A Framework for Adopting a Sustainable Reverse Logistics Service Quality for Reverse Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
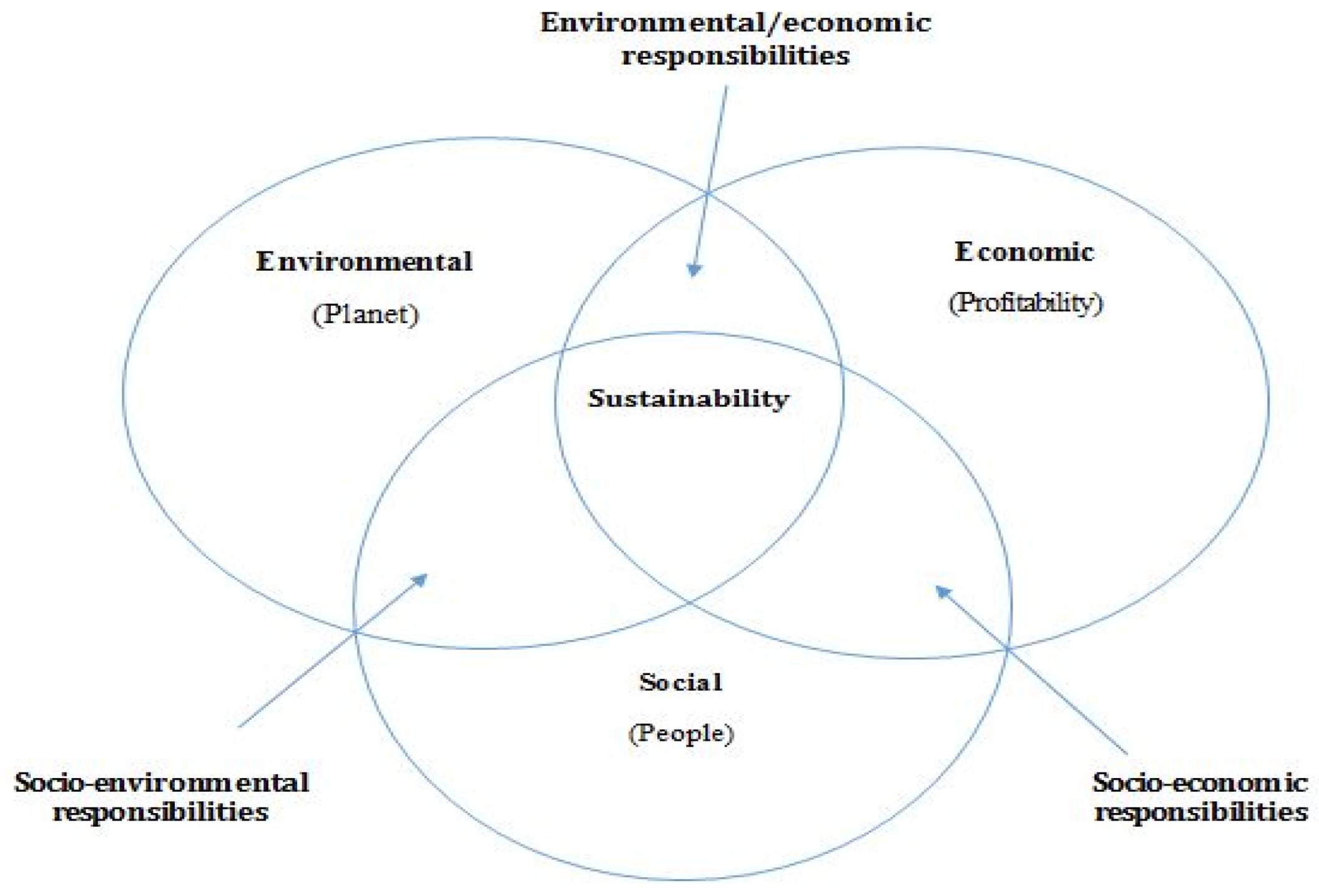
2.1. Sustainability Performance
2.2. Sustainability Performance and Reverse Logistics Services
2.3. Reverse Logistics Performance and Service Quality
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Research Sources
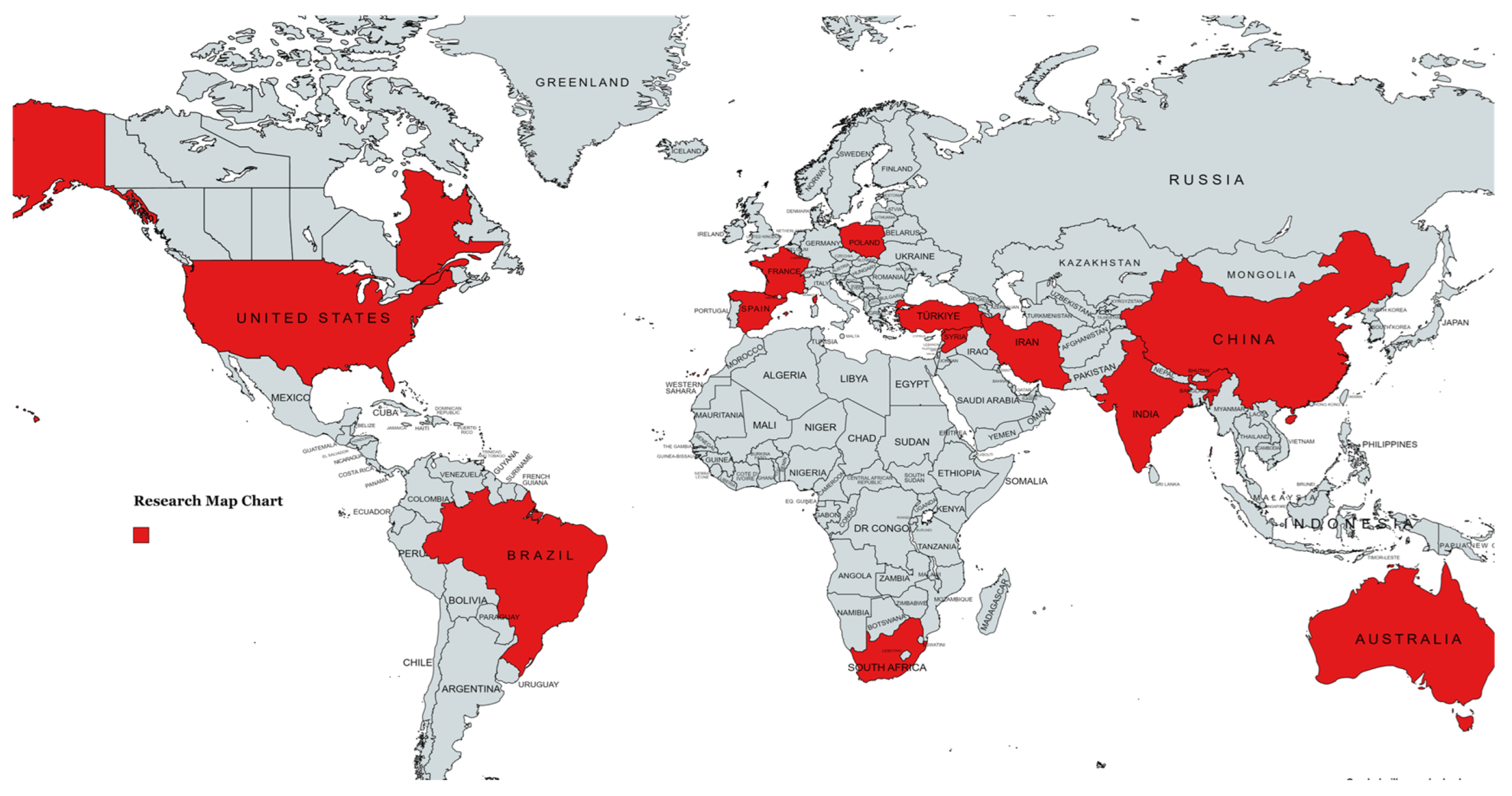
4.2. Documents by Country
4.3. Documents by study fields
4.4. Publications by Year
5. Discussion
5.1. Sustainability and Multiple Goals in Service Quality Practices
5.2. Reverse Logistics Service Quality
5.3. Customer Relationship and Operational Risk
6. Conclusions
7. Research Implications
7.1. Theoretical Implications
7.2. Practical Implications
8. Research Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, S.; Singh, R.K. Analyzing disposition decisions for sustainable reverse logistics: Triple Bottom Line approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 150, 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, B.T.; Cegielski, C.; Hanna, J. Diffusion of green supply chain management: Examining perceived quality of green reverse logistics. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2011, 22, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homrich, A.S.; Galvão, G.; Abadia, L.G.; Carvalho, M.M. The circular economy umbrella: Trends and gaps on integrating pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbakhshnia, N.; Wu, Y.; Govindan, K.; Soleimani, H. A novel hybrid multiple attribute decision-making approach for outsourcing sustainable reverse logistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, A.; Mousavi, S.M. Assessment of third-party logistics providers by introducing a new stochastic two-phase compromise solution model with last aggregation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 170, 108324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.N.; Dang, T.; Nguyen, N. Outsourcing reverse logistics for e-commerce retailers: A two-stage fuzzy optimization approach. Axioms 2021, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, J. Robust design for a multi-echelon regional construction and demolition waste reverse logistics network based on decision Maker’s conservative attitude. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U-Dominic, C.M.; Orji, I.J.; Okwu, M. Analyzing the Barriers to Reverse Logistics (RL) Implementation: A Hybrid Model Based on IF-DEMATEL-EDAS. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Dong, Q.-L.; Ahmad, N.; Zhu, Y.; Nadeem, M. Critical Barriers to Implementation of Reverse Logistics in the Manufacturing Industry: A Case Study of a Developing Country. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nureen, N.; Liu, D.; Ahmad, B.; Irfan, M. Exploring the technical and behavioral dimensions of green supply chain management: A roadmap toward environmental sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 63444–63457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Minhas, U.; NNdubisi, O.; Barrane, F. Corporate environmental management: A review and integration of green human resource management and green logistics. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Hu, W.; Dong, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. A Systematic Literature Review of Green and Sustainable Logistics: Bibliometric Analysis, Research Trend and Knowledge Taxonomy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashemi, S.E. A fuzzy multi-objective optimization model for a sustainable reverse logistics network design of municipal waste-collecting considering the reduction of emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, E.K.F.; Mateus, G.R. A capacitated plant location model for Reverse Logistics Activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjanit, C.; Rompho, N. Measuring customer-oriented product returns service performance. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2019, 30, 772–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euchi, J.; Bouzidi, D.; Bouzid, Z. Structural analysis of acute success factors of performance of reverse logistics relative to customer satisfaction. Int. J. Comb. Optim. Probl. Inform. 2019, 10, 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Marić, J.; Opazo-Basáez, M. Green Servitization for Flexible and Sustainable Supply Chain Operations: A Review of Reverse Logistics Services in Manufacturing. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2019, 20, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.N.S.; Dutt, G. The Impact of Product Disposal Strategies on Triple Bottom-Line Performance in Supply Chains: The Role of Relational Resources. In Developments in Marketing Science: Proceedings of the Academy of Marketing Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, L. Research on B2C Reverse Logistics Service Quality Evaluation System. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on E-Business and Applications—ICEBA 2019, Bangkok, Thailand, 25–28 February 2019; pp. 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, R.K.; Suri, P.K. Sustainable Service Quality Management by Logistics Service Providers: An Indian Perspective. Glob. Bus. Rev. 2018, 19, S130–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kannan, D.; Garg, K.; Gupta, S.; Gandhi, K.; Jha, P. Business orientation policy and process analysis evaluation for establishing third party providers of reverse logistics services. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauter, R.; Jonker, J.; Baumgartner, R. Going one’s own way: Drivers in developing business models for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoui, H.; Guo, Y.; Sarkis, J. Decision support for collaboration planning in sustainable supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbekler, T.M.; Ozturkoglu, Y. Analysing the importance of sustainability-oriented service quality in competition environment. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2019, 29, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markard, J.; Raven, R.; Truffer, B. Sustainability transitions: An emerging field of research and its prospects. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richnák, P.; Gubová, K. Green and Reverse Logistics in Conditions of Sustainable Development in Enterprises in Slovakia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellas, P.; Malindretos, G.; Reklitis, P. Implications of Green Logistics Management on Sustainable Business and Supply Chain Performance: Evidence from a Survey in the Greek Agri-Food Sector. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, M.; Forslund, H. Challenges Addressed by Swedish Third-Party Logistics Providers Conducting Sustainable Logistics Business Cases. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persdotter Isaksson, M.; Hulthén, H.; Forslund, H. Environmentally Sustainable Logistics Performance Management Process Integration between Buyers and 3PLs. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, H.; Singh, S.P. Sustainable procurement and logistics for disaster resilient supply chain. Ann. Oper. Res. 2016, 283, 309–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, H.; Kant, R.; Shankar, R. Bequeath life to death: State-of-art review on reverse logistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Gamal, A.; Elhoseny, M.; Chakrabortty, R.; Ryan, M. A Conceptual Hybrid Approach from a Multicriteria Perspective for Sustainable Third-Party Reverse Logistics Provider Identification. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, H.; Jin, M.; Lai, M. Two-stage remanufacturing decision makings considering product life cycle and consumer perception. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Singh, R.K.; Murtaza, Q. Disposition decisions in reverse logistics: Graph theory and matrix approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosarkani, B.M.; Amin, S.H. A multi-objective model to configure an electronic reverse logistics network and third party selection. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 662–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Mansour, S.; Karimi, B. To develop a third-party reverse logistics network for end-of-life vehicles in Iran. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 78, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P. Strategic issues in pharmaceutical supply chains: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Healthc. Mark. 2016, 10, 234–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julianelli, V.; Caiado, R.G.G.; Scavarda, L.F.; Cruz, S.P.D.M.F. Interplay between reverse logistics and circular economy: Critical success factors-based taxonomy and framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.R.; Tokman, M.; Richey, R.G.; Defee, C. Resource commitment and sustainability: A reverse logistics performance process model. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2018, 48, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Brady, M.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Simpson, M. Resolving forward-reverse logistics multi-period model using evolutionary algorithms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henninger, C.E.; Bürklin, N.; Niinimäki, K. The clothes swapping phenomenon—when consumers become suppliers. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 23, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastas, A.; Liyanage, K. Sustainable supply chain quality management: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, Ž.; Đalić, I.; Pamucar, D.; Nunić, Z.; Vesković, S.; Vasiljević, M.; Tanackov, I. A new hybrid model for quality assessment of scientific conferences based on Rough BWM and SERVQUAL. Scientometrics 2019, 119, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmata, U.M.D.; Rao, B.; Rajashekhar, B. Measuring service quality in pharmaceutical supply chain—distributor’s perspective. Int. J. Pharm. Healthc. Mark. 2016, 10, 258–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, Ž.; Tanackov, I.; Puška, A.; Jovanov, G.; Vasiljević, J.; Lojaničić, D. Development of Modified SERVQUAL–MCDM Model for Quality Determination in Reverse Logistics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K. Identification of factors affecting reverse chain performance in relation to customer satisfaction using ISM mod-elling & MICMAC analysis. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2013, 1, 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D. Producing a systematic review. In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods; Sage Publications Ltd: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 671–689. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, I.E.; Evangelinos, K.I.; Allan, S. A reverse logistics social responsibility evaluation framework based on the triple bottom line approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 56, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingfei, Y.; Mengze, Z.; Zeyu, L.; Ki-Hyung, B.; Avotra AA, R.N.; Nawaz, A. Green logistics performance and infrastructure on service trade and environment-Measuring firm’s performance and service quality. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Esposito, E. Environmental sustainability in the service industry of transportation and logistics service providers: Systematic literature review and research directions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 53, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, R.K.; Goh, M.; Zarbakhshnia, N. Sustainable third-party reverse logistic provider selection with fuzzy SWARA and fuzzy MOORA in plastic industry. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 2401–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, F.A.; Nikabadi, M.S.; Olfat, L. Developing the framework of sustainable service supply chain balanced scorecard (SSSC BSC). Int. J. Prod. Perform. Manag. 2019, 68, 148–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaron, A.A.; Backhouse, C. A systems approach for forward and reverse logistics design: Maximising value from customer involvement. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2016, 27, 947–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Talaulikar, S.; Xavier, V.; Kapoor, S. Fostering reverse logistics in India by prominent barrier identification and strategy implementation to promote circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aćimović, S.; Mijušković, V.; Rajić, V. The impact of reverse logistics onto green supply chain competitiveness evidence from Serbian consumers. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2020, 48, 1003–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, P. Environmental sustainability practices in the transport and logistics service industry: An exploratory case study investigation. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2014, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, R.K. Managing operations by a logistics company for sustainable service quality: Indian perspective. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, R.K.; Suri, P.K. Prioritizing Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Service Quality Management by Logistics Service Providers. Vision J. Bus. Perspect. 2018, 22, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Singh, R.K. Forecasting product returns and reverse logistics performance: Structural equation modelling. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Z. A Sustainable Performance Assessment Framework for Plastic Film Supply Chain Management from a Chinese Perspective. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangwan, K.S.; Bhakar, V.; Digalwar, A.K. A sustainability assessment framework for cement industry—A case study. Benchmarking Int. J. 2019, 26, 470–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbari Nouri, F.; Nikabadi, M.S.; Olfat, L. Sustainable service supply chain practices (SSSCPs): A framework development. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2019, 69, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Cagno, E.; Lepri, M.; Trianni, A. A triple bottom line balanced set of key performance indicators to measure the sustainability performance of industrial supply chains. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 648–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourneaux, F.; Gabriel, M.L.D.; Gallardo-Vazquez, D.A. Triple bottom line and sustainable performance measurement in in-dustrial companies. Rege-Rev. Gest. 2018, 25, 413–429. [Google Scholar]
- Shou, Y.; Shao, J.; Lai, K.-H.; Kang, M.; Park, Y. The impact of sustainability and operations orientations on sustainable supply management and the triple bottom line. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, T.; Barbosa-Póvoa, A.; Kraslawski, A.; Carvalho, A. Quantitative indicators for social sustainability assessment of supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 748–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, R.; Jack, L.; Brown, S. Product returns: A growing problem for business, society and environment. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020, 40, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Agarwal, V.; Darbari, J.D.; Jha, P.C. An integrated decision making model for the selection of sustainable forward and reverse logistic providers. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 273, 607–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jackson, J.E. Investigating the influential factors of return channel loyalty in omni-channel retailing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 216, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkov, G.; Dika, Z. A sustainable e-service quality model. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2015, 25, 414–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidzadeh, M.H.; Shokouhyar, S. Toward the closed-loop sustainability development model: A reverse logistics multi-criteria decision-making analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, S.; Vimal, K.E.K.; Arumugam, S.; Parthiban, J.; Sivaraman, S.K.; Kandasamy, J.; Duque, A.A. Multi-objective mixed-integer linear optimization model for sustainable closed-loop supply chain network: A case study on remanufacturing steering column. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6481–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Step No. | Step | Classification | Number of Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Proposing the research questions | The CIMO identified the performance of the reverse logistics domains (C), sustainable reverse logistics assessment methods (I), service quality indicators, tools (M), performance, efficiency, and both positive and negative impacts on reverse logistics service quality and sustainability as the main characteristics of the study (O). | |
| Step 2 | Locating studies | The database will be filtered using the following terms: reverse logistics, 3PRLP, sustainability, service quality indicators, and customer satisfaction result. In databases, such as WOS, Scopus, and Science Direct, the study string can be found in the title, summary, or article phrases. Duration of the search: 2011–2022. In English language for scholarly journals. | 147 |
| Step 3 | Study selection and evaluation | A comprehensive screening of the citation’s abstract from those chosen in the second phase, followed by the selection of those that are most related to the current research question. | 89 |
| Steps 4 and 5 | Results, Analysis, and Discussion | A comprehensive examination of the selected papers through introduction, methodology, and conclusion. Criteria for inclusion: articles addressing reverse logistics merged with service quality and the sustainability criteria: extraction and removal of irrelevant and duplicated papers. | 56 |
| No. | Research Author(s) and Title | Year | Citation | Publisher | IF |
| 1 | Nikolaou, Evangelinos [49] | 2013 | 327 | Elsevier | 3.590 |
| 2 | Bastas and Liyanage [42] | 2018 | 224 | Elsevier | 6.97 |
| 3 | Centobelli, Cerchione [51] | 2017 | 213 | Elsevier | 4.04 |
| 4 | Mavi, Goh [52] | 2017 | 203 | Springer | 3.471 |
| 5 | Prajapati, Kant [31] | 2019 | 121 | Elsevier | 8.18 |
| 6 | Hashemi [13] | 2021 | 171 | Elsevier | 10.96 |
| 7 | Zarbakhshnia, Wu [4] | 2020 | 82 | Elsevier | 9.297 |
| No. | Research Author(s) and Title | Year | Citation | Publisher | IF |
| 8 | Nouri, Nikabadi [53] | 2018 | 54 | Emerald Insight | 2.23 |
| 9 | Li, Kannan [21] | 2018 | 45 | Elsevier | 6.97 |
| 10 | Marić and Opazo-Basáez [17] | 2019 | 40 | Springer | 3.51 |
| 11 | Ozbekler and Ozturkoglu [24] | 2020 | 39 | WILEY | 8.99 |
| 12 | Persdotter Isaksson, Hulthén [29] | 2019 | 28 | MDPI | 2.96 |
| 13 | Jaaron and Backhouse [54] | 2016 | 23 | Emerald Insight | 1.95 |
| 14 | Dutta, Talaulikar [55] | 2021 | 18 | Elsevier | 10.96 |
| No. | Research Author(s) and Title | Year | Citation | Publisher | IF |
| 15 | Aćimović, Mijušković [56] | 2020 | 14 | Emerald Insight | 3.87 |
| 16 | Sajjanit and Rompho [15] | 2019 | 11 | Emerald Insight | 4.37 |
| 17 | Stevic, Tanackov [45] | 2021 | 9 | MDPI | 3.889 |
| 18 | U-Dominic, Orji [8] | 2021 | 6 | MDPI | 3.251 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabees, A.; Barakat, M.; Elbarky, S.S.; Lisec, A. A Framework for Adopting a Sustainable Reverse Logistics Service Quality for Reverse Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031755
Dabees A, Barakat M, Elbarky SS, Lisec A. A Framework for Adopting a Sustainable Reverse Logistics Service Quality for Reverse Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031755
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabees, Ahmed, Mahmoud Barakat, Sahar Sobhy Elbarky, and Andrej Lisec. 2023. "A Framework for Adopting a Sustainable Reverse Logistics Service Quality for Reverse Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031755
APA StyleDabees, A., Barakat, M., Elbarky, S. S., & Lisec, A. (2023). A Framework for Adopting a Sustainable Reverse Logistics Service Quality for Reverse Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability, 15(3), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031755






