heterogeneous than forest, and, depending on the time of the year, pasture can have similar radiation measures as dense vegetation, which might cause confusion during the classification process. Furthermore, this category is spatially well defined and detached in the landscape, being easily visually identified. For 2017, MH and MD had similar performances, with regular omission errors, while the other classifications were satisfactory. Where there are omission errors for agro-pasture, there are also more than 5% of commission errors for forest, an indication that forest pixels might be wrongly classified as agro-pasture.
River spectral signature (NIR band) and error bars (RGB bands) are overlapped with rock spectral signature for 2000 (Figure 3), where there are also Comm errors for MH and MD (Table 4), indicating that river pixels were probably classified as rocks, since for the same algorithms, Om errors for the rock class are unsatisfactory. Different river depths and spatial mixing with the rocky environment are detected in the variation of classified areas between the algorithms, higher than 50% (Figure 8). Pixel resolution issues and the heterogeneity of the different rock surfaces were detected in 2017 in all classifiers. Only ML and SVM for the year 2000 do not have significant Comm and Om errors for this class. For 2017, these same algorithms have regular Comm errors, probably because rock pixels are being classified as river due to the image resolution (both land uses are being imaged in a single pixel) and heterogeneity. Indeed, the confusion between the classifiers is evident in Figure 8, since there is a demonstrated variation of 70% for classified rock areas between the algorithms for both years: some classifiers underestimated the classification for the exposed rock area, and others, overestimated (as can be seen in Figure 6 and Figure 7).
Poor performances of MH (2000) and MD (2000 and 2017) for rocks are corroborated through PA statistics, which represents the probability of a pixel being correctly classified—for low PA numbers, high omission errors are expected–which is indeed verified for the case (Table 4). On the same hand, low UA implicates higher Comm errors—which is the situation for RF in both years for the rock class.
All the six classification algorithms, from the simplest to the most complex, had similar overall performances in detecting critical trends of LULCC in the study area. Notably, MH, MD and RF were the algorithms with major issues to properly classify the rock land cover, which ended up affecting the river area quantification, since there was confusion between the two classes.
Regarding the parametric classifiers, for both years, ML was more capable of highlighting errors in individual classes. As to the non-parametric classifiers, SVM was slightly superior when compared to NN, for both years, which demonstrate that these two algorithms are the most suitable options within the scope of this study.
The difference between the performances of parametric classifiers can be explained because, while MH and MD work by classifying a pixel based on the reflectance values of the closer pixels, ML assigns each pixel to a class using as criterion the probability that a pixel belongs to its class based on reflectance values, demonstrating it to be more accurate in a heterogeneous environment. Indeed, ML is the most common parametric classifier and is available in any commercial image processing software [66].
Regarding non-parametric algorithms, RF uses an average of several aleatory decision trees based on training samples and NN recognizes training patterns and classifies data using a neural net. While both are based on random clustering techniques, which might have biased the classification and overestimated the rock class (as seen in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8), SVM creates a hyperplane that separates data in to different categories through vectors. RF and NN might not be good choices when there are not many training classes (as is the case of the rock class as seen in Table 2), while SVM is a good option for targets with any level of spectral separability. Moreover, NN and RF can perform slowly even when training a reduced number of samples, while SVM demands less computing power. Ref. [15] found that non-parametric algorithms had some advantage in relation to traditional classification methods and the result of [42] agreed, identifying the way in which the complex biophysical environment of tropical forests induced misinterpretations, both of which corroborate our findings.
Concerning the specific characteristics of the study area that influence the classification, an important aspect must be emphasized regarding the date of the images used and the water pulse that rules the Amazonian rivers. The Xingu River is controlled by seasonal floodings, and, while individual images might offer a general trend of LULCC, important changes related to aquatic environments and wetlands, such as river and rocks, might not be properly detected. The image from the year 2000 is from May, and the one from 2017 is from July, and, although the majority of alterations are indeed caused by the river damming from 2015 onwards, the fact that the river is in different moments of the natural flood pulse in both images might influence the final classification results. This important and seasonal short term environmental characteristic does not affect forests, pasture and crops, which were indeed the best classified classes.
This important issue was also identified for the study area by other authors. Ref. [46] reported that fluctuations in water reservoirs and rivers in different seasons might cause misclassification of water and other land cover types, such as lowlands and floodplains. The alterations over the Xingu River basin are core to the research lead by Kalacska et al. In three different studies, they realized that, from 1989 to 2018, the surface water was not the focus in most classification studies for the Xingu River basin, which makes the surface water classifications rapidly out of date in an area where large LULCC are ongoing due to large engineering projects [3,60,67]. These authors point to a problem also detected in our study, which is the difficulty in properly classifying the Xingu River and the floodable habitats in the VGX area.
Another important aspect that might influence the classification in a complex landscape such as tropical forests is the reference data. In a first attempt to classify the two Landsat images using only parametric algorithms, the training stage was based on the user’s expertise of the area and on previously collected ground information data based on a 2008 raster image elaborated for the BMHC Environmental Impact Study, resulting in a poor performance of the classification algorithms [41]. Existing data are rarely acceptable for accuracy assessment, since the data might not represent the classes being mapped. This is because the existing field inventory was collected for a goal other than accuracy assessment or because the classification schemes employed to create the existing map differ from the one being used to create the new map, which was precisely the case in this previous attempt [43].
4.2. Land Use and Land Cover Changes
Based on the BMHC Environmental Impact Statement, the construction of Belo Monte reservoir was expected to deviate 42% of the Xingu River and remove 24% of the forests of the region [29]. This study confirmed both transformations in land cover: river to non-river downstream of the Xingu River (Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14), and from forest to non-forest near the reservoir (Figure 9 and Figure 10). An increase in the river area was observed upstream of the Xingu River and in a channel northward of the VGX, as seen in the non-river to river class (Figure 11 and Figure 14), due to the creation of the reservoir. This caused a conversion from a lotic (flowing water) to a lentic (still water) environment, affecting both water quality and biodiversity [69].
One of the main impacts was the conversion from river to non-river areas (Figure 11) in the south of the VGX, observed in the results from all the classification methods (Figure 12 and Table 5) and corroborated by the JRC GSW ancillary data (Figure 13 and Figure 14). For the study area, the river course deviation altered the rocks’ exposure, as observed from Figure 11 to Figure 14 and Table 5.
We can see from Figure 14 that an extensive area (east, where the rocks are predominant) changed from permanent water to seasonal water (in orange) and non-water (in red), confirming the rock exposure trend found by the classification algorithms.
From Figure 13 it is possible to confirm that this transformation dramatically deflected from the pattern observed from previous years in the period 2014–2015, a period marked by the initial deviation of the watercourse, and in the period 2015–2016, when the deviation was concluded. A very worrisome pattern is also observed in Figure 13b, where a significant extension of seasonal waters (the ones controlled by the flood pulse of the river) also turned into non-water in 2015–2016, the first year after the conclusion of the dam construction, something which would permanently change the natural flood pulse. Finally, in Figure 13c we can see how the influence of the new reservoir is clearly reproduced, when an extensive area of no water changed into seasonal/permanent water in 2015–2016. This transformation is also highlighted in Figure 14, which consists of three year-by-year maps where we can see the reservoir being created.
The rock’s exposure can pose a threat to the biodiversity that is adapted to and associated with the rocks, such as the rock vegetation, which is dependent on flood pulses, i.e., periodic river flow pulsing that supports ecosystem productivity [70]. There is a consensus that the mortality of fishes observed in 2015–2016 is directly related to the interruption of the migratory flow and the way that areas for feeding and spawning were no longer flooded due to the reduced flow of water that year [27,37]. The absence of flooded areas also affected the nutritional quality of the surviving fish. The years 2015 and 2016 light a red alert about the new hydrological flow that the Xingu River is about to be subject to after the damming.
The deforestation (forest to non-forest class) (Figure 9 and Figure 10) process is a consequence of associated activities related to great enterprises, such as roads, accommodation/workers houses, construction sites, plant structures, and equipment assembly [29]. The increase in infrastructure works attracted by the Belo Monte power plant is also responsible for improving transport access to remote areas, which may have contributed to the conversion of forest to agro-pasture (Figure 10) [71]. Indeed, it is well known that deforestation patterns are associated with road access, especially in areas of agrarian projects [72]. The region also had economic incentives for activities related to cattle ranching, resulting in a growth of 116% from 2000 to 2017 [73,74].
The literature’s recommendation states that the creation of mitigation measures, such as the intensification of environmental monitoring and the creation of protected areas, with the aim to avoid or reduce deforestation, are the most effective strategies to attenuate the harmful impacts of such great enterprises [31,75].
As there are large and small hydroelectric power plants planned to be constructed in the Amazon, it is important to understand the land use and land cover changes associated with these activities, as well as to describe reliable methods to analyze these transitions. The present study validates the use of parametric and non-parametric classification methodologies, from the simplest and widely used to the most complex and restricted available in popular software packages. All of these fulfill their purposes, mainly when associated with good ground reference information, well-selected training samples and prior knowledge of the area. When available in popular software, they are not complex to implement and are accessible to a wide range of users, even those who are not experts in image processing and geoprocessing techniques.
5. Conclusions
This research corroborates and increases the knowledge of remote sensing techniques for the VGX already gathered by other studies, reaffirming the idea that the construction of the BMHC is the current most important source of negative impacts in the VGX area. Thus, a follow-up is a relevant part of the environmental licensing of the mega project. The present study is focused on the VGX and BMHC, but it is possible to extend our findings and methodologies to the surroundings of other enterprises, given the similarity and homogeneity of the Amazon region in the context of land use and occupation.
This study points out that a combination among different classification techniques is fundamental. When possible, and if available, using non-parametric algorithms is an achievable and reliable way to detect different changes in a complex landscape such as tropical forests. In this context, fieldwork, good high-resolution dataset, and ancillary data are requirements to increase the quality of the analyses.
All the parametric and non-parametric pixel-based algorithms showed many similarities among the indexes of accuracy analyzed by the present study. All of them had general good performances in identifying classes and detecting changes, being able to provide an overall trend of the transformations from 2000 to 2017. The analysis of producer and user accuracies and omission and commission errors were more consistent in the detection of errors in misclassified classes (such as rocks), mainly when associated with ancillary data (such as the JRC GSW dataset). However, SVM and ML were the best classifiers among all options, mainly for the most heterogeneous classes (river, and mainly, rocks).
The analysis in the VGX had two major challenges specific to this study area: (1) the complex landscape and the medium resolution from Landsat imagery resulted in spectral overlapping of targets and classes and misclassification, as well as spectral mixture, and (2) the presence of clouds most of the year, preventing multitemporal images from being selected for the analysis.
In all cases, the main conversions concerning land use and land cover were from forest to agro-pasture, from forest/agro-pasture to river upstream of the Xingu River, and from river to non-river in the south of the VGX, resulting in rock exposure. These impacts were associated mainly with the construction of the reservoir, the river deviation to install the main dam of the BMHC and the expansion of agro-pasture, as demonstrated by the JRC GSW ancillary data.
Our study was able to detect a significant exposure in the rocks that once remained submerged for most of the year (and now, are permanently exposed), a transformation that has not yet been properly addressed in the literature. In addition, according to previous research, this study observed that deforestation continues to cause the most significant transformation in the VGX area.
For the future, it is mandatory that the monitoring of landscape changes continues to be undertaken in the VGX, as they will only increase from now on. It is important to keep previous data to compare with the new knowledge being produced. Time series analysis comparing the pre-dam situation with the current situation and comparing different stages of implementation of the hydroelectric complex must be continuously assessed according to the improvement of digital image processing technologies and new investigation technologies. There should be a focus on extracting as much detail as possible from the transformations underway, over the longest possible time period. Other orbital sensors, optical and radar, RPAs and even more high-resolution datasets need to be increasingly incorporated into this monitoring effort.
The authors also encourage future studies to better investigate the rocky environment of the VGX, which notably is the most complex in the area, and at the same time, most susceptible to changes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.A., S.S.M. and T.P.P.; methodology, A.A.A. and T.P.P.; validation, A.A.A. and T.P.P.; formal analysis, A.A.A., S.S.M. and T.P.P.; investigation, A.A.A., S.S.M. and T.P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.A.; writing—review & editing, A.A.A., S.S.M., T.P.P., J.A.Q., C.H.G. and L.A.C.; supervision, J.A.Q., C.H.G. and L.A.C.; funding acquisition, A.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES)—Financing Code 001 (A.A.A., S.S.M. and T.P.P.). APC was funded by PROEx (Academic Excellence Program) fund #0725/2020 / 23038.001810/2020-11. S.S.M. is a research fellow of São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP, grant #2020/07372-4,). J.A.Q. is a research fellow of Brazil’s National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, grant #305188/2020-8). L.A.C. is a research fellow of São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP, grant #19/22028-0). C.H.G. is a research fellow of Brazil’s National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq, grants #311209/2021-1).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Landsat 7 and 8 images are courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey and can be downloaded at [40].
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of São Paulo Institute of Energy and Environment and the Graduate Program in Environmental Science. The authors acknowledge Kyle Flavin, for the revision of the text. Acknowledgements are extended to the editor-in-chief, the associate editor, and the anonymous reviewers for their criticism and suggestions, which helped to improve this paper. This study was financed in part by Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Skole, D.L.; Chomentowski, W.; Salas, W.; Nobre, A.D. Physical and Human Dimensions of Deforestation in Amazonia. BioScience 1994, 44, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, O.T.; Santos, A.C.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of Land Use and Land Cover on Water Quality of Low-Order Streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed Versus Riparian Zone. CATENA 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalacska, M.; Arroyo-Mora, J.; Lucanus, O.; Sousa, L.; Pereira, T.; Vieira, T. Deciphering the Many Maps of the Xingu—An Assessment of Land Cover Classifications at Multiple Scales. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 2020, 166, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I.M.; Gabriel, C.; Carreiras, J.M. Spatial and Temporal Dimensions of Landscape Fragmentation across the Brazilian Amazon. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, E.M.; Gomes, C.S.; Roquetti, D.R.; Jordão, C.D.O. Histórico, Tendências e Perspectivas no planejamento espacial de Usinas Hidrelétricas Brasileiras: A Antiga e Atual Fronteira Amazônica. Ambiente Soc. 2012, 15, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Hidrelétricas Na Amazônia: Impactos Ambientais e Sociais Na Tomada De Decisões Sobre Grandes Obras; Editora do INPA: Belém, Brazil, 2015; Volume 2, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Athayde, S.; Duarte, C.G.; Gallardo, A.L.; Moretto, E.M.; Sangoi, L.A.; Dibo, A.P.A.; Siqueira-Gay, J.; Sánchez, L.E. Improving Policies and Instruments to Address Cumulative Impacts of Small Hydropower in the Amazon. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Souza, C.A.J.; Thonicke, K.; Burton, C.; Halladay, K.; Betts, R.A.; Alves, L.M.; Soares, W.R. Changes in climate and land use over the Amazon region: Current and future variability and Trends. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinosi, F.; Arias, M.E.; Lee, E.; Longo, M.; Pereira, F.; Livino, A.; Moorcroft, P.R.; Briscoe, J. Future climate and land use change impacts on river flows in the tapajós basin in the Brazilian Amazon. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 993–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.E.; Farinosi, F.; Lee, E.; Livino, A.; Briscoe, J.; Moorcroft, P.R. Impacts of climate change and deforestation on hydropower planning in the Brazilian Amazon. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winemiller, K.O.; McIntyre, P.B.; Castello, L.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Giarizzp, T.; Nam, S.; Saénz, L. Balancing hydropower and biodiversity in the Amazon, Congo, and Mekong. Science 2016, 351, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Calvi, M.F.; Dutra, L.V.; Li, G. Examining Impacts of the Belo Monte Hydroelectric Dam Construction on Land-Cover Changes Using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 97, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, M.F.; Moran, E.F.; da Silva, R.F.B.; Batistella, M. The Construction of the Belo Monte Dam in the Brazilian Amazon and Its Consequences on Regional Rural Labor. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, A.C.; Bohlman, S. Cumulative Impacts of Land Cover Change and Dams on the Land–Water Interface of the Tocantins River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 662904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Hetrick, S. Land-Cover Classification in a Moist Tropical Region of Brazil with Landsat Thematic Mapper Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 8207–8230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A. Review Article Digital Change Detection Techniques Using Remotely-Sensed Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A Survey of Image Classification Methods and Techniques for Improving Classification Performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Batistella, M.; Moran, E. Comparison of Land-Cover Classification Methods in the Brazilian Amazon Basin. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.A.; Cohen, W.B. Selection of Remotely Sensed Data. In Remote Sensing of Forest Environments: Concepts and Case Studies; Essay; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 13–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z. Change Detection Using Landsat Time Series: A Review of Frequencies, Preprocessing, Algorithms, and Applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P. Cloud cover in landsat observations of the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.M.; Shimbo, J.Z.; Rosa, M.R.; Parente, L.L.; Alencar, A.; Rudorff, B.F.; Hasenack, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Ferreira, L.G.; Souza-Filho, P.W.E. Reconstructing three decades of land use and land cover changes in Brazilian biomes with Landsat Archive and Earth engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, G.; Barthem, R.; Ferreira, E.J.G.; Duenas, R. The Smithsonian Atlas of the Amazon; Smithsonian Books: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barona, E.; Ramankutty, N.; Hyman, G.; Coomes, O.T. The Role of Pasture and Soybean in Deforestation of the Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Soybean Cultivation as a Threat to the Environment in Brazil. Environ. Conserv. 2001, 28, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, R.D.P.; Vieira, I.C.G.; Suemitsu, C.; Rosa, N.D.A.; de Almeida, S.S.; Amaral, D.D.D.; de Menezes, M.P.M. As Florestas De Belo Monte Na Grande Curva Do Rio Xingu, Amazônia Oriental. Bol. Mus. Para. Emílio Goeldi-Ciências Nat. 2007, 2, 57–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuanon, J.; Sawakuchi, A.; Camargo, M.; Wahnfried, I.; Sousa, L.; Akama, A.; Muriel-Cunha, J.; Ribas, C.; D’Horta, F.; Pereira, T.; et al. Condições Para a Manutenção da Dinâmica Sazonal de Inundação, a Conservação do Ecossistema Aquático e Manutenção dos Modos de Vida dos Povos da Volta Grande do Xingu. Papers NAEA 2020, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.F.; Dutra, L.V.; Calvi, M.F.; De Oliveira, M.A.F. Examining Spatial Distribution and Dynamic Change of Urban Land Covers in the Brazilian Amazon Using Multitemporal Multisensor High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletrobrás, Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S/A. Aproveitamento Hidrelétrico Belo Monte: Estudo de Impacto Ambiental; Eletrobrás: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kalacska, M.; Lucanus, O.; Sousa, L.; Arroyo-Mora, J. High-Resolution Surface Water Classifications of the Xingu River, Brazil, Pre and Post Operationalization of the Belo Monte Hydropower Complex. Data 2020, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.M.; Batista, L.M.; de Sousa, M.C.; Freitas, K.M.; Araújo, S.R. Sensoriamento Remoto Na Análise De Variáveis Ambientais Influenciadas Pela Implantação Da Usina Hidrelétrica De Belo Monte (PA). Caderno Geografia 2021, 31, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pará. Altamira: Estatística Municipal. 2011. Available online: http://iah.iec.pa.gov.br/iah/fulltext/georeferenciamento/altamira.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Sawakuchi, A.O.; Hartmann, G.A.; Pupim, F.N.; Bertassoli, D.J.; Parra, M.; Antinao, J.L.; Sousa, L.M.; Pérez, M.H.S.; Oliveira, P.E.; Santos, R.A.; et al. The Volta Grande Do Xingu: Reconstruction of Past Environments and Forecasting of Future Scenarios of a Unique Amazonian Fluvial Landscape. Sci. Drill. 2015, 20, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.B.S.; de Oliveira Santiago Santos, G.; Menezes, A.C.; de Oliveira, I.F.S.; Melo, I.C.; Santos, W.L.; Medeiros, S.L. Licenciamento Ambiental No Brasil Sobre Usinas Hidrelétricas: Um Estudo De Caso Da Usina De Belo Monte, No Rio Xingu. Cadernos Graduação 2012, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Villas-Boas, A. De Olho na Bacia do Xingu; Cartô Brasil Socioambiental; Instituto Socioambiental: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012; Volume 5, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Junk, W.J. Áreas Inundáveis—Um Desafio Para Limnologia. Acta Amazonica 1980, 10, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzuti, J.; Carneiro, C.; Mantovanelli, T.; Garzón, B.R. Xingu, o Rio Que Pulsa Em Nós. In Monitoramento Independente Para Registro De Impactos Da UHE Belo Monte No Território e No Modo De Vida Do Povo Juruna (Yudjá) Da Volta Grande Do Xingu, 1st ed.; Instituto Socioambiental: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnside, P. Brazil’s Belo Monte Dam: Struggle for the Volta Grande EnTers a New Phase (Commentary). Mongabay. 2021. Available online: https://news.mongabay.com/2021/06/brazils-belo-monte-dam-struggle-for-the-volta-grande-enters-a-new-phase-commentary/ (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Globo, O. Justiça Aceita Ação Do MPF e Reduz Vazão De Belo Monte Para Geração Elétrica. O Globo. 2021. Available online: https://oglobo.globo.com/economia/justica-aceita-acao-do-mpf-reduz-vazao-de-belo-monte-para-geracao-eletrica-25068291 (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- USGS Landsat Image Gallery Platform. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Affonso, A.A.; Mandai, S.S.; Portella, T.P.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Grohmann, C.H. Tracking Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Volta Grande Do Xingu (Pará-Brazil) between 2000 and 2017 through Three Pixel-Based Classification Methods. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022—2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 5630–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Moran, E.; Hetrick, S. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5953–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.; Hambrey, M.; Reynolds, J. ‘Structure-from-Motion’ Photogrammetry: A Low-Cost, Effective Tool for Geoscience Applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, C.D.; Grohmann, C.H.; Busarello, M.D.S.T.; Garcia, G.P.B. Structural Analysis of Clastic Dikes Using Structure from Motion-Multi-View Stereo: A Case-Study in the Paraná Basin, Southeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Geol. 2018, 48, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Calvi, M.F.; Dutra, L.V.; Batistella, M. Examining Deforestation and Agropasture Dynamics along the Brazilian TransAmazon Highway Using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Surface Water Explorer. Available online: https://global-surface-water.appspot.com/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Congedo, L. Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin: A Python Tool for the Download and Processing of Remote Sensing Images in QGIS. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Datasets NICFI in Earth Engine. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/tags/nicfi (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Dhingra, S.; Kumar, D. A Review of Remotely Sensed Satellite Image Classification. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2019, 9, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchra, H.; Belangour, A. Satellite Image Classification Methods and Techniques: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 24–26 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classification. Using Envi. Available online: https://www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/docs/classification.html (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Support Vector Machine. Using Envi. Available online: https://www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/docs/supportvectormachine.html (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Envi User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.tetracam.com/PDFs/Rec_Cite9.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Snap Machine Learning Manual–Random Forest. Manual-Snap Machine Learning Documentation. Available online: https://ibmsoe.github.io/snap-ml-doc/v1.6.0/manual.html#random-forest (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. A Practical Guide to Support Vector Classification. 2003. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Calculate Confusion Matrices. Available online: https://www.l3harrisgeospatial.com/docs/calculatingconfusionmatrices.html (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Pontius, R.G.; Millones, M. Death to Kappa: Birth of Quantity Disagreement and Allocation Disagreement for Accuracy Assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4407–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.P.; Jenkins, C.N.; Heilpern, S.; Maldonado-Ocampo, J.A.; Carvajal-Vallejos, F.M.; Encalada, A.C.; Rivadeneira, J.F.; Hidalgo, M.; Cañas, C.M.; Ortega, H.; et al. Fragmentation of Andes-to-Amazon Connectivity by Hydropower Dams. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Harshness in Image Classification Accuracy Assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3137–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Doan, T.M.; Tomppo, E.; McRoberts, R.E. Land Use/Land Cover Mapping Using Multitemporal Sentinel-2 Imagery and Four Classification Methods—A Case Study from Dak Nong, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenzel, B.G.; Treitz, P. Spectral and Spatial Filtering for Enhanced Thematic Change Analysis of Remotely Sensed Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 835–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, R.; King, D. Comparison of Techniques for Forest Change Mapping Using Landsat Data in Karnataka, India. Geocarto Int. 2006, 21, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.F.; Sant’Anna, S.J.S. Comparative Analysis of Classification Algorithms and Multiple Sensor Data for Land Use/Land Cover Classification in the Brazilian Amazon. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 061706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalacska, M.; Lucanus, O.; Sousa, L.; Arroyo-Mora, J.P. A New Multi-Temporal Forest Cover Classification for the Xingu River Basin, Brazil. Data 2019, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M. Accuracy Assessment: A User’s Perspective. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 52, 397–399. Available online: https://www.asprs.org/wp-content/uploads/pers/1986journal/mar/1986_mar_397-399.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Moran, E.F.; Lopez, M.C.; Moore, N.; Müller, N.; Hyndman, D.W. Sustainable Hydropower in the 21st Century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11891–11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junk, W.J.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Lourival, R.; Wittmann, F.; Kandus, P.; Lacerda, L.D.; Bozelli, R.L.; Esteves, F.A.; da Cunha, C.N.; Maltchik, L.; et al. Brazilian Wetlands: Their Definition, Delineation, and Classification for Research, Sustainable Management, and Protection. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2013, 24, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Hidrelétricas Na Amazônia Brasileira: Questões Ambientais e Sociais. In Hidrelétricas Na Amazônia: Impactos Ambientais e Sociais Na Tomada De Decisões Sobre Grandes Obras 3; Essay; Fearnside, P.M., Ed.; Editora do Inpa: Manaus, Brazil, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, L.D.S.; Verburg, P. Combining Remote Sensing and Household Level Data for Regional Scale Analysis of Land Cover Change in the Brazilian Amazon. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2010, 10, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, M.F. (Re) Organização Produtiva e Mudanças Na Paisagem Sob Influência Da Hidrelétrica De Belo Monte. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Pesquisa da Pecuária Municipal. Available online: https://sidra.ibge.gov.br/tabela/3939 (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- Barreto, P.; Brandão, A.; Martins, H.; Silva, D.; Souza, C.; Sales, M., Jr. Risco de Desmatamento Associado à Hidrelétrica de Belo Monte; Instituto do Homem e Meio Ambiente da Amazônia. IMAZON: Belém, Brazil, 2011; p. 98. Available online: http://www.imazon.org.br/publicacoes/livros/risco-de-desmatamento-associado-a-hidreletricade-belo-monte/at_download/file (accessed on 26 August 2020).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).