Integrating Socioeconomic Biophysical and Institutional Factors for Evaluating Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Northern Ethiopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
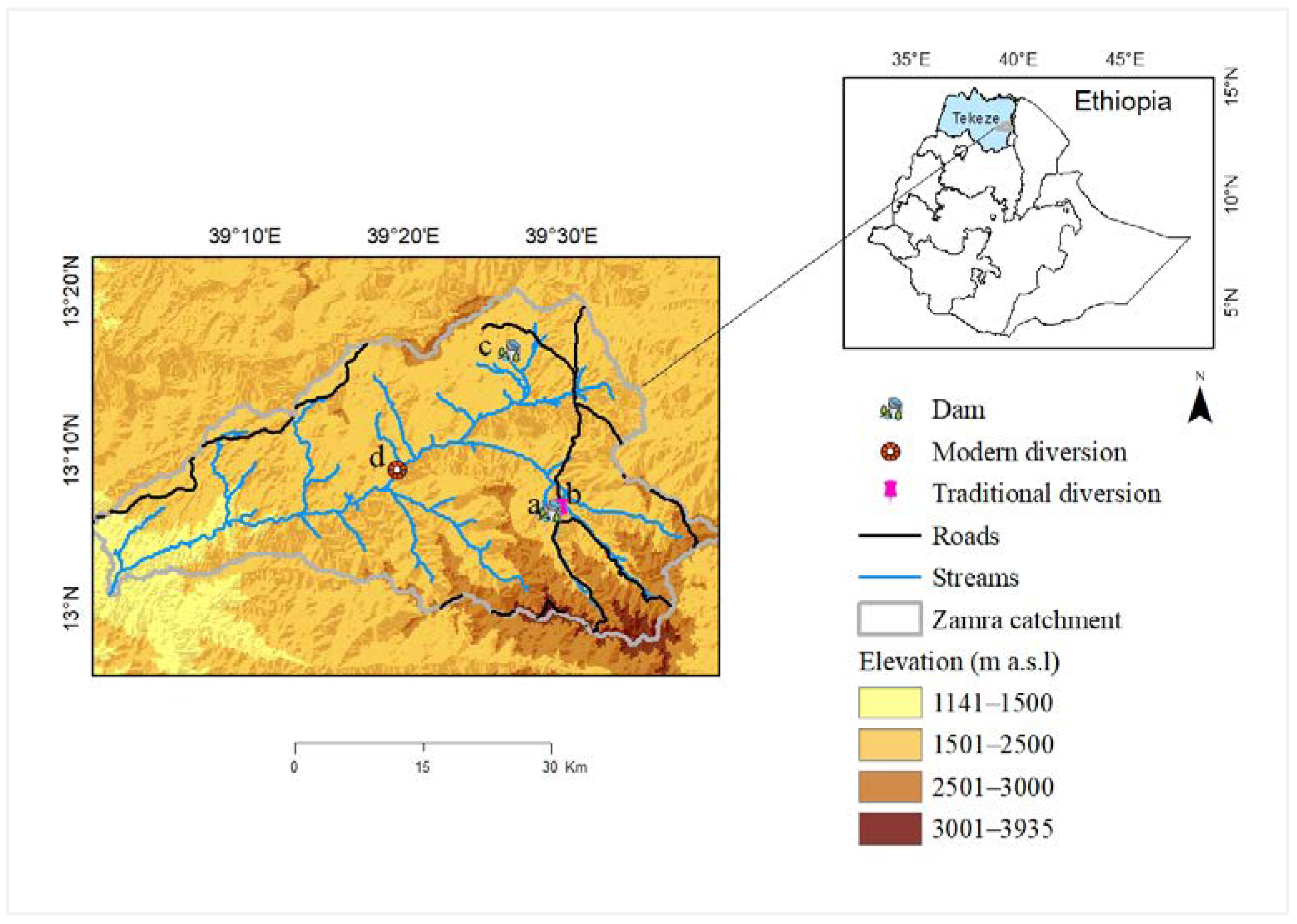
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Sampling Procedures and Data
3.3. Methodology
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of the Sample Household
4.2. Factors Affecting Small-Scale Irrigation
4.3. Production from Irrigation
4.4. Irrigation Challenges and Opportunities
4.4.1. Quantitative Results
4.4.2. Qualitative Results on Challenges and Opportunities
“I have a scarcity of irrigable land because my irrigated field is in the lower stream area, which is never irrigated during the irrigation season due to water shortages in the irrigation scheme. Accordingly, my production was lower as compared to other farmers”. (40-year-old female farmer in the Adibashay irrigation scheme)
“I am the female head of the household in the irrigation scheme. Now I rent oxen for plowing the field. If the government provided me with a credit service, I would buy oxen and reduce rent expenses. As a result, I will improve the well-being of the children and mine”. (37-year-old female farmer in Shilant-2 irrigation scheme)
“I participated in demonstrations from my side to get feedback and from other farmers to gain experience. I understand there is a follow-up from agricultural extension in one of the demonstrations, and I see the farmers have a good experience. When I compare my irrigation scheme, there is no follow-up from the agricultural extensions. So, I have a problem not getting updated information from District and Kebele experts”. (53-year-old male farmer in Adibashay irrigation scheme)
“In the irrigation scheme, there is a shortage of chemicals for pests and diseases. Moreover, there is no scientific research on pests and disease”. (54-year-old male farmer in Shilant-2 irrigation scheme)
“There is a transportation issue for selling our vegetables and fruits at the district market, so I used a donkey to transport them. As a result, vegetables are perishable, lowering their quality and reducing profit”. (50-year-old male farmer in Adibashay irrigation scheme)
“I plant a crop that is similar to my neighbor’s. It depends on water availability in the irrigation scheme, not market-oriented. Nevertheless, it is not profitable because all the farmers simultaneously sell the same crop type”. (68-year-old male farmer in Shilant-2 irrigation scheme)
“Farmers are concerned that the fields are becoming flooded and believe more water is beneficial. However, there is a problem with the plant. In this regard, when the amount of water is reduced from the dam, the irrigating time is reduced, for instance, from 3 h to 1 h”. (53-year-old male farmer in Shilant-2 irrigation scheme)
“It is difficult to control the farmers as they lack an awareness of irrigating the field. However, the committee has decided to reduce the interval of irrigating cereals from 3 weeks to one month and vegetables from one week to two weeks”. (46-year-old male farmer in Adibashay irrigation scheme)
Irrigation Major Opportunities
5. Discussion
5.1. Importance of the Multidisciplinary Approach
5.2. Impact of Irrigation on Smallholder
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


| Dependent Variable: Production (Quintal) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources of Irrigation Water | Challenges to Marketing | Access to Credit | Mean | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Traditional Diversion | Price fluctuation | Yes | 32.375 | 4.400 | 23.702 | 41.048 |
| No | 20.538 | 3.452 | 13.735 | 27.342 | ||
| Transport problem | Yes | 39.000 | 12.446 | 14.469 | 63.531 | |
| No | 15.000 | 8.800 | −2.346 | 32.346 | ||
| Distance to market | Yes | .a | . | . | . | |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Lack of store/shade | Yes | 15.000 | 12.446 | −9.531 | 39.531 | |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| No problem | Yes | 15.600 | 5.566 | 4.629 | 26.571 | |
| No | 6.667 | 7.186 | −7.496 | 20.830 | ||
| Modern Diversion | Price fluctuation | Yes | .a | . | . | . |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Transport problem | Yes | .a | . | . | . | |
| No | 16.000 | 12.446 | −8.531 | 40.531 | ||
| Distance to market | Yes | .a | . | . | . | |
| No | 8.000 | 12.446 | −16.531 | 32.531 | ||
| Lack of store/shade | Yes | 5.000 | 12.446 | −19.531 | 29.531 | |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Price fluctuation, distance to market, and transport | Yes | 13.409 | 2.653 | 8.179 | 18.639 | |
| No | 11.364 | 3.753 | 3.967 | 18.760 | ||
| Transport problem and distance to market | Yes | 9.600 | 1.968 | 5.721 | 13.479 | |
| No | 10.932 | 1.876 | 7.234 | 14.630 | ||
| Dam | Price fluctuation | Yes | 22.270 | 2.046 | 18.237 | 26.303 |
| No | 24.154 | 3.452 | 17.350 | 30.958 | ||
| Transport problem | Yes | .a | . | . | . | |
| No | 12.250 | 6.223 | −0.016 | 24.516 | ||
| Distance to market | Yes | 20.000 | 8.800 | 2.654 | 37.346 | |
| No | 11.500 | 8.800 | −5.846 | 28.846 | ||
| Lack of store/shade | Yes | 20.000 | 12.446 | −4.531 | 44.531 | |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| No problem | Yes | 15.692 | 3.452 | 8.889 | 22.496 | |
| No | 11.167 | 5.081 | 1.152 | 21.181 | ||
| Price fluctuation, distance to market, and transport | Yes | 30.000 | 12.446 | 5.469 | 54.531 | |
| No | 4.000 | 12.446 | −20.531 | 28.531 | ||
| Transport problem and distance to Market | Yes | .a | . | . | . | |
| No | 5.000 | 12.446 | −19.531 | 29.531 | ||
| None | Yes | 14.333 | 7.186 | 0.170 | 28.496 | |
| No | 12.200 | 5.566 | 1.229 | 23.171 | ||
| Dependent Variable: Production (Quintal) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources of Irrigation Water | Frequency of Advisory Service | Sufficient Irrigation Water | Mean | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Traditional Diversion | Daily | Yes | 10.000 | 12.487 | −14.611 | 34.611 |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Monthly | Yes | 9.600 | 5.584 | −1.407 | 20.607 | |
| No | 10.000 | 12.487 | −14.611 | 34.611 | ||
| Weakly | Yes | 28.333 | 4.162 | 20.130 | 36.537 | |
| No | 31.500 | 8.830 | 14.097 | 48.903 | ||
| Bi-weekly | Yes | 33.200 | 5.584 | 22.193 | 44.207 | |
| No | 10.000 | 12.487 | −14.611 | 34.611 | ||
| unconditional | Yes | 17.429 | 4.720 | 8.126 | 26.731 | |
| No | 12.000 | 8.830 | −5.403 | 29.403 | ||
| Modern Diversion | Daily | Yes | 19.000 | 8.830 | 1.597 | 36.403 |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Monthly | Yes | 9.750 | 1.882 | 6.040 | 13.460 | |
| No | 8.667 | 3.224 | 2.312 | 15.021 | ||
| Weakly | Yes | 9.917 | 2.549 | 4.893 | 14.940 | |
| No | 5.500 | 8.830 | −11.903 | 22.903 | ||
| Bi-weekly | Yes | 13.727 | 2.662 | 8.480 | 18.974 | |
| No | 7.750 | 6.244 | −4.556 | 20.056 | ||
| Unconditional | Yes | 19.286 | 4.720 | 9.983 | 28.588 | |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Dam | Daily | Yes | .a | . | . | . |
| No | .a | . | . | . | ||
| Monthly | Yes | 20.783 | 2.604 | 15.651 | 25.914 | |
| No | 23.250 | 4.415 | 14.549 | 31.951 | ||
| Weakly | Yes | 18.750 | 3.122 | 12.597 | 24.903 | |
| No | 16.750 | 3.605 | 9.645 | 23.855 | ||
| Bi-weekly | Yes | 19.615 | 3.463 | 12.789 | 26.441 | |
| No | 12.167 | 5.098 | 2.119 | 22.214 | ||
| Unconditional | Yes | 16.833 | 5.098 | 6.786 | 26.881 | |
| No | 18.000 | 5.584 | 6.993 | 29.007 | ||
References
- Awulachew, S.B.; Merrey, D.; Kamara, A.; van Koppen, B.; Penning de Vries, F.; Boelee, E. Experiences and Opportunities for Promoting Small-Scale/Micro Irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting for Food Security in Ethiopia; International Water Management Institute: Addis Abeba, Ethiopia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Behailu, M.; Haile, M. Water Harvesting in Northern Ethiopia: Environmental, Health and Socio-Economic Impacts|Mendeley. Available online: https://www.mendeley.com/search/?page=1&query=Water%20harvesting%20in%20northern%20Ethiopia%3A%20environmental%2C%20health%20and%20socio-economic%20impacts&sortBy=relevance (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Hagos, E. Development and Management of Irrigation Lands in Tigray, Ethiopia. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, UNESCO-IHE, Delft, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Poesen, J.; Nyssen, J.; de Wit, J.; Haile, M.; Govers, G.; Deckers, S. Reservoirs in Tigray (Northern Ethiopia): Characteristics and Sediment Deposition Problems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, D.; van Wesemael, B.; Vanacker, V.; Poesen, J.; Hallet, V.; Taye, G.; Deckers, J.; Haregeweyn, N. Evaluating the Performance of Reservoirs in Semi-Arid Catchments of Tigray: Tradeoff between Water Harvesting and Soil and Water Conservation. Catena 2013, 110, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, D. Multi-Scale Analysis of Surface Runoff and Water-Harvesting Dams in a Semi-Arid Region: A Case Study in Tigray (Ethiopia). Ph.D. Thesis, UCL-Université Catholique de Louvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yohannes, D.F.; Ritsema, C.J.; Solomon, H.; Froebrich, J.; van Dam, J.C. Irrigation Water Management: Farmers’ Practices, Perceptions and Adaptations at Gumselassa Irrigation Scheme, North Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 191, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.; Erkossa, T.; Namara, R.E. Irrigation Potential in Ethiopia: Constraints and Opportunities for Enhancing the System. Gates Open Res. 2010, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashu, E. The Impact of Small Scale Irrigation on the Income and Food Security Among Small-Scale Farmers in Ethiopia: A Review. Am. J. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2022, 7, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Adela, F.A.; Aurbacher, J.; Abebe, G.K. Small-Scale Irrigation Scheme Governance—Poverty Nexus: Evidence from Ethiopia. Food Secur. 2019, 11, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A. Utilization of Community Managed Irrigation Scheme in Bale Zone: The Case of Agarfa Woreda, Oromia Regional State, South East Ethiopia. J. Equity Sci. Sustain. Dev. (JESSD) 2019, 3, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sisay, B.; Fekadu, B. Small-Scale Irrigation and Household Income Linkage: Evidence from Deder District, Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 4441–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awulachew, S.B.; Ayana, M. Performance OF Irrigation: An Assessment at Different Scales in Ethiopia. Exp. Agric. 2011, 47, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amede, T. Technical and Institutional Attributes Constraining the Performance of Small-Scale Irrigation in Ethiopia. Water Resour. Rural. Dev. 2015, 6, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.M.; Assefa, T.; Belay, S.A.; Yimam, A. Evaluating the Performance of Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Sub Humid Ethiopian Highlands; a Case Study in Mugie and Fesas. Irrig. Drain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, J.A.; Adetutu, O.; Oloruntuga, I.; Ojo, O.I. Evaluation of Small Farmer Managed Irrigation Schemes in Some Fadama Communities of Oyo State, Nigeria. Ann. Fac. Eng. Hunedoara 2019, 17, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yihdego, A.G.; Gebru, A.A.; Gelaye, M.T. The Impact of Small—Scale Irrigation on Income of Rural Farm Households: Evidence from Ahferom Woreda in Tigray, Ethiopia. Int. J. Bus. Econ. Res. 2015, 4, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupaso, N.; Nyamutowa, C.; Masunda, S.; Chipunza, N.; Mugabe, D. Characterisation of Smallholder Irrigation Schemes in Chirumanzu District, Zimbabwe. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekele, A.E. Five Key Constraints to Small Scale Irrigation Development in Ethiopia: Socio-Economic View. Glob. Adv. Res. J. 2014, 3, 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Libseka, H.; Welde, K.; Degef, K. Assessment of Constraints and Opportunities of Small-Scale Irrigation Practices in South Tigray, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 5, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gebregziabher, G.; Namara, R.E.; Holden, S. Technical Efficiency of Irrigated and Rain-Fed Smallholder Agriculture in Tigray, Ethiopia: A Comparative Stochastic Frontier Production Function Analysis. Q. J. Int. Agric. 2012, 51, 203–226. [Google Scholar]
- Embaye, T.A.G.; Kahsay, G.H.; Abadi, N.; Kebede, M.M.; Dessie, D.T. Evaluation of Water Harvesting Structures on Agricultural Productivity: The Case of Tigray Region, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water. Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejene, S.; Teshome, W.; Makombe, G.; Awulachew, S.B.; Prasad, K. Institutions, Management Practices and Challenges of Small-Scale Irrigation Systems in Ethiopia: A Case Study of Two Modern Smallholders Irrigation Systems in Western Oromia, Ethiopia. 2008; 298–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mutambara, S.; Darkoh, M.B.K.; Atlhopheng, J.R. A Comparative Review of Water Management Sustainability Challenges in Smallholder Irrigation Schemes in Africa and Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataklti, Y.T. Assessing the Potential of Geonetcast Earth Observation and in Situ Data for Drought Early Warning and Monitoring in Tigray, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WaPOR, F. FAO’s Portal to Monitor Water Productivity through Open Access of Remotely Sensed Derived Data. Available online: https://wapor.apps.fao.org/home/WAPOR_2/1 (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Limon, G.; Fournié, G.; Lewis, E.G.; Dominguez-Salas, P.; Leyton-Michovich, D.; Gonzales-Gustavson, E.A.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Cabezas, A.H.; Pinto, J.; Rushton, J.; et al. Using Mixed Methods to Assess Food Security and Coping Strategies: A Case Study among Smallholders in the Andean Region. Food Secur. 2017, 9, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Qualitative Research in Psychology Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hancock, D.R.; Algozzine, B. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers, 3rd ed.; Teachers College Press: Columbia, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Central Statistical Agency (CSA). The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Central Statistical Agency Report on Area and Production of Major Crops. Stat. Bull. 2016, 1, 584. [Google Scholar]
- Mengistie, D.; Kidane, D. Assessment of the Impact of Small-Scale Irrigation on Household Livelihood Improvement at Gubalafto District, North Wollo, Ethiopia. Agriculture 2016, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawit, D.; Balta, A. Review on Impact of Small Scale Irrigations in Household Food Security in Ethiopia. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 6, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chazovachii, B. The Impact of Small Scale Irrigation Schemes on Rural Livelihoods: The Case of Panganai Irrigation Scheme Bikita District Zimbabwe. J. Sustain. Dev. Afr. 2012, 14, 217–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kassa, M.; Gebrehiwot, N.T.; Mesfin, K.A.; Nyssen, J. Small-Scale Irrigation: The Driver for Promoting Agricultural Production and Food Security (The Case of Tigray Regional State, Northern Ethiopia) Irrigation & Drainage Systems Engineering Small-Scale Irrigation: The Driver for Promoting Agricultural Production and Food Security (The Case of Tigray Regional State, Northern Ethiopia). Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2015, 4, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yami, M. Sustaining Participation in Irrigation Systems of Ethiopia: What Have We Learned about Water User Associations? Water Policy 2013, 15, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, G.G.; Asfaw, K.K. Irrigation in Ethiopia: A Review. Acad. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Haileslassie, A.; Hagos, F.; Agide, Z.; Tesema, Z.E.; Hoekstra, D.; Langan, S.J. Institutions for Irrigation Water Management in Ethiopia: Assessing Diversity and Service Delivery; International Livestock Research Institute: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oates, N.; Hisberg, A.; Rodríguez Ros, J.; Solomon, H.; Ludi, E.; Marlet, S.; Jamin, J.Y. The Implications of State Intervention for Self-Governed Irrigation Schemes: Insights from Tigray, Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checkol, G.; Alamirew, T. Technical and Institutional Evaluation of Geray Irrigation Scheme in West Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. J. Spat. Hydrol. 2008, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Iticha, M.D. Review on the Impact of Small Scale Irrigation Scheme on Household Income and Poverty Reduction in Ethiopia. J. Resour. Dev. Manag. 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astatike, A.A. Assessing the Impact of Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes on Household Income in Bahir Dar Zuria Woreda, Ethiopia. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 7, 82–88. [Google Scholar]






| Variables | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Demographic | Age and gender |
| Household resources | Land access and irrigation season crops grown |
| Access to irrigation | Access to irrigation water and flexibility in irrigation based on crop type |
| Participation in extension | Participate in demonstrations, access to credit, and frequency of advisory service |
| Irrigation production | Own production (quintal), total irrigated area (ha), irrigation experience, average yield, and income (birr) |
| Challenges | Shortage of irrigable land, water shortage for irrigation, shortage of improved seed, high post-harvest loss, pests and disease, canal problem, siltation, lack of maintenance, price fluctuation, transport problems, and distance to market |
| Major opportunities | Food self-sufficiency, teaching their children, building a house, and purchasing livestock |
| Traditional Diversion | Dam | Modern Diversion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | Mean | ||
| Irrigation experience (year) | 21.61 | 15.19 | 19.33 | |
| Irrigation production | Total irrigated area (ha) | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| Own production (kg) | 2145 | 1892 | 1095 | |
| Income (birr) | 19,582.4 | 17,475.2 | 12,923.3 |
| Cereals | Vegetables | |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Diversion |  |  |
| Modern Diversion |  |  |
| Dam |  |  |
| (I) Major Sources of Irrigation Water | (J) Major Sources of Irrigation Water | Mean Difference (I–J) | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Traditional Diversion | Modern Diversion | 6659.09091 * | 0.007 | 1806.5069 | 11,511.6749 |
| Dam | 2107.14334 | 0.410 | −2924.4193 | 7138.7060 | |
| Modern Diversion | Traditional Diversion | −6659.09091 * | 0.007 | −11,511.6749 | −1806.5069 |
| Dam | −4551.94757 * | 0.010 | −8005.4714 | −1098.4237 | |
| Dam | Traditional Diversion | −2107.14334 | 0.410 | −7138.7060 | 2924.4193 |
| Modern Diversion | 4551.94757 * | 0.010 | 1098.4237 | 8005.4714 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammedshum, A.A.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Maathuis, B.H.P.; Teka, D. Integrating Socioeconomic Biophysical and Institutional Factors for Evaluating Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Northern Ethiopia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021704
Mohammedshum AA, Mannaerts CM, Maathuis BHP, Teka D. Integrating Socioeconomic Biophysical and Institutional Factors for Evaluating Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Northern Ethiopia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021704
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammedshum, Amina Abdelkadir, Chris M. Mannaerts, Ben H. P. Maathuis, and Daniel Teka. 2023. "Integrating Socioeconomic Biophysical and Institutional Factors for Evaluating Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Northern Ethiopia" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021704
APA StyleMohammedshum, A. A., Mannaerts, C. M., Maathuis, B. H. P., & Teka, D. (2023). Integrating Socioeconomic Biophysical and Institutional Factors for Evaluating Small-Scale Irrigation Schemes in Northern Ethiopia. Sustainability, 15(2), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021704







