Removal of Magnesium in Zinc Hydrometallurgical System via Freezing Crystallization: From Laboratory Experiments to Industrial Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Feasibility Analysis
2.4. Experiment Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Freezing Crystallization Experimental Conditions
3.1.1. Effect of Temperature on the Mg Removal Efficiency
3.1.2. Effect of Time on the Mg Removal Efficiency
3.1.3. Effect of H2SO4 Concentration on the Mg Removal Efficiency
3.1.4. Effect of Adding Amount of Crystal Seed on the Mg Removal Efficiency
3.1.5. Effect of Agitation Intensity on the Mg Removal Efficiency
3.2. Verification Experiments
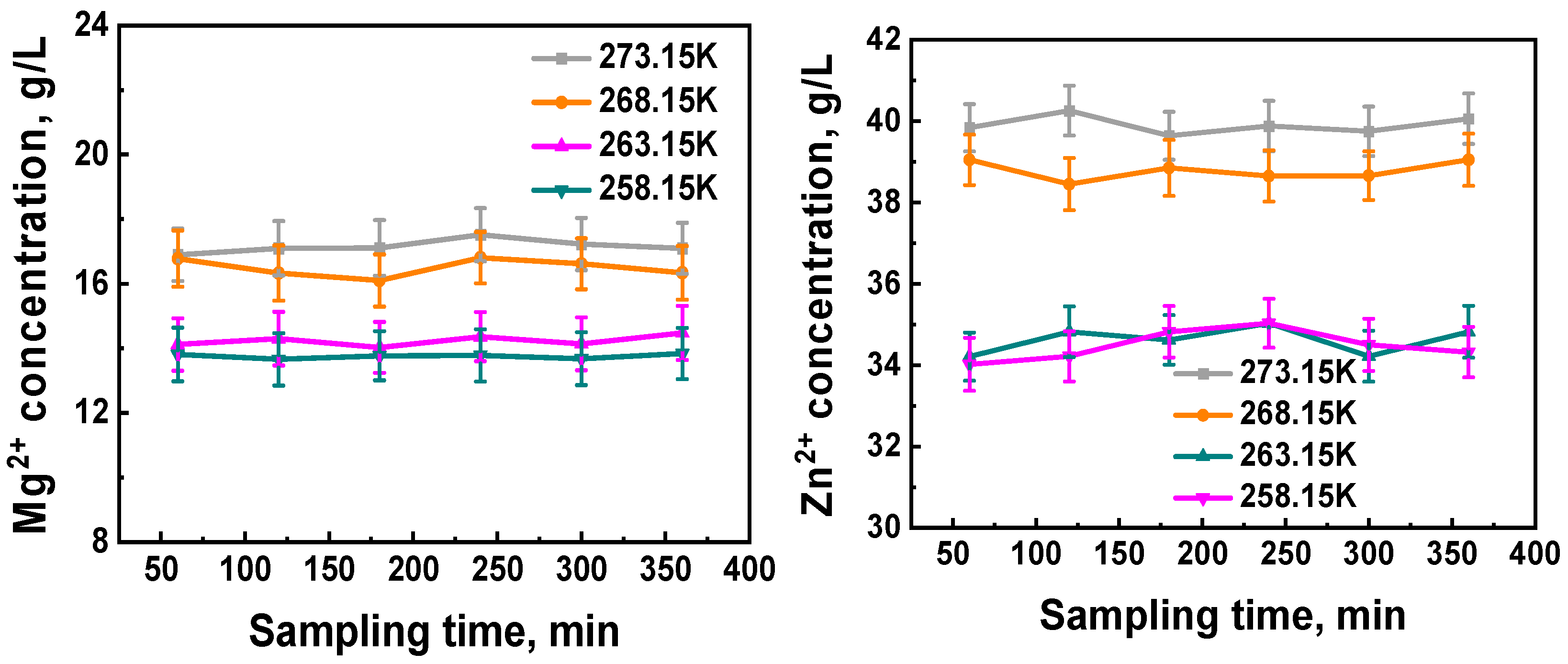
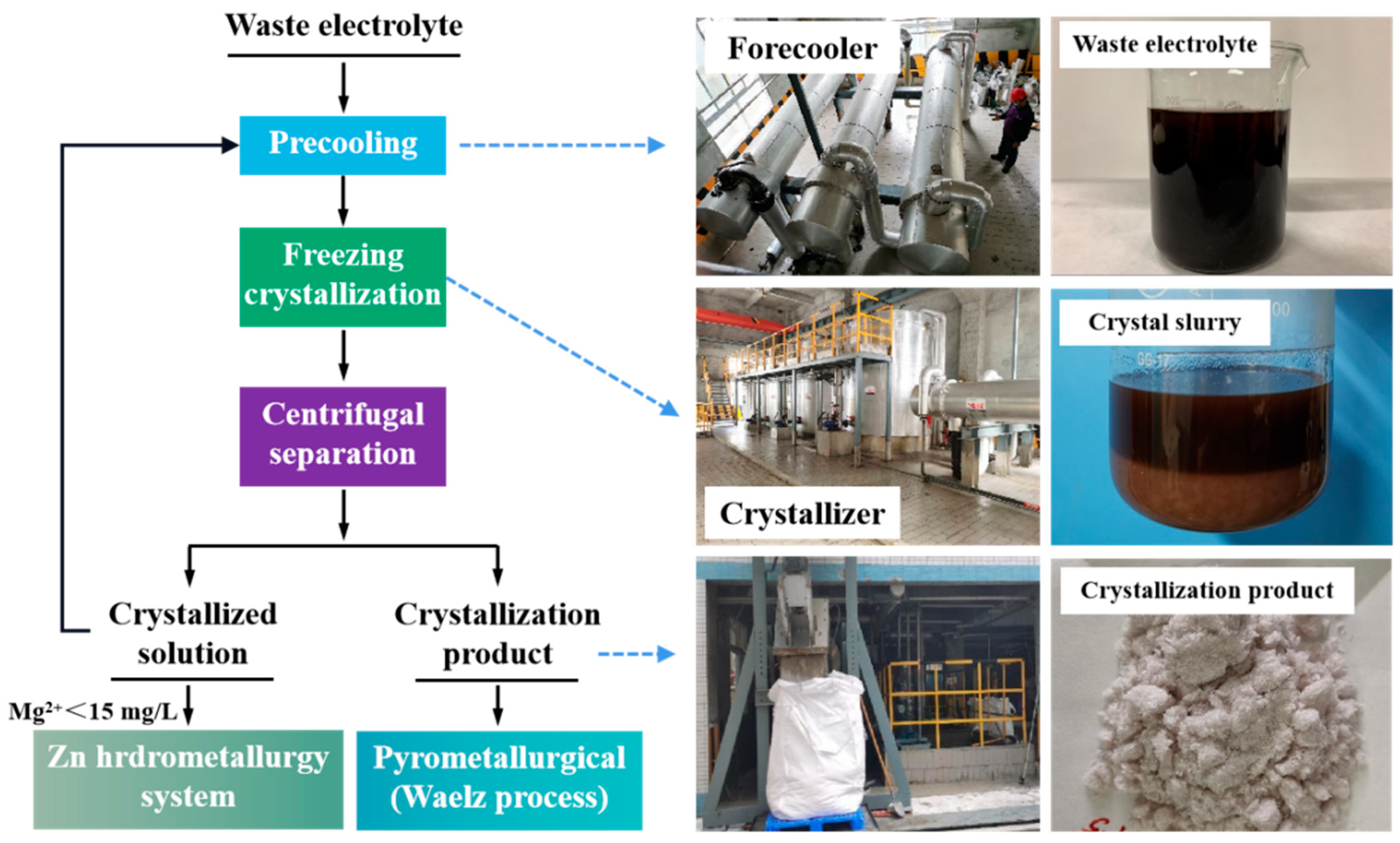
3.3. Industrial Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booster, J.; Van Sandwijk, A.; Reuter, M. Mg removal in the electrolytic Zn industry. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, I.; Newman, O.; Palmer, D. Water balance and magnesium control in electrolytic zinc plants using the E.Z. selective zinc precipitation process. Metall. Trans. B 1980, 11, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Matthew, I.G.; Hall, P.G. The development and application of the selective zinc precipitation process for controlling impurities in electrolytic zinc plant circuits. In Papers Presented at the Tasmania Conference 1977; The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Carlton, Australia, 1977; pp. 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Eksteen, J.; Pelser, M.; Onyango, M.; Lorenzen, L.; Aldrich, C.; Georgalli, G. Effects of residence time and mixing regimes on the precipitation characteristics of CaF2 and MgF2 from high ionic strength sulphate solutions. Hydrometallurgical 2008, 91, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Sato, H.; Sakaki, S.; Sugita, Y. Theoretical study of Mg fluoride in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 10553–10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalli, G.; Eksteen, J.; Pelser, M.; Lorenzen, L.; Onyango, M.S.; Aldrich, C. Fluoride based control of Ca and Mg concentrations in high ionic strength base metal sulphate solutions in hydrometallurgical circuits. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K. An approach to reduce magnesium from zinc electrolyte with recovery of zinc from disposed residue of an effluent treatment plant. Hydrometallurgical 1990, 24, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, P.; Agatzini, S. Simultaneous solvent extraction of cobalt and nickel in the presence of manganese and Mg from sulfate solutions by Cyanex 301. Hydrometallurgical 2004, 72, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D. Mechanism and process for the extraction of lithium from the high Mg brine with N,N-bis(2-ethylhexyl)-2-methoxyacetamide in kerosene and FeCl3. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.; Mansur, M. Selection of a synergistic solvent extraction system to remove calcium and magnesium from concentrated nickel sulfate solutions. Hydrometallurgical 2018, 175, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 16th ed.; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C. Purification of synthetic laterite leach solution by solvent extraction using D2EHPA. Hydrometallurgical 2000, 56, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakarinen, J.; Paatero, E. Effect of temperature on Mn-Ca selectivity with organophosphorus acid extractants. Hydrometallurgical 2011, 106, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.; Moradkhani, D.; Salarirad, M.M. Separation of zinc from manganese, magnesium, calcium and cadmium using batch countercurrent extraction simulation followed by scrubbing and stripping. Hydrometallurgical 2015, 154, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Jin, X.; Li, X.; Zhen, Y.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, M. New process for removing magnesium from waste electrolytes of zinc hydrometallurgical using freezing crystallization. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol. Min. Metall.) 2021, 52, 4219–4226. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Gu, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Fu, J. Separation of manganese from calcium and magnesium in sulfate solutions via carbonate precipitation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnanelli, F.; Garavini, M.; Veglio, F.; Toro, L. Preliminary screening of purification processes of liquor leach solutions obtained from reductive leaching of low grade manganese ores. Hydrometallurgical 2004, 71, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, h.; Lawrancel, G.; Wanless, E. Solubility of calcium sulfate salts in acidic manganese sulfate solutions from 30 to 105 °C. Hydrometallurgical 2007, 86, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himawan, C.; Kramer, H.; Witkamp, G. Study on the recovery of purified MgSO4·7H2O crystals from industrial solution by eutectic freezing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Mei, X.; Jiang, M. Separation of boron and magnesium by stepwise crystallization of sulfuric acid leachate of high-magnesium borate minerals. Hydrometallurgical 2021, 204, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Li, X.; Zhen, Y.; Luo, X.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, M. Determination of the solubility of MgSO4 in the Zinc hydrometallurgical system within the temperature range of 263.15 K–293.15 K. Can. Metall. Q. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbu, F.; Iulian, O.; Ion, A.; Ion, I. Activity Coefficients of Electrolytes in the NaCl + Na2SO4 + H2O Ternary System from Potential Difference Measurements at (298.15, 303.15, and 308.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 4935–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D. Molecular Self-Assembly, Nucleation Kinetics And Cluster Formation Associated With Solution Crystallization. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Fan, F.; Qing, B.; Shao, F.; Lei, F.; Deng, X. Green synthesis of the excellent magnesium oxysulfate whiskers under controlled reaction conditions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 195, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
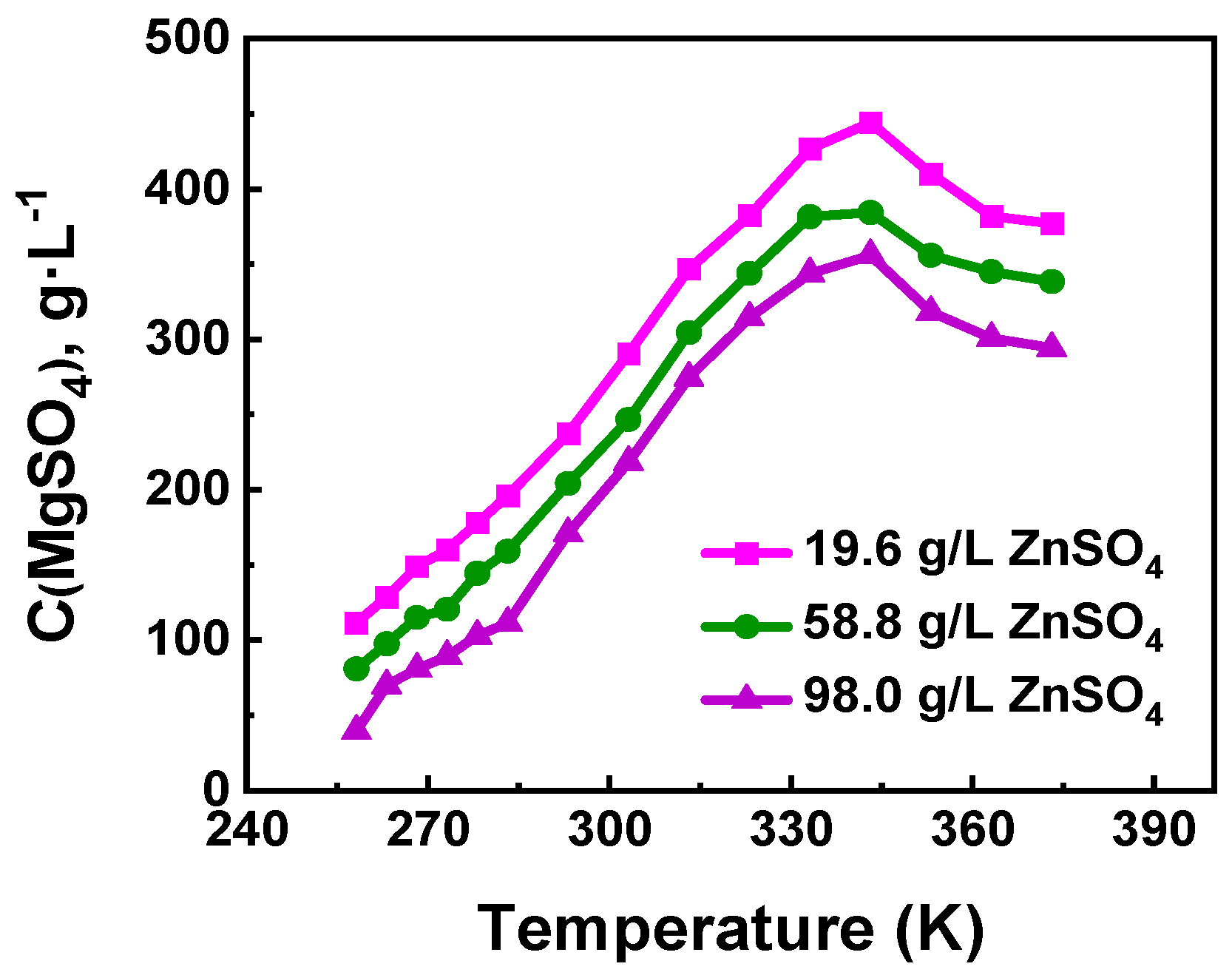



| Zn | Mg | H2SO4 | Mn | Pb | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52.50 | 23.60 | 163.70 | 4.50 | 0.002 | 0.082 |
| Components | Pre-Crystallization | Crystallized Solution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 273.15 K | 268.15 K | 263.15 K | 258.15 K | ||
| Mg2+ concentration/(g/L) | 23.60 | 17.16 | 16.50 | 14.24 | 13.76 |
| Zn2+ concentration/(g/L) | 52.50 | 39.91 | 38.79 | 34.62 | 34.49 |
| Mg content/% | - | 5.96 | 5.65 | 5.56 | 5.42 |
| Zn content/% | - | 11.67 | 11.91 | 11.66 | 11.73 |
| Phase | MgSO4∙7H2O | ZnSO4∙7H2O | MnSO4 | Pb | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 53.37 | 43.79 | 0.97 | 0.18 × 10−3 | 0.62 × 10−3 |
| Date | Mg2+ Concentration in Waste Electrolyte (g/L) | Mg2+ Concentration in Crystalized Solution (g/L) | Wet Weight of Crystal Product (t) | Mg Content in Crystal Product (%) | Yield of Metal Mg (t) | Total Waste Electrolyte Volume (m3) | Periods (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| August 2021 | 27.20 | 13.64 | 155.06 | 5.98 | 9.01 | 660.00 | 22.00 |
| September 2021 | 25.40 | 14.01 | 363.08 | 9.70 | 21.75 | 1975.00 | 23.00 |
| October 2021 | 26.43 | 13.23 | 350.70 | 8.70 | 19.68 | 3000.00 | 28.00 |
| November 2021 | 26.37 | 14.22 | 257.52 | 8.80 | 13.96 | 2833.00 | 21.00 |
| December 2021 | 27.06 | 14.21 | 210.62 | 9.20 | 13.37 | 2522.00 | 20.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; Zhen, Y.; Li, X.; Du, M.; Luo, X.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, M. Removal of Magnesium in Zinc Hydrometallurgical System via Freezing Crystallization: From Laboratory Experiments to Industrial Application. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316275
Jin X, Zhen Y, Li X, Du M, Luo X, Wei C, Deng Z, Li M. Removal of Magnesium in Zinc Hydrometallurgical System via Freezing Crystallization: From Laboratory Experiments to Industrial Application. Sustainability. 2023; 15(23):16275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316275
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xin, Yong Zhen, Xingbin Li, Min Du, Xingguo Luo, Chang Wei, Zhigan Deng, and Minting Li. 2023. "Removal of Magnesium in Zinc Hydrometallurgical System via Freezing Crystallization: From Laboratory Experiments to Industrial Application" Sustainability 15, no. 23: 16275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316275
APA StyleJin, X., Zhen, Y., Li, X., Du, M., Luo, X., Wei, C., Deng, Z., & Li, M. (2023). Removal of Magnesium in Zinc Hydrometallurgical System via Freezing Crystallization: From Laboratory Experiments to Industrial Application. Sustainability, 15(23), 16275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316275






