Does ChatGPT Play a Double-Edged Sword Role in the Field of Higher Education? An In-Depth Exploration of the Factors Affecting Student Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
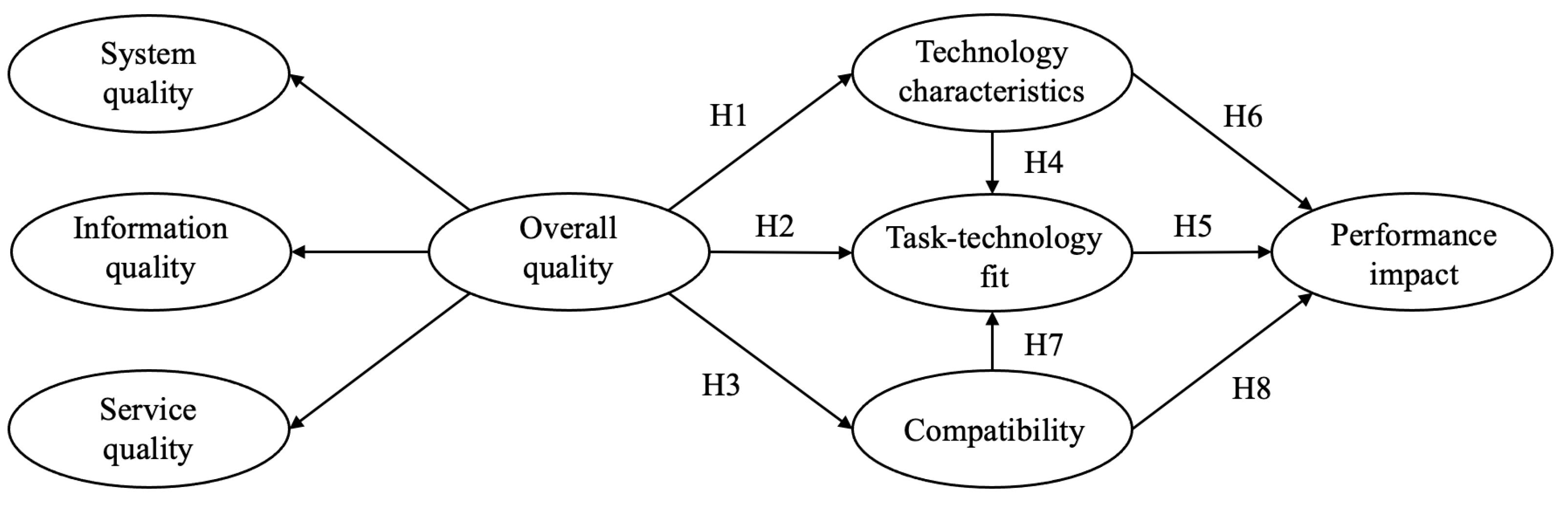
2. Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
2.1. ChatGPT in Education
2.2. Overall Quality
2.3. Task–Technology Fit
2.4. Compatibility
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design and Questionnaire Design
3.2. Data Collection
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Assessment of Measurement Model
4.2. Assessment of Structural Model
4.3. Path Analysis
4.4. Importance–Performance Map Analysis
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Sun, M.; Luo, J.; Li, T.; Wang, M. How to harness the potential of ChatGPT in education? Knowl. Manag. E-Learn. 2023, 15, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, M.M.; Almaiah, M.A.; Al-Rahmi, W.M. The role of compatibility and task-technology fit (TTF): On social networking applications (SNAs) usage as sustainability in higher education. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161668–161681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ruiz, L.M.; Moll-López, S.; Nuñez-Pérez, A.; Moraño-Fernández, J.A.; Vega-Fleitas, E. ChatGPT Challenges Blended Learning Methodologies in Engineering Education: A Case Study in Mathematics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimpel, H.; Hall, K.; Decker, S.; Eymann, T.; Lämmermann, L.; Mädche, A.; Röglinger, M.; Ruiner, C.; Schoch, M.; Schoop, M. Unlocking the Power of Generative AI Models and Systems Such as GPT-4 and ChatGPT for Higher Education: A Guide for Students and Lecturers; Hohenheim Discussion Papers in Business, Economics and Social Sciences: Stuttgart, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, I.A.; Lian, Q.L.; Sun, D. Autonomous travel decision-making: An early glimpse into ChatGPT and generative AI. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 56, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, A.; Safranek, C.W.; Huang, T.; Socrates, V.; Chi, L.; Taylor, R.A.; Chartash, D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e45312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerbaum, D.O. Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) with Chat GPT for Accounting—A business case. SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnke, L.; Moorhouse, B.L.; Zou, D. Exploring generative artificial intelligence preparedness among university language instructors: A case study. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overono, A.L.; Ditta, A.S. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence: A Clarion Call for Higher Education to Redefine Learning and Reimagine Assessment. Coll. Teach. 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, S.; Qiao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Dam, S.K.; Thwal, C.M.; Tun, Y.L.; Huy, L.L. A complete survey on generative ai (aigc): Is chatgpt from gpt-4 to gpt-5 all you need? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.11717. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Guo, Y. Generative artificial intelligence empowers educational reform: Current status, issues, and prospects. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 1183162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratten, V.; Jones, P. Generative artificial intelligence (ChatGPT): Implications for management educators. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2023, 21, 100857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M. ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: Systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. In Proceedings of the Healthcare, Sydney, Australia, 23–24 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, R.; Yilmaz, F.G.K. The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy and motivation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, S.; Aithal, P. Effects of AI-Based ChatGPT on Higher Education Libraries. Int. J. Manag. Technol. Soc. Sci. (IJMTS) 2023, 8, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- King, M.R. ChatGPT. A conversation on artificial intelligence, chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2023, 16, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroughi, B.; Senali, M.G.; Iranmanesh, M.; Khanfar, A.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Annamalai, N.; Naghmeh-Abbaspour, B. Determinants of Intention to Use ChatGPT for Educational Purposes: Findings from PLS-SEM and fsQCA. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifenthaler, D.; Schumacher, C. Reciprocal Issues of Artificial and Human Intelligence in Education; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2023; Volume 55, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecki, A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, S.; Armstrong, L. Exploring the integration of ChatGPT in education: Adapting for the future. Manag. Sustain. Arab Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzenbauer, P. ChatGPT in physics education: A pilot study on easy-to-implement activities. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2023, 15, ep430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiper, M.C.; Fried, G.; Lupinek, J.; Nordstrom, H. Artificial intelligence in sport management education: Playing the AI game with ChatGPT. J. Hosp. Leis. Sport Tour. Educ. 2023, 33, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollny, S.; Schneider, J.; Di Mitri, D.; Weidlich, J.; Rittberger, M.; Drachsler, H. Are we there yet?—A systematic literature review on chatbots in education. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 654924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: An exploratory investigation. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 13943–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lai, C. Collaborating with ChatGPT in argumentative writing classrooms. Assess. Writ. 2023, 57, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrot, J.S. Using ChatGPT for second language writing: Pitfalls and potentials. Assess. Writ. 2023, 57, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situmorang, D.D.B.; Salim, R.M.A.; Ifdil, I.; Liza, L.O.; Rusandi, M.A.; Hayati, I.R.; Amalia, R.; Muhandaz, R.; Fitriani, A. The current existence of ChatGPT in education: A double-edged sword? J. Public Health 2023, 45, e799–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, A.; Shehata, B.; Adarkwah, M.A.; Bozkurt, A.; Hickey, D.T.; Huang, R.; Agyemang, B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, J. Engineering education in the era of ChatGPT: Promise and pitfalls of generative AI for education. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Salmiya, Kuwait, 1–4 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Opara, E.; Mfon-Ette Theresa, A.; Aduke, T.C. ChatGPT for teaching, learning and research: Prospects and challenges. Glob. Acad. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2023, 5, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.-M. How does task-technology fit influence cloud-based e-learning continuance and impact? Educ. Train. 2019, 61, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, S.; Mahmood, A.; Saleem, S.; Rashid, T.; Ikram, A. Students’ performance in online learning environment: The role of task technology fit and actual usage of system during COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 759227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, O.; Aldholay, A.; Abdullah, Z.; Ramayah, T. Online learning usage within Yemeni higher education: The role of compatibility and task-technology fit as mediating variables in the IS success model. Comput. Educ. 2019, 136, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obthani, F.S.; Ameen, A. Influence of overall quality and innovativeness on actual usage of smart government: An empirical study on the UAE public sector. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Ren, Y.; Nyagoga, L.M.; Stonier, F.; Wu, Z.; Yu, L. Future of education in the era of generative artificial intelligence: Consensus among Chinese scholars on applications of ChatGPT in schools. Future Educ. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, A. The impact of ChatGPT on blended learning: Current trends and future research directions. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2023, 7, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Kidman, G. The rise of generative artificial intelligence (AI) language models-challenges and opportunities for geographical and environmental education. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2023, 32, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Artificial Intelligence education for young children: Why, what, and how in curriculum design and implementation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, H.; Tedre, M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: Crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit. Creat. 2023, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, W.; Diab, H.; Rayan, A. Artificial Intelligence Generative Tools and Conceptual Knowledge in Problem Solving in Chemistry. Information 2023, 14, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. Introducing ChatGPT. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Gill, S.S.; Xu, M.; Patros, P.; Wu, H.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, K.; Fuller, S.; Singh, M.; Arora, P.; Parlikad, A.K. Transformative effects of ChatGPT on modern education: Emerging Era of AI Chatbots. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Owusu Ansah, L. Education in the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): Understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwiesch, C. Would chat GPT3 get a Wharton MBA. In A Prediction Based on Its Performance in the Operations Management Course Philadelphia; University of Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Grassini, S. Shaping the Future of Education: Exploring the Potential and Consequences of AI and ChatGPT in Educational Settings. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berşe, S.; Akça, K.; Dirgar, E.; Kaplan Serin, E. The role and potential contributions of the artificial intelligence language model ChatGPT. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H. Reflection on whether Chat GPT should be banned by academia from the perspective of education and teaching. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1181712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, H.H. ChatGPT Is Fun, But Not an Author; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; p. 313. [Google Scholar]
- Mijwil, M.M.; Hiran, K.K.; Doshi, R.; Dadhich, M.; Al-Mistarehi, A.-H.; Bala, I. ChatGPT and the future of academic integrity in the artificial intelligence era: A new frontier. Al-Salam J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 2, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.K.M.; Shamsan, M.A.A.; Hezam, T.A.; Mohammed, A.A. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation: Teachers and students’ voices. J. Engl. Stud. Arab. Felix 2023, 2, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensch, A.-C.; Ball, S.; Herklotz, M.; Kreuter, F. Seeing ChatGPT through Students’ Eyes: An Analysis of TikTok Data. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.05349. [Google Scholar]
- Shoufan, A. Exploring Students’ Perceptions of CHATGPT: Thematic Analysis and Follow-Up Survey. IEEE Access 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, C.H.; Bang, H.C.; Cao, L. Integrating ChatGPT into Online Education System in Vietnam: Opportunities and Challenges. 2023. Available online: https://osf.io/preprints/edarxiv/hqyut (accessed on 12 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, M.; Ghazi, M.; Ali, A.H.; Abed, S.A. ChatGPT: Open possibilities. Iraqi J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2023, 4, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, A.G.R.; Silva, G.J.S.; Arocutipa, J.P.F.; Berrios, H.Q.; Rodriguez, M.A.M.; Reyes, G.Y.; Lopez, H.R.P.; Teves, R.M.V.; Rivera, H.V.H.; Arias-Gonzáles, J.L. Effect of Chat GPT on the digitized learning process of university students. J. Namib. Stud. Hist. Politics Cult. 2023, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S.; Kaur, R. ChatGPT: Vision and challenges. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, F.; Tuhuteru, L.; Sampe, F.; Ausat, A.M.A.; Hatta, H.R. Analysing the role of ChatGPT in improving student productivity in higher education. J. Educ. 2023, 5, 14886–14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A. Assessing m-Health success in Bangladesh: An empirical investigation using IS success models. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2016, 29, 774–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Inf. Syst. Res. 1992, 3, 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2003, 19, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, L.A.; Kuo, T.H.; Lin, B. Influence of online learning skills in cyberspace. Internet Res. 2010, 20, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldholay, A.; Abdullah, Z.; Isaac, O.; Mutahar, A.M. Perspective of Yemeni students on use of online learning: Extending the information systems success model with transformational leadership and compatibility. Inf. Technol. People 2020, 33, 106–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wang, Q.; Roh, T. Do information and service quality affect perceived privacy protection, satisfaction, and loyalty? Evidence from a Chinese O2O-based mobile shopping application. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 56, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petter, S.; McLean, E.R. A meta-analytic assessment of the DeLone and McLean IS success model: An examination of IS success at the individual level. Inf. Manag. 2009, 46, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, R.; Thomander, H.; Laukkanen, E. DeLone & McLean IS success model in evaluating knowledge transfer in a virtual learning environment. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Soc. Change (IJISSC) 2010, 1, 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Aldholay, A.H.; Isaac, O.; Abdullah, Z.; Ramayah, T. The role of transformational leadership as a mediating variable in DeLone and McLean information system success model: The context of online learning usage in Yemen. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyoussef, I.Y. Acceptance of e-learning in higher education: The role of task-technology fit with the information systems success model. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, G.; Madan, P.; Jaisingh, P.; Bhaskar, P. Effectiveness of e-learning portal from students’ perspective: A structural equation model (SEM) approach. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 2019, 16, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhue, D.L.; Thompson, R.L. Task-technology fit and individual performance. MIS Q. 1995, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; Wang, S.-C. What drives mobile commerce?: An empirical evaluation of the revised technology acceptance model. Inf. Manag. 2005, 42, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarzouqi, A.; Aburayya, A.; Salloum, S.A. Prediction of user’s intention to use metaverse system in medical education: A hybrid SEM-ML learning approach. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 43421–43434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M. Evaluating the use of smartwatches for learning purposes through the integration of the technology acceptance model and task-technology fit. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2021, 37, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, T.J.; Klobas, J.E. A task–technology fit view of learning management system impact. Comput. Educ. 2009, 52, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotayo, F.O.; Haliru, A. Perception of task-technology fit of digital library among undergraduates in selected universities in Nigeria. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2020, 46, 102097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rahmi, A.M.; Shamsuddin, A.; Wahab, E.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alturki, U.; Aldraiweesh, A.; Almutairy, S. Integrating the role of UTAUT and TTF model to evaluate social media use for teaching and learning in higher education. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 905968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyoussef, I.Y. Massive open online course (MOOCs) acceptance: The role of task-technology fit (TTF) for higher education sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yao, J.; Tao, D.; Yang, T. Influence of individual-technology-task-environment fit on university student online learning performance: The mediating role of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.C.; Benbasat, I. Development of an instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting an information technology innovation. Inf. Syst. Res. 1991, 2, 192–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akour, I.A.; Al-Maroof, R.S.; Alfaisal, R.; Salloum, S.A. A conceptual framework for determining metaverse adoption in higher institutions of gulf area: An empirical study using hybrid SEM-ANN approach. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philemon, N.M.; Chibisa, A.; Mabusela, M.S. Acceptance of the GeoGebra Application in Learning Circle Theorems. Int. J. Learn. Teach. Educ. Res. 2022, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M. Towards an understanding of the factors affecting m-learning acceptance: Roles of technological characteristics and compatibility. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2015, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.N. E-learning system use and its outcomes: Moderating role of perceived compatibility. Telemat. Inform. 2016, 33, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkorful, V.; Barfi, K.A.; Baffour, N.O. Factors affecting use of massive open online courses by Ghanaian students. Cogent Educ. 2022, 9, 2023281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C.; Bernstein, I.H. Psychometric Theory New York; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.; Boudreau, M.-C. Structural equation modeling and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Anderson, R.E.; Babin, B.J.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective (Vol. 7); Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). 2017. Available online: https://books.google.com.tw/books?id=6z83EAAAQBAJ&dq=A%20Primer%20on%20Partial%20Least%20Squares%20Structural%20Equation%20Modeling%20 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, Z. Structural Equation Modeling Using AMOS Graphic; Penerbit Universiti Teknologi MARA: Selangor, Malaysia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión, G.C.; Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Roldán, J.L. Prediction-oriented modeling in business research by means of PLS path modeling: Introduction to a JBR special section. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4545–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.H.; Malhotra, A.; Segars, A.H. Knowledge management: An organizational capabilities perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2001, 18, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences New York; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. In New Challenges to International Marketing; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2009; pp. 277–319. [Google Scholar]
- O’brien, R.M. A caution regarding rules of thumb for variance inflation factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Gain more insight from your PLS-SEM results: The importance-performance map analysis. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 1865–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deli, D.; Candra, I. Dampak penggunaan media pembelajaran online pada mahasiswa UIB selama pandemi COVID-19. In Proceedings of the CoMBInES-Conference on Management, Business, Innovation, Education and Social Sciences, Online, 17–19 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Khan, S.; Khan, I.H. Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system. BenchCouncil Trans. Benchmarks Stand. Eval. 2023, 3, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, C.K.; Bhat, M.A.; Khan, S.T.; Subramaniam, R.; Khan, M.A.I. What drives students toward ChatGPT? An investigation of the factors influencing adoption and usage of ChatGPT. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santandreu Calonge, D.; Aman Shah, M.; Riggs, K.; Connor, M. MOOCs and upskilling in Australia: A qualitative literature study. Cogent Educ. 2019, 6, 1687392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Han, X.; Lyu, T.; Ho, W.-H.; Xu, Y.; Hsieh, T.-C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Task-technology fit analysis of social media use for marketing in the tourism and hospitality industry: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 2677–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, A.; Gupta, N.; Healy, L.; Kumar, Y.; Li, J.; Morreale, P. A Self-Served AI Tutor for Growth Mindset Teaching. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), New York, NY, USA, 4–6 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, W.M.; Gunasekara, A.; Pallant, J.L.; Pallant, J.I.; Pechenkina, E. Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2023, 21, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-S.; Wang, C.-H. Antecedences to continued intentions of adopting e-learning system in blended learning instruction: A contingency framework based on models of information system success and task-technology fit. Comput. Educ. 2012, 58, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, S.; Daniel, S.; Haque, R.; Belkina, M.; Hassan, G.M.; Grundy, S.; Lyden, S.; Neal, P.; Sandison, C. ChatGPT versus engineering education assessment: A multidisciplinary and multi-institutional benchmarking and analysis of this generative artificial intelligence tool to investigate assessment integrity. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2023, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Construct | Items | Source |
|---|---|---|
| System quality | I believe that… | [35,64] |
| SYQ1: ChatGPT is easy to use. | ||
| SYQ2: ChatGPT is flexible and easy to interact with. | ||
| SYQ3: My interaction with Chat GPT is clear and easy to understand. | ||
| Information quality | ChatGPT provides… | |
| IQ1: The latest knowledge. | ||
| IQ2: Accurate knowledge. | ||
| IQ3: Comprehensive knowledge. | ||
| IQ4: Systematic knowledge. | ||
| Service quality | I believe that… | |
| SEQ1: ChatGPT has a good feedback speed. | ||
| SEQ2: ChatGPT is a multi-functional and well-trained language model, which can provide code writing, language translation, text generation and other functions. | ||
| SEQ3: ChatGPT realizes interactive communication. | ||
| Compatibility | I believe that… | |
| CO1: ChatGPT is consistent with my learning values. | ||
| CO2: ChatGPT adapts to my learning style. | ||
| CO3: ChatGPT can meet my needs. | ||
| Technology characteristics | I believe that… | [33] |
| TEC1: ChatGPT enables me to acquire knowledge and complete learning tasks anywhere. | ||
| TEC2: ChatGPT is able to access apps on mobile devices and present knowledge to me in an appropriate way. | ||
| TEC3: ChatGPT shares the history of PC and mobile phone, so that I can view and learn anytime and anywhere. | ||
| Task–technology fit | I believe that… | [33,35] |
| TTF1: ChatGPT is suitable for helping me complete learning tasks. | ||
| TTF2: ChatGPT is necessary for my learning task. | ||
| TTF3: ChatGPT is integrated into all aspects of my learning. | ||
| Performance impact | I believe that… | [35] |
| PI1: ChatGPT helps me to complete the learning task faster. | ||
| PI2: ChatGPT has improved my academic efficiency. | ||
| PI3: ChatGPT helps me to review and eliminate errors in learning tasks. | ||
| PI4: ChatGPT helps me achieve my future learning goals. | ||
| PI5: ChatGPT helps me acquire new skills. |
| Sample | Category | Number | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 211 | 47.1 |
| Female | 237 | 52.9 | |
| Age | 18–22 | 352 | 78.6 |
| 23–27 | 96 | 21.4 | |
| Grade | Frosh | 43 | 9.6 |
| Sophomore | 80 | 17.8 | |
| Junior | 141 | 31.5 | |
| Senior | 158 | 35.3 | |
| Postgraduates | 26 | 5.8 |
| Constructs | Items | Loadings | α | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (>0.7) | (>0.7) | (>0.7) | (>0.5) | ||
| System quality | SYQ1 | 0.796 | 0.759 | 0.861 | 0.675 |
| SYQ2 | 0.849 | ||||
| SYQ3 | 0.819 | ||||
| Information quality | IQ1 | 0.824 | 0.832 | 0.888 | 0.666 |
| IQ2 | 0.771 | ||||
| IQ3 | 0.851 | ||||
| IQ4 | 0.816 | ||||
| Service quality | SEQ1 | 0.782 | 0.737 | 0.851 | 0.656 |
| SEQ2 | 0.845 | ||||
| SEQ3 | 0.802 | ||||
| Overall quality (Second-order) | SYQ | 0.826 | 0.783 | 0.874 | 0.697 |
| IQ | 0.839 | ||||
| SEQ | 0.841 | ||||
| Technology characteristics | TEC1 | 0.838 | 0.718 | 0.841 | 0.639 |
| TEC2 | 0.804 | ||||
| TEC3 | 0.754 | ||||
| Task–technology fit | TTF1 | 0.813 | 0.782 | 0.873 | 0.696 |
| TTF2 | 0.857 | ||||
| TTF3 | 0.832 | ||||
| Compatibility | CO1 | 0.855 | 0.771 | 0.868 | 0.686 |
| CO2 | 0.811 | ||||
| CO3 | 0.818 | ||||
| Performance impact | PI1 | 0.774 | 0.839 | 0.886 | 0.608 |
| PI2 | 0.792 | ||||
| PI3 | 0.775 | ||||
| PI4 | 0.797 | ||||
| PI5 | 0.760 |
| SYQ | IQ | SEQ | TEC | TTF | CO | PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYQ1 | 0.796 | 0.370 | 0.455 | 0.388 | 0.342 | 0.383 | 0.320 |
| SYQ2 | 0.849 | 0.492 | 0.461 | 0.373 | 0.376 | 0.414 | 0.400 |
| SYQ3 | 0.819 | 0.468 | 0.437 | 0.389 | 0.416 | 0.379 | 0.405 |
| IQ1 | 0.519 | 0.824 | 0.458 | 0.427 | 0.412 | 0.483 | 0.483 |
| IQ2 | 0.423 | 0.771 | 0.395 | 0.383 | 0.407 | 0.460 | 0.447 |
| IQ3 | 0.423 | 0.851 | 0.438 | 0.488 | 0.477 | 0.522 | 0.478 |
| IQ4 | 0.399 | 0.816 | 0.498 | 0.475 | 0.482 | 0.525 | 0.453 |
| SEQ1 | 0.447 | 0.397 | 0.782 | 0.403 | 0.358 | 0.468 | 0.384 |
| SEQ2 | 0.439 | 0.494 | 0.845 | 0.511 | 0.418 | 0.573 | 0.511 |
| SEQ3 | 0.449 | 0.441 | 0.802 | 0.446 | 0.383 | 0.485 | 0.431 |
| TEC1 | 0.434 | 0.487 | 0.480 | 0.838 | 0.595 | 0.595 | 0.575 |
| TEC2 | 0.386 | 0.398 | 0.472 | 0.804 | 0.471 | 0.497 | 0.526 |
| TEC3 | 0.285 | 0.414 | 0.389 | 0.754 | 0.513 | 0.449 | 0.434 |
| TTF1 | 0.434 | 0.470 | 0.518 | 0.613 | 0.813 | 0.582 | 0.615 |
| TTF2 | 0.375 | 0.447 | 0.339 | 0.512 | 0.857 | 0.547 | 0.601 |
| TTF3 | 0.336 | 0.443 | 0.325 | 0.521 | 0.832 | 0.492 | 0.581 |
| CO1 | 0.383 | 0.530 | 0.547 | 0.530 | 0.551 | 0.855 | 0.583 |
| CO2 | 0.402 | 0.495 | 0.501 | 0.538 | 0.534 | 0.811 | 0.525 |
| CO3 | 0.403 | 0.490 | 0.516 | 0.542 | 0.532 | 0.818 | 0.571 |
| PI1 | 0.393 | 0.410 | 0.522 | 0.532 | 0.680 | 0.557 | 0.774 |
| PI2 | 0.378 | 0.410 | 0.457 | 0.472 | 0.535 | 0.543 | 0.792 |
| PI3 | 0.329 | 0.457 | 0.412 | 0.452 | 0.504 | 0.509 | 0.775 |
| PI4 | 0.330 | 0.444 | 0.311 | 0.474 | 0.545 | 0.496 | 0.797 |
| PI5 | 0.349 | 0.506 | 0.414 | 0.575 | 0.516 | 0.525 | 0.760 |
| OQ | TEC | TTF | CO | PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OQ | 0.835 | ||||
| TEC | 0.628 * | 0.799 | |||
| TTF | 0.593 * | 0.661 * | 0.834 | ||
| CO | 0.687 * | 0.648 * | 0.651 * | 0.828 | |
| PI | 0.630 * | 0.645 * | 0.719 * | 0.676 * | 0.780 |
| OQ | TEC | TTF | CO | PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OQ | |||||
| TEC | 0.830 | ||||
| TTF | 0.751 | 0.874 | |||
| CO | 0.881 | 0.864 | 0.835 | ||
| PI | 0.772 | 0.821 | 0.879 | 0.838 |
| Hypothesis | Path | Std Beta | p-Value | Results | R2 | Q2 | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | OQ→TEC | 0.628 | 0.000 | Support | 0.394 | 0.246 | 1.000 |
| H2 | OQ→TTF | 0.149 | 0.002 | Support | 0.533 | 0.359 | 2.127 |
| H3 | OQ→CO | 0.687 | 0.000 | Support | 0.472 | 0.319 | 1.000 |
| H4 | TEC→TTF | 0.366 | 0.000 | Support | 1.933 | ||
| OQ→TEC→TTF | 0.230 | 0.000 | Support | ||||
| H5 | TTF→PI | 0.406 | 0.000 | Support | 0.610 | 0.362 | 2.093 |
| OQ→TTF→PI | 0.060 | 0.004 | Support | ||||
| H6 | TEC→PI | 0.189 | 0.000 | Support | 2.079 | ||
| TEC→TTF→PI | 0.148 | 0.000 | Support | ||||
| OQ→TEC→PI | 0.119 | 0.000 | Support | ||||
| H7 | CO→TTF | 0.312 | 0.000 | Support | 2.219 | ||
| OQ→CO→TTF | 0.214 | 0.000 | Support | ||||
| H8 | CO→PI | 0.290 | 0.000 | Support | 2.030 | ||
| CO→TTF→PI | 0.126 | 0.000 | Support | ||||
| OQ→CO→PI | 0.199 | 0.000 | Support |
| Latent Constructs | Performance Impact Total Effect | Index Values |
|---|---|---|
| (Importance) | (Performance) | |
| Overall quality | 0.558 | 70.530 |
| Technology characteristics | 0.337 | 69.706 |
| Task–technology fit | 0.406 | 66.822 |
| Compatibility | 0.416 | 68.187 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Lin, J. Does ChatGPT Play a Double-Edged Sword Role in the Field of Higher Education? An In-Depth Exploration of the Factors Affecting Student Performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416928
Chen J, Zhuo Z, Lin J. Does ChatGPT Play a Double-Edged Sword Role in the Field of Higher Education? An In-Depth Exploration of the Factors Affecting Student Performance. Sustainability. 2023; 15(24):16928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416928
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiangjie, Ziqing Zhuo, and Jiacheng Lin. 2023. "Does ChatGPT Play a Double-Edged Sword Role in the Field of Higher Education? An In-Depth Exploration of the Factors Affecting Student Performance" Sustainability 15, no. 24: 16928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416928
APA StyleChen, J., Zhuo, Z., & Lin, J. (2023). Does ChatGPT Play a Double-Edged Sword Role in the Field of Higher Education? An In-Depth Exploration of the Factors Affecting Student Performance. Sustainability, 15(24), 16928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416928








