Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment for Shallow Groundwater Well Users in Arid Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
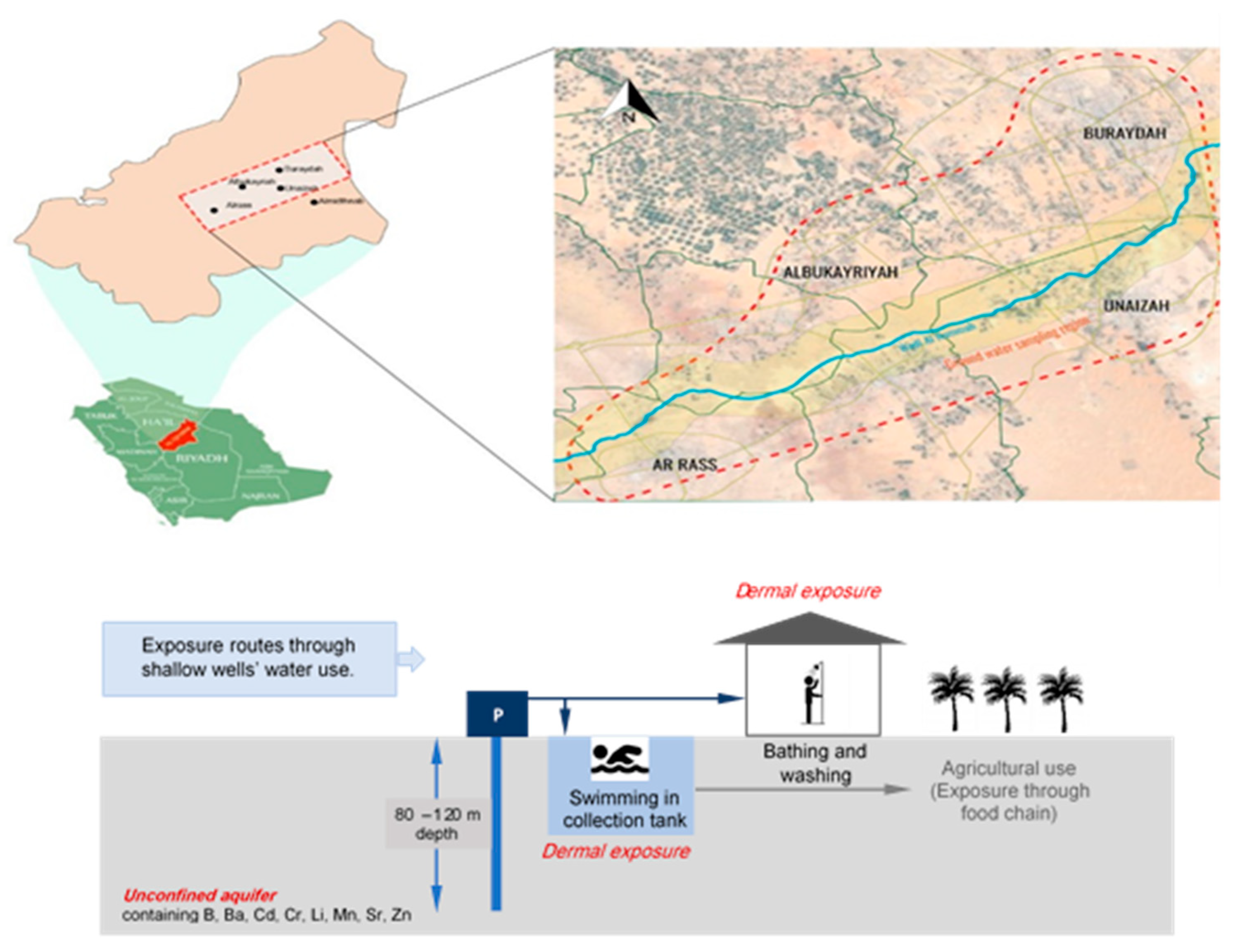
2.1. Case Study Area
2.2. Water Quality Sampling and Analysis
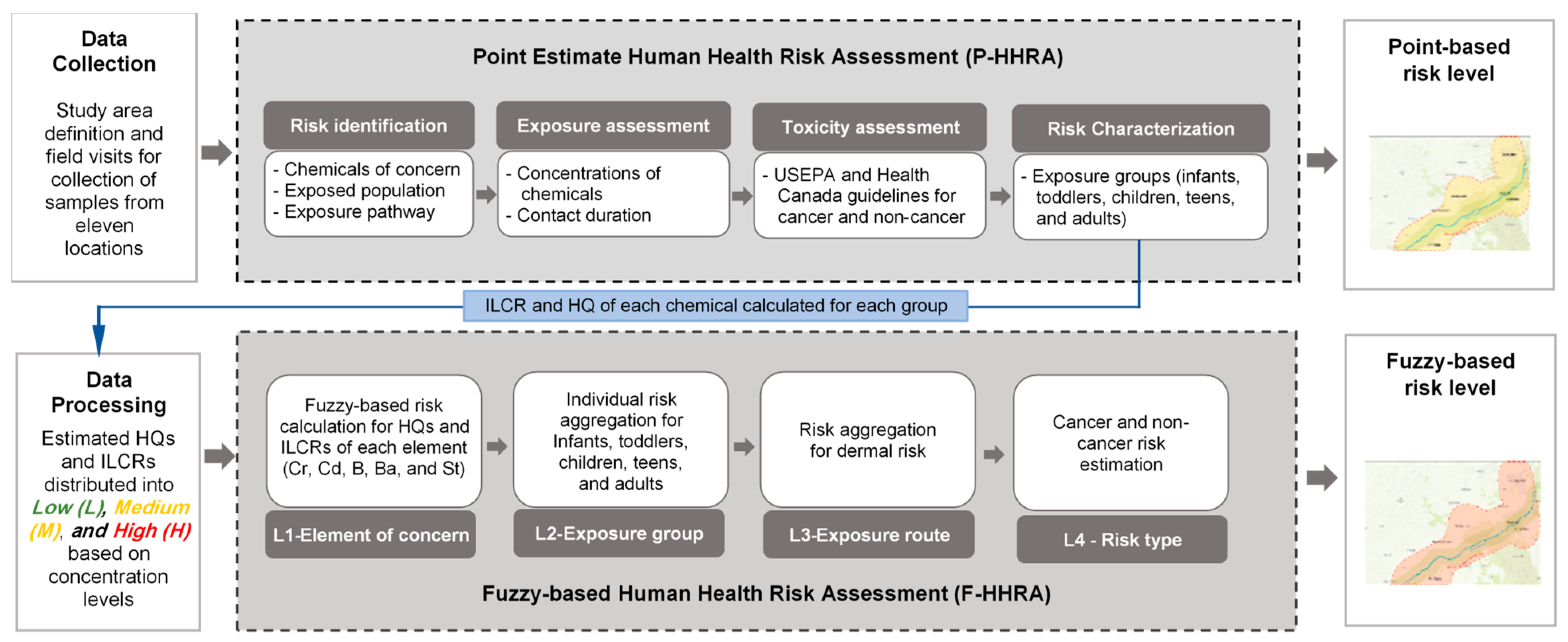
2.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Point Estimate Human Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment
- Step 1: Calculate cancer (Rc) and non-cancer (Rnc) risks for each heavy metal
- Step 2: Calculate cancer and non-cancer risk for each exposure group
- Step 3: Calculate cancer and non-cancer risk for dermal exposure route
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Monitoring
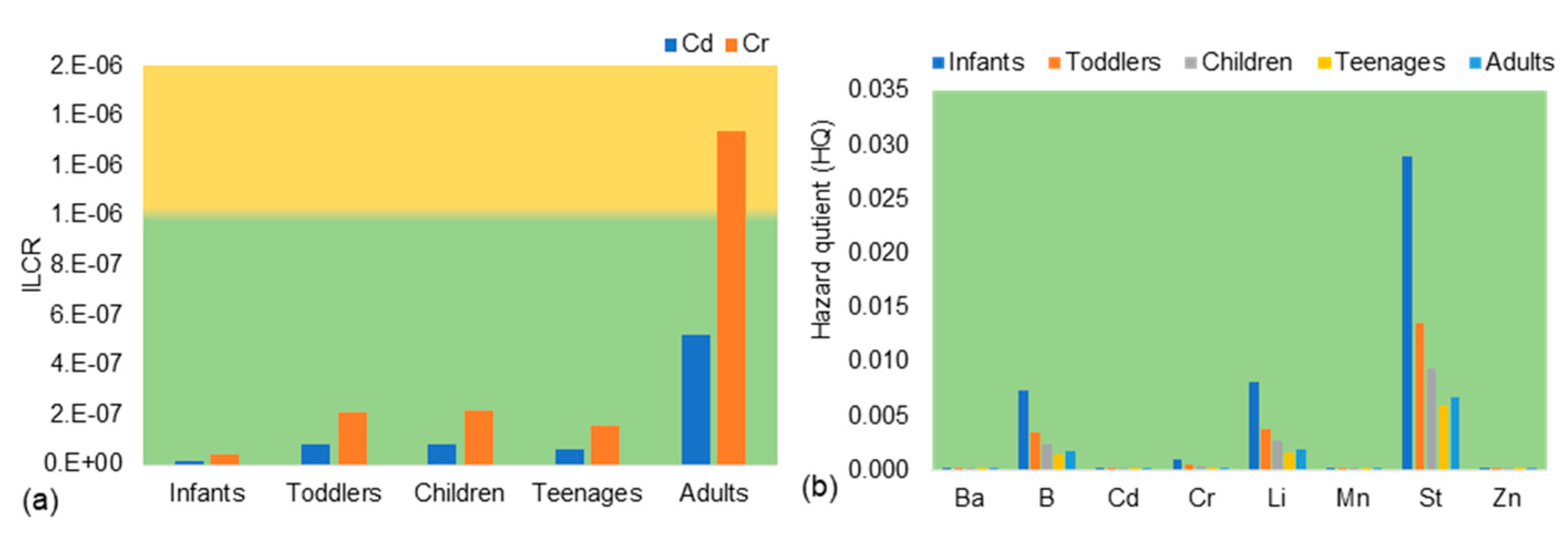
3.2. Point Estimate_HHRA
3.3. Fuzzy-Based HHRA
- Step 1: Calculate cancer and non-cancer risk for different heavy metals at level 1
- Step 2: Calculate cancer and non-cancer risks for different exposure groups
- Step 3: Calculate overall cancer and non-cancer risks for dermal exposure
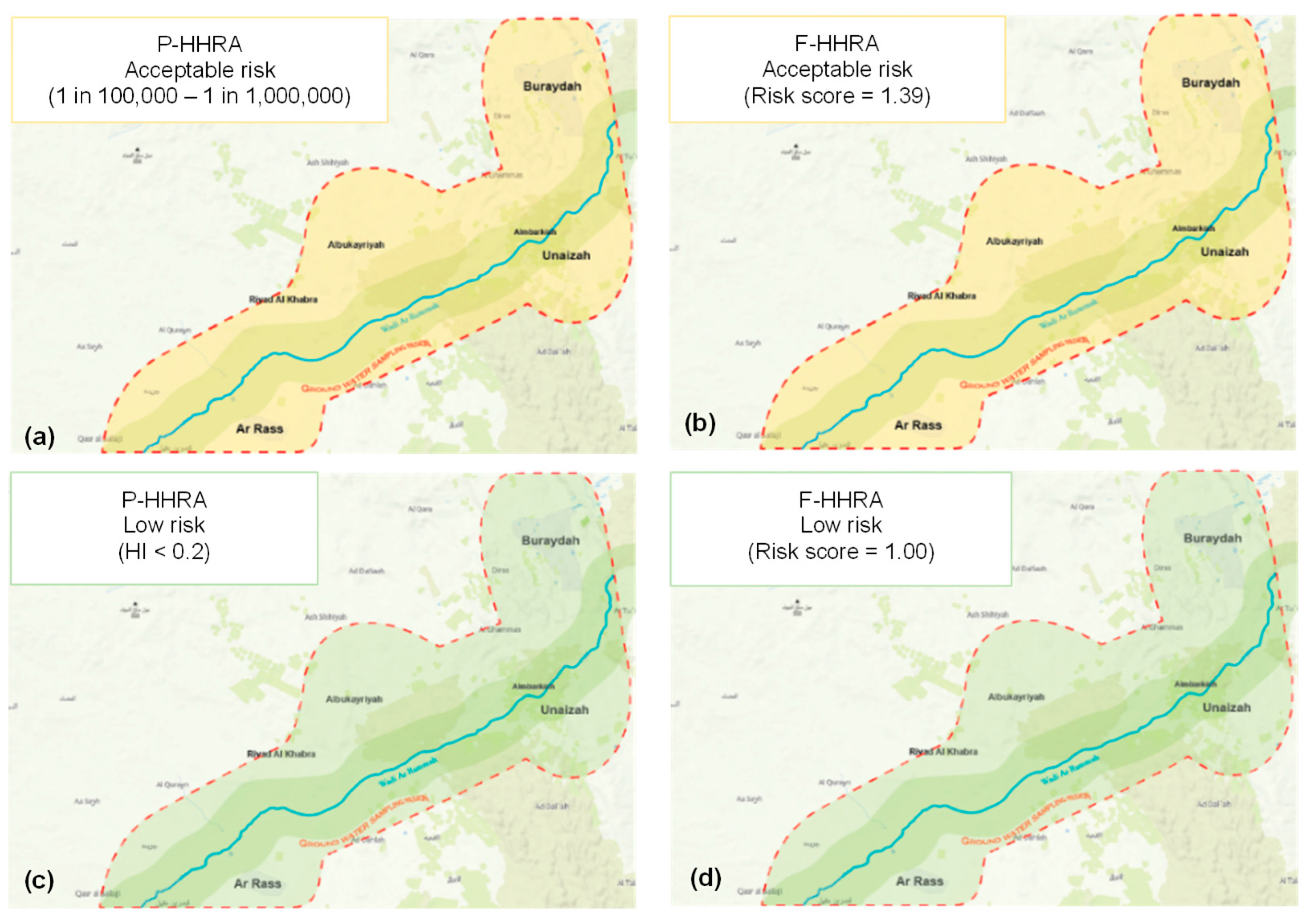
3.4. Scenario Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; Almesfer, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Alsubih, M. Groundwater Quality Studies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Prevalent Research and Management Dimensions. Water 2021, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H. Non-Cancer Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Groundwater of Qassim Region in Saudi Arabia. J. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 11, 115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi, F.; Khosravi, R.; Zarei, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Peganum Harmala Seed Extract, and Loaded on Peganum Harmala Seed Powdered Activated Carbon as New Adsorbent for Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solution. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhifeng, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, B. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediment at the Drinking Water Source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, E.M.; Mostafa, A.; Mokhtar, M.; Salman, S.A. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water on the Human Health, Assiut City, and Its Environs, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Imran, M.; Murtaza, B.; Arshad, N.M.; Nawaz, R.; Waheed, A.; Hammad, H.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K. Hydrogeochemical and Health Risk Investigation of Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater along River Sutlej Floodplain in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 5195–5209. [Google Scholar]
- Nizar, T.; Hamzaoui-Azaza, F.; Tzoraki, O.; Zammouri, M. Assessment of Potential Health Hazards of Trace Elements Contamination of Groundwater in a Shallow Aquifer: A Case Study in Guenniche (Northern Tunisia); Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Heavy Metals in Food Crops, Soil, and Water in the Lihe River Watershed of the Taihu Region and Their Potential Health Risks When Ingested. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2018, 615, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Bakhtavar, E.; Hewage, K.; Mohseni, M.; Sadiq, R. Heavy Metals Risk Assessment in Drinking Water: An Integrated Probabilistic-Fuzzy Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.; Hussain, F.; Lee, J.Y.; Shakoor, M.B.; Kwon, K.D. Groundwater Status in Pakistan: A Review of Contamination, Health Risks, and Potential Needs. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1713–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Paul, B. Assessment of Heavy Metal Toxicity Related with Human Health Risk in the Surface Water of an Industrialized Area by a Novel Technique. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 966–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Distribution and Contamination Risk Assessment of Dissolved Trace Metals in Surface Waters in the Yellow River Delta. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2013, 19, 1514–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Mian, H.R.; Dyck, R.; Mohseni, M.; Jasim, S.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Drinking Water Treatments for Arsenic and Manganese Removal and Health Risk Assessment in White Rock, Canada. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ptacek, C.J.; Groza, L.G.; Staples, R.; Blowes, D.W. Occurrence and Distribution of Emerging Contaminants in Mine-Impacted Lake Water and Potential Use as Co-Tracers of Anthropogenic Activity in the Subarctic Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Occurrence of Arsenic Contamination in Canada: Sources, Behavior and Distribution. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2006, 366, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazeli, J.; Ghalehaskar, S.; Morovati, M.; Soleimani, H.; Masoumi, S.; Sani, A.R.; Saghi, M.H.; Rastegar, A. Health Risk Assessment Techniques to Evaluate Non-Carcinogenic Human Health Risk Due to Fluoride, Nitrite and Nitrate Using Monte Carlo Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis in Groundwater of Khaf County, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 1793–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djahed, B.; Kermani, M.; Farzadkia, M.; Taghavi, M.; Norzaee, S. Exposure to Heavy Metal Contamination and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment Using Monte Carlo Simulation: A Study in the Southeast Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodrud-Doza, M.; Dida, S.M.; Islam, U.I.; Hasan, M.T.; Alam, F.; Haque, M.M.; Rakib, M.A.; Asad, M.A.; Rahman, M.A. Groundwater Pollution by Trace Metals and Human Health Risk Assessment in Central West Part of Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundranayagam, J.P. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using WQI and GIS Techniques, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu, India, Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4179–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.S.; Rana, S.; Yamazaki, S.; Aono, T.; Yoshida, S. Health Risk Assessment for Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Heavy Metal Exposures from Vegetables and Fruits of Bangladesh. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2017, 3, 1291107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vig, N.; Ravindra, K.; Mor, S. Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment of Groundwater and Associated Health Risks around Coal Thermal Power Plant, Punjab, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 6259–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Shah, M.H. Health Risk Assessment of Metals in Surface Water from Freshwater Source Lakes, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2013, 19, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhaddya, M.L. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals from Surface Water of Chott Merouane, Algeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 2177–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, N.; Ya’u, M.; Babandi, A. Heavy Metals Concentration and Human Health Risk Assessment in Groundwater and Table Water Sold in Tudun Murtala Area, Nassarawa Local Government Area, Kano State, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2019, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, H.E.S. Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination in Surface Sediments of Sabratha, Northwest Libya. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yu, H. Human Activities and Climate Variability Affecting Inland Water Surface Area in a High Latitude River Basin. Water 2020, 12, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qin, X.; Zeng, G.; Li, J. Impacts of Human Activity Modes and Climate on Heavy Metal ‘Spread’ in Groundwater Are Biased. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitsazan, M.; Aghazadeh, N.; Mirzaee, Y.; Golestan, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Impact of Anthropogenic Activity on Groundwater Quality in Suburban Area of Urmia City, Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Espinar, J.A.; Chica-Olmo, M. Impacts of Anthropogenic Activities on Groundwater Quality in a Detritic Aquifer in SE Spain. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Xue, C.; Wu, J. Progress, Opportunities, and Key Fields for Groundwater Quality Research under the Impacts of Human Activities in China with a Special Focus on Western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13224–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brima, E.I.; AlBishri, H.M. Major and Trace Elements in Water from Different Sources in Jeddah City, KSA. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial Metal Pollution in Water and Probabilistic Assessment of Human Health Risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.K.; Du, X.; Wang, J. Environment Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Fresh Water Resources of the Athabasca River Basin, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.Z.; Niyazi, B.A.M. Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Associated Health Risk in the Arid Environment, Western Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9628–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, G.; Ehenzi, J.; Jafari, H.; Moore, F.; Kazemi, G.A. Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Soil and Groundwater Resources in Arid Areas: A Case Study of the Mojen Plain, Northeast Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- üçüksümbül, A.; Akar, A.T.; Tarcan, G. Source, degree and potential health risk of metal(loid)s contamination on the water and soil in the Söke Basin, Western Anatolia, Turkey. Environ. Monit Assess 2022, 194, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, O.A. Groundwater Quality Patterns and Spatiotemporal Change in Depletion in the Regions of the Arabian Shield and Arabian Shelf. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H. Performance Assessment Framework for Groundwater Treatment Plants in Arid Environments: A Case of Buraydah, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Aly, A.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Sallam, A.S.; Al-Shayaa, M.S. Hydrochemical Characterization of Groundwater under Agricultural Land in Arid Environment: A Case Study of Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Saravanan, M.; Ponraj, M.; Selvam, M.; Pugazhendhi, A. A Critical Review of Advanced Nanotechnology and Hybrid Membrane Based Water Recycling, Reuse, and Wastewater Treatment Processes. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 132867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panqing, Y.; Abliz, A.; Xiaoli, S.; Aisaiduli, H. Human Health-Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil Based on Monte Carlo Simulation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, B.; Nambi, I.M.; Govindarajan, S.K. Human Health Risk Assessment for Exposure to BTEXN in an Urban Aquifer Using Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods: A Case Study of Chennai City, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Gharehchahi, E.; Badeenezhad, A.; Parseh, I.; Khaksefidi, R.; Golaki, M.; Dehbandi, R.; Azhdarpoor, A.; Derakhshan, Z.; Rodriguez-Chueca, J.; et al. Nitrate in Groundwater Resources of Hormozgan Province, Southern Iran: Concentration Estimation, Distribution and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment Using Monte Carlo Simulation. Water 2022, 14, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarella, G.; Masciale, R.; Maggi, S.; Vurro, M.; Castrignanò, A.A. A Probabilistic Approach to Assess the Risk of Groundwater Quality Degradation. In Geospatial Technology for Human Well-Being and Health; Faruque, F.S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, O.A.; Ahmed, M.; Cardace, D.; Boving, T.; Akanda, A.S. Assessment of Modern Recharge to Arid Region Aquifers Using an Integrated Geophysical, Geochemical, and Remote Sensing Approach. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyousef, R.A.; Alfaifi, H.J.; Zaidi, F.K.; Al-Hashim, M. Geostatistical and pollution index-based approach for assessing heavy metal pollution in the Cambro-Ordovician Saq Aquifer in Central Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varginia Department of Health, Beurue of Toxic Substances. Fact Sheet on Lithium. Available online: https://files.knowyourh2o.com/Waterlibrary/privatewell/lithium.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- IARC. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/agents-classified-by-the-iarc/ (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- MEWA. Specifications and Guidelines for Different Types of Water; Ministry of Environment, Water, and Agriculture, Deputy Ministry for Water: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition; EPA/600/R-09/052F; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality Summary Table; Prepared by the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on Drinking Water of the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on Health and the Environment March 2006. Environments (October 2014):1–16; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Health Canada. Part V: Guidance on Human Health Detailed Quantitative Risk Assessment for Chemicals (DQRAChem); Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2010; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- 2018 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Tables; Office of Water U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Sullivan, P.J.; Agardy, F.J.; Clark, J.J.J. Living with the Risk of Polluted Water, Chapter in The Environmental Science of Drinking Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 143–196. [Google Scholar]
- Aendo, P.; Netvichian, R.; Thiendedsakul, P.; Khaodhiar, S.; Tulayakul, P. Carcinogenic Risk of Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cr and Critical Ecological Risk of Cd and Cu in Soil and Groundwater around the Municipal Solid Waste Open Dump in Central Thailand. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 2022, 3062215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SASO 701 and Mkg 149; Un-Bottled Drinking Water. Saudi Arabian Standards Organization (SASO): Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2000. (In Arabic)
- DNR; EPA. Health Advisory Levels, Drinking Water Standards, Health Advisories, Toxic Substances, and Disease Registry. In Drinking Water & Groundwater Quality Standards/Advisory Levels: Table I—Drinking Water & Groundwater Quality Health Standards/Advisory Levels; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- KSA Vision 2030. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/ (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Spickett, J.; Katscherian, D.; Brown, H.; Rumchev, K. Health impact assessment: Improving its effectiveness in the enhancement of health and well-being. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendi, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Oyadeyi, A.T.; Adeyemi, A.A. Assessment of heavy metals contamination and associated risks in shallow groundwater sources from three different residential areas within Ibadan metropolis, southwest Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. 2017 Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, T.; Foster, S.; Kemper, K.; Garduno, H.; Nanni, M. Groundwater Monitoring Requirements for Managing Aquifer Response and Quality Threats; Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools, Technical Report, The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, B. Public awareness of drinking water safety and contamination accidents: A case study in Hainan Province, China. Water 2018, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, G.; Mlinárik, L.; Török, Á. Adsorption and chemical precipitation of lead and zinc from contaminated solutions in porous rocks: Possible application in environmental protection. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 122, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanu, L.D.; Kranjac-Berisavljevic, G.; Cobbina, S.J. The use of local materials to remove heavy metals for household-scale drinking water treatment: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 23, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Heavy Metal | Symbol | Maximum Allowable Concentration (MAC) (ppb) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KSA 1 | USEPA 2 | Health Canada 3 | |||
| 1 | Boron | B | 2.4 | - | 5.0 |
| 2 | Barium | Ba | 1.3 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 3 | Cadmium | Cd | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| 4 | Chromium | Cr | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| 5 | Lithium | Li | - | - | - |
| 6 | Manganese | Mn | 0.4 | - | 0.12 |
| 7 | Strontium | Sr | - | - | 7.0 |
| 8 | Zinc | Zn | 3.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Risk Factors | Units | Infants | Toddlers | Children | Teenagers | Adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average time (AT) | day | 210 | 1610 | 2555 | 2920 | 10,950 |
| Exposure duration (ED) | year | 0.583 | 4.417 | 7 | 8 | 30 |
| Exposure frequency (EF) | day/year | 365 | 365 | 365 | 365 | 365 |
| Mean daily water intake b | Liters | 0.287 | 0.340 | 0.453 | 0.673 | 1.090 |
| Time of dermal exposure (ET) | hours/day | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| Skin surface area (SA) | cm2 | 6030 | 6640 | 8660 | 12,000 | 18,000 |
| Unit conversion factor (CF) | L/cm3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Mean body weight (kg) b | Kg | 6.44 | 14.88 | 28.15 | 61.51 | 80.73 |
| Age range | years | 0 to <0.583 | 0.583 to <5 | 5 to <12 | 12 to <20 | 20 to 80 |
| Fraction for lifetime cancer risk a | - | 0.006 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.75 |
| Heavy Metals | Symbol | Reference Dose (RfD) (mg/kg/day) | Slope Factor (SF) (mg/kg/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barium | Ba | 0.2 | - |
| Boron | B | 0.2 | - |
| Cadmium | Cd | 0.0005 | 6.1 |
| Chromium | Cr | 0.003 | 0.5 |
| Lithium | Li | 0.002 | - |
| Manganese | Mn | 0.14 | - |
| Strontium | St | 0.6 | - |
| Zinc | Zn | 0.3 | - |
| Cancer Risk 1–3 | Non-Cancer Risk 1–2 | Risk Level Color Coding Scheme | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Level | Range | Level | |
| <10−6 | Low | <0.2 | Low | |
| 10−6–10−5 | Acceptable | 0.2–0.9 | Acceptable | |
| >10−5 | High | >0.9 | High | |
| No. | Scenario | P-HHRA | F-HHRA |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | In 90% of the samples, boron levels pose low and 10% high non-cancer health risk to infants. | Medium Risk (HQ = 0.2) | Acceptable (1.4) |
| S2 | In 80% of the samples, boron levels pose medium, 10% low, and 10% high non-cancer risk to infants. | Medium risk * (HQ = 0.81) | Moderately acceptable * (3.0) |
| S3 | In 60% of samples, boron levels pose high, 30% medium, and 10% low non-cancer risk to infants. | Medium Risk (HQ = 0.79) | High (4.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thabit, H.; Haider, H.; Ghumman, A.R.; Alattyih, W.; Alodah, A.; Hu, G.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment for Shallow Groundwater Well Users in Arid Regions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215792
Thabit H, Haider H, Ghumman AR, Alattyih W, Alodah A, Hu G, Shafiquzzaman M. Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment for Shallow Groundwater Well Users in Arid Regions. Sustainability. 2023; 15(22):15792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215792
Chicago/Turabian StyleThabit, Hussein, Husnain Haider, Abdul Razzaq Ghumman, Wael Alattyih, Abdullah Alodah, Guangji Hu, and Md. Shafiquzzaman. 2023. "Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment for Shallow Groundwater Well Users in Arid Regions" Sustainability 15, no. 22: 15792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215792
APA StyleThabit, H., Haider, H., Ghumman, A. R., Alattyih, W., Alodah, A., Hu, G., & Shafiquzzaman, M. (2023). Fuzzy-Based Human Health Risk Assessment for Shallow Groundwater Well Users in Arid Regions. Sustainability, 15(22), 15792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215792








