Critical Success Factors for Internet of Things (IoT) Implementation in Automotive Companies, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
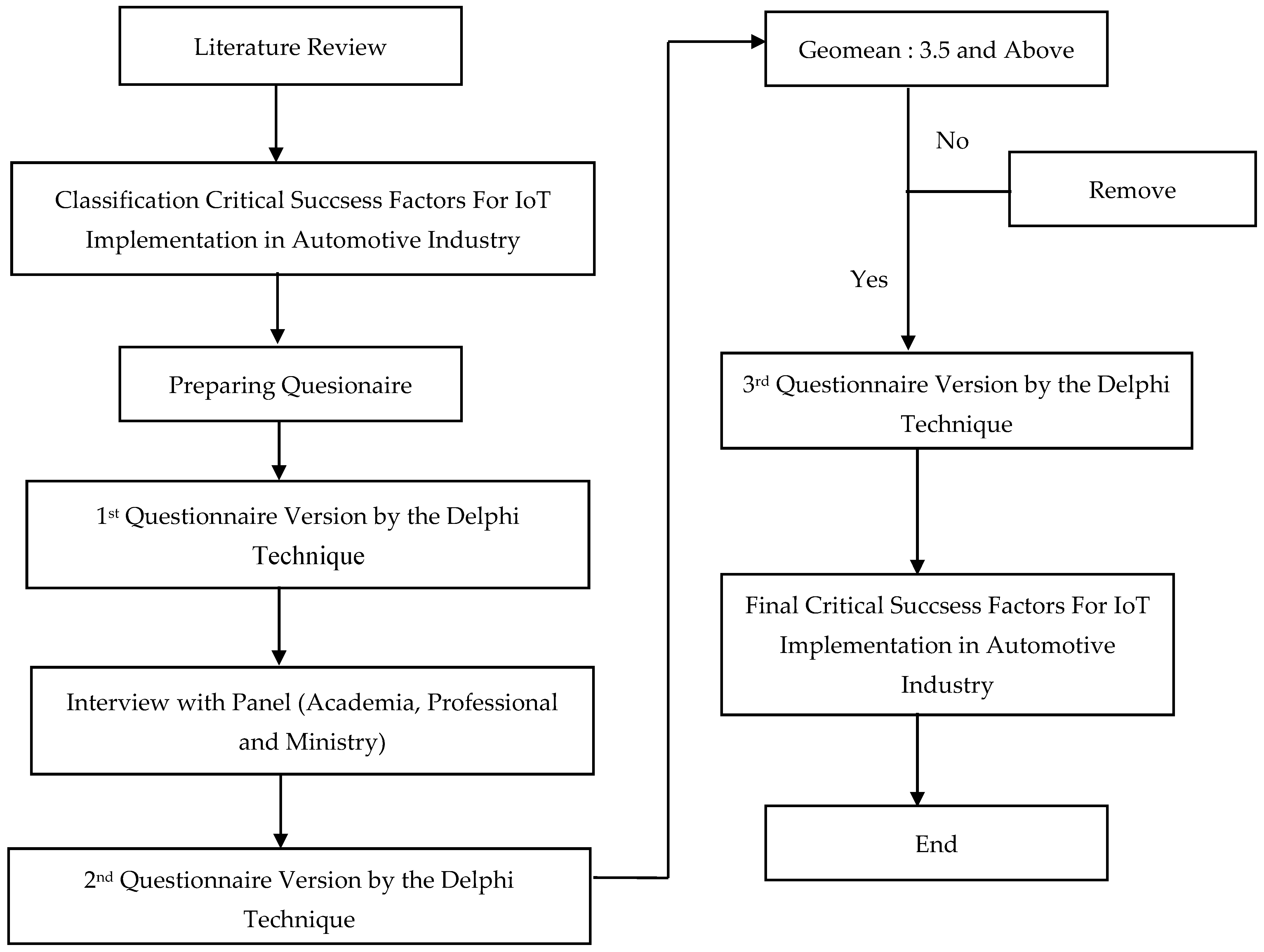
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Critical Success Factors
2.2. Delphi Method
2.3. Geomean
2.4. Panel Selection
3. Results
3.1. Geomean Data Processing Results
3.2. Statistic Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Contribution
5.2. Managerial Contribution
5.3. Limitation and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matta, P.; Bant, B. Internet of Things: Genesis, Challenges, and Applications. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 14, 1717–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, G.; Parkhe, S.S.; Thakar, C.M.; Kulkarni, V.V.; Mishra, H.G.; Gulothungan, G. Implementation of IoT in Production and Manufacturing: An Industry 4.0 Approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. The Future of Manufacturing: A New Perspective. Engineering 2018, 4, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, P.M.; Yahouni, Z.; Alpan, G. Literature Review on Using Data Mining in Production Planning and Scheduling Within The Context Of Cyber-Physical Systems. J. Ind. Inf. Int. 2022, 28, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Industry 4.0: A Survey on Technologies, Applications, and Open Research Issues. J. Ind. Inf. Int. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F. Digital Twin and Big Data Towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenperin: Industri 4.0 Solusi Peningkatan Daya Saing Indonesia. Available online: https://kemenperin.go.id/artikel/17432/Industri-4.0-Solusi-Peningkatan-Daya-Saing-Indonesia (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Kahveci, S.; Alkan, B.; Ahmad, M.H.; Ahmad, B.; Harrison, R. An end-to-end Big Data Analytics Platform For Iot-Enabled Smart Factories: A Case Study of Battery Module Assembly System For Electric Vehicles. J. Manuf. Sys. 2022, 63, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nižetić, S.; Šolić, P.; López-de-Ipiña González-de-Artaza, D.; Patrono, L. Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities, Issues, and Challenges Towards A Smart and Sustainable Future. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Ahuja, I.P.S.; Singh, H.; Singh, A. Development and Implementation of Autonomous Quality Management System (AQMS) in Automotive Manufacturing using Quality 4.0 Concept– A Case Study. Com. Ind. Eng. 2022, 168, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Asyhari, A.T.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Ramasamy, D. Evolution of IoT-enabled Connectivity and Applications in The Automotive Industry: A review. Veh. Commun. 2021, 27, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, A.; Mogale, D.G.; Bourlakis, M.; Maniraj Maiyar, L.; Moradlou, H. The Link Between Industry 4.0 and Green Supply Chain Management: Evidence from The Automotive Industry. Com. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohang, A.; Sargent, C.S.; Nord, J.H.; Paliszkiewicz, J. Internet of Things (IoT): From awareness to continued use. Int. J. Inf. Man. 2022, 62, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, K. The Internet of Things (IoT): Applications, Investments, and Challenges For Enterprises. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, M.; Leminen, S.; Rajahonka, M. Designing Business Models for the Internet of Things. Tech. Innov. Man. Rev. 2014, 4, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Joshi, S.; Kannan, D.; Govindan, K.; Singh, R.; Purohit, H.C. Internet of Things (IoT) Adoption Barriers Of Smart Cities’ Waste Management: An Indian Context. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Luthra, S.; Haleem, A.; Mangla, S.K.; Garg, D. Identification and Evaluation of Critical Factors to Technology Transfer Using The AHP Approach. Int. Strateg. Manag. Rev. 2015, 3, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, R.K.; Suri, P.K. Prioritizing Critical Success Factors for Sustainable Service Quality Management by Logistics Service Providers. Vision 2018, 22, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L. Research on Successful Factors and Influencing Mechanism of the Digital Transformation in SMEs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fui-Hoon Nah, F.; Lee-Shang Lau, J.; Kuang, J. Critical factors for Successful Implementation of Enterprise Systems. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2001, 7, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacagnella, A.C.; da Silva, S.L.; Pacífico, O.; de Arruda Ignacio, P.S.; da Silva, A.L. Critical Success Factors for Project Manufacturing Environments. Proj. Man. J. 2019, 50, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.T.; Yuen, K.F.; Li, K.X.; Balci, G.; Ma, F. A Theory-Driven Identification and Ranking of The Critical Success Factors of Sustainable Shipping Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, A.; Ibem, E.; Aduwo, E.; Tunji-Olayeni, P.; Oluwunmi, O. Critical success factors (CSFs) for e-Procurement Adoption in The Nigerian Construction Industry. Buildings 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zeng, M. Research on Key Success Factors Model for Innovation Application of Internet of Things with Grounded Theory. In Proceedings of the Fourteen Wuhan International Conference on E-Business, Wuhan, China, 19 June 2015; Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1047&context=whiceb2015 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Kiba-Janiak, M. Key Success Factors for City Logistics from the Perspective of Various Groups of Stakeholders. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 12, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, R.K.; Shankar, R. Critical Success Factors for The Implementation of Supply Chain Management In Indian Small And Medium Enterprises And Their Impact On Performance. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2015, 27, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, K. 6 Factors Crucial to The Success of Industrial. Available online: www.dxc.technology/manufacturing (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Sony, M.; Naik, S. Critical Factors for the Successful Implementation of Industry 4.0: A Review and Future Research Direction. Prod. Plan. Control. 2020, 31, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankel, M. The Reference Architectural Model INDUSTRIE4.0 (RAMI4.0).” ZWEI: Die Elektroindustrie. 2015. Available online: https://www.zvei.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Presse_und_Medien/Publikationen/2016/januar/GMA_Status_Report__Reference_Archtitecture_Model_Industrie_4.0__RAMI_4.0_/GMA-Status-Report-RAMI-40-July-2015.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Flatt, H.; Schriegel, S.; Jasperneite, J.; Trsek, H.; Adamczyk, H. Analysis of the Cyber-Security of Industry 4.0 Technologies Based on RAMI 4.0 and Identification of Requirements. In Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Attaran, M. Critical Success Factors and Challenges of Implementing RFID in Supply Chain Management. J. Supply Chain. Oper. Manag. 2012, 10, 144–167. [Google Scholar]
- Denolf, J.M.; Trienekens, J.H.; Wognum, P.M.; Van Der Vorst, J.G.A.J.; Omta, S.W.F. Towards A Framework of Critical Success Factors for Implementing Supply Chain Information Systems. Comp. Ind. 2015, 68, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, S.; Corbett, M. ERP Implementation: A Compilation and Analysis of Critical Success Factors. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2007, 13, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Mangla, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, D. Evaluating Factors in The Implementation of Successful Green Supply Chain Management Using DEMATEL: A Case Study. Int. Strateg. Manag. Rev. 2015, 3, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolina, S.; Alias, S. Critical Success Factors for Digital Manufacturing Implementation in the Context of Industry 4. In Proceedings of the 2017 Industrial and Systems Engineering Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20–23 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Y.; Chiu, A.A.; Chao, P.C.; Arniati, A. Critical Success Factors in Implementing Enterprise Resource Planning Systems for Sustainable Corporations. Sustainability. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.S.A.; Hamid, A.B.A.; Thoo, A.C. Critical Success Factors of Supply Chain Management: A Literature Survey and Pareto Analysis. Europe. J. Bus. 2015, 10, 234–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H. Value Propositions for the Internet of Things: Guidance for Entrepreneurs Selling to Enterprises. Tech. Innov. Man. 2017, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaei, H.; Chng, K.; Shameer, K.; Bin, S. The Application of IoT to Study Consumer Behaviour and Decision-Making Process. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Compt. Eng. 2022, 4, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiesch, C.; Koschmider, A.; Mecella, M.; Weber, B.; Burattin, A.; Di Ciccio, C.; Fortino, G.; Gal, A.; Kannengiesser, U.; Leotta, F.; et al. The Internet of Things Meets Business Process Management: A Manifesto. IEEE Syst. Man Cybern. Mag. 2020, 6, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, S.; Yun, J.; Lim, S.; Park, K. Flex-IoT: Secure and Resource-Efficient Network Boot System for Flexible-IoT Platform. Sensors 2021, 21, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisham, T. The Delphi technique: A method for testing complex and multifaceted topics. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2009, 2, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Sandford, B. The Delphi Technique: Making Sense of Consensus. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2007, 12, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.C.; Chen, D.-F.; Huan, J.-M.; Syr, W.-J.; Chiou, C.-F. Critical Success Factors to Improve the Business Performance of Tea Drink Chains. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, J.W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, I. Qualitative Data Analysis: A User-Friendly Guide for Social Scientists; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, M.B.; Huberman, M.; Saldana, J. Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tersine, R.J.; Riggs, W.E. The Delphi Technique: A Long-Range Planning Tool. Bus. Horiz. 1976, 19, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, C.; Goorbeman-Hill, S.; Mathie, R.; Kennedy, A.; Li, Y.; Baiz, P. Case Study for the Return on Investment of Internet of Things Using Agent-Based Modelling and Data Science. Systems 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, M. Critical Factors Influencing Interface Management of Prefabricated Building Projects: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallowell, M.R.; Gambatese, J.A. Qualitative Research: Application of the Delphi Method to CEM Research. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 136, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, M.J. Delphi: A Technique to Harness Expert Opinion for Critical Decision-making Tasks in Education. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 17, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Design of Financial Information Management System and IoT Application Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. Wireless. Comm. Comput. 2022, 2022, 2483306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osako, L.F.; Matsubayashi, M.O.; Takey, S.M.; Cauchick-Miguel, P.A.; Zancul, E. Cost Evaluation Challenges for Internet of Things (IoT) Based Product/Service-Systems (PSS). Procedia CIRP 2019, 84, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Patel, S.M.; Scholar, P.G. Internet of Things-IOT: Definition, Characteristics, Architecture, Enabling Technologies, Application & Future Challenges. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Comput. 2016, 6, 6122–6131. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, I.M.; Singgih, M.L.; Gunarta, I.K. Critical Success Factors for The Implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) in Automotive Companies: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Singapore, 7–11 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, M.L.; Lin, C.W.R.; Sujanto, R.Y.; Lim, M.K.; Bui, T.D. Assessing Sustainable Consumption in Packaged Food in Indonesia: Corporate Communication Drives Consumer Perception and Behavior. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacob, A. A Review of Internet of Things (IoT): Implementations and Challenges. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascu, E.; Severin, I.; Lascu, F.D.; Gudana, R.A.; Nalbitoru, G.; Ignat, N.D. Framework on Performance Management in Automotive Industry: A Case Study. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvetsova, O.A.; Tanubamrungsuk, P.; Lee, S. Organization Leadership in the Automobile Industry: Knowledge Management and Intellectual Capital. Open Transp. J. 2021, 15, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, I.; Albulushi, A.; Jaza’a Irtaimah, H.; Al-Khasawaneh, M.M. The Impact of ExterIoT Environment Factors on Business Continuity Management to Promoting the Higher Education Excellence in Oman. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 56, 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri, A.; Reis, J.; Amorim, M. A Conceptual Model Proposal to Assess the Effectiveness of IoT in Sustainability Orientation in Manufacturing Industry: An Environmental and Social Focus. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimsakul, S.; Samaranayake, P.; Laosirihongthong, T. Prioritizing Enabling Factors of IoT Adoption for Sustainability in Supply Chain Management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorkany, M.; FaIoT, K.; Yahya, A. Performance Evaluation oIoTot Messaging Protocol Implementation for E-Health Systems. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmar, E.E.; Kertesz, A. Investigating operational costs of IoT cloud applications. Comput. Sci. Soc. Telecommun. Eng. 2018, 189, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
| Reference | Methods | Context | Region of Study | Main Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) | General Organization | India | Identification of critical factors of the effective transfer technology process and evaluation of identified critical factors of the effective technology transfer process from an Indian perspective. |
| [19] | Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) | Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) | China | Provides practitioners with profound insights into the enterprise’s digital technology (DT) and suggests that enterprises attach importance to the improvement of organizational capabilities and use strategy and talents as important resources to promote the success of enterprise digital technology (DT). |
| [20] | Systematic Literature Review (SLR) | General Organization | USA | Classify the 11 CSFs identified into the phases of the ERP implementation life cycle from the literature review. |
| [24] | Grounded Theory | High-Tech Enterprise | China | Collects and analyzes the implementation information and data from three related IoT companies. Then this study identifies 40 key success factors and establishes a key success factors model for the innovative application of IoT in the view of technology, market, and implementation. The purpose is to improve the success rate of IoT application implementation. |
| [26] | Regression Analysis | Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) | India | Measure improvement in performance by considering different measures related to customer service and satisfaction, innovation, growth, financial performance, and internal business. Results are analyzed by testing research propositions using standard statistical tools. |
| [28] | Systematic Literature Review (SLR) | Manufacturing | India | Identity CSFs can be used by organizations as a guiding factor while implementing Industry 4.0 in their organizations. Focusing on these 10 factors will help organizations to be sustainable during the implementation of Industry 4.0. |
| [31] | Literature Review | General Organization | USA | Develop a research model for RFID success to facilitate future research integration and variable selection. The model is general and allows new factors or success variables, when identified, to be added easily. |
| [35] | Literature Review | Manufacturing | Brazil | Contributes to updating digital manufacturing CSF discussion in the new context of Industry 4.0 and it provides a guide to checking the organizational readiness for digital manufacturing. |
| [36] | The Modified Delphi Method (MDM) | Corporation | Taiwan | Identify CSFs for ERP systems in a corporation. Moreover, provide helpful information regarding selection standard for the corporation. |
| This Study | The Delphi Method | Automotive Companies | Indonesia | Identifying critical success factors (CSFs) and providing recommendations to the manufacturing industry, specifically in automotive companies in Indonesia during the implementation of IoT, and guidance for managers in automotive companies planning the implementation of IoT in the future. |
| Dimension | Sub-Dimension | Number of Sub-Dimension | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finance (4 sub-items) | System maintenance costs | (1) | [33,35] |
| Minimize and streamline costs related to the use and purchase of IoT devices in the companies | (2) | [26,35,37] | |
| Factors and the companies’ financial situation in decisions regarding the purchase (upgrade) of IoT devices at the companies | (3) | [25,34,35] | |
| Employee training costs | (4) | [26,36] | |
| Innovation and Ideas (9 sub-items) | The ability of IoT devices to detect and track problems that occur in the system | (5) | [26,35,36] |
| Compatibility of IoT devices with companies’ operational systems | (6) | [25,26] | |
| IoT technology and infrastructure integration | (7) | [24,26,28] | |
| Timely delivery of information | (8) | [24,37] | |
| Quality of information (report) displayed from IoT devices | (9) | [24,28,37] | |
| Cooperative customer support | (10) | [24,26,37] | |
| IoT device performance quality | (11) | [24,28,37] | |
| Ease of IoT devices that can later be changed and repaired | (12) | [26,35,36] | |
| The ability of IoT device components to exchange and use information while operating | (13) | [27,36,37] | |
| Marketing (4 sub-items) | The level of competition in the external scope of the companies | (14) | [24,26] |
| The need for the latest market trends | (15) | [24,26] | |
| Value proposition | (28) * | ||
| Consumer behavior | (29) * | ||
| Operations (4 sub-items) | Standardization of IoT device architecture reference to be implemented in the companies | (16) | [36,37] |
| Flexible and quality service | (17) | [26,37] | |
| Data security system | (18) | [24,28,32] | |
| System efficiency | (30) * | ||
| People and Management (5 sub-items) | Support and commitment from the managerial level in the companies | (19) | [17,28,31,33,35,36] |
| Assessment of employee skill level in operating IoT | (20) | [24,28,35,37] | |
| Effectiveness of communication between employees | (21) | [32,33,35,36,37] | |
| Employee training consistency | (31) * | ||
| Companies’ image and network | (32) * | ||
| Regulations (2 sub-items) | Government regulations and authorities | (22) | [17] |
| Companies’ policy | (33) * | ||
| Resource (3 sub-items) | The output of IoT devices focused on customer demand | (23) | [31,35] |
| Resource management capability in organizing IoT implementation | (24) | [20,28,31,35,36] | |
| The good relationship between partners and stakeholders | (25) | [26,31,37] | |
| Technology (5 sub-items) | Technology standardization. | (26) | [17,24,32,34,36,37] |
| Cooperation with IoT technology service providers | (27) | [24,31,32,35,37] | |
| Internet network support facilities | (34) * | ||
| Internet connection | (35) * | ||
| Backup systems | (36) * |
| Job Title | Industry Segment or Institution | Experience (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Advisor in Automotive Companies | Automotive Companies | 30 |
| Head of Implementation Industry 4.0 | Ministry of Industry | 15 |
| Head of Implementation IoT Training | Automotive Academia | 7 |
| Head of Information System Laboratory | Academia | 35 |
| Senior Instructor in Automotive Companies | Automotive Companies | 20 |
| Dimension | Sub-Dimension | Number of Sub-Dimension | Geomean Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finance | System maintenance costs | (1) | 4.573 | Keep |
| Minimize and streamline costs related to the use and purchase of IoT devices in the companies | (2) | 4.129 | Keep | |
| Factors and the companies’ financial situation in making decisions regarding the purchase (upgrade) of IoT devices at the companies | (3) | 4.373 | Keep | |
| Employee training costs | (4) | 4.573 | Keep | |
| Innovation and Ideas | The ability of IoT devices to detect and track problems that occur in the system | (5) | 4.514 | Keep |
| The compatibility of IoT devices with the companies’ operational systems | (6) | 4.573 | Keep | |
| IoT technology and infrastructure integration | (7) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Timely delivery of information | (8) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Quality of information (report) displayed from IoT devices | (9) | 4.373 | Keep | |
| Customer support | (10) | 4.373 | Keep | |
| IoT device performance quality | (11) | 4.183 | Keep | |
| Ease of IoT devices that can later be changed and repaired | (12) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| The ability of IoT device components to exchange and use information during operation ton | (13) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Marketing | The level of competition in the companies’ external scope | (14) | 3.776 | Keep |
| The need for the latest market trends | (15) | 4.573 | Keep | |
| Value proposition (M3) | (16) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Consumer behavior (M4) | (17) | 4.129 | Keep | |
| Operations | Standardization of IoT device architecture reference to be implemented in the Companies | (18) | 2.993 | Delete |
| Flexible and quality service | (19) | 3.776 | Keep | |
| Data security system | (20) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| System efficiency | (21) | 4.573 | Keep | |
| People and Management | Support and commitment from the managerial level in the companies | (22) | 4.514 | Keep |
| Assessment of employees’ skill level in operating IoT | (23) | 3.438 | Delete | |
| Effective communication between employees | (24) | 3.482 | Delete | |
| Employee training consistency | (25) | 3.641 | Keep | |
| Companies’ image and network | (26) | 3.366 | Delete | |
| Regulations | Government regulations and authorities | (27) | 3.565 | Keep |
| Companies’ policy | (28) | 4.129 | Keep | |
| Resource | The output of IoT devices focused on customer demand | (29) | 4.782 | Keep |
| Project management skills in organizing IoT implementation | (30) | 3.949 | Keep | |
| The good relationship between partners and stakeholders | (31) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Technology | Technology standardization | (32) | 3.949 | Keep |
| Cooperation with IoT technology service providers | (33) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Internet network Support facilities | (34) | 4.782 | Keep | |
| Internet connection | (35) | 5.000 | Keep | |
| Backup systems | (36) | 4.782 | Keep |
| Case Processing Summary | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Valid | 5 | 100 |
| Excluded | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 5 | 100 | |
| Cronbach’s Alpha | N of Item |
|---|---|
| 0.778 | 32 |
| Dimension | Sub-Dimension | Number of Sub-Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| Finance 4 sub-items | System maintenance costs | (1) |
| Minimize and streamline costs related to the use and purchase of IoT devices in the companies | (2) | |
| Factors and the companies’ financial situation in making decisions regarding the purchase (upgrade) of IoT devices at the companies | (3) | |
| Employee training costs | (4) | |
| Innovation and Ideas 9 sub-items | The ability of IoT devices to detect and track problems that occur in the system | (5) |
| The compatibility of IoT devices with the companies’ operational systems | (6) | |
| IoT technology and infrastructure integration | (7) | |
| Timely delivery of information | (8) | |
| Quality of information (report) displayed from IoT devices | (9) | |
| Customer support | (10) | |
| IoT device performance quality | (11) | |
| Ease of IoT devices that can later be changed and repaired | (12) | |
| The ability of IoT device components to exchange and use information during the operation | (13) | |
| Marketing 4 sub-items | The level of competition in the companies’ external scope | (14) |
| The need for the latest market trends | (15) | |
| Value Proposition | (16) | |
| Consumer behavior | (17) | |
| Operations 3 sub-items | Flexible and quality service | (18) |
| Data security system | (19) | |
| System efficiency | (20) | |
| People and Management 2 sub-items | Support and commitment from the managerial level in the companies | (21) |
| Employee training consistency | (22) | |
| Regulations | Government regulations and authorities | (23) |
| 2 sub-items | Companies’ policy | (24) |
| Resource 3 sub-items | The output of IoT devices focused on customer demand | (25) |
| Project management skills in organizing IoT implementation | (26) | |
| The good relationship between partners and stakeholders | (27) | |
| Technology 5 sub-items | Technology standardization | (28) |
| Cooperation with IoT technology service providers | (29) | |
| Internet network support facilities | (30) | |
| Internet connection | (31) | |
| Backup systems | (32) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakim, I.M.; Singgih, M.L.; Gunarta, I.K. Critical Success Factors for Internet of Things (IoT) Implementation in Automotive Companies, Indonesia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042909
Hakim IM, Singgih ML, Gunarta IK. Critical Success Factors for Internet of Things (IoT) Implementation in Automotive Companies, Indonesia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042909
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakim, Inaki Maulida, Moses Laksono Singgih, and I Ketut Gunarta. 2023. "Critical Success Factors for Internet of Things (IoT) Implementation in Automotive Companies, Indonesia" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042909
APA StyleHakim, I. M., Singgih, M. L., & Gunarta, I. K. (2023). Critical Success Factors for Internet of Things (IoT) Implementation in Automotive Companies, Indonesia. Sustainability, 15(4), 2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042909







