A Dynamic Scene Vision SLAM Method Incorporating Object Detection and Object Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Self-Motion-Based Methods
2.2. Semantic Segmentation-Based Methods
2.3. Object-Detection-Based Methods
3. Methods
3.1. Object Detection
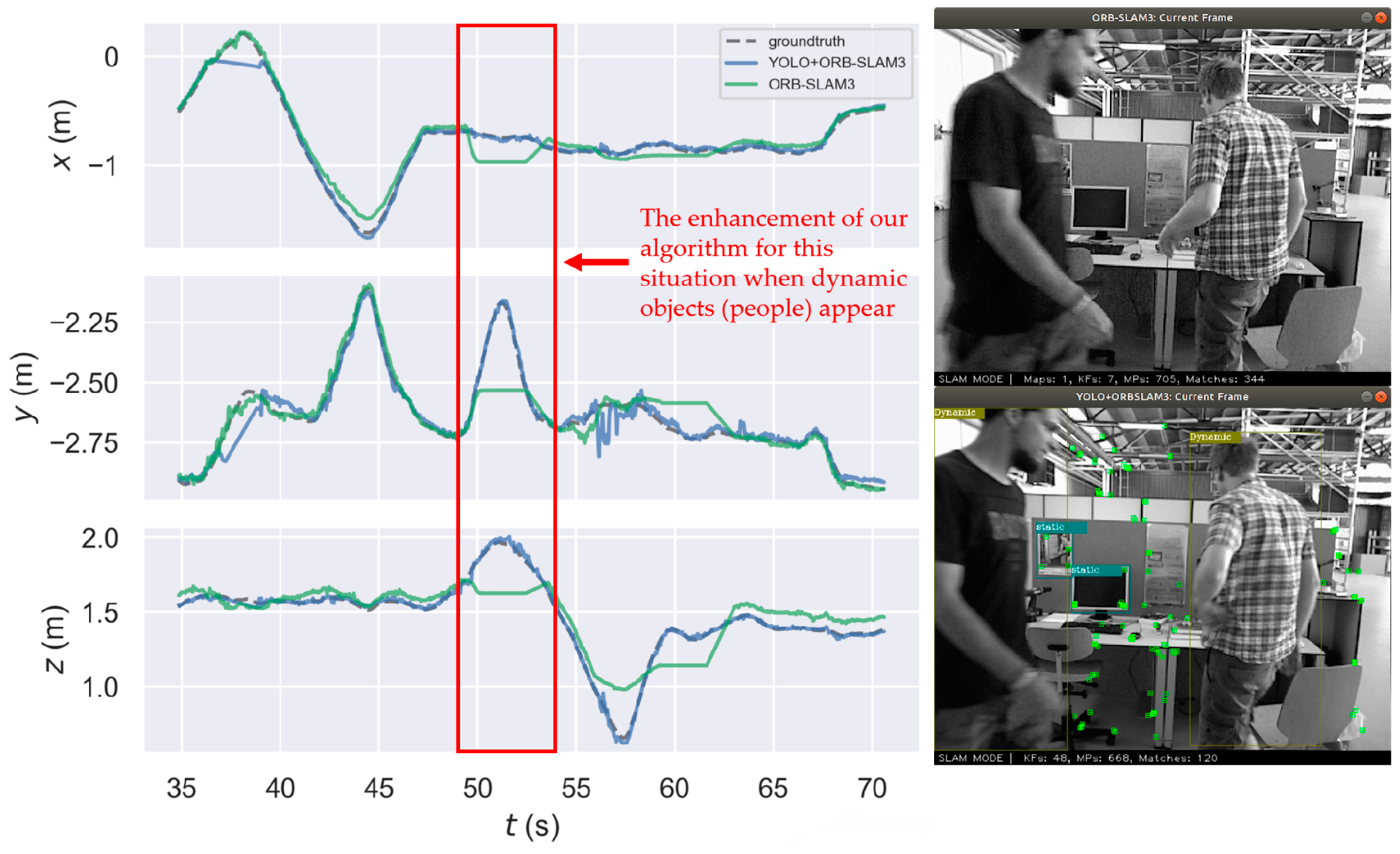
3.2. Determination and Elimination of Feature Points in the Dynamic Box
3.3. The Semi-Static Object Motion Check
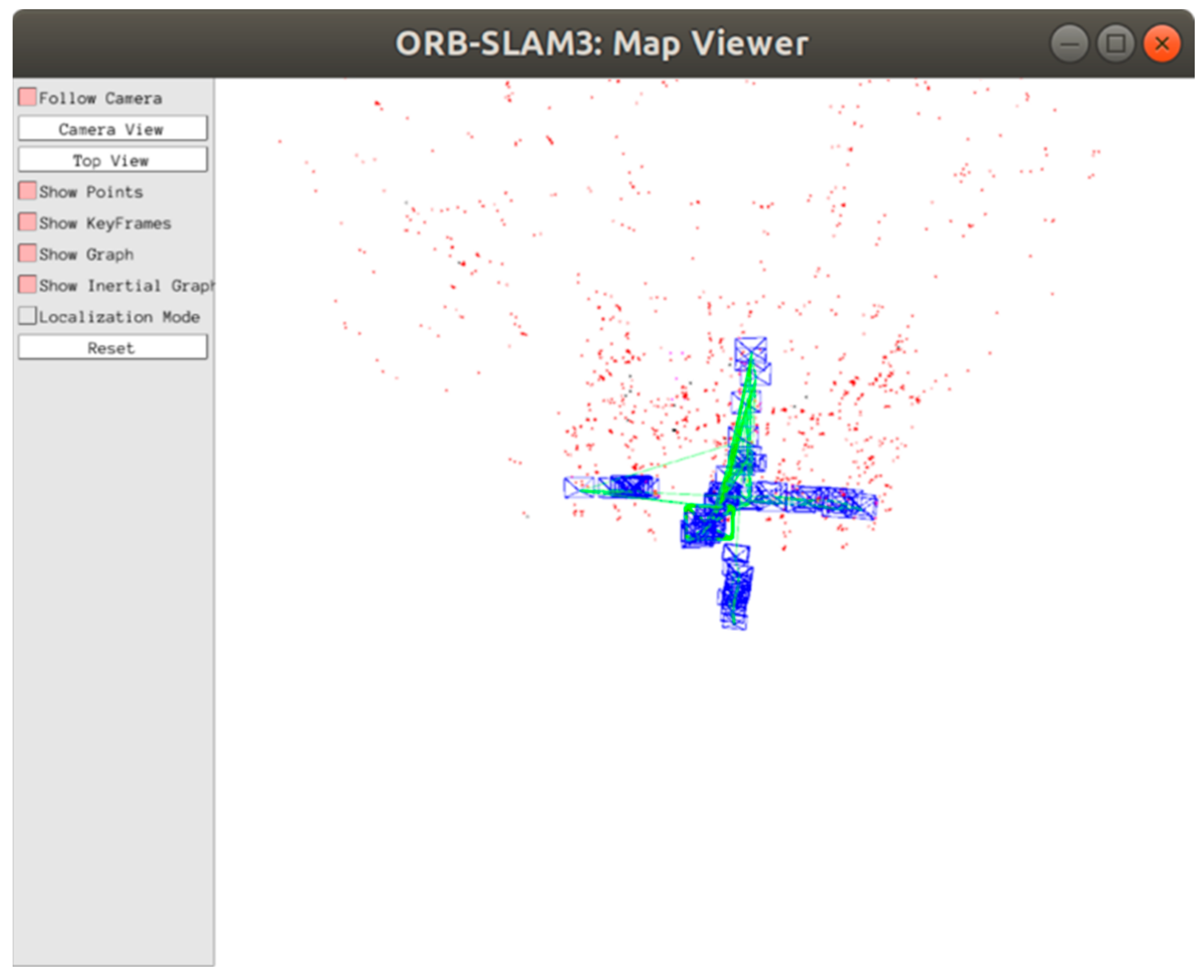
3.4. Creation of Dense Point Cloud Map
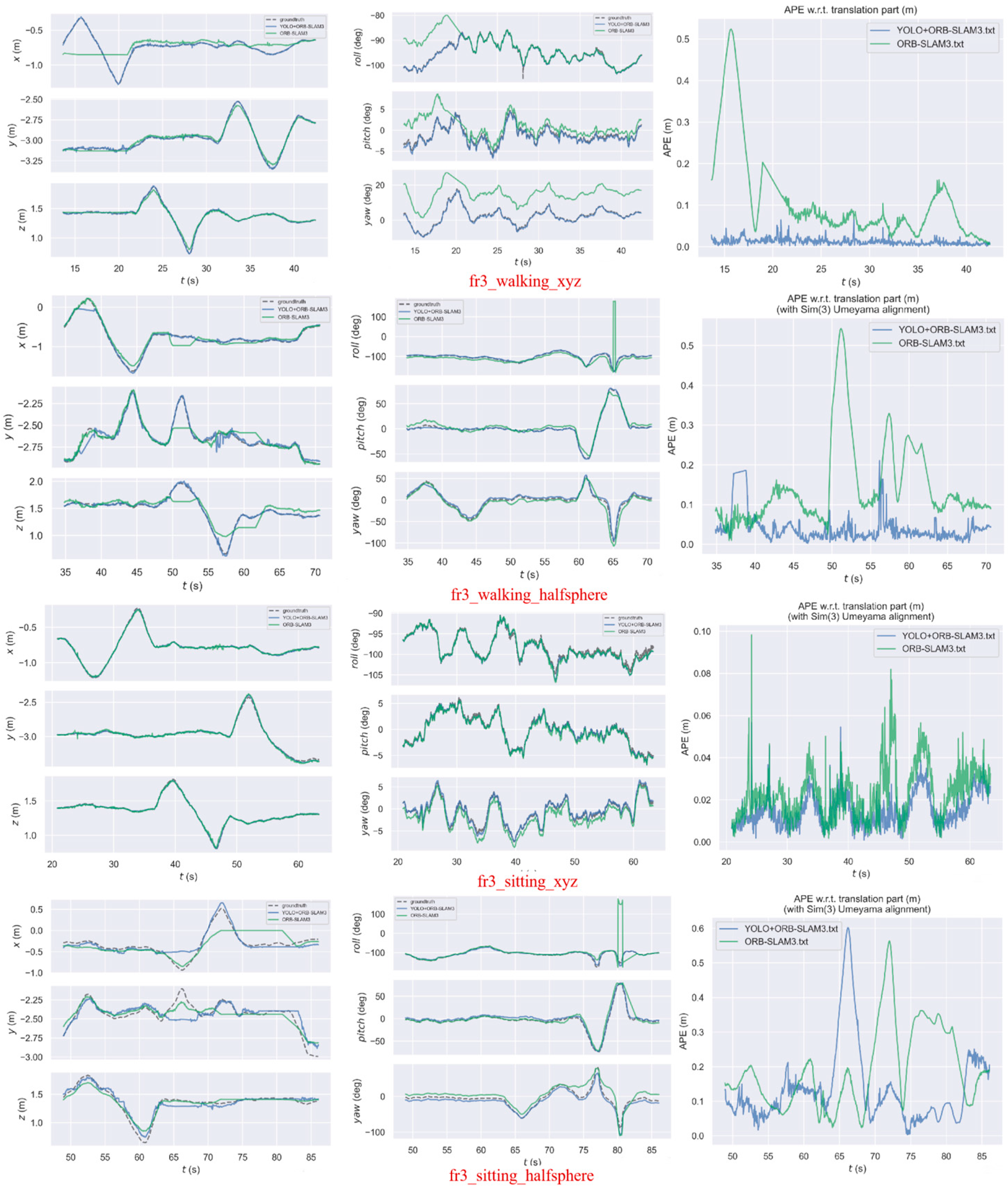
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Dynamic Feature Point Elimination
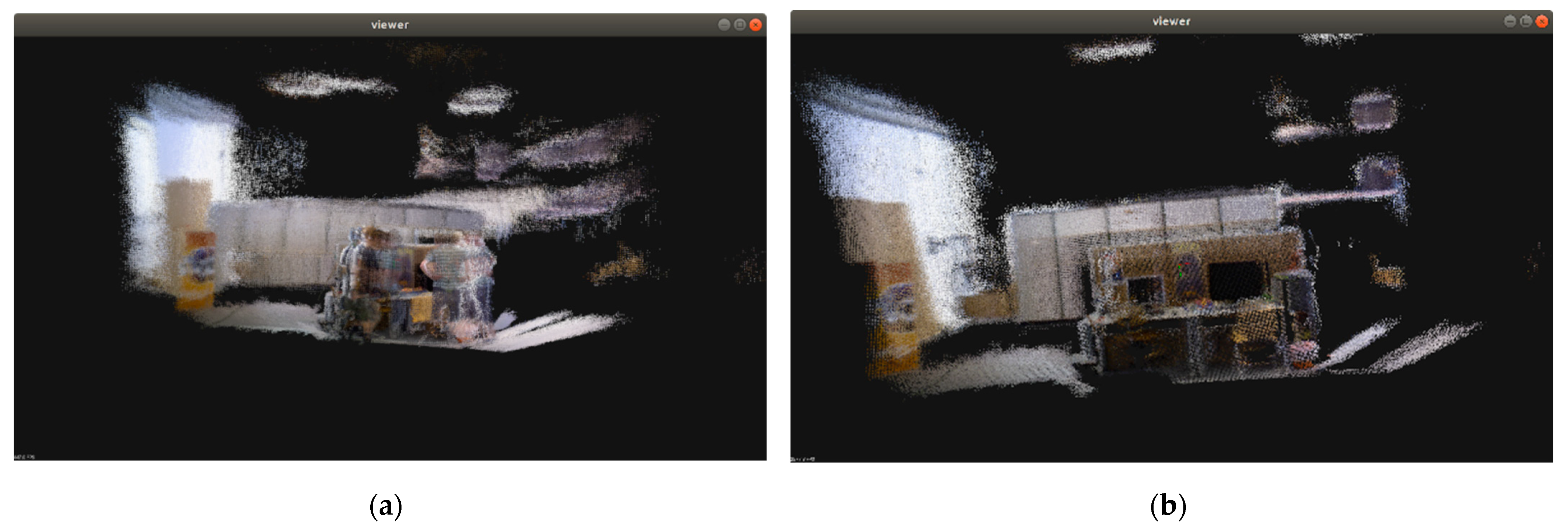
4.2. Static Dense Map Construction
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As a new object detection module, YOLO v5 was added to the ORB-SLAM3 framework. We improved the original ORB-SLAM3 tracking module using detected object dynamic information to reject dynamic feature points, and by computing the positional transformation using purely static feature points, the localization accuracy of ORB-SLAM3 in dynamic environments was improved.
- (2)
- The improved dense point cloud building module was added to ORB-SLAM3, utilizing the dynamic object information extracted by the object detection module to remove dynamic objects, resulting in the creation of a static point cloud map of the scene. Because the tracking module removes dynamic objects to obtain a clearer camera pose trajectory, and the accuracy of the constructed map is largely determined by trajectory precision, the dense point cloud map of the scene constructed using the algorithm in this paper has a high readability and reusability.
- (3)
- The comparison of this paper’s algorithm with the original ORB-SLAM3, two semantic SLAMs that perform better in dynamic environments (DS-SLAM, DynaSLAM), and two recent target detection-based dynamic SLAMs (DO-SLAM, [25]) on the TUM RGB-D dynamic dataset shows that this paper’s method can run at 30+ fps speed operation. In all four image sequences, the localization accuracy improves to varying degrees over ORB-SLAM3, and the absolute trajectory accuracy can be improved by up to 91.10%. The localization accuracy of this paper’s method is comparable to DS-SLAM, DynaSLAM, DO-SLAM, and [25], but it runs significantly faster.
- (4)
- Under some rotating shots, the horizontal detection frame frames a large number of non-dynamic backgrounds, which can result in no available static information in SLAM and, in severe cases, lost tracking. In the future, we can use the rotating detection frame method, which is commonly used in remote sensing object detection, to mark dynamic objects with greater precision, while retaining as much static background as possible.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macario Barros, A.; Michel, M.; Moline, Y.; Corre, G.; Carrel, F. A Comprehensive Survey of Visual SLAM Algorithms. Robotics 2022, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodríguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual–Inertial, and Multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Pizzoli, M.; Scaramuzza, D. SVO: Fast semi-direct monocular visual odometry. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Koltun, V.; Cremers, D. Direct Sparse Odometry. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Ma, C. SOF-SLAM: A Semantic Visual SLAM for Dynamic Environments. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 166528–166539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badias, A.; Alfaro, I.; Gonzalez, D.; Chinesta, F.; Cueto, E. MORPH-DSLAM: Model Order Reduction for Physics-Based Deformable SLAM. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 7764–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, S.; Pizarro, D.; Bartoli, A. Robust Isometric Non-Rigid Structure-From-Motion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6409–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Son, C.Y.; Kim, H.J. Robust Real-time RGB-D Visual Odometry in Dynamic Environments via Rigid Motion Model. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 6891–6898. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo, E.; Behley, J.; Lottes, P.; Giguere, P.; Stachniss, C. ReFusion: 3D Reconstruction in Dynamic Environments for RGB-D Cameras Exploiting Residuals. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 7855–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wan, W.; Wang, Y.; Di, K. A New RGB-D SLAM Method with Moving Object Detection for Dynamic Indoor Scenes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, M.R.U.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Visual SLAM and Structure from Motion in Dynamic Environments. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, N.; Bozic, A.; Lallemand, J.; Tombari, F. Semantic Monocular SLAM for Highly Dynamic Environments. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Runz, M.; Buffier, M.; Agapito, L. MaskFusion: Real-Time Recognition, Tracking and Reconstruction of Multiple Moving Objects. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Munich, Germany, 16–20 October 2018; pp. 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A. RGB-D SLAM Method Based on Object Detection and K-Means. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 20–21 August 2022; pp. 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Dong, N.; Li, D. A Real-Time Dynamic Object Segmentation Framework for SLAM System in Dynamic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Borovec, J.; NanoCode012; TaoXie; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Changyu, L.; Fang, J.; et al. Ultralytics/yolov5: v6.0—YOLOv5n ‘Nano’ Models, Roboflow Integration, TensorFlow Export, OpenCV DNN Support. Zenodo Tech. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchpor, A.A.; Shue, S.; Conrad, J.M. A survey of methods for mobile robot localization and mapping in dynamic indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Signal Processing And Communication Engineering Systems (SPACES), Vijayawada, India, 4–5 January 2018; pp. 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, M.Q.H. Improving RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments: A motion removal approach. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 89, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, S.; Huang, H.; Li, C. DM-SLAM: Monocular SLAM in Dynamic Environments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, M.Q.H. Motion removal for reliable RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 108, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerl, C.; Sturm, J.; Cremers, D. Dense visual SLAM for RGB-D cameras. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 2100–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.-J.; Xie, F.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Fei, Q. DS-SLAM: A Semantic Visual SLAM towards Dynamic Environments. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1168–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Bescos, B.; Facil, J.M.; Civera, J.; Neira, J. DynaSLAM: Tracking, Mapping, and Inpainting in Dynamic Scenes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ye, L. Object Detection-based Visual SLAM for Dynamic Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Guilin, China, 7–10 August 2022; pp. 1153–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Visual SLAM Mapping Based on YOLOv5 in Dynamic Scenes. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, O.; Matas, J.; Kittler, J. Locally Optimized RANSAC; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuki, H.; Scona, R.; Czarnowski, J.; Davison, A.J. CodeMapping: Real-Time Dense Mapping for Sparse SLAM using Compact Scene Representations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7105–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, J.; Engelhard, N.; Endres, F.; Burgard, W.; Cremers, D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]



| Object Property | Object |
|---|---|
| pure static objects | Monitor, cabinet, refrigerator, etc. |
| semi-static objects | Chair, mouse, keyboard, cup, etc. |
| dynamic objects | Human, vehicle, animal, etc. |
| In the Dynamic Object Box | In the Static Object Box | Determine as Valid Dynamic Feature Points |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | False |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
| Sequence Name | Sequence Size | Resolution | Frame Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| fr3_walking_xyz | 827 | 640 × 480 | 30 |
| fr3_walking_halfsphere | 1021 | 640 × 480 | 30 |
| fr3_sitting_xyz | 1261 | 640 × 480 | 30 |
| fr3_sitting_halfsphere | 1110 | 640 × 480 | 30 |
| Sequence of Data Sets | ORB-SLAM3 | Method in this Paper | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| fr3_walking_xyz | 0.162312 | 0.014443 | 91.10% |
| fr3_walking_halfsphere | 0.188741 | 0.055487 | 70.60% |
| fr3_sitting_xyz | 0.026101 | 0.016832 | 35.51% |
| fr3_sitting_halfsphere | 0.230181 | 0.175883 | 23.59% |
| Sequence of Data Sets | ORB-SLAM3 | Method in this Paper | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| fr3_walking_xyz | 0.034260 | 0.012871 | 62.43% |
| fr3_walking_halfsphere | 0.022132 | 0.019239 | 13.07% |
| fr3_sitting_xyz | 0.012549 | 0.008167 | 34.92% |
| fr3_sitting_halfsphere | 0.015779 | 0.017147 | −8.67% |
| Sequence of Data Sets | DS-SLAM | DynaSLAM | DO-SLAM | [25] | Method in this Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fr3_walking_xyz | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| fr3_walking_halfsphere | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.055 |
| fr3_sitting_xyz | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.013 | - | 0.018 |
| fr3_sitting_halfsphere | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.017 | - | 0.177 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, H.; Qian, C.; Wu, T.; Hu, X.; Duan, F.; Ye, X. A Dynamic Scene Vision SLAM Method Incorporating Object Detection and Object Characterization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043048
Guan H, Qian C, Wu T, Hu X, Duan F, Ye X. A Dynamic Scene Vision SLAM Method Incorporating Object Detection and Object Characterization. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043048
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Hongliang, Chengyuan Qian, Tingsong Wu, Xiaoming Hu, Fuzhou Duan, and Xinyi Ye. 2023. "A Dynamic Scene Vision SLAM Method Incorporating Object Detection and Object Characterization" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043048
APA StyleGuan, H., Qian, C., Wu, T., Hu, X., Duan, F., & Ye, X. (2023). A Dynamic Scene Vision SLAM Method Incorporating Object Detection and Object Characterization. Sustainability, 15(4), 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043048










