Abstract
Owing to factors such as climate change and human activities, ecological and environmental problems of land desertification have emerged in many regions around the world, among which the problem of land desertification in northwestern China is particularly serious. To grasp the trend of land desertification and the degree of natural vegetation degradation in northwest China is a basic prerequisite for managing the fragile ecological environment there. Visible light remote sensing images taken by a UAV can monitor the vegetation cover in desert areas on a large scale and with high time efficiency. However, as there are many low shrubs in desert areas, the shadows cast by them are darker, and the traditional RGB color-space-based vegetation index is affected by the shadow texture when extracting vegetation, so it is difficult to achieve high accuracy. For this reason, this paper proposes the Lab color-space-based vegetation index L2AVI (L-a-a vegetation index) to solve this problem. The EXG (excess green index), NGRDI (normalized green-red difference index), VDVI (visible band difference vegetation index), MGRVI (modified green-red vegetation index), and RGBVI (red-green-blue vegetation index) constructed based on RGB color space were used as control experiments in the three selected study areas. The results show that, although the extraction accuracies of the vegetation indices constructed based on RGB color space all reach more than 70%, these vegetation indices are all affected by the shadow texture to different degrees, and there are many problems of misdetection and omission. However, the accuracy of the L2AVI index can reach 99.20%, 99.73%, and 99.69%, respectively, avoiding the problem of omission due to vegetation shading and having a high extraction accuracy. Therefore, the L2AVI index can provide technical support and a decision basis for the protection and control of land desertification in northwest China.
1. Introduction
Northwest China, especially Inner Mongolia, has low vegetation coverage. Therefore, the ecological problem of land desertification is particularly serious. To control the local fragile ecological environment, it is necessary to master the trend of land desertification and vegetation coverage, and the assessment of vegetation coverage has an important impact on the production and life of local residents and the protection of ecosystems [1]. Owing to the vast area and scarce vegetation in Inner Mongolia, different vegetation coverage assessment methods have different advantages, disadvantages, and application scopes [2], and the selection of an extraction method with high accuracy is crucial [3].
As manual monitoring has many constraints in terms of time, area, and other issues, it is impossible to carry out large-scale and time-efficient monitoring of desert grassland, so remote sensing technology is widely used in the technical field of desert vegetation extraction, and there has been some progress. Among them, satellite remote sensing technology is often applied to vegetation cover estimation and has a relatively mature theoretical basis but, because of the low resolution of satellite remote sensing and other problems, the extraction of desert vegetation cannot meet the accuracy requirements [4]. However, owing to the advantages of high resolution, rich geometric texture information, high timeliness, and low cost, UAV remote sensing technology effectively makes up for the shortcomings of traditional satellite remote sensing, and has gradually become an important way to monitor and extract vegetation information [5]. Therefore, remote sensing technology has been applied to carry out more classification studies on plant communities, among which UAV remote sensing is the main platform to extract desert vegetation information by supervised classification methods and object-oriented classification methods [6]. Moreover, with the application and development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) in the field of remote sensing, the combination of UAV and remote sensing technology has been widely used in forestry and resource survey vegetation extraction [7]. In recent years, light and small UAVs have been widely used in all walks of life, and the application of UAV technology to remote sensing has become a new development trend [8]. Among them, constructing suitable vegetation indices in UAV visible light remote sensing images can reflect the surface vegetation condition more simply and effectively and is one of the main methods to extract vegetation information quickly from remote sensing images. Among them, many scholars have proposed a series of vegetation indices based on the visible light band using the characteristics of green vegetation in the visible light band [9]. For example, Wang Meng et al. [10] and Niu Yaxiao et al. [11] combined UAV remote sensing data with different threshold determination methods to classify the vegetation coverage of crops. Li Bing et al. [12] and Wang Zhenkun et al. [13] used low-altitude remote sensing data acquired by unmanned aerial vehicles to extract crop cover and quickly classify vegetation, respectively. Stefan Puliti et al. [14] and Shi Bo et al. [15] applied UAV remote sensing technology to large-scale forest investigations and achieved good results. However, the accuracy of UAV visible light remote sensing images applied to desert vegetation extraction will be affected by factors such as vegetation shading and light intensity. This paper is dedicated to solving this problem.
The main research object of this paper is visible light remote sensing images captured by UAVs. As the visible light true color sensors carried by UAVs have only three bands of RGB [16], the strong reflection characteristics of vegetation in the near-infrared band cannot be expressed. Among more than 150 vegetation index models [17] published in the literature, this paper selects the EXG (excess green) index [18], the MGRVI (modified green-red vegetation index) [19], the NGRDI (normalized green-red difference index) [20], the RGBVI (red-green-blue vegetation index) [21], and the VDVI (visible-band difference vegetation index) [22], all of which are constructed based on the RGB color space. Moreover, the contrast between vegetation and non-vegetation areas of these visible light vegetation indexes is obvious, and the vegetation information recognition effect is good, in which the vegetation area is bright white and the non-vegetation area is dark gray. Through the verification of many papers in related fields, the extraction accuracy can reach more than 75%, which has a certain reference value. Therefore, these vegetation indexes are selected as the reference objects for our experiment.
As UAV images are required to extract and classify vegetation information in desert areas, the influence of environmental factors in the desert on UAV images should be taken into account [23]. To ensure the accuracy of supervised classification, the Compute ROI Separability tool should be used to calculate the separation degree between any categories when separating different ground objects. The separation degree is based on the Jeffries–Matusita distance and transition separation degree and is used to measure the separability between different categories [24]. Its range is (0, 2). The greater the separation degree, the better the discrimination ability. If the separation degree is greater than 1.8, it is qualified; if it is greater than 1.9, it is accurate. Therefore, for each index model used as a reference in our experiments, the separation degree between different ground objects reached more than 1.9 during supervised classification. By analyzing the experimental results, it was found that vegetation shadow, UAV flight height, light intensity, and other factors affect the accuracy of vegetation extraction. In particular, vegetation shadows have a great impact on extraction accuracy, which may lead to false detections or missing detections. In existing studies, the application of the RGB color space in the RGB threshold method, the HSV (hue, saturation, value) discrimination method, and the RGB decision tree method is only used to calculate vegetation coverage from the perspective of color discrimination (especially green pixels), and these methods have certain limitations due to the changes in lighting environment [25]. Meanwhile, in image processing, color components other than green also have different degrees of influence on vegetation coverage extraction [26]. To solve this problem, a new method for vegetation extraction and shadow separation is proposed in this paper. The method is a Lab color-space-based L2AVI index model in which the L channel in the Lab color space can be used to calculate the brightness of light pixels in the image, analyze the performance of shadows in the image, and avoid the interference of light environment changes on vegetation extraction. As the chlorophyll content of vegetation in desert areas is very small, the proportion of green components in the image can be enhanced by the channel and the influence of other color components can be avoided. Thus, the vegetation can be extracted and land desertification can be monitored with high accuracy.
2. Study Area and Source of UAV Image Data
2.1. Study Area
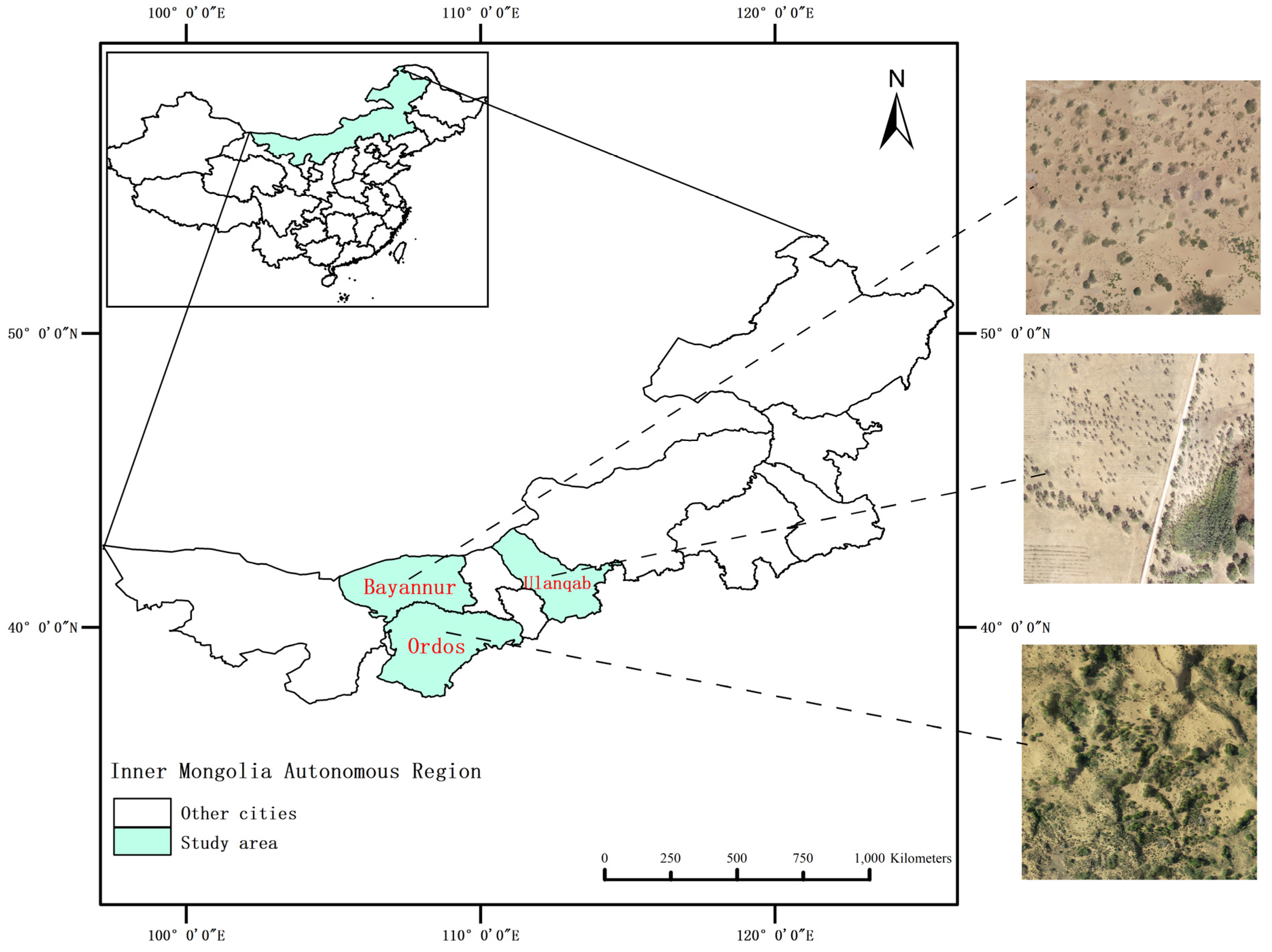
The study area is located in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. In this region, the desert steppe is mainly distributed in northwest China [27] and is an important part of the grassland in Inner Mongolia [28]. Located in this area are Bayannur (40°13′–42°28′ north latitude, 105°12′–109°53′ east longitude), Ordos (37°35′–40°51′ north latitude, 106°42′–111°27′ east longitude), and Ulanqab (40°10′–43°28′ north latitude, 110°26′–114°49′ east longitude) [29], and these three regions have a typical temperate continental climate with an average annual temperature of approximately 9.3 °C. The study area has a wide expanse of grassland plants, as well as meadows and swamp plants. Owing to the uneven distribution of vegetation and the vast geographical area, it is difficult to conduct manual collection and research [30]. The study area is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Image Source
The visible remote sensing image data of this paper were taken by the aerial survey UAV Dajiang Spirit 4 rtk. The shooting flight height was approximately 240 m and the default speed was 7.9 m/s. The shooting mode selected was for timing shooting. After completing the action, we returned, and the repetition rate was set to 65% and 40%. A 1 km × 1 km sample plot was flown according to the above task parameters. When the flight altitude was 200 m, approximately 120–130 aerial photos were taken; when the flight altitude was 300 m, approximately 60–70 aerial photos were taken.
3. Research Methods
3.1. L2AVI
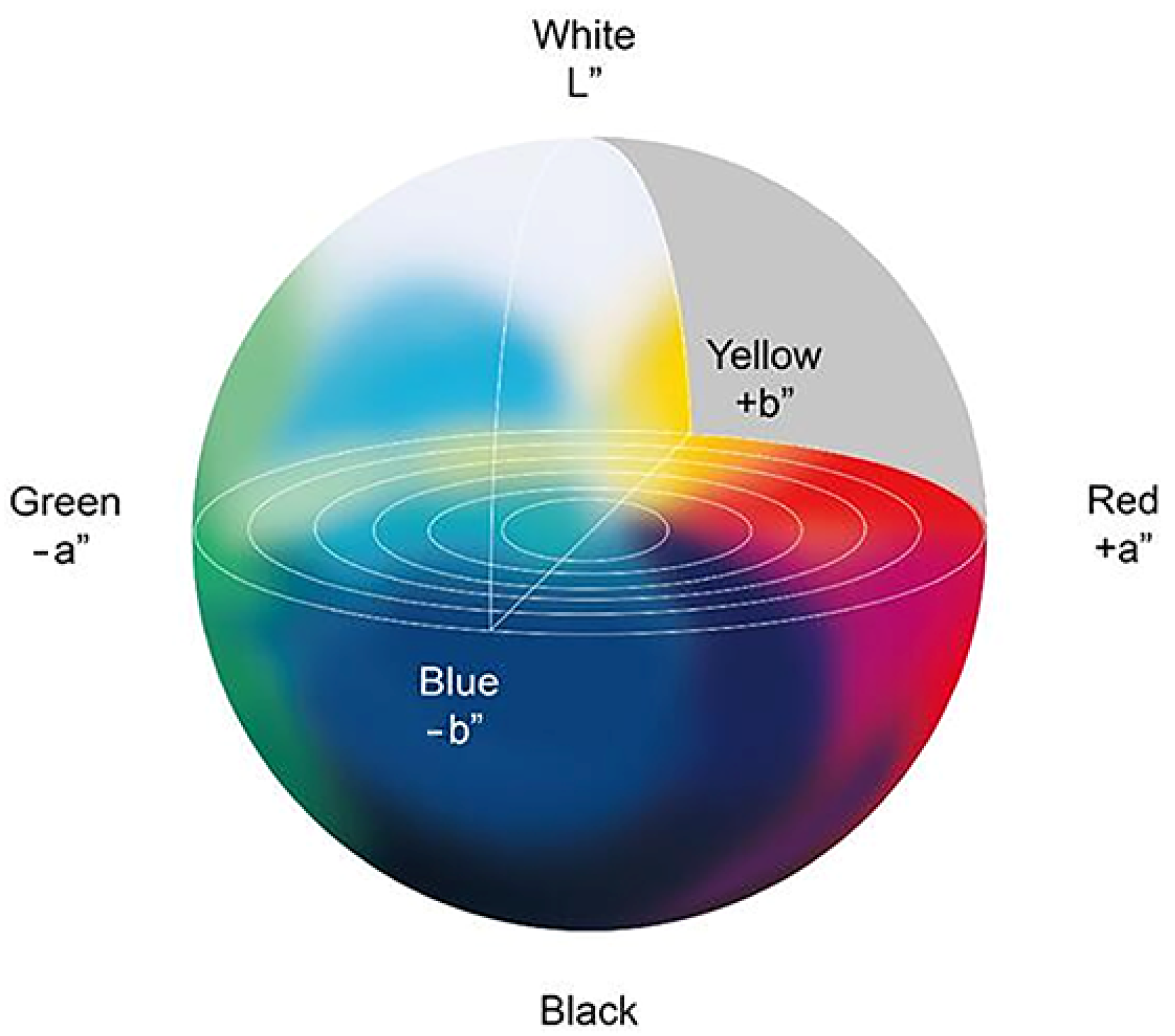
Instead of using only the three colors channels of R, G, and B, in which the correlation between channels is larger and it is difficult to quantitatively analyze the RGB color space, the Lab color space was defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) [31] in 1976 as an approximation to uniform color spaces. The Lab color space is composed of one lightness factor (L) and two chromaticity factors (a and b). The value of L ranges from 0 to 100; a changes from red to green and b changes from yellow to blue, with their values ranging from −120 to 120 [32]. The Lab color space has a broader color expression range [33]. Figure 2 shows the expression range of the Lab color space.

Figure 2.
Lab color space model.
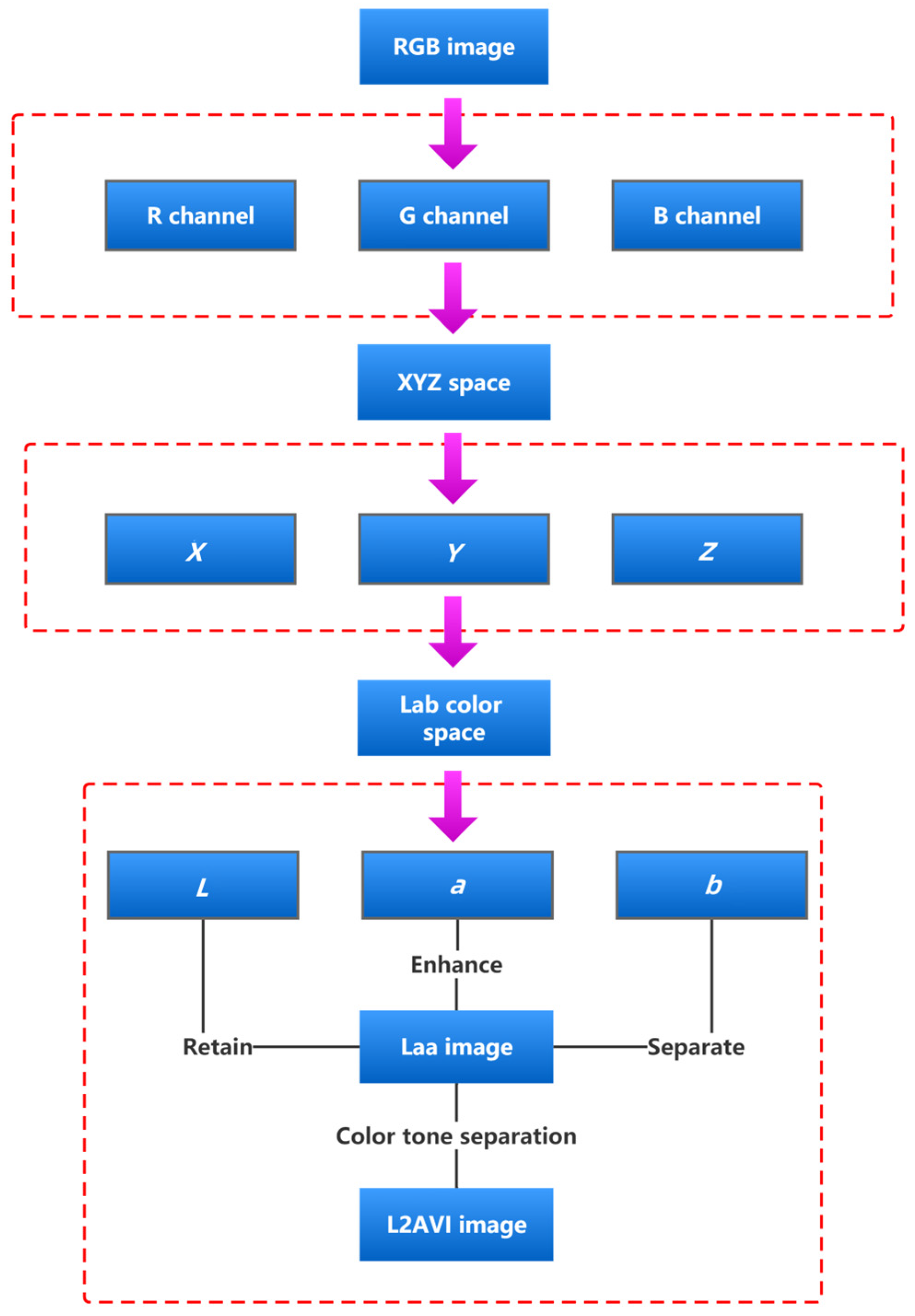
Based on the above theory, this paper proposes a new vegetation extraction index, the L2AVI model, based on the Lab color space. As the default storage mode of UAV visible remote sensing images is the RGB color space mode, RGB space must be converted to Lab space before the Lab space color image segmentation experiment can be conducted. Because RGB space and Lab space belong to two completely different color systems, which are device-related and device-independent, respectively, there is no direct linear correspondence between them, so the conversion between them needs to be completed by XYZ transition color space [34]. Through the index model, images are transformed into L2AVI images. Through the extraction and analysis of the transformed images, the high-precision, high-stability extraction of vegetation cover information in desert areas is realized. The image transformation process of the L2AVI model is as follows:
- (1)
- Convert RGB space into XYZ space, and take X, Y, and Z components as input [35]. By adjusting the reference method, we find out the most suitable linear relationship between RGB color space and XYZ color space, so that RGB color space is transformed into XYZ color space. By enhancing the weight of the R and G color channels in X-space, the weight of the G color channel in Y-space, and the weight of B-space in Z-space, the XYZ color space model with the clearest color is formed. The formula is shown in Equation (1).
- (2)
- According to the calculation formula of CIE 1976 uniform color space laboratory, the X, Y, and Z components are calculated, respectively, so that the XYZ space is transformed into Lab color space to obtain the image in Lab format, and the formula is shown in Formula (2).
Among them,
- (3)
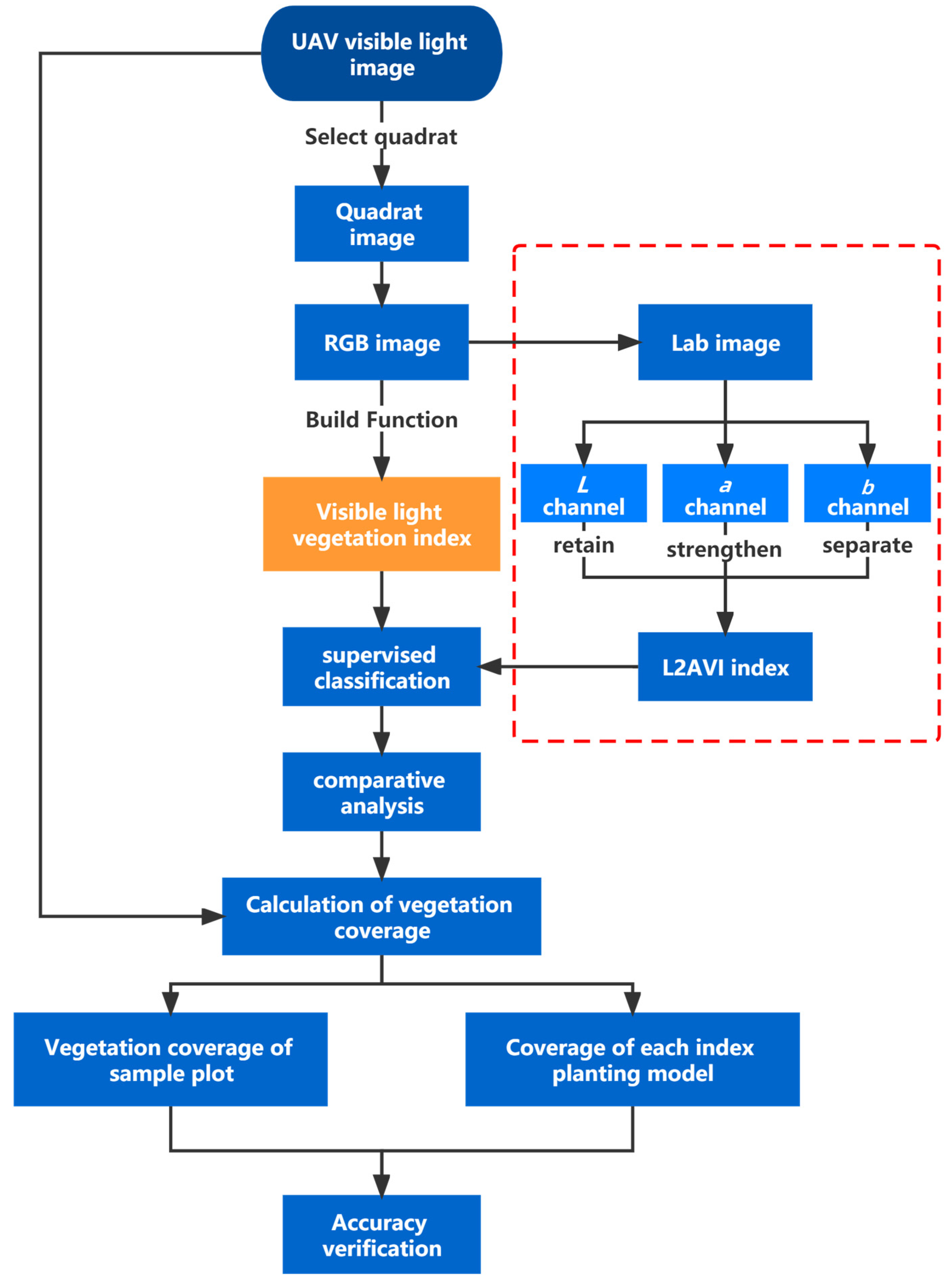
- The Lab color space contains three color channels, L, a, and b. The L channel is mainly used to control and adjust the overall brightness value of the image, the a channel includes colors from dark green to bright pink, and the b channel includes colors from dark blue to yellow. Therefore, after obtaining the Lab color space image, the L channel is enhanced to increase the luminance value, and a channel is copied to show the double a channel, thus enhancing the display of the green color component. By separating and deleting the b channel, the effect of the yellow color component is reduced, so that the final Laa image is obtained. The range of L lightness is (0, 100) [36], and the range of the a component is (−128, +127) [37]. The Laa image can adjust the tone curve of the L and a channels, respectively. First, the midpoint of the tone curve of the L channel is taken as a fixed point. Next, for the part whose input value is less than the midpoint, the output value is raised. For the parts whose input value is greater than the midpoint, the output value is lowered. Then, the midpoint of the tone curve of the a channel for a fixed point is taken, and the output value for the part whose input value is less than the midpoint is lowered. For the part whose input value is greater than the midpoint, the output value is increased. Adjusting the appropriate tone curve can make vegetation, vegetation shadow, and land color difference appear more distinct. Finally, tone separation and false color enhancement are carried out on the Laa images, and L2AVI images with obvious vegetation color characteristics are finally obtained. The specific image transformation process based on the L2AVI model is shown in Figure 3.
 Figure 3. Image transformation flow chart.
Figure 3. Image transformation flow chart.
3.2. L2AVI Threshold Selection Method
Based on the L2AVI image, the range of L lightness is (0, 100); the range of the a component is (−128, +127); the optimal threshold of the L channel and the a channel is set; and the image is classified into vegetation, shadow, and other ground objects. In the Lab color space, the low-value part of the a component is represented in green and the high-value part is represented in red. Threshold T1 and threshold T2 are selected at the position of the double peaks of the image, respectively. The value less than threshold T1 is set as the green pixel and the value greater than threshold T2 is set as the red pixel. As the vicinity of the intermediate threshold is represented by a black-and-white gray level, the value of T1 should be less than the intermediate value to remove interference. As most processed vegetation index images do not have bimodal characteristics, the determination of any threshold value has either clear or dark assumptions, and the best results cannot be achieved under any condition [38]. The selection of the threshold is affected by many factors, and the threshold methods, such as the histogram bimodal method, are not fully applicable to all images.
Therefore, according to the actual situation in different study areas, this paper selects a comparatively ideal threshold relative to the original image to distinguish vegetation from non-vegetation and extract the coverage rate. In this process, it is necessary to manually determine the threshold for repeated adjustment experiments, to maximize the distinction between vegetation and other feature types, and to obtain the best segmentation effect. For different vegetation indices after different attempts of experiments, the thresholds were stable in a certain range: the EXG vegetation index threshold was stable around 1.9, the NGRDI vegetation index threshold was stable in the range of (5, 10), the VDVI vegetation index threshold was stable around 3.6, the RGBVI vegetation index threshold was stable in the range of (2, 10), and the LAVI vegetation index threshold was stable in the range of (0, 10).
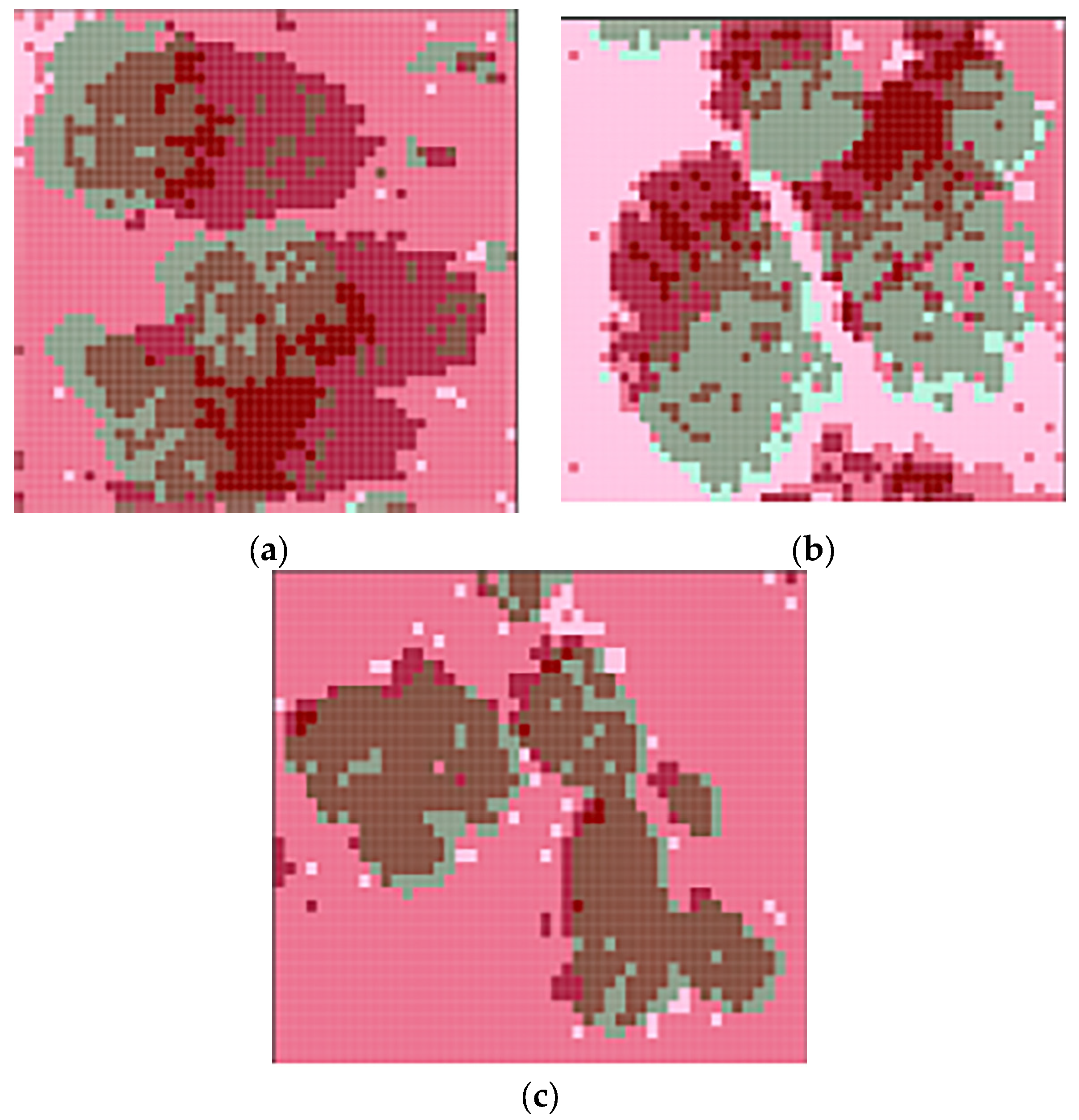
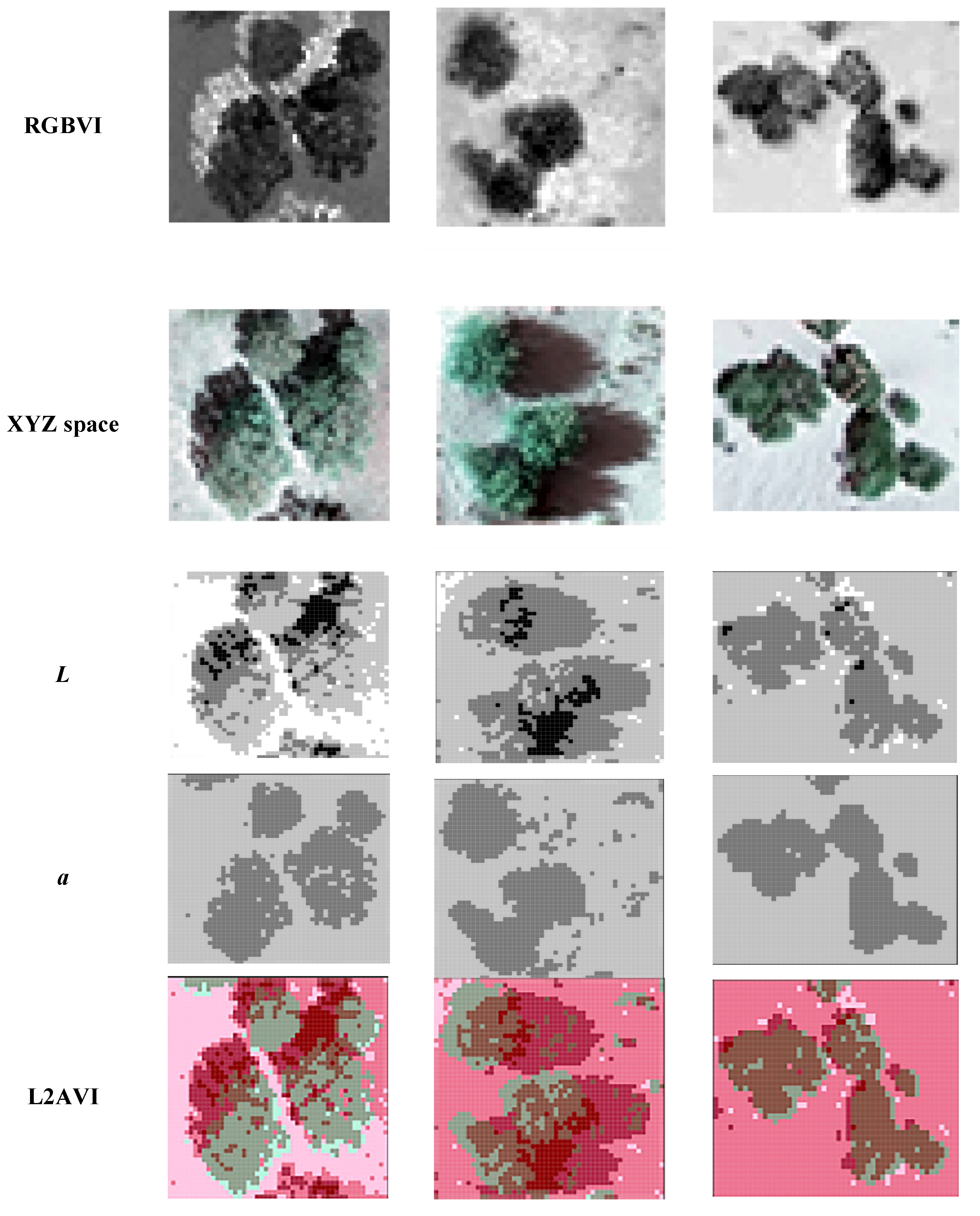
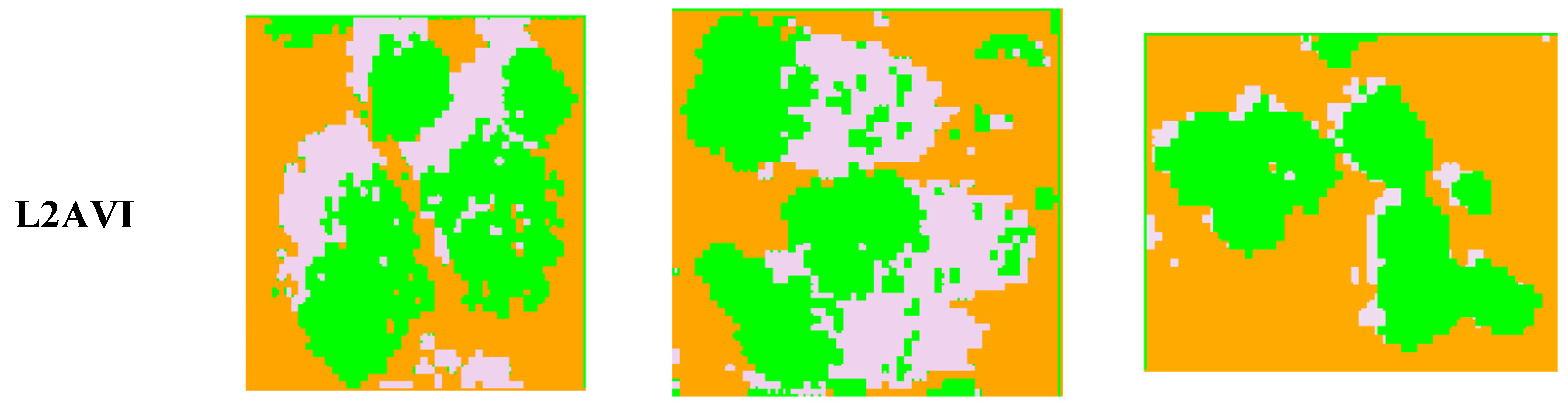
Based on the L2AVI model in this paper, the effect pictures of the three quadrats extracted are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
L2AVI index model of the sample region: (a) Ordos; (b) Ulanqab; and (c) Bayannur.
3.3. Vegetation Index Constructed Based on RGB Color Space
The vegetation index is based on the reflection and absorption characteristics of plants to electromagnetic waves and uses the linear and nonlinear combination of RGB components in visible light to describe the information of various vegetation [39]. At the same time, the vegetation index is an important index for calculating vegetation coverage and expressing vegetation growth. In recent years, the field of remote sensing has often been used in monitoring vegetation coverage of desertification and vegetation extraction [40,41,42], and hundreds of different vegetation indices have been constructed according to the differences in different bands of remote sensing images [43,44,45], with relatively few vegetation indices based on visible light bands [46]. The visible light vegetation index is listed in Table 1 below. Visible light images contain three channels, R, G, and B, so relatively few functions can be constructed. It is a common index method for extracting vegetation information in traditional RGB images. In this paper, the following five spatial index models based on RGB were used to extract and classify vegetation in the sample areas, so as to conduct a comparative experimental analysis with the proposed L2AVI model.

Table 1.
Calculation formula of RGB spatial vegetation index.
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Methods of the Process
As it is difficult to obtain a true value of vegetation coverage, to evaluate the effectiveness of the vegetation coverage extraction method, the image vectorization result is considered the true value. In this paper, representative local samples were selected for pixel-by-pixel statistics. To avoid accidental errors, the statistical results were averaged by multi-person calculation. The accurate vegetation coverage rate obtained was taken as the evaluation standard, and the separation degree was required to be above 1.9 to maintain high accuracy. After the image was processed by the vegetation index of three color spaces, the resulting image was extracted by supervised classification and the threshold method, and the difference in coverage rate and evaluation standard obtained by different vegetation indices was compared. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of the vegetation index were evaluated according to the comparison results, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Experimental flow chart.
4.2. Index Model Construction
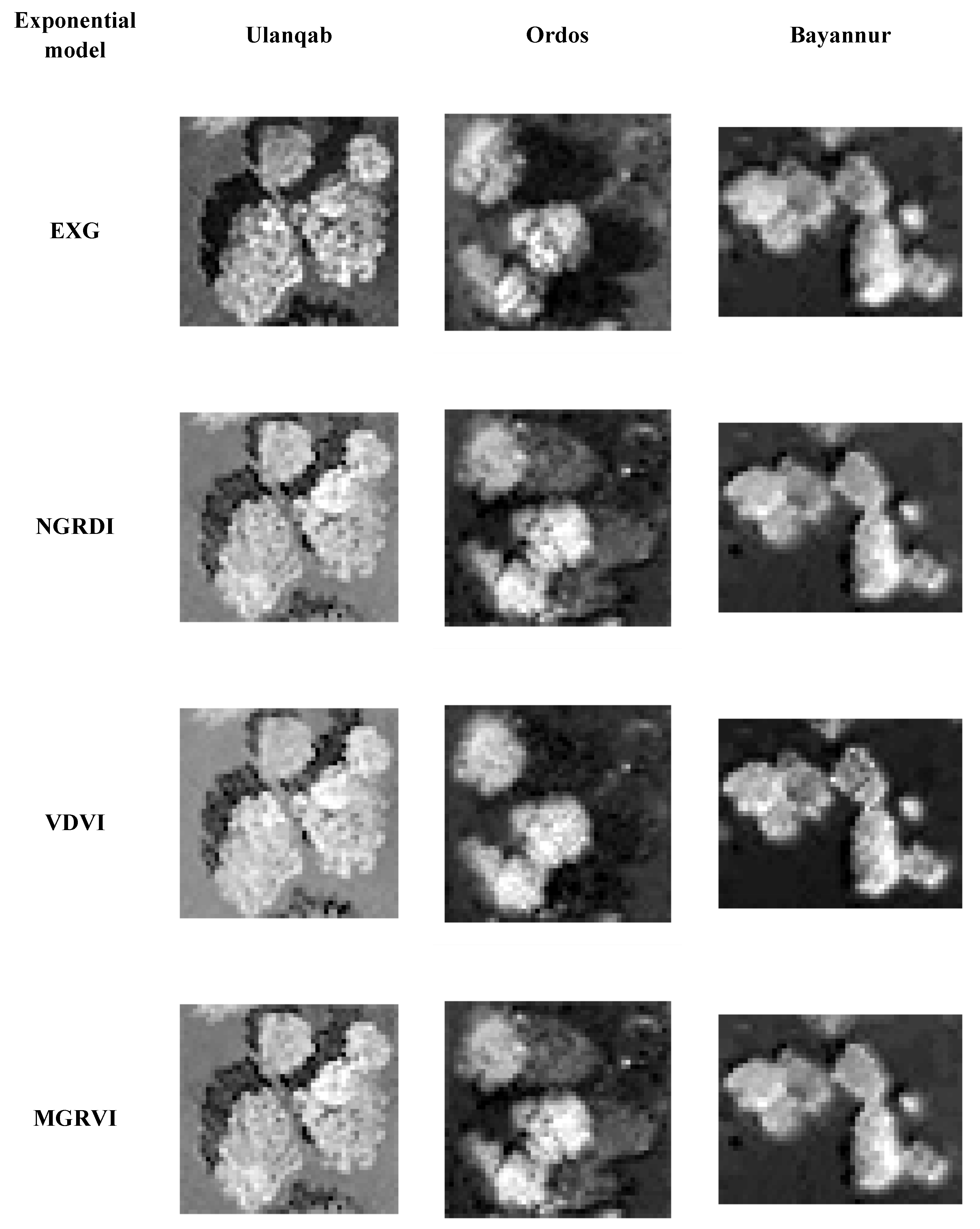
After selecting quadrats through the experimental process, the optical images taken by the UAV were classified using RGB images and Lab images, and the exponential model was constructed for RGB images according to the formula in Table 1. Next, the L, a, and b channels were separated from the Lab images. By strengthening the a channel and the L channel, the b channel was separated to construct an L channel image model, an a channel image model, and an L2AVI model. The specific model construction is shown in Figure 6.


Figure 6.
Images of different index models.
4.3. Supervised Classification
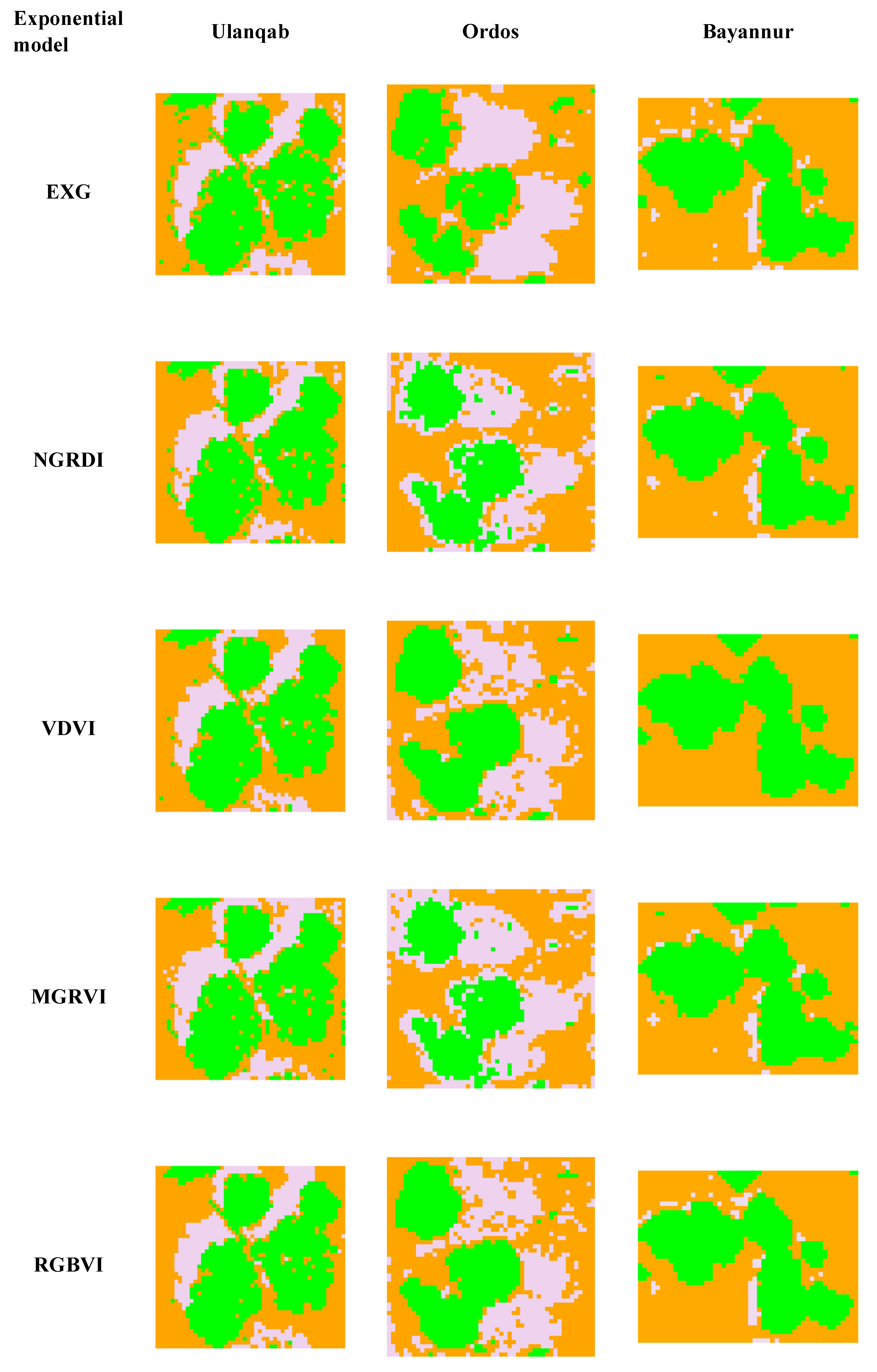
In this paper, the EXG (excess green) index, MGRVI (modified green-red vegetation index), VDVI (visible-band difference vegetation index), RGBVI (red-green-blue vegetation index), NGRDI (normalized green-red difference index), and L2AVI vegetation index based on Lab color space were selected for comparison. Figure 7 shows the comparison of the results of the classification supervised by SVMs (support vector machines) [47] for these eight planting indices (where green represents vegetation, yellow-brown represents the bare ground, and violet-gray represents shadow).


Figure 7.
Results of supervised classification.
By comparing the results in Figure 8 to the relevant literature, it can be preliminarily inferred that the accuracy of other indices is relatively low owing to the high flight altitude or the lack of chlorophyll in desert vegetation. According to the research results of Fu Shuai et al. [48], the optimal flight height for the EXG index and the NGRDI is 80–100 m, while the experimental data flight height in this paper is 240 m, resulting in the low extraction accuracy of the two indices. The VDVI index model can maintain high accuracy in vegetation extraction in Ulanqab and Ordos. However, when extracting vegetation information in the Bayannur area, the shade of low shrub vegetation is dark, so the vegetation shadow cannot be divided, meaning that vegetation information cannot be extracted stably and with high accuracy in areas with more and deeper vegetation shadows. When the MGRVI extracts vegetation information in the Ordos, owing to the large shadow areas in the Ordos research area, the shadow color in the images taken by the UAV is dark, which is reflected in the MGRVI model, resulting in the high brightness of the shadow area, making it difficult to divide the shadow and vegetation information, and having a great impact on the accuracy. In summary, the exponential model built based on the RGB color space will be affected by a large external environment, among which the vegetation shadow, lighting condition, UAV flight height, and other factors will lead to large errors in the extracted sample information. It is inferred that the brightness value of desert vegetation is lower than that of other non-vegetation elements such as roads, which is an important theoretical basis for distinguishing vegetation from non-vegetation using this index. However, because the vegetation is covered by shadow, the brightness values of vegetation are similar to those of other features and are affected by color overlap, making it difficult to distinguish them using traditional vegetation information extraction methods. In contrast, the L2AVI can adapt to higher flight altitudes and extract vegetation information stably and with high accuracy in areas with insufficient light and more shadow.

Figure 8.
Supervised classification of vegetation.
4.4. Supervise Classification Result Statistics
In this paper, the ratio between the number of pixels and the total pixels of vegetation after quadrat vectorization is used as the basis for evaluation. Supervised classification is then performed on the images after vegetation index extraction to further distinguish vegetation from land and shadow. Similarly, the ratio of the area of the extracted objects to the area of the total quadrat is used to extract the ground object coverage of the index, with the formula shown in Equation (3):
where is the coverage rate of the ground objects, represents the area of the ground objects, and denotes the area of the total quadrat.
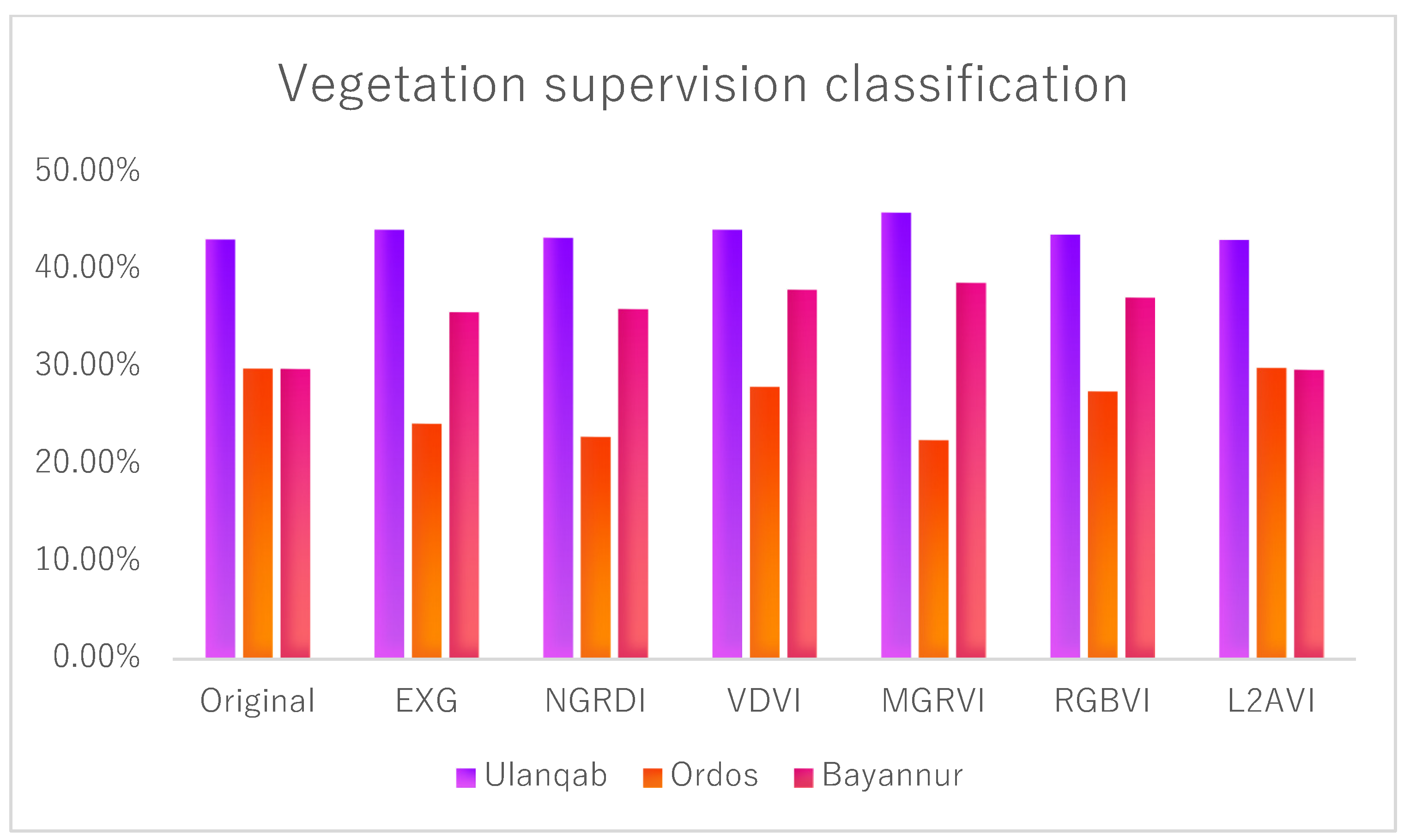
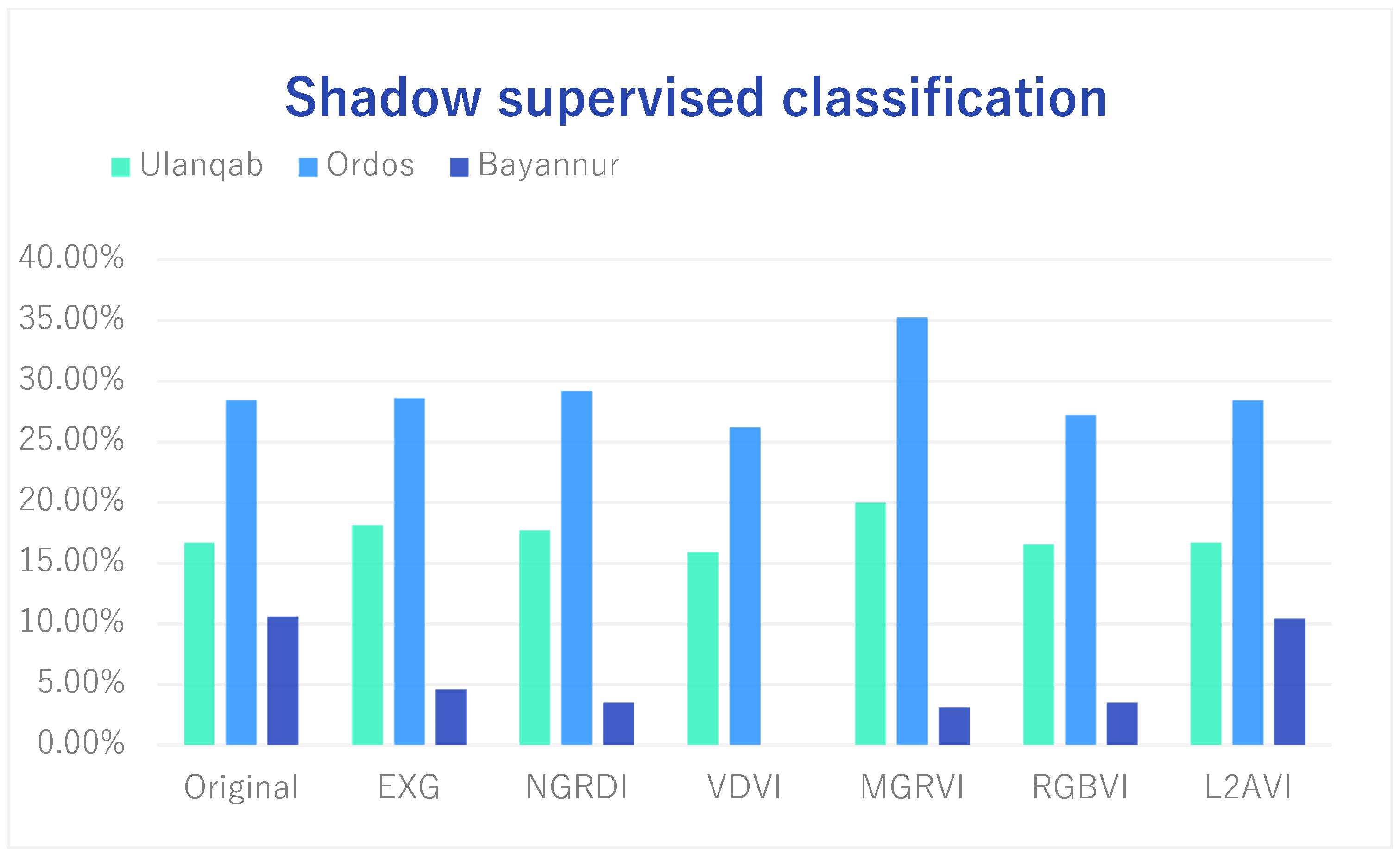
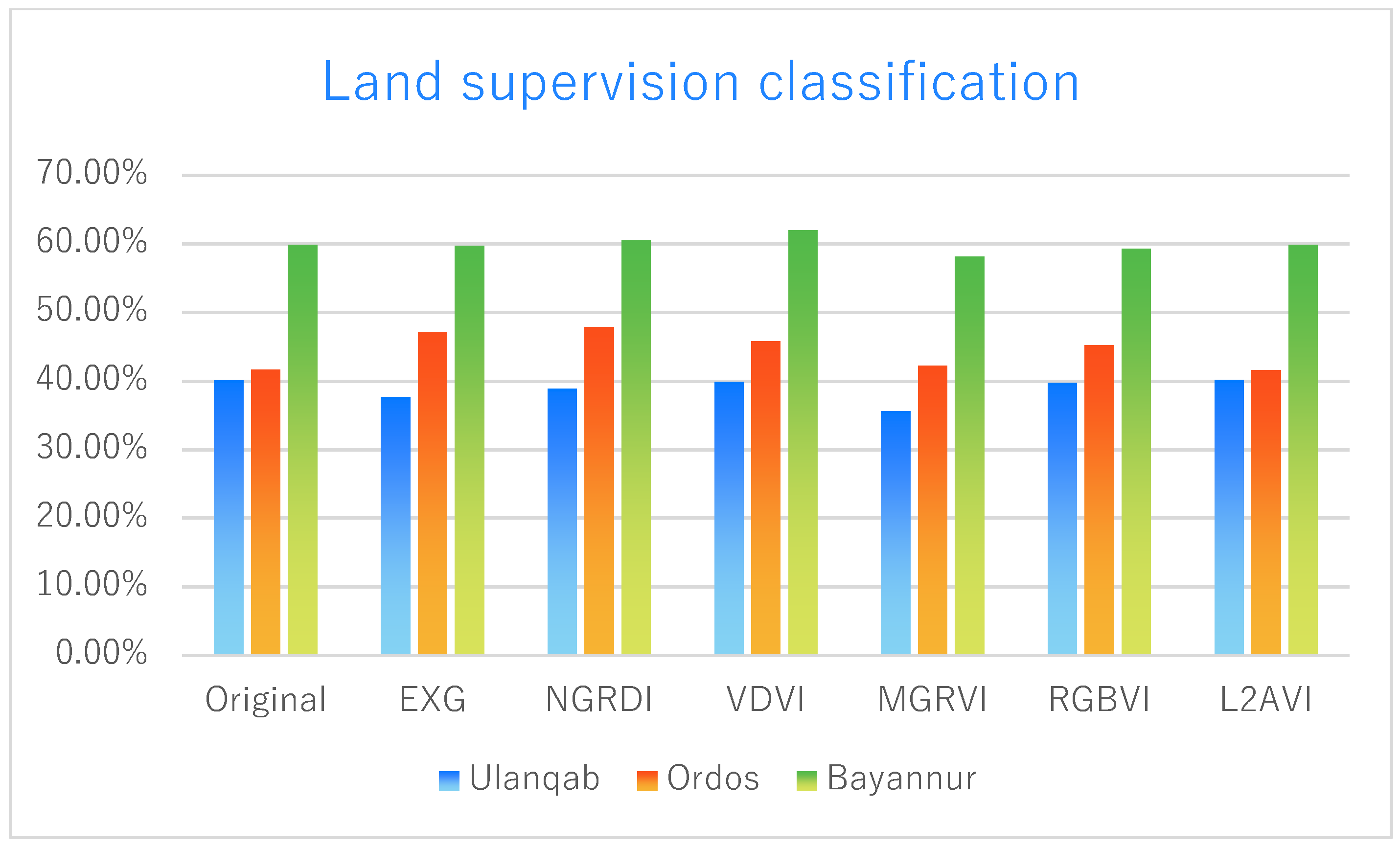
For desert areas with sparse vegetation, the appearance of the shadow is inevitable during image acquisition owing to the large gap between the vegetation. Therefore, it is very important to distinguish and extract shadows accurately for the analysis of vegetation coverage and vegetation type. Through experiments, this paper found that L2AVI had the highest ability to extract and distinguish vegetation shadows from most vegetation indices. To analyze and verify the effect of L2AVI shadow extraction, we used pixel-by-pixel quantitative analysis to obtain an accurate shadow coverage area. The vegetation coverage results are shown in Table 2, shadow coverage is shown in Table 3, and land coverage is shown in Table 4. The data in the chart are visualized to obtain Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10.

Table 2.
Analysis of supervised classification of vegetation.

Table 3.
Analysis of shadow supervised classification results.

Table 4.
Analysis of land supervised classification results.

Figure 9.
Shadow supervised classification.

Figure 10.
Supervised classification on land.
4.5. Analysis of Supervised Classification Results
To quantitatively analyze the accuracy of several index extraction methods, the following error analysis formula in Equation (4) is used:
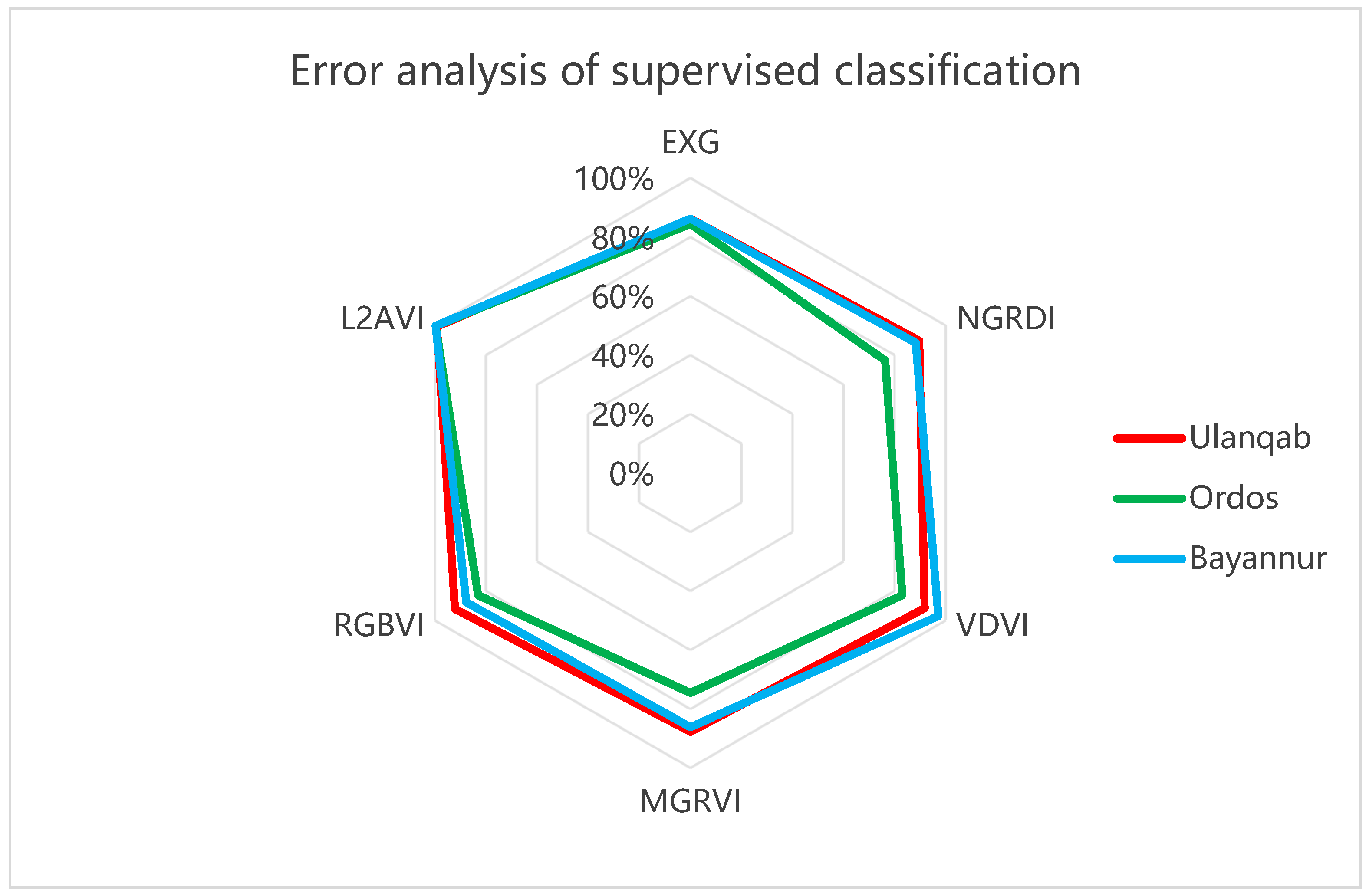
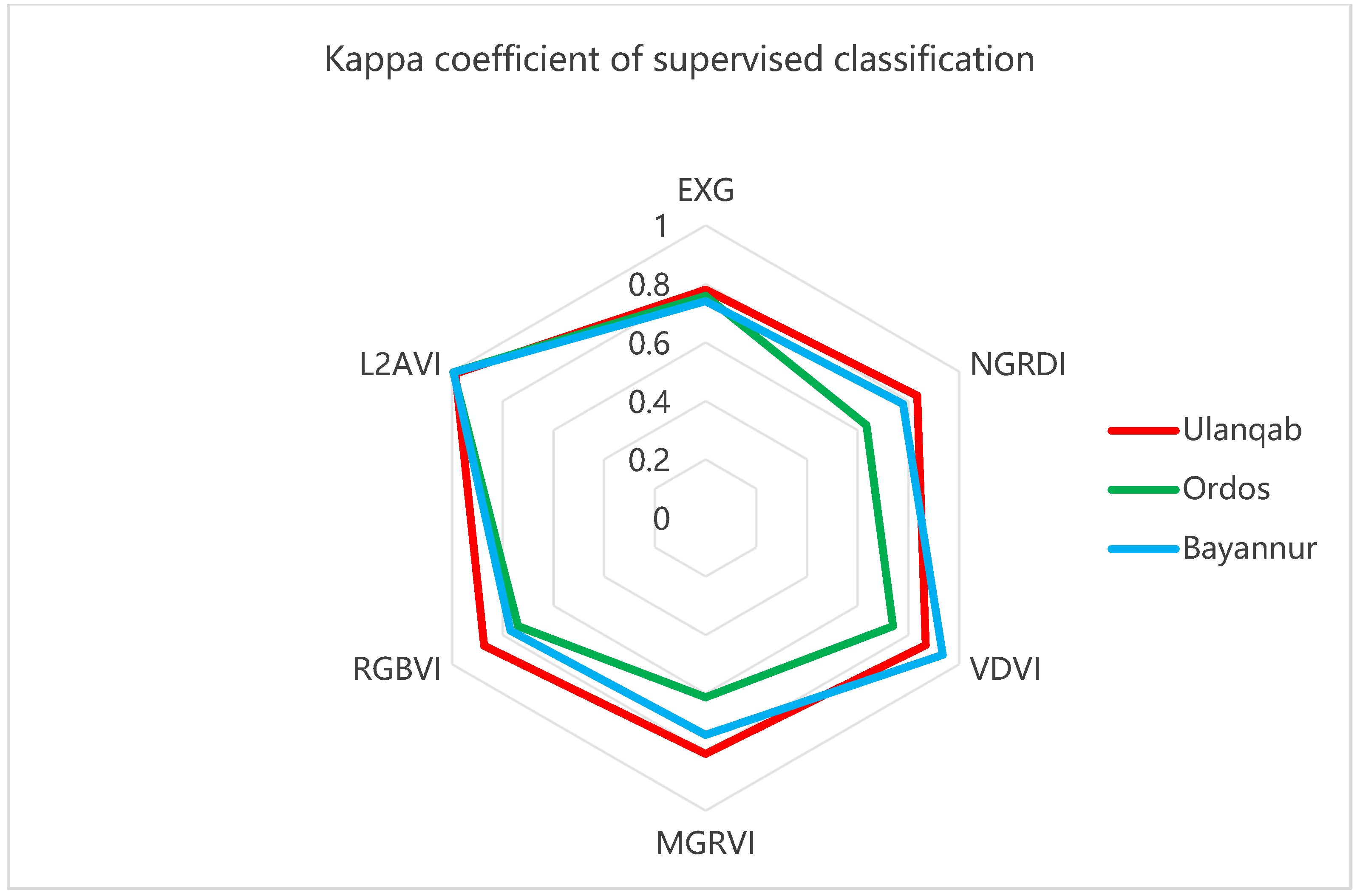
where is the vegetation coverage obtained by the vegetation extraction algorithm and represents the vegetation coverage rate obtained using manual visual interpretation [49]. The range of separation degree between different ground objects is (0, 2) and the original image is used as a control experiment for the accurate evaluation of other exponential models. Therefore, the accuracy of the supervised classification of quadrat images should be ensured. That is, to ensure accuracy , the separation degree between objects in quadrat images should be kept higher than 1.9 [50] during supervised classification. At the same time, to ensure the accuracy of the L2AVI model, the separation degree between objects should be greater than 1.9. The object separation degree of the quadrat image is shown in Table 5, the ground object separation degree of the L2AVI model is shown in Table 6, the supervised classification error analysis result of each exponential model is shown in Table 7, and the Kappa coefficient is shown in Table 8. The results of the supervised classification error analysis and the Kappa coefficient data of supervised classification in the chart were visualized to obtain Figure 11 and Figure 12.

Table 5.
Object separation degree of the quadrat image.

Table 6.
L2AVI model ground object separation degree.

Table 7.
Results of supervised classification error analysis.

Table 8.
Kappa coefficient of supervised classification.

Figure 11.
Results of supervised classification error analysis.

Figure 12.
Kappa coefficient of supervised classification.
5. Conclusions
Through the comparison of supervised classification results statistics, supervised classification results charts, and error analysis, the vegetation in the EXG vegetation index is highlighted, which can ensure the extraction accuracy of lush vegetation areas. However, owing to the large darkness of the shadow area, it is easy to encounter the problem of wrong detection and missing detection in areas with sparse vegetation growth. It is difficult to distinguish the vegetation shadow area and the sand area. Therefore, extracting vegetation information in areas with more shadows will lead to large errors.
In the MGRVI model, the regional divide between the vegetation and the land is clearer, and the light and dark details are good, so it is easier to obtain fine vegetation. However, the shadow model will have a higher brightness, which will also affect the overall precision of the division to a certain extent. For example, the shadow area in the Ordos research area is large, and the shadow color in the image taken by the UAV is dark, which is reflected in the MGRVI model. This results in the high brightness of the shadow model, which has a great impact on the accuracy. Therefore, the MGRVI can achieve the expected accuracy when collecting vegetation with less shadow. However, high-precision extraction cannot be guaranteed in areas with more vegetation shadows.
Compared with other RGB color space index models, the RGBVI model can better distinguish between shadow, land, and vegetation models, perfectly solving the method error caused by vegetation shadow in the MGRVI model. In the model of land, shadow, and vegetation, the color difference is larger, the contrast is more obvious, and the light and dark details are clearer, which is more conducive to the extraction of vegetation and the division of its features. However, the RGBVI is greatly affected by illumination, which means that good illumination conditions and suitable UAV flying altitudes are required to maintain the expected accuracy.
After supervised classification, it was found that the extraction effect of the NGRDI model was relatively ordinary, and the accuracy in several models was mid-range. The NGRDI had a certain effect in dividing the vegetation and vegetation shadow area, but it was not as significant as that in the RGBVI, the VDVI, or the L2AVI model.
Although the VDVI model has an accuracy of 91.79% and 97.07% in the Ulanqab area and the Ordos area, respectively, it is unable to classify the vegetation shadow in the Bayannur area because of the dark shade of the low shrub vegetation, so the vegetation information cannot be extracted stably in the areas with more and deeper vegetation shadow.
Meanwhile, it was found in the study that the flight altitude of the UAV directly determines the resolution of visible light images, i.e., the higher the flight altitude, the lower the resolution, such as for the extraction of desert vegetation, which usually requires the flight altitude to be controlled below 100 m. The flight speed of the drone is also the key to the image quality—too fast easily leads to blurred images. The lower the overlap rate, the better the stitching quality. The overlapping part should be minimized and the impact area should cover the whole study area. In addition, because the UAV visible images are based on RGB color space, the image information is controlled by only three bands, and relatively few vegetation indices can be constructed. In the future development trend of UAV, multispectral sensors can be used to increase the near-infrared band and then be combined with the Lab color space. In this thesis, more vegetation indices can be constructed to adapt to the extraction of vegetation information in different areas.
Through the control experiment, it can be concluded that the L2AVI proposed in this paper reached the highest accuracy, with the VDVI also obtaining high accuracy in the extraction of low plants or vegetation with less shadow. For the EXG, EGRDI, MGRVI, and RGBVI indices, the extraction accuracy is relatively general, and they cannot distinguish vegetation from non-vegetation. For the proposed L2AVI model, the index constructed through the Lab color space can avoid the traditional index model based on the RGB color space, which is unable to extract vegetation information stably and with high accuracy as a result of vegetation shadow, UAV flight height, and illumination conditions. The L2AVI model preserves the L channel, strengthens the a channel, and separates the b channel. It can effectively and stably classify and extract three ground feature elements (vegetation shadow, land, and vegetation information) in desert areas, and is not affected by the errors caused by illumination conditions and UAV flying altitude. Therefore, it is more suitable for the extraction of vegetation in desert areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. (Yuefeng Lu); Data curation, Z.S., Y.L. (Yuqing Li), Z.A. and L.Z.; Methodology, Y.L. (Yuefeng Lu) and Z.S.; Project administration, Y.L. (Yuefeng Lu) and M.L.; Supervision, G.Z.; Writing—original draft, Z.S., Y.L. (Yuqing Li), Z.A. and L.Z.; Writing—review and editing, Y.L. (Yuefeng Lu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Major Project of High Resolution Earth Observation System of China (No. GFZX0404130304); the Open Fund of Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Geo-Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping, and Remote Sensing, Hunan University of Science and Technology (No. E22201); the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP No. CAAS-ZDRW202201); a grant from State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System; and the Innovation Capability Improvement Project of Scientific and Technological Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Shandong Province of China (No. 2021TSGC1056).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data were obtained from a third party and are available from the authors with the permission of the third party. For third parties, see acknowledgments.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the data provider of the administrative divisions used in this paper; the Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/) (accessed on 10 July 2022); and UAV data providers in Bayannur region, Ordos region, and Ulanqab region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cao, Y.X.; Mao, Y.X.; Xue, J. Dynamic changes and driving factors of vegetation cover in the oasis-desert ecotone: A case study of Cele, Xinjiang. Arid. Zone Res. 2022, 39, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Gong, W.; Shi, S.; Du, L.; Sun, J.; Zhu, B.; Ma, Y.Y.; Song, S.L. Vegetation identification based on characteristics of fluorescence spectral spatial distribution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 56932–56935. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Mu, G.J.; Tang, Z.H.; Yang, X.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Xu, L.S. Remote sensing estimation models for vegetation coverage in desert regions of Xinjiang based on NDVI. Arid. Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Du, J.M. Research on recognition of desert grassland micro patches based on UAV remote sensing. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. 2022, 40, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.H.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, X.L.; Yan, L.A.; Chang, M.D.; Li, Y.K. Object oriented classification of desert vegetation based on UAV remote sensing images. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2021, 23, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Na, M.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Ha, S.T.; Li, F.; Ha, S.G. Identification of typical species of desert grassland based on UAV multispectral images. China Agric. Inf. 2022, 34, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, X.M.; Jiang, T.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.L. Summary of vegetation coverage extraction methods from UAV remote sensing. J. Northeast. Norm. Univ. 2021, 53, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Wu, Z.N.; Shi, H.L.; Hao, H.D.; Chen, J.X.; Shen, Z.Q. Application Exploration of Optical Remote Sensing Technology of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle in Measuring Bulk Trade at Sea. In Proceedings of the Seventh Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications, Kunming, China, 5–7 November 2020; SPIE: Basel, Switzerland, 2021; p. 1176372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Xu, J.; Chen, R.X. Urban vegetation information extraction based on UAV visible light image. Geospat. Inf. 2022, 20, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Duo, X.Y.; Liang, S.Z.; Hou, X.H.; Liang, Y.Q. Research on the Method of Extracting Crop Vegetation Coverage Using UAV Remote Sensing Technology. Crops 2020, 196, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Han, W.T.; Shao, G.M. Fractional Vegetation Cover Extraction Method of Winter Wheat Based on UAV Remote Sensing and Vegetation Index. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Liu, R.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhou, G.Q. Monitoring vegetation coverage variation of winter wheat by low-altitude UAV remote sensing system. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.K.; Fu, Y.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, F. Fast crop classification method based on low altitude remote sensing of unmanned aerial vehicle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Puliti, S.; Ene, L.T.; Gobakken, T. Use of partial-coverage UAV data in sampling for large scale forest inventories. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B. Analysis on the Application of UAV Remote Sensing in Forest Resources Investigation. For. Sci. Technol. Inf. Green Treasure For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 53, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.X.; Li, J.R.; Si, Q.C.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.K. Research on Extraction Method of Desert Shrub Coverage Based on UAV Visible Light Data. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, M.F.; Melo, A.G.; Honorio, L.M.; Marcato, A.L.M.; Conceicao, A.G.S.; Timotheo, A.O. Deep Learning Applied to Vegetation Identification and Removal Using Multidimensional Aerial Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Yu, K.; Aasen, H.; Bolten, A.; Bennertz, S.; Broscheit, J.; Gnyp, M.L.; Bareth, G. Combining uav-based plant height from crop surface models, visible, and near infrared vegetation indices for biomass monitoring in barley. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woebbecke, D.M.; Meyer, G.E.; Von, B.K. Color indices for weed identification under various soil, residue, and lighting conditions. Trans. ASAE 1995, 38, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Qi, Y.X.; Deng, L.F.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, S.T. New research methods for vegetation information extraction based on visible light remote sensing images from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Fu, L.Y.; Sharma, R.P.; Lei, Y.C.; Guo, J.P. A Hybrid Approach of Combining Random Forest with Texture Analysis and VDVI for Desert Vegetation Mapping Based on UAV RGB Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Tang, W.J.; Gao, D.H.; Zhao, R.M.; An, L.L.; Li, M.Z.; Sun, H.; Song, D. UAV-based chlorophyll content estimation by evaluating vegetation index responses under different crop coverages. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 196, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C. Studies on Remote Sensing Image Optimal Object Construction Classification Algorithm Based on Jeffries-Matusita Distance and Its Application. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Yantai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Cai, J.Q.; Gong, Z.; Wu, Y.H.; Xu, J.F. On the Moss Vegetation Cover Extraction Based on Lab Color Space Digital Photos. J. Hangzhou Norm. Univ. 2018, 17, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Yuan, Z.W.; Luo, X.; Feng, Z.K.; Li, X.M. Research on the best false color synthesis method and evaluation based on the extraction of green information from high-resolution satellite images. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2008, 30, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Guan, W.K.; Li, Z.P.; Zhang, P.; Ding, J.; Feng, Y.M. Research on vegetation coverage and spatial distribution characteristics in Gobi region based on UAV image. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Du, J.M.; Ruan, P.Y.; Zhu, X.B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Vegetation Classification of Desert Steppe Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and Random Forest. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.T.; Bai, J.; Li, G.L.; Luo, G.P.; Li, J.L. Comparison of methods based on MODlS for estimating sparse vegetation fraction across desert in Xinjiang. Arid. Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 502–511. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.M.; Min, Z.J.; Kan, J.M. Color image segmentation based on HSL and LAB color space. J. Guangxi Univ. 2011, 36, 976–980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Lu, C.D.; Le, W.D.; Wang, X.P. Color Harmony System Based on Lab Perceptual Uniform Color Space. J. Northwestern Polytech. Univ. 2004, 22, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Yang, H.L.; Li, X.W.; Chen, Y. An improved multi-scale Retinex image enhancement algorithm based on Lab color space. J. Crim. Investig. Police Univ. China 2020, 153, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.G.; Xu, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.F. Measuring grassland vegetation cover using digital camera images. J. Grass Ind. 2014, 23, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Jun, S. Segmentation and measurement of medical image quality using K-means clustering algorithm. Am. J. Neural Netw. Appl. 2019, 5, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.M. The Method of Color Image Segmentation Based on Color Clustering and Region Growing. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Yang, F.; Fan, Y.W.; Zang, W.Q. The dominant driving factors of rocky desertification and their variations in typical mountainous karst areas of Southwest China in the context of global change. Catena 2023, 220, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Lu, M.; Fan, Y.W.; Wu, H.W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.L. A novel-optimal monitoring index of rocky desertification based on feature space model and red edge indices that derived from sentinel-2 MSI. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W. Direct determination of threshold value from bimodal histogram. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2002, 15, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Yang, W.N. A new estimation method for fractional vegetation cover based on UAV visual light spectrum. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 45, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, R. Remote sensing-based biological and nonbiological indices for evaluating desertification in Iran: Image versus field indices. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2805–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X.G.; Liu, X.T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, X.W.; Tong, S.Z.; Lei, G.; Wang, S.; et al. Aboveground biomass and its spatial distribution pattern of herbaceous marsh vegetation in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Ma, R.; Liu, B.H.; Lu, X.G.; Jiang, M. Asymmetric impacts of diurnal warming on vegetation carbon sequestration of marshes in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2022GB007396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Jiao, Z.J.; Zhang, A.Z.; Li, F.; Fu, H.; Li, Z. Hyperspectral image-based vegetation index (HSVI): A new vegetation index for urban ecological research. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Wang, M.; Jia, M.M.; Wang, W.Q. Estimating mangrove leaf area index based on red-edge vegetation indices: A comparison among UAV, WorldView-2 and Sentinel-2 imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Shen, X.J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Xia, C.L.; Liu, Y.W.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X.G. Variation of vegetation autumn phenology and its climatic drivers in temperate grasslands of China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, Z.Q.; Han, J.Z.; Zhang, H. Green vegetation extraction based on visible light image of UAV. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.G.; Lin, Y.H.; Wen, X.L.; Jian, W.B.; Gong, Y.S. Vegetation information recognition in visible band based on UAV images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.L.; Wang, M.Z.; Peng, L.; Feng, Q.S.; Liang, T.G. Effect of Different Vegetation Index and UAV Altitude on the Accuracy of Grassland Coverage Estimation. Pratacult. Sci. 2021, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Y.; Qi, W. Measuring vegetation greenery in park using iPhone panoramic image and a new green vegetation extraction index. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 65, 127310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yang, F.; Fan, J.F.; Lu, Y.F. The Changes of Spatiotemporal Pattern of Rocky Desertification and Its Dominant Driving Factors in Typical Karst Mountainous Areas under the Background of Global Change. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).