Happy and Engaged Workforce in Industry 4.0: A New Concept of Digital Tool for HR Based on Theoretical and Practical Trends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
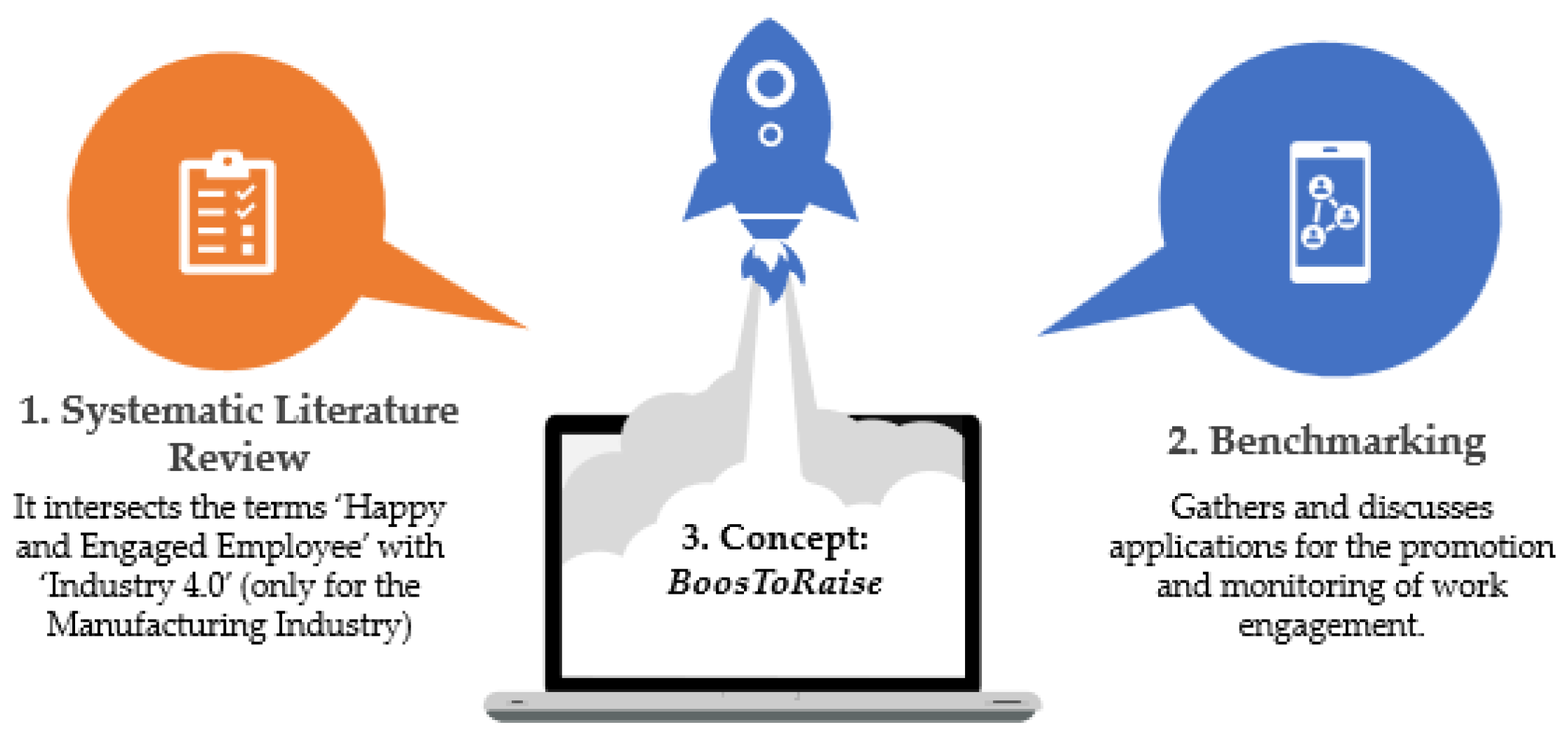
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SLR Methodology
2.2. Benchmarking Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical Perspective of a Happy and Engaged Employee: Systematic Literature Review
3.1.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1.2. Content Analysis
People’s Challenges in Industry 4.0
- The Impact of COVID-19 on the Workforce
Predictors of an Engaged and Happy Worker in Industry 4.0
- (a)
- Internal social networks enhance work engagement.
- (b)
- This type of corporate social network is a tool in which managers and leaders can communicate with their employees in a direct and uncomplicated way and, eventually, become more engaged with them. This happens, as in this type of tool there is direct communication without delays (which avoids disappointment on the part of employees), less formal criteria, as well as the chance to communicate at different hierarchical levels.
- (c)
- Internal social networks facilitate the flow of communication and collaborative work (employees who have just joined the company tend to agree more with the statement than employees who have worked for the same company for several years).
- (d)
- To establish internal social networks, the company must have a flat hierarchy and open interaction.
- (e)
- There is an interdependence between trust because of employee engagement and the successful use of internal social media. For an internal social network to be well received, there must already be trust in management, employees, and the tools themselves.
- Gamification as a Way for Achieving Engaged and Happy Workers in Industry 4.0
3.2. Practical Perspective of a Happy and Engaged Employee: Benchmarking of Practical Applications
- IBM Kenexa Talent Suite:
- IBM Watson Talent Suite:
- Microsoft Teams:
- Microsoft Viva:
- Leapsome:
- Lattice:
- Blink:
- Bitrix24
- :
- Factorial:
- 15Five:
- BetterUp:
- Motivosity:
- PeopleHum:
- DeskAlerts:
3.3. BoosToRaise: An Engagement Platform Concept
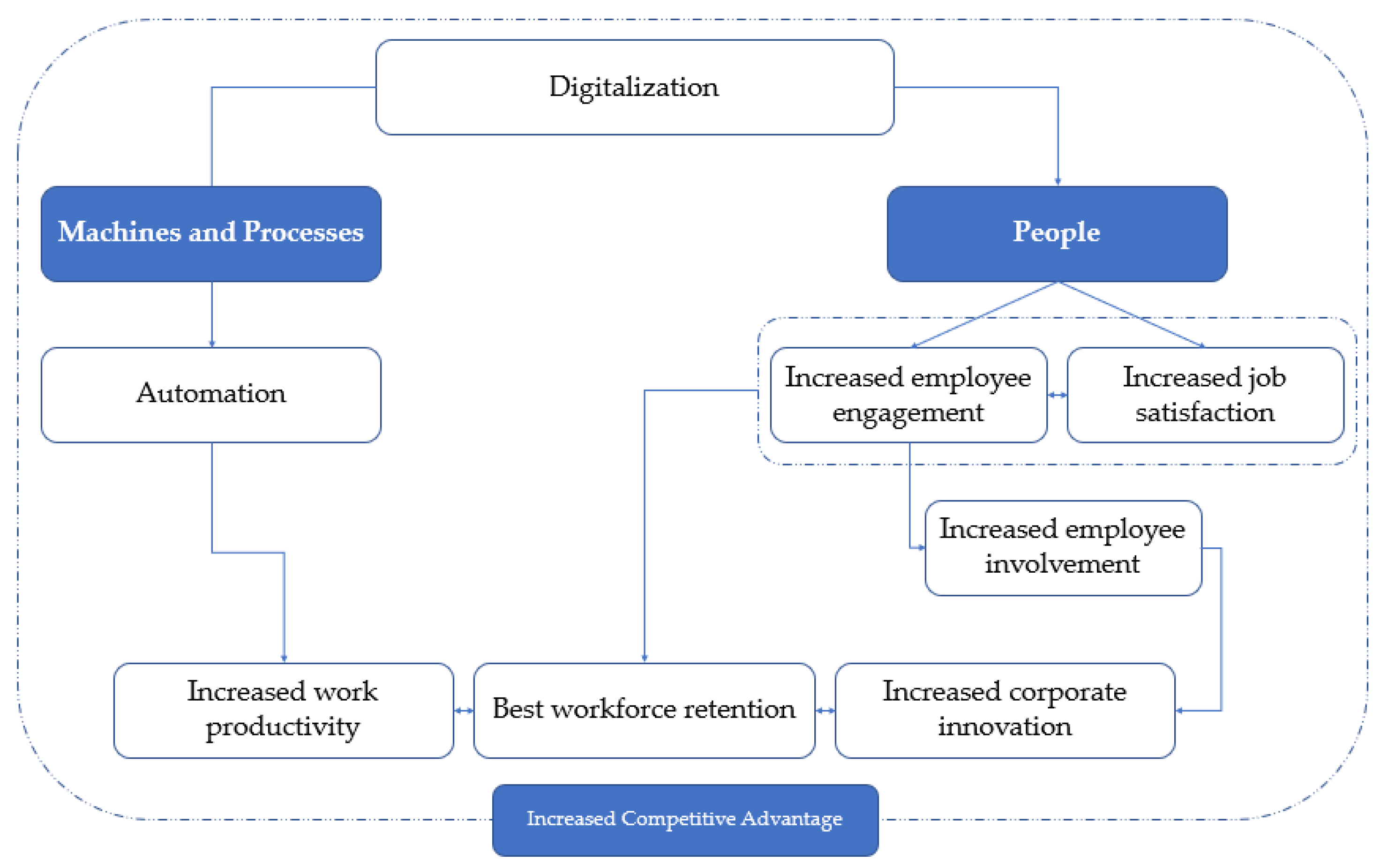
4. Discussion
5. Final Remarks and Contributions
5.1. Conclusions and Main Contributions
5.2. Limitations and Future Work
- Validation in a real industrial context of the created concept.
- Modeling and prototyping of the digital tool modules and testing in practical and industrial context.
- Auscultation and validation of the application of the engagement predictors highlighted in this paper in a real industrial context.
- Creation of a framework for sustainable human resource management 4.0, with theoretical and practical evidence.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Document Type | Region | Article Title | Source Title | Publication Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Article | Italy Cyprus | Remote working and digital transformation during the COVID-19 pandemic: Economic–financial impacts and psychological drivers for employees | Journal of Business Research | 2022 |
| 2 | Article | United States Czech Republic | Job satisfaction during COVID-19: Industry 5.0 as a driver of sustainable development and gender equality | Technological and Economic Development of Economy | 2022 |
| 3 | Article | Poland | Job Satisfaction and Work Characteristics Combinations in Industry 4.0 Environment—Insight from the Polish SMEs in the Post–Pandemic Era | Sustainability | 2022 |
| 4 | Article | Switzerland Finland Netherlands Japan | Crafting work-nonwork balance involving life domain boundaries: Development and validation of a novel scale across five countries | Frontiers in Psychology | 2022 |
| 5 | Article | South Korea | Promoting Psychological Well-Being at Workplace through Protean Career Attitude: Dual Mediating Effect of Career Satisfaction and Career Commitment | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2022 |
| 6 | Conference Paper | Germany | Job satisfaction: An explorative study on work characteristics changes of employees in Intralogistics 4.0 | Journal of Business Logistics | 2022 |
| 7 | Article | United Kingdom | The Evolution of Enterprise Gamification in the Digital Era and the Role of Value-Based Models | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 2022 |
| 8 | Article | Germany | Digitalisation and Employees’ Subjective Job Quality in the Second Half of Working Life in Germany | Social Indicators Research | 2022 |
| 9 | Article | China Pakistan | The Impact of Authentic Leadership on Innovative Work Behavior: Mediating Roles of Proactive Personality and Employee Engagement | Frontiers in Psychology | 2022 |
| 10 | Article | Spain | Working Conditions and Work Engagement by Gender and Digital Work Intensity | Information (Switzerland) | 2022 |
| 11 | Article | Switzerland | Decomposing the effects of digitalization on workers’ job satisfaction | International Review of Economics | 2022 |
| 12 | Article | Spain | The role of human resource practices in the implementation of digital transformation | International Journal of Manpower | 2022 |
| 13 | Article | Portugal | Quality Control 4.0: a way to improve the quality performance and engage shop floor operators | International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management | 2022 |
| 14 | Article | Germany | Autonomy and new modes of control in digital work contexts—a mixed-methods study of driving professions in food logistics | Employee Relations | 2022 |
| 15 | Article Review | Brazil | Digital transformation of business model in manufacturing companies: challenges and research agenda | Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing | 2022 |
| 16 | Conference Paper | Malaysia | Exploring the Factors That Influence the Success of Digitalization in An Organization’s IT Department | 2021 6th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering | 2022 |
| 17 | Article | Germany | Physiological stress in response to multitasking and work interruptions: Study protocol | PLoS ONE | 2022 |
| 18 | Article | Germany | Healthy and Happy Working from Home? Effects of Working from Home on Employee Health and Job Satisfaction | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2022 |
| 19 | Conference Paper | France Canada | Lean 4.0: typology of scenarios and case studies to characterize Industry 4.0 autonomy model | IFAC-PapersOnLine | 2022 |
| 20 | Article | Sweden Norway | The significance of employee behaviours and soft management practices to avoid digital waste during a digital transformation | International Journal of Lean Six Sigma | 2022 |
| 21 | Article | Slovakia Czech Republic | The growing importance of ecological factors to employees in the transport and logistics sector | Economic Research-Ekonomska Istrazivanja | 2022 |
| 22 | Article | Brazil | Organizational learning culture in industry 4.0: relationships with work engagement and turnover intention | Human Resource Development International | 2022 |
| 23 | Article | South Africa | The collaborative work experience of robotics and human workers in the automobile industry in South Africa | African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development | 2022 |
| 24 | Article | Austria | On the stress potential of an organisational climate of innovation: a survey study in Germany | Behaviour and Information Technology | 2022 |
| 25 | Article | Germany | Acting instead of reacting—ensuring employee retention during successful introduction of i4.0 | Applied System Innovation | 2021 |
| 26 | Article Review | Germany | Digitally connected work and its consequences for strain—a systematic review | Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology | 2021 |
| 27 | Article | Spain Taiwan | Unlocking the Contradictory Outcomes of Presenteeism Through a Temporal Model: Effort Exertion as a Mediator | Frontiers in Psychology | 2021 |
| 28 | Article | United States | The impact of automation and artificial intelligence on worker well-being | Technology in Society | 2021 |
| 29 | Article | Germany Austria | Tailor the message and change will happen? An experimental study of message tailoring as an effective communication strategy for organizational change | Journal of Strategy and Management | 2021 |
| 30 | Article | Italy | Technology acceptance and leadership 4.0: A quali-quantitative study | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2021 |
| 31 | Article | India Oman | Telecommuting during COVID-19: A moderated-mediation approach linking job resources to job satisfaction | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 2021 |
| 32 | Article | Sweden | Virtual engineering using realistic virtual models in brownfield factory layout planning | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 2021 |
| 33 | Article | Serbia | Employee autonomy and engagement in the digital age: The moderating role of remote working | Economic Horizons | 2021 |
| 34 | Article Review | Germany | How are techno-stressors associated with mental health and work outcomes? A systematic review of occupational exposure to information and communication technologies within the technostress model | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2021 |
| 35 | Conference Paper | Russian Federation | Organization of remote work in the context of digitalization | E3S Web of Conferences | 2021 |
| 36 | Article | Indonesia | Digital transformation in the indonesia manufacturing industry: The effect of e- learning, e-task and leadership style on employee engagement | International Journal of Data and Network Science | 2021 |
| 37 | Article | Romania | The influence of internal marketing and job satisfaction on task performance and counterproductive work behavior in an emerging marketing during the COVID-19 pandemic | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2021 |
| 38 | Article | Spain | Job quality and work—life balance of teleworkers | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2021 |
| 39 | Article | France Italy | Technology distraction at work. Impacts on self-regulation and work engagement | Journal of Business Research | 2021 |
| 40 | Article | Thailand New Zealand | Causal Model of Talent Utilization, Engagement and Performance among Employees in the Seafood Processing Industry | Journal of Behavioral Science | 2021 |
| 41 | Article | South Africa | The relationship between self-leadership, the future of human resource management, and work engagement | SA Journal of Human Resource Management | 2021 |
| 42 | Conference Paper | United Kingdom India | Enhanced job satisfaction under tighter technological control: The paradoxical outcomes of digitalisation | New Technology, Work and Employment | 2021 |
| 43 | Conference Paper | Germany | Influence of digitization on employee satisfaction in small and medium-sized enterprises | Procedia Computer Science | 2021 |
| 44 | Article | Belgium | Human resource practices accompanying industry 4.0 in European manufacturing industry | Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management | 2021 |
| 45 | Conference Paper | Austria | The Consideration of Job Satisfaction in the Design of Assistance Systems in Production | IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology | 2021 |
| 46 | Article | Spain | How to foster employee satisfaction by means of coaching, motivation, emotional salary and social media skills in the agri-food value chain | New Medit | 2021 |
| 47 | Article | Malaysia Taiwan | Do digital literacies matter in employee engagement in digitalised workplace? | Journal of Asia Business Studies | 2021 |
| 48 | Conference Paper | Latvia | Motivation in a Business Company Using Technology-Based Communication | Studies in Computational Intelligence | 2021 |
| 49 | Article | Brazil Italy | The mediating effect of employees’ involvement on the relationship between Industry 4.0 and operational performance improvement | Total Quality Management and Business Excellence | 2021 |
| 50 | Article | Spain | What is the future of work? A science mapping analysis | European Management Journal | 2020 |
| 51 | Article | Germany | More self-organization, more control—or even both? Inverse transparency as a digital leadership concept | Business Research | 2020 |
| 52 | Conference Paper | United States | Transforming Digital Employee Experience with Artificial Intelligence | 2020 IEEE/ITU International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Good | 2020 |
| 53 | Article | India | How do firms reorganize to implement digital transformation? | Strategic Change | 2020 |
| 54 | Article Review | United Kingdom | Psychological impacts of the new ways of working (NWW): A systematic review | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2020 |
| 55 | Conference Paper | United Arab Emirates | HR4.0: An Analytics Framework to redefine Employee Engagement in the Fourth Industrial Revolution | 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking | 2020 |
| 56 | Article | Finland Spain Austria New Zealand | Assessing the impact of socio-technical interventions on shop floor work practices | International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing | 2020 |
| 57 | Article | South Africa | Employee Motivation In Crisis Situations: The Case Of A Selected Organization In The Food And Retail Sector In Cape Town | Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal | 2020 |
| 58 | Article | Italy | The promotion of technology acceptance and work engagement in industry 4.0: From personal resources to information and training | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2020 |
| 59 | Article | Switzerland United Kingdom | The effects of a gamified human resource management system on job satisfaction and engagement | Human Resource Management Journal | 2020 |
| 60 | Article Review | India | Industry 4.0: reshaping the future of HR | Strategic Direction | 2020 |
| 61 | Article | Mexico | Industry 4.0 and digitization towards job satisfaction of organizations in Tampico, Tamaulipas, Mexico [Article@Industria 4.0 y la digitalización hacia la satisfacción laboral de las organizaciones enTampico, Tamaulipas, México | Revista de Metodos Cuantitativos para la Economia y la Empresa | 2020 |
| 62 | Conference Paper | Greece | A proposed technology solution for enhancing order picking in warehouses and distribution centers based on a gamified augmented reality application | (2020) Proceedings of the 14th IADIS International Conference Interfaces and Human Computer Interaction 2020, IHCI 2020 and Proceedings of the 13th IADIS International Conference Game and Entertainment Technologies | 2020 |
| 63 | Conference Paper | Australia Germany | Human-centered gamification framework for manufacturing systems | Procedia CIRP | 2020 |
| 64 | Conference Paper | Italy | Human-centered design for improving the workplace in the footwear sector | Procedia CIRP | 2020 |
| 65 | Conference Paper | Russian Federation | Digitalization of the economy and remote employment of women: An analysis of the situation and development prospects | Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies | 2020 |
| 66 | Article | South Korea | A study of the roles of leadership styles and attitudes with social responsibility for the 4th industrial revolution | KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems | 2020 |
| 67 | Article | Sweden | Varying involvement in digitally enhanced employee-driven innovation | European Journal of Innovation Management | 2019 |
| 68 | Conference Paper | Romania | The Integration of the Blended Learning Concept into Employee Training as a Factor in Shifting Mentalities towards the Industry 4.0 Approach | Proceedings of 2019 8th International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management | 2019 |
| 69 | Conference Paper | Russian Federation | Employee Engagement’ Management Facilitates the Recovery from Crisis Situations | Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Communication Strategies in Digital Society Seminar, ComSDS | 2019 |
| 70 | Article | China | Three-way interaction effect of job insecurity, job embeddedness and career stage on life satisfaction in a digital era | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2019 |
| 71 | Conference Paper | United States | Collaborative workspace for employee engagement leveraging social media architecture | Society of Petroleum Engineers—Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference 2019, ADIP 2019, | 2019 |
| 72 | Conference Paper | India Denmark Italy Finland | User Experiences and Wellbeing at Work | Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) | 2019 |
| 73 | Article | Slovenia | How digitalization changes the workplace | Dynamic Relationships Management Journal | 2019 |
| 74 | Article | South Korea | The relationship between job uncertainty and job satisfaction: The moderating effect of charismatic leadership, organizational communication, and self-efficacy | International Journal of Financial Research | 2019 |
| 75 | Conference Paper | Portugal | “Quality Box”, a way to achieve the employee involvement | (2019) Springer Proceedings in Mathematics and Statistics | 2019 |
| 76 | Article | Finland | Role of demands-resources in work engagement and burnout in different career stages | Journal of Vocational Behavior | 2018 |
| 77 | Article | Indonesia | The holistic work engagement: A study in indonesia oil palm industry | International Journal of Engineering and Technology | 2018 |
| 78 | Article | Germany | Engaging employees in (at least partly) disengaged companies. Results of an interview survey within about 500 German corporations on the growing importance of digital engagement via internal social media | Public Relations Review | 2017 |
| 79 | Conference Paper | Germany | The challenges of gamification in the age of Industry 4.0: Focusing on man in future machine-driven working environments | IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference, EDUCON | 2017 |
| 80 | Article | United States | Customer loyalty and employee engagement: An alignment for value | Journal of Business Strategy | 2008 |
References
- Santana, M.; Cobo, M.J. What is the future of work? A science mapping analysis. Eur. Manag. J. 2020, 38, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, S.; Saniuk, S.; Gajdzik, B. Industry 5.0: Improving humanization and sustainability of Industry 4.0. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 3117–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serenko, A. The Great Resignation: The great knowledge exodus or the onset of the Great Knowledge Revolution? J. Knowl. Manag. 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haumer, F.; Schlicker, L.; Murschetz, P.C.; Kolo, C. Tailor the message and change will happen? An experimental study of message tailoring as an effective communication strategy for organizational change. J. Strateg. Manag. 2021, 14, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela-Aro, K.; Upadyaya, K. Role of demands-resources in work engagement and burnout in different career stages. J. Vocat. Behav. 2018, 108, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, M.; Cortese, C.G.; Ghislieri, C. The promotion of technology acceptance and work engagement in industry 4.0: From personal resources to information and training. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silic, M.; Marzi, G.; Caputo, A.; Bal, P.M. The effects of a gamified human resource management system on job satisfaction and engagement. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2020, 30, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, D.; Maeso-fernandez, F. The role of human resource practices in the implementation of digital transformation. Int. J. Manpow. 2022, 43, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiotkowska, A.; Gębczyńska, M. Job Satisfaction and Work Characteristics Combinations in Industry 4.0 Environment—Insight from the Polish SMEs in the Post–Pandemic Era. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiner, C.; Klumpp, M. Autonomy and new modes of control in digital work contexts—A mixed-methods study of driving professions in food logistics. Empl. Relat. 2022, 44, 890–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nåfors, D.; Johansson, B. Virtual engineering using realistic virtual models in brownfield factory layout planning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moica, S.; Gherendi, A.; Veres, C.; Moica, T. The Integration of the Blended Learning Concept into Employee Training as a Factor in Shifting Mentalities towards the Industry 4.0 Approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management (ICITM), Cambridge, UK, 2–4 March 2019; pp. 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédéric, R.; Florian, M.; Laurent, J.; Forget, P.; Pellerin, R.; Samir, L. Lean 4.0: Typology of scenarios and case studies to characterize Industry 4.0 autonomy model. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ližbetinová, L.; Lejsková, P.; Nedeliaková, E.; Caha, Z.; Hitka, M. The growing importance of ecological factors to employees in the transport and logistics sector. Econ. Res. Istraz. 2022, 35, 4379–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, S.; Neuhuber, N.; Mörtl, P. The Consideration of Job Satisfaction in the Design of Assistance Systems in Production. In Smart Technologies for Precision Assembly; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–22. ISBN 9783030726317. [Google Scholar]
- Papetti, A.; Rossi, M.; Menghi, R.; Germani, M. Human-centered design for improving the workplace in the footwear sector. Procedia CIRP 2020, 91, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.C.; Lee, J.W. Promoting Psychological Well-Being at Workplace through Protean Career Attitude: Dual Mediating Effect of Career Satisfaction and Career Commitment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, J.; Powell, D.J. The significance of employee behaviours and soft management practices to avoid digital waste during a digital transformation. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2023, 14, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, D.A.; Urbano, B. How to foster employee satisfaction by means of coaching, motivation, emotional salary and social media skills in the agri-food value chain. New Medit 2021, 20, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, A.; Muench, J.C.; Bruckner, M.T.; Veit, D.J. Digitization or digitalization? Toward an understanding of definitions, use and application in IS research. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2021), Online, 9–13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hannola, L.; Lacueva-Pérez, F.; Pretto, P.; Richter, A.; Schafler, M.; Steinhüser, M. Assessing the impact of socio-technical interventions on shop floor work practices. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 33, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, T.; Pusterla, F. Decomposing the effects of digitalization on workers’ job satisfaction. Int. Rev. Econ. 2022, 69, 263–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cijan, A.; Jenič, L.; Lamovšek, A.; Stemberger, J. How digitalization changes the workplace. Dyn. Relatsh. Manag. J. 2019, 8, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutkar, G.; Roto, V.; Clemmensen, T.; Barricelli, B.R.; Abdelnour- Nocera, J.; Meschtscherjakov, A.; Lopes, A.G.; Campos, P.; Gonçalves, F. User Experiences and Wellbeing at Work. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11749, ISBN 978-3-030-29389-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bueechl, J.; Härting, R.C.; Schröder, M. Influence of digitization on employee satisfaction in small and medium-sized enterprises. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 2753–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Das, S. How do firms reorganize to implement digital transformation? Strateg. Chang. 2020, 29, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshin, E.M.; Ilyina, I.A.; Kulibanova, V.V.; Teor, T.R. “Employee Engagement” Management Facilitates the Recovery from Crisis Situations. In Proceedings of the 2019 Communication Strategies in Digital Society Workshop (ComSDS), St. Petersburg, Russia, 10 April 2019; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia Pereira, G.; de Lara Machado, W.; Ziebell de Oliveira, M. Organizational learning culture in industry 4.0: Relationships with work engagement and turnover intention. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 2021, 25, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhaus, S.; Grosse, E.H.; Glock, C.H. Job satisfaction: An explorative study on work characteristics changes of employees in Intralogistics 4.0. J. Bus. Logist. 2022, 43, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortmann, L.K.; Simonson, J.; Vogel, C.; Huxhold, O. Digitalisation and Employees’ Subjective Job Quality in the Second Half of Working Life in Germany. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 162, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, B. HR4.0: An Analytics Framework to redefine Employee Engagement in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Mach, M. Unlocking the Contradictory Outcomes of Presenteeism Through a Temporal Model: Effort Exertion as a Mediator. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 740411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputra, N.; Sasmoko, S.B.A. The holistic work engagement: A study In indonesia oil palm industry. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunthasiri, Y.; Intarakamhang, U.; Kongprasert, N.; Carr, S.C.; Young-Hauser, A. Causal Model of Talent Utilization, Engagement and Performance among Employees in the Seafood. J. Behav. Sci. 2014, 16, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, H.; Scholz, C. Engaging employees in (at least partly) disengaged companies. Results of an interview survey within about 500 German corporations on the growing importance of digital engagement via internal social media. Public Relat. Rev. 2017, 43, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonring, M.P. Customer loyalty and employee engagement: An alignment for value. J. Bus. Strategy 2008, 29, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, G.; Miorando, R.; Caiado, R.; Nascimento, D.; Portioli Staudacher, A. The mediating effect of employees’ involvement on the relationship between Industry 4.0 and operational performance improvement. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2021, 32, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereycken, Y.; Ramioul, M.; Desiere, S.; Bal, M. Human resource practices accompanying industry 4.0 in European manufacturing industry. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1016–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlich-Joas, M.; Hess, T.; Neuburger, R. More self-organization, more control—Or even both? Inverse transparency as a digital leadership concept. Bus. Res. 2020, 13, 921–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zel, S.; Kongar, E. Transforming Digital Employee Experience with Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE / ITU International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Good (AI4G), Geneva, Switzerland, 21-25 September 2020; pp. 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, S.; Ismail, R.; Baharum, A.; Hidayah Mat Zain, N. Exploring the Factors That Influence the Success of Digitalization in An Organization’s IT Department. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Kedah, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, E.; Alfiero, S.; Leonidou, E. Remote working and digital transformation during the COVID-19 pandemic: Economic–financial impacts and psychological drivers for employees. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 150, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Modroño, P. Working Conditions and Work Engagement by Gender and Digital Work Intensity. Information 2022, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Alalyani, W.R.; Thoudam, P.; Anwar, I.; Bino, E. Telecommuting during covid 19: A moderated-mediation approach linking job resources to job satisfaction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos-Bencze, D.; Sokolova, M.; Zubr, V.; Mohelska, H. Job Satisfaction During Covid-19: Industry 5.0 As a Driver of Sustainable Development and Gender Equality. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2022, 28, 1527–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerksieck, P.; Brauchli, R.; de Bloom, J.; Shimazu, A.; Kujanpää, M.; Lanz, M.; Bauer, G.F. Crafting work-nonwork balance involving life domain boundaries: Development and validation of a novel scale across five countries. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 892120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebuhr, F.; Borle, P.; Börner-Zobel, F.; Voelter-Mahlknecht, S. Healthy and Happy Working from Home? Effects of Working from Home on Employee Health and Job Satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesha, A.V.; Tonkikh, N.V. Digitalization of the Economy and Remote Employment ofWomen: An Analysis of the Situation and Development Prospects. In Proceedings of the International Science and Technology Conference, Vladivostok, Russia, 1–2 March 2019; pp. 557–568, ISBN 9789811522437. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, L.; Kaltenegger, H.C.; Nowak, D.; Weigl, M.; Rohleder, N. Physiological stress in response to multitasking and work interruptions: Study protocol. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, Y.; Vione, K.C. Psychological impacts of the new ways of working (NWW): A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, M.A.; Castellano, S.; Khelladi, I.; Marinelli, L.; Monge, F. Technology distraction at work. Impacts on self-regulation and work engagement. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 126, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolg, S.; Heiden, B.; Herbig, B. Digitally connected work and its consequences for strain—A systematic review. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borle, P.; Reichel, K.; Niebuhr, F.; Voelter-Mahlknecht, S. How are techno-stressors associated with mental health and work outcomes? A systematic review of occupational exposure to information and communication technologies within the technostress model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemteanu, M.S.; Dabija, D.C. The influence of internal marketing and job satisfaction on task performance and counterproductive work behavior in an emerging marketing during the covid-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Modroño, P.; López-Igual, P. Job quality and work—Life balance of teleworkers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheveleva, A.; Rogov, E. Organization of remote work in the context of digitalization. Proc. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 273, 12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazareno, L.; Schiff, D.S. The impact of automation and artificial intelligence on worker well-being. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, B.I.; Nekhwevha, F.H. The collaborative work experience of robotics and human workers in the automobile industry in South Africa. African J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2022, 14, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoretto, C.; Mendes, G.H. de S.; Filho, M.G.; Gouvea de Oliveira, M.; Ganga, G.M.D. Digital transformation of business model in manufacturing companies: Challenges and research agenda. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2022, 37, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.S.; Trusson, C.; Siwale, J.; Ravishankar, M.N. Enhanced job satisfaction under tighter technological control: The paradoxical outcomes of digitalisation. New Technol. Work Employ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.S.; Borges, A.F.; Magano, J. Quality Control 4.0: A way to improve the quality performance and engage shop floor operators. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2022, 39, 1471–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.J.; Hooi, L.W.; Ngui, K.S. Do digital literacies matter in employee engagement in digitalised workplace? J. Asia Bus. Stud. 2021, 15, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Chin, T. Three-way interaction effect of job insecurity, job embeddedness and career stage on life satisfaction in a digital era. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molino, M.; Cortese, C.G.; Ghislieri, C. Technology acceptance and leadership 4.0: A quali-quantitative study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purba, C.B. Digital transformation in the indonesia manufacturing industry: The effect of e- learning, e-task and leadership style on employee engagement. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2021, 5, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Bansal, M.; Verma, J. Industry 4.0: Reshaping the future of HR. Strateg. Dir. 2020, 36, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Martínez, M.A.; Román Salinas, R.V.; Santiago Santiago, A.D.; Barrios, C.M.; Cruz, R.Z. Industry 4.0 and digitization towards job satisfaction of organizations in Tampico, Tamaulipas, México. Rev. Métodos Cuantitativos para La Econ. La Empres. 2020, 30, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickemeyer, S.C.; Busch, J.; Liu, C.-T.; Lippke, S. Acting Instead of Reacting—Ensuring Employee Retention during Successful Introduction of i4.0. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.M. The relationship between self-leadership, the future of human resource management, and work engagement. SA J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2021, 19, a1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskovic, A. Employee Autonomy and Engagement in the Digital Age: The Moderating Role of Remote Working. Econ. Horizons 2021, 23, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Alam, M.; Gul, F.; Wang, Y. The Impact of Authentic Leadership on Innovative Work Behavior: Mediating Roles of Proactive Personality and Employee Engagement. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 879176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Riedl, R. On the stress potential of an organisational climate of innovation: A survey study in Germany. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2022, 41, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, I.; Lindberg, M. Varying involvement in digitally enhanced employee-driven innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 22, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, S.W. A study of the roles of leadership styles and attitudes with social responsibility for the 4th industrial revolution. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2020, 14, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Hahm, S.W. The relationship between job uncertainty and job satisfaction: The moderating effect of charismatic leadership, organizational communication, and self-efficacy. Int. J. Financ. Res. 2019, 10, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefi, N.P.; Asoba, S.N. Employee Motivation In Crisis Situations: The Case Of A Selected Organization In The Food And Retail Sector In Cape Town. Acad. Entrep. J. 2020, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, M.; Cakula, S. Motivation in a Business Company Using Technology-Based Communication. In Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0 A Collection of Innovative Research Case-Studies That Are Reworking the Way We Look at Industry 4.0 Thanks to Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–28. ISBN 9783030610449. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa e Silva, C.; Sousa, C. “Quality Box”, a Way to Achieve the Employee Involvement. In Industrial Engineering and Operations Management I.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 20, pp. 401–402. ISBN 9783030149680. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, K.; Lamacchia, D. Collaborative workspace for employee engagement leveraging social media architecture. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 15–18 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Epelle, I.; Olayinka, O.; Jones, P. The Evolution of Enterprise Gamification in the Digital Era and the Role of Value-Based Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuldt, J.; Friedemann, S. The challenges of gamification in the age of Industry 4.0: Focusing on man in future machine-driven working environments. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Athens, Greece, 25–28 April 2017; pp. 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakas, G.; Aretoulaki, E.; Ponis, S.T.; Agalianos, K.; Maroutas, T.N. A proposed technology solution for enhancing order picking in warehouses and distribution centers based on a gamified augmented reality application. In Proceedings of the 14th IADIS International Conference Interfaces and Human Computer Interaction 2020 (part of MCCSIS 2020), Online, 23–25 July 2020; pp. 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, J.; Braun, S.; Cheng, C.T.; Dowey, S.; Wollert, J. Human-centered gamification framework for manufacturing systems. Procedia CIRP 2020, 93, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C. “Alert-Software.” 11 Best Employee Engagement Apps You Should Definitely Try in 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.alert-software.com/blog/employee-engagement-app (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- BasuMallick, C. “Spiceworks.” Top 10 Employee Engagement Apps for 2020. 2021. Available online: https://www.spiceworks.com/hr/talent-management/articles/top-employee-engagement-apps/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Reitsma, T. “PeopleManagingPeople.” 10 Best Employee Engagement Software For 2023. 2022. Available online: https://peoplemanagingpeople.com/tools/best-employee-engagement-software/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- “Capterra.” Employee Engagement Software. Available online: https://www.capterra.com/employee-engagement-software/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Kumar, P. SpringWorks. 23 Best Employee Engagement Apps for 2023. 2022. Available online: https://www.springworks.in/blog/best-employee-engagement-apps/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- IBM. IBM Ajuda Empresas a Repensarem a Gestão de Pessoas com IA. 2018. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/blogs/ibm-comunica/ibm-ajuda-empresas-a-repensarem-a-gestao-de-pessoas-com-ia/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Microsoft Teams. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/pt-pt/microsoft-teams/compare-microsoft-teams-options-b?=&ef_id=Cj0KCQiAn4SeBhCwARIsANeF9DJTCpg-FXh1bWKreOIjRf1uT3W2vwwJ60arkJDRKN3kqK2yy1K_yWoaAhvIEALw_wcB%3AG%3As&OCID=AIDcmmhnaxwyfa_SEM_Cj0KCQiAn4SeBhCwARIsANeF9DJTCpg-FXh1bWKr (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Microsoft Viva. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/pt-pt/microsoft-viva (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Leapsome. Available online: https://www.leapsome.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Lattice. Available online: https://lattice.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Blink. Available online: https://joinblink.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Bitrix24. Available online: https://www.bitrix24.com/solutions/need/management_and_leadership.php (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Factorial. Available online: https://factorialhr.pt/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- 15Five. Available online: https://www.15five.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- BetterUp. Available online: https://www.betterup.com/?hsLang=en (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Motivosity. Available online: https://www.motivosity.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Peoplehum. 2022. Available online: https://www.peoplehum.com/ (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- DeskAlerts. Available online: https://www.alert-software.com/?hsLang=en (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Schallock, B.; Rybski, C.; Jochem, R.; Kohl, H. Learning Factory for Industry 4.0 to provide future skills beyond technical training. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 23, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadorinho, J.; Teixeira, L. Leadership coaching framework tool-based to support worker engagement and retention in Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Rome, Italy, 26–28 July 2022. [Google Scholar]






| Themes | String |
|---|---|
| Happy and Engaged Employee | (“Employee Engagement” OR “Employee Motivation” OR “Work Engagement” OR “Employee Involvement” OR “Organizational Commitment” OR “Workforce Retention” OR “Job Satisfaction”) |
| Industry 4.0 | (“Industry 4.0” OR “Fourth Industrial Revolution” OR “Digitalization” OR “Digital Transformation” OR “Operator 4.0” OR “Industry 5.0”) |
| Engagement and Job Satisfaction Drivers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tools | Employee Role | Employee Skills and Career Management | Supervision Support | Social Relationships | Gamification | Analytics |
| IBM Kenexa Talent Suites [90] | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| IBM Watson Talent Suite [90] | Watson Candidate Assistant | Watson Career Coach | - | - | Badging Leaderboards | - |
| Microsoft Teams [91] | - | - | - | Communities creation; Conversations channels; Online video calling | - | - |
| Microsoft Viva [92] | Viva Insights; Viva Topics | Viva Learning | Viva Insights | Viva Connections | Badging; Leaderboards | - |
| Leapsome [93] | Performance review | Skills Map; Learning paths; Learning Track; Learning content | Goals and OKR management; Meetings support (agenda and summary) | Public praise; Private feedback | - | Pulse surveys; Data dashboards |
| Lattice [94] | Create, launch and track assessments | Skills Map; Individual Development Plans; Career Track | Goals and OKR management | Public praise | Badging; Leaderboards | Pulse surveys; Data Dashboards |
| Blink [95] | Knowledge hub (with policies, procedures and guides) | - | - | News feed with updates; Chat with groups or individually (1:1); Public Praise | - | Creation and distribution of forms |
| Bitrix24 [96] | Built-in online time clock | - | Project monitoring and management (work reports, Gantt charts, customizable kanban boards) | Conferences Private and group chats | Badging | - |
| Factorial [97] | Notification of defined or modified shifts for employees; Customization of performance evaluations | Training management system | Goals and OKR management | - | - | - |
| 15Five [98] | Performance reviews | Coaching hub | Goals and OKR management | Public praise | Badging | Pulse surveys |
| BetterUp [99] | Coaching hub; Learning paths | - | - | Microlearning | - | |
| Motivosity [100] | - | - | Weekly collaboration processes with preparedness prompt (between supervisor and employee); Meeting notes; Goals and OKR management | Public praise | Badging; Leaderboards | Pulse surveys |
| PeopleHum [101] | Suggestion system | Learning recommendations; Skills map and potential | Goals and OKR management; Collecting and creating ideas in real time | News feed with updates; Public Praise | - | Pulse surveys |
| DeskAlerts [102] | Alerts | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvadorinho, J.; Teixeira, L. Happy and Engaged Workforce in Industry 4.0: A New Concept of Digital Tool for HR Based on Theoretical and Practical Trends. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032781
Salvadorinho J, Teixeira L. Happy and Engaged Workforce in Industry 4.0: A New Concept of Digital Tool for HR Based on Theoretical and Practical Trends. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032781
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvadorinho, Juliana, and Leonor Teixeira. 2023. "Happy and Engaged Workforce in Industry 4.0: A New Concept of Digital Tool for HR Based on Theoretical and Practical Trends" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032781
APA StyleSalvadorinho, J., & Teixeira, L. (2023). Happy and Engaged Workforce in Industry 4.0: A New Concept of Digital Tool for HR Based on Theoretical and Practical Trends. Sustainability, 15(3), 2781. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032781







