Characterizing Informal Settlement Dynamics Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis in Durban Metropolitan Area, South Africa: Linking Pattern to Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
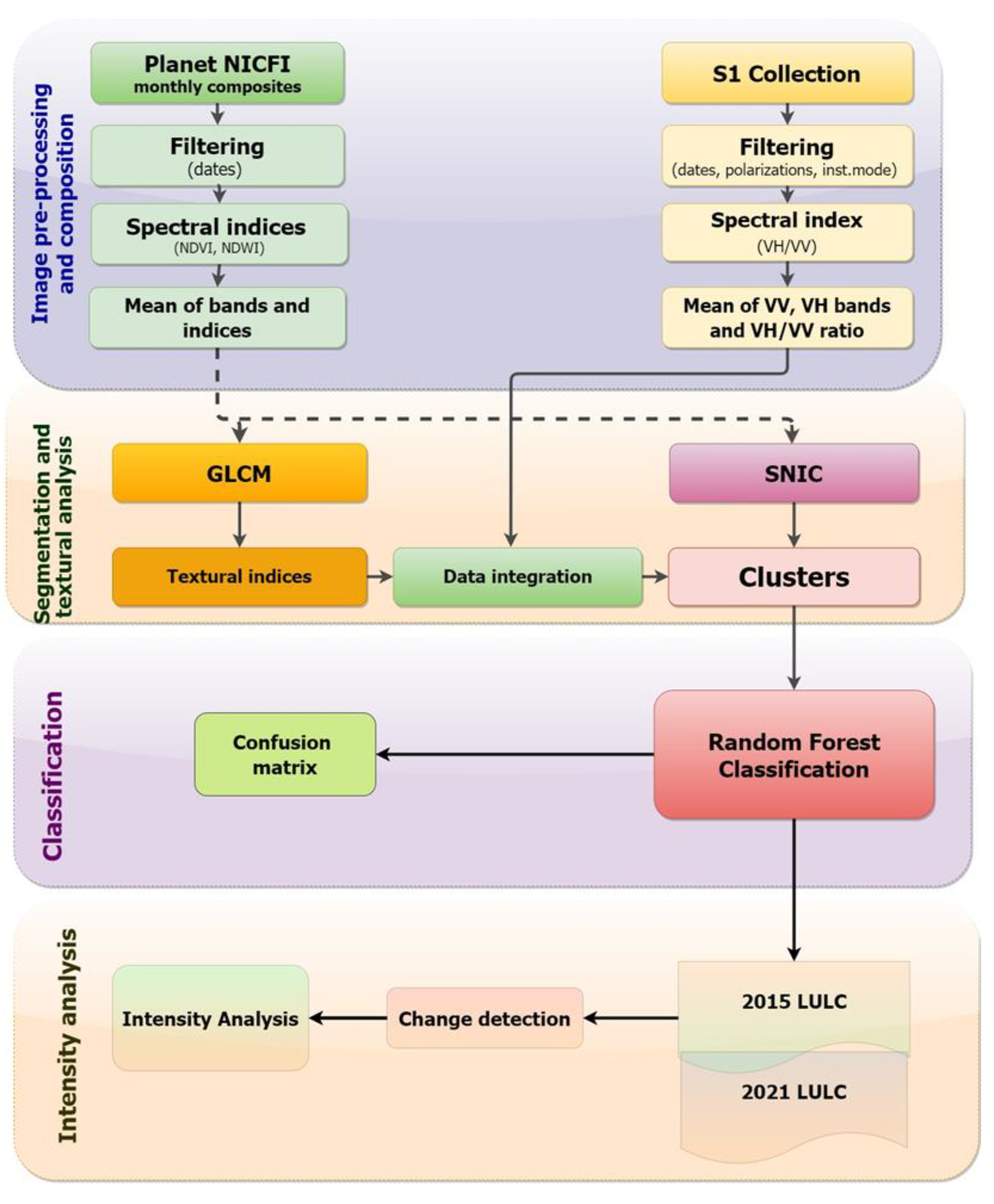
2.3. Object-Based Image Classification
2.4. Land-Cover Transition Matrix
2.5. Intensity Analysis
2.5.1. Category Level Analysis
2.5.2. Transition Level Analysis
3. Results
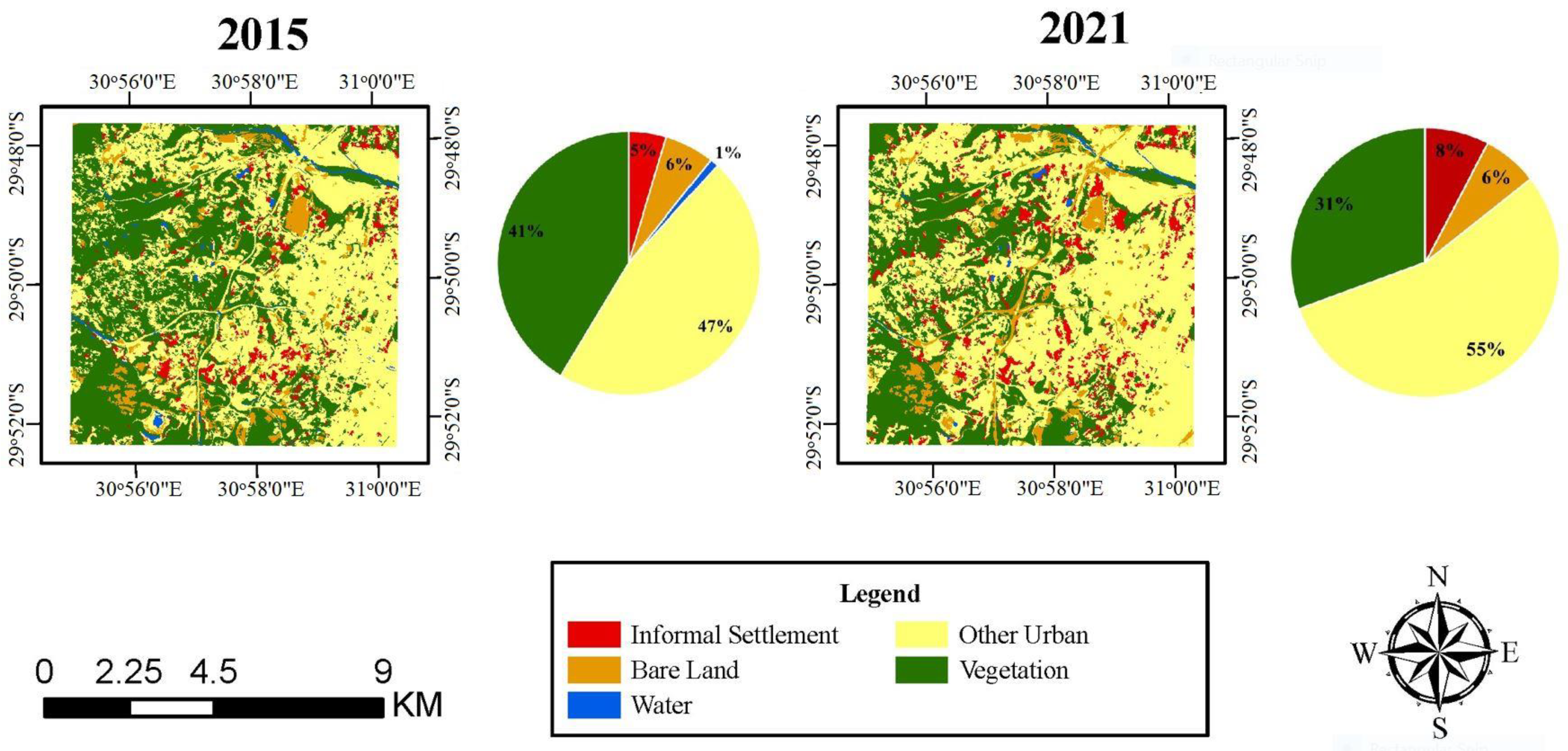
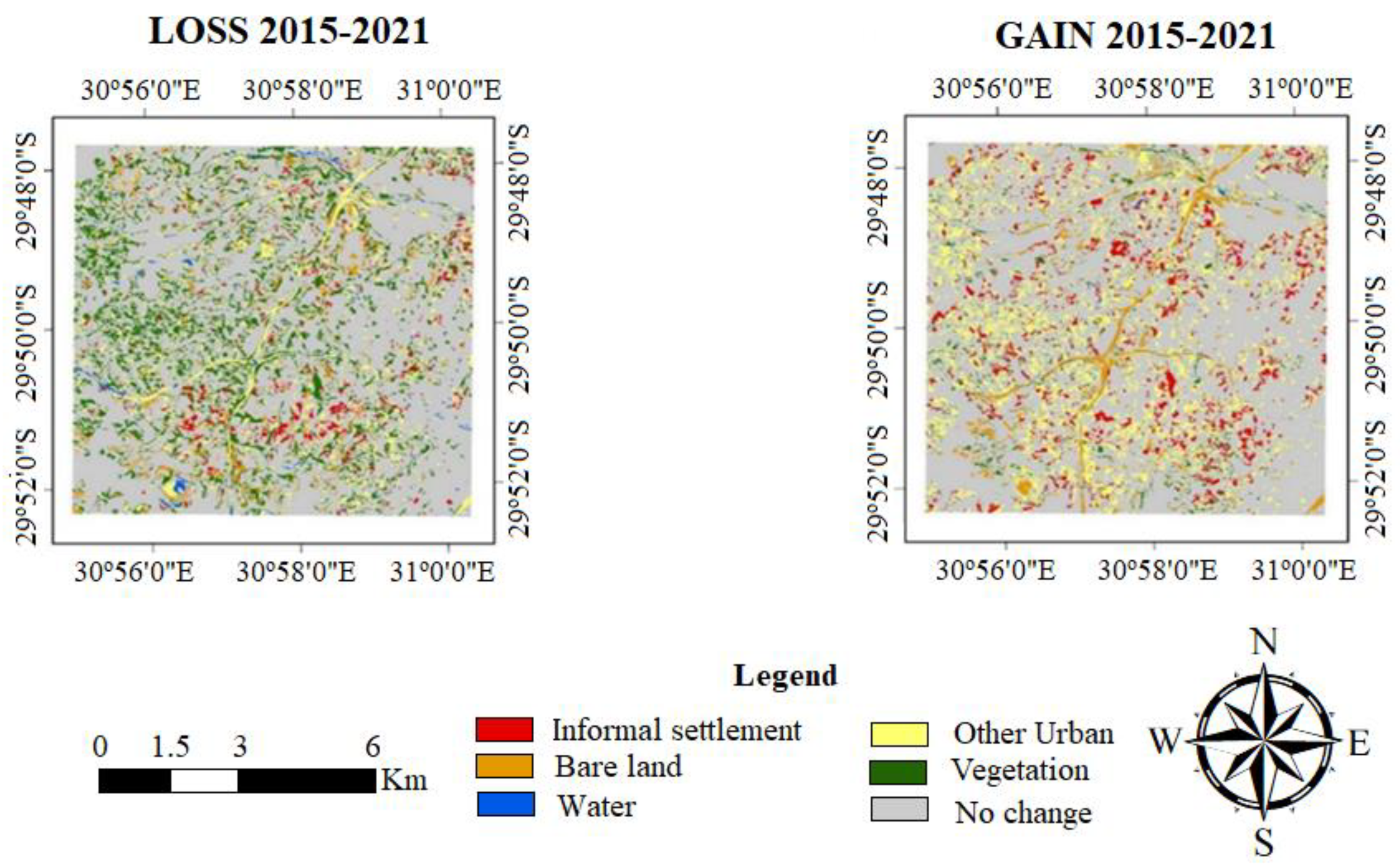
3.1. Observed Patterns of LULC Change Dynamics
3.2. Intensity Analysis
3.2.1. Category Level
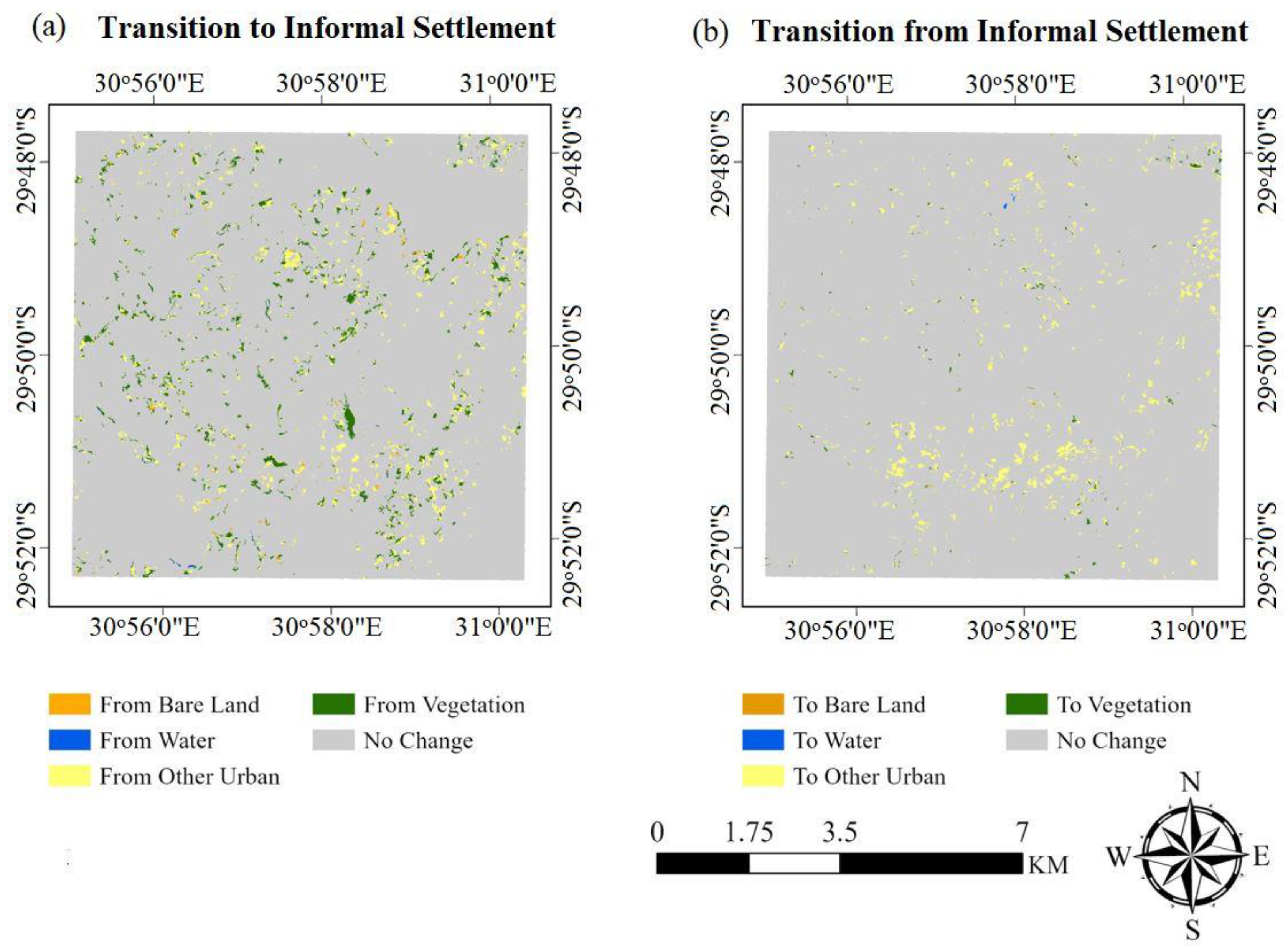
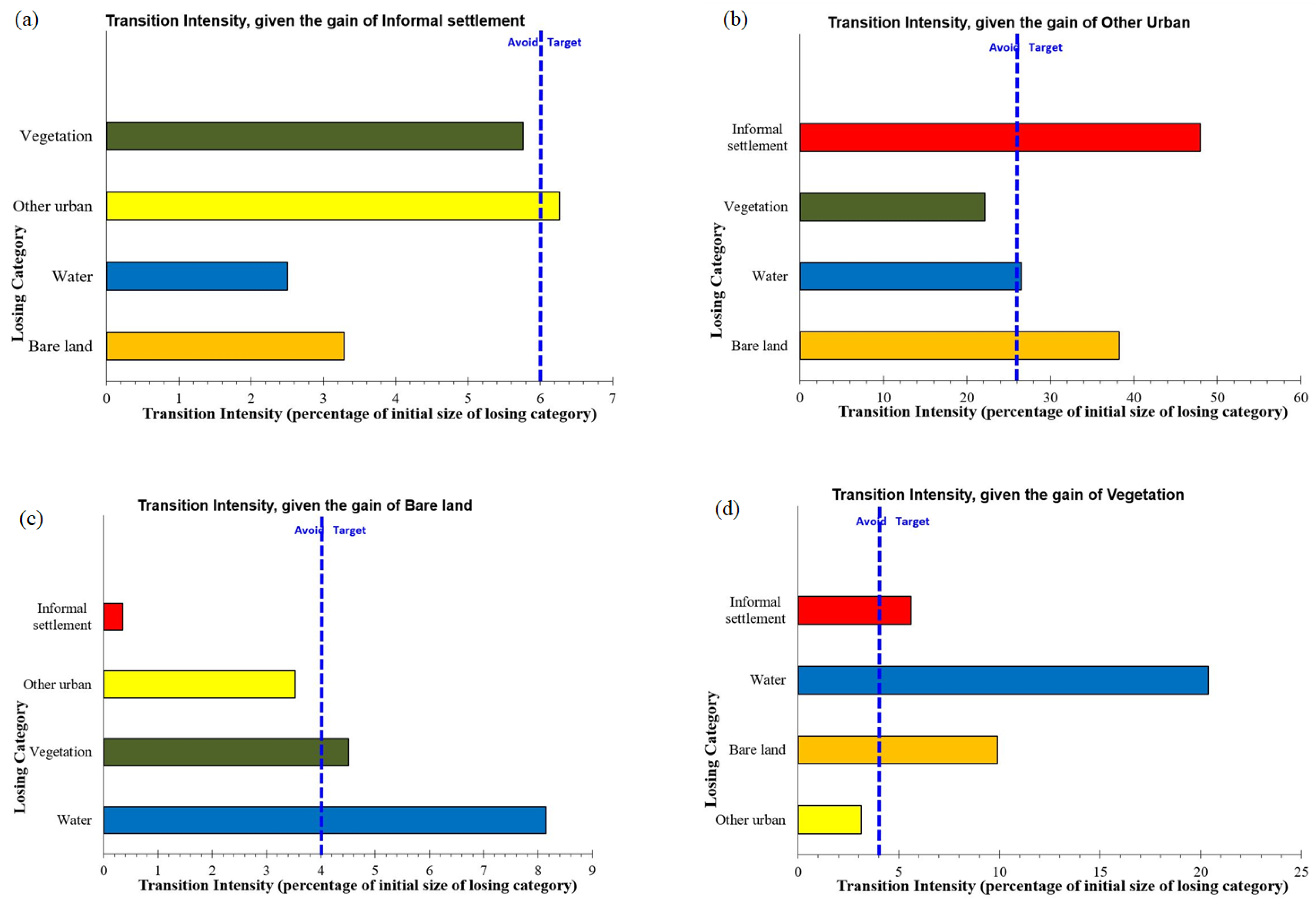
3.2.2. Transition Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez, J.M.R.; Heider, K.; Scheffran, J. Frontiers of urbanization: Identifying and explaining urbanization hot spots in the south of Mexico City using human and remote sensing. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsa-Barreiro, J.; Li, Y.; Morales, A.; Pentland, A.S. Globalization and the shifting centers of gravity of world’s human dynamics: Implications for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P. Formalizing the Informal: Understanding the Position of Informal Settlements and Slums in Sustainable Urbanization Policies and Strategies in Bandung, Indonesia. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, J.; Shelby, J.A.; Behary, D. The Paradox of Informal Settlements Revealed in an ATLAS of Informality: Findings from Mapping Growth in the Most Common Yet Unmapped Forms of Urbanization. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellman, B.; Eakin, H.; Turner, B.L. Identifying, projecting, and evaluating informal urban expansion spatial patterns. J. Land Use Sci. 2022, 17, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. An ontology of slums for image-based classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I. Extraction of Slum Areas From VHR Imagery Using GLCM Variance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R. Slums from Space—15 Years of Slum Mapping Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraff, N.J.; Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. The dynamics of poor urban areas—Analyzing morphologic transformations across the globe using Earth observation data. Cities 2020, 107, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmos, O.; Rienow, A.; Callo-Concha, D.; Greve, K.; Jürgens, C. Urban Development in West Africa—Monitoring and Intensity Analysis of Slum Growth in Lagos: Linking Pattern and Process. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solecki, W.; Seto, K.C.; Marcotullio, P.J. It’s Time for an Urbanization Science. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2013, 55, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, H.; Lariu, P.; Julich, S.; Patil, S.; McDonald, M.; Feger, K.-H. Characterizing the Intensity and Dynamics of Land-Use Change in the Mara River Basin, East Africa. Forests 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msofe, N.; Sheng, L.; Lyimo, J. Land Use Change Trends and Their Driving Forces in the Kilombero Valley Floodplain, Southeastern Tanzania. Sustainability 2019, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamud, A.M.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Shaharum, N.S.N. Monitoring Urban Expansion And Land Use/Land Cover Changes In Banadir, Somalia Using Google Earth Engine (GEE). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 767, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugiraneza, T.; Nascetti, A.; Ban, Y. Continuous Monitoring of Urban Land Cover Change Trajectories with Landsat Time Series and LandTrendr-Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudiastuti, A.; Farda, N.M.; Ramdani, D.; Wicaksono, P.; Wibowo, S.B. Mapping built-up land and settlements: A comparison of machine learning algorithms in Google Earth engine. SPIE 2021, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, N. Change detection of urban areas in Ankara through Google Earth engine. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Athens, Greece, 4–6 July 2018; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Allen, J.S. Mapping Urbanization Trends in a Forested Landscape Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 2, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R.; Herold, M.; Verburg, P.H.; Clevers, J.G.; Eberle, J. Gross changes in reconstructions of historic land cover/use for Europe between 1900 and 2010. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, R.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Pontius, R.G. Analysis of twenty years of categorical land transitions in the Lower Hunter of New South Wales, Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Huang, J.; Nitivattananon, V. Enhanced Intensity Analysis to Quantify Categorical Change and to Identify Suspicious Land Transitions: A Case Study of Nanchang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Huang, B.; Huang, J.; Li, S. Measuring Land Change in Coastal Zone around a Rapidly Urbanized Bay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Zhou, C. A method of characterizing land-cover swap changes in the arid zone of China. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 10, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. Map errors that could account for deviations from a uniform intensity of land change. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1717–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, F.O.; Pontius, R.G.; Braimoh, A.K. Land change dynamics: Insights from Intensity Analysis applied to an African emerging city. J. Spat. Sci. 2016, 106, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Hong, H. Land classification and change intensity analysis in a coastal watershed of Southeast China. Sensors 2014, 14, 11640–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, S. Use of intensity analysis to measure land use changes from 1932 to 2005 in Zhenlai County, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M.; Sakieh, Y.; Dezhkam, S.; Ardakani, T.; Salmanmahiny, A. Environmental monitoring and assessment of landscape dynamics in southern coast of the Caspian Sea through intensity analysis and imprecise land-use data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Pontius, R.G.; Song, H. Intensity Analysis to communicate land change during three time intervals in two regions of Quanzhou City, China. GIScience Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, Z.; Teixeira, H.; Marques, J.C. Systematic processes of land use/land cover change to identify relevant driving forces: Implications on water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Shusas, E.; McEachern, M. Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Use of intensity analysis to link patterns with processes of land change from 1986 to 2007 in a coastal watershed of southeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushore, T.D.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J. Determining the Influence of Long Term Urban Growth on Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Local Climate Zones and Intensity Analysis Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamekye, C.; Kwofie, S.; Ghansah, B.; Agyapong, E.; Boamah, L.A. Assessing urban growth in Ghana using machine learning and intensity analysis: A case study of the New Juaben Municipality. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Bao, G.; Rong, A.; Huang, X.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y. Comparison of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Use Changes in Four Municipalities of China Based on Intensity Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandharum, L.; Hartono, D.M.; Karsidi, A.; Ahmad, M. Monitoring Urban Expansion and Loss of Agriculture on the North Coast of West Java Province, Indonesia, Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 3123788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loggia, C.; Govender, V. A hybrid methodology to map informal settlements in Durban, South Africa. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Eng. Sustain. 2019, 5, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagarnath, M.; Thambiran, T.; Gebreslasie, M. Modelling urban land change processes and patterns for climate change planning in the Durban metropolitan area, South Africa. J. Land Use Sci. 2019, 14, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeka, B.; Phinzi, K.; Sutherland, C. Monitoring Changing Land Use-Land Cover Change to Reflect the Impact of Urbanisation on Environmental Assets in Durban, South Africa. In Sustainable Urban Futures in Africa; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 132–158. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, C.; Charlton, S. Global Report on Human Settlements; UN-HABITAT (Hg.): Durban, South Africa, 2003; pp. 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Membele, G.M.; Naidu, M.; Mutanga, O. Using local and indigenous knowledge in selecting indicators for mapping flood vulnerability in informal settlement contexts. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 71, 102836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Costa, M.M.; Celliers, L.; Sutherland, C. Informal Settlements and Flooding: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses in Local Governance for Water Management. Water 2018, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.; Costa, M.M.; Sutherland, C.; Celliers, L.; Scheffran, J. Vulnerability of informal settlements in the context of rapid urbanization and climate change. Environ. Urban. 2019, 31, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzoor, S.A.; Griffiths, G.H.; Robinson, E.; Shoyama, K.; Lukac, M. Linking Pattern to Process: Intensity Analysis of Land-Change Dynamics in Ghana as Correlated to Past Socioeconomic and Policy Contexts. Land 2022, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otunga, C.; Odindi, J.; Mutanga, O. Land Use Land Cover Change in the fringe of eThekwini Municipality: Implications for urban green spaces using remote sensing. South Afr. J. Geomat. 2014, 3, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewitt, D.; Goodman, P.S.; Erasmus, B.F.N.; O’Connor, T.G.; Witkowski, E.T.F. Systematic land-cover change in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: Implications for biodiversity. South Afr. J. Sci. 2015, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, P.; Bisaga, I.; Loggia, C.; Georgiadou, M.C.; Ojo-Aromokudu, J. Barriers and opportunities for participatory environmental upgrading: Case study of Havelock informal settlement, Durban. City Environ. Interact. 2020, 5, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfai, M.A.; Farda, N.M.; Khakhim, N.; Wicaksono, P.; Wicaksono, A. Tidal Correction Effects Analysis on Shoreline Mapping in Jepara Regency. J. Appl. Geospat. Inf. 2018, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Mahdavi, S.; Afshar, M.; Brisco, B.; Huang, W.; Mohammad Javad Mirzadeh, S.; White, L.; Banks, S.; Montgomery, J.; Hopkinson, C. Canadian Wetland Inventory using Google Earth Engine: The First Map and Preliminary Results. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The First Wetland Inventory Map of Newfoundland at a Spatial Resolution of 10 m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, M. PlanetScope, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-1 Data Integration for Object-Based Land Cover Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergni, L.; Vinci, A.; Todisco, F.; Santaga, F.S.; Vizzari, M. Comparing Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and Landsat-8 data in the early recognition of irrigated areas in central Italy. J. Agric. Eng. 2021, 52, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Pontius, R.G.; Rakshit, R. A review of accuracy assessment for object-based image analysis: From per-pixel to per-polygon approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 141, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mui, A.; He, Y.; Weng, Q. An object-based approach to delineate wetlands across landscapes of varied disturbance with high spatial resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 109, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Susstrunk, S. Superpixels and polygons using simple non-iterative clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolului, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4651–4660. [Google Scholar]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D. Object-based random forest classification for informal settlements identification in the Middle East: Jeddah a case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4421–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D.; Kohli, D. Mapping informal settlement indicators using object-oriented analysis in the Middle East. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Wallace, L.; Mitchell, D. Combining Object-Based Machine Learning with Long-Term Time-Series Analysis for Informal Settlement Identification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.; Raja, R.A.A. Urban Slum Detection Approaches from High-Resolution Satellite Data Using Statistical and Spectral Based Approaches. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.; Gao, Y.; Giner, N.; Kohyama, T.; Osaki, M.; Hirose, K. Design and Interpretation of Intensity Analysis Illustrated by Land Change in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land 2013, 2, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, C.; Psaltis, C.; Potsiou, C. Towards a strategy for control of suburban informal buildings through automatic change detection. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niya, A.K.; Huang, J.; Karimi, H.; Keshtkar, H.; Naimi, B. Use of Intensity Analysis to Characterize Land Use/Cover Change in the Biggest Island of Persian Gulf, Qeshm Island, Iran. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G. Intensity analysis to unify measurements of size and stationarity of land changes by interval, category, and transition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, M.C.; Loggia, C.; Bisaga, I.; Parikh, P. Towards sustainable informal settlements: A toolkit for community-led upgrading in Durban. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Eng. Sustain. 2021, 174, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Membele, G.M. Integrating Local, Indigenous Knowledge and Geographical Information System in Mapping Flood Vulnerability at Quarry Road West Informal Settlement in Durban. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kwazulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Plessis, D.J.D. Land-use mix in South African cities and the influence of spatial planning: Innovation or following the trend? South Afr. Geogr. J. (Suid-Afrik. Geogr. Tydskr.) 2015, 97, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odindi, J.; Mhangara, P.; Kakembo, V. Remote sensing land-cover change in Port Elizabeth during South Africa’s democratic transition. South Afr. J. Sci. 2012, 108, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mistro, R.; Hensher, D.A. Upgrading Informal Settlements in South Africa: Policy, Rhetoric and what Residents really Value. Hous. Stud. 2009, 24, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D.; Archer, D.; Colenbrander, S.; Dodman, D.; Hardoy, J.; Mitlin, D.; Patel, S. Building Resilience to Climate Change in Informal Settlements. One Earth 2020, 2, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abunyewah, M.; Gajendran, T.; Maund, K. Profiling informal settlements for disaster risks. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Risi, R.; Jalayer, F.; De Paola, F.; Iervolino, I.; Giugni, M.; Topa, M.E.; Gasparini, P. Flood risk assessment for informal settlements. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1003–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Informal settlement | Densely, irregularly built housing units that are contiguous |
| Bare land | Unused land, including barren land, exposed soil with neither grass, trees nor built up structures |
| Water | Water bodies such as dams, rivers, ponds and swamps |
| Other urban | High and low density formal residential buildings, commercial and industrial buildings, transportation networks |
| Vegetation | Area covered by grasslands, forests, croplands, small shrubs, sparse and dense trees, plantations |
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| T | number of time points |
| Yt | year at time point t |
| t | index for the initial time point of an interval (Yt − Yt+1), where t ranges from 1 to T − 1 |
| J | number of categories |
| i | index for a category at the initial time point of an interval |
| j | index for a category at the latter time point of an interval |
| n | index of the gaining category for the selected transition |
| Ctij | size of transition from category i to category j during interval (Yt − Yt+1) |
| St | annual change during interval (Yt −Yt+1) |
| Gtj | intensity of annual gain of category j during interval (Yt −Yt+1) relative to size of category j at time t + 1 |
| Lti | intensity of annual loss of category i during interval (Yt − Yt+1) relative to size of category i at time t |
| Rtin | intensity of annual transition from category i to category n during interval (Yt −Yt+1) relative to size of category i at time t |
| Wtn | uniform intensity of annual transition from all non-n categories to category n during interval (Yt − Yt+1) relative to size of all non-n categories at time t |
| 2015 | 2021 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | UA (%) | PA (%) | F-Score | UA (%) | PA (%) | F-Score |
| Informal settlement | 75 | 60 | 67 | 96 | 88 | 92 |
| Bare land | 100 | 92 | 96 | 100 | 81 | 90 |
| Water | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Other urban | 95 | 98 | 96 | 95 | 99 | 97 |
| Vegetation | 99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| OA (%) | 96 | 97 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matarira, D.; Mutanga, O.; Naidu, M.; Mushore, T.D.; Vizzari, M. Characterizing Informal Settlement Dynamics Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis in Durban Metropolitan Area, South Africa: Linking Pattern to Process. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032724
Matarira D, Mutanga O, Naidu M, Mushore TD, Vizzari M. Characterizing Informal Settlement Dynamics Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis in Durban Metropolitan Area, South Africa: Linking Pattern to Process. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032724
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatarira, Dadirai, Onisimo Mutanga, Maheshvari Naidu, Terence Darlington Mushore, and Marco Vizzari. 2023. "Characterizing Informal Settlement Dynamics Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis in Durban Metropolitan Area, South Africa: Linking Pattern to Process" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032724
APA StyleMatarira, D., Mutanga, O., Naidu, M., Mushore, T. D., & Vizzari, M. (2023). Characterizing Informal Settlement Dynamics Using Google Earth Engine and Intensity Analysis in Durban Metropolitan Area, South Africa: Linking Pattern to Process. Sustainability, 15(3), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032724











