A Big Data Approach for Investigating Bridge Deterioration and Maintenance Strategies in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
Research Motivation and Objective
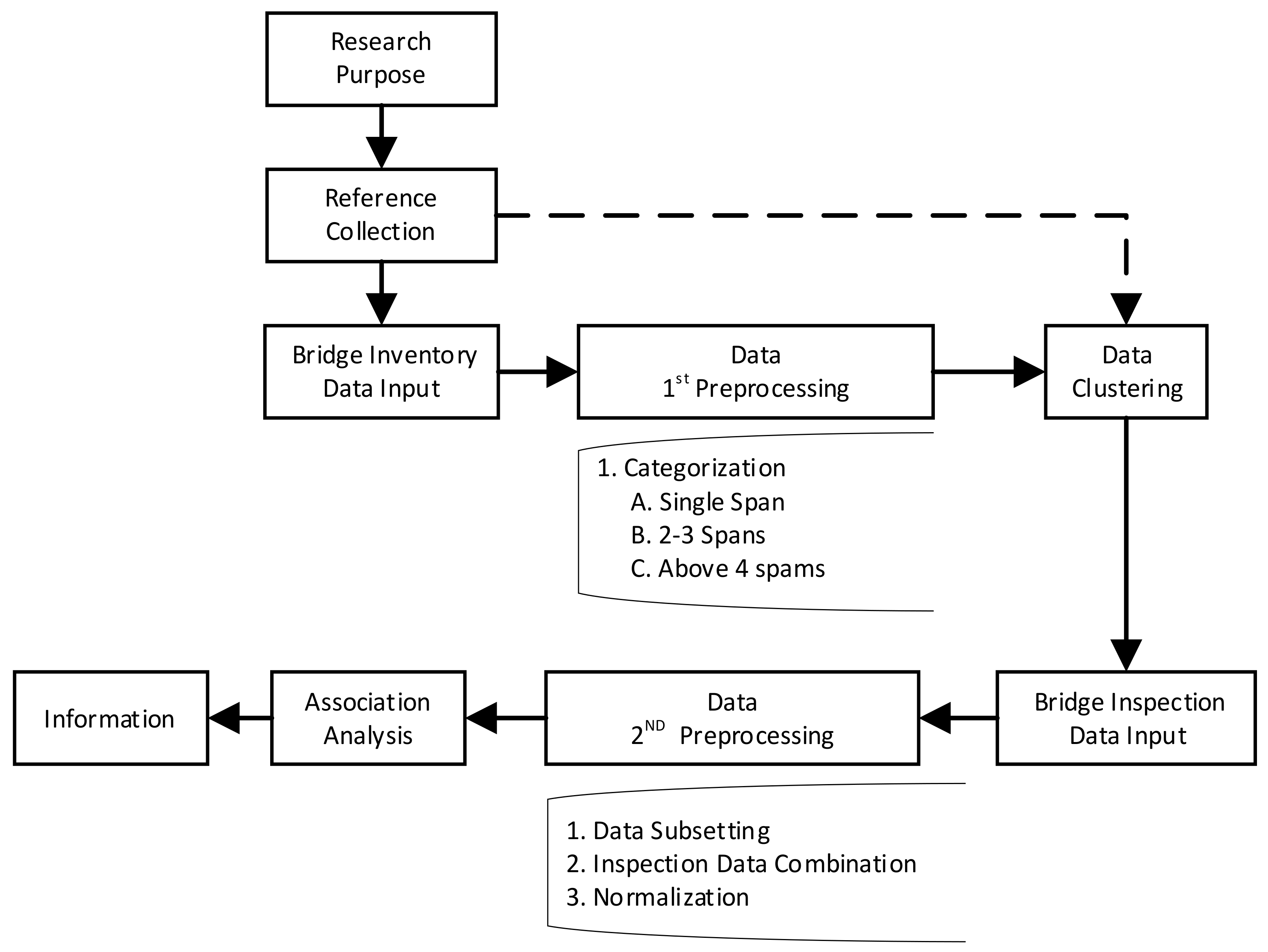
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TBMS Bridge-Inspection and Inventory-Data Overview
2.2. Bridge-Inventory and Inspection-Data Preprocessing
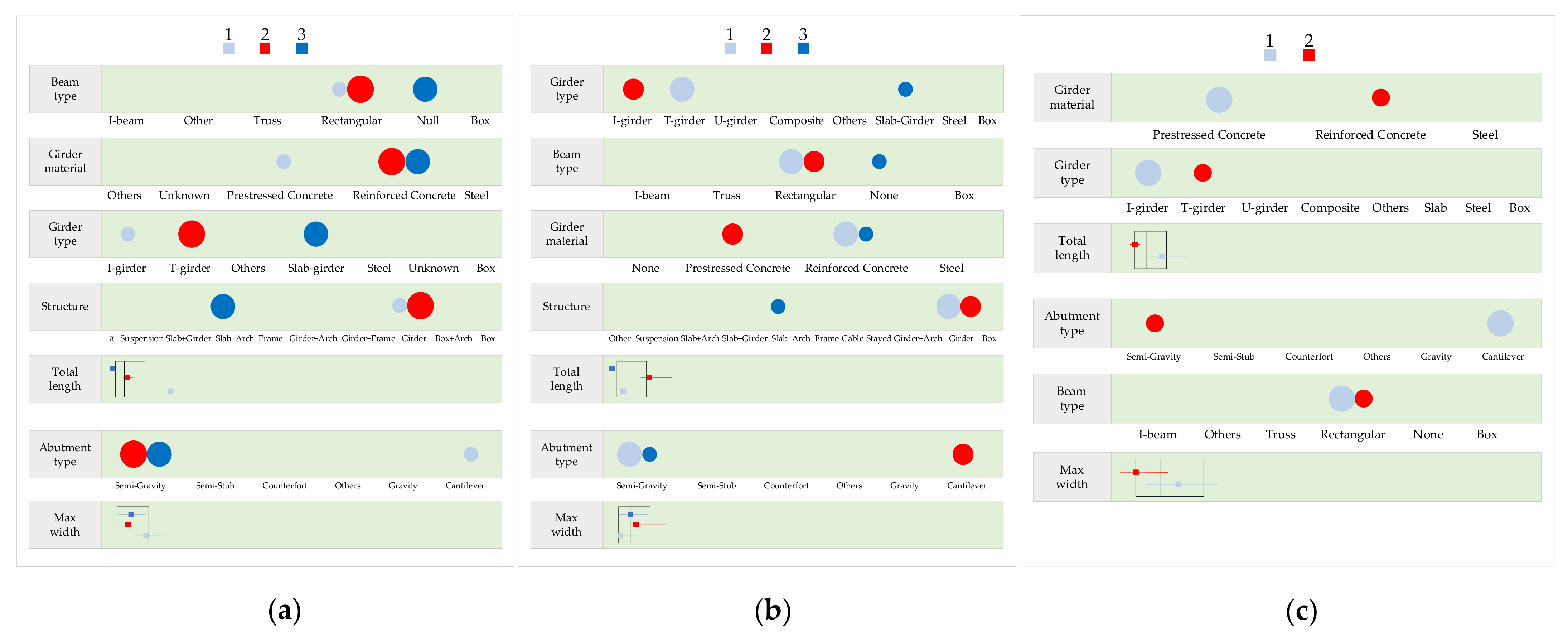
2.3. Cluster Analysis
2.4. Association Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Chen, M.; Wang, X. Critical review of data-driven decision-making in bridge operation and maintenance. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 18, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiang, F.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, X. Intelligent bridge management via big data knowledge engineering. Autom. Constr. 2022, 135, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, R.B.; Garrett, J.H.; Lee, S.R.; Brahme, R. A Knowledge Discovery Framework for Civil Infrastructure: A Case Study of the Intelligent Workplace. Eng. Comput. 2000, 16, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, U.; Stolorz, P. Data mining and KDD: Promise and challenges. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 1997, 13, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.-N.; Steinbach, M.; Karpatne, A.; Kumar, V. Introduction to Data Mining, 2nd ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Shang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S. Review of Bridge Structural Health Monitoring Aided by Big Data and Artificial Intelligence: From Condition Assessment to Damage Detection. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, M.; Ghonima, O.; Schumacher, T. Data Mining of Bridge Concrete Deck Parameters in the National Bridge Inventory by Two-Step Cluster Analysis. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2017, 3, F4016004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, N.; Peng, Y.; Ren, Y. Data mining in the construction industry: Present status, opportunities, and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2020, 119, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.S.; Toukourou, A.; Soibelman, L. Knowledge Discovery in a Facility Condition Assessment Database Using Text Clustering. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2006, 12, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wah, B.W.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y. Significance and Challenges of Big Data Research. Big Data Res. 2015, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Chatzi, E.; Sim, S.; Laflamme, S.; Blachowski, B.; Ou, J. Recent progress and future trends on damage identification methods for bridge structures. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortagi, M.; Ghosh, J. Consideration of Climate Change Effects on the Seismic Life-Cycle Cost Analysis of Deteriorating Highway Bridges. J. Bridg. Eng. 2022, 27, 04021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, S.; Gamage, S.; Sadhu, A.; Samarabandu, J. Multiclass Damage Identification in a Full-Scale Bridge Using Optimally Tuned One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2022, 36, 04021035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmaksoud, A.M.; Balomenos, G.P.; Becker, T.C. Parameterized Logistic Models for Bridge Inspection and Maintenance Scheduling. J. Bridg. Eng. 2021, 26, 04021072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chi, S. Bridge Clustering for Systematic Recognition of Damage Patterns on Bridge Elements. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 33, 04019028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Arancibia, M.; Rugar, L.; Okumus, P. Role of Skew on Bridge Performance. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2020, 2674, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Queiroz, L.B. Big Data for condition evaluation of constructed bridges. Eng. Struct. 2017, 141, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, D.K. Identifying Critical Sources of Bridge Deterioration in Cold Regions through the Constructed Bridges in North Dakota. J. Bridg. Eng. 2010, 15, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Alipour, M.; Harris, D.K. Mapping textual descriptions to condition ratings to assist bridge inspection and condition assessment using hierarchical attention. Autom. Constr. 2021, 129, 103801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Mohamed, E.; Mohsen, O.; Mohamed, Y. Comparative Study of Data Mining Models for Prediction of Bridge Future Conditions. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2020, 34, 04019108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Soibelman, L.; Grobler, F. Factor selection for delay analysis using Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Autom. Constr. 2008, 17, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Lei, X.; Wang, P.; Sun, L. A data-driven approach for regional bridge condition assessment using inspection reports. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2021, 29, e2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Xia, Y.; Deng, L.; Sun, L. A deep reinforcement learning framework for life-cycle maintenance planning of regional deteriorating bridges using inspection data. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alogdianakis, F.; Charmpis, D.C.; Balafas, I. Macroscopic effect of distance from seacoast on bridge deterioration—Statistical data assessment of structural condition recordings. Structures 2020, 27, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-C. Natural hazards in Taiwan. Geojournal 1996, 38, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Lin, C.; Wang, C.-Y. Forensic Diagnosis on Flood-Induced Bridge Failure. I: Determination of the Possible Causes of Failure. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2014, 28, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, J.; García-Gil, D.; Ramírez-Gallego, S.; García, S.; Herrera, F. Big Data Preprocessing: Enabling Smart Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- García, S.; Ramírez-Gallego, S.; Luengo, J.; Benítez, J.M.; Herrera, F. Big data preprocessing: Methods and prospects. Big Data Anal. 2016, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Pei, J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Fan, C. Data mining in building automation system for improving building operational performance. Energy Build. 2014, 75, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | Not existing | Good | Fair | Bad | Serious |
| E | * U/I | <10% | 10–30% | 30–60% | Over 60% |
| R | Uncertain | Minor | Limited | Major | Large |
| U | † N/A | Routine | In 3 years or under observation | In 1 year | Immediate |
| Bridge Age | Freeway Bridges | Highway Bridges | Railway Bridges | Country/County Bridges | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 to 10 | 60 | 285 | 42 | 611 | 998 |
| 11 to 20 | 11 | 893 | 115 | 2192 | 3211 |
| 21 to 30 | 1526 | 1182 | 218 | 4245 | 7171 |
| 31 to 40 | 51 | 729 | 340 | 4010 | 5130 |
| >40 | 589 | 689 | 572 | 3257 | 5116 |
| Unknown | 15 | 45 | 110 | 8661 | 8831 |
| Bridge Location | Slab | Girder | Box Girder | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Span | 2 to 3 Spans | ≥4 Spans | Single Span | 2 to 3 Spans | ≥4 Spans | Single Span | 2 to 3 Spans | ≥4 Spans | |
| Taichung City | 81 | 17 | 1 | 245 | 141 | 42 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Tainan City | 0 | 18 | 6 | 0 | 132 | 42 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| Kaohsiung City | 126 | 32 | 3 | 263 | 97 | 20 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Changhua County | 38 | 3 | 0 | 33 | 26 | 13 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Yunlin County | 8 | 0 | 2 | 75 | 59 | 39 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Chiayi County | 259 | 26 | 2 | 290 | 96 | 35 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Pingtung County | 153 | 40 | 6 | 199 | 100 | 46 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No. | Attribute | Type | Contents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Department | nvarchar | Taichung City, Tainan City, Kaohsiung City, Changhua County, Yunlin County, Chiayi County, Pingtung County |
| 2 | Section | nvarchar | Dajia District, Daan District, Dali District, Daya District, etc. |
| 3 | Route | nvarchar | Pingtung 127, etc. |
| 4 | Year built | int | Unknown—2013 |
| 5 | Number of spans | int | 1 to 44 |
| 6 | Length | float | 6 to 1770 m |
| 7 | Maximum span length | float | 6 to 173 m |
| 8 | Maximum net width | float | 1.74 to 80.25 m |
| 9 | Slab area | float | 12.4 to 72,216 m2 |
| 10 | Driveway | int | 1 to 10 |
| 11 | Bridge structure | nvarchar | Slab bridge, girder bridge, box-girder bridge |
| 12 | Type of support | nvarchar | Simple, fixed, continuous |
| 13 | Material of girder | nvarchar | Reinforced concrete, prestressed concrete, steel |
| 14 | Type of girder | nvarchar | Slab, I-girder, T-girder, rectangular girder, box-girder |
| 15 | Type of beam | nvarchar | I-beam, rectangular beam |
| 16 | Type of abutment | nvarchar | Cantilever, gravity, semi-gravity |
| 17 | Type of expansion | nvarchar | Finger plate, gai-top, etc. |
| 18 | Type of bearing | nvarchar | Simple clamping, synthetic rubber, pot bearing, etc. |
| 19 | Type of wingwall | nvarchar | Cantilever, gravity, semi-gravity |
| 20 | Type of pavement | nvarchar | Reinforced concrete, asphalt concrete, others |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, Y.-H.; Yau, N.-J.; Tabor, J.M.M. A Big Data Approach for Investigating Bridge Deterioration and Maintenance Strategies in Taiwan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021697
Chuang Y-H, Yau N-J, Tabor JMM. A Big Data Approach for Investigating Bridge Deterioration and Maintenance Strategies in Taiwan. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021697
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Yu-Han, Nie-Jia Yau, and John Mark M. Tabor. 2023. "A Big Data Approach for Investigating Bridge Deterioration and Maintenance Strategies in Taiwan" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021697
APA StyleChuang, Y.-H., Yau, N.-J., & Tabor, J. M. M. (2023). A Big Data Approach for Investigating Bridge Deterioration and Maintenance Strategies in Taiwan. Sustainability, 15(2), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021697






